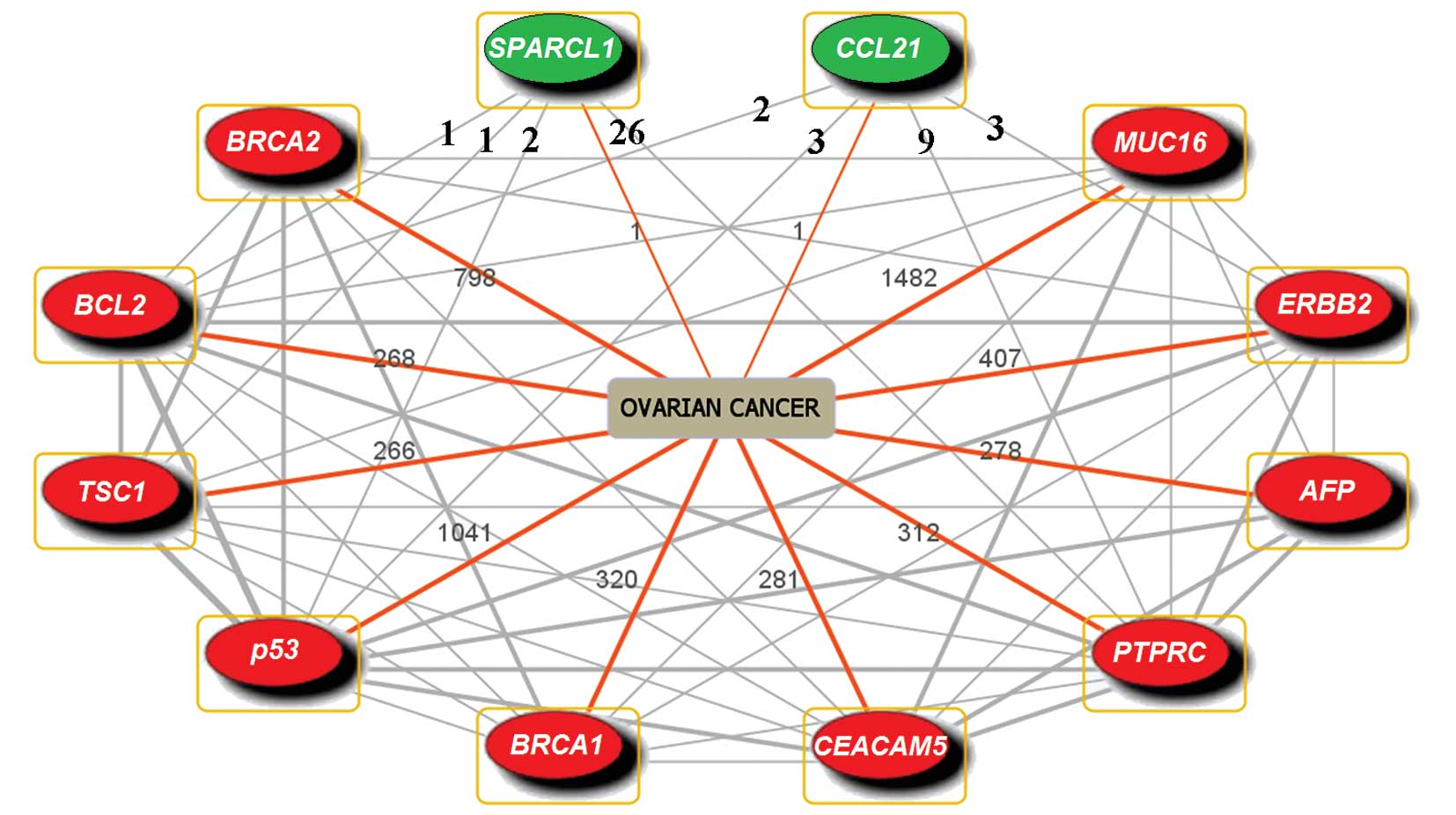
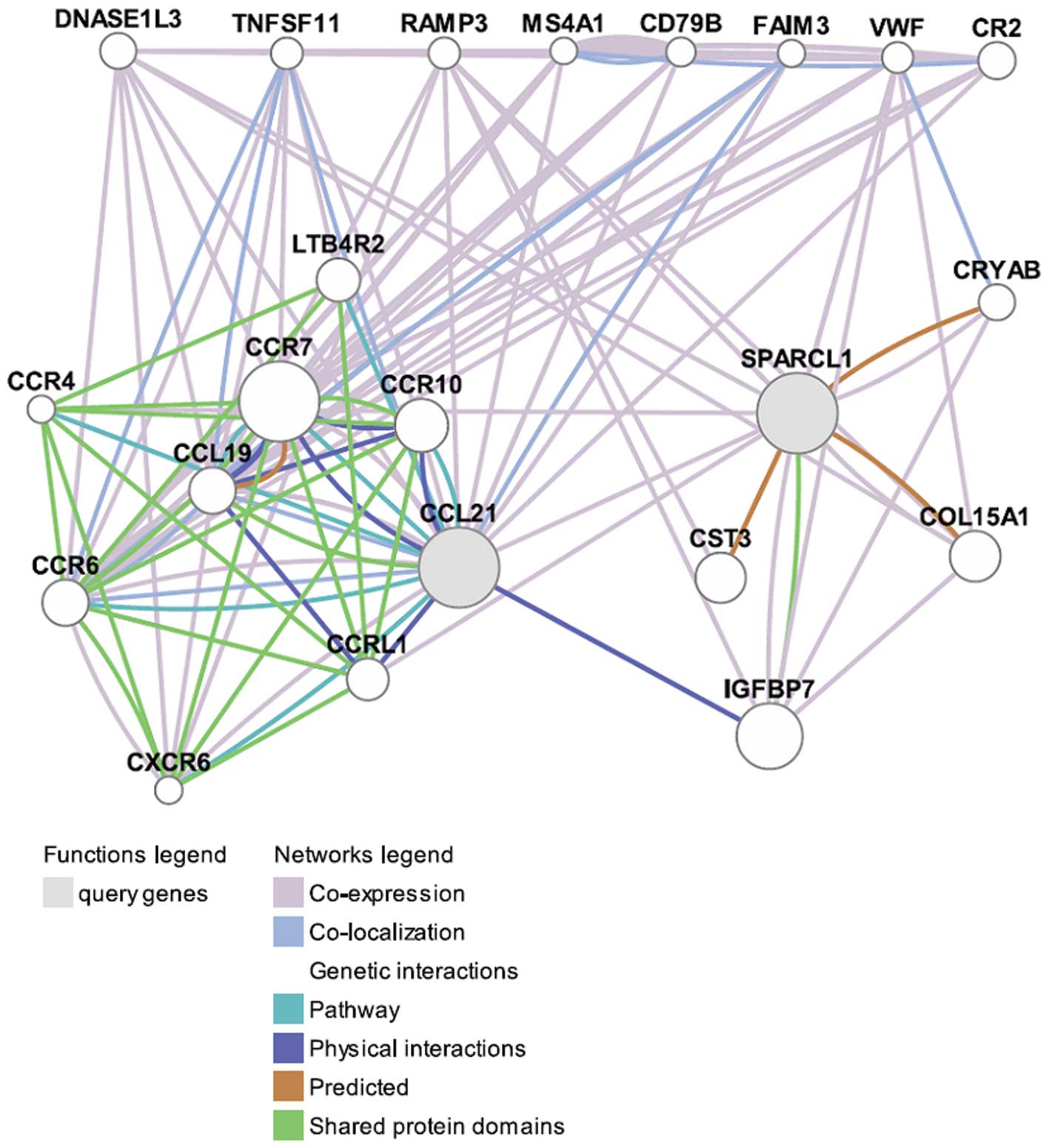
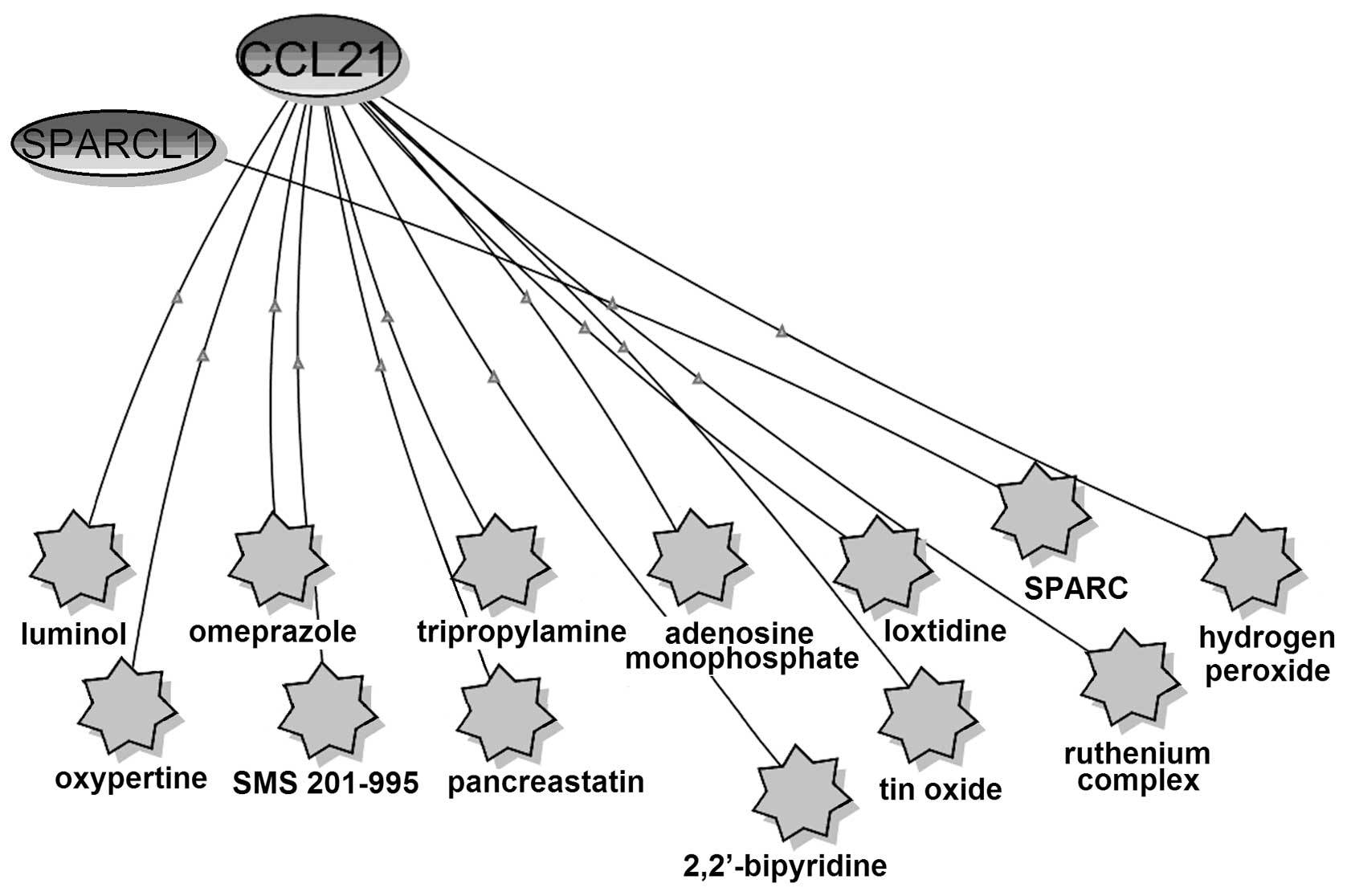
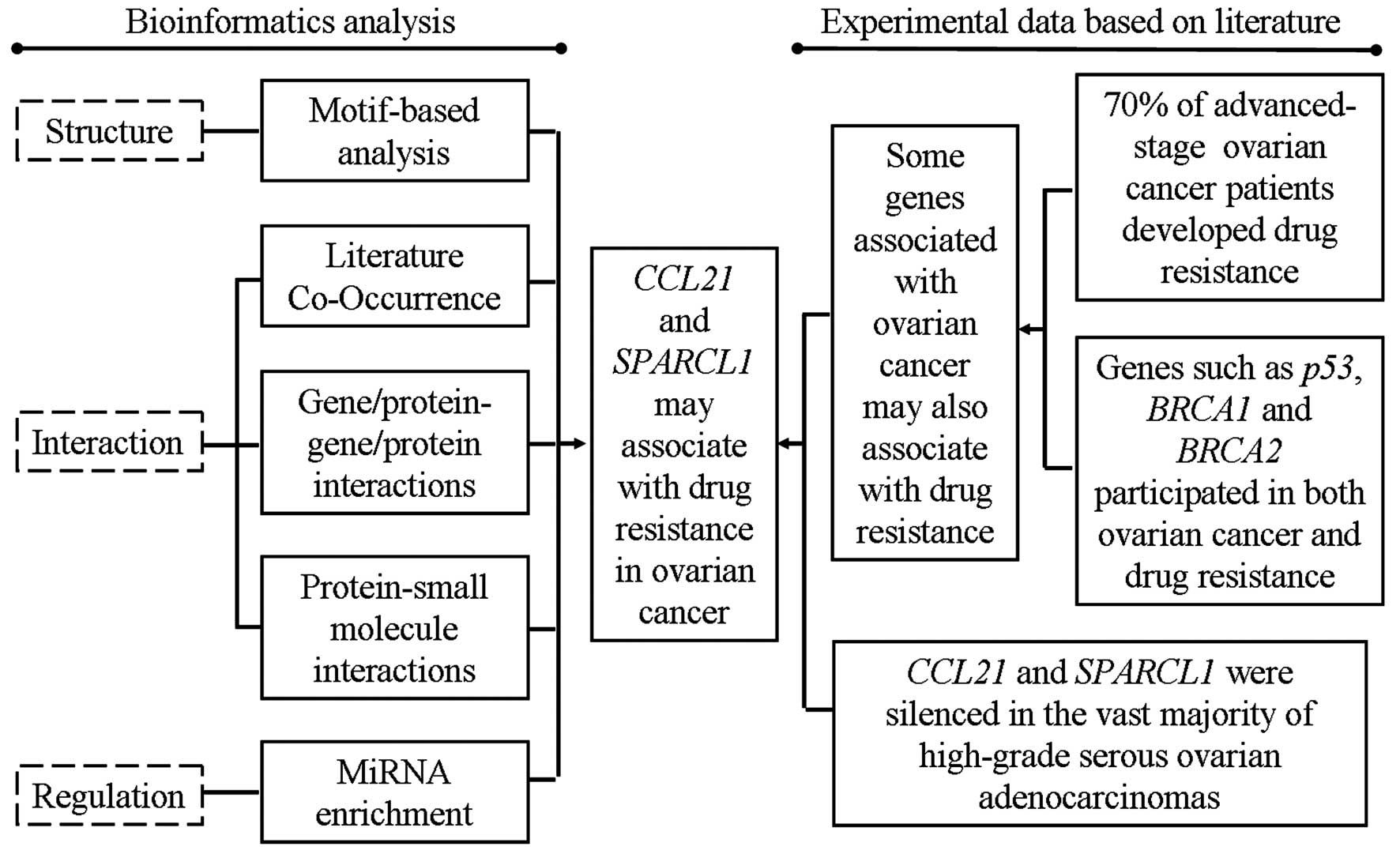
|
1
|
Balch C, Huang TH, Brown R and Nephew KP:
The epigenetics of ovarian cancer drug resistance and
resensitization. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 191:1552–1572. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J,
Murray T and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin.
58:71–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cannistra SA: Cancer of the ovary. N Engl
J Med. 351:2519–2529. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bast RC Jr, Hennessy B and Mills GB: The
biology of ovarian cancer: new opportunities for translation. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:415–428. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fraser M, Bai T and Tsang BK: Akt promotes
cisplatin resistance in human ovarian cancer cells through
inhibition of p53 phosphorylation and nuclear function. Int J
Cancer. 122:534–546. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hagopian GS, Mills GB, Khokhar AR, Bast RC
Jr and Siddik ZH: Expression of p53 in cisplatin-resistant ovarian
cancer cell lines: modulation with the novel platinum analogue (1R,
2R-diaminocyclohexane)(trans-diacetato)(dichloro)-platinum(IV).
Clin Cancer Res. 5:655–663. 1999.
|
|
7
|
Zhou C, Smith JL and Liu J: Role of BRCA1
in cellular resistance to paclitaxel and ionizing radiation in an
ovarian cancer cell line carrying a defective BRCA1. Oncogene.
22:2396–2404. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang D, Khan S, Sun Y, Hess K, Shmulevich
I, Sood AK and Zhang W: Association of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations
with survival, chemotherapy sensitivity, and gene mutator phenotype
in patients with ovarian cancer. JAMA. 306:1557–1565. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu L, Wu A and Jiang K: Effect of
antisense c-erbB2 on biologic behaviour and chemotherapeutic drug
sensitivity in human ovarian cancer cells. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za
Zhi. 31:169–172. 1996.(In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Benoit DS, Henry SM, Shubin AD, Hoffman AS
and Stayton PS: pH-responsive polymeric sirna carriers sensitize
multidrug resistant ovarian cancer cells to doxorubicin via
knockdown of polo-like kinase 1. Mol Pharm. 7:442–455. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Itamochi H: Targeted therapies in
epithelial ovarian cancer: molecular mechanisms of action. World J
Biol Chem. 1:209–220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network:
Integrated genomic analyses of ovarian carcinoma. Nature.
474:609–615. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Narod S, Moody J, Rosen B, Fan I, Risch A,
Sun P and McLaughlin J: Estimating survival rates after ovarian
cancer among women tested for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations. Clin
Genet. June 8–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
14
|
Szabova L, Yin C, Bupp S, et al:
Perturbation of Rb, p53, and Brca1 or Brca2 cooperate in inducing
metastatic serous epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 72:1–13.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Thangaraju M, Kaufmann SH and Couch FJ:
BRCA1 facilitates stress-induced apoptosis in breast and ovarian
cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem. 275:33487–33496. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Connor JP, Felder M, Kapur A and Onujiogu
N: DcR3 binds to ovarian cancer via heparan sulfate proteoglycans
and modulates tumor cells response to platinum with corresponding
alteration in the expression of BRCA1. BMC Cancer. 12:1762012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Quinn JE, James CR, Stewart GE, et al:
BRCA1 mRNA expression levels predict for overall survival in
ovarian cancer after chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 13:7413–7420.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yellaboina S, Tasneem A, Zaykin DV,
Raghavachari B and Jothi R: DOMINE: a comprehensive collection of
known and predicted domain-domain interactions. Nucleic Acids Res.
39:D730–D735. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Raghavachari B, Tasneem A, Przytycka TM
and Jothi R: DOMINE: a database of protein domain interactions.
Nucleic Acids Res. 36:D656–D661. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jenssen TK, Laegreid A, Komorowski J and
Hovig E: A literature network of human genes for high-throughput
analysis of gene expression. Nat Genet. 28:21–28. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mostafavi S, Ray D, Warde-Farley D,
Grouios C and Morris Q: GeneMANIA: a real-time multiple association
network integration algorithm for predicting gene function. Genome
Biol. 9(Suppl 1): S42008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Baitaluk M, Sedova M, Ray A and Gupta A:
BiologicalNetworks: visualization and analysis tool for systems
biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:W466–W471. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P and Gretz N:
miRWalk - database: prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by
‘walking’ the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform. 44:839–847.
2011.
|
|
24
|
Papadopoulos GL, Alexiou P, Maragkakis M,
Reczko M and Hatzigeorgiou AG: DIANA-mirPath: integrating human and
mouse microRNAs in pathways. Bioinformatics. 25:1991–1993. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Baggiolini M, Dewald B and Moser B: Human
chemokines: an update. Annu Rev Immunol. 15:675–705. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu Y, Liu L, Qiu X, et al: CCL21/CCR7
prevents apoptosis via the ERK pathway in human non-small cell lung
cancer cells. PLoS One. 7:e332622012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hwang TL, Lee LY, Wang CC, Liang Y, Huang
SF and Wu CM: CCL7 and CCL21 overexpression in gastric cancer is
associated with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis. World J
Gastroenterol. 18:1249–1256. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu Y, Liu L, Qiu X, et al: CCL21/CCR7
promotes G2/M phase progression via the ERK pathway in human
non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 6:e211192011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yousefieh N, Hahto SM, Stephens AL and
Ciavarra RP: Regulated expression of CCL21 in the prostate tumor
microenvironment inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in an
orthotopic model of prostate cancer. Cancer Microenviron. 2:59–67.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhang H, Widegren E, Wang DW and Sun XF:
SPARCL1: a potential molecule associated with tumor diagnosis,
progression and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol.
32:1225–1231. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hambrock HO, Nitsche DP, Hansen U,
Bruckner P, Paulsson M, Maurer P and Hartmann U: SC1/hevin. An
extracellular calcium-modulated protein that binds collagen I. J
Biol Chem. 278:11351–11358. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Girard JP and Springer TA: Modulation of
endothelial cell adhesion by hevin, an acidic protein associated
with high endothelial venules. J Biol Chem. 271:4511–4517. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li P, Qian J, Yu G, Chen Y, Liu K, Li J
and Wang J: Down-regulated SPARCL1 is associated with clinical
significance in human gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 105:31–37.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yu SJ, Yu JK, Ge WT, Hu HG, Yuan Y and
Zheng S: SPARCL1, Shp2, MSH2, E-cadherin, p53, ADCY-2 and MAPK are
prognosis-related in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol.
17:2028–2036. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sullivan MM and Sage EH: Hevin/SC1, a
matricellular glyco-protein and potential tumor-suppressor of the
SPARC/BM-40/Osteonectin family. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
36:991–996. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mintz MB, Sowers R, Brown KM, et al: An
expression signature classifies chemotherapy-resistant pediatric
osteosarcoma. Cancer Res. 65:1748–1754. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Song J, Wang X, Lei C, et al: Fusion of
chemotactic peptide to a single-chain bi-specific antibody (scBsAb)
potentiates its cytotoxicity to target tumour cells. Biotechnol
Appl Biochem. 45:147–154. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Biade S, Marinucci M, Schick J, et al:
Gene expression profiling of human ovarian tumours. Br J Cancer.
95:1092–1100. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lu X, Zhai C, Gopalakrishnan V and
Buchanan BG: Automatic annotation of protein motif function with
Gene Ontology terms. BMC Bioinformatics. 5:1222004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang W, Chen LP, Huang R and Huang RP:
Inhibition of IL-6 and IL-8 enhances chemosensitization in
multidrug resistant human breast cancer cells. AACR Meeting
Abstracts. 2005:1199-c2005.
|
|
41
|
Duan Z, Feller AJ, Penson RT, Chabner BA
and Seiden MV: Discovery of differentially expressed genes
associated with paclitaxel resistance using cDNA array technology:
analysis of interleukin (IL) 6, IL-8, and monocyte chemotactic
protein 1 in the paclitaxel-resistant phenotype. Clin Cancer Res.
5:3445–3453. 1999.
|
|
42
|
Soon WW, Miller LD, Black MA, et al:
Combined genomic and phenotype screening reveals secretory factor
SPINK1 as an invasion and survival factor associated with patient
prognosis in breast cancer. EMBO Mol Med. 3:451–464. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Chen T, Lee TR, Liang WG, Chang WS and Lyu
PC: Identification of trypsin-inhibitory site and structure
determination of human SPINK2 serine proteinase inhibitor.
Proteins. 77:209–219. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kutuzov MA, Bennett N and Andreeva AV:
Protein phosphatase with EF-hand domains 2 (PPEF2) is a potent
negative regulator of apoptosis signal regulating kinase-1 (ASK1).
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 42:1816–1822. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gibadulinova A, Tothova V, Pastorek J and
Pastorekova S: Transcriptional regulation and functional
implication of S100P in cancer. Amino Acids. 41:885–892. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhu W, Xu H, Zhu D, et al: miR-200bc/429
cluster modulates multidrug resistance of human cancer cell lines
by targeting BCL2 and XIAP. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 69:723–731.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hong JH, Lee E, Hong J, Shin YJ and Ahn H:
Antisense Bcl2 oligonucleotide in cisplatin-resistant bladder
cancer cell lines. BJU Int. 90:113–117. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dhar DK, Nagasue N, Yoshimura H, et al:
Overexpression of P-glycoprotein in untreated AFP-producing gastric
carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 60:50–54. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Xu Z, Wang M, Wang L, Wang Y, Zhao X, Rao
Q and Wang J: Aberrant expression of TSC2 gene in the newly
diagnosed acute leukemia. Leuk Res. 33:891–897. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liu Z and Chen S: ER regulates an
evolutionarily conserved apoptosis pathway. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 400:34–38. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, et al:
Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 406:747–752.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Dabholkar M, Bradshaw L, Parker RJ, Gill
I, Bostick-Bruton F, Muggia FM and Reed E: Cisplatin-DNA damage and
repair in peripheral blood leukocytes in vivo and in vitro. Environ
Health Perspect. 98:53–59. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jo H, Loison F, Hattori H, Silberstein LE,
Yu H and Luo HR: Natural product Celastrol destabilizes tubulin
heterodimer and facilitates mitotic cell death triggered by
microtubule-targeting anti-cancer drugs. PLoS One. 5:e103182010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Waugh DJ and Wilson C: The interleukin-8
pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6735–6741. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Herr DR: Potential use of G
protein-coupled receptor-blocking monoclonal antibodies as
therapeutic agents for cancers. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 297:45–81.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ma Q, Zhang ZS, Zhang YL and Lai ZS:
Relationship between multidrug resistance in human colon carcinoma
LoVo/Adr cell line and intracellular calcium ion concentration. Ai
Zheng. 21:846–849. 2002.(In Chinese).
|
|
57
|
Liang X and Huang Y: Intracellular free
calcium concentration and cisplatin resistance in human lung
adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Biosci Rep. 20:129–138. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Nan A, Ghandehari H, Hebert C, Siavash H,
Nikitakis N, Reynolds M and Sauk JJ: Water-soluble polymers for
targeted drug delivery to human squamous carcinoma of head and
neck. J Drug Target. 13:189–197. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Westhoff MA and Fulda S: Adhesion-mediated
apoptosis resistance in cancer. Drug Resist Updat. 12:127–136.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Benatar T, Amemiya Y, Yang W and Seth A:
Insulin-like-growth factor-binding-protein 7: an antagonist to
breast cancer. Breast Cancer - Focusing Tumor Microenvironment,
Stem cells and Metastasis. Gunduz M: InTech; Rijeka: pp. 39–68.
2011
|
|
61
|
Heesch S, Schlee C, Neumann M, et al:
BAALC-associated gene expression profiles define IGFBP7 as a novel
molecular marker in acute leukemia. Leukemia. 24:1429–1436. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lane TF, Iruela-Arispe ML, Johnson RS and
Sage EH: SPARC is a source of copper-binding peptides that
stimulate angiogenesis. J Cell Biol. 125:929–943. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Girard JP and Springer TA: Cloning from
purified high endothelial venule cells of hevin, a close relative
of the antiadhesive extracellular matrix protein SPARC. Immunity.
2:113–123. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Socha MJ, Said N, Dai Y, et al: Aberrant
promoter methylation of SPARC in ovarian cancer. Neoplasia.
11:126–135. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Tai IT, Dai M, Owen DA and Chen LB:
Genome-wide expression analysis of therapy-resistant tumors reveals
SPARC as a novel target for cancer therapy. J Clin Invest.
115:1492–1502. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
De Milito A and Fais S: Proton pump
inhibitors may reduce tumour resistance. Expert Opin Pharmacother.
6:1049–1054. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Logothetis CJ, Hossan EA and Smith TL: SMS
201–995 in the treatment of refractory prostatic carcinoma.
Anticancer Res. 14:2731–2734. 1994.
|
|
68
|
Matrone A, Grossi V, Chiacchiera F, et al:
p38alpha is required for ovarian cancer cell metabolism and
survival. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 20:203–211. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Kapitza S, Pongratz M, Jakupec MA, et al:
Heterocyclic complexes of ruthenium (III) induce apoptosis in
colorectal carcinoma cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 131:101–110.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Yokomizo A, Ono M, Nanri H, et al:
Cellular levels of thioredoxin associated with drug sensitivity to
cisplatin, mitomycin C, doxorubicin, and etoposide. Cancer Res.
55:4293–4296. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Turk D, Hall MD, Chu BF, Ludwig JA, Fales
HM, Gottesman MM and Szakacs G: Identification of compounds
selectively killing multidrug-resistant cancer cells. Cancer Res.
69:8293–8301. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Van Jaarsveld MT, Helleman J, Berns EM and
Wiemer EA: MicroRNAs in ovarian cancer biology and therapy
resistance. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 42:1282–1290. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Sorrentino A, Liu CG, Addario A, Peschle
C, Scambia G and Ferlini C: Role of microRNAs in drug-resistant
ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 111:478–486. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Yang N, Kaur S, Volinia S, et al: MicroRNA
microarray identifies Let-7i as a novel biomarker and therapeutic
target in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
68:10307–10314. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Boren T, Xiong Y, Hakam A, et al:
MicroRNAs and their target messenger RNAs associated with ovarian
cancer response to chemotherapy. Gynecol Oncol. 113:249–255. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Kumar S, Kumar A, Shah PP, Rai SN,
Panguluri SK and Kakar SS: MicroRNA signature of cis-platin
resistant vs. cisplatin sensitive ovarian cancer cell lines. J
Ovarian Res. 4:172011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Hilliard TS, Gaisina IN, Muehlbauer AG,
Gaisin AM, Gallier F and Burdette JE: Glycogen synthase kinase
3beta inhibitors induce apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells and
inhibit in-vivo tumor growth. Anticancer Drugs. 22:978–985.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Su HY, Lai HC, Lin YW, et al: Epigenetic
silencing of SFRP5 is related to malignant phenotype and
chemoresistance of ovarian cancer through Wnt signaling pathway.
Int J Cancer. 127:555–567. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Bellone S, Siegel ER, Cocco E, et al:
Overexpression of epithelial cell adhesion molecule in primary,
metastatic, and recurrent/chemotherapy-resistant epithelial ovarian
cancer: implications for epithelial cell adhesion molecule-specific
immunotherapy. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 19:860–866. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Chen JY, Shen C, Yan Z, Brown DP and Wang
M: A systems biology case study of ovarian cancer drug resistance.
Comput Syst Bioinformatics Conf. 389–398. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Shah MA and Schwartz GK: Cell
cycle-mediated drug resistance: an emerging concept in cancer
therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 7:2168–2181. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Miller DH, Fischer AK, Chu KF, Burr R,
Hillenmeyer S, Brard L and Brodsky AS: T0901317 inhibits
cisplatin-induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells [corrected].
Int J Gynecol Cancer. 21:1350–1356. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Trinh XB, van Dam PA, Dirix LY, Vermeulen
PB and Tjalma WA: The rationale for mTOR inhibition in epithelial
ovarian cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 18:1885–1891. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Li J, Feng Q, Kim JM, et al: Human ovarian
cancer and cisplatin resistance: possible role of inhibitor of
apoptosis proteins. Endocrinology. 142:370–380. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Luo T, Yu J, Nguyen J, et al: Electron
transfer-based combination therapy of cisplatin with
tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine for ovarian, cervical, and lung
cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:10175–10180. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Nessa MU, Beale P, Chan C, Yu JQ and Huq
F: Combinations of resveratrol, cisplatin and oxaliplatin applied
to human ovarian cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 32:53–59.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Kumaran GC, Jayson GC and Clamp AR:
Antiangiogenic drugs in ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer. 100:1–7. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Zhang Y, Cheng Y, Ren X, et al: NAC1
modulates sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin by
altering the HMGB1-mediated autophagic response. Oncogene.
31:1055–1064. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Buys TP, Chari R, Lee EH, et al: Genetic
changes in the evolution of multidrug resistance for cultured human
ovarian cancer cells. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 46:1069–1079. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Auner V, Sehouli J, Oskay-Oezcelik G,
Horvat R, Speiser P and Zeillinger R: ABC transporter gene
expression in benign and malignant ovarian tissue. Gynecol Oncol.
117:198–201. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Chikazawa N, Tanaka H, Tasaka T, Nakamura
M, Tanaka M, Onishi H and Katano M: Inhibition of Wnt signaling
pathway decreases chemotherapy-resistant side-population colon
cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 30:2041–2048. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Wang S, Li W, Xue Z, et al: Molecular
imaging of p53 signal pathway in lung cancer cell cycle arrest
induced by cisplatin. Mol Carcinog. Jun 5–2012.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Leon-Galicia I, Diaz-Chavez J,
Garcia-Villa E, et al: Resveratrol induces downregulation of DNA
repair genes in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Eur J Cancer Prev.
22:11–20. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Han W, Pan H, Chen Y, et al: EGFR tyrosine
kinase inhibitors activate autophagy as a cytoprotective response
in human lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 6:e186912011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Liu LZ, Zhou XD, Qian G, Shi X, Fang J and
Jiang BH: AKT1 amplification regulates cisplatin resistance in
human lung cancer cells through the mammalian target of
rapamycin/p70S6K1 pathway. Cancer Res. 67:6325–6332. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Chung AS, Kowanetz M, Wu X, et al:
Differential drug class-specific metastatic effects following
treatment with a panel of angiogenesis inhibitors. J Pathol.
227:404–416. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Waldner MJ and Neurath MF: Targeting the
VEGF signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
16:5–13. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Ishdorj G, Li L and Gibson SB: Regulation
of autophagy in hematological malignancies: role of reactive oxygen
species. Leuk Lymphoma. 53:26–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Liu L, Yang M, Kang R, et al:
DAMP-mediated autophagy contributes to drug resistance. Autophagy.
7:112–114. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Fisher C, Coleman T and Plant N:
Probabilistic orthology analysis of the ATP-binding cassette
transporters: implications for the development of multiple drug
resistance phenotype. Drug Metab Dispos. 40:1397–1402. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Shukla S, Chen ZS and Ambudkar SV:
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors as modulators of ABC
transporter-mediated drug resistance. Drug Resist Updat. 15:70–80.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Longley DB and Johnston PG: Molecular
mechanisms of drug resistance. J Pathol. 205:275–292. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Johnson SW, Ozols RF and Hamilton TC:
Mechanisms of drug resistance in ovarian cancer. Cancer.
71:644–649. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Sharan R, Ulitsky I and Shamir R:
Network-based prediction of protein function. Mol Syst Biol.
3:882007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Behm-Ansmant I, Rehwinkel J and Izaurralde
E: MicroRNAs silence gene expression by repressing protein
expression and/or by promoting mRNA decay. Cold Spring Harb Symp
Quant Biol. 71:523–530. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Kloosterman WP and Plasterk RH: The
diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease.
Dev Cell. 11:441–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Croce CM and Calin GA: miRNAs, cancer, and
stem cell division. Cell. 122:6–7. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Gandhi V, Plunkett
W, Sampath D and Calin GA: miRNAs and their potential for use
against cancer and other diseases. Future Oncol. 3:521–537. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|