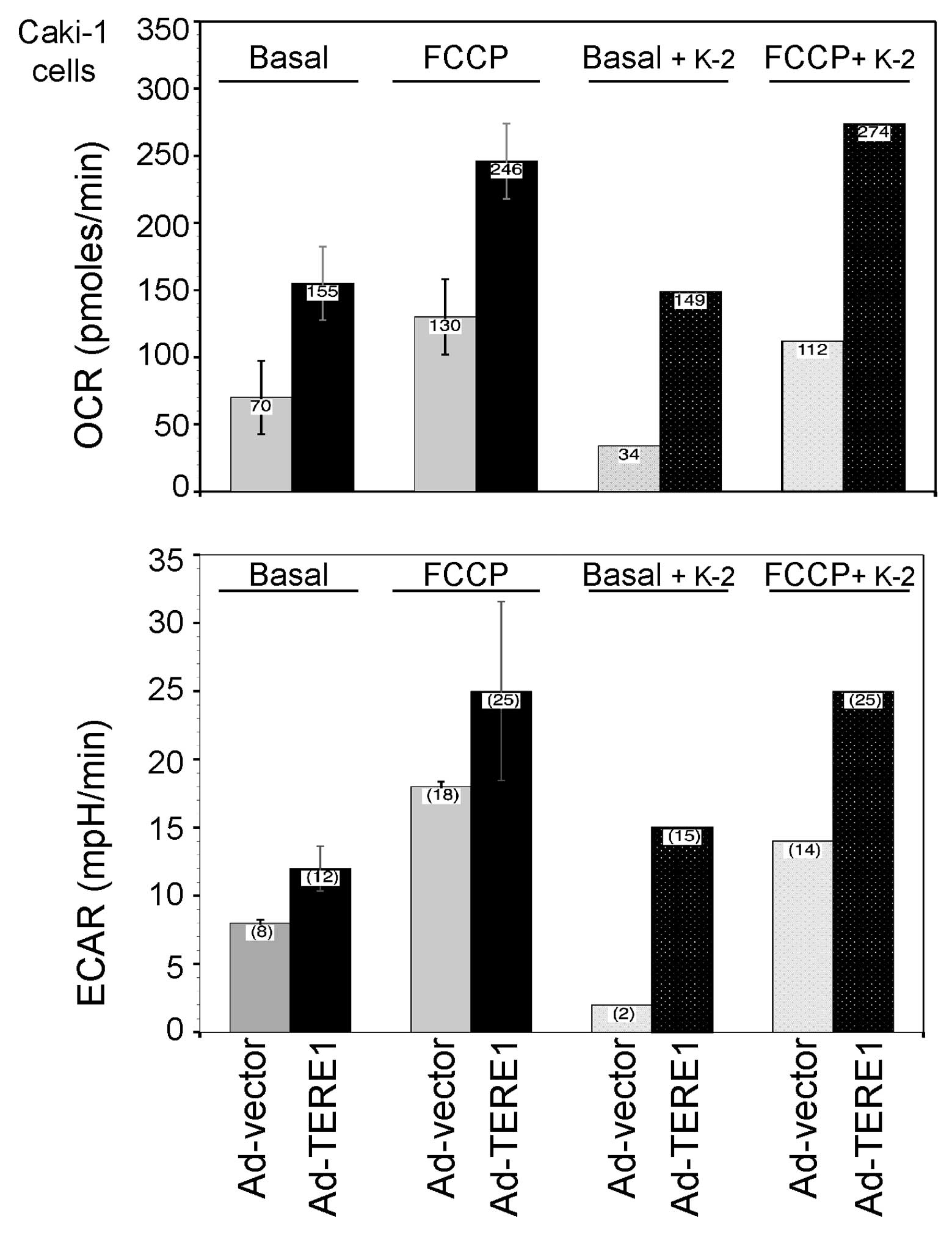
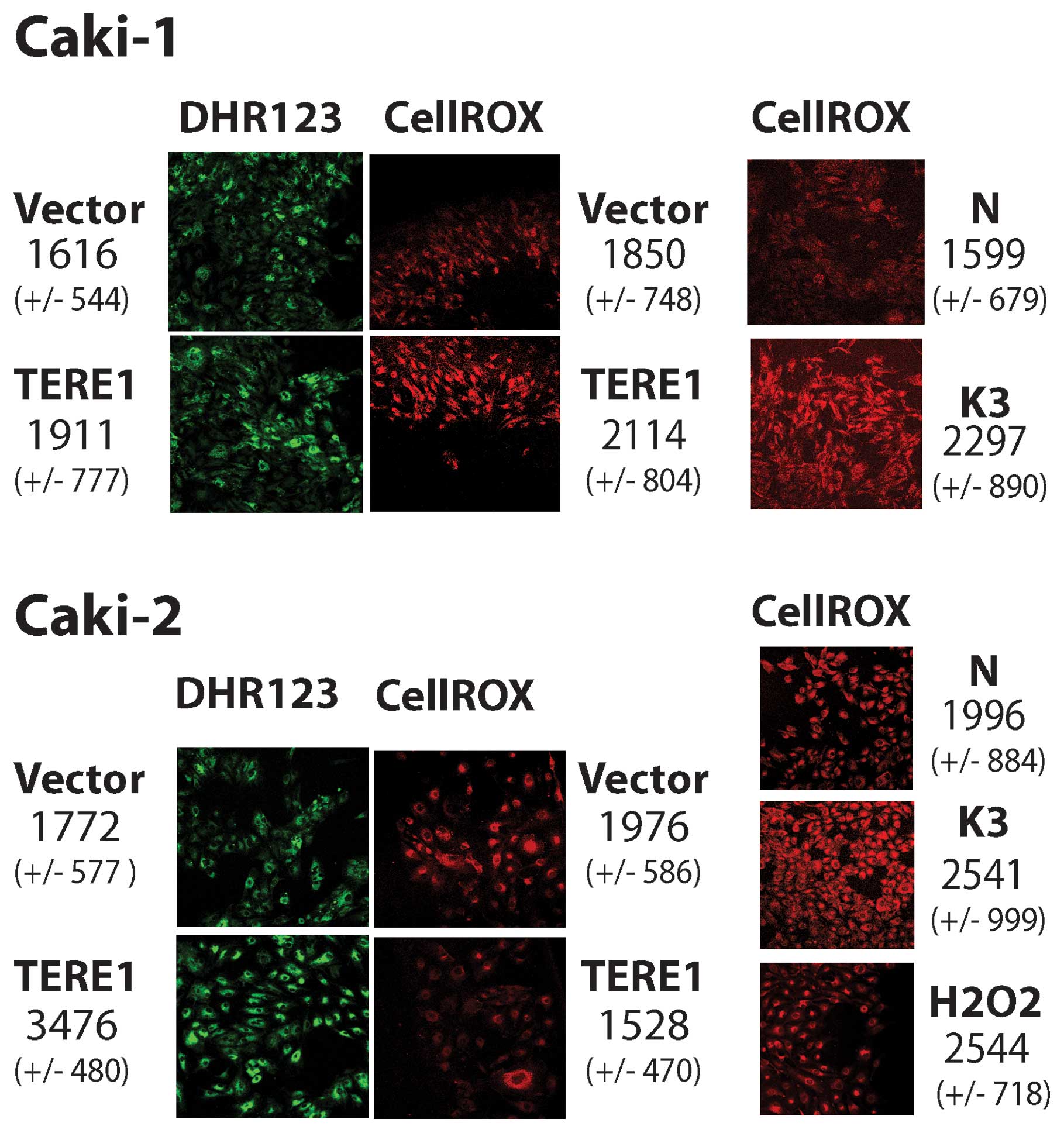
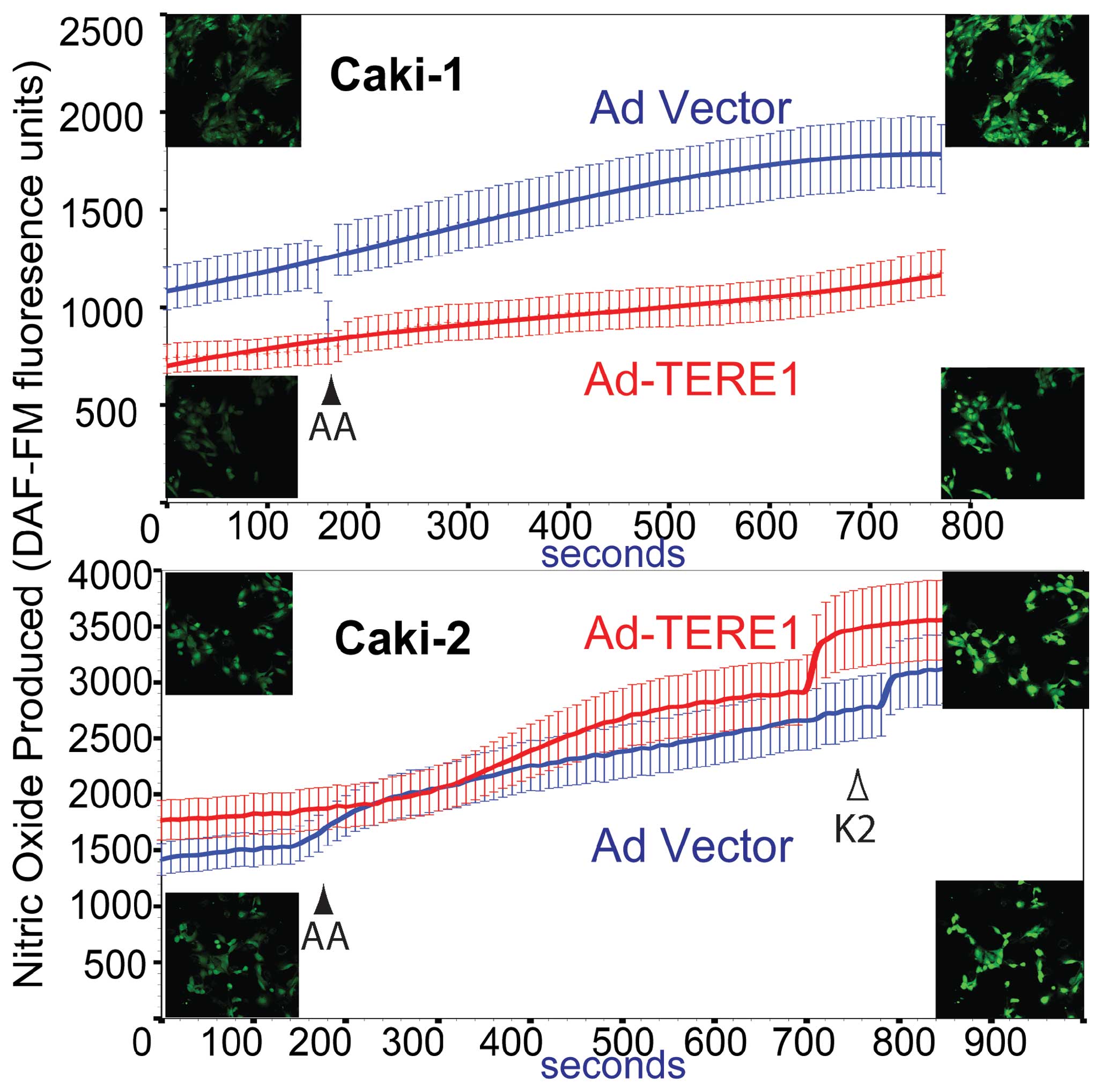
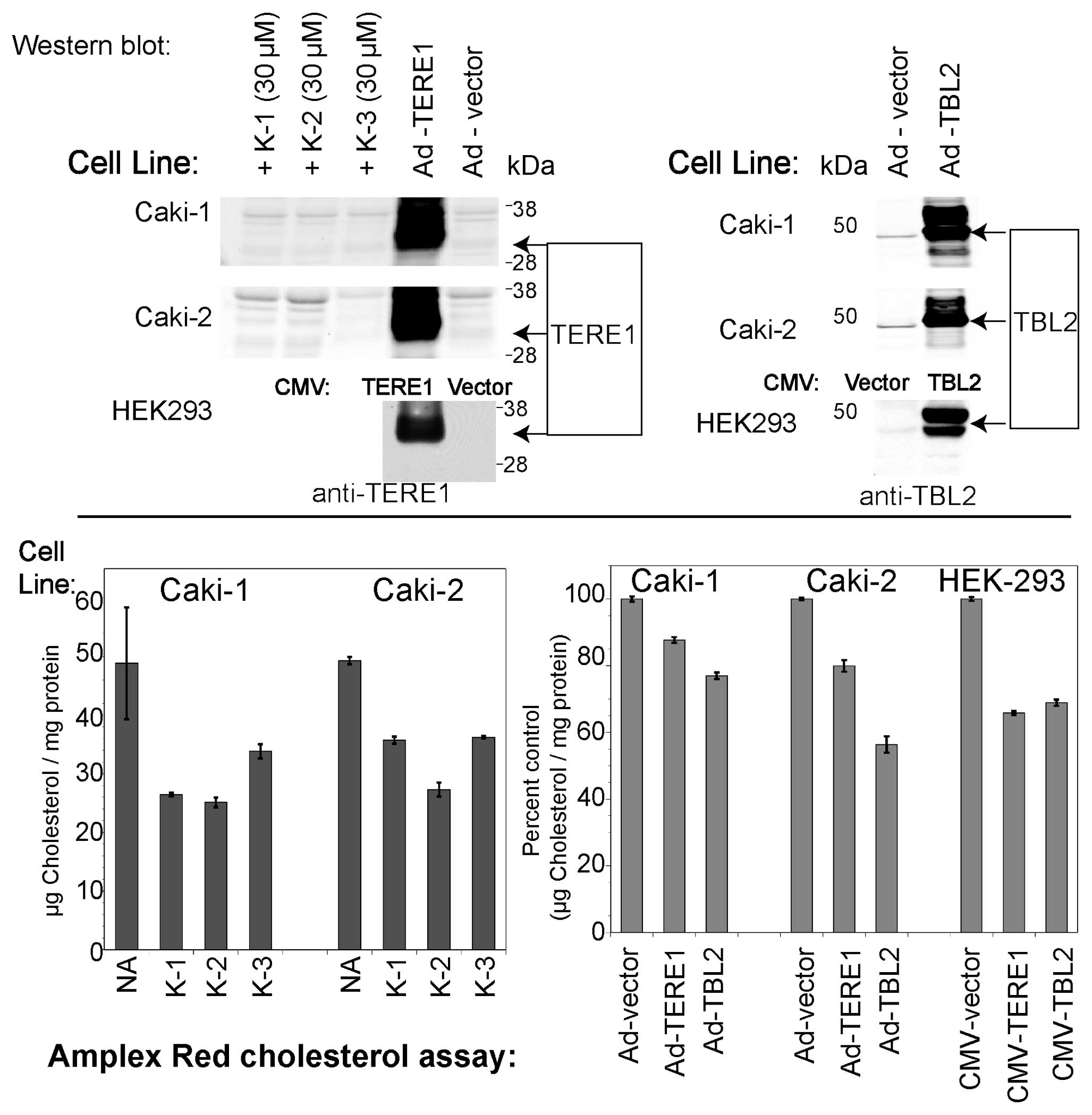
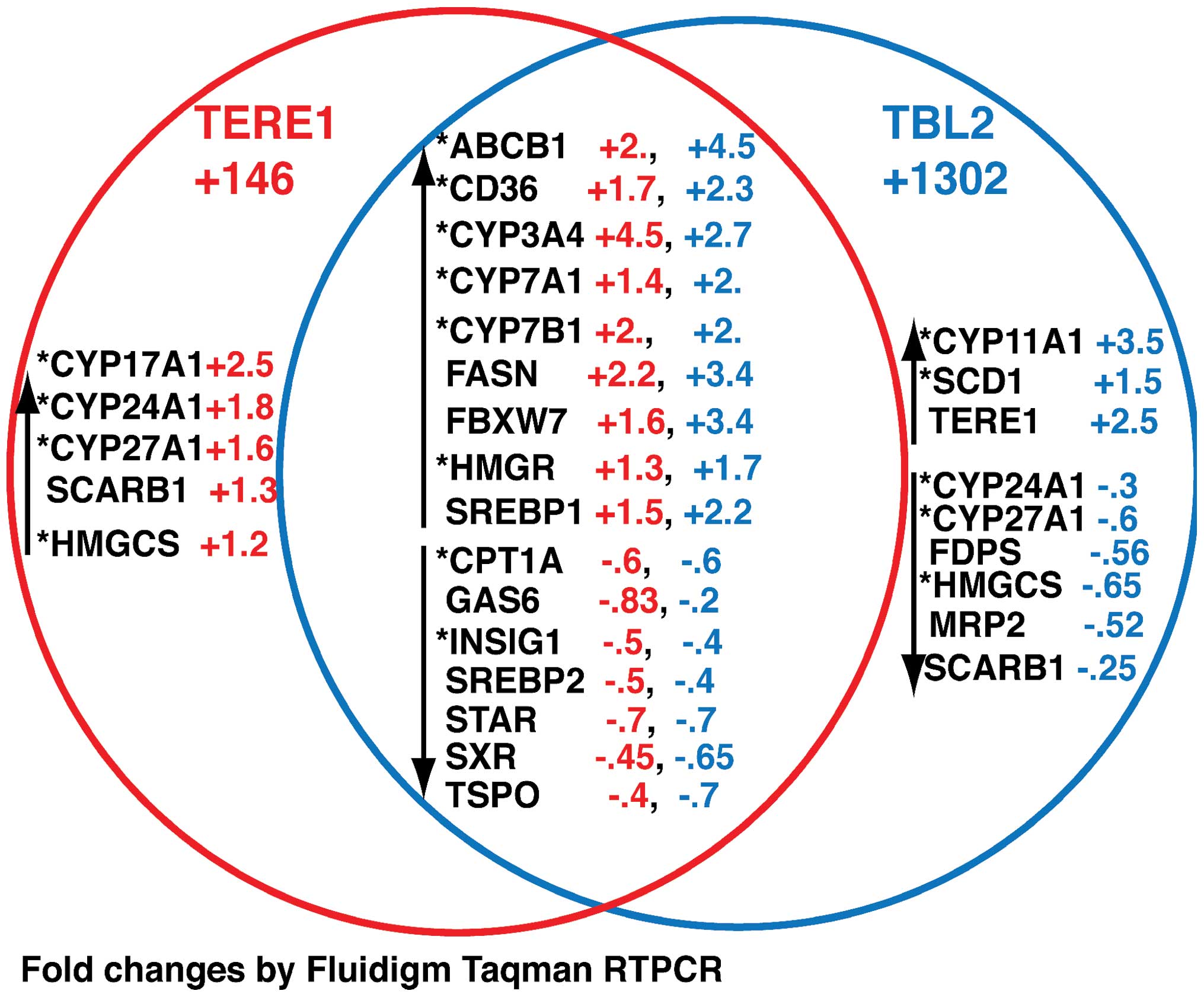
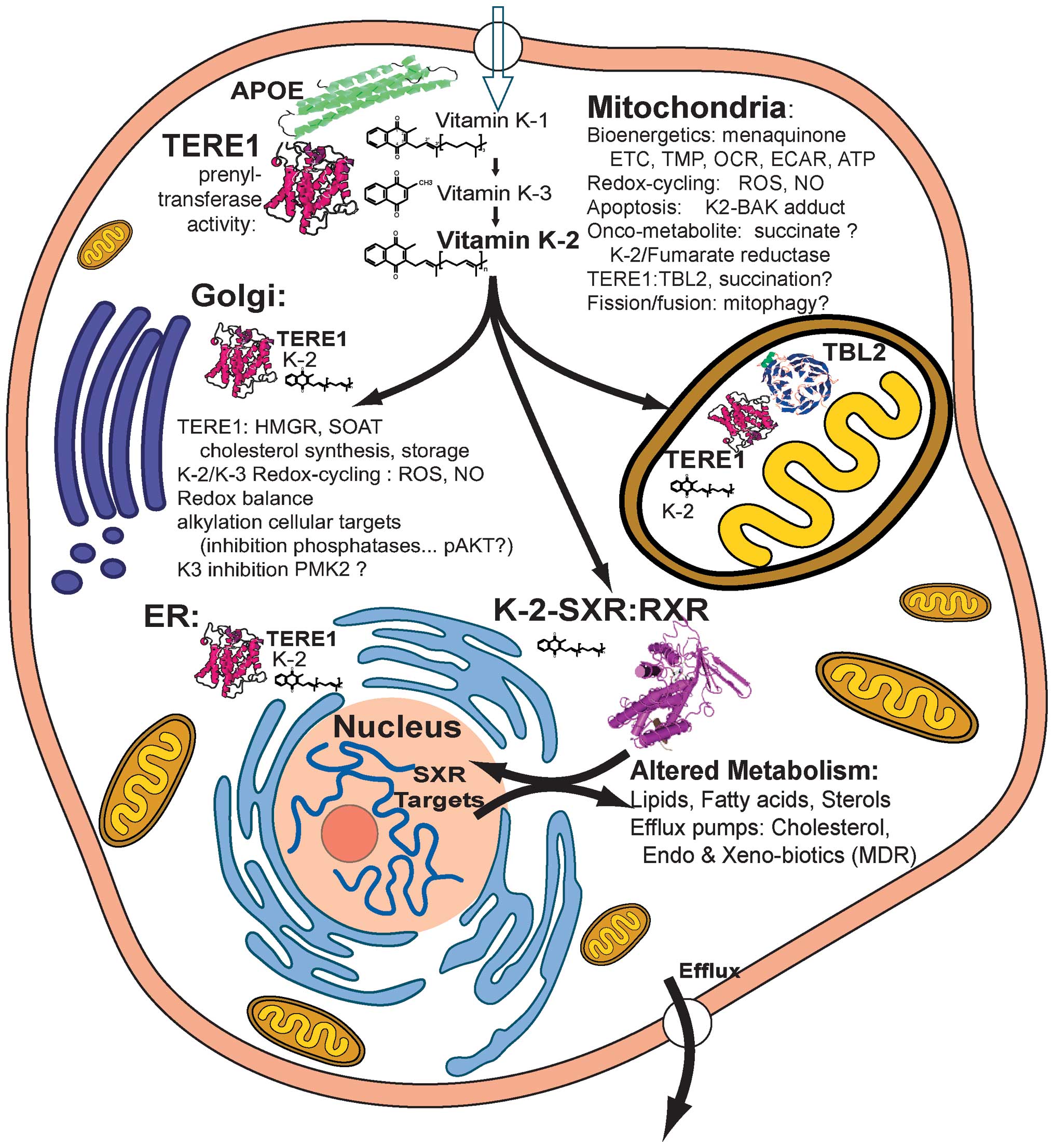
|
1.
|
Li L and Kaelin WG Jr: New insights into
the biology of renal cell carcinoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am.
25:667–686. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Messer J, Drabick J and Kaag M: Rational
therapy for renal cell carcinoma based on its genetic targets. Adv
Exp Med Biol. 779:291–308. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Pischon T, Nöthlings U and Boeing H:
Obesity and cancer. Proc Nutr Soc. 67:128–145. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Drabkin HA and Gemmill RM: Obesity,
cholesterol, and clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Adv Cancer
Res. 107:39–56. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Baldewijns MM, van Vlodrop IJ, Vermeulen
PB, Soetekouw PM, van Engeland M and De Bruine AP: VHL and HIF
signalling in renal cell carcinogenesis. J Pathol. 221:125–138.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Keith B, Johnson RS and Simon MC:
HIF1alpha and HIF2alpha: sibling rivalry in hypoxic tumour growth
and progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:9–22. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Banumathy G and Cairns P: Signaling
pathways in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 10:658–664.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Linehan WM, Bratslavsky G, Pinto PA, et
al: Molecular diagnosis and therapy of kidney cancer. Annu Rev Med.
61:329–343. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Mihaly Z, Sztupinszki Z, Surowiak P and
Gyorffy B: A comprehensive overview of targeted therapy in
metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Curr Cancer Drug Targets.
12:857–872. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Pal SK, Williams S, Josephson DY,
Carmichael C, Vogelzang NJ and Quinn DI: Novel therapies for
metastatic renal cell carcinoma: efforts to expand beyond the
VEGF/mTOR signaling paradigm. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:526–537. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Gebhard RL, Clayman RV, Prigge WF, et al:
Abnormal cholesterol metabolism in renal clear cell carcinoma. J
Lipid Res. 28:1177–1184. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Christenson E, Merlin S, Saito M and
Schlesinger P: Cholesterol effects on BAX pore activation. J Mol
Biol. 381:1168–1183. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Li YC, Park MJ, Ye SK, Kim CW and Kim YN:
Elevated levels of cholesterol-rich lipid rafts in cancer cells are
correlated with apoptosis sensitivity induced by
cholesterol-depleting agents. Am J Pathol. 168:1107–1118. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Martinez-Abundis E, Garcia N, Correa F,
Franco M and Zazueta C: Changes in specific lipids regulate
BAX-induced mitochondrial permeability transition. FEBS J.
274:6500–6510. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Oh HY, Lee EJ, Yoon S, Chung BH, Cho KS
and Hong SJ: Cholesterol level of lipid raft microdomains regulates
apoptotic cell death in prostate cancer cells through EGFR-mediated
Akt and ERK signal transduction. Prostate. 67:1061–1069. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Swinnen JV, Brusselmans K and Verhoeven G:
Increased lipogenesis in cancer cells: new players, novel targets.
Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 9:358–365. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Prenen H, Gil T and Awada A: New
therapeutic developments in renal cell cancer. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 69:56–63. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Srinivasan R, Armstrong AJ, Dahut W and
George DJ: Anti-angiogenic therapy in renal cell cancer. BJU Int.
99:1296–1300. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Selak MA, Armour SM, MacKenzie ED, et al:
Succinate links TCA cycle dysfunction to oncogenesis by inhibiting
HIF-alpha prolyl hydroxylase. Cancer Cell. 7:77–85. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Ashrafian H, O’Flaherty L, Adam J, et al:
Expression profiling in progressive stages of fumarate-hydratase
deficiency: the contribution of metabolic changes to tumorigenesis.
Cancer Res. 70:9153–9165. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
O’Flaherty L, Adam J, Heather LC, et al:
Dysregulation of hypoxia pathways in fumarate hydratase-deficient
cells is independent of defective mitochondrial metabolism. Hum Mol
Genet. 19:3844–3851. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Yang Y, Valera VA, Padilla-Nash HM, et al:
UOK 262 cell line, fumarate hydratase deficient (FH-/FH-)
hereditary leiomyomatosis renal cell carcinoma: in vitro and in
vivo model of an aberrant energy metabolic pathway in human cancer.
Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 196:45–55. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23.
|
Nakagawa K, Hirota Y, Sawada N, et al:
Identification of UBIAD1 as a novel human menaquinone-4
biosynthetic enzyme. Nature. 468:117–121. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Fredericks WJ, McGarvey T, Wang H, et al:
The TERE1 (UBIAD1) bladder tumor suppressor protein interacts with
mitochondrial TBL2: regulation of trans-membrane potential,
oxidative stress and SXR signaling to the nucleus. J Cell Biochem.
View Article : Google Scholar : 2013.[Epub ahead
of print].
|
|
25.
|
McGarvey TW, Nguyen T, Tomaszewski JE,
Monson FC and Malkowicz SB: Isolation and characterization of the
TERE1 gene, a gene down-regulated in transitional cell carcinoma of
the bladder. Oncogene. 20:1042–1051. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
McGarvey TW, Nguyen T, Puthiyaveettil R,
Tomaszewski JE and Malkowicz SB: TERE1, a novel gene affecting
growth regulation in prostate carcinoma. Prostate. 54:144–155.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Fredericks WJ, McGarvey T, Wang H, et al:
The bladder tumor suppressor protein TERE1 (UBIAD1) modulates cell
cholesterol: implications for tumor progression. DNA Cell Biol.
30:851–864. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
McGarvey TW, Nguyen TB and Malkowicz SB:
An interaction between apolipoprotein E and TERE1 with a possible
association with bladder tumor formation. J Cell Biochem.
95:419–428. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Weiss JS, Kruth HS, Kuivaniemi H, et al:
Mutations in the UBIAD1 gene on chromosome short arm 1, region 36,
cause Schnyder crystalline corneal dystrophy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis
Sci. 48:5007–5012. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Nickerson ML, Kostiha BN, Brandt W, et al:
UBIAD1 mutation alters a mitochondrial prenyltransferase to cause
Schnyder corneal dystrophy. PLoS One. 5:e107602010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Nickerson ML, Bosley AD, Weiss JS, et al:
The UBIAD1 prenyltransferase links menaquione-4 synthesis to
cholesterol metabolic enzymes. Hum Mutat. 34:317–329. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Ihunnah CA, Jiang M and Xie W: Nuclear
receptor PXR, transcriptional circuits and metabolic relevance.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1812:956–963. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Zhou C, Verma S and Blumberg B: The
steroid and xenobiotic receptor (SXR), beyond xenobiotic
metabolism. Nucl Recept Signal. 7:e0012009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Lamson DW and Plaza SM: The anticancer
effects of vitamin K. Altern Med Rev. 8:303–318. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Nishikawa Y, Wang Z, Kerns J, Wilcox CS
and Carr BI: Inhibition of hepatoma cell growth in vitro by
arylating and non-arylating K vitamin analogs. Significance of
protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibition. J Biol Chem.
274:34803–34810. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Gilloteaux J, Jamison JM, Neal DR, Loukas
M, Doberzstyn T and Summers JL: Cell damage and death by
autoschizis in human bladder (RT4) carcinoma cells resulting from
treatment with ascorbate and menadione. Ultrastruct Pathol.
34:140–160. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Nowicka B and Kruk J: Occurrence,
biosynthesis and function of isoprenoid quinones. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1797:1587–1605. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Tielens AG, Rotte C, van Hellemond JJ and
Martin W: Mitochondria as we don’t know them. Trends Biochem Sci.
27:564–572. 2002.
|
|
39.
|
Vos M, Esposito G, Edirisinghe JN, et al:
Vitamin K2 is a mitochondrial electron carrier that rescues pink1
deficiency. Science. 336:1306–1310. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Spurgeon SL, Jones RC and Ramakrishnan R:
High throughput gene expression measurement with real time PCR in a
microfluidic dynamic array. PLoS One. 3:e16622008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Mugoni V, Postel R, Catanzaro V, et al:
Ubiad1 is an antioxidant enzyme that regulates eNOS activity by
CoQ10 synthesis. Cell. 152:504–518. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Jamin N, Neumann JM, Ostuni MA, et al:
Characterization of the cholesterol recognition amino acid
consensus sequence of the peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor.
Mol Endocrinol. 19:588–594. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Hulce JJ, Cognetta AB, Niphakis MJ, Tully
SE and Cravatt BF: Proteome-wide mapping of cholesterol-interacting
proteins in mammalian cells. Nat Methods. 10:259–264. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Wu M, Neilson A, Swift AL, et al:
Multiparameter metabolic analysis reveals a close l link between
attenuated mitochondrial bioenergetic function and enhanced
glycolysis dependency in human tumor cells. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 292:C125–C136. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45.
|
Klaus V, Hartmann T, Gambini J, et al:
1,4-Naphthoquinones as inducers of oxidative damage and stress
signaling in HaCaT human keratinocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys.
496:93–100. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Sano M, Fujita H, Morita I, Uematsu H and
Murota S: Vitamin K2 (menatetrenone) induces iNOS in bovine
vascular smooth muscle cells: no relationship between nitric oxide
production and gamma-carboxylation. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo).
45:711–723. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47.
|
Bhalerao S and Clandinin TR: Cell biology.
Vitamin K2 takes charge. Science. 336:1241–1242. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Shearer MJ and Newman P: Metabolism and
cell biology of vitamin K. Thromb Haemost. 100:530–547. 2008.
|
|
49.
|
Zhou C, King N, Chen KY and Breslow JL:
Activation of PXR induces hypercholesterolemia in wild-type and
accelerates atherosclerosis in apoE deficient mice. J Lipid Res.
50:2004–2013. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Landes N: Homologous metabolic and gene
activating routes for vitamins E and K. Mol Aspects Med.
24:337–344. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Lim YP and Huang JD: Interplay of pregnane
X receptor with other nuclear receptors on gene regulation. Drug
Metab Pharmacokinet. 23:14–21. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Brown AJ and Jessup W: Oxysterols:
sources, cellular storage and metabolism, and new insights into
their roles in cholesterol homeostasis. Mol Aspects Med.
30:111–122. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Sonoda J, Chong LW, Downes M, et al:
Pregnane X receptor prevents hepatorenal toxicity from cholesterol
metabolites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:2198–2203. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Wang Y, Rogers PM, Su C, Varga G, Stayrook
KR and Burris TP: Regulation of cholesterologenesis by the
oxysterol receptor, LXRalpha. J Biol Chem. 283:26332–26339. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55.
|
Wang X and Rader DJ: Molecular regulation
of macrophage reverse cholesterol transport. Curr Opin Cardiol.
22:368–372. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
Wang X, Collins HL, Ranalletta M, et al:
Macrophage ABCA1 and ABCG1, but not SR-BI, promote macrophage
reverse cholesterol transport in vivo. J Clin Invest.
117:2216–2224. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57.
|
Lordan S, Mackrill JJ and O’Brien NM:
Oxysterols and mechanisms of apoptotic signaling: implications in
the pathology of degenerative diseases. J Nutr Biochem. 20:321–336.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58.
|
Shibayama-Imazu T, Aiuchi T and Nakaya K:
Vitamin K2-mediated apoptosis in cancer cells: role of
mitochondrial trans-membrane potential. Vitam Horm. 78:211–226.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59.
|
Jamison JM, Gilloteaux J, Nassiri MR,
Venugopal M, Neal DR and Summers JL: Cell cycle arrest and
autoschizis in a human bladder carcinoma cell line following
Vitamin C and Vitamin K3 treatment. Biochem Pharmacol. 67:337–351.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60.
|
Jamison JM, Gilloteaux J, Perlaky L, et
al: Nucleolar changes and fibrillarin redistribution following
apatone treatment of human bladder carcinoma cells. J Histochem
Cytochem. 58:635–651. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61.
|
Karasawa S, Azuma M, Kasama T, et al:
Vitamin K2 covalently binds to Bak and induces Bak-mediated
apoptosis. Mol Pharmacol. 83:613–620. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62.
|
Dranka BP, Hill BG and Darley-Usmar VM:
Mitochondrial reserve capacity in endothelial cells: the impact of
nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species. Free Radic Biol Med.
48:905–914. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63.
|
Benz CC, Atsriku C, Yau C, et al: Novel
pathways associated with quinone-induced stress in breast cancer
cells. Drug Metab Rev. 38:601–613. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64.
|
Bolton JL, Trush MA, Penning TM, Dryhurst
G and Monks TJ: Role of quinones in toxicology. Chem Res Toxicol.
13:135–160. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65.
|
Lamson DW, Gu YH, Plaza SM, Brignall MS,
Brinton CA and Sadlon AE: The vitamin C: vitamin K3 system -
enhancers and inhibitors of the anticancer effect. Altern Med Rev.
15:345–351. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66.
|
Ambs S and Glynn SA: Candidate pathways
linking inducible nitric oxide synthase to a basal-like
transcription pattern and tumor progression in human breast cancer.
Cell Cycle. 10:619–624. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67.
|
Lee J, Giordano S and Zhang J: Autophagy,
mitochondria and oxidative stress: cross-talk and redox signalling.
Biochem J. 441:523–540. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68.
|
Doulias PT, Tenopoulou M, Greene JL, Raju
K and Ischiropoulos H: Nitric oxide regulates mitochondrial fatty
acid metabolism through reversible protein S-nitrosylation. Sci
Signal. 6:rs12013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69.
|
Lusini L, Tripodi SA, Rossi R, et al:
Altered glutathione anti-oxidant metabolism during tumor
progression in human renal-cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 91:55–59.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70.
|
Fitzgerald JP, Nayak B, Shanmugasundaram
K, et al: Nox4 mediates renal cell carcinoma cell invasion through
hypoxia-induced interleukin 6- and 8- production. PLoS One.
7:e307122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71.
|
Abdelmohsen K: Epidermal growth factor
receptor is a common mediator of quinone-induced signaling leading
to phosphorylation of connexin-43: Role of glutathione and tyrosine
phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 278:38360–38367. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72.
|
Suhara Y, Hanada N, Okitsu T, et al:
Structure-activity relationship of novel menaquinone-4 analogues:
modification of the side chain affects their biological activities.
J Med Chem. 55:1553–1558. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73.
|
Suhara Y, Watanabe M, Motoyoshi S, et al:
Synthesis of new vitamin K analogues as steroid and xenobiotic
receptor (SXR) agonists: insights into the biological role of the
side chain part of vitamin K. J Med Chem. 54:4918–4922. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74.
|
Mazurek S: Pyruvate kinase type M2: a key
regulator of the metabolic budget system in tumor cells. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 43:969–980. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75.
|
Wong N, De Melo J and Tang D: PKM2, a
central point of regulation in cancer metabolism. Int J Cell Biol.
2013:2425132013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76.
|
Chen J, Jiang Z, Wang B, Wang Y and Hu X:
Vitamin K(3) and K(5) are inhibitors of tumor pyruvate kinase M2.
Cancer Lett. 316:204–210. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77.
|
Anastasiou D, Poulogiannis G, Asara JM, et
al: Inhibition of pyruvate kinase M2 by reactive oxygen species
contributes to cellular antioxidant responses. Science.
334:1278–1283. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78.
|
Zaunmuller T, Kelly DJ, Glockner FO and
Unden G: Succinate dehydrogenase functioning by a reverse redox
loop mechanism and fumarate reductase in sulphate-reducing
bacteria. Microbiology. 152:2443–2453. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79.
|
Sakai C, Tomitsuka E, Esumi H, Harada S
and Kita K: Mitochondrial fumarate reductase as a target of
chemotherapy: from parasites to cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1820:643–651. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80.
|
Tomitsuka E, Kita K and Esumi H: The
NADH-fumarate reductase system, a novel mitochondrial energy
metabolism, is a new target for anticancer therapy in tumor
microenvironments. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1201:44–49. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81.
|
Tomitsuka E, Kita K and Esumi H: An
anticancer agent, pyrvinium pamoate inhibits the NADH-fumarate
reductase system - a unique mitochondrial energy metabolism in
tumour microenvironments. J Biochem. 152:171–183. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82.
|
Tomlinson IP, Alam NA, Rowan AJ, et al:
Germline mutations in FH predispose to dominantly inherited uterine
fibroids, skin leiomyomata and papillary renal cell cancer. Nat
Genet. 30:406–410. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83.
|
Yang Y, Valera V, Sourbier C, et al: A
novel fumarate hydratase-deficient HLRCC kidney cancer cell line,
UOK268: a model of the Warburg effect in cancer. Cancer Genet.
205:377–390. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84.
|
Ternette N, Yang M, Laroyia M, et al:
Inhibition of mitochondrial aconitase by succination in fumarate
hydratase deficiency. Cell Rep. 3:689–700. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85.
|
Barrios-Rodiles M, Brown KR, Ozdamar B, et
al: High-throughput mapping of a dynamic signaling network in
mammalian cells. Science. 307:1621–1625. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86.
|
Behrends C, Sowa ME, Gygi SP and Harper
JW: Network organization of the human autophagy system. Nature.
466:68–76. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87.
|
Perez Jurado LA, Wang YK, Francke U and
Cruces J: TBL2, a novel transducin family member in the WBS
deletion: characterization of the complete sequence, genomic
structure, transcriptional variants and the mouse ortholog.
Cytogenet Cell Genet. 86:277–284. 1999.
|
|
88.
|
Tieu Q and Nunnari J: Mdv1p is a WD repeat
protein that interacts with the dynamin-related GTPase, Dnm1p, to
trigger mitochondrial division. J Cell Biol. 151:353–366. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89.
|
Tieu Q, Okreglak V, Naylor K and Nunnari
J: The WD repeat protein, Mdv1p, functions as a molecular adaptor
by interacting with Dnm1p and Fis1p during mitochondrial fission. J
Cell Biol. 158:445–452. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90.
|
Feng Y, Zhang C, Luo Q, et al: A novel
WD-repeat protein, WDR26, inhibits apoptosis of cardiomyocytes
induced by oxidative stress. Free Radic Res. 46:777–784. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91.
|
Blattmann P, Schuberth C, Pepperkok R and
Runz H: RNAi-based functional profiling of loci from blood lipid
genome-wide association studies identifies genes with
cholesterol-regulatory function. PLoS Genet. 9:e10033382013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92.
|
Rothblat GH, De la Llera-Moya M, Atger V,
Kellner-Weibel G, Williams DL and Phillips MC: Cell cholesterol
efflux: integration of old and new observations provides new
insights. J Lipid Res. 40:781–796. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93.
|
Hoekstra M, van Berkel TJ and van Eck M:
Scavenger receptor BI: a multi-purpose player in cholesterol and
steroid metabolism. World J Gastroenterol. 16:5916–5924.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94.
|
Maitra U and Li L: Molecular mechanisms
responsible for the reduced expression of cholesterol transporters
from macrophages by low-dose endotoxin. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 33:24–33. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95.
|
Saddar S, Carriere V, Lee WR, et al:
Scavenger receptor class B type I is a plasma membrane cholesterol
sensor. Circ Res. 112:140–151. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96.
|
Crestani M, De Fabiani E, Caruso D, et al:
LXR (liver X receptor) and HNF-4 (hepatocyte nuclear factor-4): key
regulators in reverse cholesterol transport. Biochem Soc Trans.
32:92–96. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97.
|
Tu K, Zheng X, Yin G, Zan X, Yao Y and Liu
Q: Evaluation of Fbxw7 expression and its correlation with
expression of SREBP-1 in a mouse model of NAFLD. Mol Med Rep.
6:525–530. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98.
|
Kumadaki S, Karasawa T, Matsuzaka T, et
al: Inhibition of ubiquitin ligase F-box and WD repeat
domain-containing 7alpha (Fbw7alpha) causes hepatosteatosis through
Kruppel-like factor 5 (KLF5)/peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor gamma2 (PPARgamma2) pathway but not SREBP-1c protein in
mice. J Biol Chem. 286:40835–40846. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99.
|
Ntambi JM, Miyazaki M and Dobrzyn A:
Regulation of stearoyl-CoA desaturase expression. Lipids.
39:1061–1065. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100.
|
Wang J, Ban MR, Zou GY, et al: Polygenic
determinants of severe hypertriglyceridemia. Hum Mol Genet.
17:2894–2899. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101.
|
Kathiresan S, Melander O, Guiducci C, et
al: Six new loci associated with blood low-density lipoprotein
cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol or triglycerides
in humans. Nat Genet. 40:189–197. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102.
|
Verma S, Tabb MM and Blumberg B:
Activation of the steroid and xenobiotic receptor, SXR, induces
apoptosis in breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 9:32009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103.
|
Pani G, Galeotti T and Chiarugi P:
Metastasis: cancer cell’s escape from oxidative stress. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 29:351–378. 2010.
|
|
104.
|
Montero J, Morales A, Llacuna L, et al:
Mitochondrial cholesterol contributes to chemotherapy resistance in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 68:5246–5256. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105.
|
Garcia-Ruiz C, Mari M, Colell A, et al:
Mitochondrial cholesterol in health and disease. Histol
Histopathol. 24:117–132. 2009.
|
|
106.
|
Bonuccelli G, Tsirigos A, Whitaker-Menezes
D, et al: Ketones and lactate ‘fuel’ tumor growth and metastasis:
evidence that epithelial cancer cells use oxidative mitochondrial
metabolism. Cell Cycle. 9:3506–3514. 2010.
|
|
107.
|
Bonuccelli G, Whitaker-Menezes D,
Castello-Cros R, et al: The reverse Warburg effect: glycolysis
inhibitors prevent the tumor promoting effects of caveolin-1
deficient cancer associated fibroblasts. Cell Cycle. 9:1960–1971.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108.
|
Behrend L, Henderson G and Zwacka RM:
Reactive oxygen species in oncogenic transformation. Biochem Soc
Trans. 31:1441–1444. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109.
|
Ralph SJ, Rodríguez-Enríquez S, Neuzil J,
Saavedra E and Moreno-Sánchez R: The causes of cancer revisited:
‘Mitochondrial malignancy’ and ROS-induced oncogenic transformation
- why mitochondria are targets for cancer therapy. Mol Aspects Med.
31:145–170. 2010.
|
|
110.
|
Sone H, Akanuma H and Fukuda T:
Oxygenomics in environmental stress. Redox Rep. 15:98–114. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|