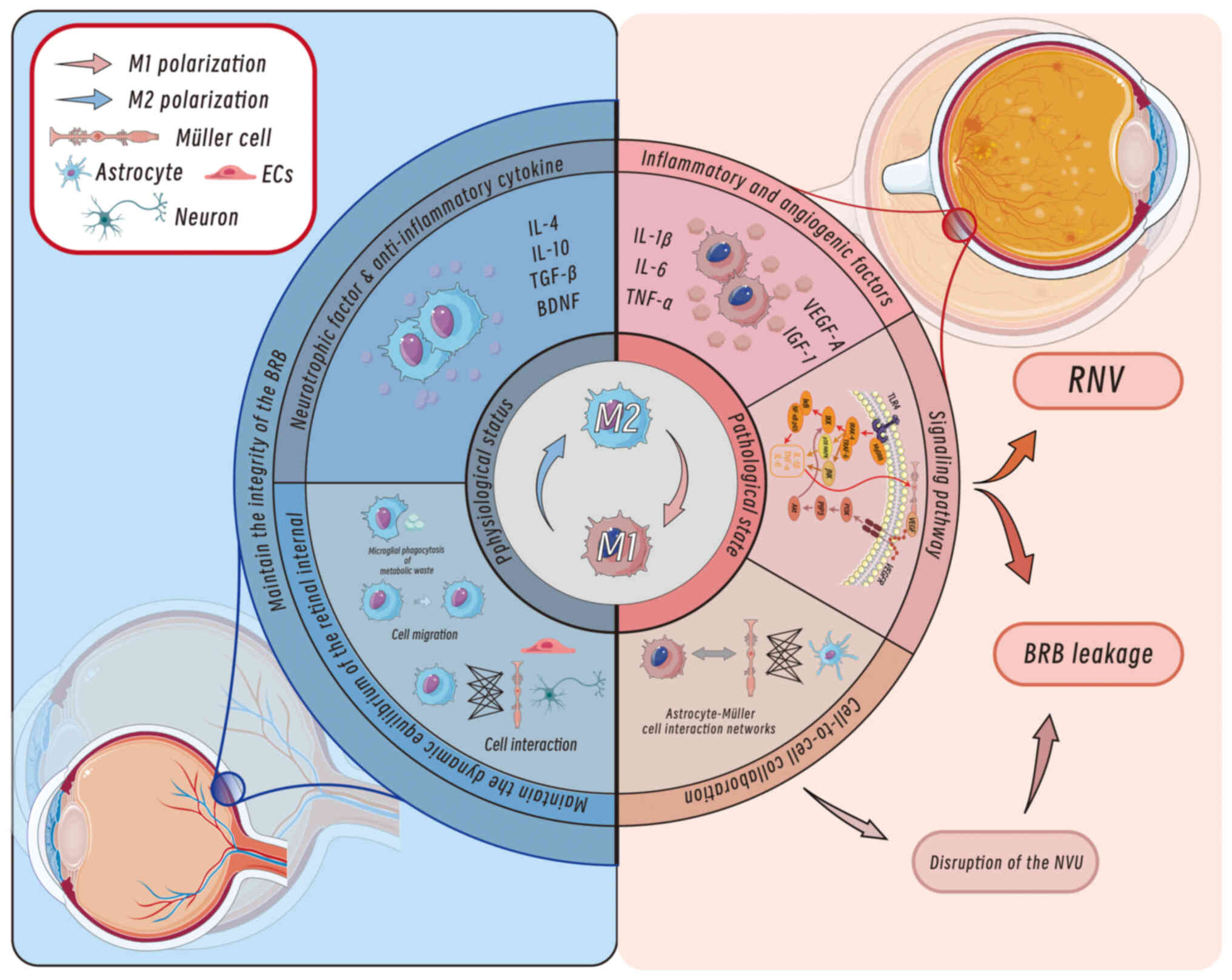
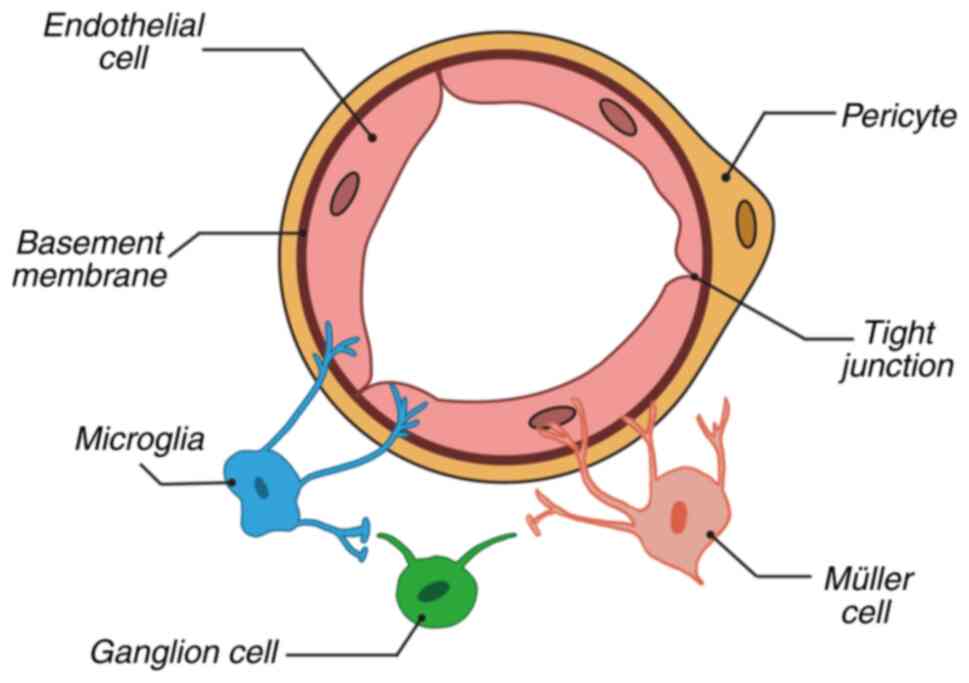
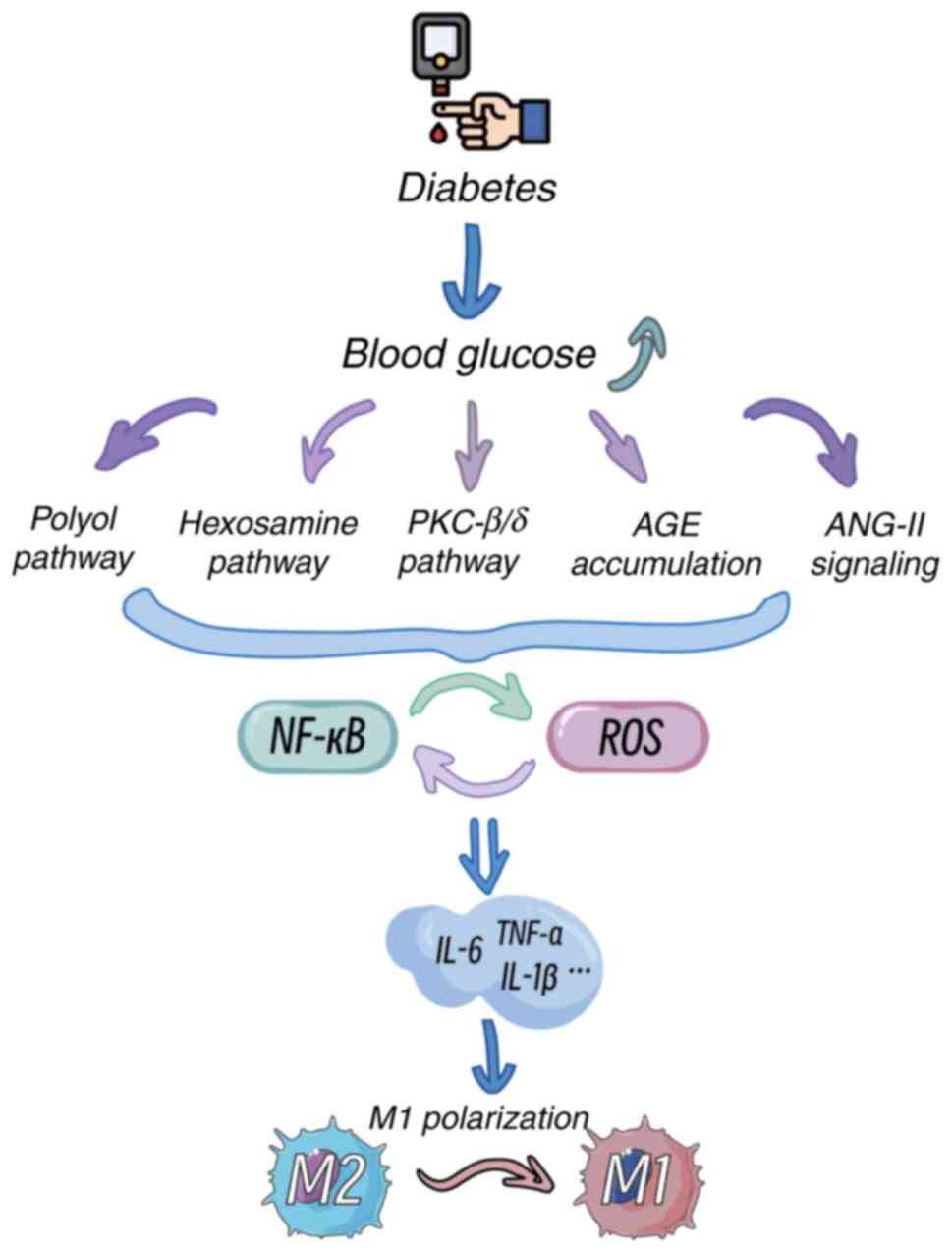
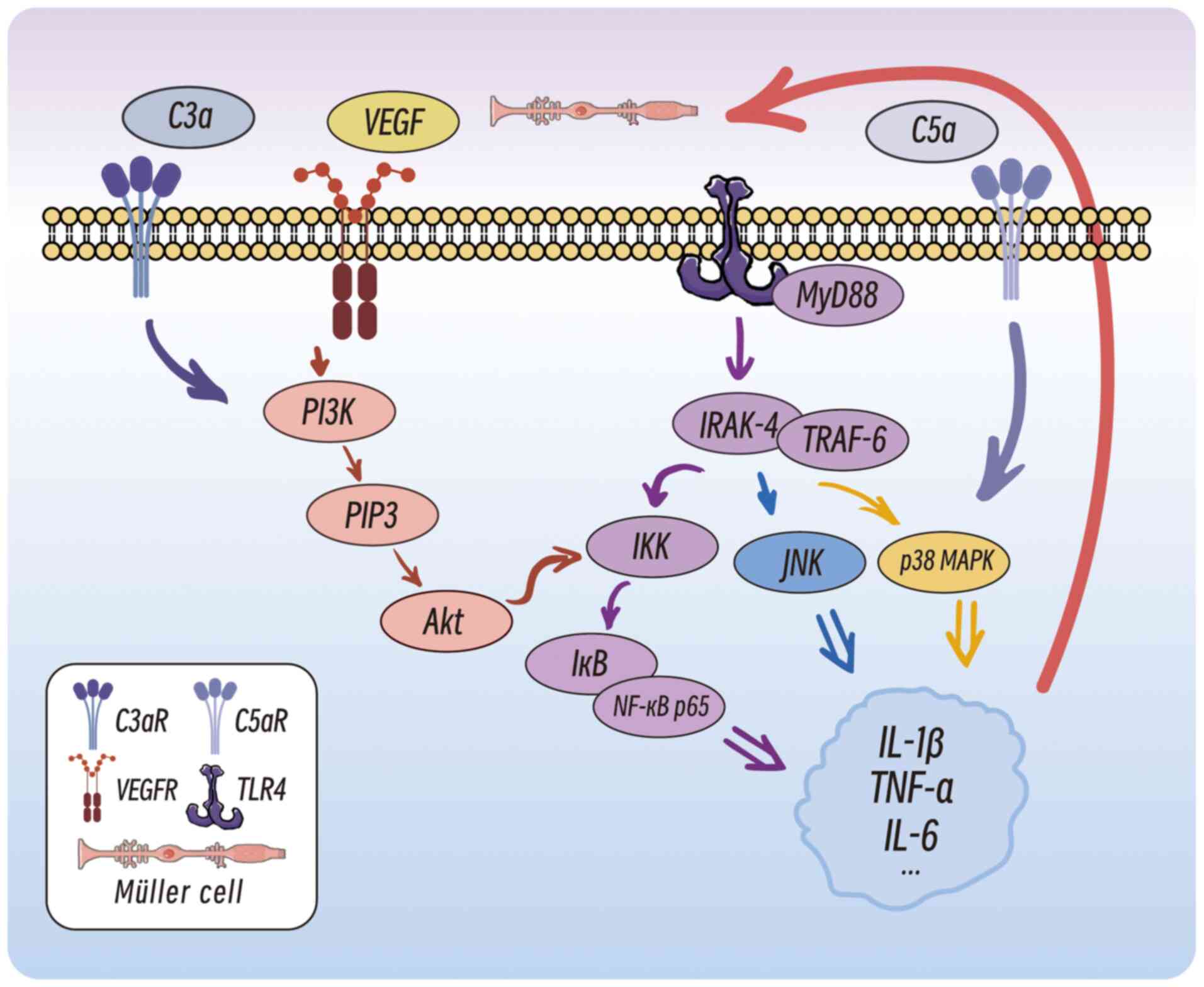
|
1
|
World Health Organization (WHO): Global
report on diabetes. WHO; Geneva: pp. 1–88. 2016
|
|
2
|
Altmann C and Schmidt MHH: The role of
microglia in diabetic retinopathy: Inflammation, microvasculature
defects and neurodegeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 19:1102018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Obrosova IG and Kador PF: Aldose
reductase/polyol inhibitors for diabetic retinopathy. Curr Pharm
Biotechnol. 12:373–385. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Cheung N, Mitchell P and Wong TY: Diabetic
retinopathy. Lancet. 376:124–136. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Teo ZL, Tham YC, Yu M, Chee ML, Rim TH,
Cheung N, Bikbov MM, Wang YX, Tang Y, Lu Y, et al: Global
prevalence of diabetic retinopathy and projection of burden through
2045: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology.
128:1580–1591. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang QH, Zhang Y, Zhang XM and Li XR:
Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy, proliferative diabetic
retinopathy and non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy in Asian
T2DM patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J
Ophthalmol. 12:302–311. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cheyne CP, Burgess PI, Broadbent DM,
García-Fiñana M, Stratton IM, Criddle T, Wang A, Alshukri A, Rahni
MM, Vazquez-Arango P, et al: Incidence of sight-threatening
diabetic retinopathy in an established urban screening programme:
An 11-year cohort study. Diabet Med. 38:e145832021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Das A, Stroud S, Mehta A and Rangasamy S:
New treatments for diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Obes Metab.
17:219–230. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wei L, Sun X, Fan C, Li R, Zhou S and Yu
H: The pathophysiological mechanisms underlying diabetic
retinopathy. Front Cell Dev Biol. 10:9636152022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Arroba AI, Alcalde-Estevez E,
García-Ramírez M, Cazzoni D, de la Villa P, Sánchez-Fernández EM,
Mellet CO, García Fernández JM, Hernández C, Simó R and Valverde
ÁM: Modulation of microglia polarization dynamics during diabetic
retinopathy in db/db mice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1862:1663–1674.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kinuthia UM, Wolf A and Langmann T:
Microglia and inflammatory responses in diabetic retinopathy. Front
Immunol. 11:5640772020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Arnett HA, Mason J, Marino M, Suzuki K,
Matsushima GK and Ting JPY: TNF alpha promotes proliferation of
oligodendrocyte progenitors and remyelination. Nat Neurosci.
4:1116–1122. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Prinz M, Jung S and Priller J: Microglia
biology: One century of evolving concepts. Cell. 179:292–311. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang S, Zhang J and Chen L: The cells
involved in the pathological process of diabetic retinopathy.
Biomed Pharmacother. 132:1108182020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Van Furth R, Cohn ZA, Hirsch JG, Humphrey
JH, Spector WG and Langevoort HL: The mononuclear phagocyte system:
A new classification of macrophages, monocytes, and their precursor
cells. Bull World Health Organ. 46:845–852. 1972.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rao B, Liu X, Xiao J, Wu X, He F, Yang Q,
Zhao W, Lin X and Zhang J: Microglia heterogeneity during
neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in the mouse retina. Brain
Struct Funct. 230:192024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Karlstetter M, Scholz R, Rutar M, Wong WT,
Provis JM and Langmann T: Retinal microglia: Just bystander or
target for therapy? Prog Retin Eye Res. 45:30–57. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Usui Y: Elucidation of pathophysiology and
novel treatment for diabetic macular edema derived from the concept
of neurovascular unit. JMA J. 3:201–207. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hughes S, Yang H and Chan-Ling T:
Vascularization of the human fetal retina: Roles of vasculogenesis
and angiogenesis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 41:1217–1228.
2000.
|
|
20
|
Frost JL and Schafer DP: Microglia:
Architects of the developing nervous system. Trends Cell Biol.
26:587–597. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rymo SF, Gerhardt H, Wolfhagen Sand F,
Lang R, Uv A and Betsholtz C: A two-way communication between
microglial cells and angiogenic sprouts regulates angiogenesis in
aortic ring cultures. PLoS One. 6:e158462011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Haupt F, Krishnasamy K, Napp LC,
Augustynik M, Limbourg A, Gamrekelashvili J, Bauersachs J, Haller H
and Limbourg FP: Retinal myeloid cells regulate tip cell selection
and vascular branching morphogenesis via Notch ligand Delta-like 1.
Sci Rep. 9:97982019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Endo Y, Asanuma D, Namiki S, Sugihara K,
Hirose K, Uemura A, Kubota Y and Miura T: Quantitative modeling of
regular retinal microglia distribution. Sci Rep. 11:226712021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Asare-Bediako B, Adu-Agyeiwaah Y, Abad A,
Li Calzi S, Floyd JL, Prasad R, DuPont M, Asare-Bediako R, Bustelo
XR and Grant MB: Hematopoietic cells influence vascular development
in the retina. Cells. 11:32072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Perochon T, Krsnik Z, Massimo M, Ruchiy Y,
Romero AL, Mohammadi E, Li X, Long KR, Parkkinen L, Blomgren K, et
al: Unraveling microglial spatial organization in the developing
human brain with DeepCellMap, a deep learning approach coupled with
spatial statistics. Nat Commun. 16:15772025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li F, Jiang D and Samuel MA: Microglia in
the developing retina. Neural Dev. 14:122019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhou LY, Liu ZG, Sun YQ, Li YZ, Teng ZQ
and Liu CM: Preserving blood-retinal barrier integrity: A path to
retinal ganglion cell protection in glaucoma and traumatic optic
neuropathy. Cell Regen. 14:132025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Klaassen I, Van Noorden CJF and
Schlingemann RO: Molecular basis of the inner blood-retinal barrier
and its breakdown in diabetic macular edema and other pathological
conditions. Prog Retin Eye Res. 34:19–48. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Guymer RH, Bird AC and Hageman GS:
Cytoarchitecture of choroidal capillary endothelial cells. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 45:1660–1666. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hormel TT, Jia Y, Jian Y, Hwang TS, Bailey
ST, Pennesi ME, Wilson DJ, Morrison JC and Huang D: Plexus-specific
retinal vascular anatomy and pathologies as seen by
projection-resolved optical coherence tomographic angiography. Prog
Retin Eye Res. 80:1008782021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Amoaku WM, Ghanchi F, Bailey C, Banerjee
S, Banerjee S, Downey L, Gale R, Hamilton R, Khunti K, Posner E, et
al: Diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular oedema pathways and
management: UK consensus working group. Eye (Lond). 34(Suppl 1):
S1–S51. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Opdenakker G and Abu El-Asrar A:
Metalloproteinases mediate diabetes-induced retinal neuropathy and
vasculopathy. Cell Mol Life Sci. 76:3157–3166. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
O'Leary F and Campbell M: The blood-retina
barrier in health and disease. FEBS J. 290:878–891. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Schafer DP, Lehrman EK, Kautzman AG,
Koyama R, Mardinly AR, Yamasaki R, Ransohoff RM, Greenberg ME,
Barres BA and Stevens B: Microglia sculpt postnatal neural circuits
in an activity and complement-dependent manner. Neuron. 74:691–705.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhu X, Hong J and Zhou X: Biological
immune mechanism of retina. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 28:3632023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kumar A, Kumar A, Kumar J, Bai G, Jeewnani
R, Dembra M, Kanwal K, Qadeer U, Khawar MH, Yaseen Khan I, et al:
Comparative efficacy of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor
(anti-VEGF) agents and corticosteroids in managing diabetic
retinopathy-associated diabetic macular edema: A meta-analysis and
comprehensive systematic review. Cureus. 16:e519102024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee WJ, Kang MH, Seong M and Cho HY:
Comparison of aqueous concentrations of angiogenic and inflammatory
cytokines in diabetic macular oedema and macular oedema due to
branch retinal vein occlusion. Br J Ophthalmol. 96:1426–1430. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Meng C, Gu C, He S, Su T, Lhamo T, Draga D
and Qiu Q: Pyroptosis in the retinal neurovascular unit: New
insights into diabetic retinopathy. Front Immunol. 12:7630922021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Romero-Aroca P, Baget-Bernaldiz M,
Pareja-Rios A, Lopez-Galvez M, Navarro-Gil R and Verges R: Diabetic
macular edema pathophysiology: Vasogenic versus inflammatory. J
Diabetes Res. 2016:21562732016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang Y, Zhao L, Wang X, Ma W, Lazere A,
Qian HH, Zhang J, Abu-Asab M, Fariss RN, Roger JE and Wong WT:
Repopulating retinal microglia restore endogenous organization and
function under CX3CL1-CX3CR1 regulation. Sci Adv. 4:eaap84922018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhao L, Zabel MK, Wang X, Ma W, Shah P,
Fariss RN, Qian H, Parkhurst CN, Gan WB and Wong WT: Microglial
phagocytosis of living photoreceptors contributes to inherited
retinal degeneration. EMBO Mol Med. 7:1179–1197. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang J, He W and Zhang J: A richer and
more diverse future for microglia phenotypes. Heliyon.
9:e147132023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fouda AY, Xu Z, Suwanpradid J, Rojas M,
Shosha E, Lemtalsi T, Patel C, Xing J, Zaidi SA, Zhi W, et al:
Targeting proliferative retinopathy: Arginase 1 limits
vitreoretinal neovascularization and promotes angiogenic repair.
Cell Death Dis. 13:7452022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li X, Yu ZW, Li HY, Yuan Y, Gao XY and
Kuang HY: Retinal microglia polarization in diabetic retinopathy.
Vis Neurosci. 38:E0062021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ikeda T, Nakamura K, Kida T and Oku H:
Possible roles of anti-type II collagen antibody and innate
immunity in the development and progression of diabetic
retinopathy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 260:387–403. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
46
|
Ibrahim AS, El-Shishtawy MM, Peña A Jr and
Liou GI: Genistein attenuates retinal inflammation associated with
diabetes by targeting of microglial activation. Mol Vis.
16:2033–2042. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cukras CA, Petrou P, Chew EY, Meyerle CB
and Wong WT: Oral minocycline for the treatment of diabetic macular
edema (DME): Results of a phase I/II clinical study. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 53:3865–3874. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Madeira MH, Boia R, Santos PF, Ambrósio AF
and Santiago AR: Contribution of microglia-mediated
neuroinflammation to retinal degenerative diseases. Mediators
Inflamm. 2015:6730902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Grigsby JG, Cardona SM, Pouw CE, Muniz A,
Mendiola AS, Tsin ATC, Allen DM and Cardona AE: The role of
microglia in diabetic retinopathy. J Ophthalmol. 2014:7057832014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Paolicelli RC, Sierra A, Stevens B,
Tremblay ME, Aguzzi A, Ajami B, Amit I, Audinat E, Bechmann I,
Bennett M, et al: Microglia states and nomenclature: A field at its
crossroads. Neuron. 110:3458–3483. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sun N, Victor MB, Park YP, Xiong X,
Scannail AN, Leary N, Prosper S, Viswanathan S, Luna X, Boix CA, et
al: Human microglial state dynamics in Alzheimer's disease
progression. Cell. 186:4386–4403.e29. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
He J, Fu Y, Ge L, Dai J, Fang Y, Li Y, Gu
X, Tao Z, Zou T, Li M, et al: Disease-associated microglial
activation prevents photoreceptor degeneration by suppressing the
accumulation of cell debris and neutrophils in degenerating rat
retinas. Theranostics. 12:2687–2706. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Shemer A, Grozovski J, Tay TL, Tao J,
Volaski A, Süß P, Ardura-Fabregat A, Gross-Vered M, Kim JS, David
E, et al: Engrafted parenchymal brain macrophages differ from
microglia in transcriptome, chromatin landscape and response to
challenge. Nat Commun. 9:52062018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Buttgereit A, Lelios I, Yu X, Vrohlings M,
Krakoski NR, Gautier EL, Nishinakamura R, Becher B and Greter M:
Sall1 is a transcriptional regulator defining microglia identity
and function. Nat Immunol. 17:1397–1406. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Jurga AM, Paleczna M and Kuter KZ:
Overview of general and discriminating markers of differential
microglia phenotypes. Front Cell Neurosci. 14:1982020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wolf J, Boneva S, Rosmus DD, Agostini H,
Schlunck G, Wieghofer P, Schlecht A and Lange C: In-depth molecular
profiling specifies human retinal microglia identity. Front
Immunol. 13:8631582022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Masuda T, Amann L, Sankowski R, Staszewski
O, Lenz M, D'Errico P, Snaidero N, Costa Jordão MJ, Böttcher C,
Kierdorf K, et al: Novel Hexb-based tools for studying microglia in
the CNS. Nat Immunol. 21:802–815. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kenkhuis B, Somarakis A, Kleindouwel LRT,
Van Roon-Mom WMC, Höllt T and Van Der Weerd L: Co-expression
patterns of microglia markers Iba1, TMEM119 and P2RY12 in
Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis. 167:1056842022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Qin Z, He S, Yang C, Yung JSY, Chen C,
Leung CKS, Liu K and Qu JY: Adaptive optics two-photon microscopy
enables near-diffraction-limited and functional retinal imaging in
vivo. Light Sci Appl. 9:792020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wu MY, Yiang GT, Lai TT and Li CJ: The
oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction during the
pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Oxidative Med Cell Longev.
2018:34201872018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Lv K, Ying H, Hu G, Hu J, Jian Q and Zhang
F: Integrated multi-omics reveals the activated retinal microglia
with intracellular metabolic reprogramming contributes to
inflammation in STZ-induced early diabetic retinopathy. Front
Immunol. 13:9427682022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Du XL, Edelstein D, Rossetti L, Fantus IG,
Goldberg H, Ziyadeh F, Wu J and Brownlee M: Hyperglycemia-induced
mitochondrial superoxide overproduction activates the hexosamine
pathway and induces plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression by
increasing Sp1 glycosylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:12222–12226. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Du X, Matsumura T, Edelstein D, Rossetti
L, Zsengellér Z, Szabó C and Brownlee M: Inhibition of GAPDH
activity by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activates three major
pathways of hyperglycemic damage in endothelial cells. J Clin
Investig. 112:1049–1057. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Kowluru RA: Effect of advanced glycation
end products on accelerated apoptosis of retinal capillary cells
under in vitro conditions. Life Sci. 76:1051–1060. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Glomb MA and Monnier VM: Mechanism of
protein modification by glyoxal and glycolaldehyde, reactive
intermediates of the maillard reaction. J Biol Chem.
270:10017–10026. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Funatsu H and Yamashita H: Pathogenesis of
diabetic retinopathy and the renin-angiotensin system. Ophthalmic
Physiol Opt. 23:495–501. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Cai Y, Li W, Tu H, Chen N, Zhong Z, Yan P
and Dong J: Curcumolide reduces diabetic retinal vascular
leukostasis and leakage partly via inhibition of the p38MAPK/NF-κB
signaling. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 27:1835–1839. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Stitt AW: The role of advanced glycation
in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Exp Mol Pathol.
75:95–108. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yamagishi SI and Matsui T: Advanced
glycation end products (AGEs), oxidative stress and diabetic
retinopathy. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 12:362–368. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Song J and Lee JE: ASK1 modulates the
expression of microRNA Let7A in microglia under high glucose in
vitro condition. Front Cell Neurosci. 9:1982015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Du A, Xie Y, Ouyang H, Lu B, Jia W, Xu H
and Ji L: Si-miao-yong-an decoction for diabetic retinopathy: A
combined network pharmacological and in vivo approach. Front
Pharmacol. 12:7631632021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Vargas-Soria M, García-Alloza M and
Corraliza-Gómez M: Effects of diabetes on microglial physiology: A
systematic review of in vitro, preclinical and clinical studies. J
Neuroinflammation. 20:572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Quiriconi P, Hristov V, Aburaya M,
Greferath U, Jobling AI and Fletcher EL: The role of microglia in
the development of diabetic retinopathy. NPJ Metab Health Dis.
2:72024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Cai L, Xia M and Zhang F: Redox regulation
of immunometabolism in microglia underpinning diabetic retinopathy.
Antioxidants (Basel). 13:4232024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Yamaguchi M, Nakao S, Arima M, Little K,
Singh A, Wada I, Kaizu Y, Zandi S, Garweg JG, Matoba T, et al:
Heterotypic macrophages/microglia differentially contribute to
retinal ischaemia and neovascularisation. Diabetologia.
67:2329–2345. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Wang J, Liu X, Wei W, Yang J, Li Q, Chu S,
Liu P, Zhang J and He W: Regulation of oxygen-glucose
deprivation/reperfusion-induced inflammatory responses and M1-M2
phenotype switch of BV2 microglia by lobetyolin. Metab Brain Dis.
38:2627–2644. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Nian S, Lo ACY, Mi Y, Ren K and Yang D:
Neurovascular unit in diabetic retinopathy: Pathophysiological
roles and potential therapeutical targets. Eye Vis (Lond Engl).
8:152021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Inada M, Xu H, Takeuchi M, Ito M and Chen
M: Microglia increase tight-junction permeability in coordination
with Müller cells under hypoxic condition in an in vitro model of
inner blood-retinal barrier. Exp Eye Res. 205:1084902021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Fang M, Wan W, Li Q, Wan W, Long Y, Liu H
and Yang X: Asiatic acid attenuates diabetic retinopathy through
TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB p65 mediated modulation of microglia polarization.
Life Sci. 277:1195672021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Mehrabadi AR, Korolainen MA, Odero G,
Miller DW and Kauppinen TM: Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 regulates
microglia mediated decrease of endothelial tight junction
integrity. Neurochem Int. 108:266–271. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Usui-Ouchi A, Usui Y, Kurihara T, Aguilar
E, Dorrell MI, Ideguchi Y, Sakimoto S, Bravo S and Friedlander M:
Retinal microglia are critical for subretinal neovascular
formation. JCI Insight. 5:e1373172020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Xie H, Zhang C, Liu D, Yang Q, Tang L,
Wang T, Tian H, Lu L, Xu JY, Gao F, et al: Erythropoietin protects
the inner blood-retinal barrier by inhibiting microglia
phagocytosis via Src/Akt/cofilin signalling in experimental
diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia. 64:211–225. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Zhang T, Ouyang H, Mei X, Lu B, Yu Z, Chen
K, Wang Z and Ji L: Erianin alleviates diabetic retinopathy by
reducing retinal inflammation initiated by microglial cells via
inhibiting hyperglycemia-mediated ERK1/2-NF-κB signaling pathway.
FASEB J. 33:11776–11790. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Behnke V, Wolf A and Langmann T: The role
of lymphocytes and phagocytes in age-related macular degeneration
(AMD). Cell Mol Life Sci. 77:781–788. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Ogura S, Baldeosingh R, Bhutto IA,
Kambhampati SP, McLeod DS, Edwards MM, Rais R, Schubert W and Lutty
GA: A role for mast cells in geographic atrophy. FASEB J.
34:10117–10131. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Lueck K, Busch M, Moss SE, Greenwood J,
Kasper M, Lommatzsch A, Pauleikhoff D and Wasmuth S: Complement
stimulates retinal pigment epithelial cells to undergo
pro-inflammatory changes. Ophthalmic Res. 54:195–203. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Fu X, Feng S, Qin H, Yan L, Zheng C and
Yao K: Microglia: The breakthrough to treat neovascularization and
repair blood-retinal barrier in retinopathy. Front Mol Neurosci.
16:11002542023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Ding X, Gu R, Zhang M, Ren H, Shu Q, Xu G
and Wu H: Microglia enhanced the angiogenesis, migration and
proliferation of co-cultured RMECs. BMC Ophthalmol. 18:2492018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Hu A, Schmidt MHH and Heinig N: Microglia
in retinal angiogenesis and diabetic retinopathy. Angiogenesis.
27:311–331. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Tang L, Xu GT and Zhang JF: Inflammation
in diabetic retinopathy: Possible roles in pathogenesis and
potential implications for therapy. Neural Regen Res. 18:976–982.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
91
|
Ogura S, Kurata K, Hattori Y, Takase H,
Ishiguro-Oonuma T, Hwang Y, Ahn S, Park I, Ikeda W, Kusuhara S, et
al: Sustained inflammation after pericyte depletion induces
irreversible blood-retina barrier breakdown. JCI Insight.
2:e909052017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
He C, Liu Y, Huang Z, Yang Z, Zhou T, Liu
S, Hao Z, Wang J, Feng Q, Liu Y, et al: A specific RIP3+
subpopulation of microglia promotes retinopathy through a
hypoxia-triggered necroptotic mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
118:e20232901182021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Connor KM, SanGiovanni JP, Lofqvist C,
Aderman CM, Chen J, Higuchi A, Hong S, Pravda EA, Majchrzak S,
Carper D, et al: Increased dietary intake of
omega-3-polyunsaturated fatty acids reduces pathological retinal
angiogenesis. Nat Med. 13:868–873. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Yin J, Xu WQ, Ye MX, Zhang Y, Wang HY,
Zhang J, Li Y and Wang YS: Up-regulated basigin-2 in microglia
induced by hypoxia promotes retinal angiogenesis. J Cell Mol Med.
21:3467–3480. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Zhao C, Liu Y, Meng J, Wang X, Liu X, Li
W, Zhou Q, Xiang J, Li N and Hou S: LGALS3BP in microglia promotes
retinal angiogenesis through PI3K/AKT pathway during hypoxia.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 63:252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Murinello S, Usui Y, Sakimoto S, Kitano M,
Aguilar E, Friedlander HM, Schricker A, Wittgrove C, Wakabayashi Y,
Dorrell MI, et al: miR-30a-5p inhibition promotes interaction of
Fas+ endothelial cells and FasL+ microglia to decrease
pathological neovascularization and promote physiological
angiogenesis. Glia. 67:332–344. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Luo Q, Jiang Z, Jiang J, Wan L, Li Y,
Huang Y, Qiu J, Yu K and Zhuang J: Tsp-1+ microglia
attenuate retinal neovascularization by maintaining the expression
of Smad3 in endothelial cells through exosomes with decreased
miR-27a-5p. Theranostics. 13:3689–3706. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
98
|
Hu Y, Wei T, Gao S and Cheng Q:
Anti-angiogenic and anti-inflammatory effects of CD200-CD200R1 axis
in oxygen-induced retinopathy mice model. Inflamm Res. 68:945–955.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Dejda A, Mawambo G, Daudelin JF, Miloudi
K, Akla N, Patel C, Andriessen EMMA, Labrecque N, Sennlaub F and
Sapieha P: Neuropilin-1-expressing microglia are associated with
nascent retinal vasculature yet dispensable for developmental
angiogenesis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 57:1530–1536. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Dejda A, Mawambo G, Cerani A, Miloudi K,
Shao Z, Daudelin JF, Boulet S, Oubaha M, Beaudoin F, Akla N, et al:
Neuropilin-1 mediates myeloid cell chemoattraction and influences
retinal neuroimmune crosstalk. J Clin Investig. 124:4807–4822.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Bai Q, Wang X, Yan H, Wen L, Zhou Z, Ye Y,
Jing Y, Niu Y, Wang L, Zhang Z, et al: Microglia-derived Spp1
promotes pathological retinal neovascularization via activating
endothelial Kit/Akt/mTOR signaling. J Pers Med. 13:1462023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Zhou ZY, Chang TF, Lin ZB, Jing YT, Wen
LS, Niu YL, Bai Q, Guo CM, Sun JX, Wang YS and Dou GR: Microglial
Galectin3 enhances endothelial metabolism and promotes pathological
angiogenesis via notch inhibition by competitively binding to Jag1.
Cell Death Dis. 14:3802023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Li L, Sun B, Harris OA and Luo J: TGF-β
signaling in microglia: A key regulator of development, homeostasis
and reactivity. Biomedicines. 12:24682024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Wiens KR, Wasti N, Ulloa OO and Klegeris
A: Diversity of microglia-derived molecules with neurotrophic
properties that support neurons in the central nervous system and
other tissues. Molecules. 29:55252024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Liu W, Tong B, Xiong J, Zhu Y, Lu H, Xu H,
Yang X, Wang F, Yu P and Hu Y: Identification of macrophage
polarisation and mitochondria-related biomarkers in diabetic
retinopathy. J Transl Med. 23:232025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Amankwa CE, Acha LG, Dibas A, Chavala SH,
Roth S, Mathew B and Acharya S: Neuroprotective and
anti-inflammatory activities of hybrid small-molecule SA-10 in
ischemia/reperfusion-induced retinal neuronal injury models. Cells.
13:3962024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Paisley CE and Kay JN: Seeing stars:
Development and function of retinal astrocytes. Dev Biol.
478:144–154. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Chan-Ling T: Development of the retinal
vasculature. Encyclopedia of the eye. D'Amore P: Academic Press;
Cambridge: pp. 22–33. 2010, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Gnanaguru G, Tabor SJ, Bonilla GM,
Sadreyev R, Yuda K, Köhl J and Connor KM: Microglia refine
developing retinal astrocytic and vascular networks through the
complement C3/C3aR axis. Development. 150:dev2010472023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Checchin D, Sennlaub F, Levavasseur E,
Leduc M and Chemtob S: Potential role of microglia in retinal blood
vessel formation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 47:3595–3602. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Wang M, Ma W, Zhao L, Fariss RN and Wong
WT: Adaptive Müller cell responses to microglial activation mediate
neuroprotection and coordinate inflammation in the retina. J
Neuroinflammation. 8:1732011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Tewari M, Michalski S and Egan TM:
Modulation of microglial function by ATP-gated P2X7 receptors:
Studies in rat, mice and human. Cells. 13:1612024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Kong H, Zhao H, Chen T, Song Y and Cui Y:
Targeted P2X7/NLRP3 signaling pathway against inflammation,
apoptosis, and pyroptosis of retinal endothelial cells in diabetic
retinopathy. Cell Death Dis. 13:3362022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Antonetti DA, Silva PS and Stitt AW:
Current understanding of the molecular and cellular pathology of
diabetic retinopathy. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 17:195–206. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Wang X, Ye J and Liu W: GPER-mediated
inhibition of astrocyte activation mitigates retinal
neovascularization in oxygen-induced retinopathy mice. J Army Med
Univ. 46:1369–1377. 2024.
|
|
116
|
Kaur C, Foulds W and Ling E: Blood-retinal
barrier in hypoxic ischaemic conditions: Basic concepts, clinical
features and management. Prog Retin Eye Res. 27:622–647. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Puebla M, Tapia PJ and Espinoza H: Key
role of astrocytes in postnatal brain and retinal angiogenesis. Int
J Mol Sci. 23:26462022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Navarro HI, Daly AE, Rodriguez B, Wu S,
Ngo KA, Fraser A, Schiffman A, Liu Y, Smale ST, Chia JJ and
Hoffmann A: NF-κB RelB suppresses the inflammatory gene expression
programs of dendritic cells by competing with RelA for binding to
target gene promoters. Cell Discov. 11:132025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Acioglu C and Elkabes S: Innate immune
sensors and regulators at the blood brain barrier: Focus on
toll-like receptors and inflammasomes as mediators of neuro-immune
crosstalk and inflammation. J Neuroinflammation. 22:392025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Song Y, Dou H, Gong W, Liu X, Yu Z, Li E,
Tan R and Hou Y: Bis-N-norgliovictin, a small-molecule compound
from marine fungus, inhibits LPS-induced inflammation in
macrophages and improves survival in sepsis. Eur J Pharmacol.
705:49–60. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Abcouwer SF: Neural inflammation and the
microglial response in diabetic retinopathy. J Ocul Biol Dis Infor.
4:25–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
122
|
Sun H, Ma X, Ma H, Li S, Xia Y, Yao L,
Wang Y, Pang X, Zhong J, Yao G, et al: High glucose levels
accelerate atherosclerosis via NLRP3-IL/MAPK/NF-κB-related
inflammation pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 704:1497022024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
He Y, Sun MM, Zhang GG, Yang J, Chen KS,
Xu WW and Li B: Targeting PI3K/Akt signal transduction for cancer
therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:4252021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Chidiac R, Zhang Y, Tessier S, Faubert D,
Delisle C and Gratton JP: Comparative phosphoproteomics analysis of
VEGF and angiopoietin-1 signaling reveals ZO-1 as a critical
regulator of endothelial cell proliferation. Mol Cell Proteom.
15:1511–1525. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Greene C, Hanley N and Campbell M:
Claudin-5: Gatekeeper of neurological function. Fluids Barriers
CNS. 16:32019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Zhao H, Lv Y, Xu J, Song X, Wang Q, Zhai
X, Ma X, Qiu J, Cui L and Sun Y: The activation of microglia by the
complement system in neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res Rev.
104:1026362025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Ricklin D, Hajishengallis G, Yang K and
Lambris JD: Complement: A key system for immune surveillance and
homeostasis. Nat Immunol. 11:785–797. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Ayyubova G and Madhu LN: Microglial NLRP3
inflammasomes in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis: From interaction
with autophagy/mitophagy to therapeutics. Mol Neurobiol.
62:7124–7143. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Yanai R, Thanos A and Connor KM:
Complement involvement in neovascular ocular diseases. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 946:161–183. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Padmakumar L, Menon RN, Gopala S and
Vilanilam GC: MTH1 in the disorders of the central nervous system:
Scope beyond brain tumors and challenges. Acta Neurol Belg. Feb
17–2025.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Chung J, Jernigan J, Menees KB and Lee JK:
RGS10 mitigates high glucose-induced microglial inflammation via
the reactive oxidative stress pathway and enhances synuclein
clearance in microglia. Front Cell Neurosci. 18:13742982024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Homme RP, Sandhu HS, George AK, Tyagi SC
and Singh M: Sustained inhibition of NF-κB activity mitigates
retinal vasculopathy in diabetes. Am J Pathol. 191:947–964. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Park SS: Retinal glia and NF-κB in
diabetic retinopathy pathogenesis. Ann Transl Med. 11:3072023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Chen W, Wu Z, Cheng Z, Zhang Y, Luo Q and
Yin M: HO-1 represses NF-κB signaling pathway to mediate microglia
polarization and phagocytosis in intracerebral hemorrhage.
Neuroscience. 566:17–27. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Gonzalez-Cortes JH, Martinez-Pacheco VA,
Gonzalez-Cantu JE, Bilgic A, de Ribot FM, Sudhalkar A,
Mohamed-Hamsho J, Kodjikian L and Mathis T: Current treatments and
innovations in diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema.
Pharmaceutics. 15:1222022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Mounirou BAM, Adam ND, Yakoura AKH, Aminou
MSM, Liu YT and Tan LY: Diabetic retinopathy: An overview of
treatments. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 26:111–118. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Arrigo A, Aragona E and Bandello F:
VEGF-targeting drugs for the treatment of retinal
neovascularization in diabetic retinopathy. Ann Med. 54:1089–1111.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Zhang W, Geng J and Sang A: Effectiveness
of panretinal photocoagulation plus intravitreal anti-VEGF
treatment against PRP alone for diabetic retinopathy: A systematic
review with meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
13:8076872022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Shukla UV and Tripathy K: Diabetic
retinopathy. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure
Island, FL: 2025
|
|
140
|
Vergmann AS, Nguyen TT, Lee Torp T,
Kawasaki R, Wong TY, Peto T and Grauslund J: Efficacy and side
effects of individualized panretinal photocoagulation. Ophthalmol
Retina. 4:642–644. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Xu W, Cheng W, Cui X and Xu G: Therapeutic
effect against retinal neovascularization in a mouse model of
oxygen-induced retinopathy: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem
cells versus Conbercept. BMC Ophthalmol. 20:72020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Martinez-Alejo JM, Baiza-Duran LM and
Quintana-Hau JDD: Novel therapies for proliferative retinopathies.
Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 13:204062232211403952022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Xu W, Hu Z, Lv Y, Dou G, Zhang Z, Wang H
and Wang Y: Microglial density determines the appearance of
pathological neovascular tufts in oxygen-induced retinopathy. Cell
Tissue Res. 374:25–38. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Qin S, Zhang C, Qin H, Xie H, Luo D, Qiu
Q, Liu K and Zhang J, Xu G and Zhang J: Hyperreflective foci and
subretinal fluid are potential imaging biomarkers to evaluate
anti-VEGF effect in diabetic macular edema. Front Physiol.
12:7914422021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Rojo Arias JE, Englmaier VE and Jászai J:
VEGF-trap modulates retinal inflammation in the murine
oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR) model. Biomedicines. 10:2012022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Palmhof M, Lohmann S, Schulte D, Stute G,
Wagner N, Dick HB and Joachim SC: Fewer functional deficits and
reduced cell death after ranibizumab treatment in a retinal
ischemia model. Int J Mol Sci. 19:16362018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Xu Y, Lu X, Hu Y, Yang B, Tsui CK, Yu S,
Lu L and Liang X: Melatonin attenuated retinal neovascularization
and neuroglial dysfunction by inhibition of HIF-1α-VEGF pathway in
oxygen-induced retinopathy mice. J Pineal Res. 64:e124732018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Wang JH, Lin FL, Chen J, Zhu L, Chuang YF,
Tu L, Ma C, Ling D, Hewitt AW, Tseng CL, et al: TAK1 blockade as a
therapy for retinal neovascularization. Pharmacol Res.
187:1066172023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Church KA, Rodriguez D, Mendiola AS,
Vanegas D, Gutierrez IL, Tamayo I, Amadu A, Velazquez P, Cardona
SM, Gyoneva S, et al: Pharmacological depletion of microglia
alleviates neuronal and vascular damage in the diabetic CX3CR1-WT
retina but not in CX3CR1-KO or
hCX3CR1I249/M280-expressing retina. Front Immunol.
14:11307352023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
Church KA, Rodriguez D, Vanegas D,
Gutierrez IL, Cardona SM, Madrigal JLM, Kaur T and Cardona AE:
Models of microglia depletion and replenishment elicit protective
effects to alleviate vascular and neuronal damage in the diabetic
murine retina. J Neuroinflammation. 19:3002022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Zhao F, Gao X, Ge X, Cui J and Liu X:
Cyanidin-3-o-glucoside (C3G) inhibits vascular leakage regulated by
microglial activation in early diabetic retinopathy and
neovascularization in advanced diabetic retinopathy. Bioengineered.
12:9266–9278. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Yang B, Xu Y, Yu S, Huang Y, Lu L and
Liang X: Anti-angiogenic and anti-inflammatory effect of Magnolol
in the oxygen-induced retinopathy model. Inflamm Res. 65:81–93.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
153
|
Tang X, Cui K, Lu X, Wu P, Yu S, Yang B,
Xu Y and Liang X: A novel hypoxia-inducible factor 1α inhibitor
KC7F2 attenuates oxygen-induced retinal neovascularization. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 63:132022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Song GJ and Suk K: Pharmacological
modulation of functional phenotypes of microglia in
neurodegenerative diseases. Front Aging Neurosci. 9:1392017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Sun X, Ma L, Li X, Wang J, Li Y and Huang
Z: Ferulic acid alleviates retinal neovascularization by modulating
microglia/macrophage polarization through the ROS/NF-κB axis. Front
Immunol. 13:9767292022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
156
|
Wang Y, Chang T, Wu T, Xu W, Dou G, Wang Y
and Guo C: M2 macrophages promote vasculogenesis during retinal
neovascularization by regulating bone marrow-derived cells via
SDF-1/VEGF. Cell Tissue Res. 380:469–486. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Zhou Y, Yoshida S, Nakao S, Yoshimura T,
Kobayashi Y, Nakama T, Kubo Y, Miyawaki K, Yamaguchi M, Ishikawa K,
et al: M2 macrophages enhance pathological neovascularization in
the mouse model of oxygen-induced retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 56:4767–4777. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Caldwell RW, Rodriguez PC, Toque HA,
Narayanan SP and Caldwell RB: Arginase: A multifaceted enzyme
important in health and disease. Physiol Rev. 98:641–665. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Monticelli LA, Buck MD, Flamar AL, Saenz
SA, Tait Wojno ED, Yudanin NA, Osborne LC, Hepworth MR, Tran SV,
Rodewald HR, et al: Arginase 1 is an innate lymphoid-cell-intrinsic
metabolic checkpoint controlling type 2 inflammation. Nat Immunol.
17:656–665. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Chen T, Huang X, Zhao YX, Zhou ZW and Zhou
WS: NEAT1 inhibits the angiogenic activity of cerebral arterial
endothelial cells by inducing the M1 polarization of microglia
through the AMPK signaling pathway. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 29:622024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Niu G and Chen X: Vascular endothelial
growth factor as an anti-angiogenic target for cancer therapy. Curr
Drug Targets. 11:1000–1017. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Cho H, Kambhampati SP, Lai MJ, Zhou L, Lee
G, Xie Y, Hui Q, Kannan RM and Duh EJ: Dendrimer-triamcinolone
acetonide reduces neuroinflammation, pathological angiogenesis, and
neuroretinal dysfunction in ischemic retinopathy. Adv Ther (Weinh).
4:20001812021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Fan W, Huang W, Chen J, Li N, Mao L and
Hou S: Retinal microglia: Functions and diseases. Immunology.
166:268–286. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Wang S, Zhang J, Chen J, Tang L, Ke M, Xue
Y, He Y, Gong Y and Li Z: ω-3PUFAs inhibit hypoxia-induced retinal
neovascularization via regulating microglial pyroptosis through
METTL14-mediated m6A modification of IFNB1 mRNA. Appl Biochem
Biotechnol. 196:5936–5952. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Mei X, Zhou L, Zhang T, Lu B, Sheng Y and
Ji L: Chlorogenic acid attenuates diabetic retinopathy by reducing
VEGF expression and inhibiting VEGF-mediated retinal
neoangiogenesis. Vasc Pharmacol. 101:29–37. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
166
|
Yu Z, Zhang T, Gong C, Sheng Y, Lu B, Zhou
L, Ji L and Wang Z: Erianin inhibits high glucose-induced retinal
angiogenesis via blocking ERK1/2-regulated HIF-1α-VEGF/VEGFR2
signaling pathway. Sci Rep. 6:343062016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
167
|
Zhao K, Jiang Y, Zhang J, Shi J, Zheng P,
Yang C and Chen Y: Celastrol inhibits pathologic neovascularization
in oxygen-induced retinopathy by targeting the
miR-17-5p/HIF-1α/VEGF pathway. Cell Cycle. 21:2091–2108. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Guo L, Choi S, Bikkannavar P and Cordeiro
MF: Microglia: Key players in retinal ageing and neurodegeneration.
Front Cell Neurosci. 16:8047822022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Shao F, Wang X, Wu H, Wu Q and Zhang J:
Microglia and neuroinflammation: Crucial pathological mechanisms in
traumatic brain injury-induced neurodegeneration. Front Aging
Neurosci. 14:8250862022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Gao C, Jiang J, Tan Y and Chen S:
Microglia in neurodegenerative diseases: Mechanism and potential
therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:3592023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Yang I, Han SJ, Kaur G, Crane C and Parsa
AT: The role of microglia in central nervous system immunity and
glioma immunology. J Clin Neurosci. 17:6–10. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
172
|
Masuda T, Sankowski R, Staszewski O and
Prinz M: Microglia heterogeneity in the single-cell era. Cell Rep.
30:1271–1281. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Jiao W, Ji J, Li F, Guo J, Zheng Y, Li S
and Xu W: Activation of the Notch-Nox4-reactive oxygen species
signaling pathway induces cell death in high glucose-treated human
retinal endothelial cells. Mol Med Rep. 19:667–677. 2019.
|
|
174
|
Seo H, Park SJ and Song M: Diabetic
retinopathy (DR): Mechanisms, current therapies, and emerging
strategies. Cells. 14:3762025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Radwan SES, El-Kamel A, Zaki EI,
Burgalassi S, Zucchetti E and El-Moslemany RM: Hyaluronic-coated
albumin nanoparticles for the non-invasive delivery of apatinib in
diabetic retinopathy. Int J Nanomedicine. 16:4481–4494. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Wang S, Yang H, Zheng J, Tong A, Mu S,
Wang D, Zhao M and Li J: Recent advances and prospects of
nanoparticle-based drug delivery for diabetic ocular complications.
Theranostics. 15:3551–3570. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|