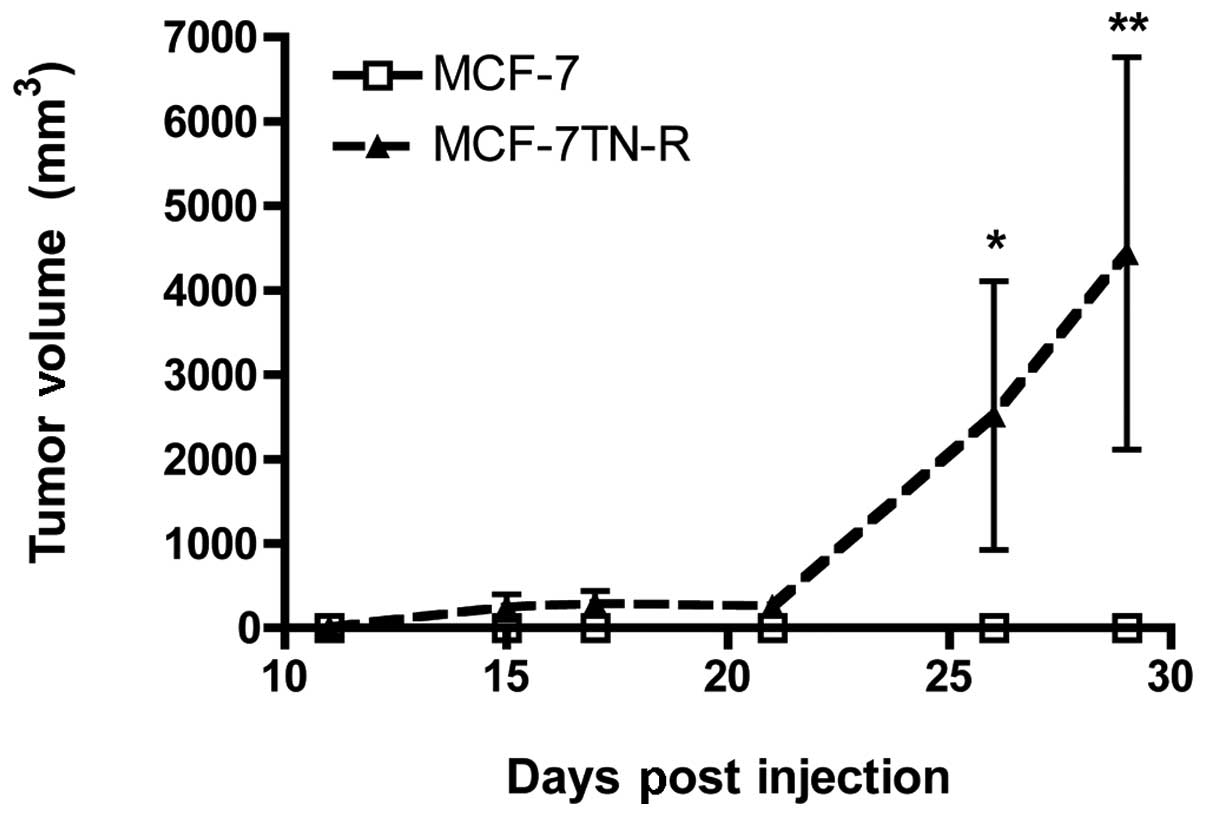
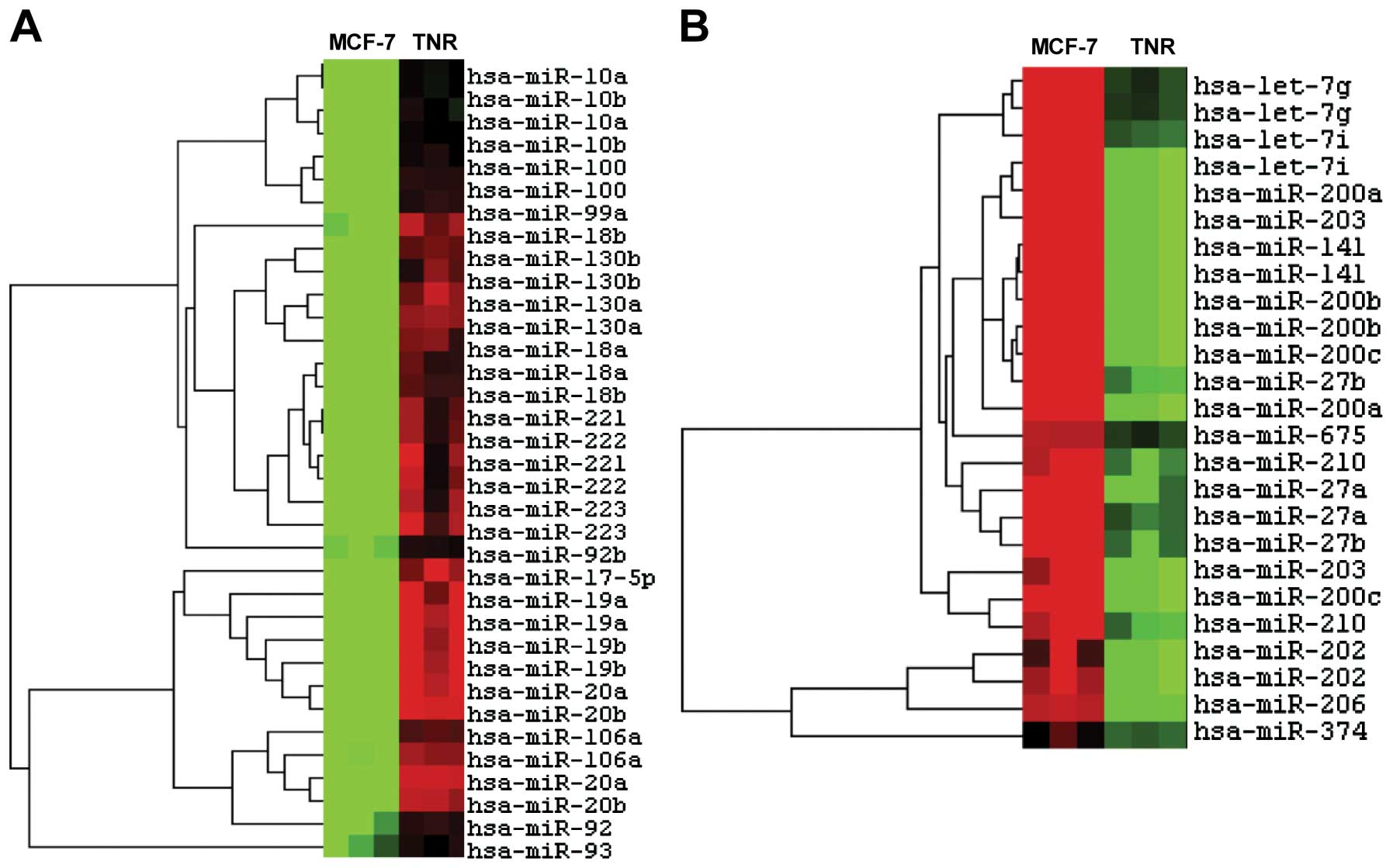
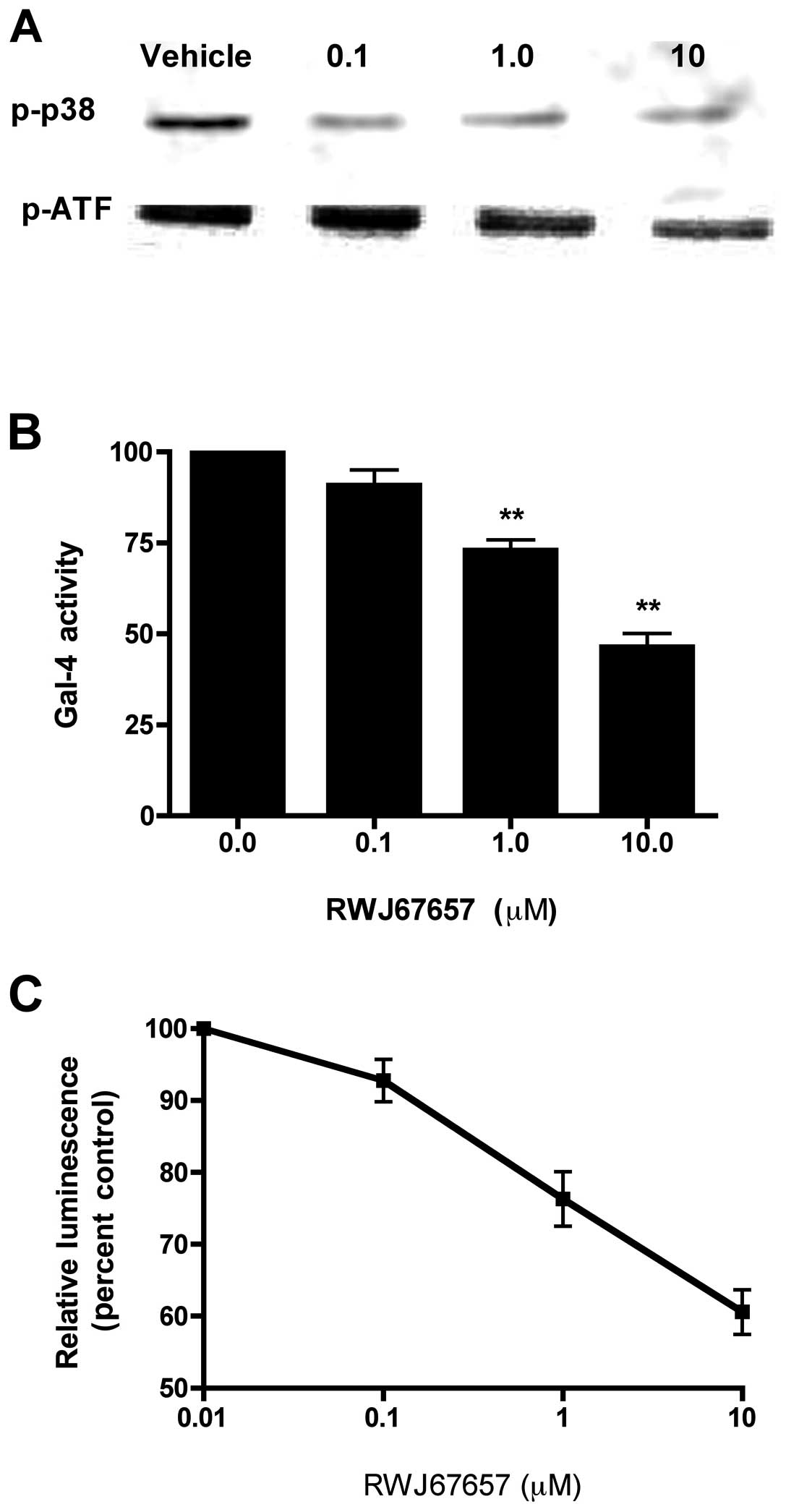
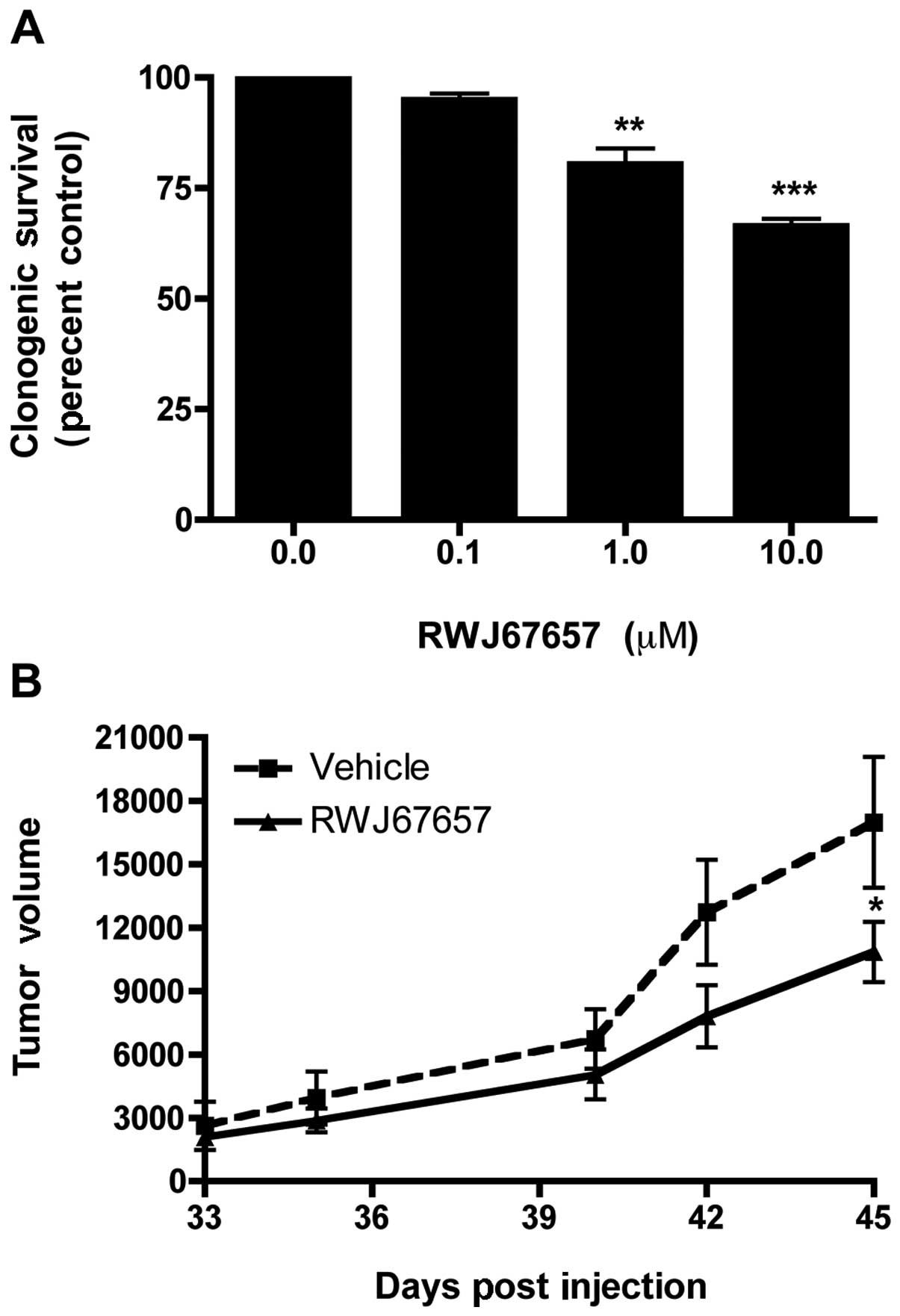
|
1
|
Kaufmann SH and Earnshaw WC: Induction of
apoptosis by cancer chemotherapy. Exp Cell Res. 256:42–49. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Seidman AD: Chemotherapy for advanced
breast cancer: a current perspective. Semin Oncol. 23:55–59.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hsu H, Xiong J and Goeddel DV: The TNF
receptor 1-associated protein TRADD signals cell death and NF-kappa
B activation. Cell. 81:495–504. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Herrnring C, Reimer T, Jeschke U, et al:
Expression of the apoptosis-inducing ligands FasL and TRAIL in
malignant and benign human breast tumors. Histochem Cell Biol.
113:189–194. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zyad A, Benard J, Tursz T, Clarke R and
Chouaib S: Resistance to TNF-alpha and adriamycin in the human
breast cancer MCF-7 cell line: relationship to MDR1, MnSOD, and TNF
gene expression. Cancer Res. 54:825–831. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zyad A, Branellec D, Mahe Y, Tursz T and
Chouaib S: The development of human tumor-cell resistance to
TNF-alpha does not confer resistance to cytokine-induced cellular
cytotoxic mechanisms. Int J Cancer. 52:953–958. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gatti L and Zunino F: Overview of tumor
cell chemoresistance mechanisms. Methods Mol Med. 111:127–148.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gottesman MM: Mechanisms of cancer drug
resistance. Annu Rev Med. 53:615–627. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huber MA, Azoitei N, Baumann B, et al:
NF-kappaB is essential for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
metastasis in a model of breast cancer progression. J Clin Invest.
114:569–581. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Radisky DC and Bissell MJ: NF-kappaB links
oestrogen receptor signalling and EMT. Nat Cell Biol. 9:361–363.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Park S, Song J, Joe CO and Shin I: Akt
stabilizes estrogen receptor alpha with the concomitant reduction
in its transcriptional activity. Cell Signal. 20:1368–1374. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Frigo DE, Vigh KA, Struckhoff AP, et al:
Xenobiotic-induced TNF-alpha expression and apoptosis through the
p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Toxicol Lett. 155:227–238. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Thomas RS, Sarwar N, Phoenix F, Coombes RC
and Ali S: Phosphorylation at serines 104 and 106 by Erk1/2 MAPK is
important for estrogen receptor-alpha activity. J Mol Endocrinol.
40:173–184. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Santen RJ, Song RX, McPherson R, et al:
The role of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase in breast
cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 80:239–256. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ballif BA and Blenis J: Molecular
mechanisms mediating mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase
(MAPK) kinase (MEK)-MAPK cell survival signals. Cell Growth Differ.
12:397–408. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Geh E, Meng Q, Mongan M, et al:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 1 (MAP3K1)
integrates developmental signals for eyelid closure. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 108:17349–17354. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kyriakis JM and Avruch J: Mammalian
mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways
activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev. 81:807–869.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo YL, Kang B, Han J and Williamson JR:
p38beta MAP kinase protects rat mesangial cells from
TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis. J Cell Biochem. 82:556–565. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bulavin DV, Saito S, Hollander MC, et al:
Phosphorylation of human p53 by p38 kinase coordinates N-terminal
phosphorylation and apoptosis in response to UV radiation. EMBO J.
18:6845–6854. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Driggers PH, Segars JH and Rubino DM: The
proto- oncoprotein Brx activates estrogen receptor beta by a p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Biol Chem.
276:46792–46797. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Madrid LV, Mayo MW, Reuther JY and Baldwin
AS Jr: Akt stimulates the transactivation potential of the RelA/p65
subunit of NF-kappa B through utilization of the Ikappa B kinase
and activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38. J Biol
Chem. 276:18934–18940. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zimmermann J, Lamerant N, Grossenbacher R
and Furst P: Proteasome- and p38-dependent regulation of ERK3
expression. J Biol Chem. 276:10759–10766. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Waas WF, Lo HH and Dalby KN: The kinetic
mechanism of the dual phosphorylation of the ATF2 transcription
factor by p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase alpha.
Implications for signal/response profiles of MAP kinase pathways. J
Biol Chem. 276:5676–5684. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bradham C and McClay DR: p38 MAPK in
development and cancer. Cell Cycle. 5:824–828. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Maemura M, Iino Y, Koibuchi Y, Yokoe T and
Morishita Y: Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in breast
cancer. Oncology. 57(Suppl 2): 37–44. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Weldon CB, Burow ME, Rolfe KW, Clayton JL,
Jaffe BM and Beckman BS: NF-kappa B-mediated chemoresistance in
breast cancer cells. Surgery. 130:143–150. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Weldon CB, Parker AP, Patten D, et al:
Sensitization of apoptotically-resistant breast carcinoma cells to
TNF and TRAIL by inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
signaling. Int J Oncol. 24:1473–1480. 2004.
|
|
28
|
Weldon CB, Scandurro AB, Rolfe KW, et al:
Identification of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase as a
chemoresistant pathway in MCF-7 cells by using gene expression
microarray. Surgery. 132:293–301. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Frigo DE, Tang Y, Beckman BS, et al:
Mechanism of AP-1-mediated gene expression by select
organochlorines through the p38 MAPK pathway. Carcinogenesis.
25:249–261. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J and Weinberg RA:
Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast
cancer. Nature. 449:682–688. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Si ML, Zhu S, Wu H, Lu Z, Wu F and Mo YY:
miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene. 26:2799–2803. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen GQ, Zhao ZW, Zhou HY, Liu YJ and Yang
HJ: Systematic analysis of microRNA involved in resistance of the
MCF-7 human breast cancer cell to doxorubicin. Med Oncol.
27:406–415. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Park SM, Gaur AB, Lengyel E and Peter ME:
The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer
cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes
Dev. 22:894–907. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Antoon JW, Liu J, Gestaut MM, Burow ME,
Beckman BS and Foroozesh M: Design, synthesis, and biological
activity of a family of novel ceramide analogues in chemoresistant
breast cancer cells. J Med Chem. 52:5748–5752. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Struckhoff AP, Bittman R, Burow ME, et al:
Novel ceramide analogs as potential chemotherapeutic agents in
breast cancer. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 309:523–532. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhou C, Nitschke AM, Xiong W, et al:
Proteomic analysis of tumor necrosis factor-alpha resistant human
breast cancer cells reveals a MEK5/Erk5-mediated
epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype. Breast Cancer Res.
10:R105:2008.
|
|
37
|
Antoon JW, Lai R, Struckhoff AP, et al:
Altered death receptor signaling promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition and acquired chemoresistance. Sci Rep. 2:5392012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Antoon JW, White MD, Burow ME and Beckman
BS: Dual inhibition of sphingosine kinase isoforms ablates
TNF-induced drug resistance. Oncol Rep. 27:1779–1786.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Antoon JW, White MD, Slaughter EM, et al:
Targeting NFκB mediated breast cancer chemoresistance through
selective inhibition of sphingosine kinase-2. Cancer Biol Ther.
11:678–689. 2011.
|
|
40
|
Wadsworth SA, Cavender DE, Beers SA, et
al: RWJ 67657, a potent, orally active inhibitor of p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
291:680–687. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Antoon JW, Bratton MR, Guillot LM, et al:
Pharmacology and anti-tumor activity of RWJ67657, a novel inhibitor
of p38 mitogen activated protein kinase. Am J Cancer Res.
2:446–458. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Antoon JW, Bratton MR, Guillot LM,
Wadsworth S, Salvo VA and Burow ME: Inhibition of p38-MAPK alters
SRC coactivation and estrogen receptor phosphorylation. Cancer Biol
Ther. 13:1026–1033. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Antoon JW, Liu J, Ponnapakkam AP, Gestaut
MM, Foroozesh M and Beckman BS: Novel D: -erythro N-octanoyl
sphingosine analogs as chemo- and endocrine-resistant breast cancer
therapeutics. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 65:1191–1195. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Antoon JW and Beckman BS:
Anti-proliferative effects of the novel ceramide analog
(S)-2-(benzylideneamino)-3-hydroxy-N-tetrade-cylpropanamide in
chemoresistant cancer. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 22:2624–2628. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rhodes LV, Nitschke AM, Segar HC, et al:
The histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A alters microRNA
expression profiles in apoptosis-resistant breast cancer cells.
Oncol Rep. 27:10–16. 2012.
|
|
46
|
Antoon JW, White MD, Driver JL, Burow ME
and Beckman BS: Sphingosine kinase isoforms as a therapeutic target
in endocrine therapy resistant luminal and basal-A breast cancer.
Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 237:832–844. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Schmittgen TD, Zakrajsek BA, Mills AG,
Gorn V, Singer MJ and Reed MW: Quantitative reverse
transcription-polymerase chain reaction to study mRNA decay:
comparison of endpoint and real-time methods. Anal Biochem.
285:194–204. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Antoon JW, Meacham WD, Bratton MR, et al:
Pharmacological inhibition of sphingosine kinase isoforms alters
estrogen receptor signaling in human breast cancer. J Mol
Endocrinol. 46:205–216. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bratton MR, Antoon JW, Duong BN, et al:
Gαo potentiates estrogen receptor α activity via the ERK signaling
pathway. J Endocrinol. 214:45–54. 2012.
|
|
50
|
Collins-Burow BM, Antoon JW, Frigo DE, et
al: Antiestrogenic activity of flavonoid phytochemicals mediated
via the c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase pathway. Cell-type specific
regulation of estrogen receptor alpha. Journal Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 132:186–193. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Antoon JW, White MD, Meacham WD, et al:
Antiestrogenic effects of the novel sphingosine kinase-2 inhibitor
ABC294640. Endocrinology. 151:5124–5135. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Payton-Stewart F, Schoene NW, Kim YS, et
al: Molecular effects of soy phytoalexin glyceollins in human
prostate cancer cells LNCaP. Mol Carcinog. 48:862–871. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Rhodes LV, Antoon JW, Muir SE, Elliott S,
Beckman BS and Burow ME: Effects of human mesenchymal stem cells on
ER-positive human breast carcinoma cells mediated through
ER-SDF-1/CXCR4 crosstalk. Mol Cancer. 9:2952010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Rhodes LV, Short SP, Neel NF, et al:
Cytokine receptor CXCR4 mediates estrogen-independent
tumorigenesis, metastasis, and resistance to endocrine therapy in
human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 71:603–613. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Walker CH, Drew BA, Antoon JW, Kalueff AV
and Beckman BS: Neurocognitive effects of chemotherapy and
endocrine therapies in the treatment of breast cancer: recent
perspectives. Cancer Invest. 30:135–148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Clarke R, Thompson EW, Leonessa F, et al:
Hormone resistance, invasiveness, and metastatic potential in
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 24:227–239. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Nakanishi H, Taylor RM, Chrest FJ, et al:
Progression of hormone-dependent adenocarcinoma cells to
hormone-independent spindle carcinoma cells in vitro in a clonal
spontaneous rat mammary tumor cell line. Cancer Res. 55:399–407.
1995.
|
|
58
|
Murphy LC and Dotzlaw H: Variant estrogen
receptor mRNA species detected in human breast cancer biopsy
samples. Mol Endocrinol. 3:687–693. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Rhodes LV, Muir SE, Elliott S, et al:
Adult human mesenchymal stem cells enhance breast tumorigenesis and
promote hormone independence. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 121:293–300.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Di Leva G, Gasparini P, Piovan C, et al:
MicroRNA cluster 221–222 and estrogen receptor alpha interactions
in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 102:706–721. 2010.
|
|
61
|
Sonkoly E, Lovén J, Xu N, et al:
MicroRNA-203 functions as a tumor suppressor in basal cell
carcinoma. Oncogenesis. 1:e32012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Burk U, Schubert J, Wellner U, et al: A
reciprocal repression between ZEB1 and members of the miR-200
family promotes EMT and invasion in cancer cells. EMBO Rep.
9:582–589. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
le Sage C, Nagel R, Egan DA, et al:
Regulation of the p27(Kip1) tumor suppressor by miR-221 and miR-222
promotes cancer cell proliferation. EMBO J. 26:3699–3708.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Massarweh S, Osborne CK, Creighton CJ, et
al: Tamoxifen resistance in breast tumors is driven by growth
factor receptor signaling with repression of classic estrogen
receptor genomic function. Cancer Res. 68:826–833. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Massarweh S and Schiff R: Unraveling the
mechanisms of endocrine resistance in breast cancer: new
therapeutic opportunities. Clin Cancer Res. 13:1950–1954. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Obrero M, Yu DV and Shapiro DJ: Estrogen
receptor-dependent and estrogen receptor-independent pathways for
tamoxifen and 4-hydroxytamoxifen-induced programmed cell death. J
Biol Chem. 277:45695–45703. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
St-Laurent V, Sanchez M, Charbonneau C and
Tremblay A: Selective hormone-dependent repression of estrogen
receptor beta by a p38-activated ErbB2/ErbB3 pathway. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 94:23–37. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Cannell IG, Kong YW, Johnston SJ, et al:
p38 MAPK/MK2-mediated induction of miR-34c following DNA damage
prevents Myc-dependent DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:5375–5380. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yang F, Yin Y, Wang F, et al: miR-17-5p
promotes migration of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through
the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-heat shock protein 27
pathway. Hepatology. 51:1614–1623. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Rajaram MV, Ni B, Morris JD, et al:
Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipomannan blocks TNF biosynthesis by
regulating macrophage MAPK-activated protein kinase 2 (MK2) and
microRNA miR-125b. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:17408–17413. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Akhtar N, Rasheed Z, Ramamurthy S,
Anbazhagan AN, Voss FR and Haqqi TM: MicroRNA-27b regulates the
expression of matrix metalloproteinase 13 in human osteoarthritis
chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 62:1361–1371. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ben-Hamo R and Efroni S: Gene expression
and network-based analysis reveals a novel role for hsa-miR-9 and
drug control over the p38 network in glioblastoma multiforme
progression. Genome Med. 3:772011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Zaman MS, Shahryari V, Deng G, et al:
Up-regulation of microRNA-21 correlates with lower kidney cancer
survival. PloS One. 7:e310602012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Alam J, Wicks C, Stewart D, et al:
Mechanism of heme oxygenase-1 gene activation by cadmium in MCF-7
mammary epithelial cells. Role of p38 kinase and Nrf2 transcription
factor. J Biol Chem. 275:27694–27702. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Liu Z, Zhu J, Cao H, Ren H and Fang X:
miR-10b promotes cell invasion through RhoC-AKT signaling pathway
by targeting HOXD10 in gastric cancer. Int J Oncol. 40:1553–1560.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Li G, Wu Z, Peng Y, et al: MicroRNA-10b
induced by Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein-1
promotes the metastasis of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.
Cancer Lett. 299:29–36. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Ng YH, Zhu H and Leung PC: Twist modulates
human trophoblastic cell invasion via regulation of N-cadherin.
Endocrinology. 153:925–936. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Alexander NR, Tran NL, Rekapally H,
Summers CE, Glackin C and Heimark RL: N-cadherin gene expression in
prostate carcinoma is modulated by integrin-dependent nuclear
translocation of Twist1. Cancer Res. 66:3365–3369. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Kovalchuk O, Filkowski J, Meservy J, et
al: Involvement of microRNA-451 in resistance of the MCF-7 breast
cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin. Mol Cancer Ther.
7:2152–2159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Yang H, Kong W, He L, et al: MicroRNA
expression profiling in human ovarian cancer: miR-214 induces cell
survival and cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN. Cancer Res.
68:425–433. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Ma J, Dong C and Ji C: MicroRNA and drug
resistance. Cancer Gene Ther. 17:523–531. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Xin F, Li M, Balch C, et al: Computational
analysis of microRNA profiles and their target genes suggests
significant involvement in breast cancer antiestrogen resistance.
Bioinformatics. 25:430–434. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Burow ME, Weldon CB, Melnik LI, et al:
PI3-K/AKT regulation of NF-kappaB signaling events in suppression
of TNF-induced apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 271:342–345.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Frigo DE, Basu A, Nierth-Simpson EN, et
al: p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase stimulates
estrogen-mediated transcription and proliferation through the
phosphorylation and potentiation of the p160 coactivator
glucocorticoid receptor-interacting protein 1. Mol Endocrinol.
20:971–983. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Bourguignon LY, Wong G, Earle C, Krueger K
and Spevak CC: Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction promotes c-Src-mediated
twist signaling, microRNA-10b expression, and RhoA/RhoC
up-regulation, leading to Rho-kinase-associated cytoskeleton
activation and breast tumor cell invasion. J Biol Chem.
285:36721–36735. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Zhu S, Wu H, Wu F, Nie D, Sheng S and Mo
YY: MicroRNA-21 targets tumor suppressor genes in invasion and
metastasis. Cell Res. 18:350–359. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Grund EM, Kagan D, Tran CA, et al: Tumor
necrosis factor-alpha regulates inf lammatory and mesenchymal
responses via mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, p38, and
nuclear factor kappaB in human endometriotic epithelial cells. Mol
Pharmacol. 73:1394–1404. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Kolosova I, Nethery D and Kern JA: Role of
Smad2/3 and p38 MAP kinase in TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of pulmonary epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol.
226:1248–1254. 2011.
|
|
90
|
Strippoli R, Benedicto I, Foronda M, et
al: p38 maintains E-cadherin expression by modulating TAK1-NF-kappa
B during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Sci.
123:4321–4331. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|