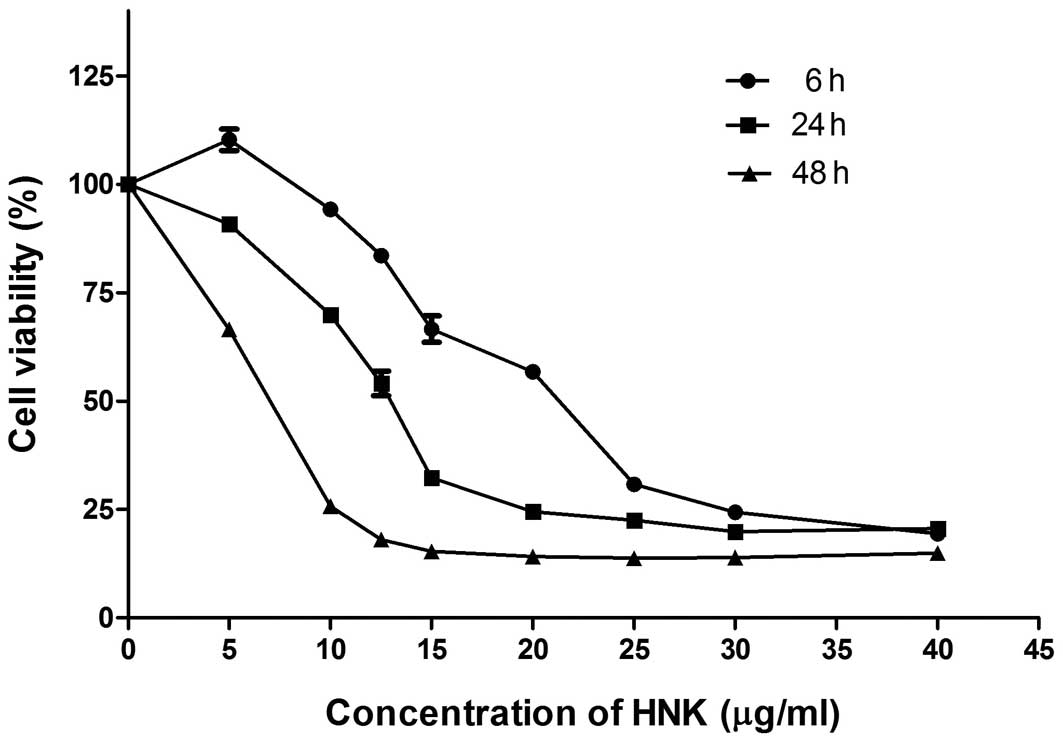
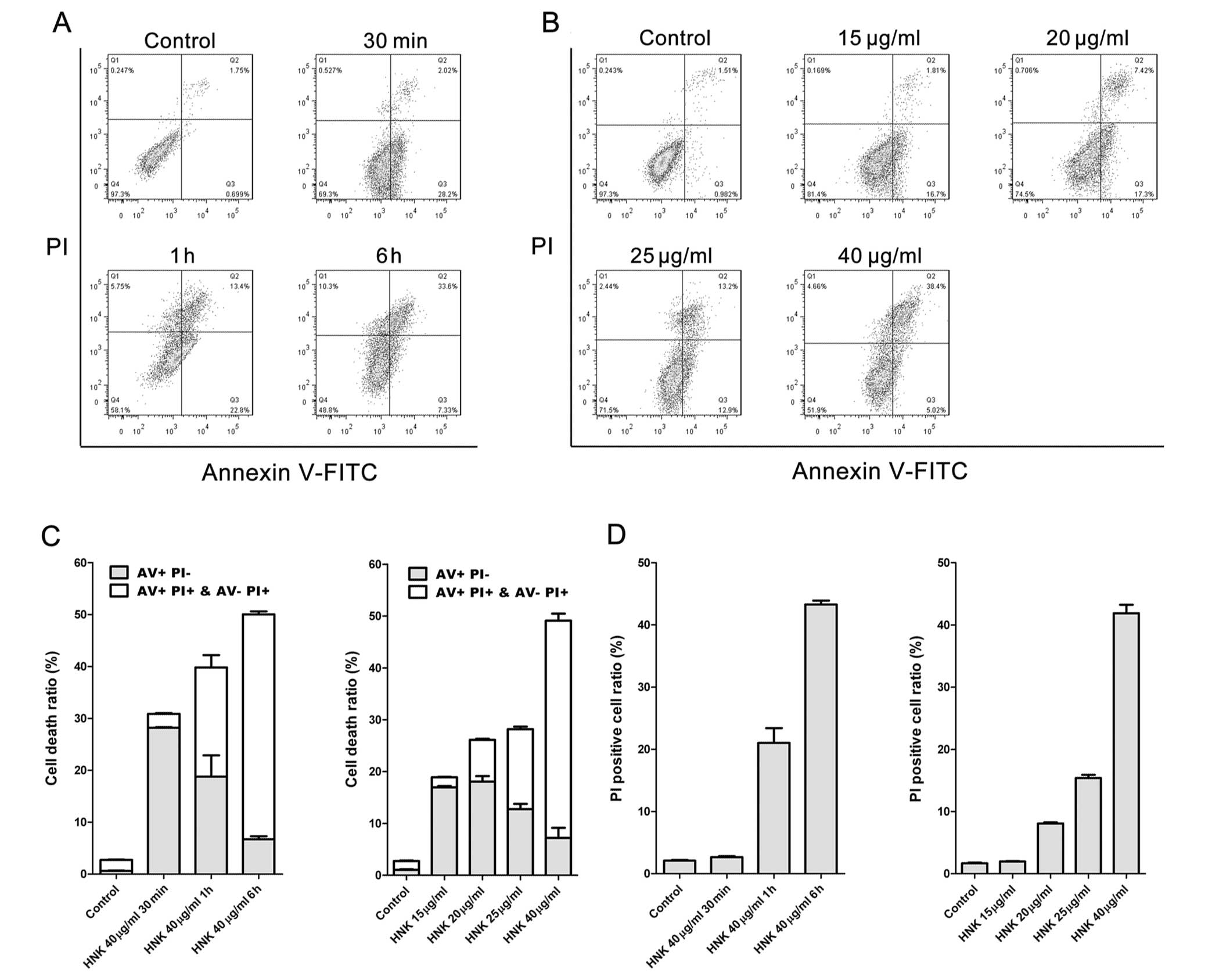
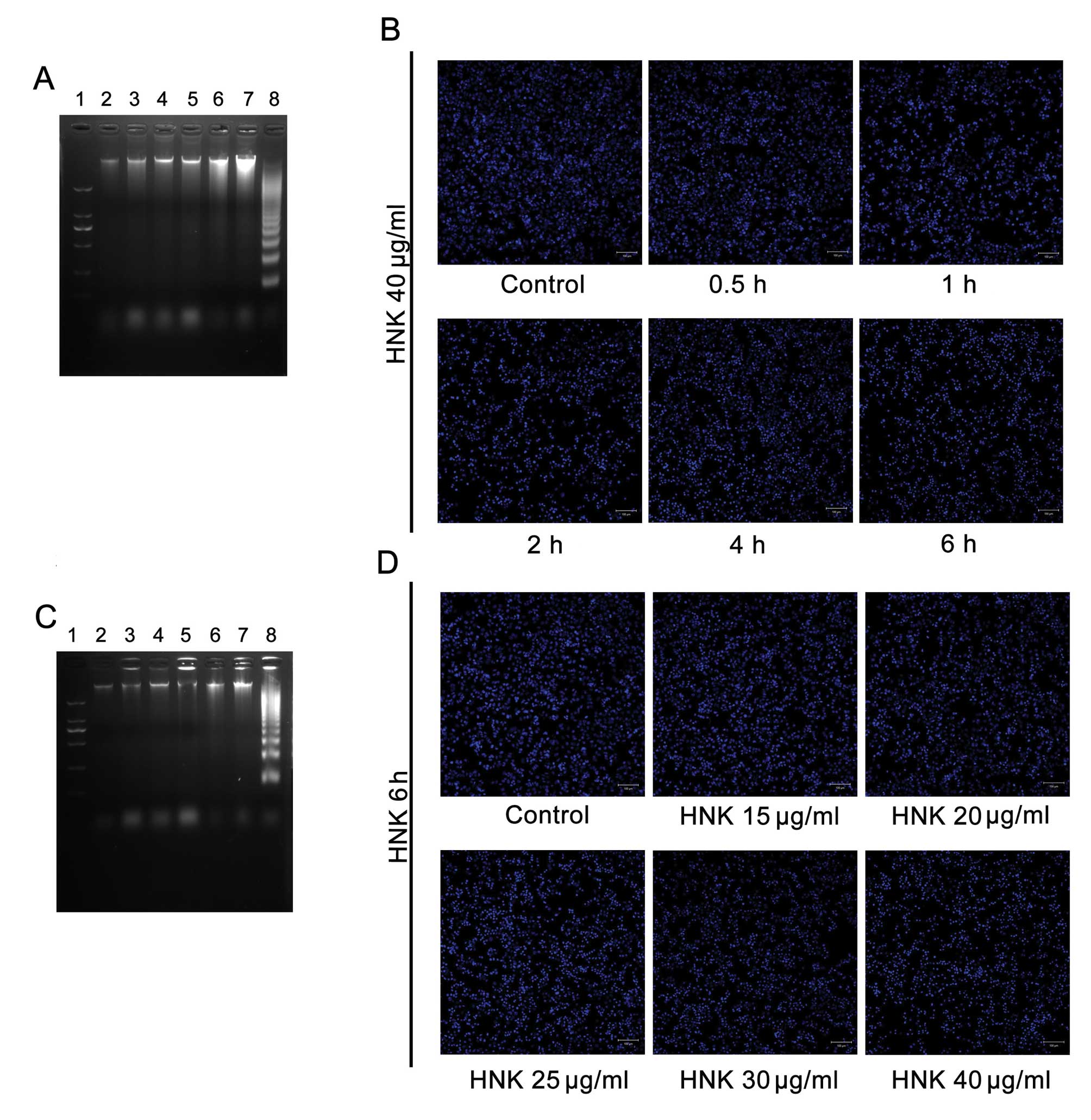
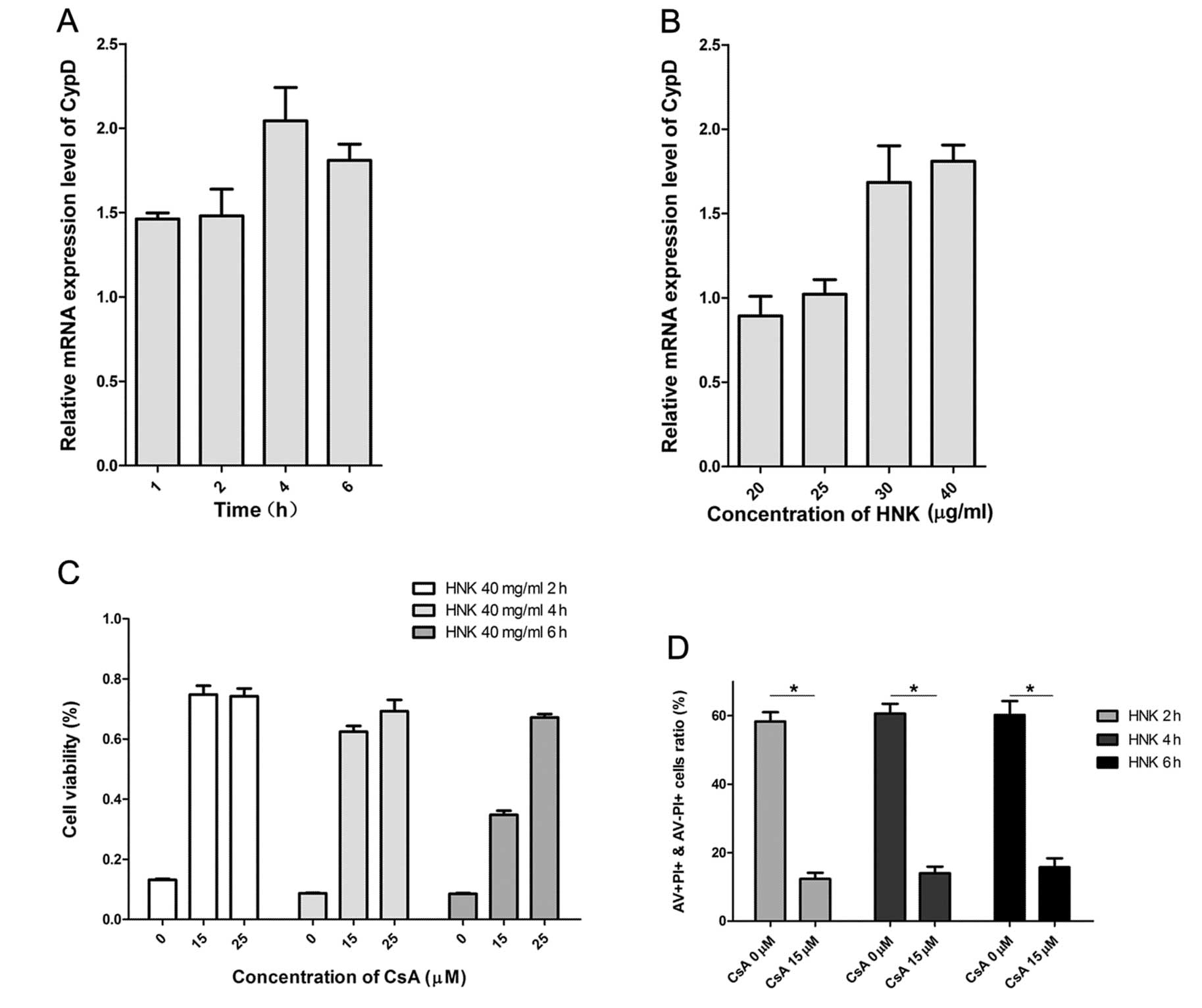
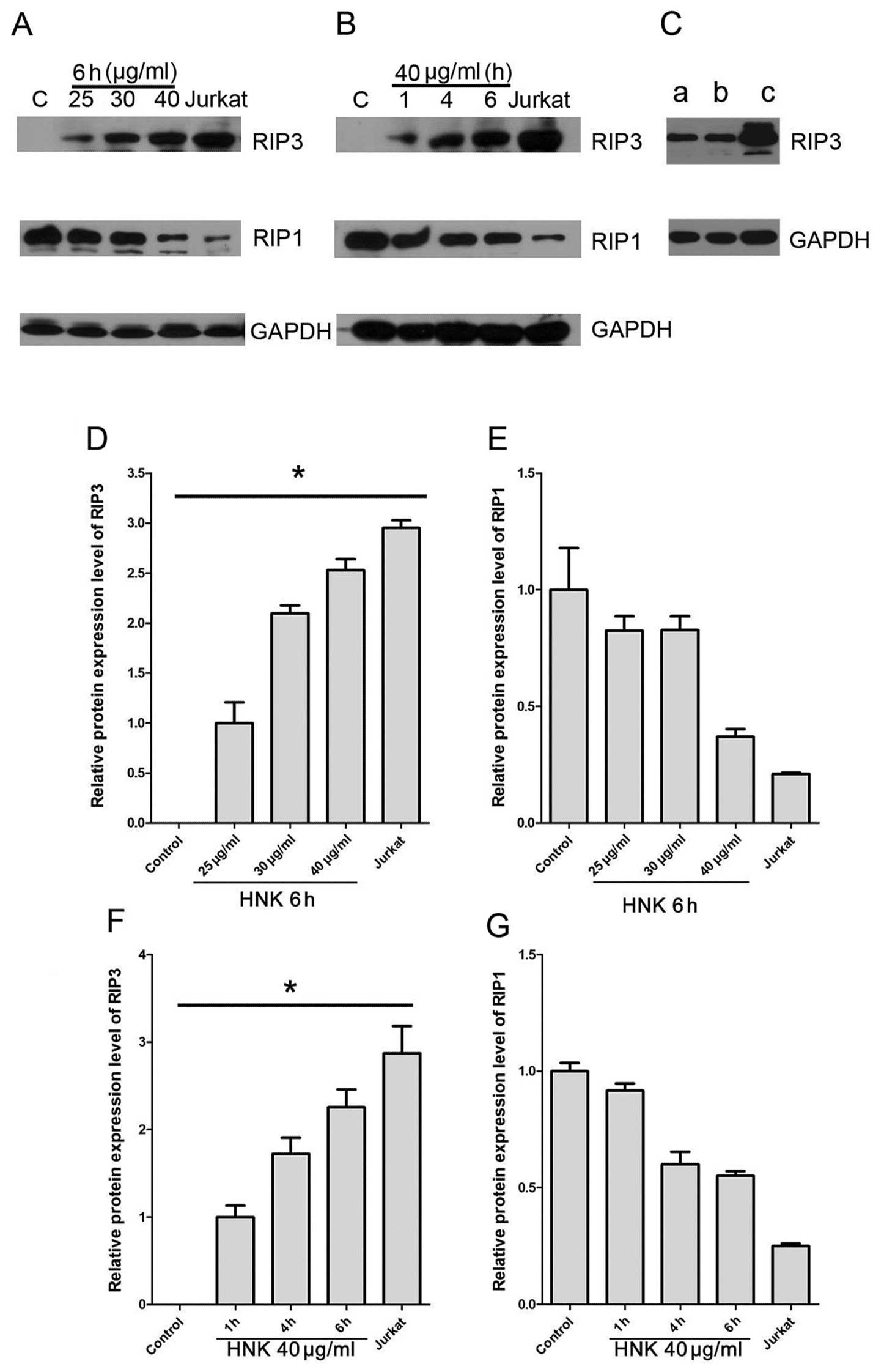
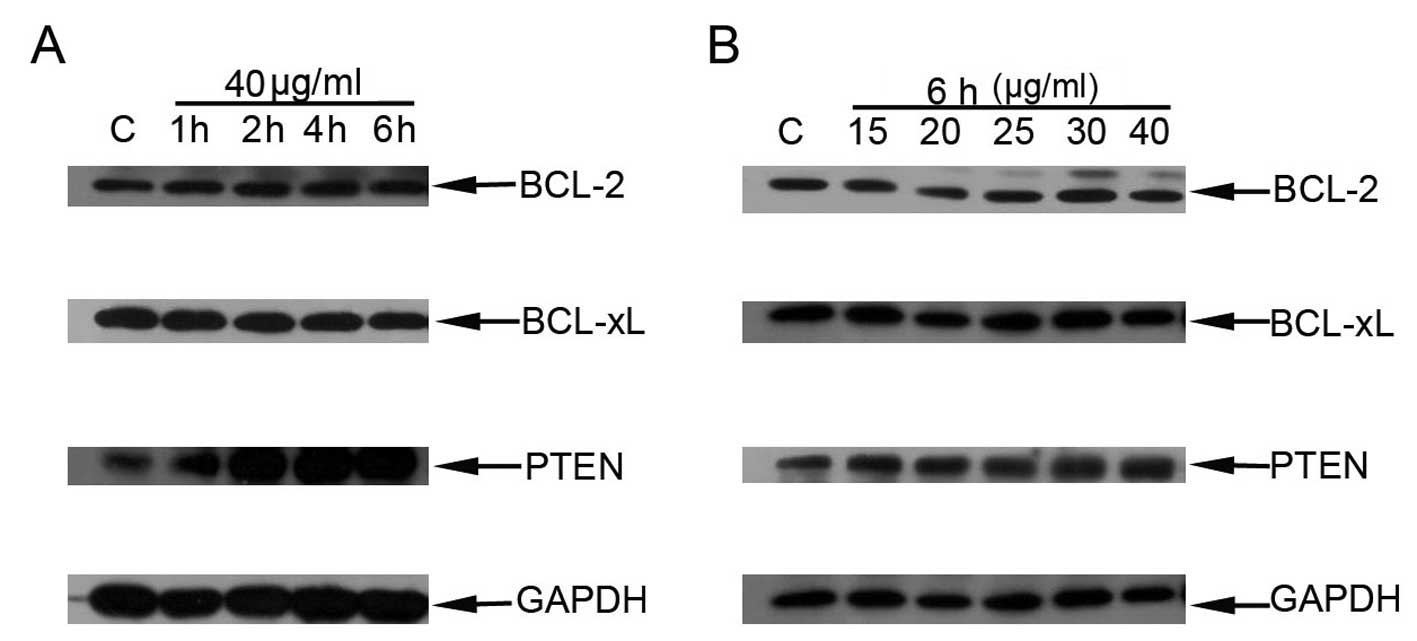
|
1.
|
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Abrams JM, et al:
Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: recommendations of
the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2012. Cell Death Differ.
19:107–120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Vanlangenakker N, Vanden Berghe T and
Vandenabeele P: Many stimuli pull the necrotic trigger, an
overview. Cell Death Differ. 19:75–86. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Han J, Zhong CQ and Zhang DW: Programmed
necrosis: backup to and competitor with apoptosis in the immune
system. Nat Immunol. 12:1143–1149. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Tian W, Xu D and Deng YC: Honokiol, a
multifunctional tumor cell death inducer. Pharmazie. 67:811–816.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Battle TE, Arbiser J and Frank DA: The
natural product honokiol induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in
B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) cells. Blood.
106:690–697. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Park EJ, Min HY, Chung HJ, et al:
Down-regulation of c-Src/EGFR-mediated signaling activation is
involved in the honokiol-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in
MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 277:133–140.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Raja SM, Chen S, Yue P, et al: The natural
product honokiol preferentially inhibits cellular FLICE-inhibitory
protein and augments death receptor-induced apoptosis. Mol Cancer
Ther. 7:2212–2223. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Shigemura K, Arbiser JL, Sun SY, et al:
Honokiol, a natural plant product, inhibits the bone metastatic
growth of human prostate cancer cells. Cancer. 109:1279–1289. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Chen YJ, Wu CL, Liu JF, et al: Honokiol
induces cell apoptosis in human chondrosarcoma cells through
mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cancer
Lett. 291:20–30. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Mannal PW, Schneider J, Tangada A,
McDonald D and McFadden DW: Honokiol produces anti-neoplastic
effects on melanoma cells in vitro. J Surg Oncol. 104:260–264.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Li L, Han W, Gu Y, et al: Honokiol induces
a necrotic cell death through the mitochondrial permeability
transition pore. Cancer Res. 67:4894–4903. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Xu D, Lu Q and Hu X: Down-regulation of
P-glycoprotein expression in MDR breast cancer cell MCF-7/ADR by
honokiol. Cancer Lett. 243:274–280. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Orrenius S, Nicotera P and Zhivotovsky B:
Cell death mechanisms and their implications in toxicology. Toxicol
Sci. 119:3–19. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Nakagawa T, Shimizu S, Watanabe T, et al:
Cyclophilin D dependent mitochondrial permeability transition
regulates some necrotic but not apoptotic cell death. Nature.
434:652–658. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Schubert A and Grimm S: Cyclophilin D, a
component of the permeability transition-pore, is an apoptosis
repressor. Cancer Res. 64:85–93. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Eliseev RA, Malecki J, Lester T, Zhang Y,
Humphrey J and Gunter TE: Cyclophilin D interacts with Bcl2 and
exerts an anti-apoptotic effect. J Biol Chem. 284:9692–9699. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Rasola A and Bernardi P: The mitochondrial
permeability transition pore and its involvement in cell death and
in disease pathogenesis. Apoptosis. 12:815–833. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Zhang DW, Zheng M, Zhao J, et al: Multiple
death pathways in TNF-treated fibroblasts: RIP3- and RIP1-dependent
and independent routes. Cell Res. 21:368–371. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Kreuzaler P and Watson CJ: Killing a
cancer: what are the alternatives? Nat Rev Cancer. 12:411–424.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Zhang DW, Shao J, Lin J, et al: RIP3, an
energy metabolism regulator that switches TNF-induced cell death
from apoptosis to necrosis. Science. 325:332–336. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
He S, Wang L, Miao L, et al: Receptor
interacting protein kinase-3 determines cellular necrotic response
to TNF-alpha. Cell. 137:1100–1111. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Li J, McQuade T, Siemer AB, et al: The
RIP1/RIP3 necrosome forms a functional amyloid signaling complex
required for programmed necrosis. Cell. 150:339–350. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Moquin D and Chan FK: The molecular
regulation of programmed necrotic cell injury. Trends Biochem Sci.
35:434–441. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Declercq W, Vanden Berghe T and
Vandenabeele P: RIP kinases at the crossroads of cell death and
survival. Cell. 138:229–232. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Kurokawa M and Kornbluth S: Caspases and
kinases in a death grip. Cell. 138:838–854. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Kelly PN and Strasser A: The role of Bcl-2
and its pro-survival relatives in tumourigenesis and cancer
therapy. Cell Death Differ. 18:1414–1424. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Song MS, Salmena L and Pandolfi PP: The
functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 13:283–296. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Martelli AM, Evangelisti C, Chappell W, et
al: Targeting the translational apparatus to improve leukemia
therapy: roles of the PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathway. Leukemia.
25:1064–1079. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Wolf I, O’Kelly J, Wakimoto N, et al:
Honokiol, a natural biphenyl, inhibits in vitro and in
vivo growth of breast cancer through induction of apoptosis and
cell cycle arrest. Int J Oncol. 30:1529–1537. 2007.
|
|
32.
|
Liu H, Zang C, Emde A, et al: Anti-tumor
effect of honokiol alone and in combination with other anti-cancer
agents in breast cancer. Eur J Pharmacol. 591:43–51. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Mocarski ES, Upton JW and Kaiser WJ: Viral
infection and the evolution of caspase 8-regulated apoptotic and
necrotic death pathways. Nat Rev Immunol. 12:79–88. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Sun L, Wang H, Wang Z, et al: Mixed
lineage kinase domain-like protein mediates necrosis signaling
downstream of RIP3 kinase. Cell. 148:213–227. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Motani K, Kushiyama H, Imamura R,
Kinoshita T, Nishiuchi T and Suda T: Caspase-1 protein induces
apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase
recruitment domain (ASC)-mediated necrosis independently of its
catalytic activity. J Biol Chem. 286:33963–33972. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36.
|
Cho YS, Challa S, Moquin D, et al:
Phosphorylation-driven assembly of the RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates
programmed necrosis and virus-induced inflammation. Cell.
137:1112–1123. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Upton JW, Kaiser WJ and Mocarski ES: Virus
inhibition of RIP3-dependent necrosis. Cell Host Microbe.
7:302–313. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Rebsamen M, Heinz LX, Meylan E, et al:
DAI/ZBP1 recruits RIP1 and RIP3 through RIP homotypic interaction
motifs to activate NF-kappaB. EMBO Rep. 10:916–922. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Ono K, Wang X, Kim SO, Armstrong LC,
Bornstein P and Han J: Metaxin deficiency alters mitochondrial
membrane permeability and leads to resistance to TNF-induced cell
killing. Protein Cell. 1:161–173. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Jeong JJ, Lee JH, Chang KC and Kim HJ:
Honokiol exerts an anticancer effect in T98G human glioblastoma
cells through the induction of apoptosis and the regulation of
adhesion molecules. Int J Oncol. 41:1358–1364. 2012.
|
|
41.
|
Arora S, Bhardwaj A, Srivastava SK, et al:
Honokiol arrests cell cycle, induces apoptosis, and potentiates the
cytotoxic effect of gemcitabine in human pancreatic cancer cells.
PLoS One. 6:e215732011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Han LL, Xie LP, Li LH, Zhang XW, Zhang RQ
and Wang HZ: Reactive oxygen species production and Bax/Bcl-2
regulation in honokiol-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 28:97–103.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Deng J, Qian Y, Geng L, et al: Involvement
of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in honokiol-induced
apoptosis in a human hepatoma cell line (hepG2). Liver Int.
28:1458–1464. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Hahm ER, Arlotti JA, Marynowski SW and
Singh SV: Honokiol, a constituent of oriental medicinal herb
Magnolia officinalis, inhibits growth of PC-3 xenografts in
vivo in association with apoptosis induction. Clin Cancer Res.
14:1248–1257. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|