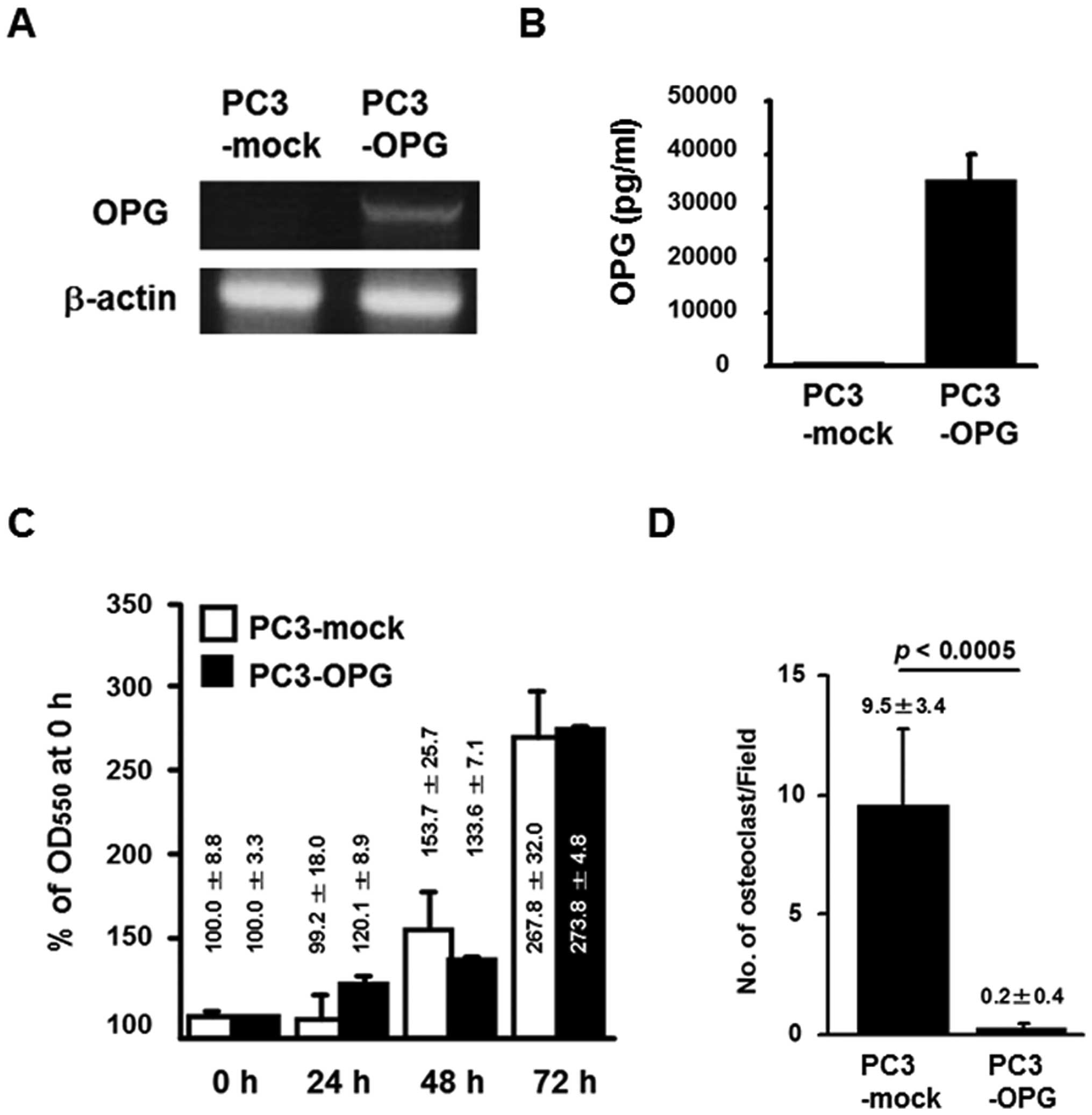
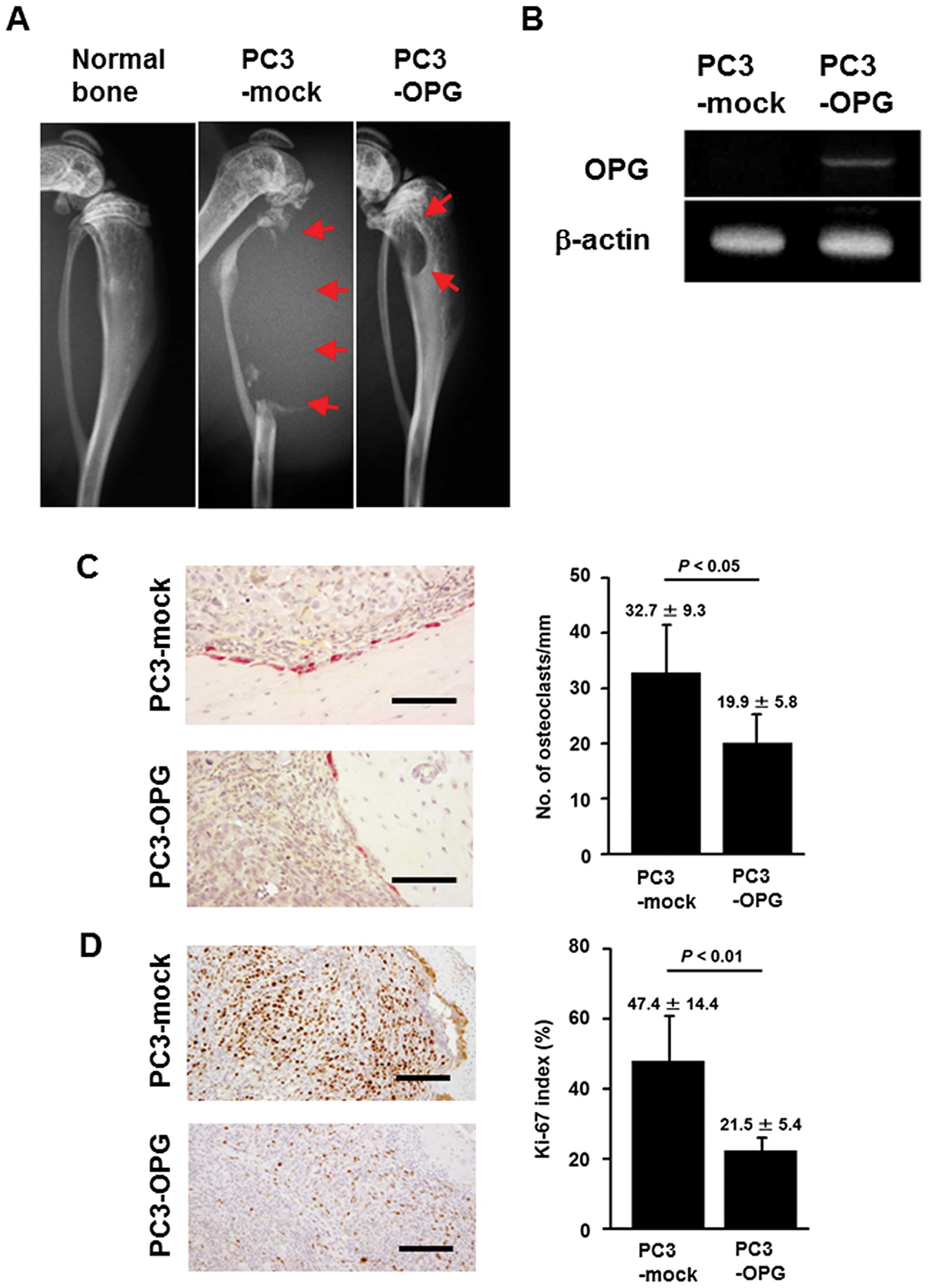
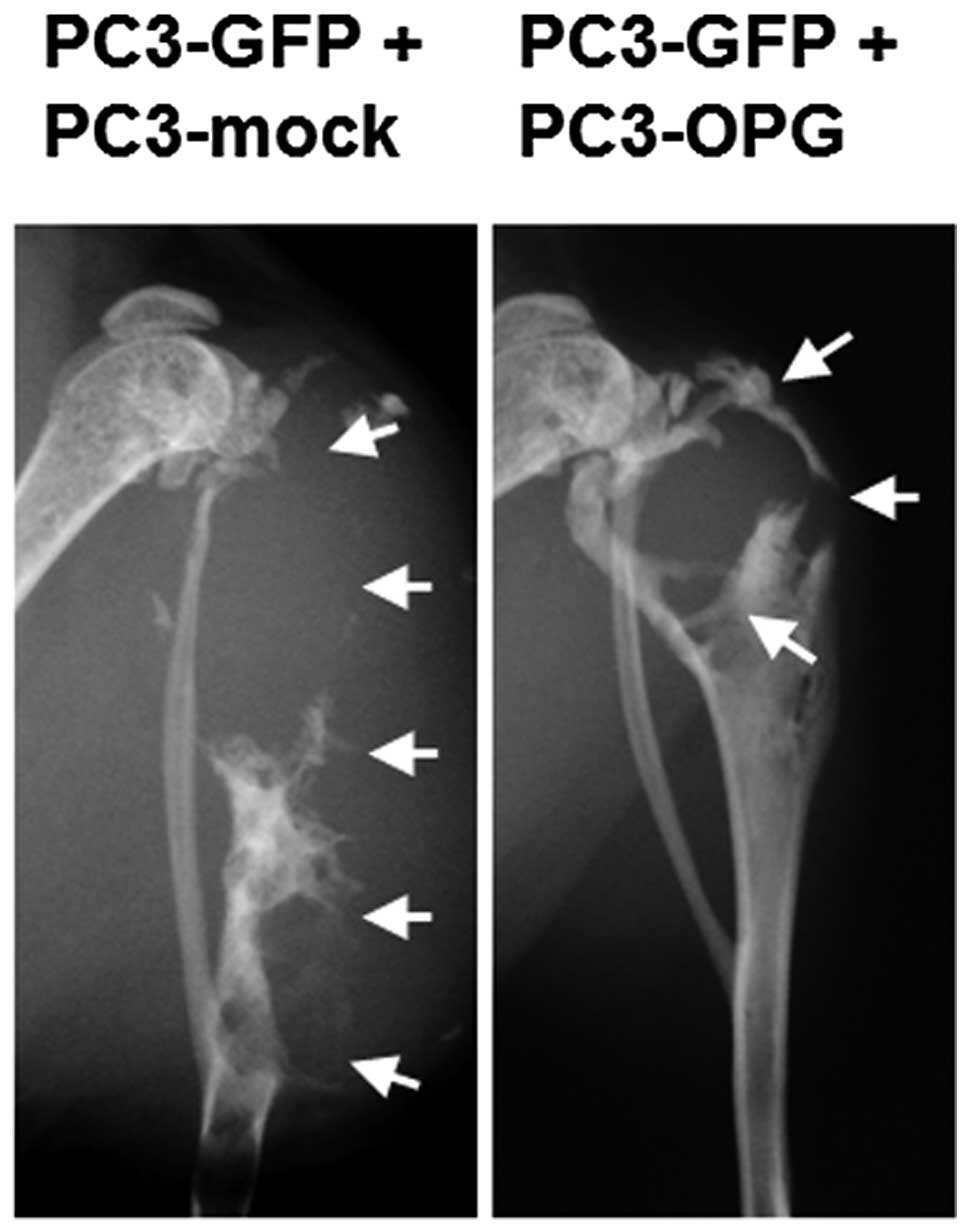
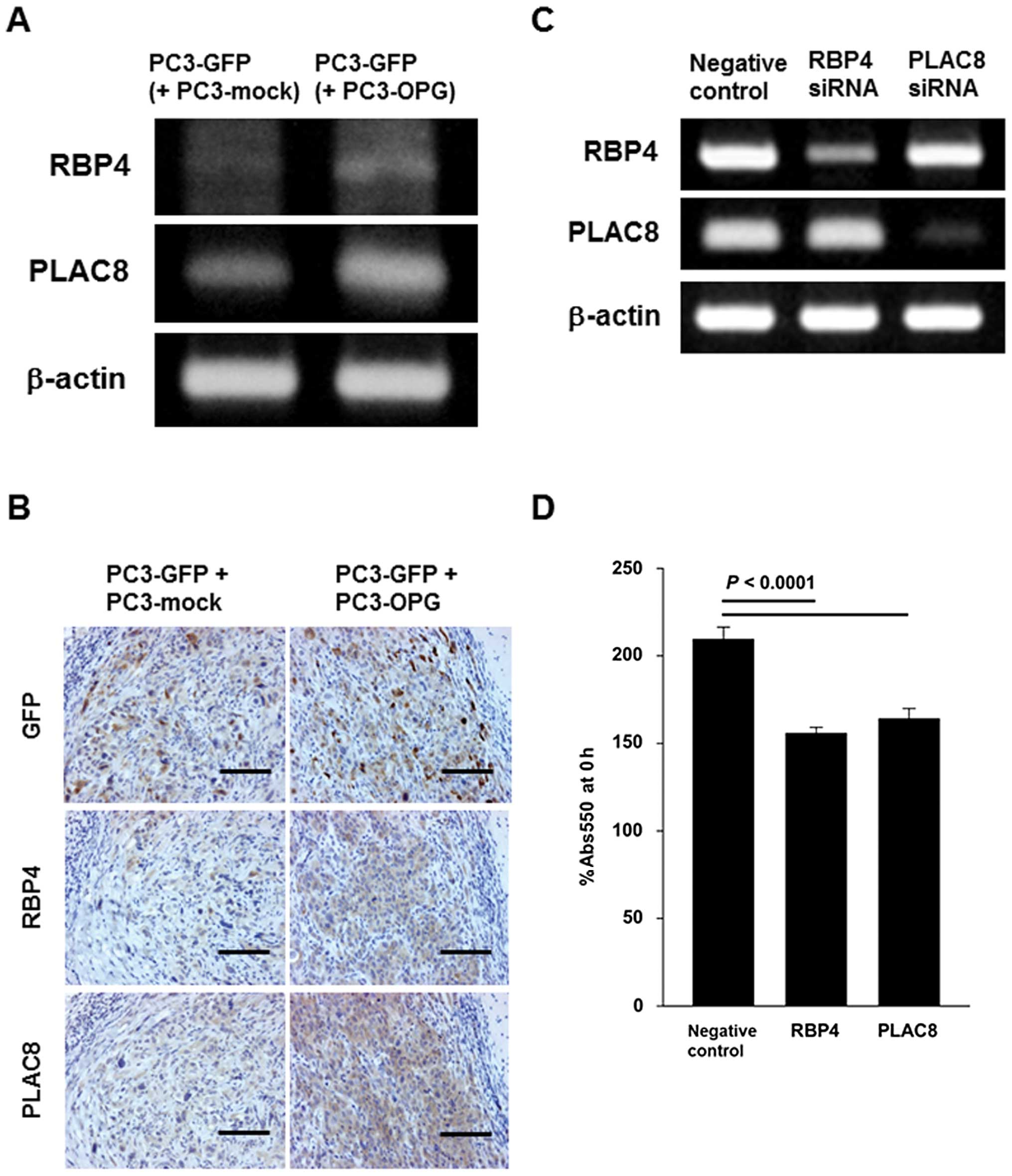
|
1.
|
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic
and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:212–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Bubendorf L, Schopfer A, Wagner U, et al:
Metastatic patterns of prostate cancer: an autopsy study of 1,589
patients. Hum Pathol. 31:578–583. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Brown JE, Cook RJ, Major P, et al: Bone
turnover markers as predictors of skeletal complications in
prostate cancer, lung cancer and other solid tumors. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 97:59–69. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Roodman GD: Mechanisms of bone metastasis.
N Engl J Med. 350:1655–1664. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Demers LM: Bone markers in the management
of patients with skeletal metastases. Cancer. 97:874–879. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Percival RC, Urwin GH, Harris S, et al:
Biochemical and histological evidence that carcinoma of the
prostate is associated with increased bone resorption. Eur J Surg
Oncol. 13:41–49. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Freedland SJ, Richhariya A, Wang H, Chung
K and Shore ND: Treatment patterns in patients with prostate cancer
and bone metastasis among US community-based urology group
practices. Urology. 80:293–298. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Coleman R, Gnant M, Morgan G and Clezardin
P: Effects of bone-targeted agents on cancer progression and
mortality. J Natl Cancer Inst. 104:1059–1067. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Mundy GR: Mechanisms of osteolytic bone
destruction. Bone. 12(Suppl 1): S1–S6. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Lacey DL, Timms E, Tan HL, et al:
Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast
differentiation and activation. Cell. 93:165–176. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, et al:
Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the
regulation of bone density. Cell. 89:309–319. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Bucay N, Sarosi I, Dunstan CR, et al:
Osteoprotegerin-deficient mice develop early onset osteoporosis and
arterial calcification. Genes Dev. 12:1260–1268. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Zhang J, Dai J, Qi Y, et al:
Osteoprotegerin inhibits prostate cancer-induced osteoclastogenesis
and prevents prostate tumor growth in the bone. J Clin Invest.
107:1235–1244. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Corey E, Brown LG, Kiefer JA, et al:
Osteoprotegerin in prostate cancer bone metastasis. Cancer Res.
65:1710–1718. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Zhang J, Dai J, Yao Z, Lu Y, Dougall W and
Keller ET: Soluble receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB Fc
diminishes prostate cancer progression in bone. Cancer Res.
63:7883–7890. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Shipman CM and Croucher PI:
Osteoprotegerin is a soluble decoy receptor for tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand/Apo2 ligand and can
function as a paracrine survival factor for human myeloma cells.
Cancer Res. 63:912–916. 2003.
|
|
17.
|
Holen I, Croucher PI, Hamdy FC and Eaton
CL: Osteoprotegerin (OPG) is a survival factor for human prostate
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 62:1619–1623. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
McGonigle JS, Giachelli CM and Scatena M:
Osteoprotegerin and RANKL differentially regulate angiogenesis and
endothelial cell function. Angiogenesis. 12:35–46. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Peddi P, Lopez-Olivo MA, Pratt GF and
Suarez-Almazor ME: Denosumab in patients with cancer and skeletal
metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Treat
Rev. 39:97–104. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Brown-Glaberman U and Stopeck AT: Role of
denosumab in the management of skeletal complications in patients
with bone metastases from solid tumors. Biologics. 6:89–99.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Uehara H, Kim SJ, Karashima T, et al:
Effects of blocking platelet-derived growth factor-receptor
signaling in a mouse model of experimental prostate cancer bone
metastases. J Natl Cancer Inst. 95:458–470. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Uemura H, Yanagisawa M, Ikeda I, et al:
Possible anti-tumor activity of initial treatment with zoledronic
acid with hormonal therapy for bone-metastatic prostate cancer in
multicenter clinical trial. Int J Clin Oncol. Apr 11–2012, (Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
23.
|
Smith MR, Saad F, Coleman R, et al:
Denosumab and bone-metastasis-free survival in men with
castration-resistant prostate cancer: results of a phase 3,
randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 379:39–46. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24.
|
Smith MR, Egerdie B, Hernandez Toriz N, et
al: Denosumab in men receiving androgen-deprivation therapy for
prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 361:745–755. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Fizazi K, Lipton A, Mariette X, et al:
Randomized phase II trial of denosumab in patients with bone
metastases from prostate cancer, breast cancer, or other neoplasms
after intravenous bisphosphonates. J Clin Oncol. 27:1564–1571.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Lipton A, Steger GG, Figueroa J, et al:
Randomized active-controlled phase II study of denosumab efficacy
and safety in patients with breast cancer-related bone metastases.
J Clin Oncol. 25:4431–4437. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Lipton A, Fizazi K, Stopeck AT, et al:
Superiority of denosumab to zoledronic acid for prevention of
skeletal-related events: a combined analysis of 3 pivotal,
randomised, phase 3 trials. Eur J Cancer. 48:3082–3092. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Ford JA, Jones R, Elders A, et al:
Denosumab for treatment of bone metastases secondary to solid
tumours: systematic review and network meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer.
49:416–430. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Stopeck AT, Lipton A, Body JJ, et al:
Denosumab compared with zoledronic acid for the treatment of bone
metastases in patients with advanced breast cancer: a randomized,
double-blind study. J Clin Oncol. 28:5132–5139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30.
|
Feldman BJ and Feldman D: The development
of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 1:34–45.
2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Ting HJ, Hsu J, Bao BY and Lee YF:
Docetaxel-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis in androgen
independent prostate cancer cells are enhanced by
1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Cancer Lett. 247:122–129. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Bao BY, Hu YC, Ting HJ and Lee YF:
Androgen signaling is required for the vitamin D-mediated growth
inhibition in human prostate cancer cells. Oncogene. 23:3350–3360.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Arah IN, Song K, Seth P, Cowan KH and
Sinha BK: Role of wild-type p53 in the enhancement of camptothecin
cytotoxicity against human prostate tumor cells. Anticancer Res.
18:1845–1849. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Fisher JL, Thomas-Mudge RJ, Elliott J, et
al: Osteoprotegerin overexpression by breast cancer cells enhances
orthotopic and osseous tumor growth and contrasts with that
delivered therapeutically. Cancer Res. 66:3620–3628. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35.
|
Flower DR: The lipocalin protein family:
structure and function. Biochem J. 318:1–14. 1996.
|
|
36.
|
Newcomer ME and Ong DE: Plasma retinol
binding protein: structure and function of the prototypic
lipocalin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1482:57–64. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Tsutsumi C, Okuno M, Tannous L, et al:
Retinoids and retinoid-binding protein expression in rat
adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 267:1805–1810. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Kovacs P, Geyer M, Berndt J, et al:
Effects of genetic variation in the human retinol binding protein-4
gene (RBP4) on insulin resistance and fat depot-specific mRNA
expression. Diabetes. 56:3095–3100. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Graham TE, Yang Q, Bluher M, et al:
Retinol-binding protein 4 and insulin resistance in lean, obese and
diabetic subjects. N Engl J Med. 354:2552–2563. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Yang Q, Graham TE, Mody N, et al: Serum
retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in
obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 436:356–362. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Abel ED, Peroni O, Kim JK, et al:
Adipose-selective targeting of the GLUT4 gene impairs insulin
action in muscle and liver. Nature. 409:729–733. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Abulaizi M, Tomonaga T, Satoh M, et al:
The application of a three-step proteome analysis for
identification of new biomarkers of pancreatic cancer. Int J
Proteomics. 2011:6287872011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Patz EF Jr, Campa MJ, Gottlin EB,
Kusmartseva I, Guan XR and Herndon JE II: Panel of serum biomarkers
for the diagnosis of lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 25:5578–5583. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Mourtada-Maarabouni M, Watson D, Munir M,
Farzaneh F and Williams GT: Apoptosis suppression by candidate
oncogene PLAC8 is reversed in other cell types. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 13:80–91. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Li Y, Rogulski K, Zhou Q, Sims PJ and
Prochownik EV: The negative c-Myc target onzin affects
proliferation and apoptosis via its obligate interaction with
phospholipid scramblase 1. Mol Cell Biol. 26:3401–3413. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Rogulski K, Li Y, Rothermund K, et al:
Onzin, a c-Myc-repressed target, promotes survival and
transformation by modulating the Akt-Mdm2-p53 pathway. Oncogene.
24:7524–7541. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|