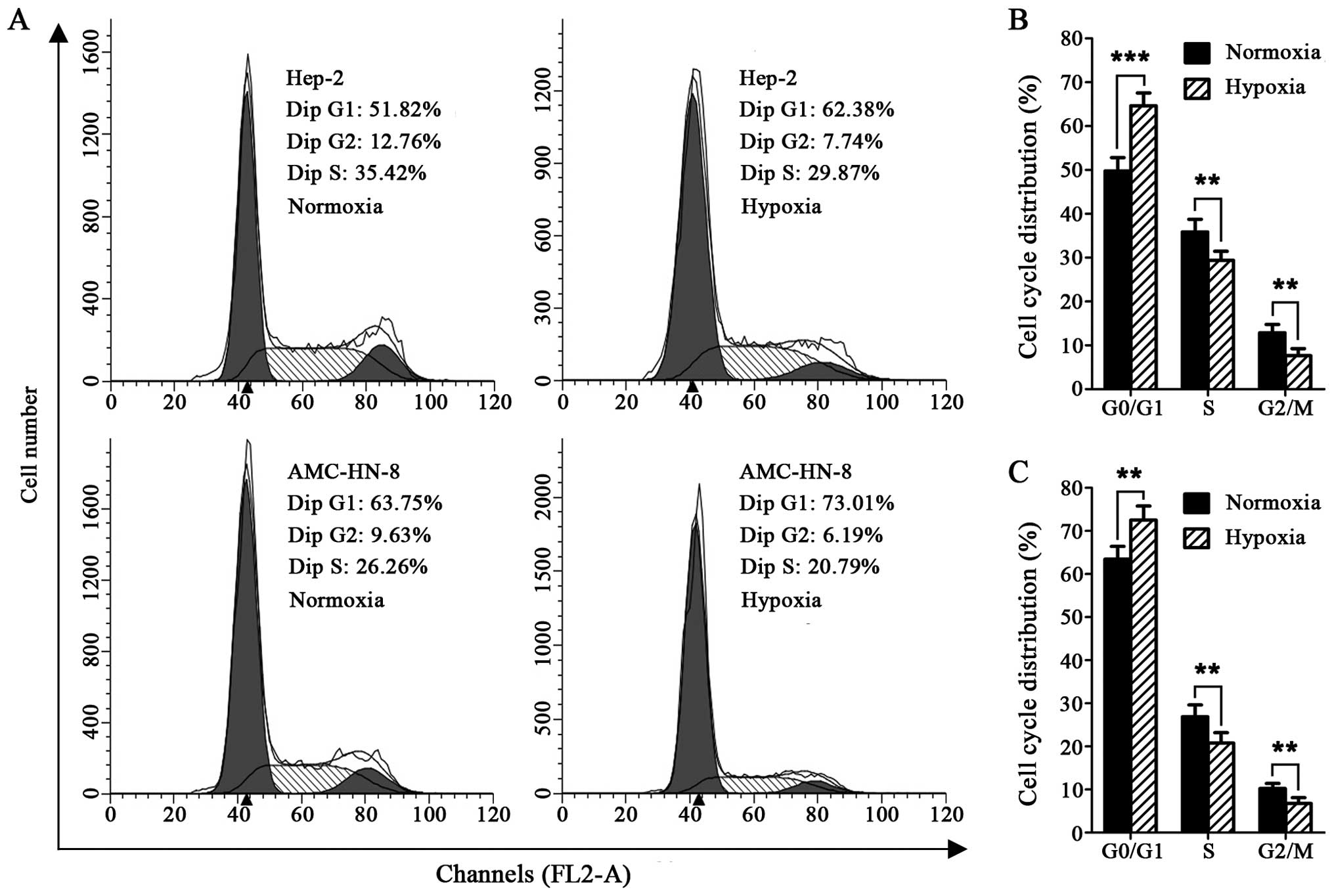
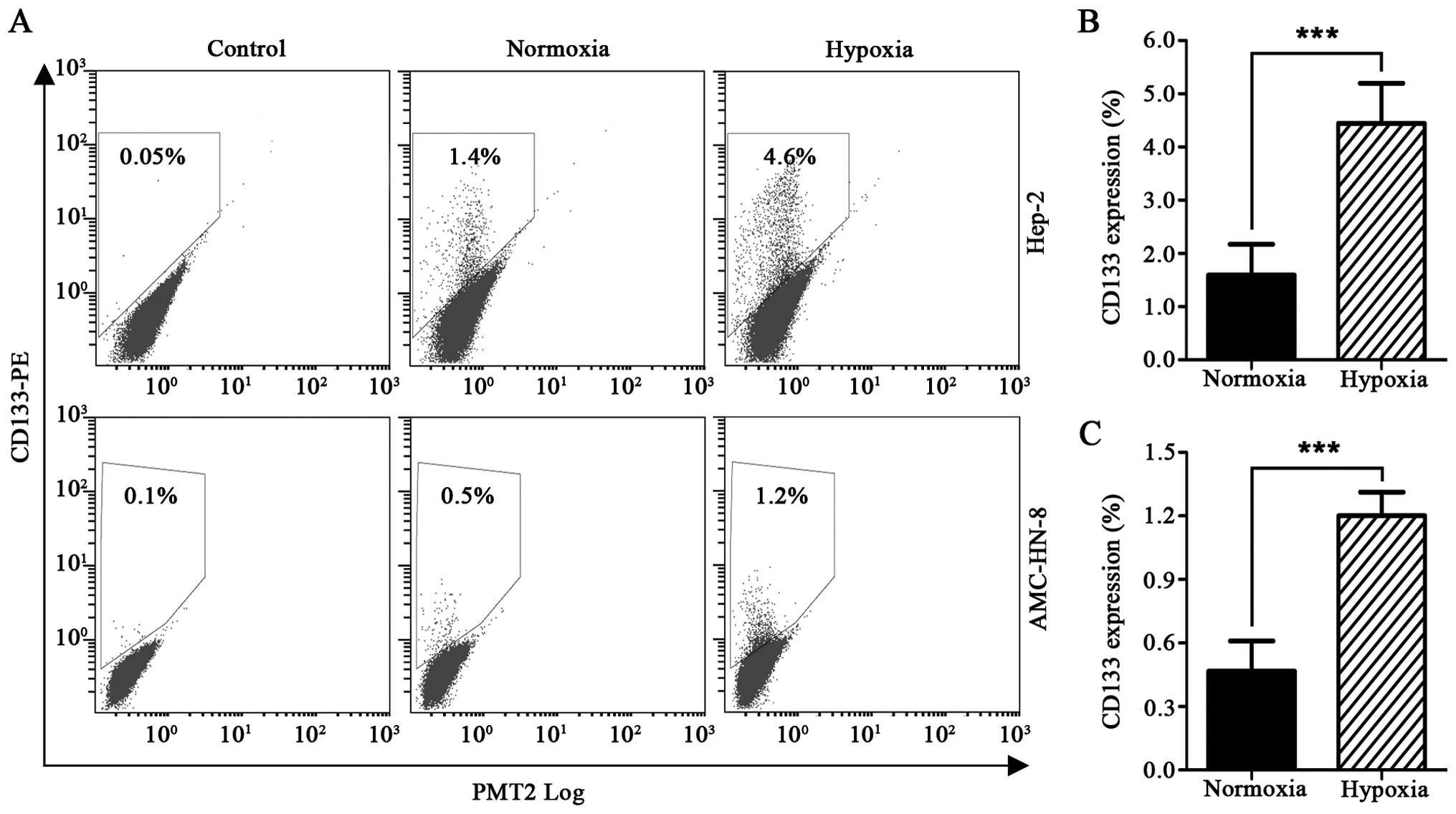
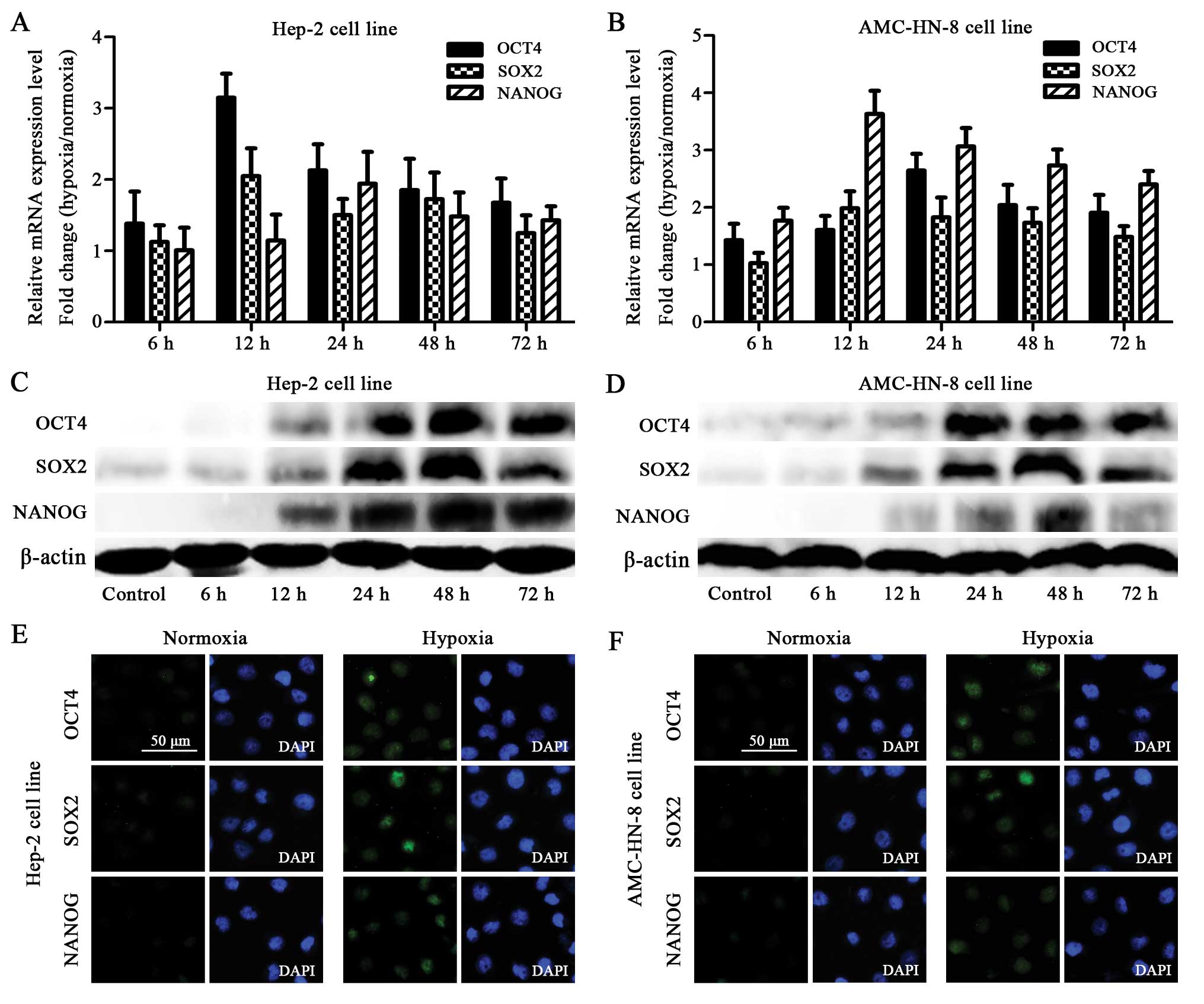
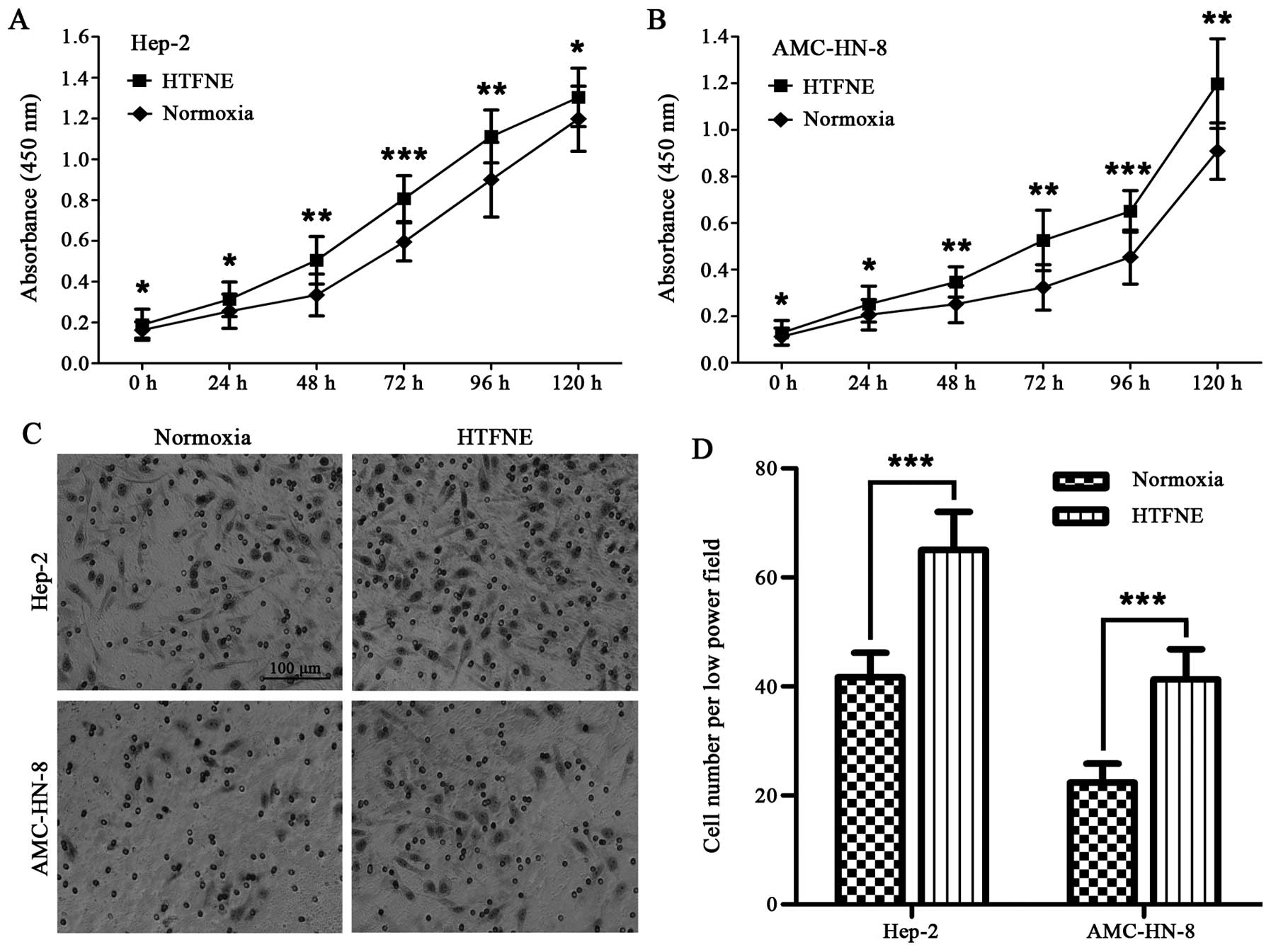
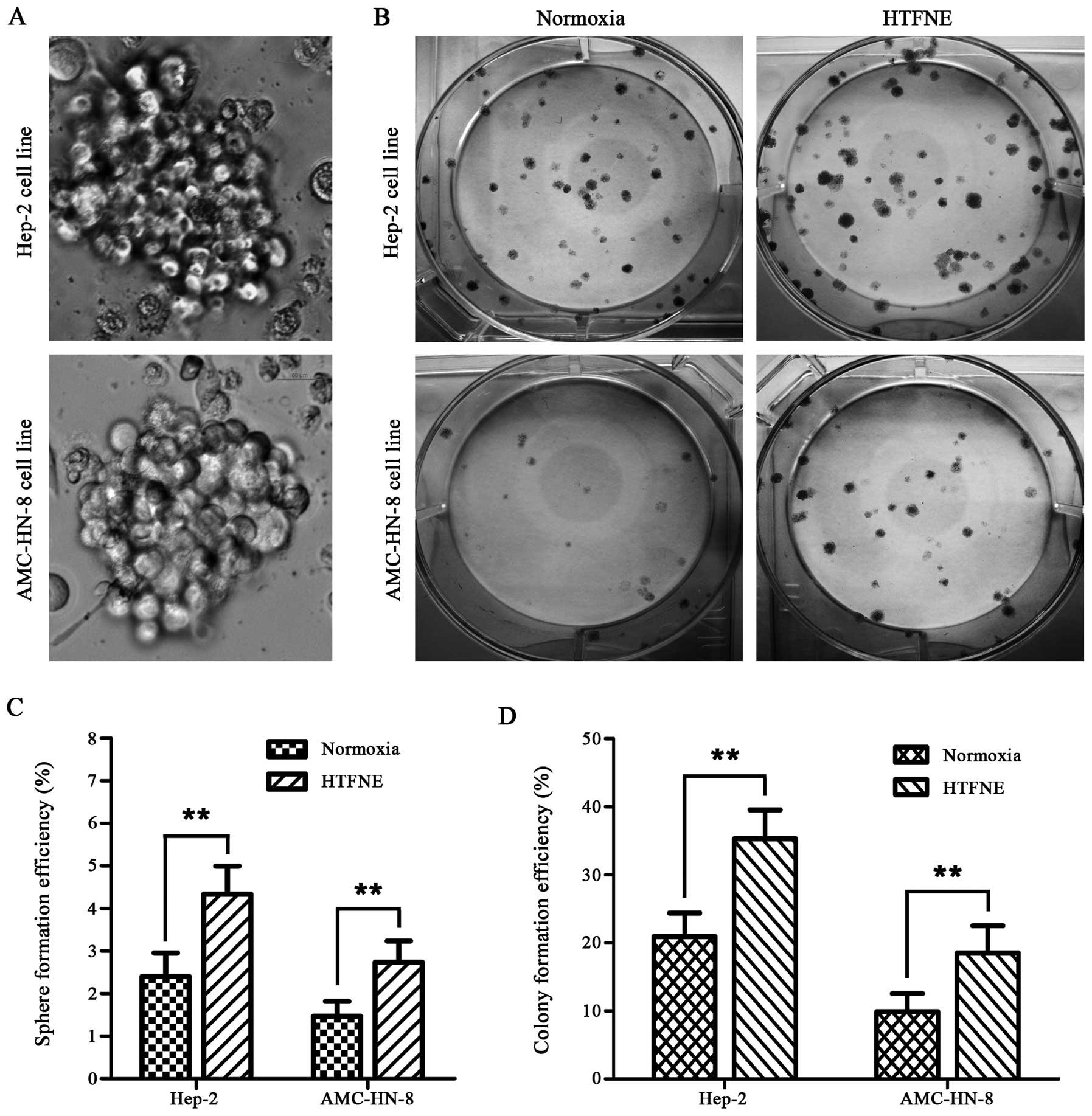
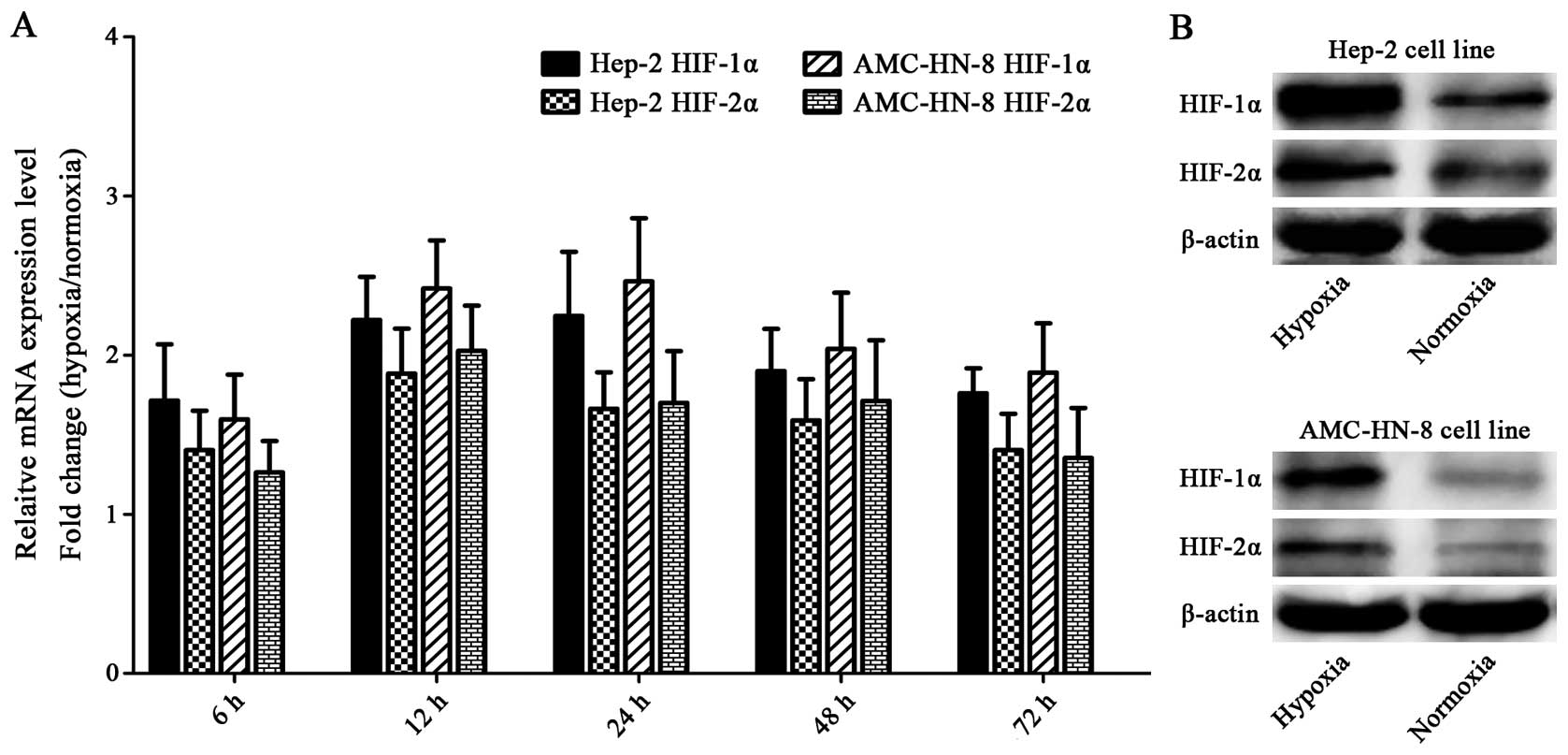
|
1.
|
Visvader JE and Lindeman GJ: Cancer stem
cells in solid tumours: accumulating evidence and unresolved
questions. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:755–768. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Akhtar K, Bussen W and Scott SP: Cancer
stem cells - from initiation to elimination, how far have we
reached? (Review). Int J Oncol. 34:1491–1503. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Bhaijee F, Pepper DJ, Pitman KT and Bell
D: Cancer stem cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a
review of current knowledge and future applications. Head Neck.
34:894–899. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Sneddon JB and Werb Z: Location, location,
location: the cancer stem cell niche. Cell Stem Cell. 1:607–611.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Borovski T, De Sousa E, Melo F, Vermeulen
L and Medema JP: Cancer stem cell niche: the place to be. Cancer
Res. 71:634–639. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Takakura N: Formation and regulation of
the cancer stem cell niche. Cancer Sci. 103:1177–1181. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Keith B and Simon MC: Hypoxia-inducible
factors, stem cells, and cancer. Cell. 129:465–472. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Sun QJ, Li XM, Lu XY and Di B: Cancer stem
cells may be mostly maintained by fluctuating hypoxia. Med
Hypotheses. 76:471–473. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Lin Q and Yun Z: Impact of the hypoxic
tumor microenvironment on the regulation of cancer stem cell
characteristics. Cancer Biol Ther. 9:949–956. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Hill RP, Marie-Egyptienne DT and Hedley
DW: Cancer stem cells, hypoxia and metastasis. Semin Radiat Oncol.
19:106–111. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Conley SJ, Gheordunescu E, Kakarala P, et
al: Antiangiogenic agents increase breast cancer stem cells via the
generation of tumor hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:2784–2789.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Ma YY, Liang DM, Liu J, et al: Prostate
cancer cell lines under hypoxia exhibit greater stem-like
properties. PLoS One. 6:e291702011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Liang DM, Ma YY, Liu J, Trope CG, Holm R,
Nesland JM and Suo ZH: The hypoxic microenvironment upgrades
stem-like properties of ovarian cancer cells. BMC Cancer.
12:2012012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Li PC, Zhou C, Xu LS and Xiao HL: Hypoxia
enhances stemness of cancer stem cells in glioblastoma: an in vitro
study. Int J Med Sci. 10:399–407. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Zhou L, Wei XD, Cheng L, Tian J and Jiang
JJ: CD133, one of the markers of cancer stem cells in Hep-2 cell
line. Laryngoscope. 117:455–460. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Wei XD, Zhou L, Cheng L, Tian J, Jiang JJ
and MacCallum J: In vivo investigation of CD133 as a putative
marker of cancer stem cells in Hep-2 cell line. Head Neck.
31:94–101. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Chen H, Zhou L, Dou TH, Wan GL, Tang HQ
and Tian J: BMI1’s maintenance of the proliferative capacity of
laryngeal cancer stem cells. Head Neck. 33:1115–1125. 2011.
|
|
18.
|
Guppy M: The hypoxic core: a possible
answer to the cancer paradox. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
299:676–680. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Tsujinaka S, Soda K, Kano Y and Konishi F:
Spermine accelerates hypoxia-initiated cancer cell migration. Int J
Oncol. 38:305–312. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Clevers H: The cancer stem cell: premises,
promises and challenges. Nat Med. 17:313–319. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Yoshiba S, Ito D, Nagumo T, Shirota T,
Hatori M and Shintani S: Hypoxia induces resistance to
5-fluorouracil in oral cancer cells via G(1) phase cell cycle
arrest. Oral Oncol. 45:109–115. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Box AH and Demetrick DJ: Cell cycle kinase
inhibitor expression and hypoxia-induced cell cycle arrest in human
cancer cell lines. Carcinogenesis. 25:2325–2335. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Hashimoto O, Shimizu K, Semba S, Chiba S,
Ku Y, Yokozaki H and Hori Y: Hypoxia induces tumor aggressiveness
and the expansion of CD133-positive cells in a hypoxia-inducible
factor-1alpha-dependent manner in pancreatic cancer cells.
Pathobiology. 78:181–192. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24.
|
Soeda A, Park M, Lee D, et al: Hypoxia
promotes expansion of the CD133-positive glioma stem cells through
activation of HIF-1alpha. Oncogene. 28:3949–3959. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Shi G and Jin Y: Role of Oct4 in
maintaining and regaining stem cell pluripotency. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 1:392010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Schmidt R and Plath K: The roles of the
reprogramming factors Oct4, Sox2 and Klf4 in resetting the somatic
cell epigenome during induced pluripotent stem cell generation.
Genome Biol. 13:2512012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27.
|
Luo W, Li S, Peng B, Ye Y, Deng X and Yao
K: Embryonic stem cells markers SOX2, OCT4 and Nanog expression and
their correlations with epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e563242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Takahashi K and Yamanaka S: Induction of
pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast
cultures by defined factors. Cell. 126:663–676. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Huangfu D, Osafune K, Maehr R, et al:
Induction of pluripotent stem cells from primary human fibroblasts
with only Oct4 and Sox2. Nat Biotechnol. 26:1269–1275. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Kolenda J, Jensen SS, Aaberg-Jessen C,
Christensen K, Andersen C, Brunner N and Kristensen BW: Effects of
hypoxia on expression of a panel of stem cell and chemoresistance
markers in glioblastoma-derived spheroids. J Neurooncol. 103:43–58.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Iida H, Suzuki M, Goitsuka R and Ueno H:
Hypoxia induces CD133 expression in human lung cancer cells by
up-regulation of OCT3/4 and SOX2. Int J Oncol. 40:71–79.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Covello KL, Kehler J, Yu H, et al:
HIF-2alpha regulates Oct-4: effects of hypoxia on stem cell
function, embryonic development, and tumor growth. Genes Dev.
20:557–570. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Mathieu J, Zhang Z, Zhou W, et al: HIF
induces human embryonic stem cell markers in cancer cells. Cancer
Res. 71:4640–4652. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Li DW, Zhou L, Jin B, Xie J and Dong P:
Expression and significance of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and
survivin in laryngeal carcinoma tissue and cells. Otolaryngol Head
Neck Surg. 148:75–81. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Pietras A, Hansford LM, Johnsson AS, et
al: HIF-2alpha maintains an undifferentiated state in neural
crest-like human neuroblastoma tumor-initiating cells. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 106:16805–16810. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36.
|
Sun HC, Qiu ZJ, Liu J, et al: Expression
of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and associated proteins in
pancreatic ductal adeno-carcinoma and their impact on prognosis.
Int J Oncol. 30:1359–1367. 2007.
|
|
37.
|
Jubb AM, Buffa FM and Harris AL:
Assessment of tumour hypoxia for prediction of response to therapy
and cancer prognosis. J Cell Mol Med. 14:18–29. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Lundgren K, Holm C and Landberg G: Hypoxia
and breast cancer: prognostic and therapeutic implications. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 64:3233–3247. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|