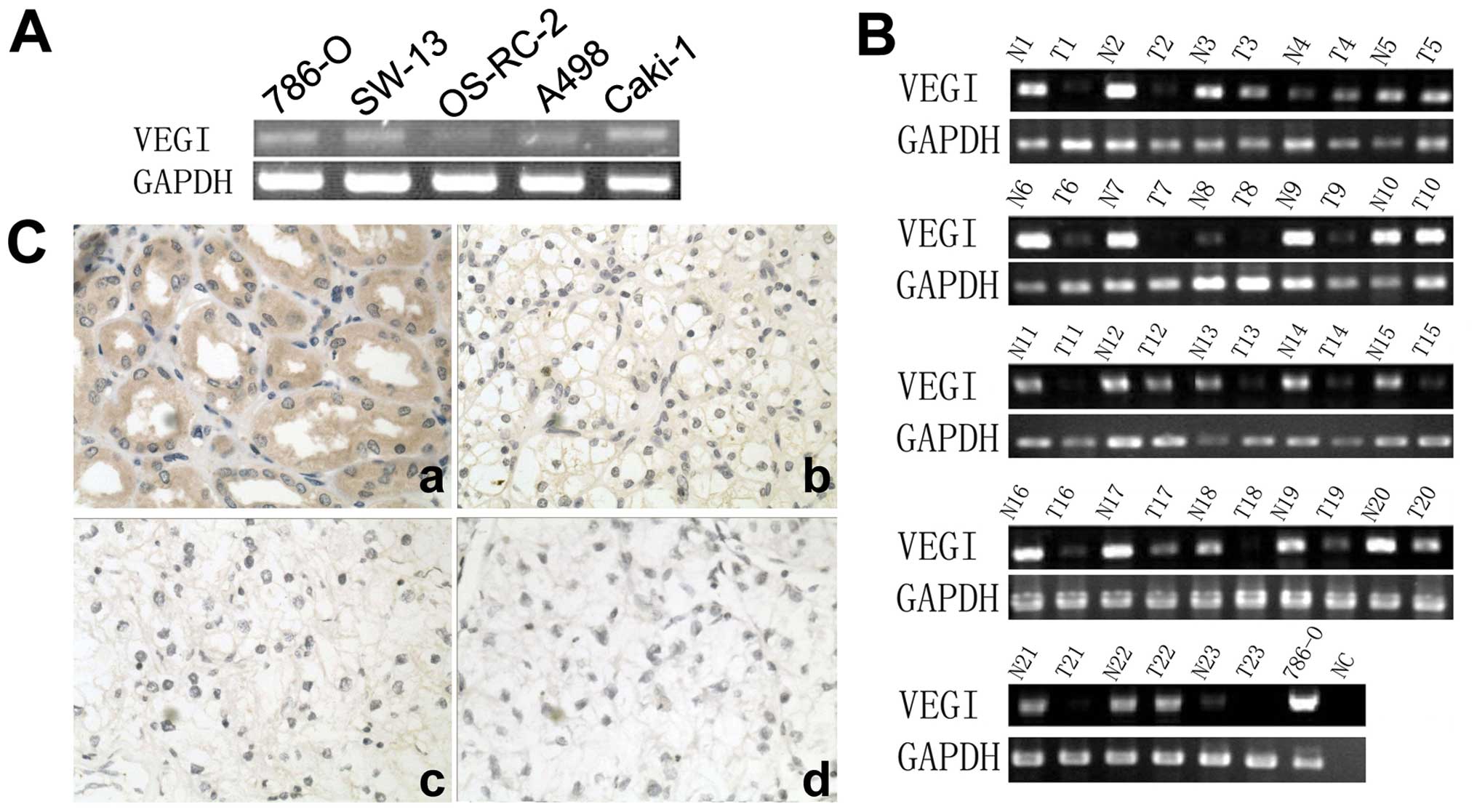
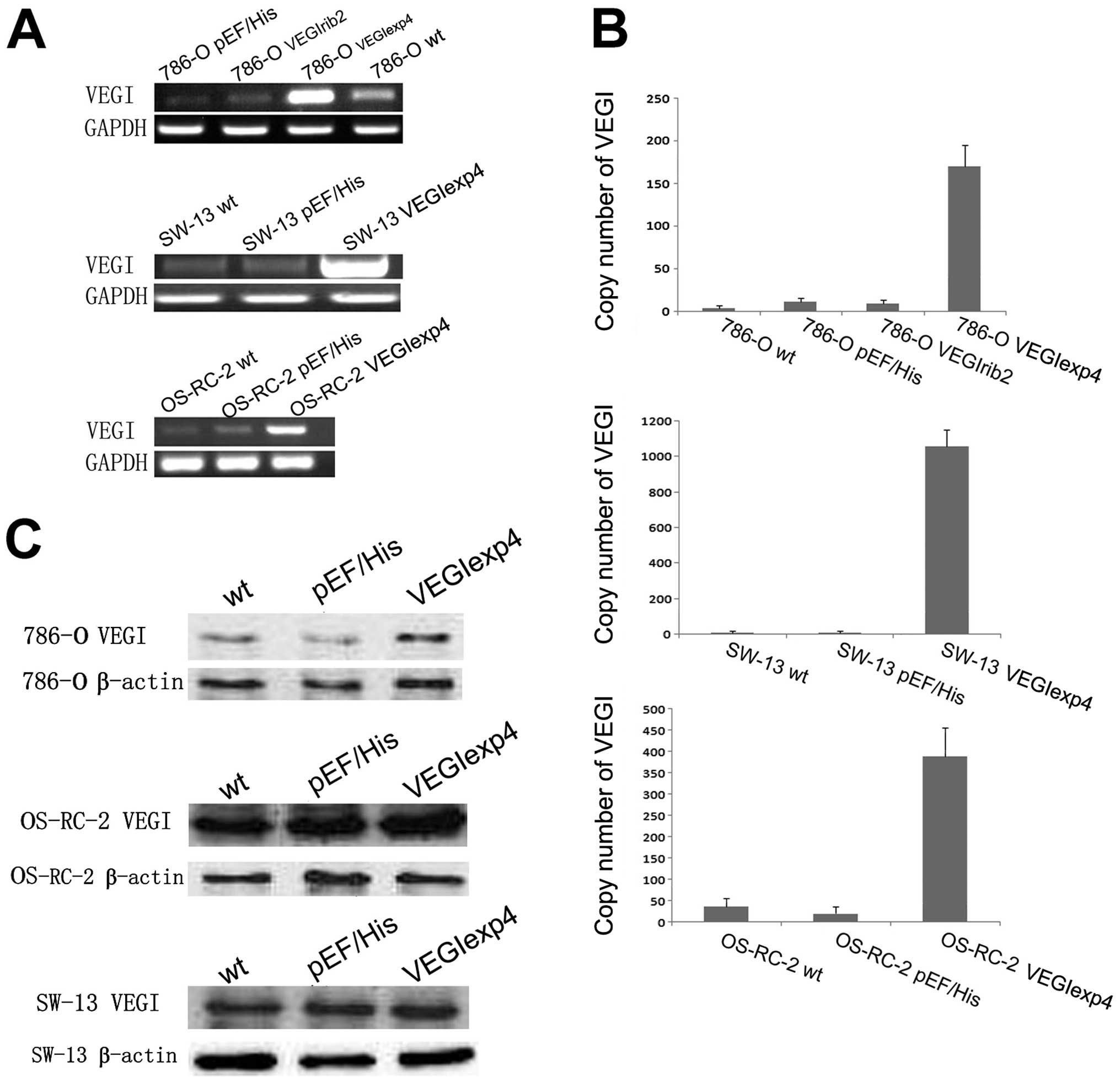
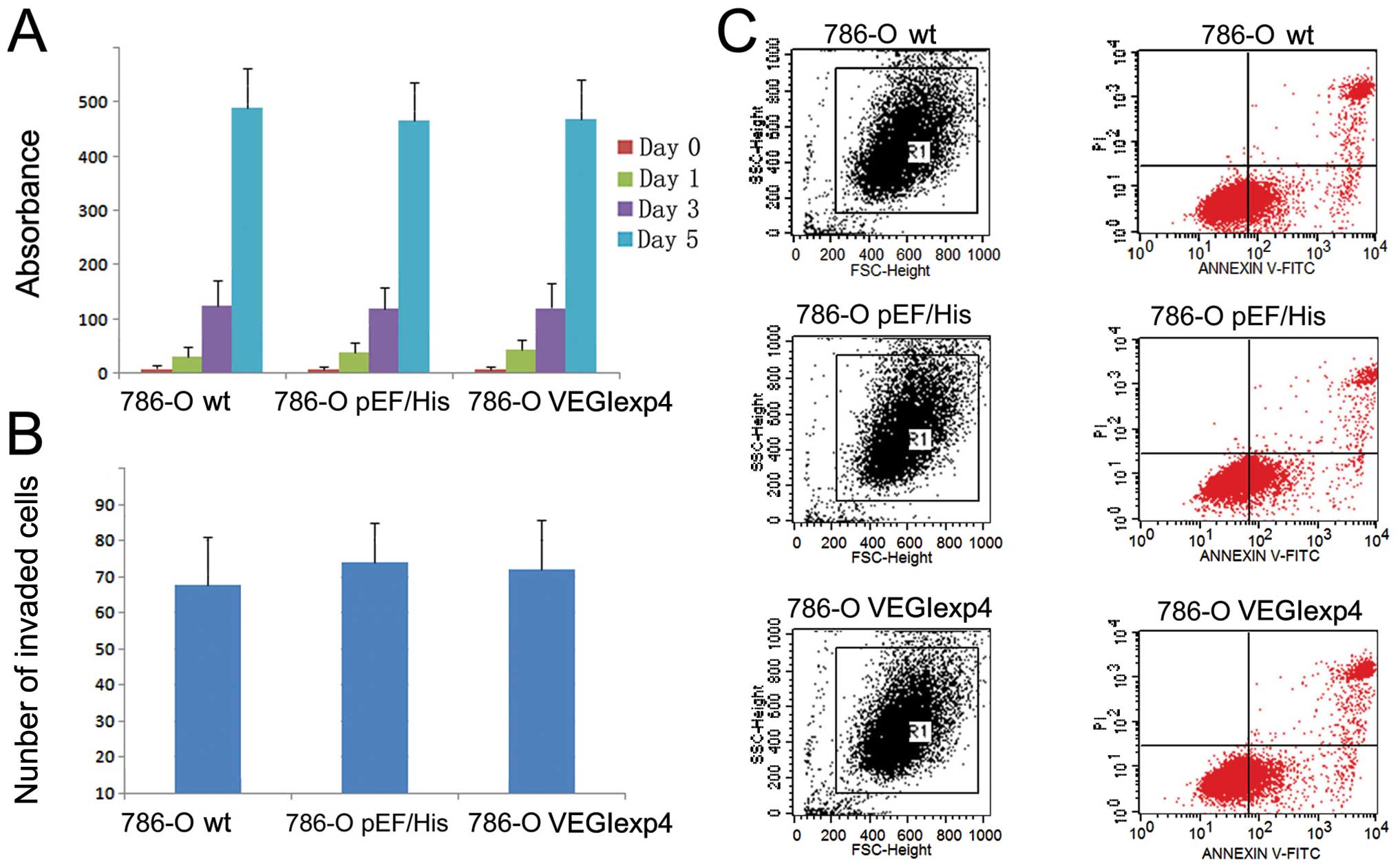
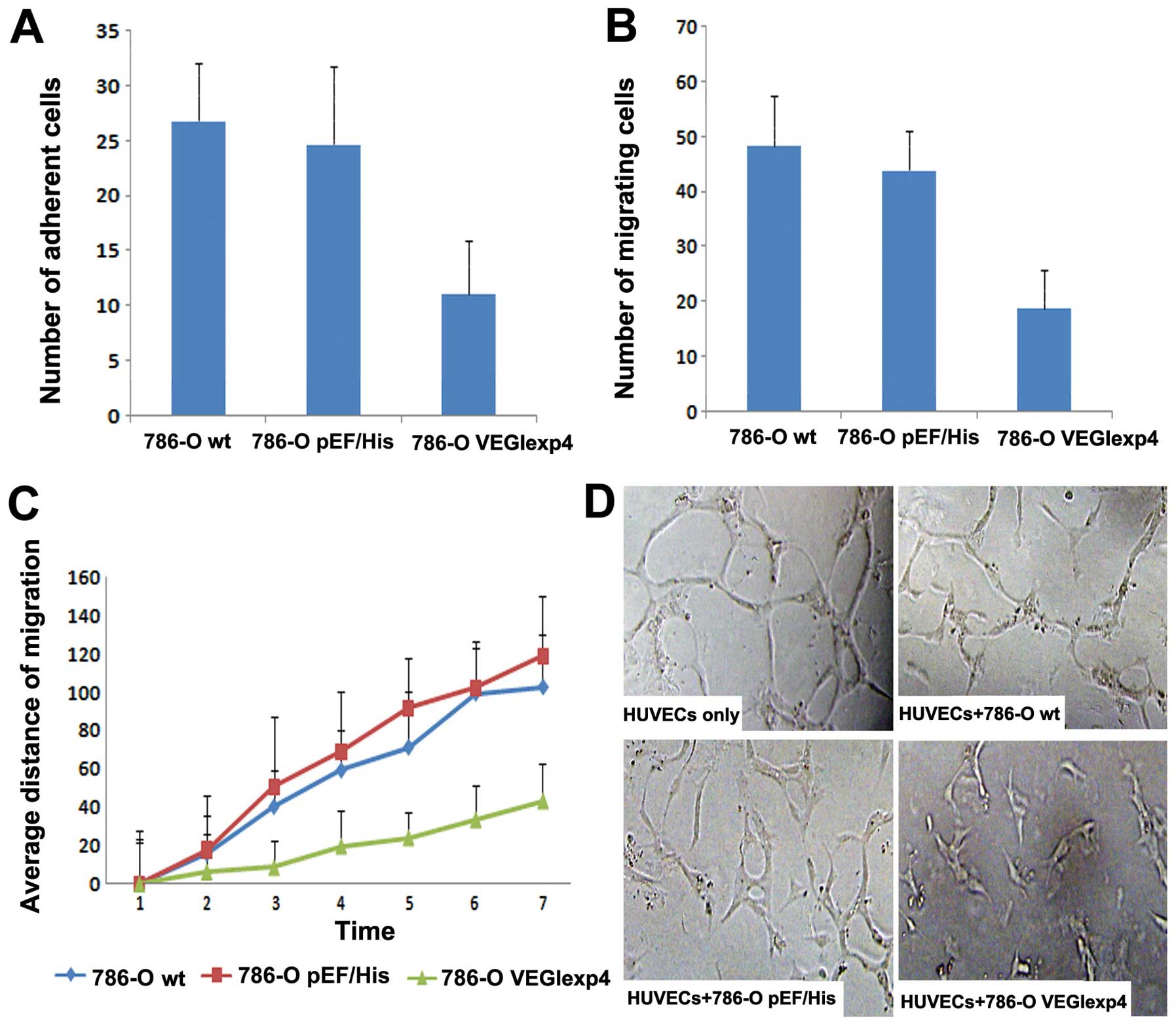
|
1.
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Bellmunt J and Guix M: The medical
management of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: integrating new
guidelines and recommendations. BJU Int. 103:572–577. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Chow WH, Devesa SS, Warren JL and Fraumeni
JF Jr: Rising incidence of renal cell cancer in the United States.
JAMA. 281:1628–1631. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Ferlay J, Autier P, Boniol M, Heanue M,
Colombet M and Boyle P: Estimates of the cancer incidence and
mortality in Europe in 2006. Ann Oncol. 18:581–592. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Bechtold RE and Zagoria RJ: Imaging
approach to staging of renal cell carcinoma. Urol Clin North Am.
24:507–522. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Kane CJ, Mallin K, Ritchey J, Cooperberg
MR and Carroll PR: Renal cell cancer stage migration: analysis of
the National Cancer Data Base. Cancer. 113:78–83. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Bellmunt J, Eisen T, Fishman M and Quinn
D: Experience with sorafenib and adverse event management. Crit Rev
Oncol Hematol. 78:24–32. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Decastro GJ and McKiernan JM:
Epidemiology, clinical staging and presentation of renal cell
carcinoma. Urol Clin North Am. 35:581–592. vi:2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Wallen EM, Pruthi RS, Joyce GF and Wise M:
Kidney cancer. J Urol. 177:2006–2018. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Hock LM, Lynch J and Balaji KC: Increasing
incidence of all stages of kidney cancer in the last 2 decades in
the United States: an analysis of surveillance, epidemiology and
end results program data. J Urol. 167:57–60. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Grandinetti CA and Goldspiel BR: Sorafenib
and sunitinib: novel targeted therapies for renal cell cancer.
Pharmacotherapy. 27:1125–1144. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Motzer RJ and Russo P: Systemic therapy
for renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 163:408–417. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Vakkalanka BK and Rini BI: Targeted
therapy in renal cell carcinoma. Curr Opin Urol. 18:481–487. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Fisher RI, Rosenberg SA and Fyfe G:
Long-term survival update for high-dose recombinant interleukin-2
in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Cancer J Sci Am. 6(Suppl 1):
S55–S57. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Wilhelm SM, Adnane L, Newell P, Villanueva
A, Llovet JM and Lynch M: Preclinical overview of sorafenib, a
multikinase inhibitor that targets both Raf and VEGF and PDGF
receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:3129–3140.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Sonpavde G, Choueiri TK, Escudier B,
Ficarra V, Hutson TE, Mulders PF, Patard JJ, Rini BI, Staehler M,
Sternberg CN and Stief CG: Sequencing of agents for metastatic
renal cell carcinoma: can we customize therapy? Eur Urol.
61:307–316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Porta C, Szczylik C and Escudier B:
Combination or sequencing strategies to improve the outcome of
metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients: a critical review. Crit
Rev Oncol Hematol. 82:323–337. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Paez-Ribes M, Allen E, Hudock J, Takeda T,
Okuyama H, Vinals F, Inoue M, Bergers G, Hanahan D and Casanovas O:
Antiangiogenic therapy elicits malignant progression of tumors to
increased local invasion and distant metastasis. Cancer Cell.
15:220–231. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Huang D, Ding Y, Zhou M, Rini BI, Petillo
D, Qian CN, Kahnoski R, Futreal PA, Furge KA and Teh BT:
Interleukin-8 mediates resistance to antiangiogenic agent sunitinib
in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 70:1063–1071. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Finke J, Ko J, Rini B, Rayman P, Ireland J
and Cohen P: MDSC as a mechanism of tumor escape from sunitinib
mediated anti-angiogenic therapy. Int Immunopharmacol. 11:856–861.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Tan KB, Harrop J, Reddy M, Young P,
Terrett J, Emery J, Moore G and Truneh A: Characterization of a
novel TNF-like ligand and recently described TNF ligand and TNF
receptor superfamily genes and their constitutive and inducible
expression in hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells. Gene.
204:35–46. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22.
|
Zhai Y, Yu J, Iruela-Arispe L, Huang WQ,
Wang Z, Hayes AJ, Lu J, Jiang G, Rojas L, Lippman ME, Ni J, Yu GL
and Li LY: Inhibition of angiogenesis and breast cancer xenograft
tumor growth by VEGI, a novel cytokine of the TNF superfamily. Int
J Cancer. 82:131–136. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Zhai Y, Ni J, Jiang GW, Lu J, Xing L,
Lincoln C, Carter KC, Janat F, Kozak D, Xu S, Rojas L, Aggarwal BB,
Ruben S, Li LY, Gentz R and Yu GL: VEGI, a novel cytokine of the
tumor necrosis factor family, is an angiogenesis inhibitor that
suppresses the growth of colon carcinomas in vivo. FASEB J.
13:181–189. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Chew LJ, Pan H, Yu J, Tian S, Huang WQ,
Zhang JY, Pang S and Li LY: A novel secreted splice variant of
vascular endothelial cell growth inhibitor. FASEB J. 16:742–744.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Yue TL, Ni J, Romanic AM, Gu JL, Keller P,
Wang C, Kumar S, Yu GL, Hart TK, Wang X, Xia Z, DeWolf WE Jr and
Feuerstein GZ: TL1, a novel tumor necrosis factor-like cytokine,
induces apoptosis in endothelial cells. Involvement of activation
of stress protein kinases (stress-activated protein kinase and p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase) and caspase-3-like protease. J
Biol Chem. 274:1479–1486. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Zhang N, Sanders AJ, Ye L, Kynaston HG and
Jiang WG: Expression of vascular endothelial growth inhibitor
(VEGI) in human urothelial cancer of the bladder and its effects on
the adhesion and migration of bladder cancer cells in vitro.
Anticancer Res. 30:87–95. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Zhang N, Sanders AJ, Ye L, Kynaston HG and
Jiang WG: Vascular endothelial growth inhibitor, expression in
human prostate cancer tissue and the impact on adhesion and
migration of prostate cancer cells in vitro. Int J Oncol.
35:1473–1480. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Xiao Q, Hsu CY, Chen H, Ma X, Xu J and Lee
JM: Characterization of cis-regulatory elements of the vascular
endothelial growth inhibitor gene promoter. Biochem J. 388:913–920.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Hou W, Medynski D, Wu S, Lin X and Li LY:
VEGI-192, a new isoform of TNFSF15, specifically eliminates tumor
vascular endothelial cells and suppresses tumor growth. Clin Cancer
Res. 11:5595–5602. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Yao JJ, Zhang M, Miao XH, Zhao P, Zhu SY,
Ding H and Qi ZT: Isoform of vascular endothelial cell growth
inhibitor (VEGI72-251) increases interleukin-2 production by
activation of T lymphocytes. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
38:249–253. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Jin T, Kim S, Guo F, Howard A and Zhang
YZ: Purification and crystallization of recombinant human TNF-like
ligand TL1A. Cytokine. 40:115–122. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Park SS, Lillehoj HS, Hong YH and Lee SH:
Functional characterization of tumor necrosis factor superfamily 15
(TNFSF15) induced by lipopolysaccharides and Eimeria infection. Dev
Comp Immunol. 31:934–944. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Cai J, Jiang WG and Mansel RE: Inhibition
of the expression of VE-cadherin/catenin complex by gamma linolenic
acid in human vascular endothelial cells and its impact on
angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 258:113–118. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Zhang N, Sanders AJ, Ye L and Jiang WG:
Vascular endothelial growth inhibitor in human cancer (Review). Int
J Mol Med. 24:3–8. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Migone TS, Zhang J, Luo X, Zhuang L, Chen
C, Hu B, Hong JS, Perry JW, Chen SF, Zhou JX, Cho YH, Ullrich S,
Kanakaraj P, Carrell J, Boyd E, Olsen HS, Hu G, Pukac L, Liu D, Ni
J, Kim S, Gentz R, Feng P, Moore PA, Ruben SM and Wei P: TL1A is a
TNF-like ligand for DR3 and TR6/DcR3 and functions as a T cell
costimulator. Immunity. 16:479–492. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Bamias G, Mishina M, Nyce M, Ross WG,
Kollias G, Rivera-Nieves J, Pizarro TT and Cominelli F: Role of
TL1A and its receptor DR3 in two models of chronic murine ileitis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:8441–8446. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Prehn JL, Thomas LS, Landers CJ, Yu QT,
Michelsen KS and Targan SR: The T cell costimulator TL1A is induced
by FcgammaR signaling in human monocytes and dendritic cells. J
Immunol. 178:4033–4038. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Parr C, Gan CH, Watkins G and Jiang WG:
Reduced vascular endothelial growth inhibitor (VEGI) expression is
associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients.
Angiogenesis. 9:73–81. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Chen X, Wu J, Liu H, He Z, Gu M, Wang N,
Ma J, Hu J, Xia L, He H, Yuan J, Li J, Li L, Li M and Zhu X:
Approaches to efficient production of recombinant angiogenesis
inhibitor rhVEGI-192 and characterization of its structure and
antiangiogenic function. Protein Sci. 19:449–457. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Liang PH, Tian F, Lu Y, Duan B, Stolz DB
and Li LY: Vascular endothelial growth inhibitor (VEGI; TNFSF15)
inhibits bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cell
incorporation into Lewis lung carcinoma tumors. Angiogenesis.
14:61–68. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Haridas V, Shrivastava A, Su J, Yu GL, Ni
J, Liu D, Chen SF, Ni Y, Ruben SM, Gentz R and Aggarwal BB: VEGI, a
new member of the TNF family activates nuclear factor-kappa B and
c-Jun N-terminal kinase and modulates cell growth. Oncogene.
18:6496–6504. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
McGuire BB and Fitzpatrick JM: Biomarkers
in renal cell carcinoma. Curr Opin Urol. 19:441–446. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Li XQ, Pei DS, Qian GW, Yin XX, Cheng Q,
Li LT, Li HZ and Zheng JN: The effect of methylated oligonucleotide
targeting Ki-67 gene in human 786-0 renal carcinoma cells. Tumour
Biol. 32:863–872. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Oka S, Uramoto H, Shimokawa H, Iwanami T
and Tanaka F: The expression of Ki-67, but not proliferating cell
nuclear antigen, predicts poor disease free survival in patients
with adenocarcinoma of the lung. Anticancer Res. 31:4277–4282.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Carmeliet P: VEGF as a key mediator of
angiogenesis in cancer. Oncology. 69(Suppl 3): 4–10. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Hicklin DJ and Ellis LM: Role of the
vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and
angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol. 23:1011–1027. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Yang CR, Hsieh SL, Teng CM, Ho FM, Su WL
and Lin WW: Soluble decoy receptor 3 induces angiogenesis by
neutralization of TL1A, a cytokine belonging to tumor necrosis
factor superfamily and exhibiting angiostatic action. Cancer Res.
64:1122–1129. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Cassatella MA, Pereira-da-Silva G, Tinazzi
I, Facchetti F, Scapini P, Calzetti F, Tamassia N, Wei P, Nardelli
B, Roschke V, Vecchi A, Mantovani A, Bambara LM, Edwards SW and
Carletto A: Soluble TNF-like cytokine (TL1A) production by immune
complexes stimulated monocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol.
178:7325–7333. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|