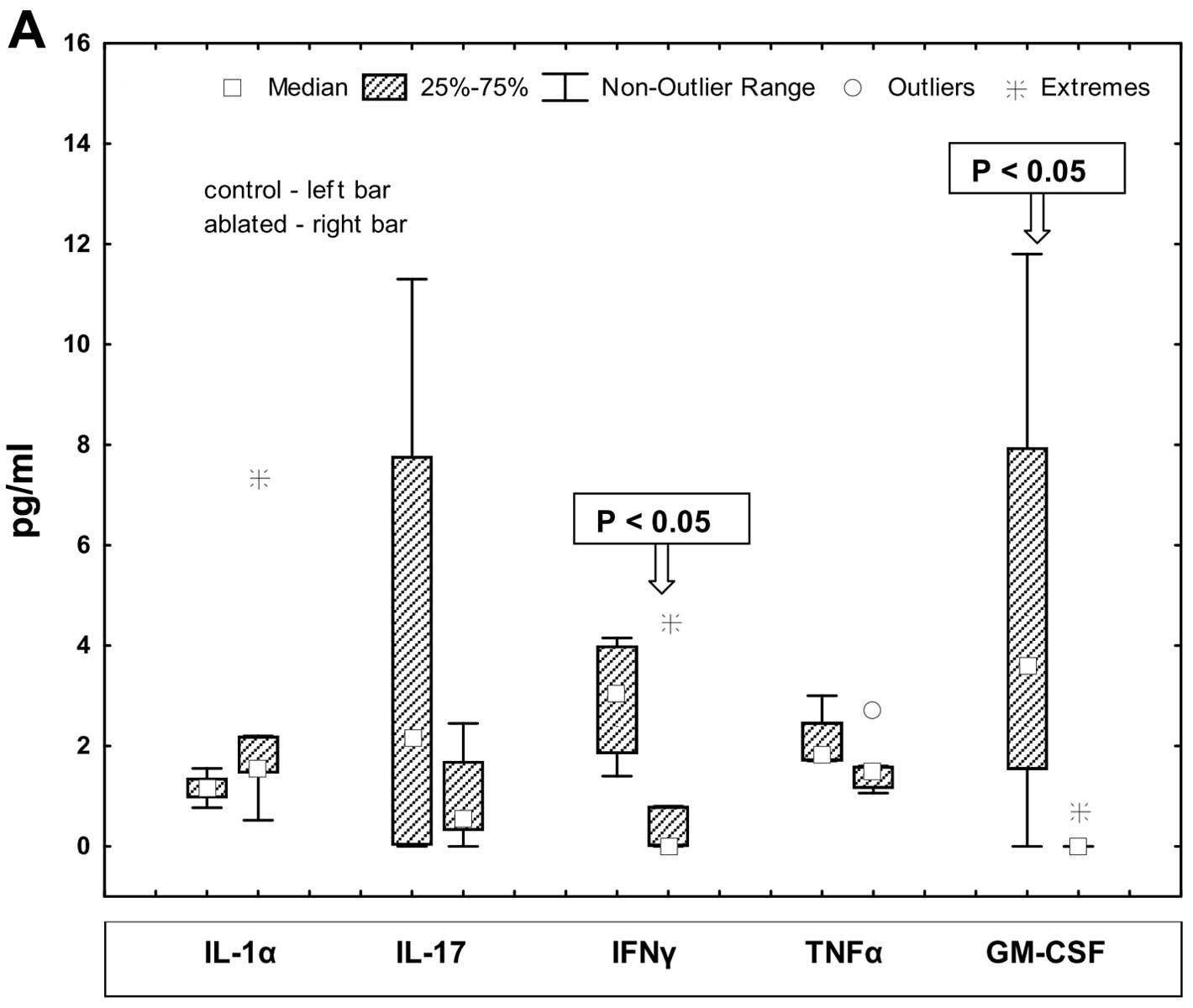
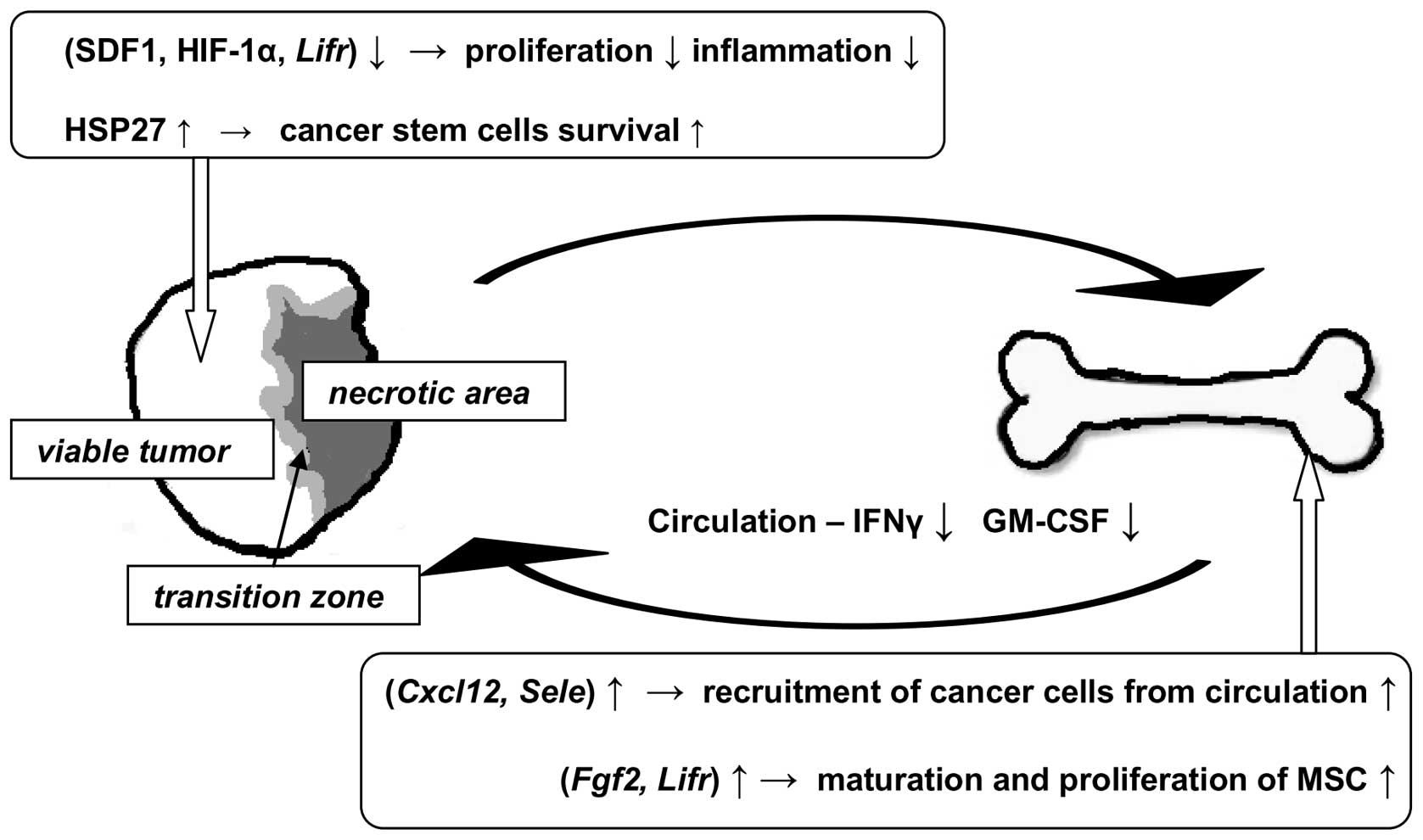
|
1.
|
Shah DR, Green S, Elliot A, McGahan JP and
Khatri VP: Current oncologic applications of radiofrequency
ablation therapies. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 5:71–80. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Oto A, Sethi I, Karczmar G, et al: MR
imaging-guided focal laser ablation for prostate cancer: phase I
trial. Radiology. 267:932–940. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Merckel LG, Bartels LW, Kohler MO, et al:
MR-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation of breast
cancer with a dedicated breast platform. Cardiovasc Intervent
Radiol. 36:292–301. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Shafirstein G, Hennings L, Kaufmann Y, et
al: Conductive interstitial thermal therapy (CITT) device
evaluation in VX2 rabbit model. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
6:235–246. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Shafirstein G, Novák P, Moros EG, et al:
Conductive interstitial thermal therapy device for surgical margin
ablation: in vivo verification of a theoretical model. Int J
Hyperthermia. 23:477–492. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Shafirstein G, Kaufmann Y, Hennings L, et
al: Conductive interstitial thermal therapy (CITT) inhibits
recurrence and metastasis in rabbit VX2 carcinoma model. Int J
Hyperthermia. 25:446–454. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Przybyla BD, Shafirstein G, Koonce NA,
Webber JS and Griffin RJ: Conductive thermal ablation of 4T1 murine
breast carcinoma reduces severe hypoxia in surviving tumour. Int J
Hyperthermia. 28:156–162. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Dromi SA, Walsh MP, Herby S, et al:
Radiofrequency ablation induces antigen-presenting cell
infiltration and amplification of weak tumor-induced immunity.
Radiology. 251:58–66. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
van der Bilt JD, Soeters ME, Duyverman AM,
et al: Perinecrotic hypoxia contributes to
ischemia/reperfusion-accelerated outgrowth of colorectal
micrometastases. Am J Pathol. 170:1379–1388. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Peters BA, Diaz LA, Polyak K, et al:
Contribution of bone marrow-derived endothelial cells to human
tumor vasculature. Nat Med. 11:261–262. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Bunt SK, Sinha P, Clements VK, Leips J and
Ostrand-Rosenberg S: Inflammation induces myeloid-derived
suppressor cells that facilitate tumor progression. J Immunol.
176:284–290. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Di Rosa F: T-lymphocyte interaction with
stromal, bone and hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow. Immunol
Cell Biol. 87:20–29. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Evans SS, Fisher DT, Skitzki JJ and Chen
Q: Targeted regulation of a lymphocyte-endothelial-interleukin-6
axis by thermal stress. Int J Hyperthermia. 24:67–78. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Peer AJ, Grimm MJ, Zynda ER and Repasky
EA: Diverse immune mechanisms may contribute to the survival
benefit seen in cancer patients receiving hyperthermia. Immunol
Res. 46:137–154. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Baronzio G, Gramaglia A and Fiorentini G:
Hyperthermia and immunity. A brief overview. In Vivo. 20:689–695.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Chantrain CF, Feron O, Marbaix E and
DeClerck YA: Bone mrrow microenvironment and tumor progression.
Cancer Microenviron. 1:23–35. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Heppner GH, Miller FR and Shekhar PM:
Nontransgenic models of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res.
2:331–334. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Lippold HJ: Quantitative succinic
dehydrogenases histochemistry. A comparison of different
tetrazolium salts. Histochemistry. 76:381–405. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Schmittgen TD, Lee EJ and Jiang J:
High-throughput real-time PCR. Methods Mol Biol. 429:89–98. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Wiggermann P, Zeman F, Niessen C, et al:
Percutaneous irreversible electroporation (IRE) of hepatic
malignant tumours: contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) findings.
Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 52:417–427. 2012.
|
|
21.
|
Uchida T, Nakano M, Hongo S, et al:
High-intensity focused ultrasound therapy for prostate cancer. Int
J Urol. 19:187–201. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22.
|
Zhao Z and Wu F: Minimally-invasive
thermal ablation of early-stage breast cancer: a systemic review.
Eur J Surg Oncol. 36:1149–1155. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Yoon J, Cho J, Kim N, et al:
High-frequency microwave ablation method for enhanced cancer
treatment with minimized collateral damage. Int J Cancer.
129:1970–1978. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Hung WK, Mak KL, Ying M and Chan M:
Radiofrequency ablation of breast cancer: a comparative study of
two needle designs. Breast Cancer. 18:124–128. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Nijkamp MW, van der Bilt JD, de Bruijn MT,
et al: Accelerated perinecrotic outgrowth of colorectal liver
metastases following radiofrequency ablation is a hypoxia-driven
phenomenon. Ann Surg. 249:814–823. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
St Hill CA: Interactions between
endothelial selectins and cancer cells regulate metastasis. Front
Biosci. 16:3233–3251. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Hofer EL, Labovsky V, La Russa V, et al:
Mesenchymal stromal cells, colony-forming unit fibroblasts, from
bone marrow of untreated advanced breast and lung cancer patients
suppress fibroblast colony formation from healthy marrow. Stem
Cells Dev. 19:359–370. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28.
|
Oskowitz AZ, Lu J, Penfornis P, et al:
Human multipotent stromal cells from bone marrow and microRNA:
regulation of differentiation and leukemia inhibitory factor
expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:18372–18377. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Whitney MJ, Lee A, Ylostalo J, Zeitouni S,
Tucker A and Gregory CA: Leukemia inhibitory factor secretion is a
predictor and indicator of early progenitor status in adult bone
marrow stromal cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 15:33–44. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
McAllister SS and Weinberg RA: Tumor-host
interactions: a far-reaching relationship. J Clin Oncol.
28:4022–4028. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Castano Z, Tracy K and McAllister SS: The
tumor macro-environment and systemic regulation of breast cancer
progression. Int J Dev Biol. 55:889–897. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Hirbe AC, Morgan EA and Weilbaecher KN:
The CXCR4/SDF-1 chemokine axis: a potential therapeutic target for
bone metastases? Curr Pharm Des. 16:1284–1290. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Meads MB, Hazlehurst LA and Dalton WS: The
bone marrow microenvironment as a tumor sanctuary and contributor
to drug resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2519–2526. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Cronin PA, Wang JH and Redmond HP: Hypoxia
increases the metastatic ability of breast cancer cells via
upregulation of CXCR4. BMC Cancer. 10:2252010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Teicher BA and Fricker SP: CXCL12
(SDF-1)/CXCR4 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2927–2931.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Kucia M, Jankowski K, Reca R, et al:
CXCR4-SDF-1 signalling, locomotion, chemotaxis and adhesion. J Mol
Histol. 35:233–245. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Petit I, Jin D and Rafii S: The
SDF-1-CXCR4 signaling pathway: a molecular hub modulating
neo-angiogenesis. Trends Immunol. 28:299–307. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Du R, Lu KV, Petritsch C, et al: HIF1alpha
induces the recruitment of bone marrow-derived vascular modulatory
cells to regulate tumor angiogenesis and invasion. Cancer Cell.
13:206–220. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Sceneay J, Chow MT, Chen A, et al: Primary
tumor hypoxia recruits CD11b+/Ly6Cmed/Ly6G+
immune suppressor cells and compromises NK cell cytotoxicity in the
premetastatic niche. Cancer Res. 72:3906–3911. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Murphy ME: The HSP70 family and cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 34:1181–1188. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Teng LS, Jin KT, Han N and Cao J:
Radiofrequency ablation, heat shock protein 70 and potential
anti-tumor immunity in hepatic and pancreatic cancers: a
minireview. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 9:361–365.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Ciocca DR and Calderwood SK: Heat shock
proteins in cancer: diagnostic, prognostic, predictive, and
treatment implications. Cell Stress Chaperones. 10:86–103. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Gibert B, Hadchity E, Czekalla A, et al:
Inhibition of heat shock protein 27 (HspB1) tumorigenic functions
by peptide aptamers. Oncogene. 30:3672–3681. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Wei L, Liu TT, Wang HH, et al: Hsp27
participates in the maintenance of breast cancer stem cells through
regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and nuclear
factor-kappaB. Breast Cancer Res. 13:R1012011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Hsu HS, Lin JH, Huang WC, et al:
Chemoresistance of lung cancer stemlike cells depends on activation
of Hsp27. Cancer. 117:1516–1528. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Lin EY, Gouon-Evans V, Nguyen AV and
Pollard JW: The macrophage growth factor CSF-1 in mammary gland
development and tumor progression. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia.
7:147–162. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Tsavaris N, Kosmas C, Vadiaka M,
Kanelopoulos P and Boulamatsis D: Immune changes in patients with
advanced breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy with taxanes. Br J
Cancer. 87:21–27. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Haen SP, Pereira PL, Salih HR, Rammensee
HG and Gouttefangeas C: More than just tumor destruction:
immuno-modulation by thermal ablation of cancer. Clin Dev Immunol.
2011:1602502011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Li J, Bouton-Verville H, Holmes LM, et al:
Inhibition or promotion of tumor growth by granulocyte-macrophage
colony stimulating factor derived from engineered tumor cells is
dose-dependent. Anticancer Res. 24:2717–2721. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Eubank TD, Roberts RD, Khan M, et al:
Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor inhibits breast
cancer growth and metastasis by invoking an anti-angiogenic program
in tumor-educated macrophages. Cancer Res. 69:2133–2140. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|