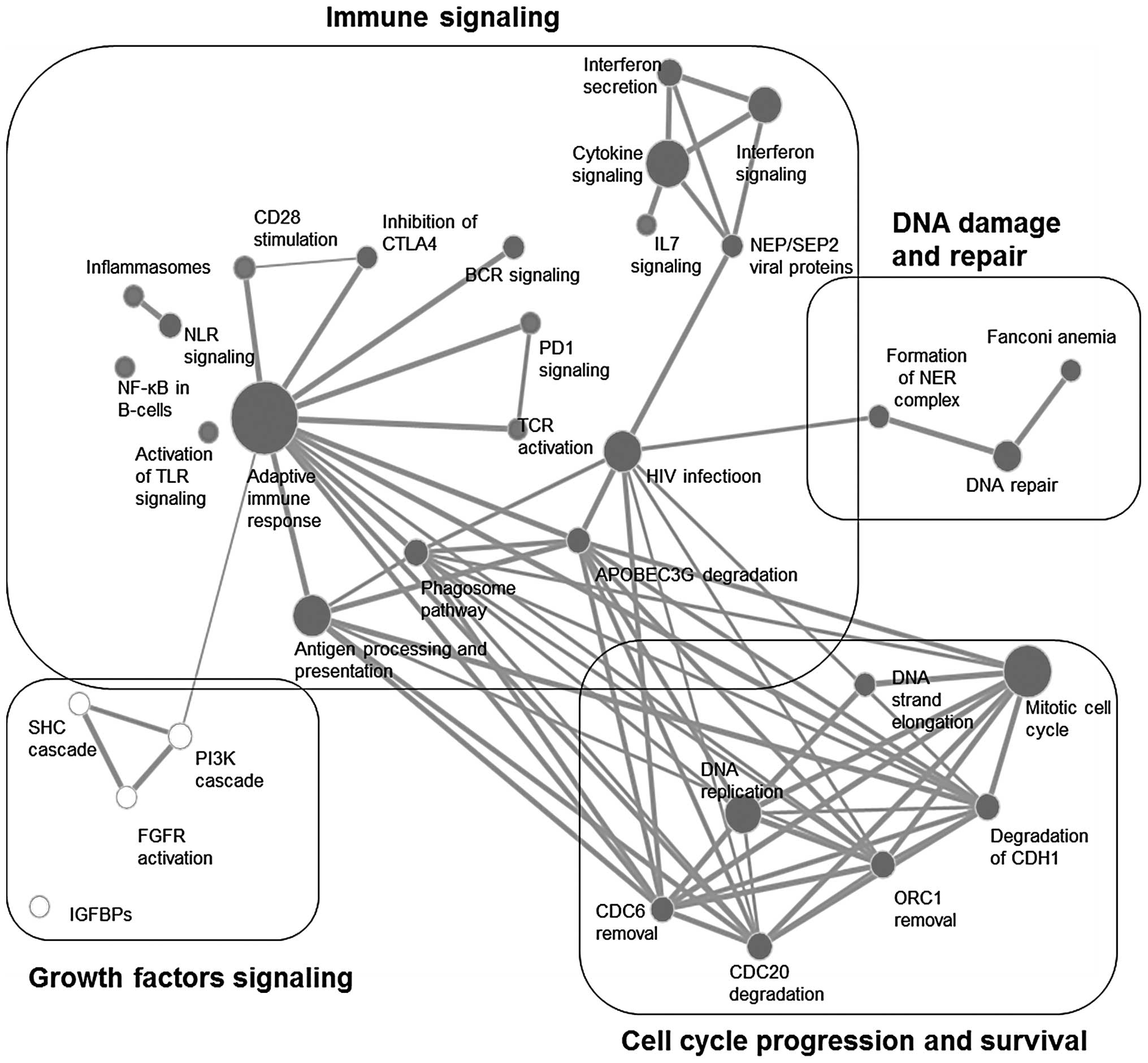
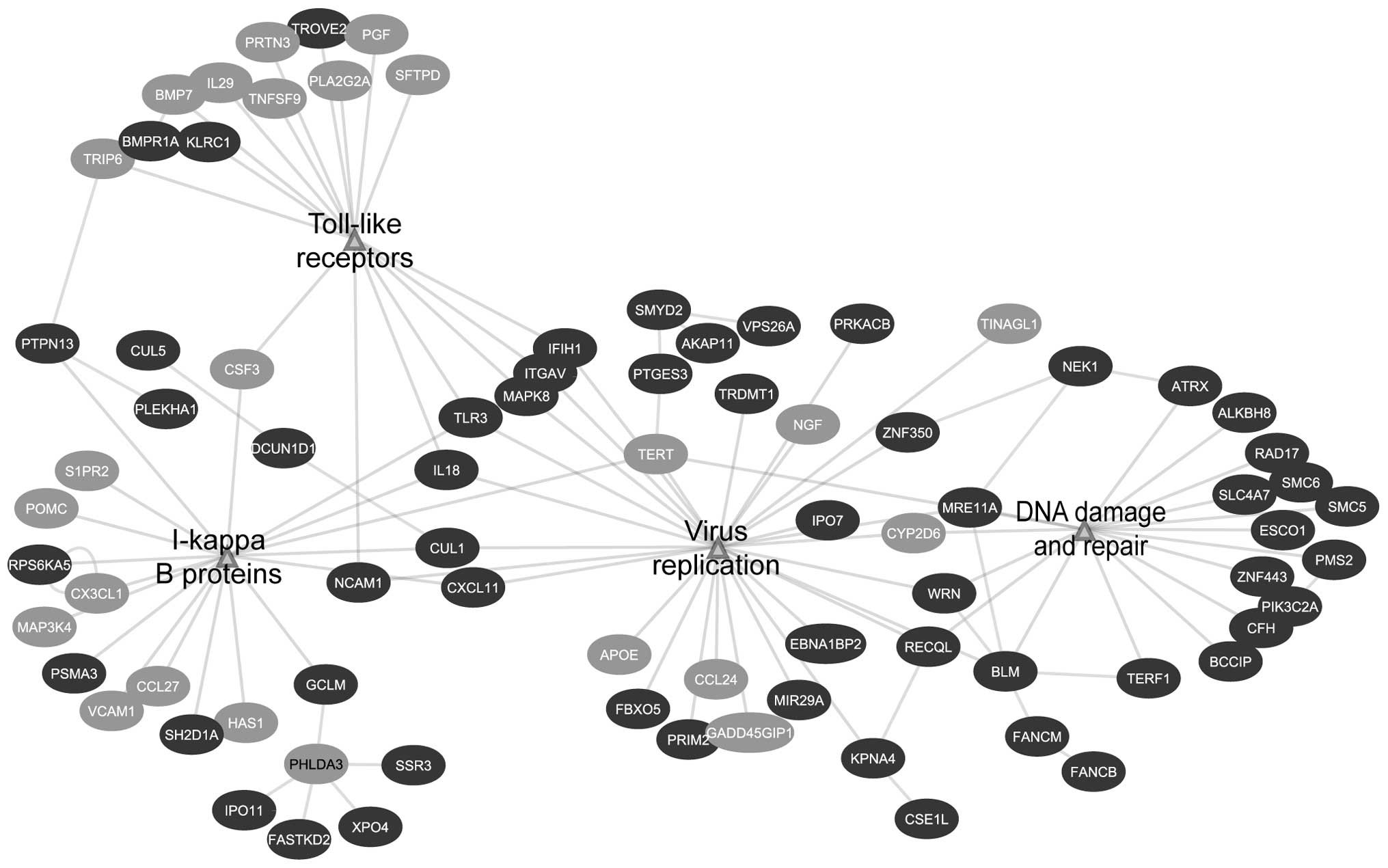
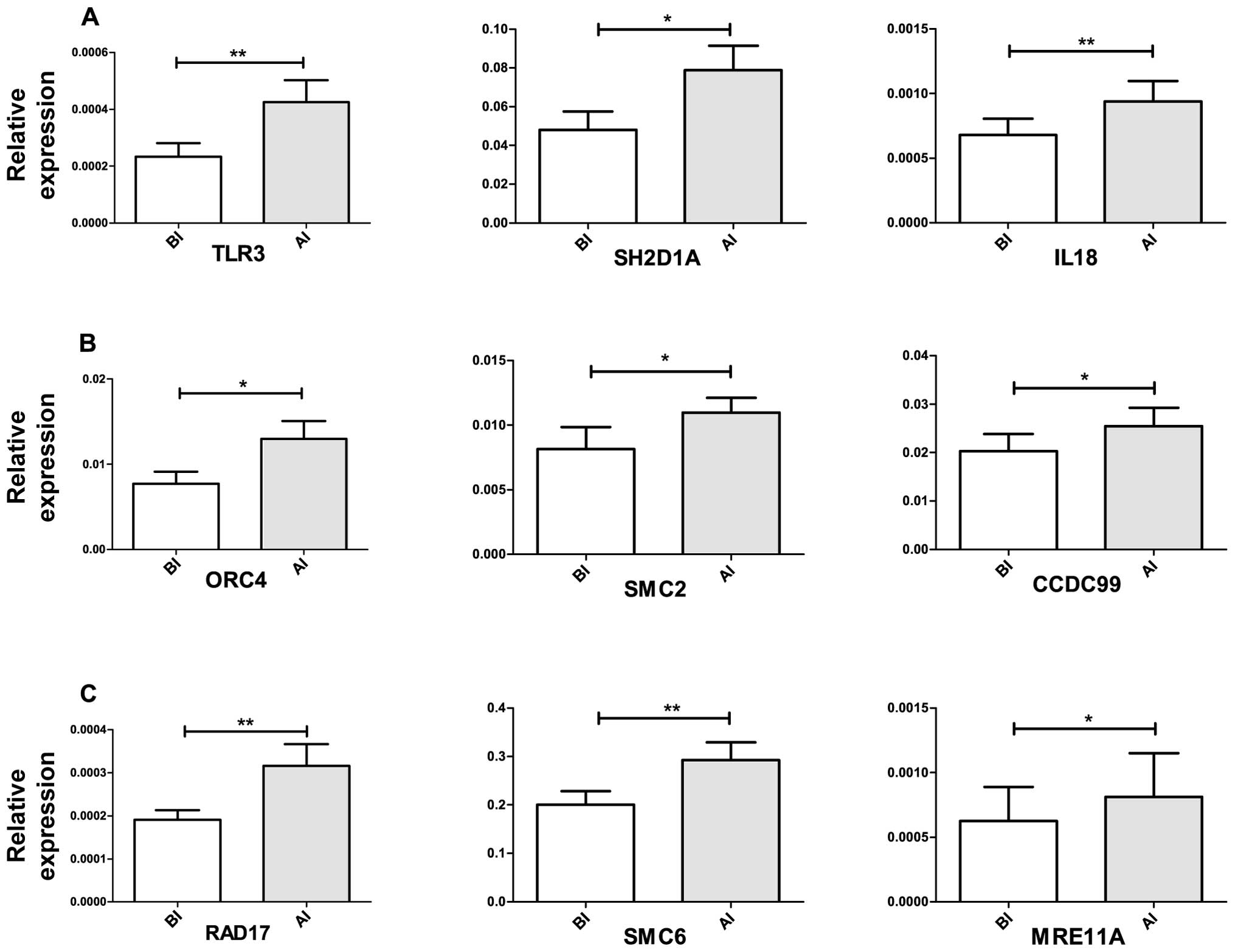
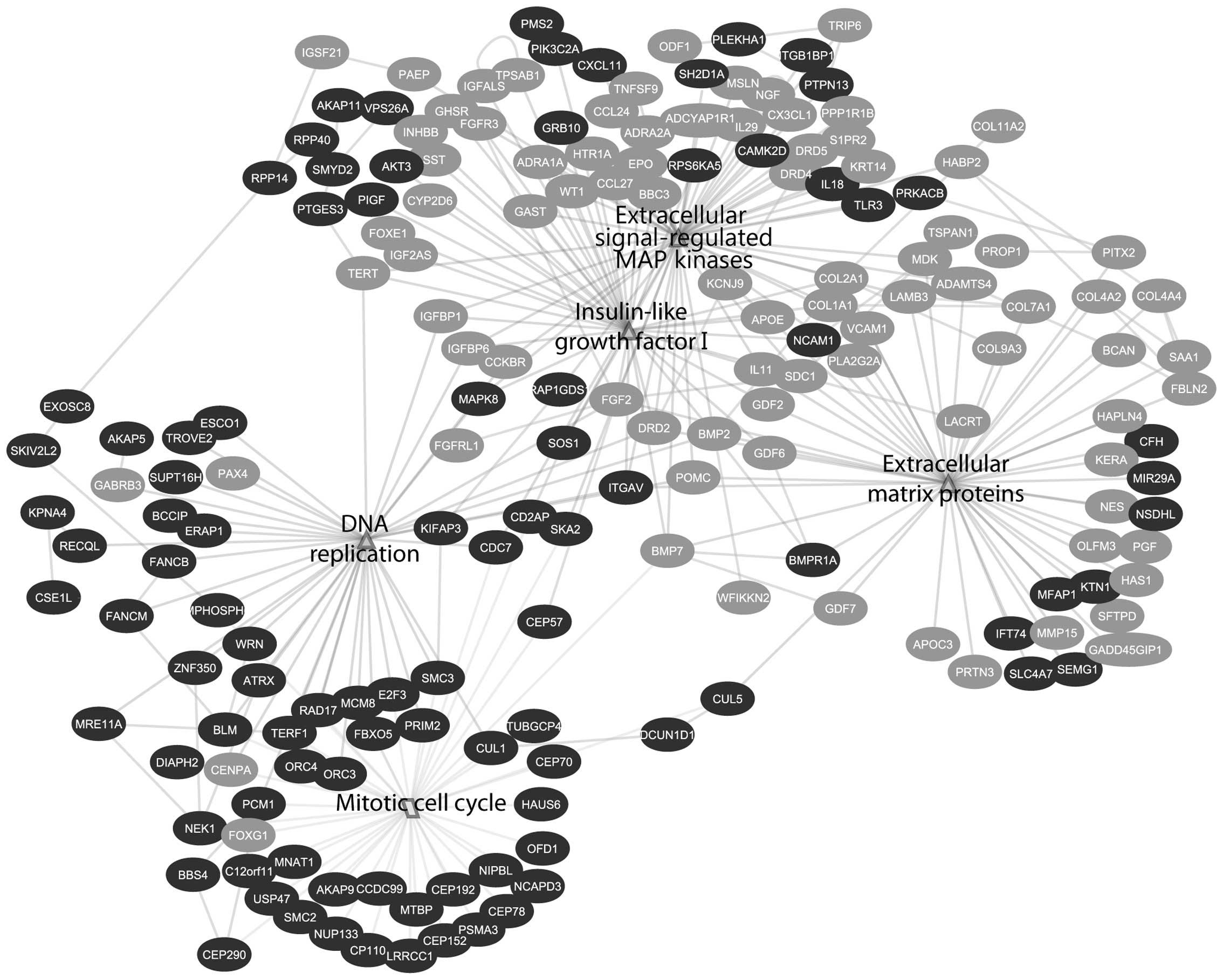
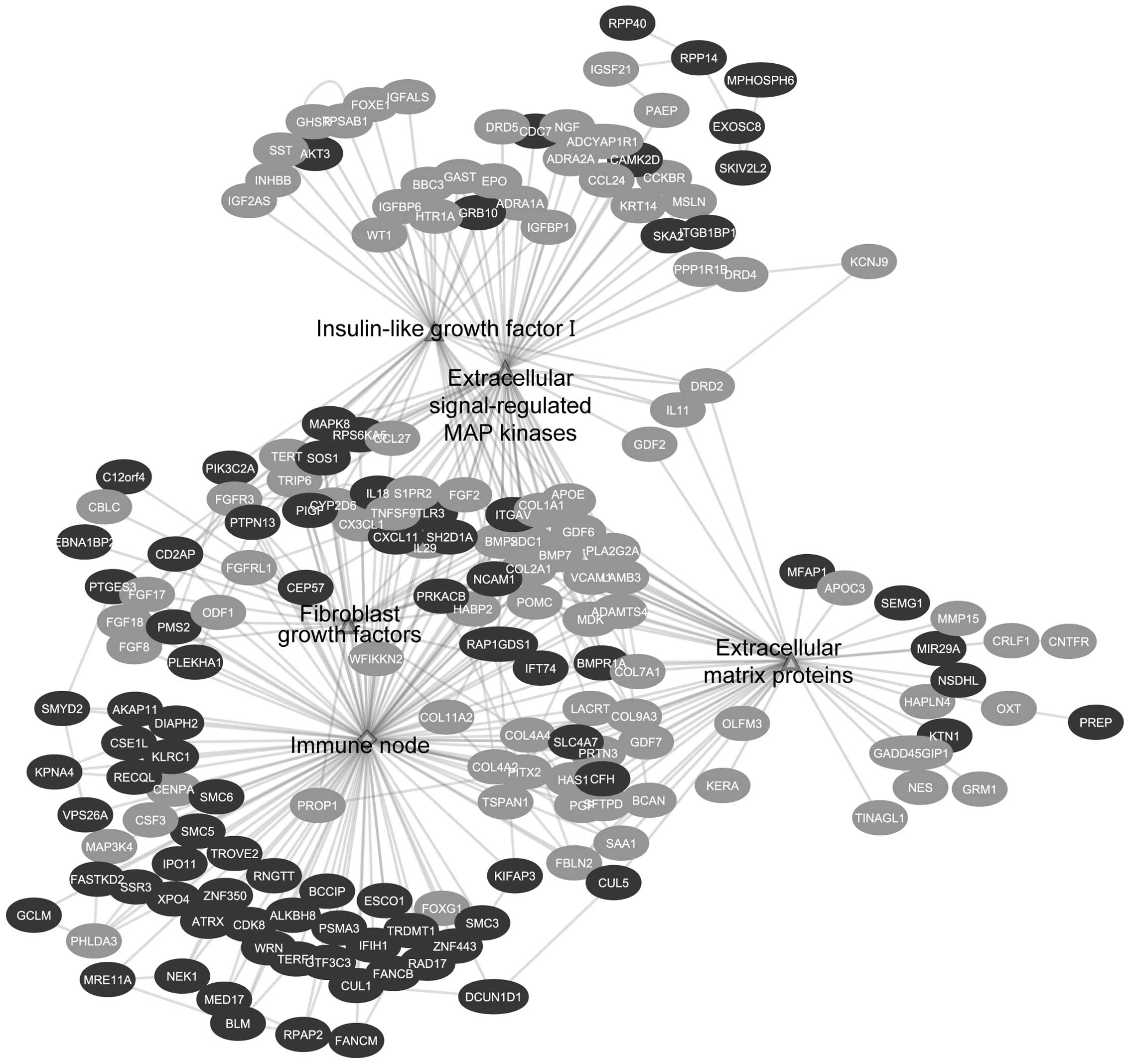
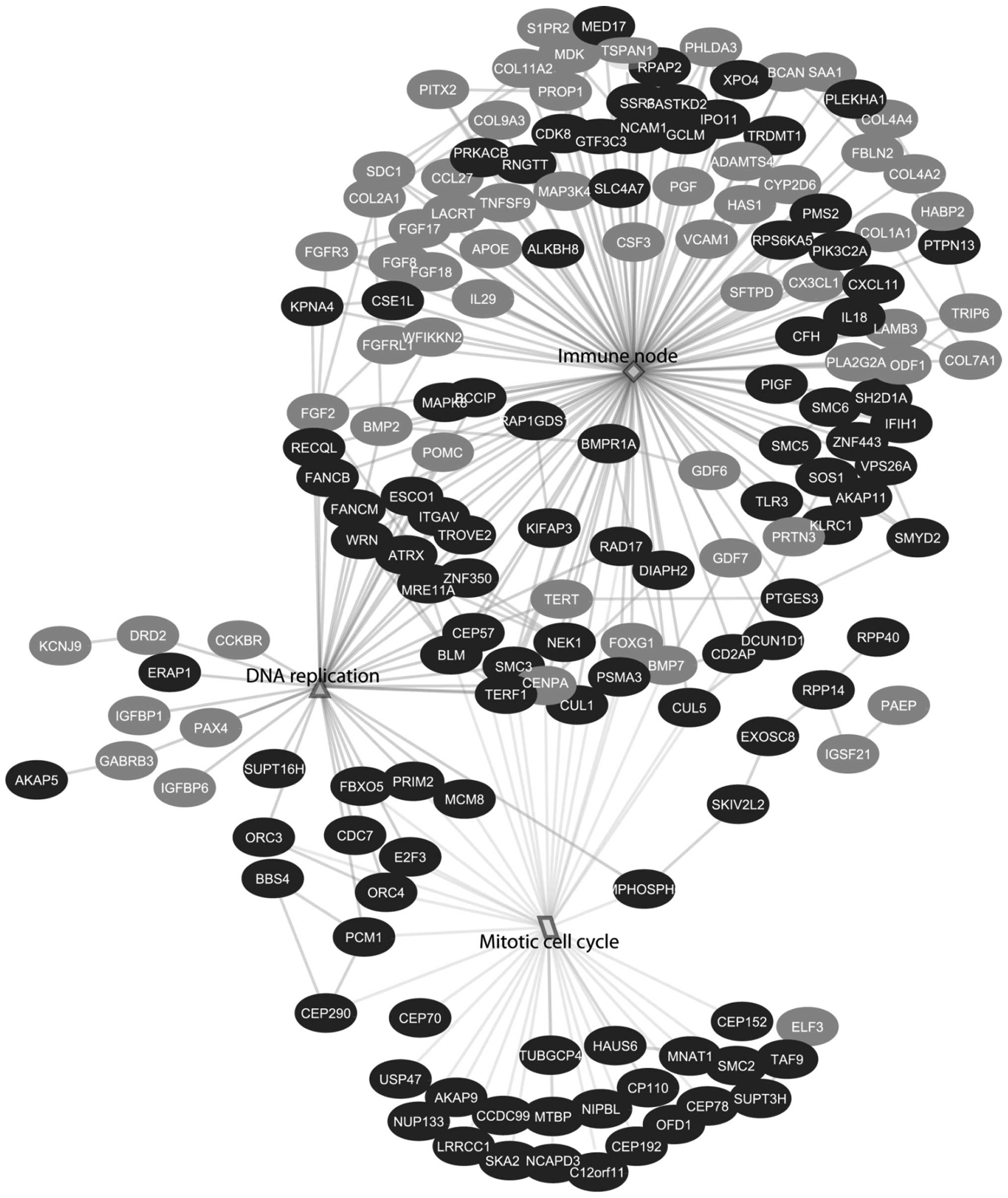
|
1.
|
Ahmad SS, Duke S, Jena R, Williams MV and
Burnet NG: Advances in radiotherapy. BMJ. 345:e77652012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Hall EJ and Wuu CS: Radiation-induced
second cancers: the impact of 3D-CRT and IMRT. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 56:83–88. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Purdy JA: Dose to normal tissues outside
the radiation therapy patient’s treated volume: a review of
different radiation therapy techniques. Health Phys. 95:666–676.
2008.
|
|
4.
|
Hall EJ: Intensity-modulated radiation
therapy, protons, and the risk of second cancers. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 65:1–7. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Ruben JD, Davis S, Evans C, et al: The
effect of intensity-modulated radiotherapy on radiation-induced
second malignancies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 70:1530–1536.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Ost P, Speleers B, De Meerleer G, et al:
Volumetric arc therapy and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for
primary prostate radiotherapy with simultaneous integrated boost to
intraprostatic lesion with 6 and 18 MV: a planning comparison
study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 79:920–926. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Murray L, Henry A, Hoskin P, Siebert FA
and Venselaar J: BRAPHYQS/PROBATE group of the GEC ESTRO: Second
primary cancers after radiation for prostate cancer: a review of
data from planning studies. Radiat Oncol. 8:1722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Wyrobek AJ, Manohar CF, Krishnan VV, et
al: Low dose radiation response curves, networks and pathways in
human lymphoblastoid cells exposed from 1 to 10 cGy of acute gamma
radiation. Mutat Res. 722:119–130. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Yunis R, Albrecht H, Kalanetra KM, Wu S
and Rocke DM: Genomic characterization of a three-dimensional skin
model following exposure to ionizing radiation. J Radiat Res.
53:860–875. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Ray M, Yunis R, Chen X and Rocke DM:
Comparison of low and high dose ionising radiation using
topological analysis of gene coexpression networks. BMC Genomics.
13:1902012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
El-Saghire H, Thierens H, Monsieurs P,
Michaux A, Vandevoorde C and Baatout S: Gene set enrichment
analysis highlights different gene expression profiles in whole
blood samples X-irradiated with low and high doses. Int J Radiat
Biol. 89:628–638. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Pernot E, Hall J, Baatout S, et al:
Ionizing radiation biomarkers for potential use in epidemiological
studies. Mutat Res. 751:258–286. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, et al:
Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for
interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Werbrouck J, De Ruyck K, Beels L, et al:
Prediction of late normal tissue complications in RT treated
gynaecological cancer patients: potential of the gamma-H2AX foci
assay and association with chromosomal radiosensitivity. Oncol Rep.
23:571–578. 2010.
|
|
15.
|
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F, et al:
Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density
oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 4:249–264.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16.
|
Merico D, Isserlin R, Stueker O, Emili A
and Bader GD: Enrichment map: a network-based method for gene-set
enrichment visualization and interpretation. PLoS One.
5:e139842010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Pfaffl MW: A new mathematical model for
relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res.
29:e452001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Oakley JD, Taher MM, Hershey CM, Aggarwal
PC, Estwani IB and Valerie K: Triggering of apoptosis is not
sufficient to induce human immunodeficiency virus gene expression.
IUBMB Life. 55:415–427. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Nowarski R, Wilner OI, Cheshin O, et al:
APOBEC3G enhances lymphoma cell radioresistance by promoting
cytidine deaminase-dependent DNA repair. Blood. 120:366–375. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Zhu J, Ghosh A, Coyle EM, et al:
Differential effects of phenethyl isothiocyanate and
D,L-sulforaphane on TLR3 signaling. J Immunol. 190:4400–4407. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Amarante MK and Watanabe MA: Toll-like
receptor 3: involvement with exogenous and endogenous RNA. Int Rev
Immunol. 29:557–573. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Bauernfeind F, Ablasser A, Kim S, Bartok E
and Hornung V: An unexpected role for RNA in the recognition of DNA
by the innate immune system. RNA Biol. 7:151–157. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Vercammen E, Staal J and Beyaert R:
Sensing of viral infection and activation of innate immunity by
toll-like receptor 3. Clin Microbiol Rev. 21:13–25. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Chuang HC, Wang JM, Hsieh WC, Chang Y and
Su IJ: Up-regulation of activating transcription factor-5
suppresses SAP expression to activate T cells in hemophagocytic
syndrome associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection and immune
disorders. Am J Pathol. 173:1397–1405. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25.
|
Surjit M, Varshney B and Lal SK: The ORF2
glycoprotein of hepatitis E virus inhibits cellular NF-kappaB
activity by blocking ubiquitination mediated proteasomal
degradation of IkappaBalpha in human hepatoma cells. BMC Biochem.
13:72012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: NF-kappaB, the
first quarter-century: remarkable progress and outstanding
questions. Genes Dev. 26:203–234. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Liu SZ, Jin SZ, Liu XD and Sun YM: Role of
CD28/B7 costimulation and IL-12/IL-10 interaction in the
radiation-induced immune changes. BMC Immunol. 2:82001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Shan YX, Jin SZ, Liu XD, Liu Y and Liu SZ:
Ionizing radiation stimulates secretion of pro-inflammatory
cytokines: dose-response relationship, mechanisms and implications.
Radiat Environ Biophys. 46:21–29. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Riley JL: PD-1 signaling in primary T
cells. Immunol Rev. 229:114–125. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Kim SJ, Dix DJ, Thompson KE, et al:
Effects of storage, RNA extraction, genechip type, and donor sex on
gene expression profiling of human whole blood. Clin Chem.
53:1038–1045. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Liang X, So YH, Cui J, et al: The low-dose
ionizing radiation stimulates cell proliferation via activation of
the MAPK/ERK pathway in rat cultured mesenchymal stem cells. J
Radiat Res. 52:380–386. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Sofia Vala I, Martins LR, Imaizumi N, et
al: Low doses of ionizing radiation promote tumor growth and
metastasis by enhancing angiogenesis. PLoS One.
5:e112222010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Marcinkowska E, Superat K and Wiedlocha A:
FGF-1 as a possible carrier for targeted drug delivery. Oncol Res.
16:27–34. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Shi M, Lin TH, Appell KC and Berg LJ: Cell
cycle progression following naive T cell activation is independent
of Jak3/common gamma-chain cytokine signals. J Immunol.
183:4493–4501. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Fernet M, Megnin-Chanet F, Hall J and
Favaudon V: Control of the G2/M checkpoints after exposure to low
doses of ionising radiation: implications for
hyper-radiosensitivity. DNA Repair. 9:48–57. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Wood ME, Vogel V, Ng A, Foxhall L, Goodwin
P and Travis LB: Second malignant neoplasms: assessment and
strategies for risk reduction. J Clin Oncol. 30:3734–3745. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Rashi-Elkeles S, Elkon R, Shavit S, et al:
Transcriptional modulation induced by ionizing radiation: p53
remains a central player. Mol Oncol. 5:336–348. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Aviv Y and Kirshenbaum LA: Novel
phosphatase PHLPP-1 regulates mitochondrial Akt activity and
cardiac cell survival. Circ Res. 107:448–450. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Alam MJ, Fatima N, Devi GR, Ravins and
Singh RK: The enhancement of stability of p53 in MTBP induced
p53-MDM2 regulatory network. Biosystems. 110:74–83. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Newhauser WD and Durante M: Assessing the
risk of second malignancies after modern radiotherapy. Nat Rev
Cancer. 11:438–448. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|