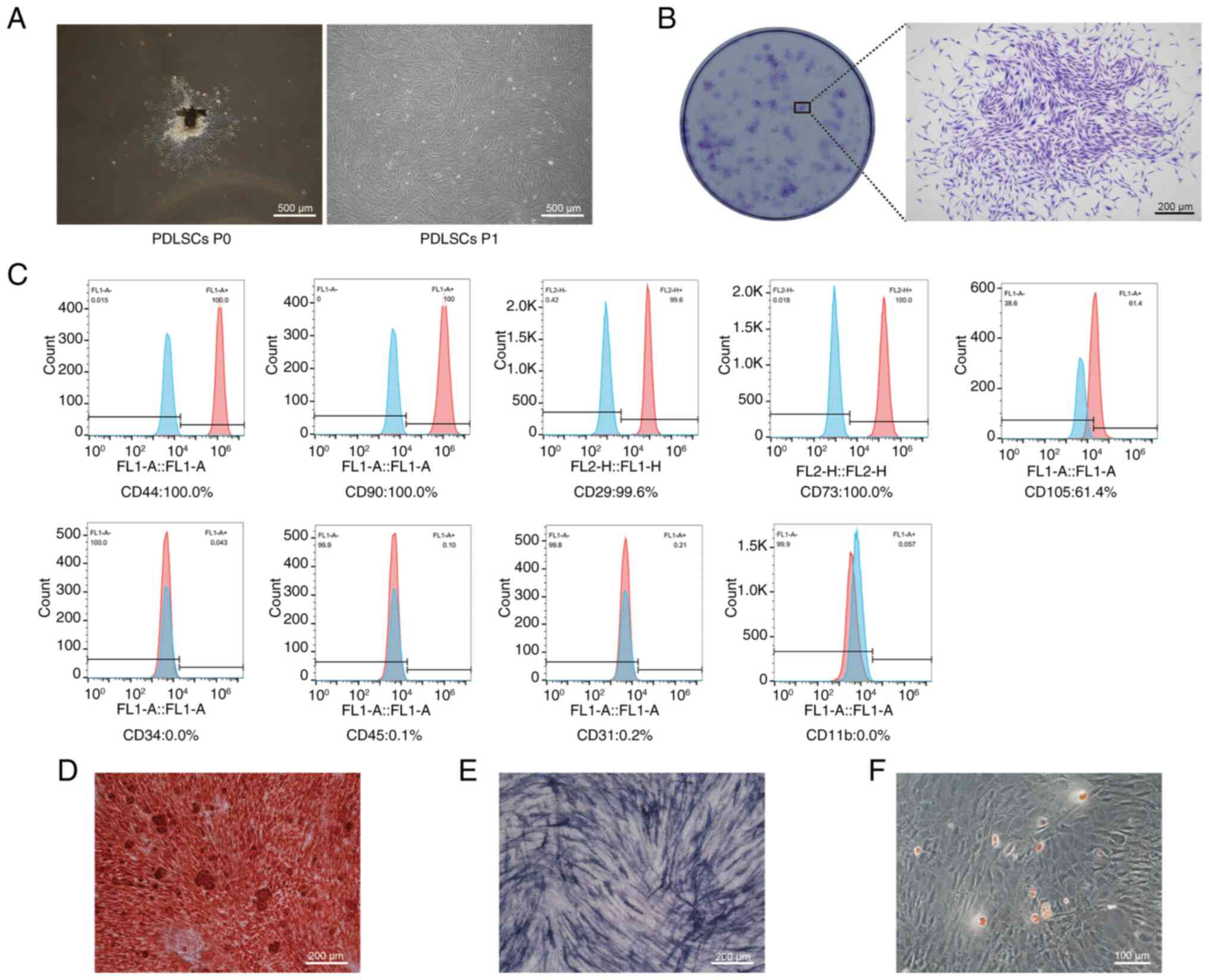
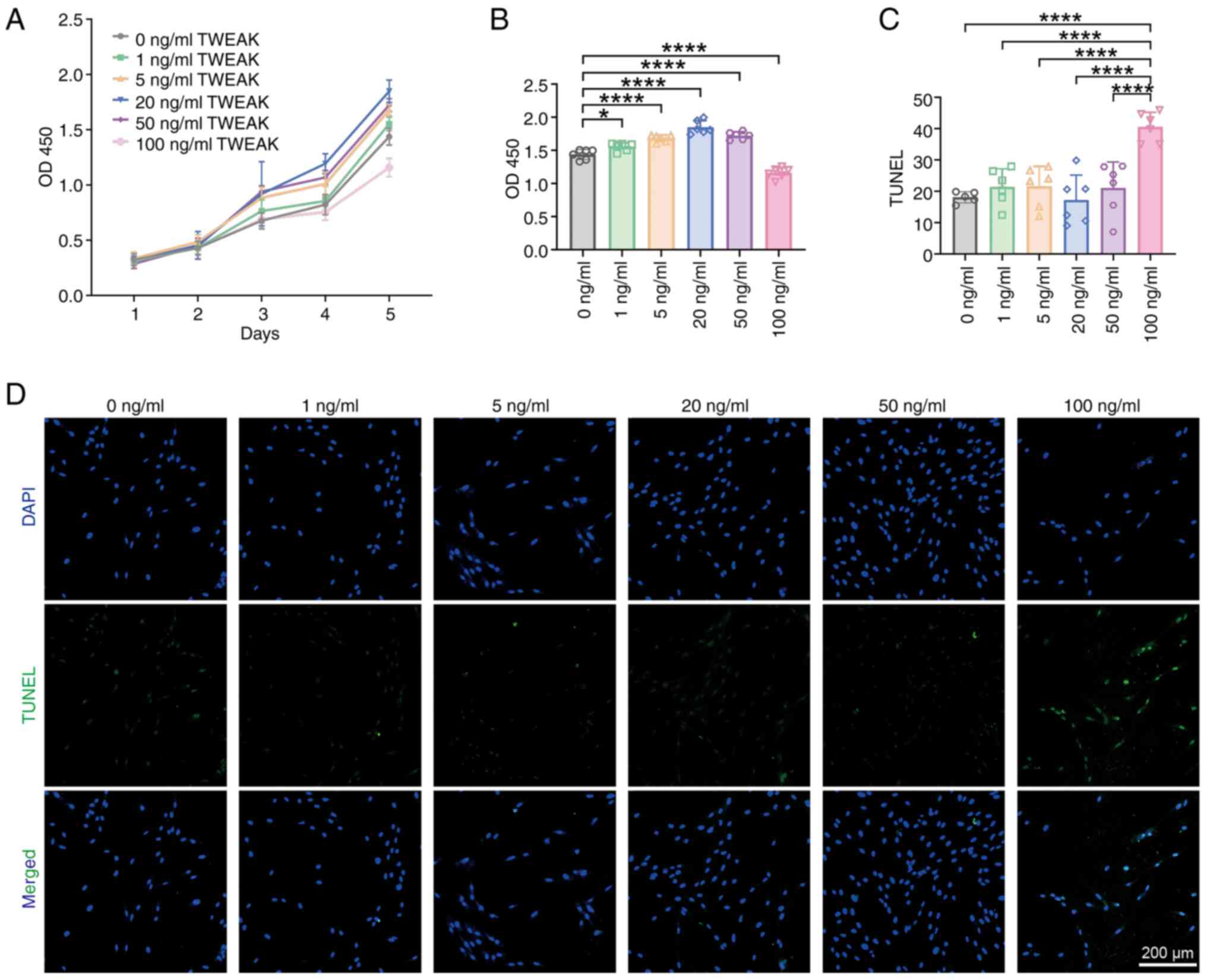
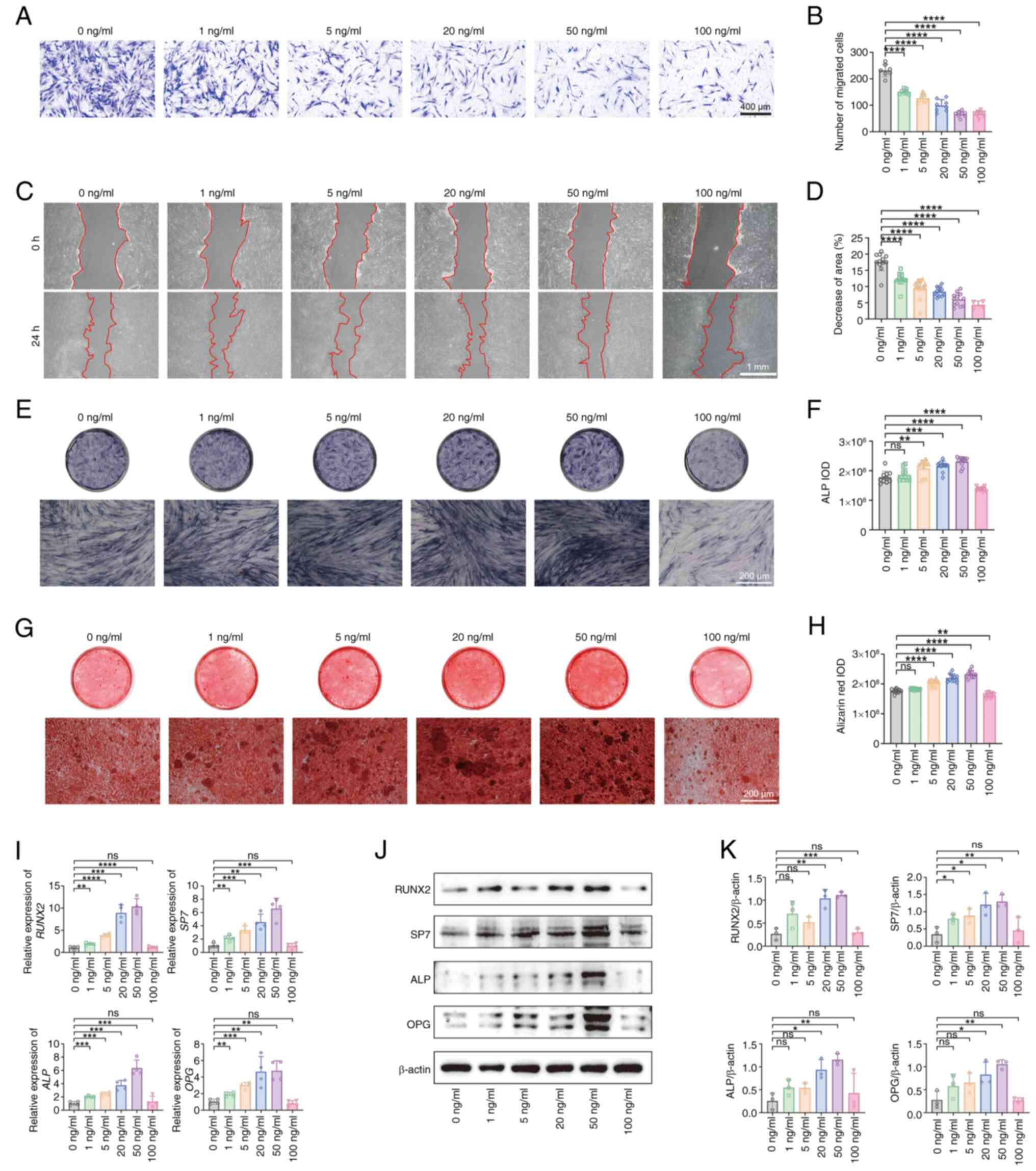
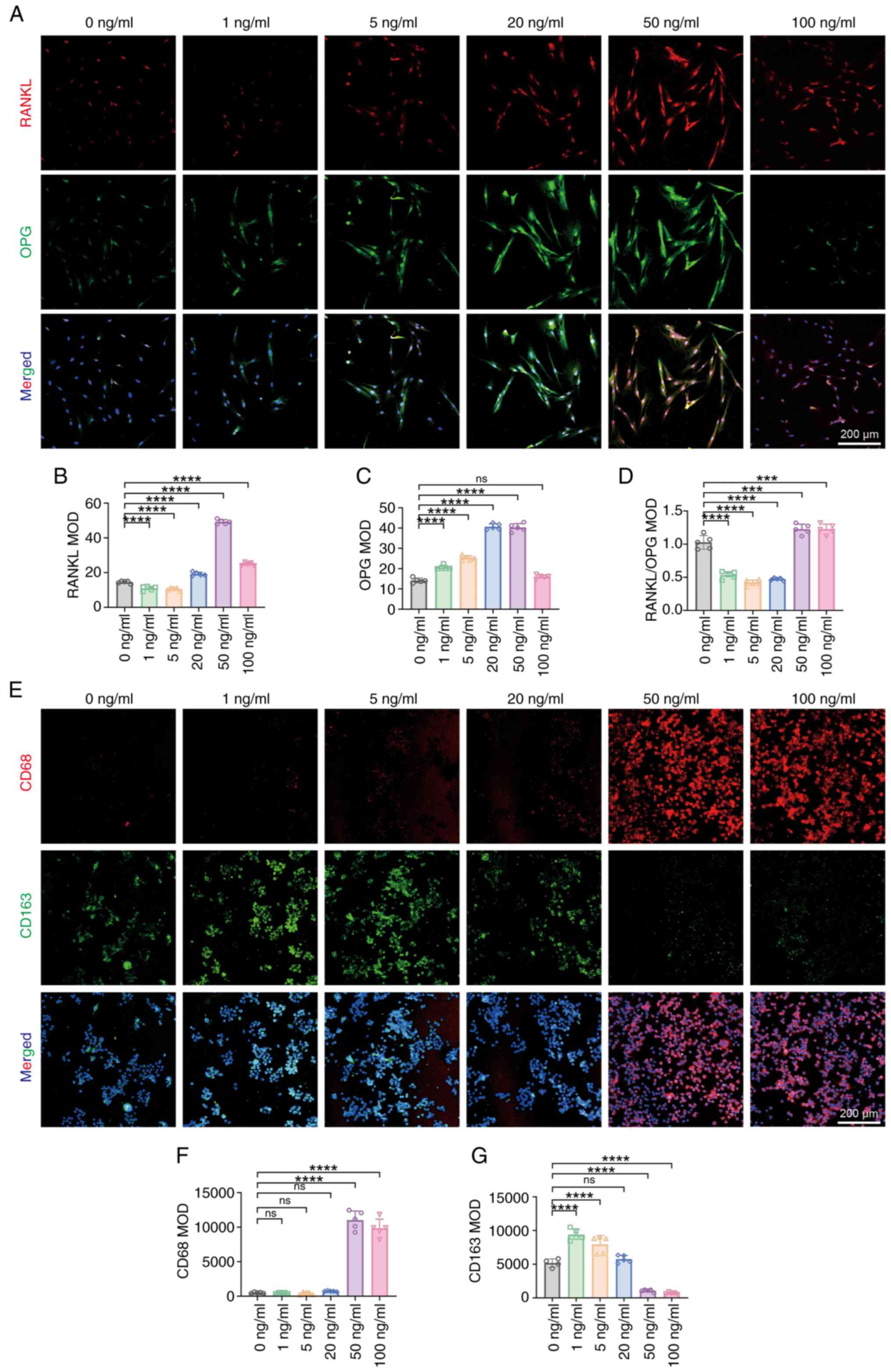
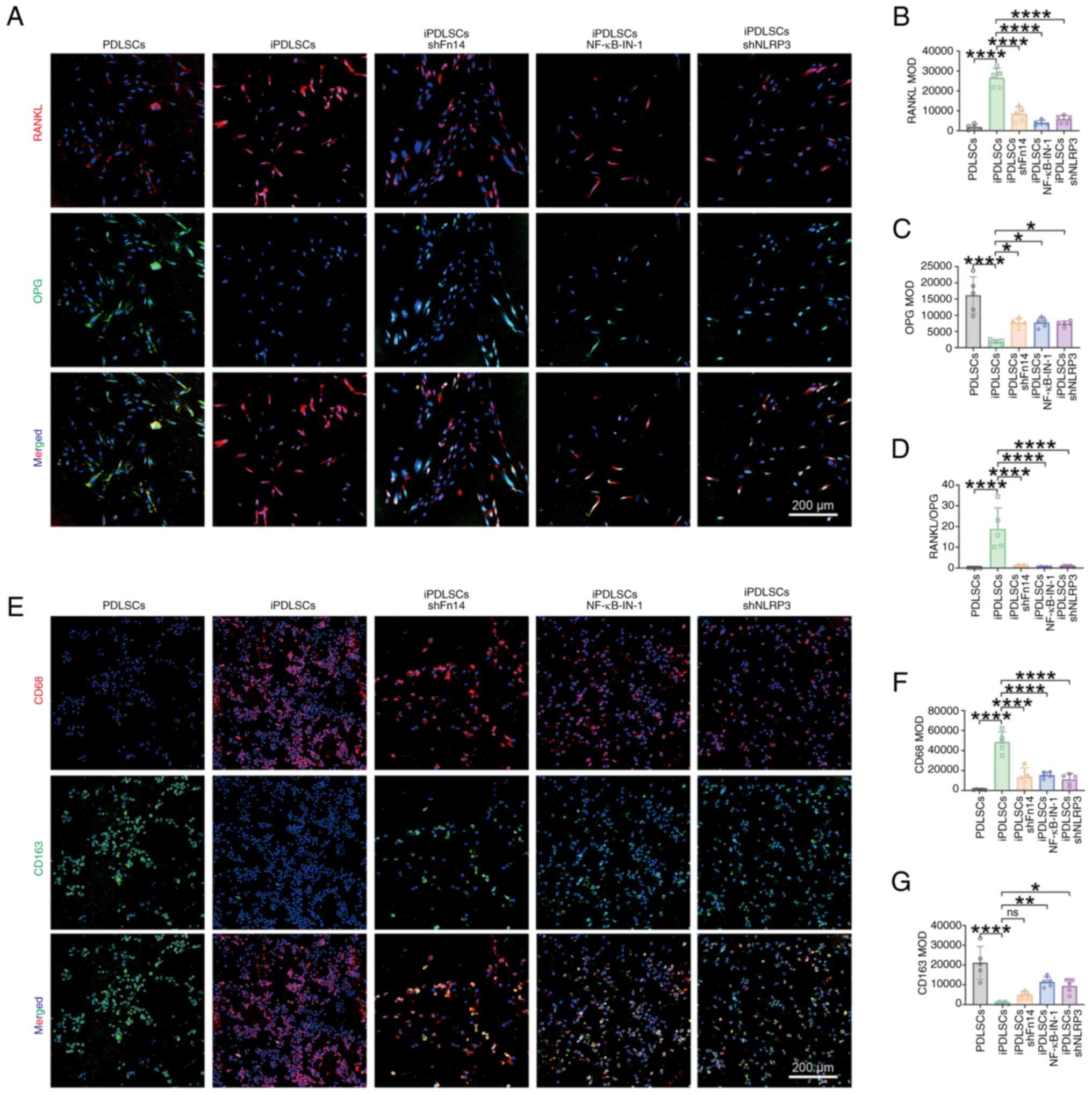
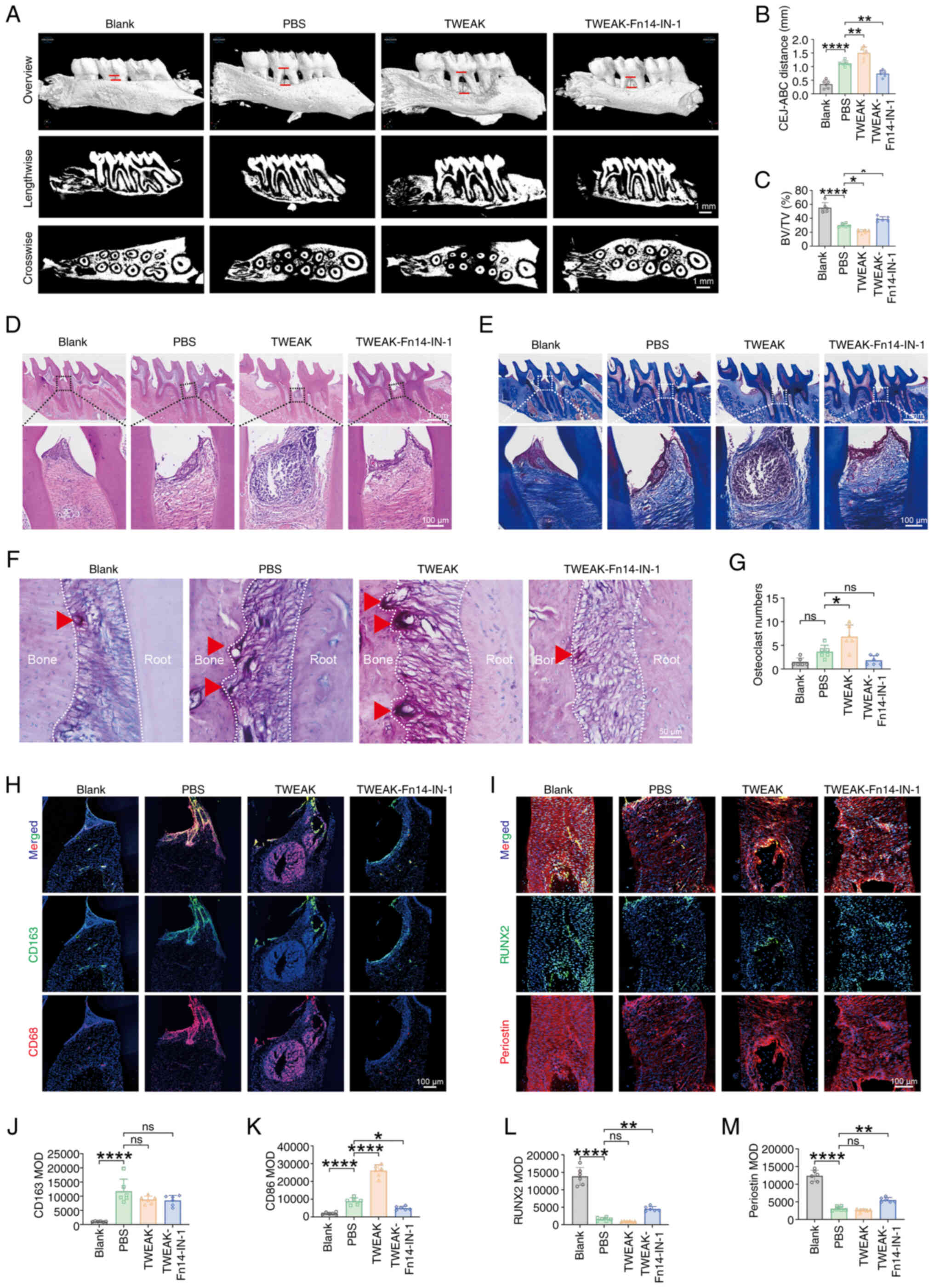
|
1
|
Chicheportiche Y, Bourdon PR, Xu H, Hsu
YM, Scott H, Hession C, Garcia I and Browning JL: TWEAK, a new
secreted ligand in the tumor necrosis factor family that weakly
induces apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 272:32401–32410. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Liu Q, Xiao S and Xia Y: TWEAK/Fn14
activation participates in skin inflammation. Mediators Inflamm.
2017:67468702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu J, Liu Y, Peng L, Li J, Wu K, Xia L,
Wu J, Wang S, Wang X, Liu Q, et al: TWEAK/Fn14 signals mediate burn
wound repair. J Invest Dermatol. 139:224–234. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wang A, Zhang F, Xu H, Xu M, Cao Y, Wang
C, Xu Y, Su M, Zhang M and Zhuge Y: TWEAK/Fn14 promotes
pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion in hepatic stellate cells via
NF-κB/STAT3 pathways. Mol Immunol. 87:67–75. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Johnston AJ and Hoogenraad NJ: Fn14: A new
player in cancer-induced cachexia. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care.
19:316–318. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Burkly LC, Michaelson JS and Zheng TS:
TWEAK/Fn14 pathway: An immunological switch for shaping tissue
responses. Immunol Rev. 244:99–114. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ratajczak W, Atkinson SD and Kelly C: The
TWEAK/Fn14/CD163 axis-implications for metabolic disease. Rev
Endocr Metab Disord. 23:449–462. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Xu WD, Zhao Y and Liu Y: Role of the
TWEAK/Fn14 pathway in autoimmune diseases. Immunol Res. 64:44–50.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wang S, Li L, Cook C, Zhang Y, Xia Y and
Liu Y: A potential fate decision landscape of the TWEAK/Fn14 axis
on stem and progenitor cells: A systematic review. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 13:2702022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yakar N, Guncu GN, Akman AC, Pınar A,
Karabulut E and Nohutcu RM: Evaluation of gingival crevicular fluid
and peri-implant crevicular fluid levels of sclerostin, TWEAK,
RANKL and OPG. Cytokine. 113:433–439. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kataria NG, Bartold PM, Dharmapatni AA,
Atkins GJ, Holding CA and Haynes DR: Expression of tumor necrosis
factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) and its receptor,
fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 protein (Fn14), in healthy
tissues and in tissues affected by periodontitis. J Periodontal
Res. 45:564–573. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gur AT, Guncu GN, Akman AC, Pinar A,
Karabulut E and Nohutcu RM: Evaluation of GCF IL-17, IL-10, TWEAK,
and sclerostin levels after scaling and root planing and adjunctive
use of diode laser application in patients with periodontitis. J
Periodontol. 93:1161–1172. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Luan X, Zhou X, Trombetta-eSilva J,
Francis M, Gaharwar AK, Atsawasuwan P and Diekwisch TGH: MicroRNAs
and periodontal homeostasis. J Dent Res. 96:491–500. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Deng DK, Zhang JJ, Gan D, Zou JK, Wu RX,
Tian Y, Yin Y, Li X, Chen FM and He XT: Roles of extracellular
vesicles in periodontal homeostasis and their therapeutic
potential. J Nanobiotechnology. 20:5452022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ravidà A, Qazi M, Rodriguez MV, Galli M,
Saleh MHA, Troiano G and Wang HL: The influence of the interaction
between staging, grading and extent on tooth loss due to
periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. 48:648–658. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang D, Lin W, Jiang S, Deng P, Liu L,
Wang Q, Sheng R, Shu HS, Wang L, Zou W, et al: Lepr-Expressing
PDLSCs contribute to periodontal homeostasis and respond to
mechanical force by piezo1. Adv Sci. 10:e23032912023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang Z, Deng M, Hao M and Tang J:
Periodontal ligament stem cells in the periodontitis niche:
Inseparable interactions and mechanisms. J Leukoc Biol.
110:565–576. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tomokiyo A, Wada N and Maeda H:
Periodontal ligament stem cells: Regenerative potency in
periodontium. Stem Cells Dev. 28:974–985. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu J, Chen B, Bao J, Zhang Y, Lei L and
Yan F: Macrophage polarization in periodontal ligament stem cells
enhanced periodontal regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 10:3202019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jin SS, He DQ, Wang Y, Zhang T, Yu HJ, Li
ZX, Zhu LS, Zhou YH and Liu Y: Mechanical force modulates
periodontal ligament stem cell characteristics during bone
remodelling via TRPV4. Cell Prolif. 53:e129122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Z, Shuai Y, Zhou F, Yin J, Hu J, Guo
S, Wang Y and Liu W: PDLSCs regulate angiogenesis of periodontal
ligaments via VEGF transferred by exosomes in periodontitis. Int J
Med Sci. 17:558–567. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qiu X, Du Y, Lou B, Zuo Y, Shao W, Huo Y,
Huang J, Yu Y, Zhou B, Du J, et al: Synthesis and identification of
new 4-arylidene curcumin analogues as potential anticancer agents
targeting nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway. J Med Chem.
53:8260–73. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Seo BM, Miura M, Gronthos S, Bartold PM,
Batouli S, Brahim J, Young M, Robey PG, Wang CY and Shi S:
Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human
periodontal ligament. Lancet. 364:149–55. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao X, Lin H, Ding T, Wang Y, Liu N and
Shen Y: Overview of the main biological mechanisms linked to
changes in periodontal ligament stem cells and the inflammatory
microenvironment. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 24:373–386. 2023.In
English, Chinese. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jin S, Jiang H, Sun Y, Li F, Xia J, Li Y,
Zheng J and Qin Y: Osteogenic differentiation of periodontal
membrane stem cells in inflammatory environments. Open Life Sci.
17:1240–1248. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Silva I and Branco JC: Rank/Rankl/opg:
Literature review. Acta Reumatol Port. 36:209–218. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li P, Ou Q, Shi S and Shao C:
Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells/dental stem
cells and their therapeutic applications. Cell Mol Immunol.
20:558–569. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nakao Y, Fukuda T, Zhang Q, Sanui T,
Shinjo T, Kou X, Chen C, Liu D, Watanabe Y, Hayashi C, et al:
Exosomes from TNF-α-treated human gingiva-derived MSCs enhance M2
macrophage polarization and inhibit periodontal bone loss. Acta
Biomater. 122:306–324. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Huang X, Deng Y, Xiao J, Wang H, Yang Q
and Cao Z: Genetically engineered M2-like macrophage-derived
exosomes for P. gingivalis-suppressed cementum regeneration: From
mechanism to therapy. Bioact Mater. 32:473–487. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zaitseva O, Hoffmann A, Otto C and Wajant
H: Targeting fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-inducible 14 (Fn14) for
tumor therapy. Front Pharmacol. 13:9350862022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Saitoh T, Nakayama M, Nakano H, Yagita H,
Yamamoto N and Yamaoka S: TWEAK induces NF-kappaB2 p100 processing
and long lasting NF-kappaB activation. J Biol Chem.
278:36005–36012. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Guo L, Zhang Y, Liu H, Cheng Q, Yang S and
Yang D: All-trans retinoic acid inhibits the osteogenesis of
periodontal ligament stem cells by promoting IL-1β production via
NF-κB signaling. Int Immunopharmacol. 108:1087572022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Okić Đorđević I, Kukolj T, Živanović M,
Momčilović S, Obradović H, Petrović A, Mojsilović S, Trivanović D
and Jauković A: The role of doxycycline and IL-17 in regenerative
potential of periodontal ligament stem cells: Implications in
periodontitis. Biomolecules. 13:14372023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhang B, Yang Y, Yi J, Zhao Z and Ye R:
Hyperglycemia modulates M1/M2 macrophage polarization via reactive
oxygen species overproduction in Ligature-induced periodontitis. J
Periodontal Res. 56:991–1005. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Almubarak A, Tanagala KKK, Papapanou PN,
Lalla E and Momen-Heravi F: Disruption of monocyte and macrophage
homeostasis in periodontitis. Front Immunol. 11:3302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang C, Zhao Q, Chen C, Li J, Zhang J, Qu
S, Tang H, Zeng H and Zhang Y: CD301b+ macrophage: The new booster
for activating bone regeneration in periodontitis treatment. Int J
Oral Sci. 15:192023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Wang Y, Zhang X, Wang J, Zhang Y, Ye Q,
Wang Y, Fei D and Wang Q: Inflammatory periodontal ligament stem
cells drive M1 macrophage polarization via exosomal
miR-143-3p-mediated regulation of PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling. Stem
Cells. 41:184–199. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Qian JK, Ma Y, Huang X, Li XR, Xu YF, Liu
ZY, Gu Y, Shen K, Tian LJ, Wang YT, et al: The CD163/TWEAK/Fn14
axis: A potential therapeutic target for alleviating inflammatory
bone loss. J Orthop Translat. 49:82–95. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Winkles JA: The TWEAK-Fn14
cytokine-receptor axis: Discovery, biology and therapeutic
targeting. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 7:411–425. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang W, Shi X, Feng J, Le Y, Jin L, Lu D,
Zhang Q and Wang C: Perinatal exposure to PBEB aggravates liver
injury via macrophage-derived TWEAK in male adult offspring mice
under western diet. J Hazard Mater. 479:1357352024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu L, Wu P, Wei Y, Lu M, Ge H, Wang P,
Sun J, Horng T, Liu X, Shen X, et al: TWEAK-Fn14 signaling protects
mice from pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting fibroblast activation
and recruiting pro-regenerative macrophages. Cell Rep.
44:1152202025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Vincent C, Findlay DM, Welldon KJ,
Wijenayaka AR, Zheng TS, Haynes DR, Fazzalari NL, Evdokiou A and
Atkins GJ: Pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-related weak inducer of
apoptosis (TWEAK) and TNFα induce the mitogen-activated protein
kinase (MAPK)-dependent expression of sclerostin in human
osteoblasts. J Bone Miner Res. 24:1434–1449. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Holmberg R, Robinson M, Gilbert SF,
Lujano-Olazaba O, Waters JA, Kogan E, Velasquez CLR, Stevenson D,
Cruz LS, Alexander LJ, et al: TWEAK-Fn14-RelB signaling cascade
promotes stem Cell-like features that contribute to
Post-chemotherapy ovarian cancer relapse. Mol Cancer Res.
21:170–186. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Liu W, Gao L, Hou X, Feng S, Yan H, Pan H,
Zhang S, Yang X, Jiang J, Ye F, et al: TWEAK Signaling-induced ID1
expression drives malignant transformation of hepatic progenitor
cells during hepatocarcinogenesis. Adv Sci. 10:e23003502023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ando T, Ichikawa J, Wako M, Hatsushika K,
Watanabe Y, Sakuma M, Tasaka K, Ogawa H, Hamada Y, Yagita H and
Nakao A: TWEAK/Fn14 interaction regulates RANTES production,
BMP-2-induced differentiation, and RANKL expression in mouse
osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 8:R1462006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zou X, Tian Y, Peng L, Luo M, Yan Z, Xue
Z, Liu X and Xia Y: TWEAK regulates the functions of hair follicle
stem cells via the Fn14-Wnt/β-catenin-CXCR4 signalling axis. Wound
Repair Regen. 33:e700322025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Wang Y, Wang L, Sun T, Shen S, Li Z, Ma X,
Gu X, Zhang X, Peng A, Xu X and Feng Q: Study of the inflammatory
activating process in the early stage of Fusobacterium nucleatum
infected PDLSCs. Int J Oral Sci. 15:82023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang P, Tian H, Zhang Z and Wang Z: EZH2
regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontal ligament stem cell
proliferation and osteogenesis through TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway.
Stem Cells Int. 2021:76251342021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Guan XX, Yang HH, Zhong WJ, Duan JX, Zhang
CY, Jiang HL, Xiang Y, Zhou Y and Guan CX: Fn14 exacerbates acute
lung injury by activating the NLRP3 inflammasome in mice. Mol Med.
28:852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhao Y, Quan Y, Lei T, Fan L, Ge X and Hu
S: The role of inflammasome NLPR3 in the development and therapy of
periodontitis. Int J Med Sci. 19:1603–1614. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Mao H, Gong T, Sun Y, Yang S, Qiao X and
Yang D: Bacterial growth stage determines the yields, protein
composition, and periodontal pathogenicity of porphyromonas
gingivalis outer membrane vesicles. Front Cell Infect Microbiol.
13:11931982023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Liang F and Huang S: PGC-1α inhibits NLRP3
signaling through transcriptional activation of POP1 to alleviate
inflammation and strengthen osteogenic differentiation of
lipopolysaccharide-induced human periodontal stem cells.
Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 174:1068532024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Michaelson JS and Burkly LC: Therapeutic
targeting of TWEAK/Fn14 in cancer: Exploiting the intrinsic tumor
cell killing capacity of the pathway. Results Probl Cell Differ.
49:145–160. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Roessler M, Vega-Harring SM, Jarutat T,
Geho D, Wang K, DeMario M, Goss GD and Schellens JH: Exposure and
tumor Fn14 expression as determinants of pharmacodynamics of the
Anti-TWEAK monoclonal antibody RG7212 in patients with
Fn14-positive solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 22:858–867. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Alvarez de Cienfuegos A, Cheung LH,
Mohamedali KA, Whitsett TG, Winkles JA, Hittelman WN and Rosenblum
MG: Therapeutic efficacy and safety of a human fusion construct
targeting the TWEAK receptor Fn14 and containing a modified
granzyme B. J Immunother Cancer. 8:e0011382020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Keshtvarz M, Rezaei E, Amani J, Pourmand
MR, Salimian J, Sarial S and Douraghi M: A novel shiga based
immunotoxin against Fn-14 receptor on colorectal and lung cancer.
Int Immunopharmacol. 110:1090762022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Schneider CS, Perez JG, Cheng E, Zhang C,
Mastorakos P, Hanes J, Winkles JA, Woodworth GF and Kim AJ:
Minimizing the non-specific binding of nanoparticles to the brain
enables active targeting of Fn14-positive glioblastoma cells.
Biomaterials. 42:42–51. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Guerrero-Hue M, Vallejo-Mudarra M,
García-Caballero C, Córdoba-David GM, Palomino-Antolín A, Herencia
C, Vendrell-Casana B, Rubio-Navarro A, Egido J, Blanco-Colio LM and
Moreno JA: Tweak/Fn14 system is involved in rhabdomyolysis-induced
acute kidney injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 169:1159252023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Hotta K, Sho M, Yamato I, Shimada K,
Harada H, Akahori T, Nakamura S, Konishi N, Yagita H, Nonomura K
and Nakajima Y: Direct targeting of fibroblast growth
factor-inducible 14 protein protects against renal ischemia
reperfusion injury. Kidney Int. 79:179–188. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Dou Y, Li C, Li L, Guo J and Zhang J:
Bioresponsive drug delivery systems for the treatment of
inflammatory diseases. J Control Release. 327:641–666. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|