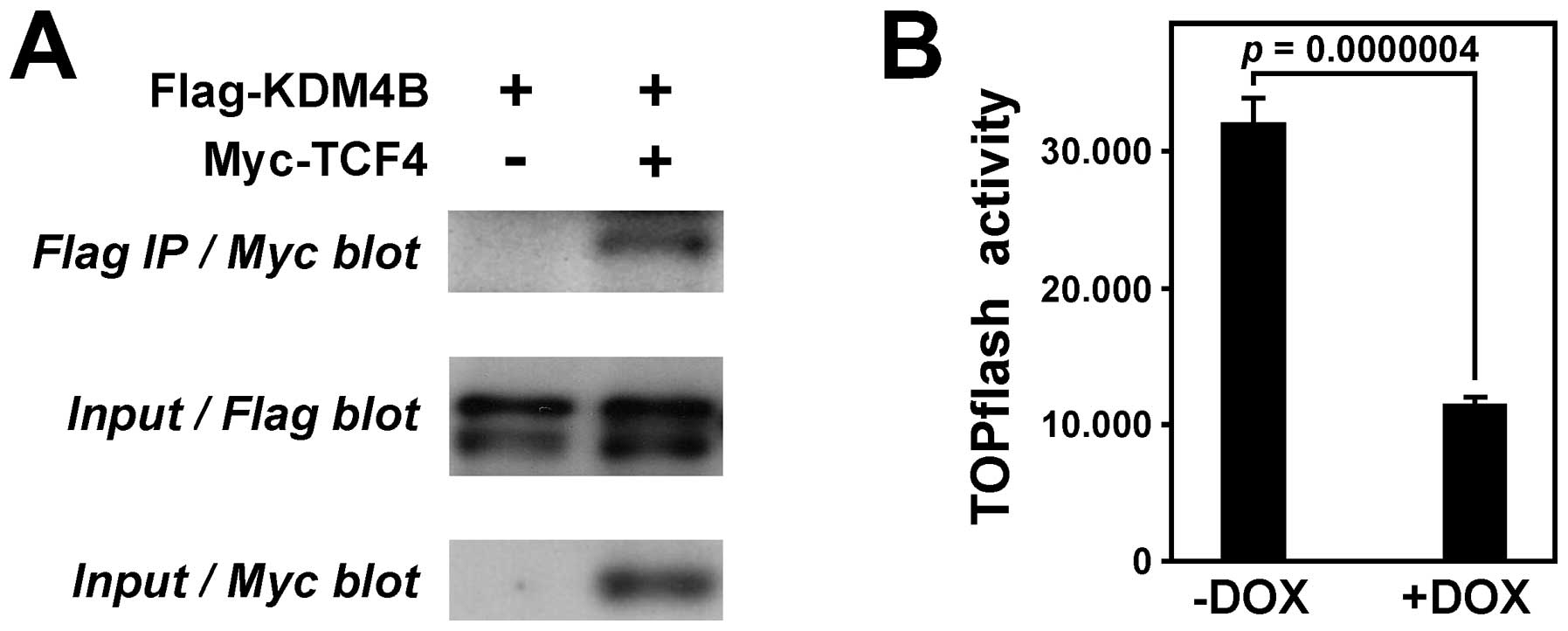
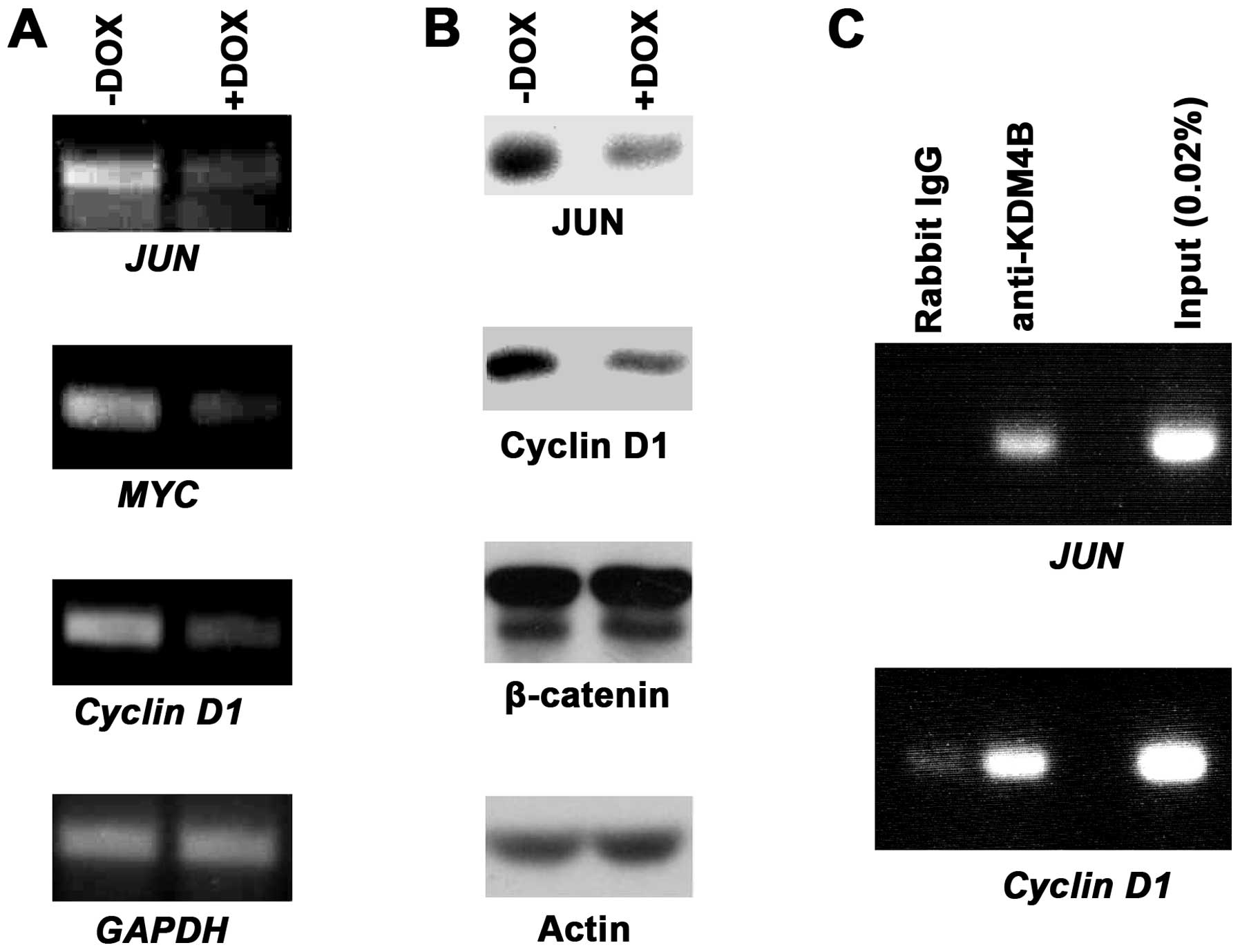
|
1.
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Clevers H: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in
development and disease. Cell. 127:469–480. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Chi P, Allis CD and Wang GG: Covalent
histone modifications--miswritten, misinterpreted and mis-erased in
human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:457–469. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Kulis M and Esteller M: DNA methylation
and cancer. Adv Genet. 70:27–56. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Dawson MA and Kouzarides T: Cancer
epigenetics: from mechanism to therapy. Cell. 150:12–27. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Black JC, Van Rechem C and Whetstine JR:
Histone lysine methylation dynamics: establishment, regulation, and
biological impact. Mol Cell. 48:491–507. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Kooistra SM and Helin K: Molecular
mechanisms and potential functions of histone demethylases. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 13:297–311. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Berry WL and Janknecht R: KDM4/JMJD2
histone demethylases: epigenetic regulators in cancer cells. Cancer
Res. 73:2936–2942. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Whetstine JR, Nottke A, Lan F, Huarte M,
Smolikov S, Chen Z, Spooner E, Li E, Zhang G, Colaiacovo M and Shi
Y: Reversal of histone lysine trimethylation by the JMJD2 family of
histone demethylases. Cell. 125:467–481. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Cloos PA, Christensen J, Agger K, Maiolica
A, Rappsilber J, Antal T, Hansen KH and Helin K: The putative
oncogene GASC1 demethylates tri- and dimethylated lysine 9 on
histone H3. Nature. 442:307–311. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Klose RJ, Yamane K, Bae Y, Zhang D,
Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Wong J and Zhang Y: The
transcriptional repressor JHDM3A demethylates trimethyl histone H3
lysine 9 and lysine 36. Nature. 442:312–316. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12.
|
Fodor BD, Kubicek S, Yonezawa M,
O’Sullivan RJ, Sengupta R, Perez-Burgos L, Opravil S, Mechtler K,
Schotta G and Jenuwein T: Jmjd2b antagonizes H3K9 trimethylation at
pericentric heterochromatin in mammalian cells. Genes Dev.
20:1557–1562. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Shin S and Janknecht R: Diversity within
the JMJD2 histone demethylase family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
353:973–977. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Trojer P, Zhang J, Yonezawa M, Schmidt A,
Zheng H, Jenuwein T and Reinberg D: Dynamic histone H1 isotype 4
methylation and demethylation by histone lysine methyltransferase
G9a/KMT1C and the Jumonji domain-containing JMJD2/KDM4 proteins. J
Biol Chem. 284:8395–8405. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Weiss T, Hergeth S, Zeissler U, Izzo A,
Tropberger P, Zee BM, Dundr M, Garcia BA, Daujat S and Schneider R:
Histone H1 variant-specific lysine methylation by G9a/KMT1C and
Glp1/KMT1D. Epigenetics Chromatin. 3:72010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Liu G, Bollig-Fischer A, Kreike B, van de
Vijver MJ, Abrams J, Ethier SP and Yang ZQ: Genomic amplification
and oncogenic properties of the GASC1 histone demethylase gene in
breast cancer. Oncogene. 28:4491–4500. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Yang J, Jubb AM, Pike L, Buffa FM, Turley
H, Baban D, Leek R, Gatter KC, Ragoussis J and Harris AL: The
histone demethylase JMJD2B is regulated by estrogen receptor alpha
and hypoxia, and is a key mediator of estrogen induced growth.
Cancer Res. 70:6456–6466. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Kawazu M, Saso K, Tong KI, McQuire T, Goto
K, Son DO, Wakeham A, Miyagishi M, Mak TW and Okada H: Histone
demethylase JMJD2B functions as a co-factor of estrogen receptor in
breast cancer proliferation and mammary gland development. PLoS
One. 6:e178302011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Shi L, Sun L, Li Q, Liang J, Yu W, Yi X,
Yang X, Li Y, Han X, Zhang Y, Xuan C, Yao Z and Shang Y: Histone
demethylase JMJD2B coordinates H3K4/H3K9 methylation and promotes
hormonally responsive breast carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 108:7541–7546. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Berry WL, Shin S, Lightfoot SA and
Janknecht R: Oncogenic features of the JMJD2A histone demethylase
in breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 41:1701–1706. 2012.
|
|
21.
|
Gaughan L, Stockley J, Coffey K, O’Neill
D, Jones DL, Wade M, Wright J, Moore M, Tse S, Rogerson L and
Robson CN: KDM4B is a master regulator of the estrogen receptor
signalling cascade. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:6892–6904. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22.
|
Wissmann M, Yin N, Muller JM, Greschik H,
Fodor BD, Jenuwein T, Vogler C, Schneider R, Gunther T, Buettner R,
Metzger E and Schule R: Cooperative demethylation by JMJD2C and
LSD1 promotes androgen receptor-dependent gene expression. Nat Cell
Biol. 9:347–353. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23.
|
Shin S and Janknecht R: Activation of
androgen receptor by histone demethylases JMJD2A and JMJD2D.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 359:742–746. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Coffey K, Rogerson L, Ryan-Munden C,
Alkharaif D, Stockley J, Heer R, Sahadevan K, O’Neill D, Jones D,
Darby S, Staller P, Mantilla A, Gaughan L and Robson CN: The lysine
demethylase, KDM4B, is a key molecule in androgen receptor
signalling and turnover. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:4433–4446. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Pollard PJ, Loenarz C, Mole DR, McDonough
MA, Gleadle JM, Schofield CJ and Ratcliffe PJ: Regulation of
Jumonji-domain-containing histone demethylases by hypoxia-inducible
factor (HIF)-1alpha. Biochem J. 416:387–394. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Beyer S, Kristensen MM, Jensen KS,
Johansen JV and Staller P: The histone demethylases JMJD1A and
JMJD2B are transcriptional targets of hypoxia-inducible factor HIF.
J Biol Chem. 283:36542–36552. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27.
|
Kim TD, Oh S, Shin S and Janknecht R:
Regulation of tumor suppressor p53 and HCT116 cell physiology by
histone demethylase JMJD2D/KDM4D. PLoS One. 7:e346182012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28.
|
Oh S, Shin S, Lightfoot SA and Janknecht
R: 14-3-3 proteins modulate the ETS transcription factor ETV1 in
prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 73:5110–5119. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Mooney SM, Grande JP, Salisbury JL and
Janknecht R: Sumoylation of p68 and p72 RNA helicases affects
protein stability and transactivation potential. Biochemistry.
49:1–10. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Janknecht R: Regulation of the ER81
transcription factor and its coactivators by mitogen- and
stress-activated protein kinase 1 (MSK1). Oncogene. 22:746–755.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Dowdy SC, Mariani A and Janknecht R:
HER2/Neu- and TAK1-mediated up-regulation of the transforming
growth factor beta inhibitor Smad7 via the ETS protein ER81. J Biol
Chem. 278:44377–44384. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32.
|
Goel A and Janknecht R: Concerted
activation of ETS protein ER81 by p160 coactivators, the
acetyltransferase p300 and the receptor tyrosine kinase HER2/Neu. J
Biol Chem. 279:14909–14916. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Papoutsopoulou S and Janknecht R:
Phosphorylation of ETS transcription factor ER81 in a complex with
its coactivators CREB-binding protein and p300. Mol Cell Biol.
20:7300–7310. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Knebel J, De Haro L and Janknecht R:
Repression of transcription by TSGA/Jmjd1a, a novel interaction
partner of the ETS protein ER71. J Cell Biochem. 99:319–329. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Wu J and Janknecht R: Regulation of the
ETS transcription factor ER81 by the 90-kDa ribosomal S6 kinase 1
and protein kinase A. J Biol Chem. 277:42669–42679. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Rossow KL and Janknecht R: The Ewing’s
sarcoma gene product functions as a transcriptional activator.
Cancer Res. 61:2690–2695. 2001.
|
|
37.
|
Mooney SM, Goel A, D’Assoro AB, Salisbury
JL and Janknecht R: Pleiotropic effects of p300-mediated
acetylation on p68 and p72 RNA helicase. J Biol Chem.
285:30443–30452. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Goel A and Janknecht R:
Acetylation-mediated transcriptional activation of the ETS protein
ER81 by p300, P/CAF, and HER2/Neu. Mol Cell Biol. 23:6243–6254.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Oh S and Janknecht R: Histone demethylase
JMJD5 is essential for embryonic development. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 420:61–65. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Shin S, Oh S, An S and Janknecht R: ETS
variant 1 regulates matrix metalloproteinase-7 transcription in
LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 29:306–314. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
DiTacchio L, Bowles J, Shin S, Lim DS,
Koopman P and Janknecht R: Transcription factors ER71/ETV2 and SOX9
participate in a positive feedback loop in fetal and adult mouse
testis. J Biol Chem. 287:23657–23666. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Shin S, Kim TD, Jin F, van Deursen JM,
Dehm SM, Tindall DJ, Grande JP, Munz JM, Vasmatzis G and Janknecht
R: Induction of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and modulation
of androgen receptor by ETS variant 1/ETS-related protein 81.
Cancer Res. 69:8102–8110. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43.
|
Kaiser S, Park YK, Franklin JL, Halberg
RB, Yu M, Jessen WJ, Freudenberg J, Chen X, Haigis K, Jegga AG,
Kong S, Sakthivel B, Xu H, Reichling T, Azhar M, Boivin GP, Roberts
RB, Bissahoyo AC, Gonzales F, Bloom GC, Eschrich S, Carter SL,
Aronow JE, Kleimeyer J, Kleimeyer M, Ramaswamy V, Settle SH, Boone
B, Levy S, Graff JM, Doetschman T, Groden J, Dove WF, Threadgill
DW, Yeatman TJ, Coffey RJ Jr and Aronow BJ: Transcriptional
recapitulation and subversion of embryonic colon development by
mouse colon tumor models and human colon cancer. Genome Biol.
8:R1312007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44.
|
Kurashina K, Yamashita Y, Ueno T, Koinuma
K, Ohashi J, Horie H, Miyakura Y, Hamada T, Haruta H, Hatanaka H,
Soda M, Choi YL, Takada S, Yasuda Y, Nagai H and Mano H: Chromosome
copy number analysis in screening for prognosis-related genomic
regions in colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 99:1835–1840. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Yap KL and Zhou MM: Keeping it in the
family: diverse histone recognition by conserved structural folds.
Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 45:488–505. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Mosimann C, Hausmann G and Basler K:
Beta-catenin hits chromatin: regulation of Wnt target gene
activation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:276–286. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48.
|
He TC, Sparks AB, Rago C, Hermeking H,
Zawel L, da Costa LT, Morin PJ, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW:
Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science.
281:1509–1512. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Mann B, Gelos M, Siedow A, Hanski ML,
Gratchev A, Ilyas M, Bodmer WF, Moyer MP, Riecken EO, Buhr HJ and
Hanski C: Target genes of beta-catenin-T
cell-factor/lymphoid-enhancer-factor signaling in human colorectal
carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:1603–1608. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50.
|
Shtutman M, Zhurinsky J, Simcha I,
Albanese C, D’Amico M, Pestell R and Ben-Ze’ev A: The Cyclin D1
gene is a target of the beta-catenin/LEF-1 pathway. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 96:5522–5527. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Tetsu O and McCormick F: Beta-catenin
regulates expression of Cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature.
398:422–426. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Kouzarides T: Chromatin modifications and
their function. Cell. 128:693–705. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Daujat S, Zeissler U, Waldmann T, Happel N
and Schneider R: HP1 binds specifically to Lys26-methylated histone
H1.4, whereas simultaneous Ser27 phosphorylation blocks HP1
binding. J Biol Chem. 280:38090–38095. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Wagner EJ and Carpenter PB: Understanding
the language of Lys36 methylation at histone H3. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 13:115–126. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55.
|
Eilers M and Eisenman RN: Myc’s broad
reach. Genes Dev. 22:2755–2766. 2008.
|
|
56.
|
Eferl R and Wagner EF: AP-1: a
double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:859–868.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57.
|
Smith DR, Myint T and Goh HS:
Over-expression of the c-myc proto-oncogene in colorectal
carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 68:407–413. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58.
|
Magrisso IJ, Richmond RE, Carter JH, Pross
CB, Gilfillen RA and Carter HW: Immunohistochemical detection of
RAS, JUN, FOS, and p53 oncoprotein expression in human colorectal
adenomas and carcinomas. Lab Invest. 69:674–681. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59.
|
Nateri AS, Spencer-Dene B and Behrens A:
Interaction of phosphorylated c-Jun with TCF4 regulates intestinal
cancer development. Nature. 437:281–285. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60.
|
Gan XQ, Wang JY, Xi Y, Wu ZL, Li YP and Li
L: Nuclear Dvl, c-Jun, beta-catenin, and TCF form a complex leading
to stabilization of beta-catenin-TCF interaction. J Cell Biol.
180:1087–1100. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61.
|
Suto R, Tominaga K, Mizuguchi H, Sasaki E,
Higuchi K, Kim S, Iwao H and Arakawa T: Dominant-negative mutant of
c-Jun gene transfer: a novel therapeutic strategy for colorectal
cancer. Gene Ther. 11:187–193. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62.
|
Bartkova J, Lukas J, Strauss M and Bartek
J: The PRAD-1/Cyclin D1 oncogene product accumulates aberrantly in
a subset of colorectal carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 58:568–573. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63.
|
Hulit J, Wang C, Li Z, Albanese C, Rao M,
Di Vizio D, Shah S, Byers SW, Mahmood R, Augenlicht LH, Russell R
and Pestell RG: Cyclin D1 genetic heterozygosity regulates colonic
epithelial cell differentiation and tumor number in ApcMin mice.
Mol Cell Biol. 24:7598–7611. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64.
|
Fu L, Chen L, Yang J, Ye T, Chen Y and
Fang J: HIF-1alpha-induced histone demethylase JMJD2B contributes
to the malignant phenotype of colorectal cancer cells via an
epigenetic mechanism. Carcinogenesis. 33:1664–1673. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65.
|
Luo W, Chang R, Zhong J, Pandey A and
Semenza GL: Histone demethylase JMJD2C is a coactivator for
hypoxia-inducible factor 1 that is required for breast cancer
progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:E3367–E3376. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66.
|
Kim TD, Shin S, Berry WL, Oh S and
Janknecht R: The JMJD2A demethylase regulates apoptosis and
proliferation in colon cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 113:1368–1376.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67.
|
Mallette FA, Mattiroli F, Cui G, Young LC,
Hendzel MJ, Mer G, Sixma TK and Richard S: RNF8- and
RNF168-dependent degradation of KDM4A/JMJD2A triggers 53BP1
recruitment to DNA damage sites. EMBO J. 31:1865–1878. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68.
|
Young LC, McDonald DW and Hendzel MJ:
Kdm4b histone demethylase is a DNA damage response protein and
confers a survival advantage following gamma-irradiation. J Biol
Chem. 288:21376–21388. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69.
|
Slee RB, Steiner CM, Herbert BS, Vance GH,
Hickey RJ, Schwarz T, Christan S, Radovich M, Schneider BP,
Schindelhauer D and Grimes BR: Cancer-associated alteration of
pericentromeric heterochromatin may contribute to chromosome
instability. Oncogene. 31:3244–3253. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70.
|
Toyokawa G, Cho HS, Iwai Y, Yoshimatsu M,
Takawa M, Hayami S, Maejima K, Shimizu N, Tanaka H, Tsunoda T,
Field HI, Kelly JD, Neal DE, Ponder BA, Maehara Y, Nakamura Y and
Hamamoto R: The histone demethylase JMJD2B plays an essential role
in human carcinogenesis through positive regulation of
cyclin-dependent kinase 6. Cancer Prev Res. 4:2051–2061. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71.
|
Dawson MA, Prinjha RK, Dittmann A,
Giotopoulos G, Bantscheff M, Chan WI, Robson SC, Chung CW, Hopf C,
Savitski MM, Huthmacher C, Gudgin E, Lugo D, Beinke S, Chapman TD,
Roberts EJ, Soden PE, Auger KR, Mirguet O, Doehner K, Delwel R,
Burnett AK, Jeffrey P, Drewes G, Lee K, Huntly BJ and Kouzarides T:
Inhibition of BET recruitment to chromatin as an effective
treatment for MLL-fusion leukaemia. Nature. 478:529–533. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72.
|
Zuber J, Shi J, Wang E, Rappaport AR,
Herrmann H, Sison EA, Magoon D, Qi J, Blatt K, Wunderlich M, Taylor
MJ, Johns C, Chicas A, Mulloy JC, Kogan SC, Brown P, Valent P,
Bradner JE, Lowe SW and Vakoc CR: RNAi screen identifies Brd4 as a
therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 478:524–528.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|