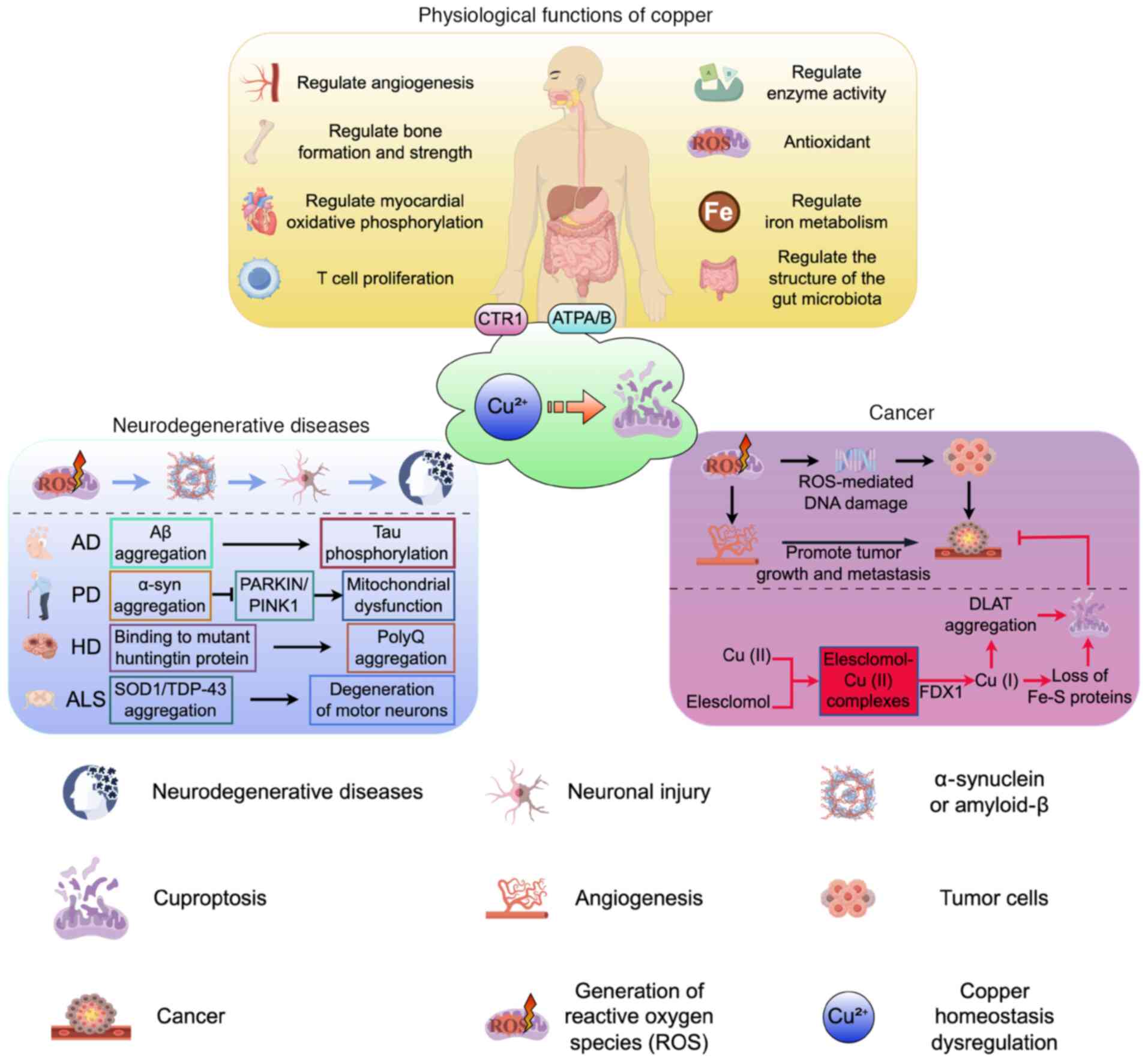
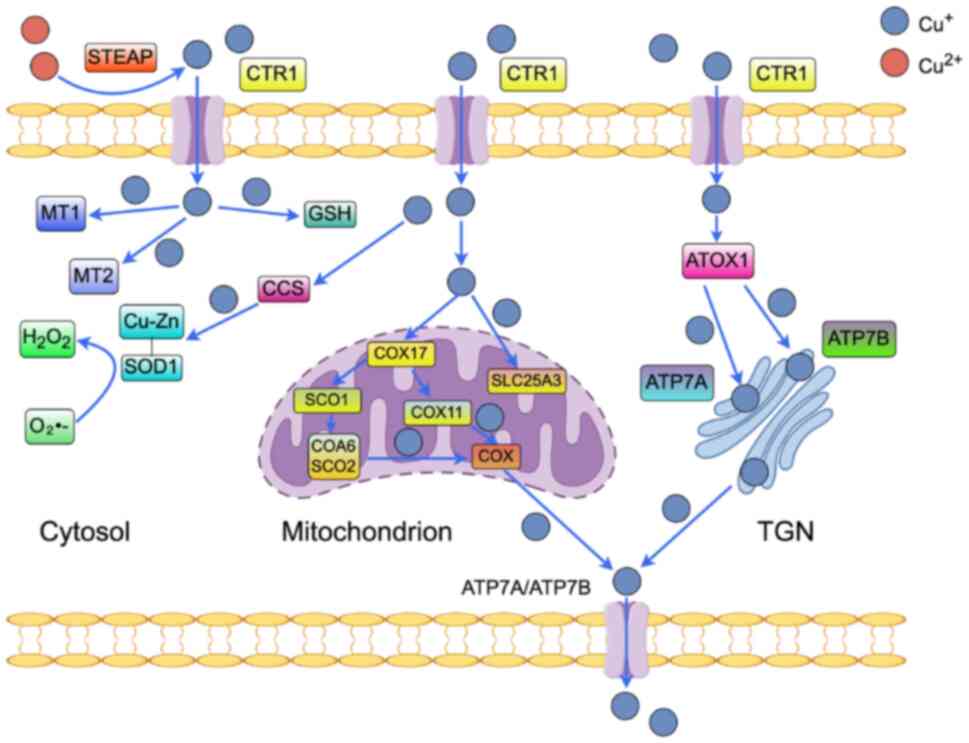
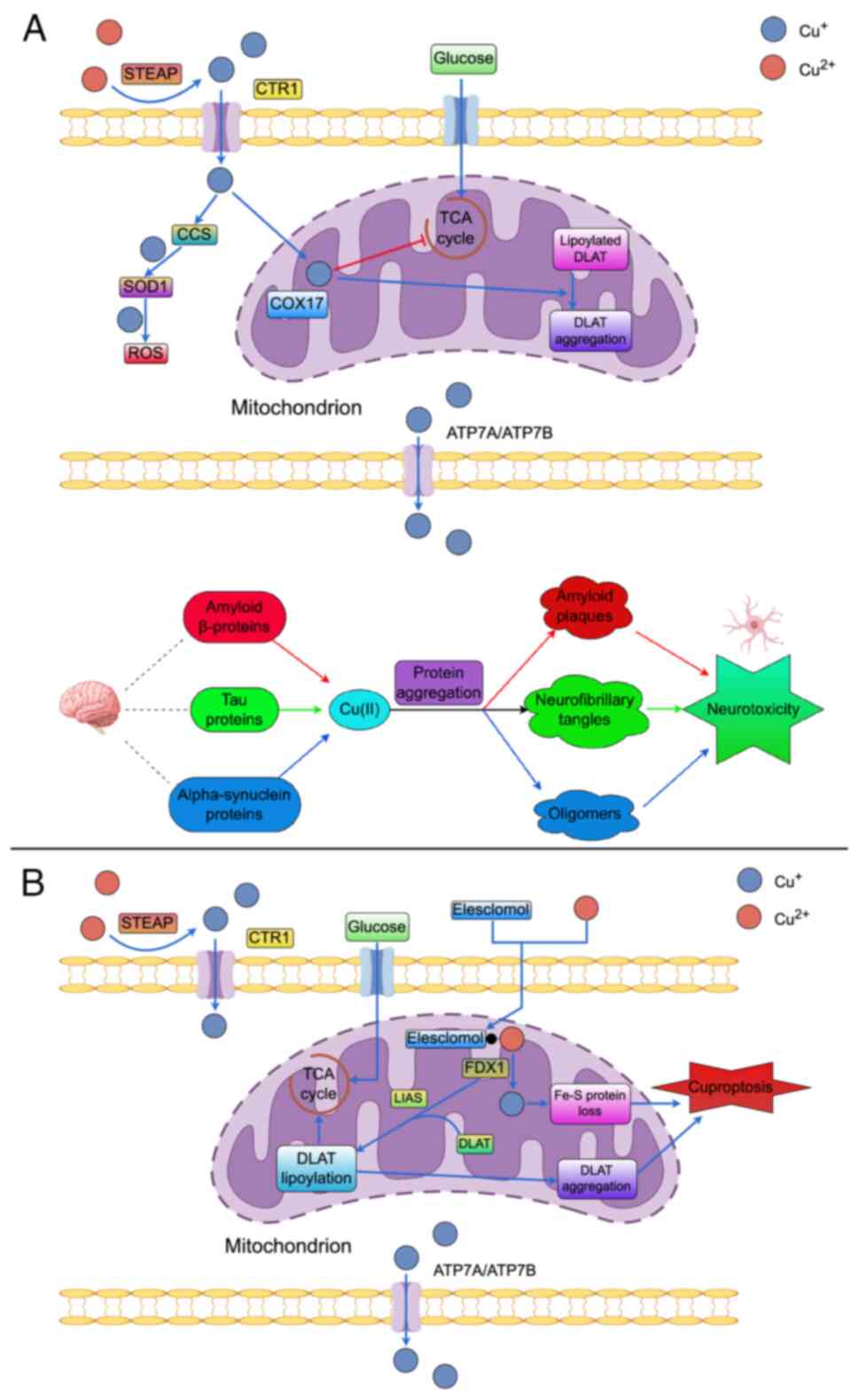
|
1
|
Bost M, Houdart S, Oberli M, Kalonji E,
Huneau JF and Margaritis I: Dietary copper and human health:
Current evidence and unresolved issues. J Trace Elem Med Biol.
35:107–115. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huang F, Lu X, Kuai L, Ru Y, Jiang J, Song
J, Chen S, Mao L, Li Y, Li B, et al: Dual-Site Biomimetic Cu/Zn-MOF
for atopic dermatitis catalytic therapy via suppressing
FcүR-mediated phagocytosis. J Am Chem Soc. 146:3186–3199. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ash D, Sudhahar V, Youn SW, Okur MN, Das
A, O'Bryan JP, McMenamin M, Hou Y, Kaplan JH, Fukai T and
Ushio-Fukai M: The P-type ATPase transporter ATP7A promotes
angiogenesis by limiting autophagic degradation of VEGFR2. Nat
Commun. 12:30912021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ding H, Gao YS, Wang Y, Hu C, Sun Y and
Zhang C: Dimethyloxaloylglycine increases the bone healing capacity
of adipose-derived stem cells by promoting osteogenic
differentiation and angiogenic potential. Stem Cells Dev.
23:990–1000. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Akhtar H, Alhamoudi FH, Marshall J, Ashton
T, Darr JA, Rehman IU, Chaudhry AA and Reilly G: Synthesis of
cerium, zirconium, and copper doped zinc oxide nanoparticles as
potential biomaterials for tissue engineering applications.
Heliyon. 10:e291502024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Han J, Luo J, Wang C, Kapilevich L and
Zhang XA: Roles and mechanisms of copper homeostasis and
cuproptosis in osteoarticular diseases. Biomed Pharmacother.
174:1165702024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wei M, Huang Q, Dai Y, Zhou H, Cui Y, Song
W, Di D, Zhang R, Li C, Wang Q and Jing T: Manganese, iron, copper,
and selenium co-exposure and osteoporosis risk in Chinese adults. J
Trace Elem Med Biol. 72:1269892022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xiao T, Ackerman CM, Carroll EC, Jia S,
Hoagland A, Chan J, Thai B, Liu CS, Isacoff EY and Chang CJ: Copper
regulates rest-activity cycles through the locus
coeruleus-norepinephrine system. Nat Chem Biol. 14:655–663. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Benatar M, Robertson J and Andersen PM:
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis caused by SOD1 variants: From genetic
discovery to disease prevention. Lancet Neurol. 24:77–86. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Horvath R, Kemp JP, Tuppen HA, Hudson G,
Oldfors A, Marie SK, Moslemi AR, Servidei S, Holme E, Shanske S, et
al: Molecular basis of infantile reversible cytochrome c oxidase
deficiency myopathy. Brain. 132(Pt 11): 3165–3174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qu Y, Zhan Q, Du S, Ding Y, Fang B, Du W,
Wu Q, Yu H, Li L and Huang W: Catalysis-based specific detection
and inhibition of tyrosinase and their application. J Pharm Anal.
10:414–425. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Foehr R, Anderson K, Dombrowski O, Foehr A
and Foehr ED: Dysregulation of extracellular matrix and lysyl
oxidase in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV skin fibroblasts.
Orphanet J Rare Dis. 19:92024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wassenberg T, Deinum J, van Ittersum FJ,
Kamsteeg EJ, Pennings M, Verbeek MM, Wevers RA, van Albada ME, Kema
IP, Versmissen J, et al: Clinical presentation and long-term
follow-up of dopamine beta hydroxylase deficiency. J Inherit Metab
Dis. 44:554–565. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
De Feyter S, Beyens A and Callewaert B:
ATP7A-related copper transport disorders: A systematic review and
definition of the clinical subtypes. J Inherit Metab Dis.
46:163–173. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stalke A, Behrendt A, Hennig F, Gohlke H,
Buhl N, Reinkens T, Baumann U, Schlegelberger B, Illig T, Pfister
ED and Skawran B: Functional characterization of novel or yet
uncharacterized ATP7B missense variants detected in patients with
clinical Wilson's disease. Clin Genet. 104:174–185. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Y, Ma J, Wang R, Luo Y, Zheng S and
Wang X: Zinc transporter 1 functions in copper uptake and
cuproptosis. Cell Metab. 36:2118–2129 e6. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ohgami RS, Campagna DR, McDonald A and
Fleming MD: The Steap proteins are metalloreductases. Blood.
108:1388–1394. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wyman S, Simpson RJ, McKie AT and Sharp
PA: Dcytb (Cybrd1) functions as both a ferric and a cupric
reductase in vitro. FEBS Lett. 582:1901–1906. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kleven MD, Dlakic M and Lawrence CM:
Characterization of a Single b-type Heme, FAD, and metal binding
sites in the transmembrane domain of six-transmembrane epithelial
antigen of the prostate (STEAP) family proteins. J Biol Chem.
290:22558–22569. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kirsipuu T, Zadorožnaja A, Smirnova J,
Friedemann M, Plitz T, Tõugu V and Palumaa P: Copper(II)-binding
equilibria in human blood. Sci Rep. 10:56862020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Linder MC: Ceruloplasmin and other copper
binding components of blood plasma and their functions: An update.
Metallomics. 8:887–905. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Moriya M, Ho YH, Grana A, Nguyen L,
Alvarez A, Jamil R, Ackland ML, Michalczyk A, Hamer P, Ramos D, et
al: Copper is taken up efficiently from albumin and
alpha2-macroglobulin by cultured human cells by more than one
mechanism. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 295:C708–C721. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu N, Lo LS, Askary SH, Jones L, Kidane
TZ, Trang T, Nguyen M, Goforth J, Chu YH, Vivas E, et al:
Transcuprein is a macroglobulin regulated by copper and iron
availability. J Nutr Biochem. 18:597–608. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang Y, Hodgkinson V, Zhu S, Weisman GA
and Petris MJ: Advances in the understanding of mammalian copper
transporters. Adv Nutr. 2:129–137. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Chen L, Li N, Zhang M, Sun M, Bian J, Yang
B, Li Z, Wang J, Li F, Shi X, et al: APEX2-based proximity labeling
of Atox1 Identifies CRIP2 as a nuclear copper-binding protein that
regulates autophagy activation. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl.
60:25346–25355. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
González-Ballesteros MM, Sánchez-Sánchez
L, Espinoza-Guillén A, Espinal-Enríquez J, Mejía C, Hernández-Lemus
E and Ruiz-Azuara L: Antitumoral and antimetastatic activity by
mixed chelate copper(II) Compounds (Casiopeínas®) on
triple-negative breast cancer, in vitro and in vivo models. Int J
Mol Sci. 25:88032024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kuo YM, Gybina AA, Pyatskowit JW,
Gitschier J and Prohaska JR: Copper transport protein (Ctr1) levels
in mice are tissue specific and dependent on copper status. J Nutr.
136:21–26. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Vizcaíno C, Mansilla S and Portugal J: Sp1
transcription factor: A long-standing target in cancer
chemotherapy. Pharmacol Ther. 152:111–124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xue Q, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, Tang D, Liu J
and Chen X: Copper metabolism in cell death and autophagy.
Autophag. 19:2175–2195. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liang ZD, Tsai WB, Lee MY, Savaraj N and
Kuo MT: Specificity protein 1 (sp1) oscillation is involved in
copper homeostasis maintenance by regulating human high-affinity
copper transporter 1 expression. Mol Pharmacol. 81:455–464. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Ohse VA, Klotz LO and Priebs J: Copper
homeostasis in the model organism C. elegans. Cells. 13:7272024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hatori Y and Lutsenko S: The role of
copper chaperone Atox1 in coupling redox homeostasis to
intracellular copper distribution. Antioxidants (Basel). 5:252016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lutsenko S, Barnes NL, Bartee MY and
Dmitriev OY: Function and regulation of human copper-transporting
ATPases. Physiol Rev. 87:1011–1046. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sturtz LA, Diekert K, Jensen LT, Lill R
and Culotta VC: A fraction of yeast Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase and
its metallochaperone, CCS, localize to the intermembrane space of
mitochondria. A physiological role for SOD1 in guarding against
mitochondrial oxidative damage. J Biol Chem. 276:38084–38089. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang Y, Branicky R, Noë A and Hekimi S:
Superoxide dismutases: Dual roles in controlling ROS damage and
regulating ROS signaling. J Cell Biol. 217:1915–1928. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Miriyala S, Spasojevic I, Tovmasyan A,
Salvemini D, Vujaskovic Z, St Clair D and Batinic-Haberle I:
Manganese superoxide dismutase, MnSOD and its mimics. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1822:794–814. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Boyd SD, Calvo JS, Liu L, Ullrich MS,
Skopp A, Meloni G and Winkler DD: The yeast copper chaperone for
copper-zinc superoxide dismutase (CCS1) is a multifunctional
chaperone promoting all levels of SOD1 maturation. J Biol Chem.
294:1956–1966. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Ding Y, Chen Y, Wu Z, Yang N, Rana K, Meng
X, Liu B, Wan H and Qian W: SsCox17, a copper chaperone, is
required for pathogenic process and oxidative stress tolerance of
Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Plant Sci. 322:1113452022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Banci L, Bertini I, Ciofi-Baffoni S,
Hadjiloi T, Martinelli M and Palumaa P: Mitochondrial copper(I)
transfer from Cox17 to Sco1 is coupled to electron transfer. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:6803–6808. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ge EJ, Bush AI, Casini A, Cobine PA, Cross
JR, DeNicola GM, Dou QP, Franz KJ, Gohil VM, Gupta S, et al:
Connecting copper and cancer: From transition metal signalling to
metalloplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 22:102–113. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
McCann C, Quinteros M, Adelugba I, Morgada
MN, Castelblanco AR, Davis EJ, Lanzirotti A, Hainer SJ, Vila AJ,
Navea JG and Padilla-Benavides T: The mitochondrial Cu(+)
transporter PiC2 (SLC25A3) is a target of MTF1 and contributes to
the development of skeletal muscle in vitro. Front Mol Biosci.
9:10379412022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
van Rensburg MJ, van Rooy M, Bester MJ,
Serem JC, Venter C and Oberholzer HM: Oxidative and haemostatic
effects of copper, manganese and mercury, alone and in combination
at physiologically relevant levels: An ex vivo study. Hum Exp
Toxicol. 38:419–433. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Ruturaj, Mishra M, Saha S, Maji S,
Rodriguez-Boulan E, Schreiner R and Gupta A: Regulation of the
apico-basolateral trafficking polarity of the homologous
copper-ATPases ATP7A and ATP7B. J Cell Sci. 137:jcs2612582024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Guttmann S, Nadzemova O, Grünewald I,
Lenders M, Brand E, Zibert A and Schmidt HH: ATP7B knockout
disturbs copper and lipid metabolism in Caco-2 cells. PLoS One.
15:e02300252020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dmitriev OY and Patry J: Structure and
mechanism of the human copper transporting ATPases: Fitting the
pieces into a moving puzzle. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr.
1866:1843062024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Percival SS: Copper and immunity. Am J
Clin Nutr. 67(5 Suppl): 1064S–1068S. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Jonny, Sitepu EC, Nidom CA, Wirjopranoto
S, Sudiana IK, Ansori ANM and Putranto TA: Ex vivo-generated
tolerogenic dendritic cells: Hope for a definitive therapy of
autoimmune diseases. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 46:4035–4048. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Backal A, Velinov M, Garcia J and Louis
CL: Novel, likely pathogenic variant in ATP7A associated with
Menkes disease diagnosed with ultrarapid genome sequencing. BMJ
Case Rep. 17:e2597922024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tümer Z and Møller LB: Menkes disease. Eur
J Hum Genet. 18:511–518. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Moller LB, Mogensen M, Weaver DD and
Pedersen PA: Occipital horn syndrome as a result of splice site
mutations in ATP7A. no activity of ATP7A splice variants missing
exon 10 or exon 15. Front Mol Neurosci. 14:5322912021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Batzios S, Tal G, DiStasio AT, Peng Y,
Charalambous C, Nicolaides P, Kamsteeg EJ, Korman SH, Mandel H,
Steinbach PJ, et al: Newly identified disorder of copper metabolism
caused by variants in CTR1, a high-affinity copper transporter. Hum
Mol Genet. 31:4121–4130. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Garnica A, Chan WY and Rennert O:
Copper-histidine treatment of Menkes disease. J Pediatr.
125:336–338. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Moini M, To U and Schilsky ML: Recent
advances in Wilson disease. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 6:212021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Weiss KH, Członkowska A, Hedera P and
Ferenci P: WTX101 - an investigational drug for the treatment of
Wilson disease. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 27:561–567. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kreuder J, Otten A, Fuder H, Tümer Z,
Tønnesen T, Horn N and Dralle D: Clinical and biochemical
consequences of copper-histidine therapy in Menkes disease. Eur J
Pediatr. 152:828–832. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Christodoulou J, Danks DM, Sarkar B,
Baerlocher KE, Casey R, Horn N, Tümer Z and Clarke JT: Early
treatment of Menkes disease with parenteral copper-histidine:
Long-term follow-up of four treated patients. Am J Med Genet.
76:154–164. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ramchandani D, Berisa M, Tavarez DA, Li Z,
Miele M, Bai Y, Lee SB, Ban Y, Dephoure N, Hendrickson RC, et al:
Copper depletion modulates mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation
to impair triple negative breast cancer metastasis. Nat Commun.
12:73112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Xu B, Wang S, Li R, Chen K, He L, Deng M,
Kannappan V, Zha J, Dong H and Wang W: Disulfiram/copper
selectively eradicates AML leukemia stem cells in vitro and in vivo
by simultaneous induction of ROS-JNK and inhibition of NF-κB and
Nrf2. Cell Death Dis. 8:e27972017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Theophanides T and Anastassopoulou J:
Copper and carcinogenesis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 42:57–64. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhong CC, Zhao T, Hogstrand C, Chen F,
Song CC and Luo Z: Copper (Cu) induced changes of lipid metabolism
through oxidative stress-mediated autophagy and Nrf2/PPARγ
pathways. J Nutr Biochem. 100:1088832022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Wang Q, Sun Y, Zhao A, Cai X, Yu A, Xu Q,
Liu W, Zhang N, Wu S, Chen Y and Wang W: High dietary copper intake
induces perturbations in the gut microbiota and affects host
ovarian follicle development. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf.
255:1148102023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Tsang T, Posimo JM, Gudiel AA, Cicchini M,
Feldser DM and Brady DC: Copper is an essential regulator of the
autophagic kinases ULK1/2 to drive lung adenocarcinoma. Nat Cell
Biol. 22:412–424. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Conforti RA, Delsouc MB, Zorychta E,
Telleria CM and Casais M: Copper in gynecological diseases. Int J
Mol Sci. 24:175782023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Compston A: Progressive lenticular
degeneration: a familial nervous disease associated with cirrhosis
of the liver, by S. A. Kinnier Wilson, (From the National Hospital,
and the Laboratory of the National Hospital, Queen Square, London)
Brain 1912: 34; 295-509. Brain. 132:1997–2001. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kipker N, Alessi K, Bojkovic M, Padda I
and Parmar MS: Neurological-type wilson disease: Epidemiology,
clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management. Cureus.
15:e381702023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Członkowska A, Litwin T, Dusek P, Ferenci
P, Lutsenko S, Medici V, Rybakowski JK, Weiss KH and Schilsky ML:
Wilson disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 4:212018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Kirk FT, Munk DE, Swenson ES, Quicquaro
AM, Vendelbo MH, Larsen A, Schilsky ML, Ott P and Sandahl TD:
Effects of tetrathiomolybdate on copper metabolism in healthy
volunteers and in patients with Wilson disease. J Hepatol.
80:586–595. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Bruha R, Marecek Z, Pospisilova L,
Nevsimalova S, Vitek L, Martasek P, Nevoral J, Petrtyl J, Urbanek
P, Jiraskova A and Ferenci P: Long-term follow-up of Wilson
disease: natural history, treatment, mutations analysis and
phenotypic correlation. Liver Int. 31:83–91. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Członkowska A, Litwin T, Karliński M,
Dziezyc K, Chabik G and Czerska M: D-penicillamine versus zinc
sulfate as first-line therapy for Wilson's disease. Eur J Neurol.
21:599–606. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Brewer GJ: Practical recommendations and
new therapies for Wilson's disease. Drugs. 50:240–249. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Xie J, Yang Y, Gao Y and He J:
Cuproptosis: Mechanisms and links with cancers. Mol Cancer.
22:462023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Członkowska A and Litwin T: Wilson disease
- currently used anticopper therapy. Handb Clin Neurol.
142:181–191. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Lambert C, Beraldo H, Lievre N,
Garnier-Suillerot A, Dorlet P and Salerno M: Bis(thiosemicarbazone)
copper complexes: Mechanism of intracellular accumulation. J Biol
Inorg Chem. 18:59–69. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Ayton S and Bush AI: β-amyloid: The known
unknowns. Ageing Res Rev. 65:1012122021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Egan MF, Kost J, Voss T, Mukai Y, Aisen
PS, Cummings JL, Tariot PN, Vellas B, van Dyck CH, Boada M, et al:
Randomized Trial of Verubecestat for Prodromal Alzheimer's Disease.
N Engl J Med. 380:1408–1420. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Doody RS, Thomas RG, Farlow M, Iwatsubo T,
Vellas B, Joffe S, Kieburtz K, Raman R, Sun X, Aisen PS, et al:
Phase 3 trials of solanezumab for mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's
disease. N Engl J Med. 370:311–321. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Salloway S, Sperling R, Fox NC, Blennow K,
Klunk W, Raskind M, Sabbagh M, Honig LS, Porsteinsson AP, Ferris S,
et al: Two phase 3 trials of bapineuzumab in mild-to-moderate
Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 370:322–333. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Scheltens P, De Strooper B, Kivipelto M,
Holstege H, Chételat G, Teunissen CE, Cummings J and van der Flier
WM: Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 397:1577–1590. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Mazur T, Malik M and Bienko DC: The impact
of chelating compounds on Cu(2+), Fe(2+)/(3+), and Zn(2+) ions in
Alzheimer's disease treatment. J Inorg Biochem. 257:1126012024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Xu J, Church SJ, Patassini S, Begley P,
Waldvogel HJ, Curtis MA, Faull RLM, Unwin RD and Cooper GJS:
Evidence for widespread, severe brain copper deficiency in
Alzheimer's dementia. Metallomics. 9:1106–1119. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Rembach A, Hare DJ, Lind M, Fowler CJ,
Cherny RA, McLean C, Bush AI, Masters CL and Roberts BR: Decreased
copper in Alzheimer's disease brain is predominantly in the soluble
extractable fraction. Int J Alzheimers Dis.
2013:6232412013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Scholefield M, Church SJ, Xu J and Cooper
GJS: Metallomic analysis of brain tissues distinguishes between
cases of dementia with Lewy bodies, Alzheimer's disease, and
Parkinson's disease dementia. Front Neurosci. 18:14123562024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Squitti R, Simonelli I, Ventriglia M,
Siotto M, Pasqualetti P, Rembach A, Doecke J and Bush AI:
Meta-analysis of serum non-ceruloplasmin copper in Alzheimer's
disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 38:809–822. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Jiao Y and Yang P: Mechanism of copper(II)
inhibiting Alzheimer's amyloid beta-peptide from aggregation: A
molecular dynamics investigation. J Phys Chem B. 111:7646–7655.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Gomes LM, Vieira RP, Jones MR, Wang MC,
Dyrager C, Souza-Fagundes EM, Da Silva JG, Storr T and Beraldo H:
8-Hydroxyquinoline Schiff-base compounds as antioxidants and
modulators of copper-mediated Aβ peptide aggregation. J Inorg
Biochem. 139:106–116. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Pedersen JT, Østergaard J, Rozlosnik N,
Gammelgaard B and Heegaard NH: Cu(II) mediates kinetically
distinct, non-amyloidogenic aggregation of amyloid-beta peptides. J
Biol Chem. 286:26952–26963. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Reybier K, Ayala S, Alies B, Rodrigues JV,
Bustos Rodriguez S, La Penna G, Collin F, Gomes CM, Hureau C and
Faller P: Free Superoxide is an intermediate in the production of
H2O2 by Copper(I)-Aβ Peptide and O2. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl.
55:1085–1089. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Fanlo-Ucar H, Picón-Pagès P,
Herrera-Fernández V, Ill-Raga G and Muñoz FJ: The dual role of
amyloid beta-peptide in oxidative stress and inflammation:
Unveiling Their connections in Alzheimer's disease etiopathology.
Antioxidants (Basel). 13:12082024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Xia Y, Dore V, Fripp J, Bourgeat P, Laws
SM, Fowler CJ, Rainey-Smith SR, Martins RN, Rowe C, Masters CL, et
al: Association of basal forebrain atrophy with cognitive decline
in early Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 103:e2096262024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Lang M, Fan Q, Wang L, Zheng Y, Xiao G,
Wang X, Wang W, Zhong Y and Zhou B: Inhibition of human
high-affinity copper importer Ctr1 orthologous in the nervous
system of Drosophila ameliorates Aβ42-induced Alzheimer's
disease-like symptoms. Neurobiol Aging. 34:2604–2612. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Ceccom J, Coslédan F, Halley H, Francès B,
Lassalle JM and Meunier B: Copper chelator induced efficient
episodic memory recovery in a non-transgenic Alzheimer's mouse
model. PLoS One. 2012(7): e431052012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Quinn JF, Harris CJ, Cobb KE, Domes C,
Ralle M, Brewer G and Wadsworth TL: A copper-lowering strategy
attenuates amyloid pathology in a transgenic mouse model of
Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 21:903–914. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Chen C, Jiang X, Li Y, Yu H, Li S, Zhang
Z, Xu H, Yang Y, Liu G, Zhu F, et al: Low-dose oral copper
treatment changes the hippocampal phosphoproteomic profile and
perturbs mitochondrial function in a mouse model of Alzheimer's
disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 135:144–156. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Yao D, Jing T, Niu L, Huang X, Wang Y,
Deng X and Wang M: Amyloidogenesis induced by diet cholesterol and
copper in a model mouse for Alzheimer's disease and protection
effects of zinc and fluvastatin. Brain Res Bull. 143:1–8. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Maynard CJ, Cappai R, Volitakis I,
Laughton KM, Masters CL, Bush AI and Li QX: Chronic exposure to
high levels of zinc or copper has little effect on brain metal
homeostasis or Abeta accumulation in transgenic APP-C100 mice. Cell
Mol Neurobiol. 29:757–767. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Acevedo KM, Hung YH, Dalziel AH, Li QX,
Laughton K, Wikhe K, Rembach A, Roberts B, Masters CL, Bush AI and
Camakaris J: Copper promotes the trafficking of the amyloid
precursor protein. J Biol Chem. 286:8252–8262. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
97
|
Borchardt T, Camakaris J, Cappai R,
Masters CL, Beyreuther K and Multhaup G: Copper inhibits
beta-amyloid production and stimulates the non-amyloidogenic
pathway of amyloid-precursor-protein secretion. Biochem J.
344:461–467. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Afsar A, Chacon Castro MDC, Soladogun AS
and Zhang L: Recent development in the understanding of molecular
and cellular mechanisms underlying the etiopathogenesis of
Alzheimer's disease. Int J Mol Sci. 24:72582023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Wang Y, Chen Y, Zhang J, Yang Y, Fleishman
JS, Wang Y, Wang J, Chen J, Li Y and Wang H: Cuproptosis: A novel
therapeutic target for overcoming cancer drug resistance. Drug
Resist Updat. 72:1010182024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Kumar V, Singh AP, Wheeler N, Galindo CL
and Kim JJ: Safety profile of D-penicillamine: A comprehensive
pharmacovigilance analysis by FDA adverse event reporting system.
Expert Opin Drug Saf. 20:1443–1450. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Lee EJ, Woo MH, Moon JS and Ko JS:
Efficacy and safety of D-penicillamine, trientine, and zinc in
pediatric Wilson disease patients. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 19:2612024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Perez DR, Sklar LA and Chigaev A:
Clioquinol: To harm or heal. Pharmacol Ther. 199:155–163. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Relkin N: Testing the mettle of PBT2 for
Alzheimer's disease. Lancet Neurol. 7:762–763. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Daniel KG, Chen D, Orlu S, Cui QC, Miller
FR and Dou QP: Clioquinol and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate complex
with copper to form proteasome inhibitors and apoptosis inducers in
human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 7:R897–R908. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Crouch PJ, Hung LW, Adlard PA, Cortes M,
Lal V, Filiz G, Perez KA, Nurjono M, Caragounis A, Du T, et al:
Increasing Cu bioavailability inhibits Abeta oligomers and tau
phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:381–386. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Schimmer AD: Clioquinol - a novel
copper-dependent and independent proteasome inhibitor. Curr Cancer
Drug Targets. 11:325–331. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Costello LC and Franklin RB: A proposed
efficacious treatment with clioquinol (Zinc Ionophore) and
Cabergoline (Prolactin Dopamine Agonist) for the treatment of
terminal androgen-independent prostate cancer. Why and How? J Clin
Res Oncol. Feb 27–2019.Epub ahead of print. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Donnelly PS, Caragounis A, Du T, Laughton
KM, Volitakis I, Cherny RA, Sharples RA, Hill AF, Li QX, Masters
CL, et al: Selective intracellular release of copper and zinc ions
from bis(thiosemicarbazonato) complexes reduces levels of Alzheimer
disease amyloid-beta peptide. J Biol Chem. 283:4568–4577. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Drew SC: Chelator PBT2 forms a ternary
Cu(2+) Complex with β-Amyloid That has high stability but low
specificity. Int J Mol Sci. 24:92672023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Scholefield M, Patassini S, Xu J and
Cooper GJS: Widespread selenium deficiency in the brain of cases
with Huntington's disease presents a new potential therapeutic
target. Ebiomedicine. 97:1048242023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Upadhyay A, Chhangani D, Rao NR, Kofler J,
Vassar R, Rincon-Limas DE and Savas JN: Amyloid fibril proteomics
of AD brains reveals modifiers of aggregation and toxicity. Mol
Neurodegener. 18:612023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Hands SL, Mason R, Sajjad MU, Giorgini F
and Wyttenbach A: Metallothioneins and copper metabolism are
candidate therapeutic targets in Huntington's disease. Biochem Soc
Trans. 38:552–558. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Zhu Z, Song M, Ren J, Liang L, Mao G and
Chen M: Copper homeostasis and cuproptosis in central nervous
system diseases. Cell Death Dis. 15:8502024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Cherny RA, Ayton S, Finkelstein DI, Bush
AI, McColl G and Massa SM: PBT2 Reduces Toxicity in a C. elegans
Model of polyQ aggregation and extends lifespan, reduces striatal
atrophy and improves motor performance in the R6/2 mouse model of
Huntington's disease. J Huntingtons Dis. 1:211–219. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Jahanshahi M, Krack P,
Litvan I, Macias R, Bezard E and Obeso JA: Initial clinical
manifestations of Parkinson's disease: Features and
pathophysiological mechanisms. Lancet Neurol. 8:1128–1139. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Davies KM, Hare DJ, Cottam V, Chen N,
Hilgers L, Halliday G, Mercer JF and Double KL: Localization of
copper and copper transporters in the human brain. Metallomics.
5:43–51. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Dexter DT, Wells FR, Lees AJ, Agid F, Agid
Y, Jenner P and Marsden CD: Increased nigral iron content and
alterations in other metal ions occurring in brain in Parkinson's
disease. J Neurochem. 52:1830–1836. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Ayton S, Lei P, Duce JA, Wong BX,
Sedjahtera A, Adlard PA, Bush AI and Finkelstein DI: Ceruloplasmin
dysfunction and therapeutic potential for Parkinson disease. Ann
Neurol. 73:554–559. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Bisaglia M and Bubacco L: Copper ions and
Parkinson's disease: Why Is homeostasis so relevant? Biomolecules.
10:1952020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Hemmati-Dinarvand M, Saedi S, Valilo M,
Kalantary-Charvadeh A, Alizadeh Sani M, Kargar R, Safari H and
Samadi N: Oxidative stress and Parkinson's disease: Conflict of
oxidant-antioxidant systems. Neurosci Lett. 709:1342962019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Trist BG, Davies KM, Cottam V, Genoud S,
Ortega R, Roudeau S, Carmona A, De Silva K, Wasinger V, Lewis SJG,
et al: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-like superoxide dismutase 1
proteinopathy is associated with neuronal loss in Parkinson's
disease brain. Acta Neuropathol. 134:113–127. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Zhang MS, Liang JH, Yang MJ, Ren YR, Cheng
DH, Wu QH, He Y and Yin J: Low serum superoxide dismutase is
associated with a high risk of cognitive impairment after mild
acute ischemic stroke. Front Aging Neurosci. 14:8341142022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Quinn PMJ, Moreira PI, Ambrósio AF and
Alves CH: PINK1/PARKIN signalling in neurodegeneration and
neuroinflammation. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 8:1892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Cummins N and Götz J: Shedding light on
mitophagy in neurons: What is the evidence for PINK1/Parkin
mitophagy in vivo? Cell Mol Life Sci. 75:1151–1162. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Aschner M, Skalny AV, Lu R, Martins AC,
Tizabi Y, Nekhoroshev SV, Santamaria A, Sinitskiy AI and Tinkov AA:
Mitochondrial pathways of copper neurotoxicity: Focus on
mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy. Front Mol Neurosci.
17:15048022024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Ling Z, Ge X, Jin C, Song Z, Zhang H, Fu
Y, Zheng K, Xu R and Jiang H: Copper doped bioactive glass promotes
matrix vesicles-mediated biomineralization via osteoblast mitophagy
and mitochondrial dynamics during bone regeneration. Bioact Mater.
46:195–212. 2024.
|
|
127
|
Synhaivska O, Bhattacharya S, Campioni S,
Thompson D and Nirmalraj PN: Single-particle resolution of
copper-associated annular α-synuclein oligomers reveals potential
therapeutic targets of neurodegeneration. ACS Chem Neurosci.
13:1410–1421. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Triscott J, Rose Pambid M and Dunn SE:
Concise review: Bullseye: Targeting cancer stem cells to improve
the treatment of gliomas by repurposing disulfiram. Stem Cells.
33:1042–1046. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Kannappan V, Ali M, Small B, Rajendran G,
Elzhenni S, Taj H, Wang W and Dou QP: Recent advances in
repurposing disulfiram and disulfiram derivatives as
copper-dependent anticancer agents. Front Mol Biosci. 8:7413162021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Zhou Q, Zhang Y, Lu L, Zhang H, Zhao C, Pu
Y and Yin L: Copper induces microglia-mediated neuroinflammation
through ROS/NF-κB pathway and mitophagy disorder. Food Chem
Toxicol. 168:1133692022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Chidambaram SB, Anand N, Varma SR,
Ramamurthy S, Vichitra C, Sharma A, Mahalakshmi AM and Essa MM:
Superoxide dismutase and neurological disorders. IBRO Neurosci Rep.
16:373–394. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Cukierman DS, Pinheiro AB,
Castiñeiras-Filho SL, da Silva AS, Miotto MC, De Falco A, de P
Ribeiro T, Maisonette S, da Cunha AL, Hauser-Davis RA, et al: A
moderate metal-binding hydrazone meets the criteria for a
bioinorganic approach towards Parkinson's disease: Therapeutic
potential, blood-brain barrier crossing evaluation and preliminary
toxicological studies. J Inorg Biochem. 170:160–168. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Vavere AL and Lewis JS: Cu-ATSM: A
radiopharmaceutical for the PET imaging of hypoxia. Dalton Trans.
4893–4902. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Ikawa M, Okazawa H, Kudo T, Kuriyama M,
Fujibayashi Y and Yoneda M: Evaluation of striatal oxidative stress
in patients with Parkinson's disease using [62Cu]ATSM PET. Nucl Med
Biol. 38:945–951. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Hung LW, Villemagne VL, Cheng L, Sherratt
NA, Ayton S, White AR, Crouch PJ, Lim S, Leong SL, Wilkins S, et
al: The hypoxia imaging agent CuII(atsm) is neuroprotective and
improves motor and cognitive functions in multiple animal models of
Parkinson's disease. J Exp Med. 209:837–854. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Rowlands BD, Trist BG, Karozis C, Schaffer
G, Mor D, Harwood R, Rosolen SA, Cottam V, Persson-Carboni F,
Richardson M, et al: Copper supplementation mitigates
Parkinson-like wild-type SOD1 pathology and nigrostriatal
degeneration in a novel mouse model. Acta Neuropathol Commun.
13:1332025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Al-Chalabi A and Hardiman O: The
epidemiology of ALS: A conspiracy of genes, environment and time.
Nat Rev Neurol. 9:617–628. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Min JH, Sarlus H and Harris RA: Copper
toxicity and deficiency: The vicious cycle at the core of protein
aggregation in ALS. Front Mol Neurosci. 17:14081592024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Moriyama H and Yokota T: Recent progress
of antisense oligonucleotide therapy for
superoxide-dismutase-1-mutated amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Focus
on tofersen. Genes (Basel). 15:13422024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Jerusalem F, Pohl C, Karitzky J and Ries
F: ALS. Neurology. 47(Suppl 4): S218–S220. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Gurney ME, Pu H, Chiu AY, Dal Canto MC,
Polchow CY, Alexander DD, Caliendo J, Hentati A, Kwon YW, Deng HX,
et al: Motor neuron degeneration in mice that express a human Cu,
Zn superoxide dismutase mutation. Science. 264:1772–1775. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Ansori ANM, Widyananda MH, Antonius Y,
Murtadlo AAA, Kharisma VD, Wiradana PA, Sahadewa S, Durry FD,
Maksimiuk N, Rebezov M and Zainul R: A review of cancer-related
hypercalcemia: Pathophysiology, current treatments, and future
directions. J Med Pharm Chem Res. 6:944–952. 2024.
|
|
144
|
Wu T, Sempos CT, Freudenheim JL, Muti P
and Smit E: Serum iron, copper and zinc concentrations and risk of
cancer mortality in US adults. Ann Epidemiol. 14:195–201. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Hyvönen MT, Ucal S, Pasanen M, Peräniemi
S, Weisell J, Khomutov M, Khomutov AR, Vepsäläinen J, Alhonen L and
Keinänen TA: Triethylenetetramine modulates polyamine and energy
metabolism and inhibits cancer cell proliferation. Biochem J.
473:1433–1441. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Pavithra V, Sathisha TG, Kasturi K,
Mallika DS, Amos SJ and Ragunatha S: Serum levels of metal ions in
female patients with breast cancer. J Clin Diagn Res. 9:BC25–c27.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Jakhmola V, Parashar T, Ghildiyal P,
Ansori ANM, Sharma RK, Rao NGR, Kalra K, Singh N, Nainwal N, Singh
RK, et al: An in silico study to explore the role of EGFR in
ovarian cancer. Pharmacog J. 14:817–821. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Zhang X and Yang Q: Association between
serum copper levels and lung cancer risk: A meta-analysis. J Int
Med Res. 46:4863–4873. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Saleh SAK, Adly HM, Abdelkhaliq AA and
Nassir AM: Serum levels of selenium, zinc, copper, manganese, and
iron in prostate cancer patients. Curr Urol. 14:44–49. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Atakul T, Altinkaya SO, Abas BI and
Yenisey C: Serum copper and zinc levels in patients with
endometrial cancer. Biol Trace Elem Res. 195:46–54. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Fang AP, Chen PY, Wang XY, Liu ZY, Zhang
DM, Luo Y, Liao GC, Long JA, Zhong RH, Zhou ZG, et al: Serum copper
and zinc levels at diagnosis and hepatocellular carcinoma survival
in the Guangdong liver cancer cohort. Int J Cancer. 144:2823–2832.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Lun X, Wells JC, Grinshtein N, King JC,
Hao X, Dang NH, Wang X, Aman A, Uehling D, Datti A, et al:
Disulfiram when combined with copper enhances the therapeutic
effects of temozolomide for the treatment of glioblastoma. Clin
Cancer Res. 22:3860–3875. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Li Y, Chen F, Chen J, Chan S, He Y, Liu W
and Zhang G: Disulfiram/copper induces antitumor activity against
both nasopharyngeal cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts
through ROS/MAPK and ferroptosis pathways. Cancers (Basel).
12:1382020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Mcauslan BR and Reilly W: Endothelial cell
phagokinesis in response to specific metal ions. Exp Cell Res.
130:147–157. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Narayanan G, R BS, Vuyyuru H, Muthuvel B
and Konerirajapuram Natrajan S: CTR1 Silencing inhibits
angiogenesis by limiting copper entry into endothelial cells. PLoS
One. 8:e719822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Mandinov L, Mandinova A, Kyurkchiev S,
Kyurkchiev D, Kehayov I, Kolev V, Soldi R, Bagala C, de Muinck ED,
Lindner V, et al: Copper chelation represses the vascular response
to injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:6700–6705. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Nurzynska A, Klimek K, Swierzycka I, Palka
K and Ginalska G: Porous curdlan-based hydrogels modified with
copper ions as potential dressings for prevention and management of
bacterial wound infection-an in vitro assessment. Polymers (Basel).
12:18932020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Badet J, Soncin F, Guitton JD, Lamare O,
Cartwright T and Barritault D: Specific binding of angiogenin to
calf pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
86:8427–8431. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Zhao YN, Chen LH, Yang XL, Dong JY, Wu WB,
Chen D, Geng RM, Ke NW and Liu J: Inhibition of copper
transporter-1 by ammonium tetrathiocarbolybdate in the treatment of
pancreatic cancer. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 51:643–649.
2020.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Pan Q, Bao LW and Merajver SD:
Tetrathiomolybdate inhibits angiogenesis and metastasis through
suppression of the NFkappaB signaling cascade. Mol Cancer Res.
1:701–706. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Pan Q, Kleer CG, van Golen KL, Irani J,
Bottema KM, Bias C, De Carvalho M, Mesri EA, Robins DM, Dick RD, et
al: Copper deficiency induced by tetrathiomolybdate suppresses
tumor growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 62:4854–4859.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Li Y, Fang M, Xu Z and Li X:
Tetrathiomolybdate as an old drug in a new use: As a
chemotherapeutic sensitizer for non-small cell lung cancer. J Inorg
Biochem. 233:1118652022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Crowe A, Jackaman C, Beddoes KM, Ricciardo
B and Nelson DJ: Rapid copper acquisition by developing murine
mesothelioma: Decreasing bioavailable copper slows tumor growth,
normalizes vessels and promotes T cell infiltration. PLoS One.
8:e736842013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Cosimo RD, Scarpelli A, Lappano R, Pisano
A, Santolla MF, De Marco P, Cirillo F, Cappello AR, Dolce V,
Belfiore A, et al: Copper activates HIF-1α/GPER/VEGF signalling in
cancer cells. Oncotarget. 6:34158–34177. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Mammoto T, Jiang A, Jiang E, Panigrahy D,
Kieran MW and Mammoto A: Role of collagen matrix in tumor
angiogenesis and glioblastoma multiforme progression. Am J Pathol.
183:1293–1305. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Baldari S, Di Rocco G, Heffern MC, Su TA,
Chang CJ and Toietta G: Effects of copper chelation on BRAF(V600E)
positive colon carcinoma cells. Cancers (Basel). 11:6592019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Brady DC, Crowe MS, Turski ML, Hobbs GA,
Yao X, Chaikuad A, Knapp S, Xiao K, Campbell SL, Thiele DJ and
Counter CM: Copper is required for oncogenic BRAF signalling and
tumorigenesis. Nature. 509:492–496. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Brady DC, Crowe MS, Greenberg DN and
Counter CM: Copper chelation inhibits BRAFV600E-driven
melanomagenesis and counters resistance to BRAFV600E and MEK1/2
inhibitors. Cancer Res. 77:6240–6252. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Ross MO, Xie Y, Owyang RC, Ye C, Zbihley
ONP, Lyu R, Wu T, Wang P, Karginova O, Olopade OI, et al: PTPN2
copper-sensing relays copper level fluctuations into EGFR/CREB
activation and associated CTR1 transcriptional repression. Nat
Commun. 15:69472024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Voli F, Valli E, Lerra L, Kimpton K,
Saletta F, Giorgi FM, Mercatelli D, Rouaen JRC, Shen S, Murray JE,
et al: Intratumoral copper modulates PD-L1 expression and
influences tumor immune evasion. Cancer Res. 80:4129–4144. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Xu M, Casio M, Range DE, Sosa JA and
Counter CM: Copper chelation as targeted therapy in a mouse model
of oncogenic BRAF-Driven papillary thyroid cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
24:4271–4281. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Akins NS, Nielson TC and Le HV: Inhibition
of glycolysis and glutaminolysis: An emerging drug discovery
approach to combat cancer. Curr Top Med Chem. 18:494–504. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Carneiro BA and El-Deiry WS: Targeting
apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 17:395–417. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Achmad AB, Proboningrat A, Ansori ANM,
Fadholly A, Rochmi SE, Samsudin RR, Hidayatik N, Hendarti GA and
Jayanti S: Stem bark ethanolic extract of Pinus merkusii induces
caspase 9-mediated apoptosis in HeLa cells. Open Vet J.
14:2628–2633. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Weinlich R, Oberst A, Beere HM and Green
DR: Necroptosis in development, inflammation and disease. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 18:127–136. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
Bergsbaken T, Fink SL and Cookson BT:
Pyroptosis: Host cell death and inflammation. Nat Rev Microbiol.
7:99–109. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Gao W, Huang Z, Duan J, Nice EC, Lin J and
Huang C: Elesclomol induces copper-dependent ferroptosis in
colorectal cancer cells via degradation of ATP7A. Mol Oncol.
15:3527–3544. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Pan C, Ji Z, Wang Q, Zhang Z, Wang Z, Li
C, Lu S and Ge P: Cuproptosis: Mechanisms, biological significance,
and advances in disease treatment-A systematic review. CNS Neurosci
Ther. 30:e700392024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Huang Z, Wang L, Chen L, Zhang Y and Shi
P: Induction of cell cycle arrest via the p21, p27-cyclin E,A/Cdk2
pathway in SMMC-7721 hepatoma cells by clioquinol. Acta Pharm.
65:463–471. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Tsvetkov P, Detappe A, Cai K, Keys HR,
Brune Z, Ying W, Thiru P, Reidy M, Kugener G, Rossen J, et al:
Mitochondrial metabolism promotes adaptation to proteotoxic stress.
Nat Chem Biol. 15:681–689. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Tardito S, Bassanetti I, Bignardi C,
Elviri L, Tegoni M, Mucchino C, Bussolati O, Franchi-Gazzola R and
Marchiò L: Copper binding agents acting as copper ionophores lead
to caspase inhibition and paraptotic cell death in human cancer
cells. J Am Chem Soc. 133:6235–6242. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Tardito S, Barilli A, Bassanetti I, Tegoni
M, Bussolati O, Franchi-Gazzola R, Mucchino C and Marchiò L:
Copper-dependent cytotoxicity of 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives
correlates with their hydrophobicity and does not require caspase
activation. J Med Chem. 55:10448–10459. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Nagai M, Vo NH, Shin Ogawa L, Chimmanamada
D, Inoue T, Chu J, Beaudette-Zlatanova BC, Lu R, Blackman RK,
Barsoum J, et al: The oncology drug elesclomol selectively
transports copper to the mitochondria to induce oxidative stress in
cancer cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 52:2142–2150. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Shimada K, Reznik E, Stokes ME,
Krishnamoorthy L, Bos PH, Song Y, Quartararo CE, Pagano NC, Carpizo
DR, deCarvalho AC, et al: Copper-binding small molecule induces
oxidative stress and cell-cycle arrest in
glioblastoma-patient-derived cells. Cell Chem Biol. 25:585–594 e7.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Yip NC, Fombon IS, Liu P, Brown S,
Kannappan V, Armesilla AL, Xu B, Cassidy J, Darling JL and Wang W:
Disulfiram modulated ROS-MAPK and NFĸB pathways and targeted breast
cancer cells with cancer stem cell-like properties. Br J Cancer.
104:1564–1574. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Chen D, Cui QC, Yang H and Dou QP:
Disulfiram, a clinically used anti-alcoholism drug and
copper-binding agent, induces apoptotic cell death in breast cancer
cultures and xenografts via inhibition of the proteasome activity.
Cancer Res. 66:10425–10433. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Liu N, Huang H, Dou QP and Liu J:
Inhibition of 19S proteasome-associated deubiquitinases by
metal-containing compounds. Oncoscience. 2:457–466. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Baldari S, Di Rocco G and Toietta G:
Current biomedical use of copper chelation therapy. Int J Mol Sci.
21:10692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Tsvetkov P, Coy S, Petrova B, Dreishpoon
M, Verma A, Abdusamad M, Rossen J, Joesch-Cohen L, Humeidi R,
Spangler RD, et al: Copper induces cell death by targeting
lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science. 375:1254–1261. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Li P, Sun Q, Bai S, Wang H and Zhao L:
Combination of the cuproptosis inducer disulfiram and anti-PD-L1
abolishes NSCLC resistance by ATP7B to regulate the HIF-1 signaling
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 53:192024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
192
|
Huang N, Feng Y, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Liu L,
Zhang B, Zhang T, Su Z, Xue L and Wu ZB: Disulfiram mediated
anti-tumour effect in pituitary neuroendocrine tumours by inducing
cuproptosis. Int Immunopharmacol. 134:1121592024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Guo B, Yang F, Zhang L, Zhao Q, Wang W,
Yin L, Chen D, Wang M, Han S, Xiao H and Xing N: Cuproptosis
induced by ROS responsive nanoparticles with elesclomol and copper
combined with αPD-L1 for enhanced cancer immunotherapy. Adv Mater.
35:e22122672023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
194
|
Sun L, Zhang Y, Yang B, Sun S, Zhang P,
Luo Z, Feng T, Cui Z, Zhu T, Li Y, et al: Lactylation of METTL16
promotes cuproptosis via m(6)A-modification on FDX1 mRNA in gastric
cancer. Nat Commun. 14:65232023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Buccarelli M, D'Alessandris QG, Matarrese
P, Mollinari C, Signore M, Cappannini A, Martini M, D'Aliberti P,
De Luca G, Pedini F, et al: Elesclomol-induced increase of
mitochondrial reactive oxygen species impairs glioblastoma
stem-like cell survival and tumor growth. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
40:2282021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Solmonson A and DeBerardinis RJ: Lipoic
acid metabolism and mitochondrial redox regulation. J Biol Chem.
293:7522–7530. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
197
|
Harris IS, Endress JE, Coloff JL, Selfors
LM, McBrayer SK, Rosenbluth JM, Takahashi N, Dhakal S, Koduri V,
Oser MG, et al: Deubiquitinases maintain protein homeostasis and
survival of cancer cells upon glutathione depletion. Cell Metab.
29:1166–1181.e6. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Zhou S, Kachhap S and Singh KK:
Mitochondrial impairment in p53-deficient human cancer cells.
Mutagenesis. 18:287–292. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Matoba S, Kang JG, Patino WD, Wragg A,
Boehm M, Gavrilova O, Hurley PJ, Bunz F and Hwang PM: p53 regulates
mitochondrial respiration. Science. 312:1650–1653. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Saleem A, Adhihetty PJ and Hood DA: Role
of p53 in mitochondrial biogenesis and apoptosis in skeletal
muscle. Physiol Genomics. 37:58–66. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
201
|
Zhang C, Lin M, Wu R, Wang X, Yang B,
Levine AJ, Hu W and Feng Z: Parkin, a p53 target gene, mediates the
role of p53 in glucose metabolism and the Warburg effect. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 108:16259–16264. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Contractor T and Harris CR: p53 negatively
regulates transcription of the pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase Pdk2.
Cancer Res. 72:560–567. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
203
|
Bischoff ME, Shamsaei B, Yang J, Secic D,
Vemuri B, Reisz JA, D'Alessandro A, Bartolacci C, Adamczak R,
Schmidt L, et al: Copper drives remodeling of metabolic state and
progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Discov.
15:401–426. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
204
|
Gan Y, Liu T, Feng W, Wang L, Li LI and
Ning Y: Drug repositioning of disulfiram induces endometrioid
epithelial ovarian cancer cell death via the both apoptosis and
cuproptosis pathways. Oncol Res. 31:333–343. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Liu X, Luo B, Wu X and Tang Z: Cuproptosis
and cuproptosis-related genes: Emerging potential therapeutic
targets in breast cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer.
1878:1890132023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Liu T, Zhou Z, Zhang M, Lang P, Li J, Liu
Z, Zhang Z, Li L and Zhang L: Cuproptosis-immunotherapy using PD-1
overexpressing T cell membrane-coated nanosheets efficiently treats
tumor. J Control Release. 362:502–512. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Lu X, Deng W, Wang S, Zhao S, Zhu B, Bai
B, Mao Y, Lin J, Yi Y, Xie Z, et al: PEGylated
Elesclomol@Cu(II)-based Metal-organic framework with effective
nanozyme performance and cuproptosis induction efficacy for
enhanced PD-L1-based immunotherapy. Mater Today Bio. 29:1013172024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
208
|
Hasinoff BB, Wu X, Yadav AA, Patel D,
Zhang H, Wang DS, Chen ZS and Yalowich JC: Cellular mechanisms of
the cytotoxicity of the anticancer drug elesclomol and its complex
with Cu(II). Biochem Pharmacol. 93:266–276. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Jiao Y, Hannafon BN and Ding WQ:
Disulfiram's anticancer activity: Evidence and mechanisms.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 16:1378–1384. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Xie L, Gong J, He Z, Zhang W and Wang H,
Wu S, Wang X, Sun P, Cai L, Wu Z and Wang H: A copper-manganese
based nanocomposite induces cuproptosis and potentiates anti-tumor
immune responses. Small. 21:e24121742025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Deng L, Liu T, Liu CA, Zhang Q, Song MM,
Lin SQ, Wang YM, Zhang QS and Shi HP: The association of metabolic
syndrome score trajectory patterns with risk of all cancer types.
Cancer. 130:2150–2159. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Song M, Liu T, Liu H, Zhang Q, Zhang Q,
Wang Y, Ma X, Cao L and Shi H: Association between metabolic
syndrome, C-reactive protein, and the risk of primary liver cancer:
A large prospective study. BMC Cancer. 22:8532022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Gathirua-Mwangi WG, Song Y, Monahan PO,
Champion VL and Zollinger TW: Associations of metabolic syndrome
and C-reactive protein with mortality from total cancer,
obesity-linked cancers and breast cancer among women in NHANES III.
Int J Cancer. 143:535–542. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Springer C, Humayun D and Skouta R:
Cuproptosis: Unraveling the mechanisms of copper-induced cell death
and its implication in cancer therapy. Cancers (Basel). 16:6472024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Chen Z, Li Y, Yin Y, Song M, Wang F and
Jiang G: Cu Nanowires trigger efficient cuproptosis via special
intracellular distribution and excessive Cu Ion release. Nano Lett.
24:11446–11453. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Shao R, Visser I, Fros JJ and Yin X:
Versatility of the zinc-finger antiviral protein (ZAP) As a
modulator of viral infections. Int J Biol Sci. 20:4585–4600. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Zhang N, Yu X, Xie J and Xu H: New
insights into the role of ferritin in iron homeostasis and
neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Neurobiol. 58:2812–2823. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Ermini ML and Voliani V: Antimicrobial
nano-agents: The copper age. ACS Nano. 15:6008–6029. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Lu X, Chen X, Lin C, Yi Y, Zhao S, Zhu B,
Deng W, Wang X, Xie Z, Rao S, et al: Elesclomol loaded copper oxide
nanoplatform triggers cuproptosis to enhance antitumor
immunotherapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 11:e23099842024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Zheng P, Zhou C, Lu L, Liu B and Ding Y:
Elesclomol: A copper ionophore targeting mitochondrial metabolism
for cancer therapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 41:2712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Woźniak-Budych MJ, Staszak K and Staszak
M: Copper and copper-based nanoparticles in medicine-perspectives
and challenges. Molecules. 28:66872023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
222
|
Brewer GJ: Tetrathiomolybdate anticopper
therapy for Wilson's disease inhibits angiogenesis, fibrosis and
inflammation. J Cell Mol Med. 7:11–20. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Kim YJ, Tsang T, Anderson GR, Posimo JM
and Brady DC: Inhibition of BCL2 family members increases the
efficacy of copper chelation in BRAFV600E-Driven melanoma. Cancer
Res. 80:1387–1400. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Ishida S, McCormick F, Smith-McCune K and
Hanahan D: Enhancing tumor-specific uptake of the anticancer drug
cisplatin with a copper chelator. Cancer Cell. 17:574–583. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Lin X, Chen W, Li B, Zhao Z, Yu Z, Zhao
XY, Zhou X, Feng Z, Lin C and Cao W: Targeting intratumoral copper
inhibits tumor progression via p62-Mediated EZH2 degradation and
potentiates Anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Adv Sci (Weinh). Jul 28–2025.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
226
|
Xue Q, Yan D, Chen X, Li X, Kang R,
Klionsky DJ, Kroemer G, Chen X, Tang D and Liu J: Copper-dependent
autophagic degradation of GPX4 drives ferroptosis. Autophagy.
19:1982–1996. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Li F, Wu X, Liu H, Liu M, Yue Z, Wu Z, Liu
L and Li F: Copper depletion strongly enhances ferroptosis via
mitochondrial perturbation and reduction in antioxidative
mechanisms. Antioxidants (Basel). 11:20842022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Derseh HB, Perera KUE, Dewage SNV, Stent
A, Koumoundouros E, Organ L, Pagel CN and Snibson KJ:
Tetrathiomolybdate treatment attenuates bleomycin-induced
angiogenesis and lung pathology in a sheep model of pulmonary
fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. 12:7009022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Brewer GJ: The promise of copper lowering
therapy with tetrathiomolybdate in the cure of cancer and in the
treatment of inflammatory disease. J Trace Elem Med Biol.
28:372–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Zhang M, Qiu H, Mao L, Wang B, Li N, Fan
Y, Weng P, Hu S, Dong X, Qin X, et al: Ammonium tetrathiomolybdate
triggers autophagy-dependent NRF2 activation in vascular
endothelial cells. Cell Death Dis. 13:7332022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Wang T, Lu W, Cheng Z, Wang L, Jiang Z,
Yue Y, Jiang P, Xia Z, He L, Wang F, et al: Oral engineered
extracellular vesicles based on ion exchange strategy for
multipronged management of Wilson's disease complicated with
reproductive dysfunction therapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 12:e016892025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Ke Y, Wu C, Zeng Y, Chen M, Li Y, Xie C,
Zhou Y, Zhong Y and Yu H: Radiosensitization of clioquinol combined
with zinc in the nasopharyngeal cancer stem-like cells by
inhibiting autophagy in vitro and in vivo. Int J Biol Sci.
16:777–789. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
233
|
Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Yoshii J, Ikenaka
Y, Noguchi R, Yanase K, Namisaki T, Yamazaki M, Tsujinoue H, Imazu
H and Fukui H: The copper-chelating agent, trientine, attenuates
liver enzyme-altered preneoplastic lesions in rats by angiogenesis
suppression. Oncol Rep. 10:1369–1373. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Yang M, Wu X, Hu J, Wang Y, Wang Y, Zhang
L, Huang W, Wang X, Li N, Liao L, et al: COMMD10 inhibits HIF1α/CP
loop to enhance ferroptosis and radiosensitivity by disrupting
Cu-Fe balance in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 76:1138–1150.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Wang Y, Li W, Patel SS, Cong J, Zhang N,
Sabbatino F, Liu X, Qi Y, Huang P, Lee H, et al: Blocking the
formation of radiation-induced breast cancer stem cells.
Oncotarget. 5:3743–3755. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
Wu L, Meng F, Dong L, Block CJ, Mitchell
AV, Wu J, Jang H, Chen W, Polin L, Yang Q, et al: Disulfiram and
BKM120 in combination with chemotherapy impede tumor progression
and delay tumor recurrence in tumor initiating cell-rich TNBC. Sci
Rep. 9:2362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
237
|
Sun T, Yang W, Toprani SM, Guo W, He L,
DeLeo AB, Ferrone S, Zhang G, Wang E, Lin Z, et al: Induction of
immunogenic cell death in radiation-resistant breast cancer stem
cells by repurposing anti-alcoholism drug disulfiram. Cell Commun
Signal. 18:362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
238
|
Zhou P, Qin J, Zhou C, Wan G, Liu Y, Zhang
M, Yang X, Zhang N and Wang Y: Multifunctional nanoparticles based
on a polymeric copper chelator for combination treatment of
metastatic breast cancer. Biomaterials. 195:86–99. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
239
|
Hu H, Hua S, Lu F, Zhang W, Zhang Z, Cui
J, Lei X, Xia J, Xu F and Zhou M: Mucous permeable nanoparticle for
inducing cuproptosis-like death in broad-spectrum bacteria for
nebulized treatment of acute pneumonia. Adv Sci (Weinh).
12:e24085802025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
240
|
Wu A, Yin N, Li Z, Zhang X, Zhang Z, Zhong
T, Xia F, Pan J, Wang D, Liu L and Dong J: FDX1 facilitates
elesclomol-induced cuproptosis and promotes glioblastoma
development via transcription factor NFKB1. Biochem Pharmacol.
241:1171862025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
241
|
Wang W, Lu K, Jiang X, Wei Q, Zhu L, Wang
X, Jin H and Feng L: Ferroptosis inducers enhanced cuproptosis
induced by copper ionophores in primary liver cancer. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 42:1422023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Zulkifli M, Spelbring AN, Zhang Y, Soma S,
Chen S, Li L, Le T, Shanbhag V, Petris MJ, Chen TY, et al:
FDX1-dependent and independent mechanisms of elesclomol-mediated
intracellular copper delivery. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
120:e22167221202023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
243
|
Chisholm CL, Wang H, Wong AH,
Vazquez-Ortiz G, Chen W, Xu X and Deng CX: Ammonium
tetrathiomolybdate treatment targets the copper transporter ATP7A
and enhances sensitivity of breast cancer to cisplatin. Oncotarget.
7:84439–84452. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
244
|
Feng L, Wu TZ, Guo XR, Wang YJ, Wang XJ,
Liu SX, Zhang R, Ma Y, Tan NH, Bian JL and Wang Z: Discovery of
natural resorcylic acid lactones as novel potent copper ionophores
covalently targeting PRDX1 to induce cuproptosis for
triple-negative breast cancer therapy. ACS Cent Sci. 11:357–370.
2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
245
|
Wen H, Qu C, Wang Z, Gao H, Liu W, Wang H,
Sun H, Gu J, Yang Z and Wang X: Cuproptosis enhances docetaxel
chemosensitivity by inhibiting autophagy via the DLAT/mTOR pathway
in prostate cancer. FASEB J. 37:e231452023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
246
|
Ahire JJ, Neveling DP and Dicks LMT:
Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofibres spun with copper nanoparticles:
An anti-Escherichia coli membrane for water treatment. Appl
Microbiol Biotechnol. 102:7171–7181. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
247
|
Cendrowska-Pinkosz M, Krauze M, Juśkiewicz
J, Fotschki B and Ognik K: The influence of copper nanoparticles on
neurometabolism marker levels in the brain and intestine in a rat
model. Int J Mol Sci. 24:113212023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
248
|
Geng X, Liu K, Wang J, Su X, Shi Y and
Zhao L: Preparation of ultra-small copper nanoparticles-loaded
self-healing hydrogels with antibacterial, inflammation-suppressing
and angiogenesis-enhancing properties for promoting diabetic wound
healing. Int J Nanomedicine. 18:3339–3358. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
249
|
Li L, Tai Z, Liu W, Luo Y, Wu Y, Lin S,
Liu M, Gao B and Liu JX: Copper overload impairs hematopoietic stem
and progenitor cell proliferation via prompting HSF1/SP1
aggregation and the subsequently downregulating FOXM1-Cytoskeleton
axis. iScience. 26:1064062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
250
|
Petruzzelli R and Polishchuk RS: Activity
and trafficking of copper-transporting ATPases in tumor development
and defense against platinum-based drugs. Cells. 8:10802019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
251
|
Nayagam JS, Jeyaraj R, Foskett P, Dhawan
A, Ala A, Joshi D, Bomford A and Thompson RJ: ATP7B genotype and
chronic liver disease treatment outcomes in wilson disease: Worse
survival with loss-of-function variants. Clin Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 21:1323–1329.e4. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
252
|
Wang Y, Li D, Xu K, Wang G and Zhang F:
Copper homeostasis and neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen
Res. 20:3124–3143. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
253
|
Chan N, Willis A, Kornhauser N, Ward MM,
Lee SB, Nackos E, Seo BR, Chuang E, Cigler T, Moore A, et al:
Influencing the tumor microenvironment: A phase II study of copper
depletion using tetrathiomolybdate in patients with breast cancer
at high risk for recurrence and in preclinical models of lung
metastases. Clin Cancer Res. 23:666–676. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
254
|
Yang Z, Su W, Wei X, Pan Y, Xing M, Niu L,
Feng B, Kong W, Ren X, Huang F, et al: Hypoxia inducible factor-1α
drives cancer resistance to cuproptosis. Cancer Cell.
43:937–954.e9. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
255
|
Zhang J, Han H, Wang L, Wang W, Yang M and
Qin Y: Overcoming the therapeutic resistance of hepatomas by
targeting the tumor microenvironment. Front Oncol. 12:9889562022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
256
|
Chen L, Ma S, Wu H, Zheng L, Yi Y, Liu G,
Li B, Sun J, Du Y, Wang B, et al: Zonated copper-driven breast
cancer progression countered by a copper-depleting nanoagent for
immune and metabolic reprogramming. Adv Sci (Weinh).
12:e24124342025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|