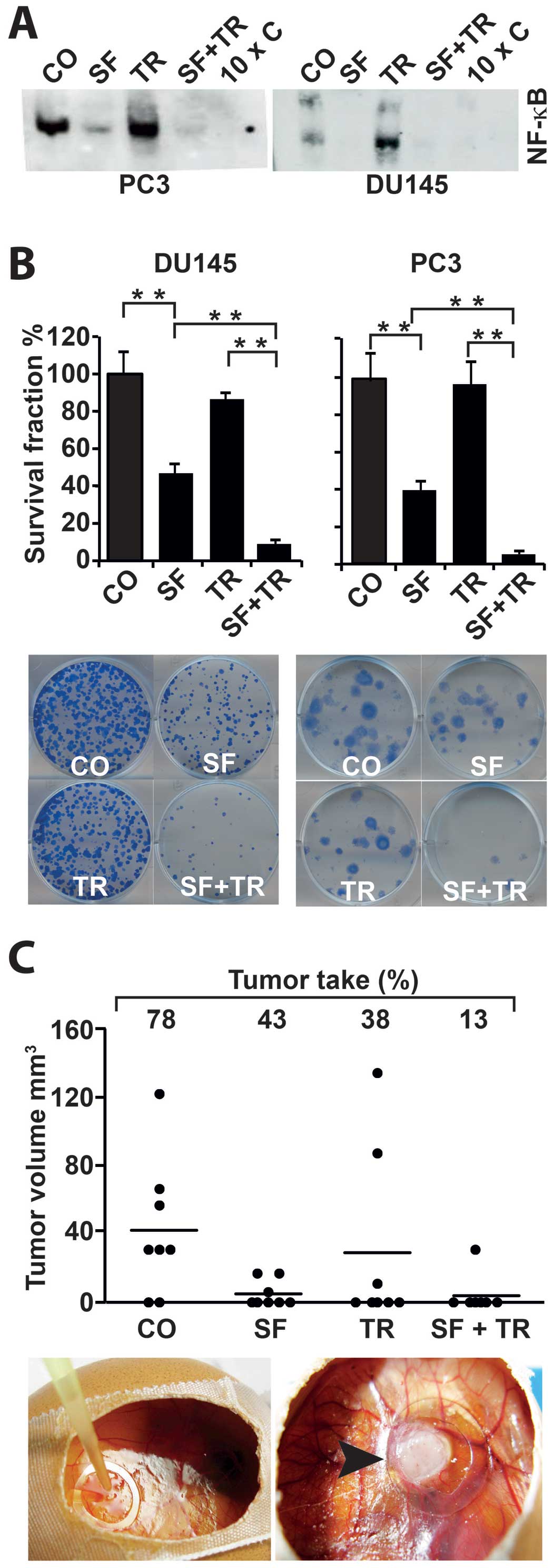
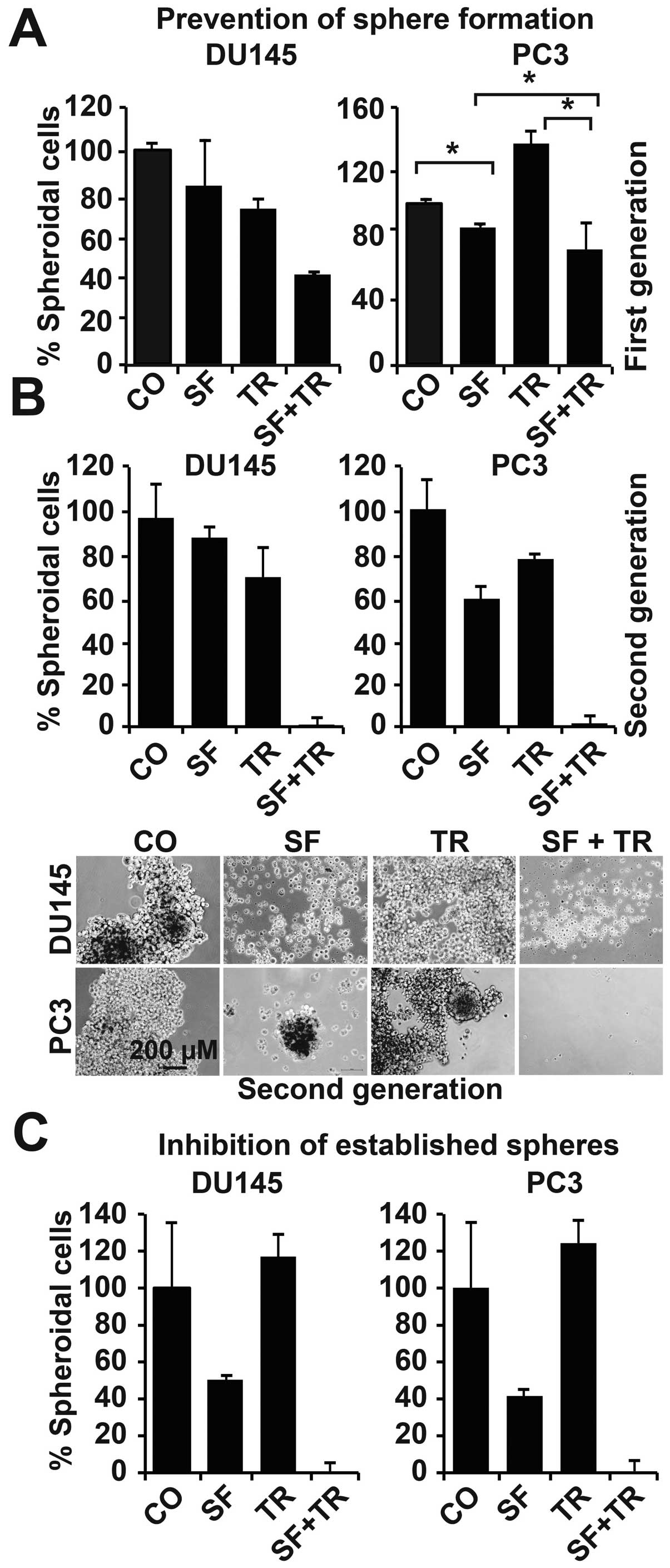
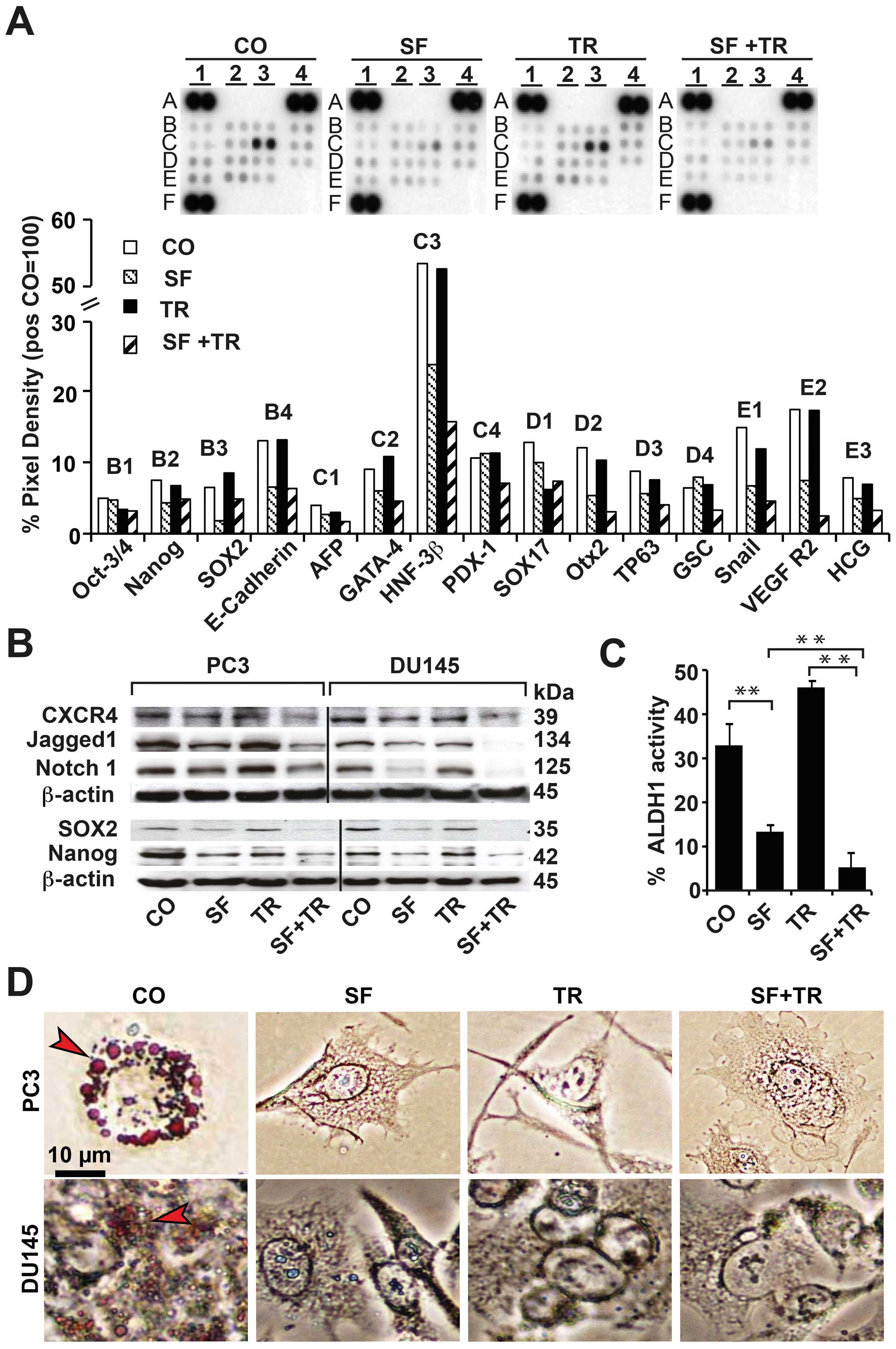
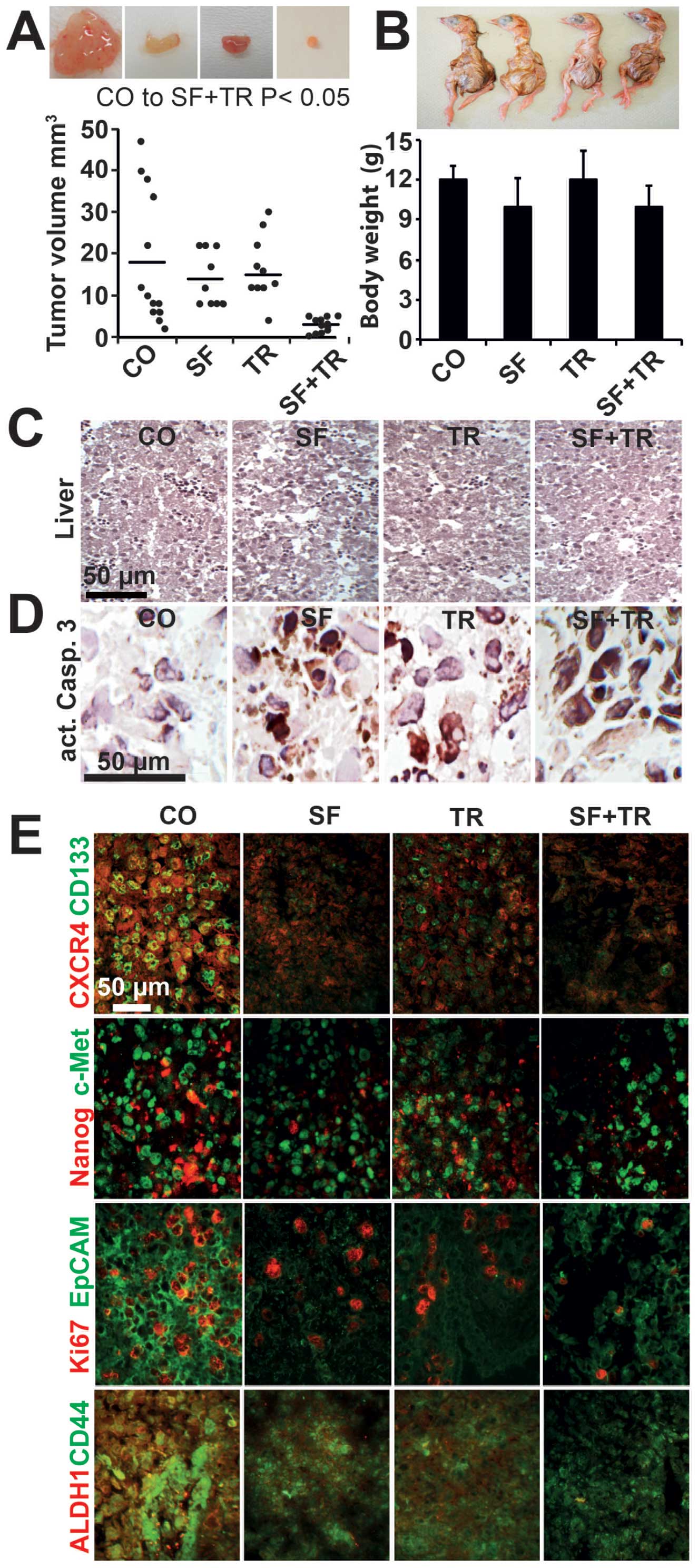
|
1.
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Feldman BJ and Feldman D: The development
of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 1:34–45.
2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Sharpe B, Beresford M, Bowen R, Mitchard J
and Chalmers AD: Searching for prostate cancer stem cells: markers
and methods. Stem Cell Rev. 9:721–730. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Abbott A: Cancer: the root of the problem.
Nature. 442:742–743. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Stuckey DW and Shah K: TRAIL on trial:
preclinical advances in cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med. 19:685–694.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Szegezdi E, O’Reilly A, Davy Y, et al:
Stem cells are resistant to TRAIL receptor-mediated apoptosis. J
Cell Mol Med. 13:4409–4414. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Herr I and Büchler MW: Dietary
constituents of broccoli and other cruciferous vegetables:
implications for prevention and therapy of cancer. Cancer Treat
Rev. 36:377–383. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Shankar S, Ganapathy S and Srivastava RK:
Sulforaphane enhances the therapeutic potential of TRAIL in
prostate cancer orthotopic model through regulation of apoptosis,
metastasis, and angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6855–6866. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Kallifatidis G, Rausch V, Baumann B, et
al: Sulforaphane targets pancreatic tumour-initiating cells by
NF-kappaB-induced anti-apoptotic signalling. Gut. 58:949–963. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Herr I, Lozanovski V, Houben P, Schemmer P
and Buchler MW: Sulforaphane and related mustard oils in focus of
cancer prevention and therapy. Wien Med Wochenschr. 163:80–88.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Liu L, Salnikov AV, Bauer N, et al:
Triptolide reverses hypoxia-induced EMT and stem-like features in
pancreatic cancer by NF-kappa B downregulation. Int J Cancer. (In
press).
|
|
12.
|
Apel A, Herr I, Schwarz H, Rodemann HP and
Mayer A: Blocked autophagy sensitizes resistant carcinoma cells to
radiation therapy. Cancer Res. 68:1485–1494. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Balke M, Neumann A, Szuhai K, et al: A
short-term in vivo model for giant cell tumor of bone. BMC Cancer.
11:2412011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
van Bokhoven A, Varella-Garcia M, Korch C,
et al: Molecular characterization of human prostate carcinoma cell
lines. Prostate. 57:205–225. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Pfeiffer MJ and Schalken JA: Stem cell
characteristics in prostate cancer cell lines. Eur Urol.
57:246–255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
van den Hoogen C, van der Horst G, Cheung
H, et al: High aldehyde dehydrogenase activity identifies
tumor-initiating and metastasis-initiating cells in human prostate
cancer. Cancer Res. 70:5163–5173. 2010.
|
|
17.
|
Hurt EM, Kawasaki BT, Klarmann GJ, Thomas
SB and Farrar WL: CD44+CD24(-) prostate cells are early
cancer progenitor/stem cells that provide a model for patients with
poor prognosis. Br J Cancer. 98:756–765. 2008.
|
|
18.
|
Li H, Chen X, Calhoun-Davis T, Claypool K
and Tang DG: PC3 human prostate carcinoma cell holoclones contain
self-renewing tumor-initiating cells. Cancer Res. 68:1820–1825.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19.
|
Patrawala L, Calhoun T,
Schneider-Broussard R, et al: Highly purified CD44+
prostate cancer cells from xenograft human tumors are enriched in
tumorigenic and metastatic progenitor cells. Oncogene.
25:1696–1708. 2006.
|
|
20.
|
Glinsky GV: ‘Stemness’ genomics law
governs clinical behavior of human cancer: implications for
decision making in disease management. J Clin Oncol. 26:2846–2853.
2008.
|
|
21.
|
Luk SU, Yap WN, Chiu YT, et al:
Gamma-tocotrienol as an effective agent in targeting prostate
cancer stem cell-like population. Int J Cancer. 128:2182–2191.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Patrawala L, Calhoun-Davis T,
Schneider-Broussard R and Tang DG: Hierarchical organization of
prostate cancer cells in xenograft tumors: the
CD44+alpha2beta1+cell population is enriched
in tumor-initiating cells. Cancer Res. 67:6796–6805. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Klarmann GJ, Hurt EM, Mathews LA, et al:
Invasive prostate cancer cells are tumor initiating cells that have
a stem cell-like genomic signature. Clin Exp Metastasis.
26:433–446. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Shukla S, Maclennan GT, Hartman DJ, Fu P,
Resnick MI and Gupta S: Activation of PI3K-Akt signaling pathway
promotes prostate cancer cell invasion. Int J Cancer.
121:1424–1432. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Zhao Y, Yan Q, Long X, Chen X and Wang Y:
Vimentin affects the mobility and invasiveness of prostate cancer
cells. Cell Biochem Funct. 26:571–577. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Tomasi TB Jr: Structure and function of
alpha-fetoprotein. Annu Rev Med. 28:453–465. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Niwa H, Miyazaki J and Smith AG:
Quantitative expression of Oct-3/4 defines differentiation,
dedifferentiation or self-renewal of ES cells. Nat Genet.
24:372–376. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Mitsui K, Tokuzawa Y, Itoh H, et al: The
homeoprotein Nanog is required for maintenance of pluripotency in
mouse epiblast and ES cells. Cell. 113:631–642. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Niwa H, Ogawa K, Shimosato D and Adachi K:
A parallel circuit of LIF signalling pathways maintains
pluripotency of mouse ES cells. Nature. 460:118–122. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Hazan RB, Qiao R, Keren R, Badano I and
Suyama K: Cadherin switch in tumor progression. Ann NY Acad Sci.
1014:155–163. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31.
|
Akiyama Y, Watkins N, Suzuki H, et al:
GATA-4 and GATA-5 transcription factor genes and potential
downstream antitumor target genes are epigenetically silenced in
colorectal and gastric cancer. Mol Cell Biol. 23:8429–8439. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32.
|
Liu M, Lee DF, Chen CT, et al: IKKalpha
activation of NOTCH links tumorigenesis via FOXA2 suppression. Mol
Cell. 45:171–184. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Song Y, Washington MK and Crawford HC:
Loss of FOXA1/2 is essential for the epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 70:2115–2125. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34.
|
Zhou Q, Brown J, Kanarek A, Rajagopal J
and Melton DA: In vivo reprogramming of adult pancreatic exocrine
cells to beta-cells. Nature. 455:627–632. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Niakan KK, Ji H, Maehr R, et al: Sox17
promotes differentiation in mouse embryonic stem cells by directly
regulating extraembryonic gene expression and indirectly
antagonizing self-renewal. Genes Dev. 24:312–326. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Bai RY, Staedtke V, Lidov HG, Eberhart CG
and Riggins GJ: OTX2 represses myogenic and neuronal
differentiation in medulloblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 72:5988–6001.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Flores ER and Lozano G: The p53 family
grows old. Genes Dev. 26:1997–2000. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Kalisz M, Winzi M, Bisgaard HC and Serup
P: EVEN-SKIPPED HOMEOBOX 1 controls human ES cell differentiation
by directly repressing GOOSECOID expression. Dev Biol. 362:94–103.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Davidson NE and Sukumar S: Of Snail, mice,
and women. Cancer Cell. 8:173–174. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Holmes DI and Zachary IC: Vascular
endothelial growth factor regulates stanniocalcin-1 expression via
neuropilin-1-dependent regulation of KDR and synergism with
fibroblast growth factor-2. Cell Signal. 20:569–579. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Triozzi PL and Stevens VC: Human chorionic
gonadotropin as a target for cancer vaccines. Oncol Rep. 6:7–17.
1999.
|
|
42.
|
Gassmann P, Haier J, Schluter K, et al:
CXCR4 regulates the early extravasation of metastatic tumor cells
in vivo. Neoplasia. 11:651–661. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Leong KG and Gao WQ: The Notch pathway in
prostate development and cancer. Differentiation. 76:699–716. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44.
|
Douville J, Beaulieu R and Balicki D:
ALDH1 as a functional marker of cancer stem and progenitor cells.
Stem Cells Dev. 18:17–25. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Ding L, Yuan C, Wei F, et al: Cisplatin
restores TRAIL apoptotic pathway in glioblastoma-derived stem cells
through up-regulation of DR5 and down-regulation of c-FLIP. Cancer
Invest. 29:511–520. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46.
|
Rajasekhar VK, Studer L, Gerald W, Socci
ND and Scher HI: Tumour-initiating stem-like cells in human
prostate cancer exhibit increased NF-kappaB signalling. Nat Commun.
2:1622011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Peinado H, Olmeda D and Cano A: Snail, Zeb
and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the
epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 7:415–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Kirsh VA, Peters U, Mayne ST, et al:
Prospective study of fruit and vegetable intake and risk of
prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 99:1200–1209. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Richman EL, Carroll PR and Chan JM:
Vegetable and fruit intake after diagnosis and risk of prostate
cancer progression. Int J Cancer. 131:201–210. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|