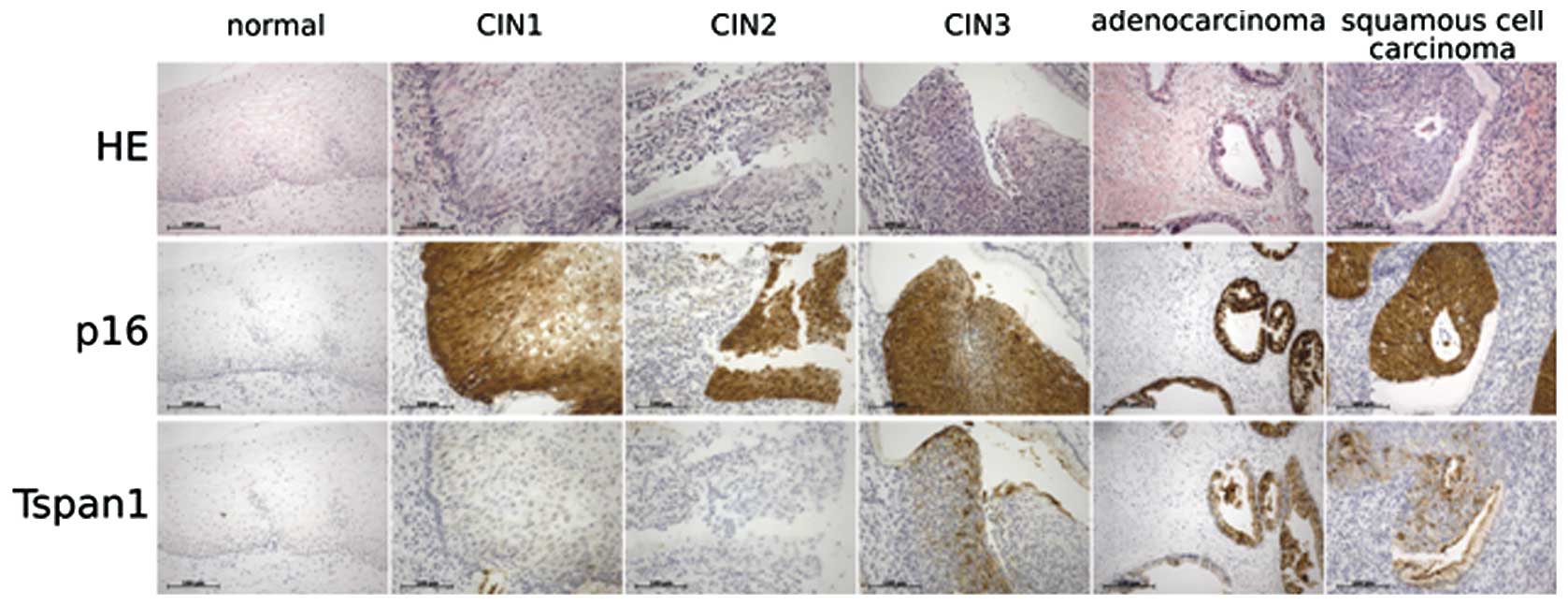
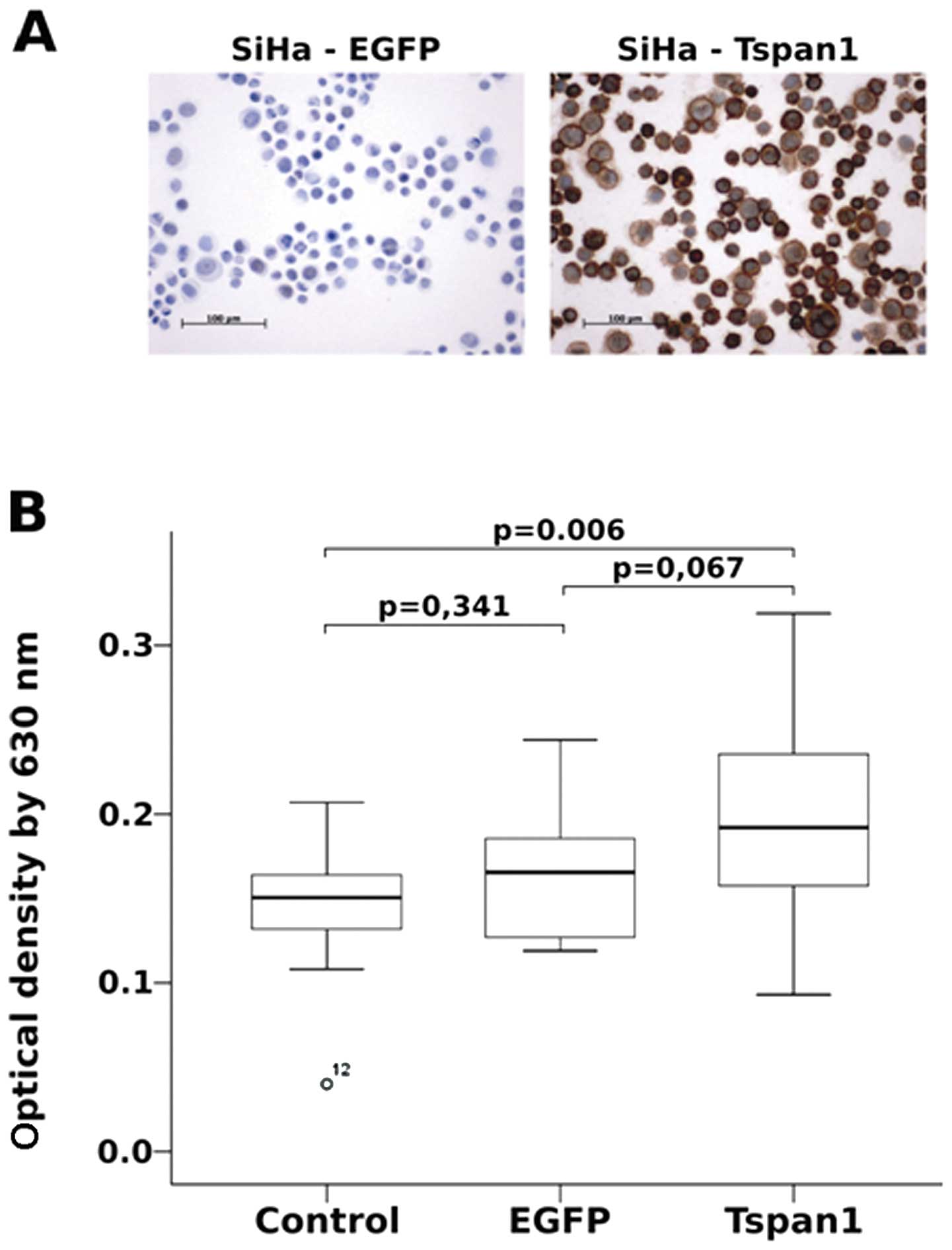
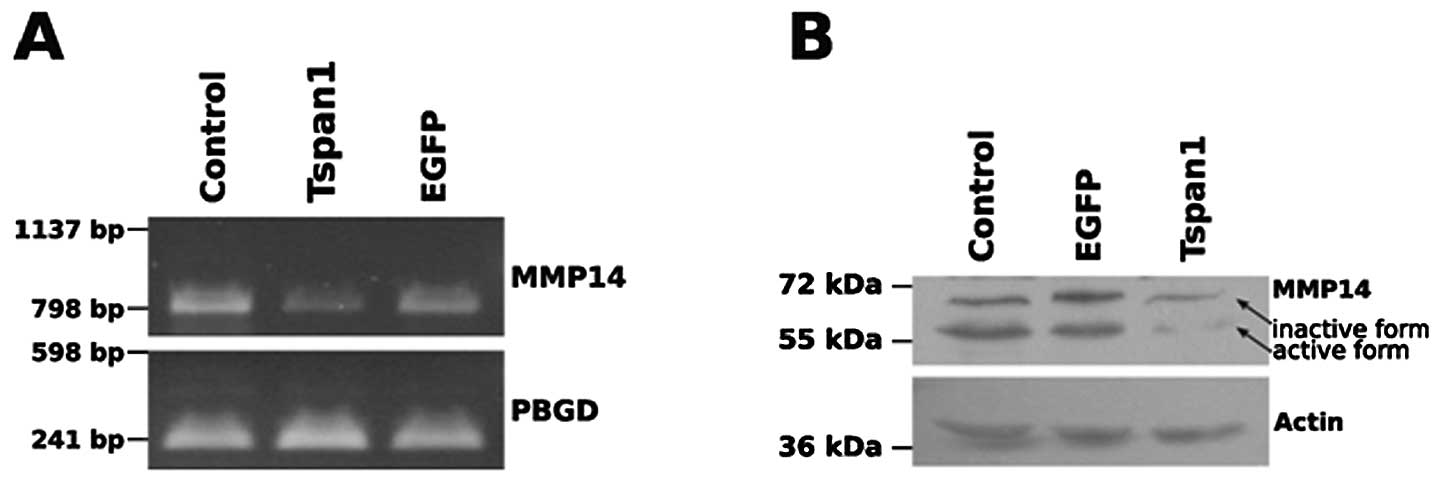
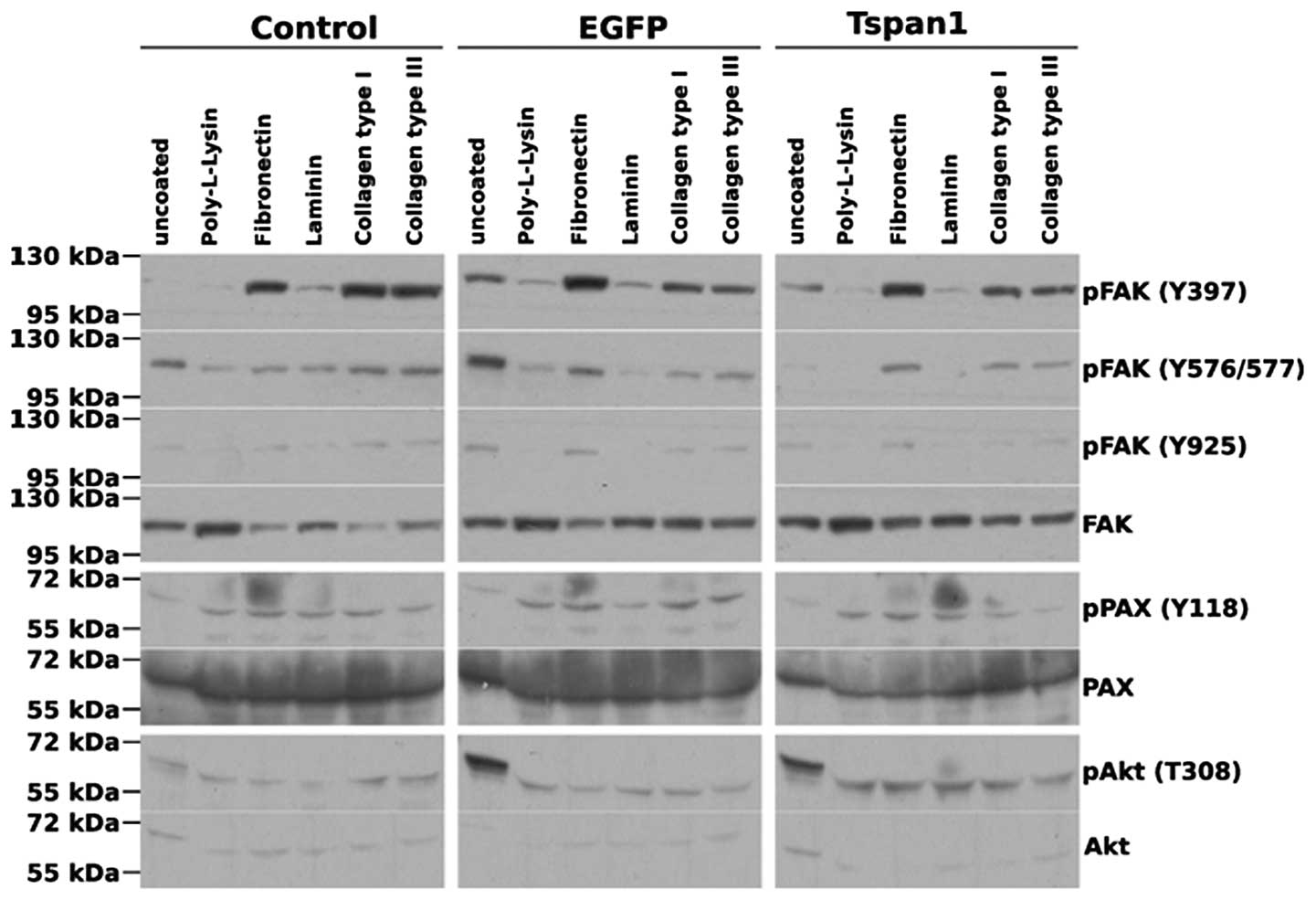
|
1.
|
GLOBOCAN 2008 (IARC), Section of Cancer
Information. International Agency for Research on Cancer 2008;
(accessed 13/12/2012).
|
|
2.
|
Walboomers J, Jacobs M, Manos M, et al:
Human papilloma-virus is a necessary cause of invasive cervical
cancer worldwide. J Pathol. 189:12–19. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
de Villiers E, Fauquet C, Broker T,
Bernard H and zur Hausen H: Classification of papillomaviruses.
Virology. 324:17–27. 2004.
|
|
4.
|
zur Hausen H: Papillomaviruses causing
cancer: evasion from host-cell control in early events in
carcinogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 92:690–698. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Munoz N, Bosch F, de Sanjose S, et al:
Epidemiologic classification of human papillomavirus types
associated with cervical cancer. N Engl J Med. 348:518–527. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Munoz N, Castellsague X, de Gonzalez AB
and Gissmann L: Chapter 1: HPV in the etiology of human cancer.
Vaccine. 24(Suppl 3): S3/1–10. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Schwarz E, Freese U, Gissmann L, Mayer W,
Roggenbuck B, Stremlau A and Hausen H: Structure and transcription
of human papillomavirus sequences in cervical-carcinoma cells.
Nature. 314:111–114. 1985. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Phelps W, Yee C, Munger K and Howley P:
The human papillomavirus type-16 E7 gene encodes transactivation
and transformation functions similar to those of adenovirus-E1a.
Cell. 53:539–547. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Munger K, Phelps W, Bubb V, Howley P and
Schlegel R: The E6-gene and E7-gene of the human papillomavirus
type-16 together are necessary and sufficient for transformation of
primary human keratinocytes. J Virol. 63:4417–4421. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Hawleynelson P, Vousden KH, Hubbert NL,
Lowy DR and Schiller JT: HPV16 E6-proteins and E7-proteins
cooperate to immortalize human foreskin keratinocytes. EMBO J.
8:3905–3910. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Halbert C, Demers G and Galloway D: The E7
gene of human papillomavirus type-16 is sufficient for
immortalization of human epithelial cells. J Virol. 65:473–478.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
zur Hausen H: Papillomaviruses and cancer:
from basic studies to clinical application. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:342–350. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Huang S, Yuan S, Dong M, et al: The
phylogenetic analysis of tetraspanins projects the evolution of
cell-cell interactions from unicellular to multicellular organisms.
Genomics. 86:674–684. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Hotta H, Ross A, Huebner K, et al:
Molecular-cloning and characterization of an antigen associated
with early stages of melanoma tumor progression. Cancer Res.
48:2955–2962. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Oren R, Takahashi S, Doss C, Levy R and
Levy S: Tapa-1, the target of an antiproliferative antibody,
defines a new family of transmembrane proteins. Mol Cell Biol.
10:4007–4015. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Boucheix C, Benoit P, Frachet P, Billard
M, Worthington R, Gagnon J and Uzan G: Molecular-cloning of the Cd9
antigen - a new family of cell-surface proteins. J Biol Chem.
266:117–122. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Levy S, Nguyen VQ, Andria ML and Takahashi
S: Structure and membrane topology of tapa-1. J Biol Chem.
266:14597–14602. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Wright MD and Tomlinson MG: The ins and
outs of the trans-membrane-4 superfamily. Immunol Today.
15:588–594. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Maecker HT, Todd SC and Levy S: The
tetraspanin superfamily: Molecular facilitators. FASEB J.
11:428–442. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Kitadokoro K, Bordo D, Galli G, et al:
CD81 extracellular domain 3D structure: Insight into the
tetraspanin superfamily structural motifs. EMBO J. 20:12–18. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Seigneuret M, Delaguillaumie A,
Lagaudriere-Gesbert C and Conjeaud H: Structure of the tetraspanin
main extracellular domain - a partially conserved fold with a
structurally variable domain insertion. J Biol Chem.
276:40055–40064. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Charrin S, Manie S, Oualid M, Billard M,
Boucheix C and Rubinstein E: Differential stability of
tetraspanin/tetraspanin interactions: Role of palmitoylation. FEBS
Lett. 516:139–144. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Escola JM, Kleijmeer MJ, Stoorvogel W,
Griffith JM, Yoshie O and Geuze HJ: Selective enrichment of
tetraspan proteins on the internal vesicles of multivesicular
endosomes and on exosomes secreted by human B-lymphocytes. J Biol
Chem. 273:20121–20127. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Wubbolts R, Leckie RS, Veenhuizen PTM, et
al: Proteomic and biochemical analyses of human B cell-derived
exosomes - potential implications for their function and
multivesicular body formation. J Biol Chem. 278:10963–10972. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Boucheix C and Rubinstein E: Tetraspanins.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 58:1189–1205. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Rubinstein E, Le Naour F,
Lagaudrière-Gesbert C, Billard M, Conjeaud H and Boucheix C: CD9,
CD63, CD81 and CD82 are components of a surface tetraspan network
connected to HLA-DR and VLA integrins. Eur J Immunol. 26:2657–2665.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Berditchevski F, Odintsova E, Sawada S and
Gilbert E: Expression of the palmitoylation-deficient CD151 weakens
the association of alpha(3)beta(1) integrin with the
tetraspanin-enriched micro-domains and affects integrin-dependent
signaling. J Biol Chem. 277:36991–37000. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28.
|
Tokuhara T, Hasegawa H, Hattori N, et al:
Clinical significance of CD151 gene expression in non-small cell
lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 7:4109–4114. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Ang J, Lijovic M, Ashman LK, Kan K and
Frauman AG: CD151 protein expression predicts the clinical outcome
of low-grade primary prostate cancer better than histologic
grading: a new prognostic indicator? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 13:1717–1721. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Sadej R, Romanska H, Baldwin G, et al:
CD151 regulates tumori-genesis by modulating the communication
between tumor cells and endothelium. Mol Cancer Res. 7:787–798.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Voss MA, Gordon N, Maloney S, et al:
Tetraspanin CD151 is a novel prognostic marker in poor outcome
endometrial cancer. Br J Cancer. 104:1611–1618. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Yang XH, Richardson AL, Torres-Arzayus MI,
et al: CD151 accelerates breast cancer by regulating alpha(6)
integrin function, signaling and molecular organization. Cancer
Res. 68:3204–3213. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Ikeyama S, Koyama M, Yamaoko M, Sasada R
and Miyake M: Suppression of cell motility and metastasis by
transfection with human motility-related protein (mrp-1/cd9) dna. J
Exp Med. 177:1231–1237. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Miyake M, Nakano K, Ieki Y, et al:
Motility related protein-1 (mrp-1/cd9) expression - inverse
correlation with metastases in breast cancer. Cancer Res.
55:4127–4131. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Miyake M, Nakano K, Itoi S, Koh T and Taki
T: Motility-related protein-1 (MRP-1/CD9) reduction as a factor of
poor prognosis in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 56:1244–1249.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Higashiyama M, Taki T, Ieki Y, et al:
Reduced motility related protein-1 (mrp-1/cd9) gene-expression as a
factor of poor-prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Res.
55:6040–6044. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Pileri P, Uematsu Y, Campagnoli S, et al:
Binding of hepatitis C virus to CD81. Science. 282:938–941. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Nydegger S, Khurana S, Krementsov DN, Foti
M and Thali M: Mapping of tetraspanin-enriched microdomains that
can function as gateways for HIV-1. J Cell Biol. 173:795–807. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Spoden G, Freitag K, Husmann M, Boller K,
Sapp M, Lambert C and Florin L: Clathrin- and caveolin-independent
entry of human papillomavirus type 16-involvement of
tetraspanin-enriched microdomains (TEMs). Plos One. 3:e33132008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Nees M, van Wijngaarden E, Bakos E,
Schneider A and Durst M: Identification of novel molecular markers
which correlate with HPV-induced tumor progression. Oncogene.
16:2447–2458. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Wollscheid V, Kuhne-Heid R, Stein I,
Jansen L, Kollner S, Schneider A and Durst M: Identification of a
new proliferation-associated protein NET-1/C4.8 characteristic for
a subset of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and
cervical carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 99:771–775. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42.
|
Chen L, Wang Z, Zhan X, Li D, Zhu Y and
Zhu J: Association of NET-1 gene expression with human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Surg Pathol. 15:346–353. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Chen L, Li X, Wang G, Wang Y, Zhu Y and
Zhu J: Clinicopathological significance of overexpression of
TSPAN1, K167 and CD34 in gastric carcinoma. Tumori. 94:531–538.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Chen L, Zhu Y, Zhang X, et al: TSPAN1
protein expression: a significant prognostic indicator for patients
with colorectal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol.
15:2270–2276. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Scholz C, Kurzeder C, Koretz K, Windisch
J, Kreienberg R, Sauer G and Deissler H: Tspan-1 is a tetraspanin
preferentially expressed by mucinous and endometrioid subtypes of
human ovarian carcinomas. Cancer Lett. 275:198–203. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Chen L, Yuan D, Zhao R, Li H and Zhu J:
Suppression of TSPAN1 by RNA interference inhibits proliferation
and invasion of colon cancer cells in vitro. Tumori. 96:744–750.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Chen L, Zhu Y, Li H, et al: Knockdown of
TSPAN1 by RNA silencing and antisense technique inhibits
proliferation and infiltration of human skin squamous carcinoma
cells. Tumori. 96:289–295. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Saito K, Oku T, Ata N, Miyashiro H,
Hattori M and Saiki I: A modified and convenient method for
assessing tumor cell invasion and migration and its application to
screening for inhibitors. Biol Pharm Bull. 20:345–348. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Koehrmann A, Kammerer U, Kapp M, Dietl J
and Anacker J: Expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in
primary human breast cancer and breast cancer cell lines: New
findings and review of the literature. BMC Cancer. 9:1882009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Stamenkovic I: Matrix metalloproteinases
in tumor invasion and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 10:415–433.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Bellis SL, Miller JT and Turner CE:
Characterization of tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin in vitro
by focal adhesion kinase. J Biol Chem. 270:17437–17441. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Ueda M, Ueki M, Terai Y, Morimoto A, Fujii
H, Yoshizawa K and Yanagihara T: Stimulatory effects of EGF and
TGF-alpha on invasive activity and 5′-deoxy-5-fluorouridine
sensitivity in uterine cervical-carcinoma SKG-IIIb cells. Int J
Cancer. 72:1027–1033. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Ueda M, Fujii H, Yoshizawa K, Terai Y,
Kumagai K, Ueki K and Ueki M: Effects of EGF and TGF-alpha on
invasion and proteinase expression of uterine cervical
adenocarcinoma OMC-4 cells. Invasion Metastasis. 18:176–183. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Narayanan R, Kim HN, Narayanan NK, Nargi D
and Narayanan B: Epidermal growth factor-stimulated human cervical
cancer cell growth is associated with EGFR and cyclin D1
activation, independent of COX-2 expression levels. Int J Oncol.
40:13–20. 2012.
|
|
55.
|
Beeser A, Jaffer ZM, Hofmann C and
Chernoff J: Role of group A p21-activated kinases in activation of
extracellular-regulated kinase by growth factors. J Biol Chem.
280:36609–36615. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
Antonyak MA, Li B, Regan AD, Feng Q,
Dusaban SS and Cerione RA: Tissue transglutaminase is an essential
participant in the epidermal growth factor-stimulated signaling
pathway leading to cancer cell migration and invasion. J Biol Chem.
284:17914–17925. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57.
|
Angelisova P, Hilgert I and Horejsi V:
Association of four antigens of the tetraspans family (CD37, CD53,
TAPA-1, and R2/C33) with MHC class II glycoproteins.
Immunogenetics. 39:249–256. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58.
|
Rubinstein E, Lenaour F, Billard M,
Prenant M and Boucheix C: Cd9 antigen is an accessory subunit of
the vla integrin complexes. Eur J Immunol. 24:3005–3013. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59.
|
Berditchevski F, Bazzoni G and Hemler ME:
Specific association of Cd63 with the vla-3 and vla-6 integrins. J
Biol Chem. 270:17784–17790. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60.
|
Berditchevski F, Zutter MM and Hemler ME:
Characterization of novel complexes on the cell surface between
integrins and proteins with 4 transmembrane domains (TM4 proteins).
Mol Biol Cell. 7:193–207. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61.
|
Masellissmith A, Jensen GS, Seehafer JG,
Slupsky JR and Shaw ARE: Anti-Cd9 monoclonal-antibodies induce
homotypic adhesion of pre-B cell-lines by a novel mechanism. J
Immunol. 144:1607–1613. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62.
|
Miyake M, Koyama M, Seno M and Ikeyama S:
Identification of the motility-related protein (mrp-1), recognized
by monoclonal-antibody M31-15, which inhibits cell motility. J Exp
Med. 174:1347–1354. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63.
|
Olweus J, Lundjohansen F and Horejsi V:
Cd53, a protein with 4 membrane-spanning domains, mediates
signal-transduction in human monocytes and B-cells. J Immunol.
151:707–716. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64.
|
Schick MR, Nguyen VQ and Levy S:
Anti-tapa-1 antibodies induce protein-tyrosine phosphorylation that
is prevented by increasing intracellular thiol levels. J Immunol.
151:1918–1925. 1993.
|
|
65.
|
Testa JE, Brooks PC, Lin JM and Quigley
JP: Eukaryotic expression cloning with an antimetastatic monoclonal
antibody identifies a tetraspanin (PETA-3/CD151) as an effector of
human tumor cell migration and metastasis. Cancer Res.
59:3812–3820. 1999.
|
|
66.
|
Ang J, Fang B, Ashman LK and Frauman AG:
The migration and invasion of human prostate cancer cell lines
involves CD151 expression. Oncol Rep. 24:1593–1597. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67.
|
Sauer G, Windisch J, Kurzeder C, Heilmann
V, Kreienberg R and Deissler H: Progression of cervical carcinomas
is associated with down-regulation of CD9 but strong local
re-expression at sites of transendothelial invasion. Clin Cancer
Res. 9:6426–6431. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68.
|
Lafleur MA, Xu D and Hemler ME:
Tetraspanin proteins regulate membrane type-1 matrix
metalloproteinase-dependent pericellular proteolysis. Mol Biol
Cell. 20:2030–2040. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69.
|
Takino T, Watanabe Y, Matsui M, Miyamori
H, Kudo T, Seiki M and Sato H: Membrane-type 1 matrix
metalloproteinase modulates focal adhesion stability and cell
migration. Exp Cell Res. 312:1381–1389. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70.
|
Berditchevski F and Odintsova E:
Characterization of integrintetraspanin adhesion complexes: Role of
tetraspanins in integrin signaling. J Cell Biol. 146:477–492. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71.
|
Ovalle S, Gutierrez-Lopez MD, Olma N, et
al: The tetraspanin CD9 inhibits the proliferation and
tumorigenicity of human colon carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer.
121:2140–2152. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72.
|
Ruseva Z, Geiger PXC, Hutzler P, et al:
Tumor suppressor KAI1 affects integrin alphavbeta3-mediated ovarian
cancer cell adhesion, motility, and proliferation. Exp Cell Res.
315:1759–1771. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73.
|
He B, Liu L, Cook GA, Grgurevich S,
Jennings LK and Zhang XA: Tetraspanin CD82 attenuates cellular
morphogenesis through down-regulating integrin alpha 6-mediated
cell adhesion. J Biol Chem. 280:3346–3354. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74.
|
Lee H, Park I, Byun H, Jeoung D, Kim Y and
Lee H: Metastasis suppressor KAI1/CD82 attenuates the matrix
adhesion of human prostate cancer cells by suppressing fibronectin
expression and beta(1) integrin activation. Cell Physiol Biochem.
27:575–586. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75.
|
Murayama Y, Miyagawa JI, Oritani K, et al:
CD9-mediated activation of the p46 shc isoform leads to apoptosis
in cancer cells. J Cell Sci. 117:3379–3388. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76.
|
Ko E, Lee IY, Cheon IS, et al: Monoclonal
antibody to CD9 inhibits platelet-induced human endothelial cell
proliferation. Mol Cells. 22:70–77. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|