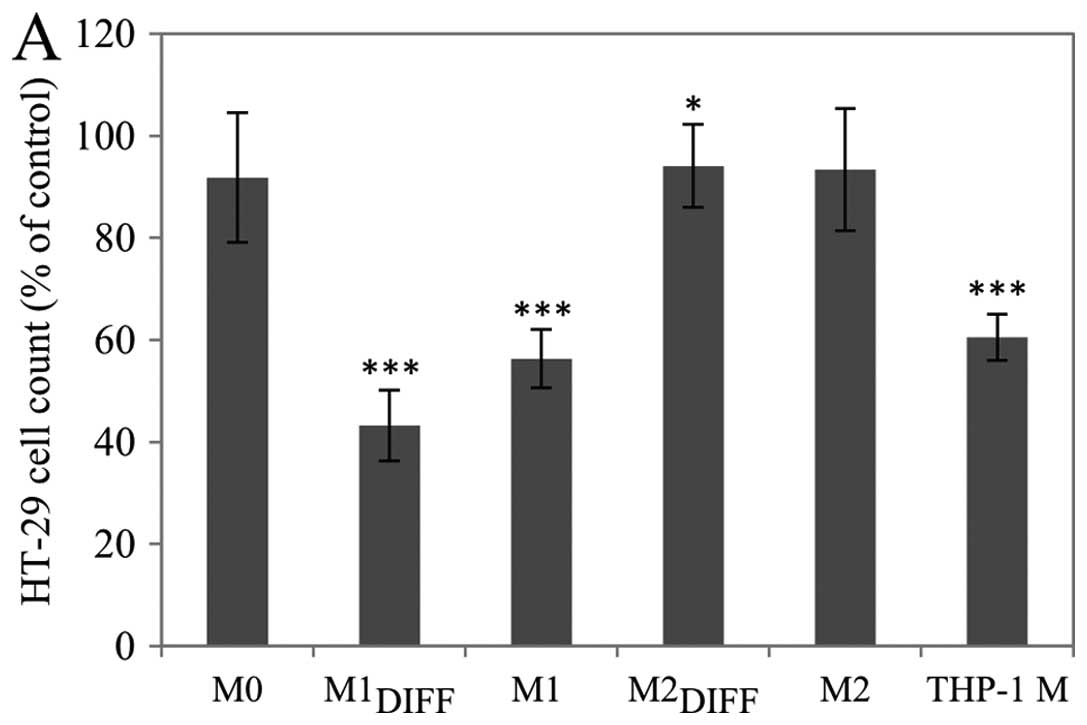
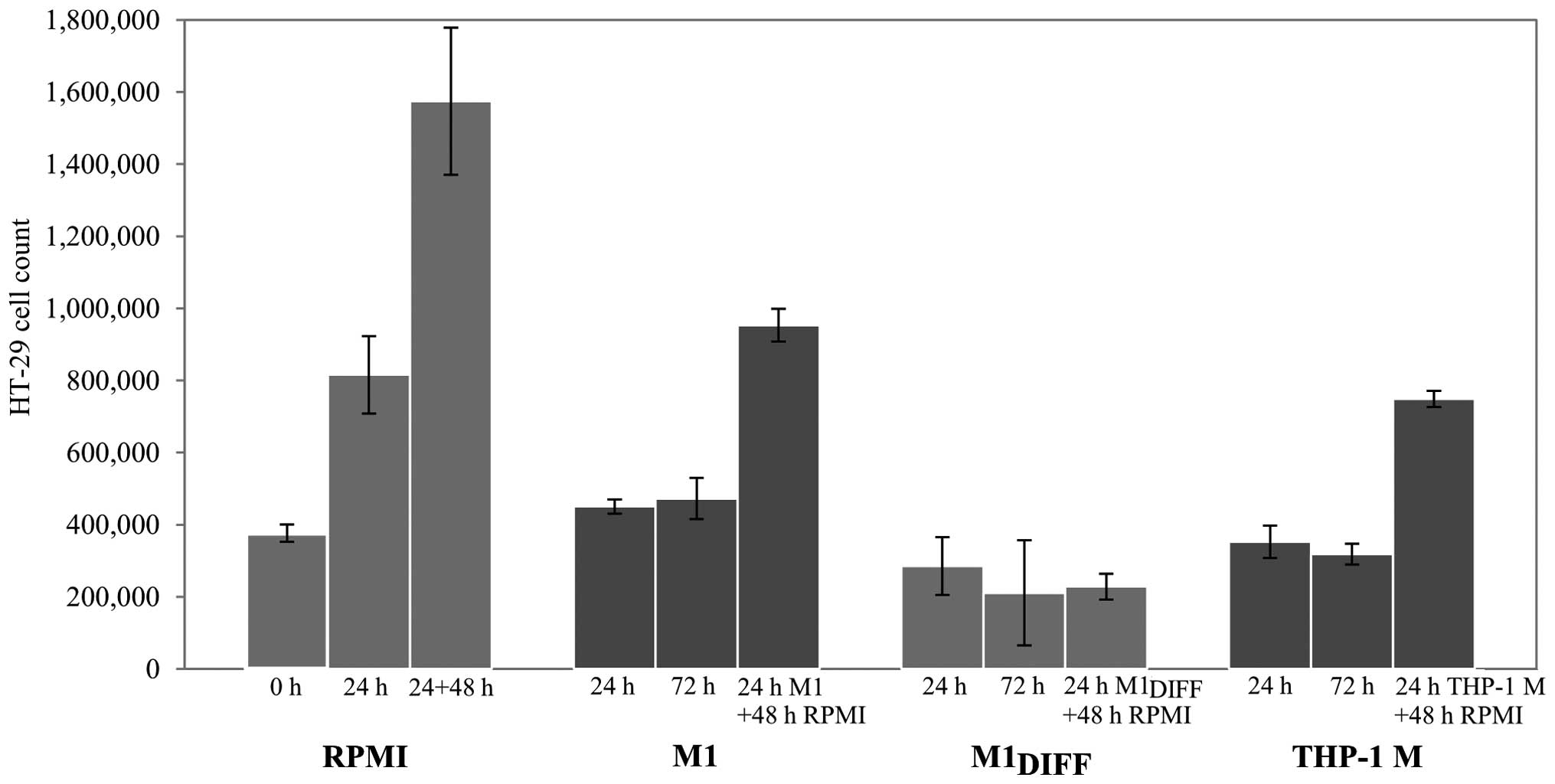
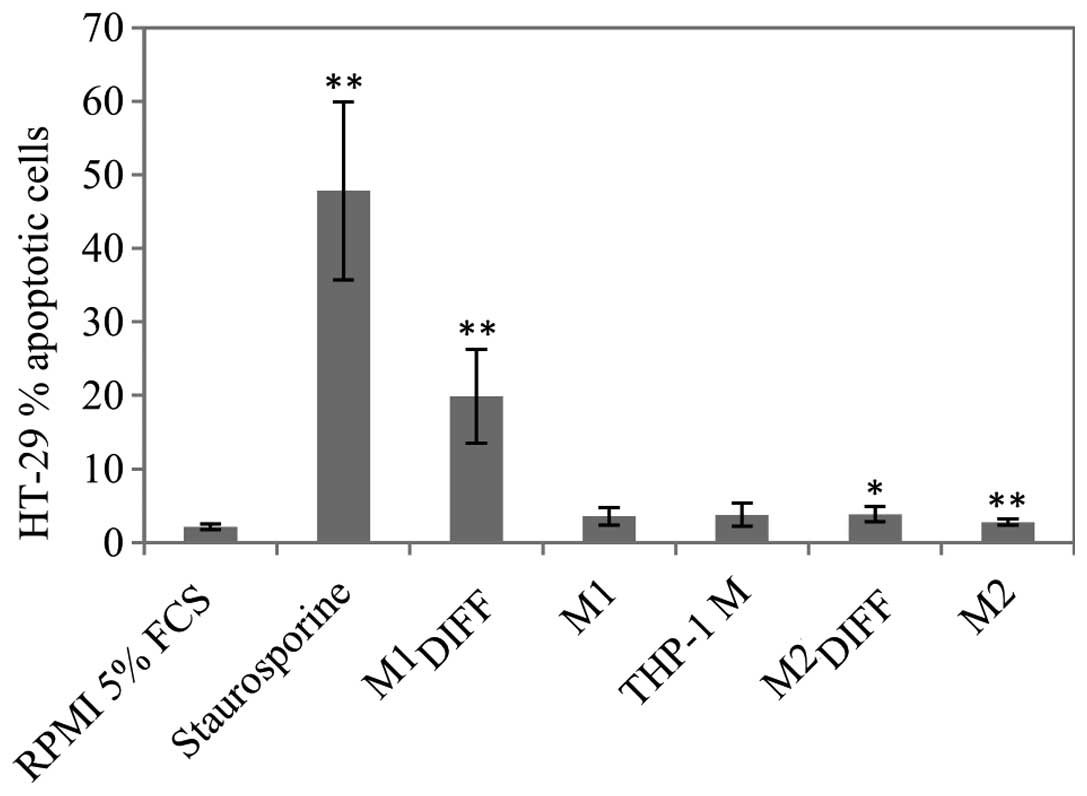
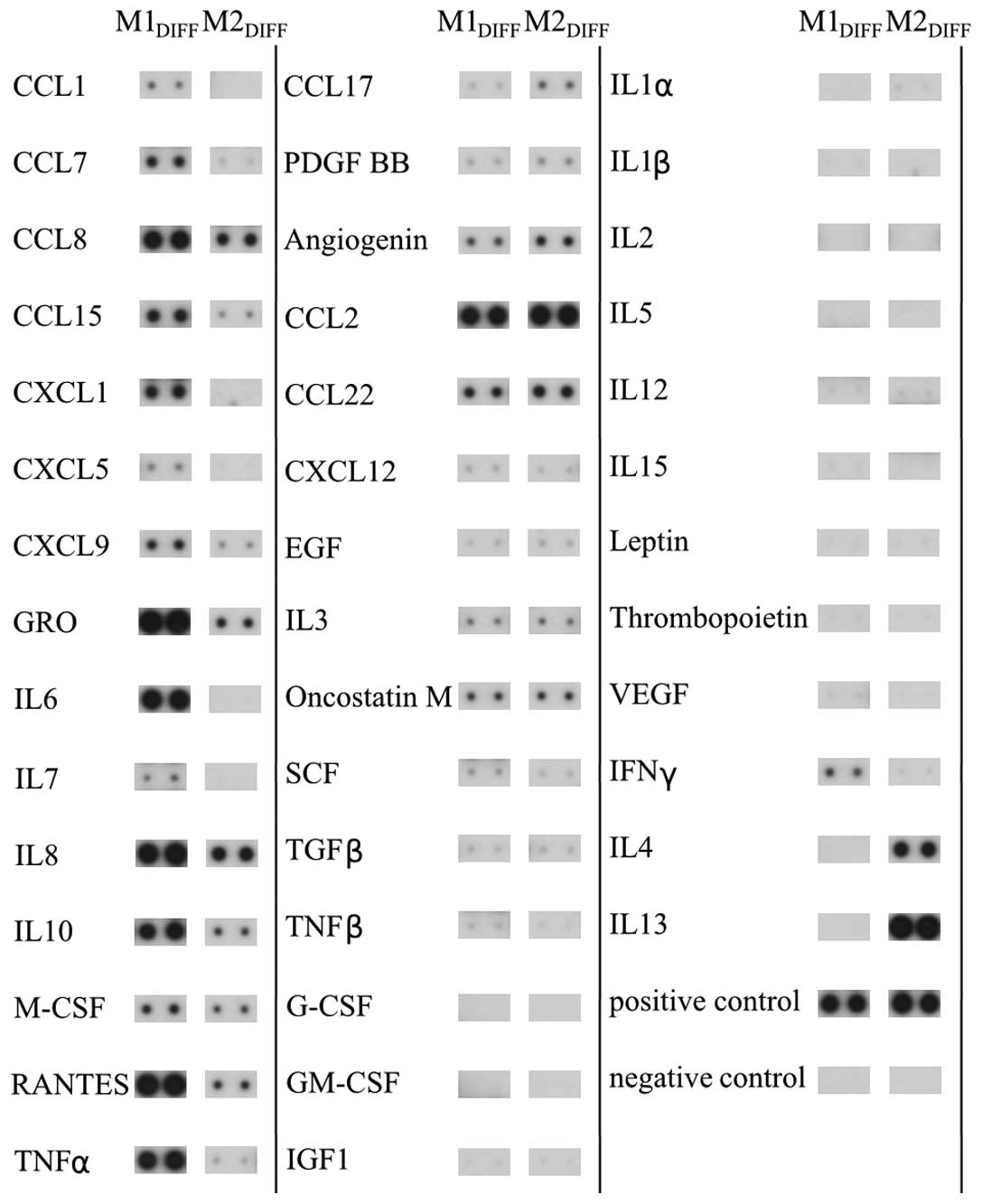
|
1.
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, et al:
Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age
groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global
Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 380:2095–2128. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Power DG, Gloglowski E and Lipkin SM:
Clinical genetics of hereditary colorectal cancer. Hematol Oncol
Clin North Am. 24:837–859. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Peyrin-Biroulet L, Lepage C, Jooste V,
Gueant JL, Faivre J and Bouvier AM: Colorectal cancer in
inflammatory bowel diseases: a population-based study (1976–2008).
Inflamm Bowel Dis. 18:2247–2251. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Vargas AJ and Thompson PA: Diet and
nutrient factors in colorectal cancer risk. Nutr Clin Pract.
27:613–623. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Vipperla K and O’Keefe SJ: The microbiota
and its metabolites in colonic mucosal health and cancer risk. Nutr
Clin Pract. 27:624–635. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Al-Sohaily S, Biankin A, Leong R,
Kohonen-Corish M and Warusavitarne J: Molecular pathways in
colorectal cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27:1423–1431. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Cui G, Shi Y, Cui J, Tang F and Florholmen
J: Immune micro-environmental shift along human colorectal
adenoma-carcinoma sequence: is it relevant to tumor development,
biomarkers and biotherapeutic targets? Scand J Gastroenterol.
47:367–377. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Taketo MM: Roles of stromal
microenvironment in colon cancer progression. J Biochem.
151:477–481. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Quante M, Varga J, Wang TC and Greten FR:
The gastrointestinal tumor microenvironment. Gastroenterology.
145:63–78. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Chen JJ, Yao PL, Yuan A, et al:
Up-regulation of tumor inter-leukin-8 expression by infiltrating
macrophages: its correlation with tumor angiogenesis and patient
survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 9:729–737.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Lewis CE and Pollard JW: Distinct role of
macrophages in different tumor microenvironments. Cancer Res.
66:605–612. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Solinas G, Schiarea S, Liguori M, et al:
Tumor-conditioned macrophages secrete migration-stimulating factor:
a new marker for M2-polarization, influencing tumor cell motility.
J Immunol. 185:642–652. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Martinez FO, Gordon S, Locati M and
Mantovani A: Transcriptional profiling of the human
monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation and polarization: new
molecules and patterns of gene expression. J Immunol.
177:7303–7311. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Watkins SK, Egilmez NK, Suttles J and
Stout RD: IL-12 rapidly alters the functional profile of
tumor-associated and tumor-infiltrating macrophages in vitro and in
vivo. J Immunol. 178:1357–1362. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Sica A and Mantovani A: Macrophage
plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest.
122:787–795. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18.
|
Biswas SK, Allavena P and Mantovani A:
Tumor-associated macrophages: functional diversity, clinical
significance, and open questions. Semin Immunopathol. 35:585–600.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Rey-Giraud F, Hafner M and Ries CH: In
vitro generation of monocyte-derived macrophages under serum-free
conditions improves their tumor promoting functions. PLoS One.
7:e426562012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Diaz-Gandarilla JA, Osorio-Trujillo C,
Hernandez-Ramirez VI and Talamas-Rohana P: PPAR activation induces
M1 macrophage polarization via cPLA(2)-COX-2 inhibition, activating
ROS production against Leishmania mexicana. Biomed Res Int.
2013:2152832013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Mosser DM and Edwards JP: Exploring the
full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:958–969.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Pello OM, De Pizzol M, Mirolo M, et al:
Role of c-MYC in alternative activation of human macrophages and
tumor-associated macrophage biology. Blood. 119:411–421. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Ruffell B, Affara NI and Coussens LM:
Differential macrophage programming in the tumor microenvironment.
Trends Immunol. 33:119–126. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena
P, Vecchi A and Locati M: The chemokine system in diverse forms of
macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 25:677–686.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Kim S, Takahashi H, Lin WW, et al:
Carcinoma-produced factors activate myeloid cells through TLR2 to
stimulate metastasis. Nature. 457:102–106. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Rogers TL and Holen I: Tumour macrophages
as potential targets of bisphosphonates. J Transl Med. 9:1772011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Erreni M, Mantovani A and Allavena P:
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) and inflammation in colorectal
cancer. Cancer Microenviron. 4:141–154. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Sica A, Schioppa T, Mantovani A and
Allavena P: Tumour-associated macrophages are a distinct M2
polarised population promoting tumour progression: potential
targets of anti-cancer therapy. Eur J Cancer. 42:717–727. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Barbera-Guillem E, Nyhus JK, Wolford CC,
Friece CR and Sampsel JW: Vascular endothelial growth factor
secretion by tumor-infiltrating macrophages essentially supports
tumor angiogenesis, and IgG immune complexes potentiate the
process. Cancer Res. 62:7042–7049. 2002.
|
|
30.
|
Pancione M, Forte N, Sabatino L, et al:
Reduced beta-catenin and peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor-gamma expression levels are associated with colorectal
cancer metastatic progression: correlation with tumor-associated
macrophages, cyclooxygenase 2, and patient outcome. Hum Pathol.
40:714–725. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31.
|
Bailey C, Negus R, Morris A, et al:
Chemokine expression is associated with the accumulation of tumour
associated macrophages (TAMs) and progression in human colorectal
cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis. 24:121–130. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Algars A, Irjala H, Vaittinen S, et al:
Type and location of tumor-infiltrating macrophages and lymphatic
vessels predict survival of colorectal cancer patients. Int J
Cancer. 131:864–873. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Forssell J, Oberg A, Henriksson ML,
Stenling R, Jung A and Palmqvist R: High macrophage infiltration
along the tumor front correlates with improved survival in colon
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:1472–1479. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Zhou Q, Peng RQ, Wu XJ, et al: The density
of macrophages in the invasive front is inversely correlated to
liver metastasis in colon cancer. J Transl Med. 8:132010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Herrera M, Herrera A, Dominguez G, et al:
Cancer-associated fibroblast and M2 macrophage markers together
predict outcome in colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Sci.
104:437–444. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Recalcati S, Locati M, Marini A, et al:
Differential regulation of iron homeostasis during human macrophage
polarized activation. Eur J Immunol. 40:824–835. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Jedinak A, Dudhgaonkar S and Sliva D:
Activated macrophages induce metastatic behavior of colon cancer
cells. Immunobiology. 215:242–249. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Park EK, Jung HS, Yang HI, Yoo MC, Kim C
and Kim KS: Optimized THP-1 differentiation is required for the
detection of responses to weak stimuli. Inflamm Res. 56:45–50.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Lolmede K, Campana L, Vezzoli M, et al:
Inflammatory and alternatively activated human macrophages attract
vessel-associated stem cells, relying on separate HMGB1- and
MMP-9-dependent pathways. J Leukoc Biol. 85:779–787. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Sica A, Larghi P, Mancino A, et al:
Macrophage polarization in tumour progression. Semin Cancer Biol.
18:349–355. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Gordon S and Martinez FO: Alternative
activation of macrophages: mechanism and functions. Immunity.
32:593–604. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Kwan WH, Boix C, Gougelet N, Fridman WH
and Mueller CG: LPS induces rapid IL-10 release by
M-CSF-conditioned tolerogenic dendritic cell precursors. J Leukoc
Biol. 82:133–141. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Park ES, Yoo JM, Yoo HS, Yoon DY, Yun YP
and Hong J: IL-32gamma enhances TNF-alpha-induced cell death in
colon cancer. Mol Carcinog. Dec 19–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
44.
|
Min HY, Chung HJ, Kim EH, Kim S, Park EJ
and Lee SK: Inhibition of cell growth and potentiation of tumor
necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha)-induced apoptosis by a
phenanthroindolizidine alkaloid antofine in human colon cancer
cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 80:1356–1364. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45.
|
Rivas MA, Carnevale RP, Proietti CJ, et
al: TNF alpha acting on TNFR1 promotes breast cancer growth via
p42/P44 MAPK, JNK, Akt and NF-kappa B-dependent pathways. Exp Cell
Res. 314:509–529. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Gasperini S, Marchi M, Calzetti F, et al:
Gene expression and production of the monokine induced by IFN-gamma
(MIG), IFN-inducible T cell alpha chemoattractant (I-TAC), and
IFN-gamma-inducible protein-10 (IP-10) chemokines by human
neutrophils. J Immunol. 162:4928–4937. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Erreni M, Bianchi P, Laghi L, et al:
Expression of chemokines and chemokine receptors in human colon
cancer. Methods Enzymol. 460:105–121. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Han X, Wu Z, Di J, et al: CXCL9 attenuated
chemo-therapy-induced intestinal mucositis by inhibiting
proliferation and reducing apoptosis. Biomed Pharmacother.
65:547–554. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Andersson A, Srivastava MK, Harris-White
M, et al: Role of CXCR3 ligands in IL-7/IL-7R alpha-Fc-mediated
antitumor activity in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 17:3660–3672.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|