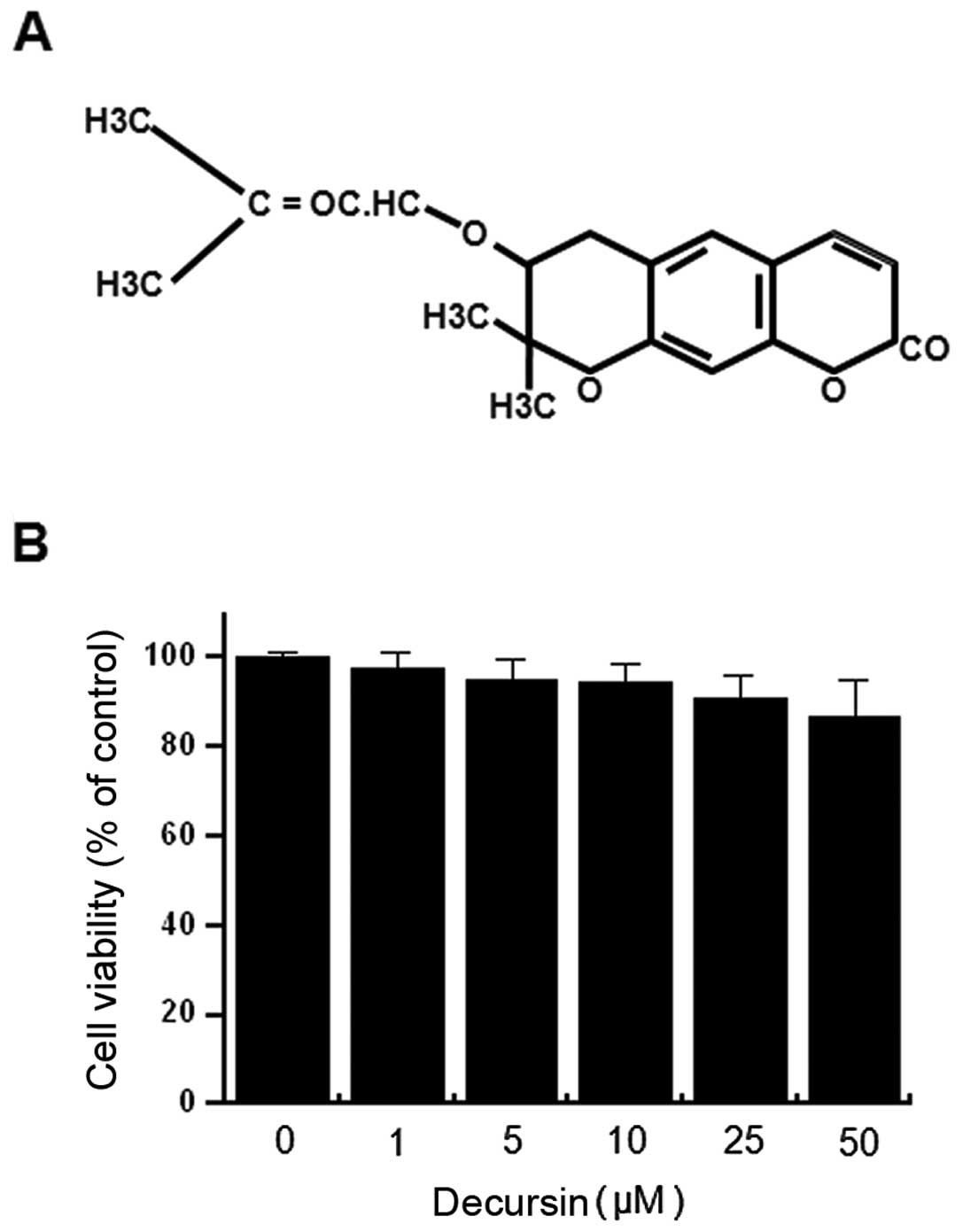
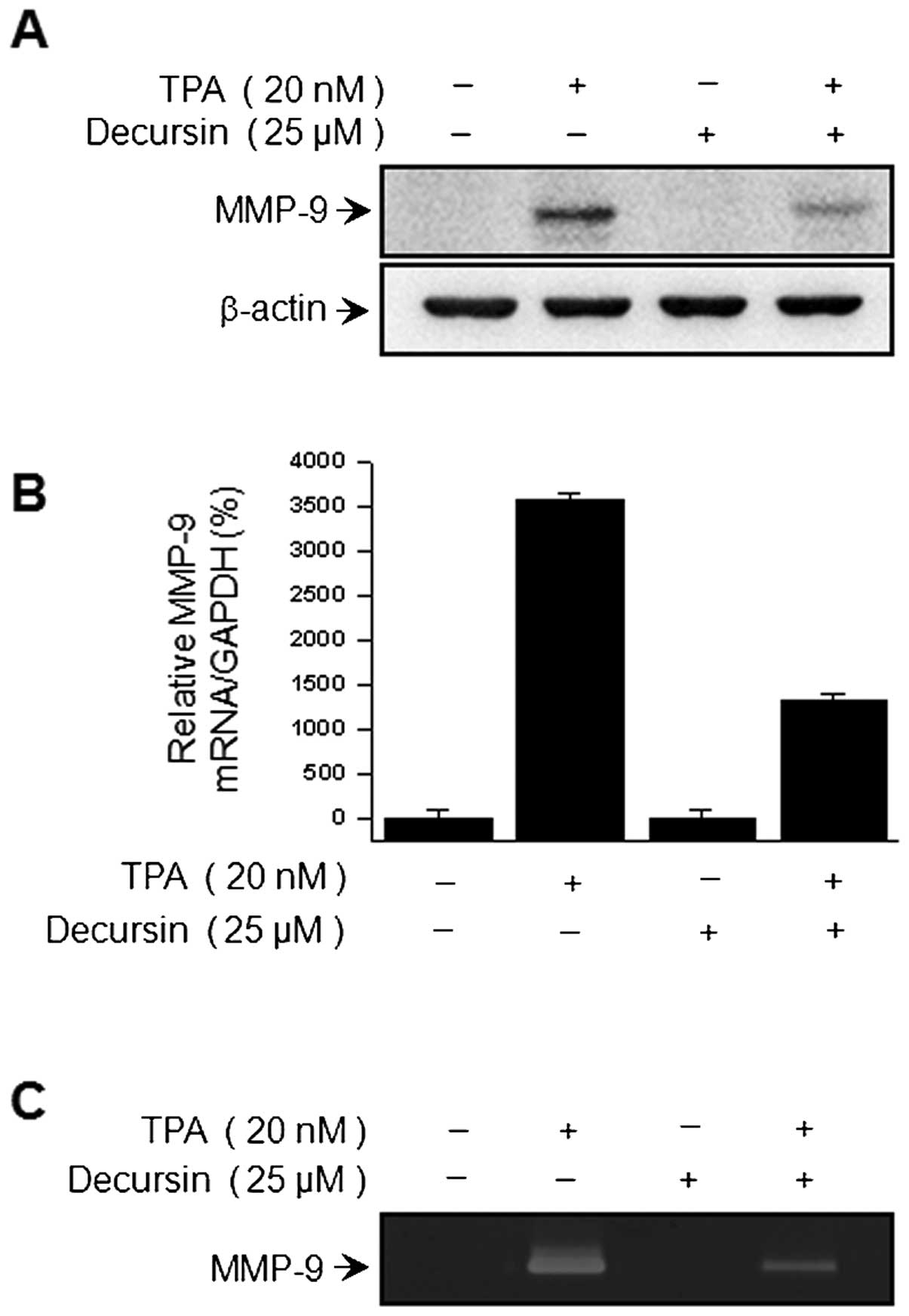
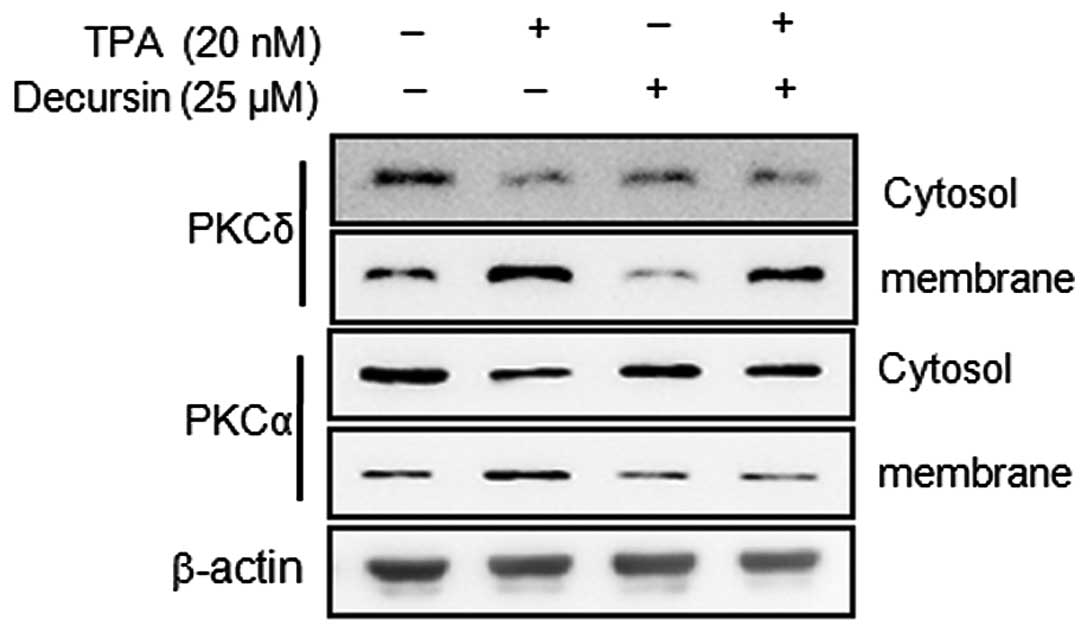
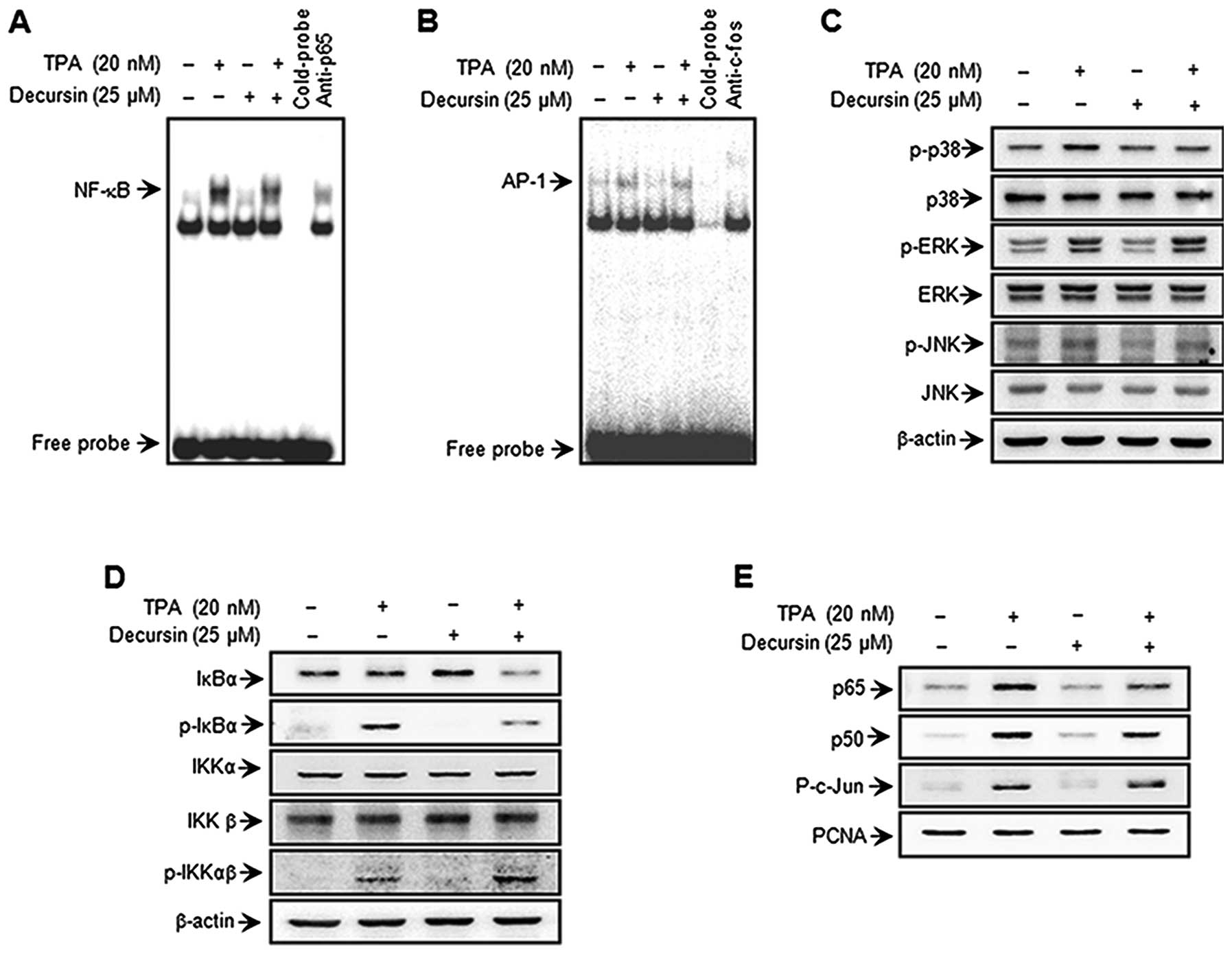
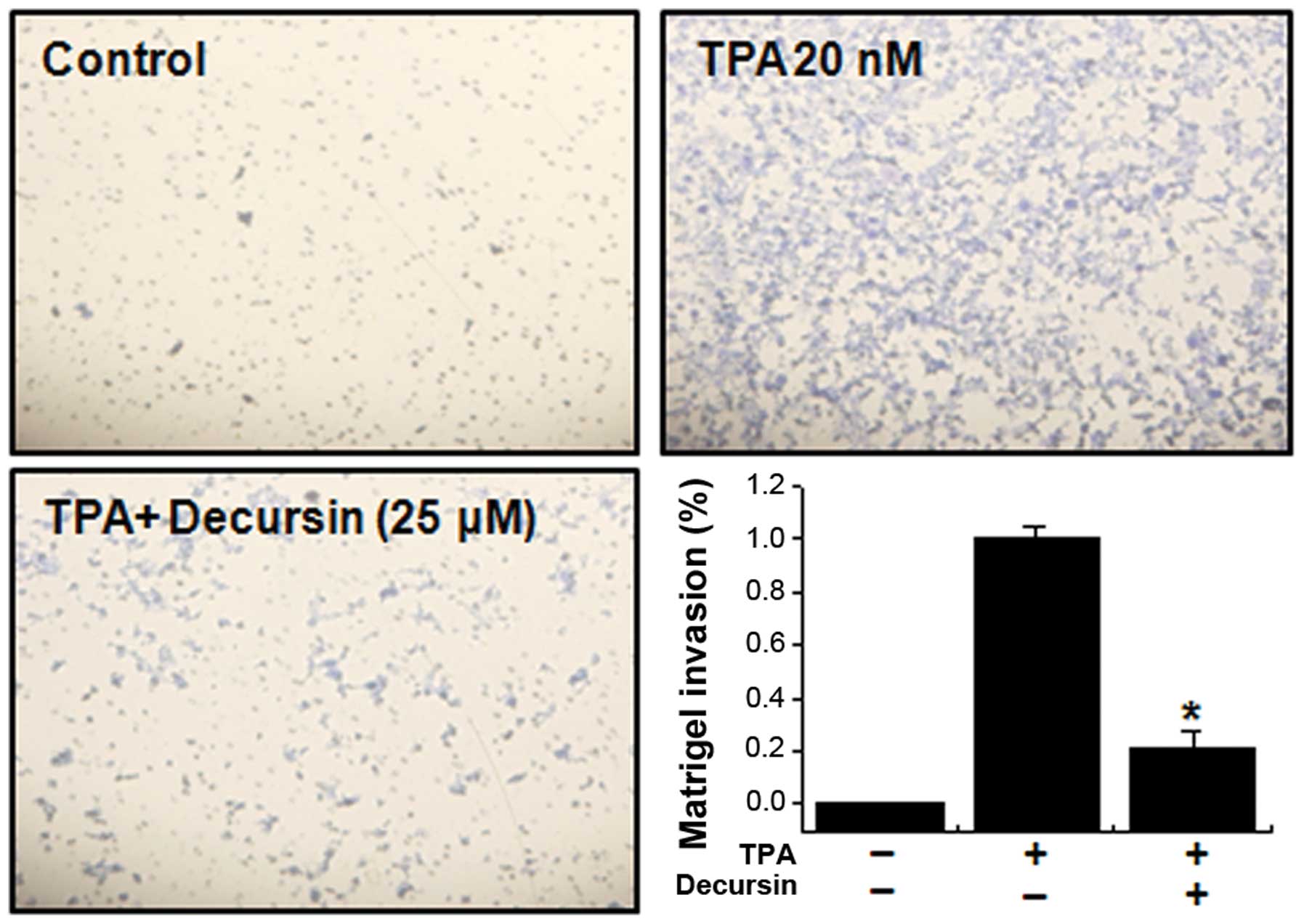
|
1.
|
Jemal A, Murray T, Ward E, Samuels A,
Tiwari RC, Ghafoor A, Feuer EJ and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics,
2005. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:10–30. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Friedel G, Pastorino U, Ginsberg RJ,
Goldstraw P, Johnston M, Pass H, Putnam JB and Toomes H: Results of
lung metastasectomy from breast cancer: prognostic criteria on the
basis of 467 cases of the International Registry of Lung
Metastases. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 22:335–344. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Zwiefel K and Janni W: Current standards
in the treatment of breast cancer. Med Monatsschr Pharm.
34:280–290. 2011.(In German).
|
|
4.
|
Chambers AF and Matrisian LM: Changing
views of the role of matrix metalloproteinases in metastasis. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 89:1260–1270. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Woessner JF Jr: Matrix metalloproteinases
and their inhibitors in connective tissue remodeling. FASEB J.
5:2145–2154. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Nakajima M, Welch DR, Belloni PN and
Nicolson GL: Degradation of basement membrane type IV collagen and
lung subendothelial matrix by rat mammary adenocarcinoma cell
clones of differing metastatic potentials. Cancer Res.
47:4869–4876. 1987.
|
|
7.
|
Brinckerhoff CE and Matrisian LM: Matrix
metalloproteinases: a tail of a frog that became a prince. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 3:207–214. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Velinov N, Poptodorov G, Gabrovski N and
Gabrovski S: The role of matrixmetalloproteinases in the tumor
growth and metastasis. Khirurgiia. 1:44–49. 2010.(In
Bulgarian).
|
|
9.
|
Zeigler ME, Chi Y, Schmidt T and Varani J:
Role of ERK and JNK pathways in regulating cell motility and matrix
metalloproteinase 9 production in growth factor-stimulated human
epidermal keratinocytes. J Cell Physiol. 180:271–284. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Hozumi A, Nishimura Y, Nishiuma T, Kotani
Y and Yokoyama M: Induction of MMP-9 in normal human bronchial
epithelial cells by TNF-alpha via NF-kappa B-mediated pathway. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 281:L1444–L1452. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Weng CJ, Chau CF, Hsieh YS, Yang SF and
Yen GC: Lucidenic acid inhibits PMA-induced invasion of human
hepatoma cells through inactivating MAPK/ERK signal transduction
pathway and reducing binding activities of NF-kappaB and AP-1.
Carcinogenesis. 29:147–156. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Newton AC: Regulation of protein kinase C.
Curr Opin Cell Biol. 9:161–167. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Lin CW, Hou WC, Shen SC, Juan SH, Ko CH,
Wang LM and Chen YC: Quercetin inhibition of tumor invasion via
suppressing PKCdelta/ERK/AP-1-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-9
activation in breast carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 29:1807–1815.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Hong S, Park KK, Magae J, Ando K, Lee TS,
Kwon TK, Kwak JY, Kim CH and Chang YC: Ascochlorin inhibits matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression by suppressing activator
protein-1-mediated gene expression through the ERK1/2 signaling
pathway: inhibitory effects of ascochlorin on the invasion of renal
carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 280:25202–25209. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15.
|
Woo MS, Jung SH, Kim SY, Hyun JW, Ko KH,
Kim WK and Kim HS: Curcumin suppresses phorbol ester-induced matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression by inhibiting the PKC to MAPK
signaling pathways in human astroglioma cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 335:1017–1025. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Eberhardt W, Huwiler A, Beck KF, Walpen S
and Pfeilschifter J: Amplification of IL-1 beta-induced matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression by superoxide in rat glomerular
mesangial cells is mediated by increased activities of NF-kappa B
and activating protein-1 and involves activation of the
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. J Immunol.
165:5788–5797. 2000.
|
|
17.
|
Madrid LV, Mayo MW, Reuther JY and Baldwin
AS Jr: Akt stimulates the transactivation potential of the RelA/p65
subunit of NF-kappaB through utilization of the Ikappa B kinase and
activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38. J Biol
Chem. 276:18934–18940. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18.
|
Ahn Q, Jeong SJ, Lee HJ, Kwon HY, Han I,
Kim HS, Lee EO, Ahn KS, Jung MH, Zhu S, Chen CY and Kim SH:
Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2-dependent survivin mediates
decursin-induced apoptosis in human KBM-5 myeloid leukemia cells.
Cancer Lett. 298:212–221. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Yim D, Singh RP, Agarwal C, Lee S, Chi H
and Agarwal R: A novel anticancer agent, decursin, induces G1
arrest and apoptosis in human prostate carcinoma cells. Cancer Res.
65:1035–1044. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Jiang C, Guo J, Wang Z, Xiao B, Lee HJ,
Lee EO, Kim SH and Lu J: Decursin and decursinol angelate inhibit
estrogen-stimulated and estrogen-independent growth and survival of
breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 9:R772007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Kim WJ, Lee SJ, Choi YD and Moon SK:
Decursin inhibits growth of human bladder and colon cancer cells
via apoptosis, G1-phase cell cycle arrest and extracellular
signal-regulated kinase activation. Int J Mol Med. 25:635–641.
2010.
|
|
22.
|
Kim JH, Jeong JH, Jeon ST, Kim H, Ock J,
Suk K, Kim SI, Song KS and Lee WH: Decursin inhibits induction of
inflammatory mediators by blocking nuclear factor-kappaB activation
in macrophages. Mol Pharmacol. 69:1783–1790. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Lee SH, Lee JH, Kim EJ, Kim WJ, Suk K, Kim
JH, Song GY and Lee WH: A novel derivative of decursin, CSL-32,
blocks migration and production of inflammatory mediators and
modulates PI3K and NF-kappaB activities in HT1080 cells. Cell Biol
Int. 36:683–688. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Zhang J, Anastasiadis PZ, Liu Y, Thompson
EA and Fields AP: Protein kinase C (PKC) betaII induces cell
invasion through a Ras/Mek-, PKC iota/Rac 1-dependent signaling
pathway. J Biol Chem. 279:22118–22123. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Fortino V, Torricelli C, Capurro E, Sacchi
G, Valacchi G and Maioli E: Antiproliferative and survival
properties of PMA in MCF-7 breast cancer cell. Cancer Invest.
26:13–21. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Kim WJ, Lee MY, Kim JH, Suk K and Lee WH:
Decursinol angelate blocks transmigration and inflammatory
activation of cancer cells through inhibition of PI3K, ERK and
NF-kappaB activation. Cancer Lett. 296:35–42. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Hwang BM, Noh EM, Kim JS, Kim JM, Hwang
JK, Kim HK, Kang JS, Kim DS, Chae HJ, You YO, Kwon KB and Lee YR:
Decursin inhibits UVB-induced MMP expression in human dermal
fibroblasts via regulation of nuclear factor-κB. Int J Mol Med.
31:477–483. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Lee SO, Jeong YJ, Kim M, Kim CH and Lee
IS: Suppression of PMA-induced tumor cell invasion by capillarisin
via the inhibition of NF-kappaB-dependent MMP-9 expression. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 366:1019–1024. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Deryugina EI and Quigley JP: Matrix
metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
25:9–34. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30.
|
Scorilas A, Karameris A, Arnogiannaki N,
Ardavanis A, Bassilopoulos P, Trangas T and Talieri M:
Overexpression of matrix-metalloproteinase-9 in human breast
cancer: a potential favourable indicator in node-negative patients.
Br J Cancer. 84:1488–1496. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Yan C and Boyd DD: Regulation of matrix
metalloproteinase gene expression. J Cell Physiol. 211:19–26. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Kim JM, Noh EM, Kwon KB, Kim JS, You YO,
Hwang JK, Hwang BM, Kim BS, Lee SH, Lee SJ, Jung SH, Youn HJ and
Lee YR: Curcumin suppresses the TPA-induced invasion through
inhibition of PKCalpha-dependent MMP-expression in MCF-7 human
breast cancer cells. Phytomedicine. 19:1085–1092. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Yao J, Xiong S, Klos K, Nguyen N, Grijalva
R, Li P and Yu D: Multiple signaling pathways involved in
activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) by heregulin-beta1
in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 20:8066–8074. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Chung TW, Moon SK, Chang YC, Ko JH, Lee
YC, Cho G, Kim SH, Kim JG and Kim CH: Novel and therapeutic effect
of caffeic acid and caffeic acid phenyl ester on hepatocarcinoma
cells: complete regression of hepatoma growth and metastasis by
dual mechanism. FASEB J. 18:1670–1681. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Lee YR, Noh EM, Oh HJ, Hur H, Kim JM, Han
JH, Hwang JK, Park BH, Park JW, Youn HJ, Jung SH, Kim BS, Jung JY,
Lee SH, Park CS and Kim JS: Dihydroavenanthramide D inhibits human
breast cancer cell invasion through suppression of MMP-9
expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 405:552–557. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|