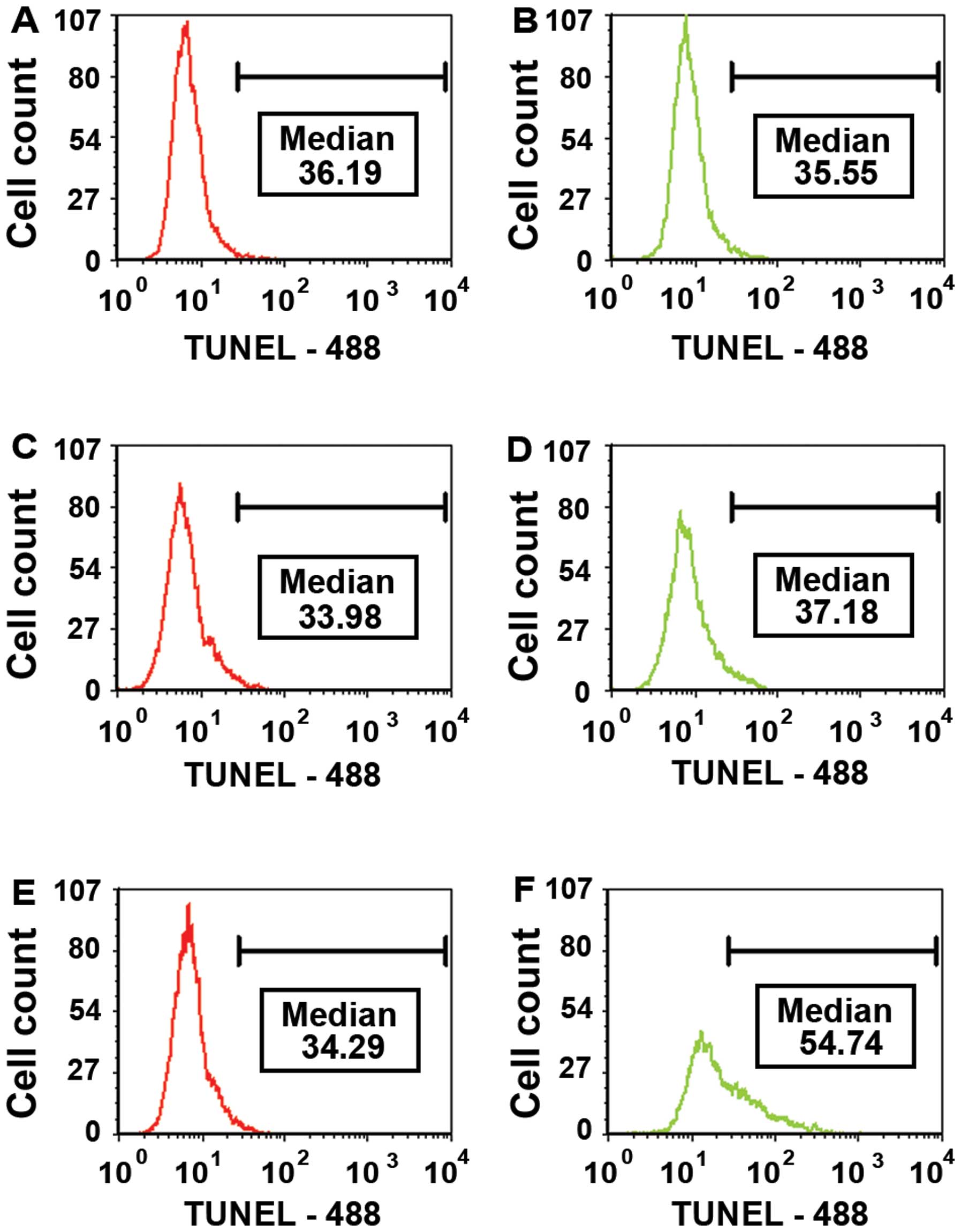
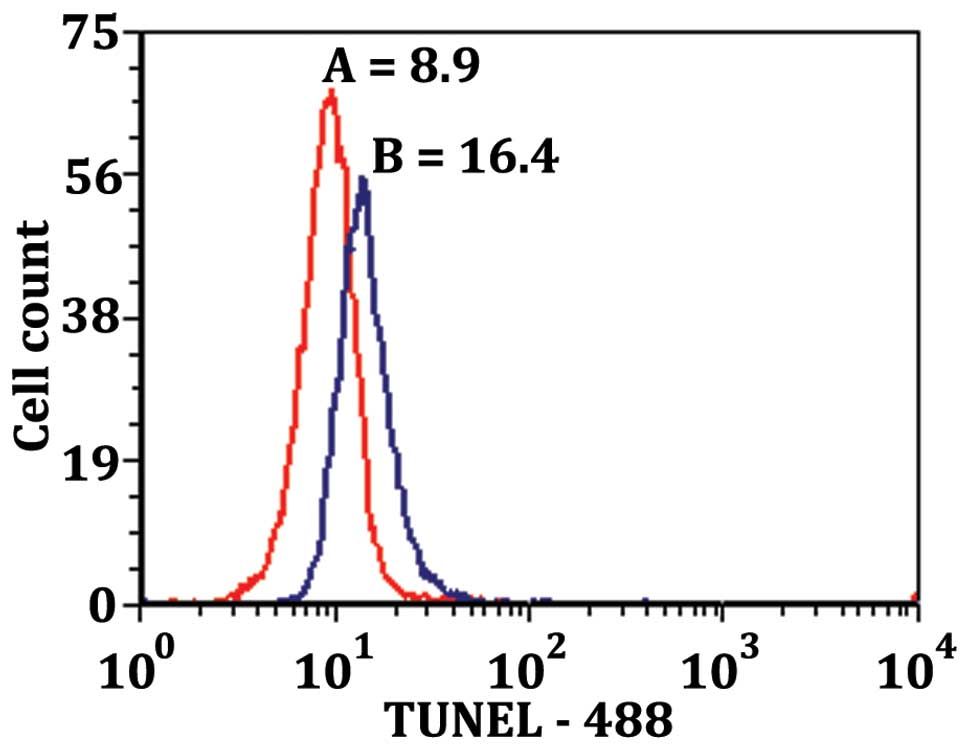
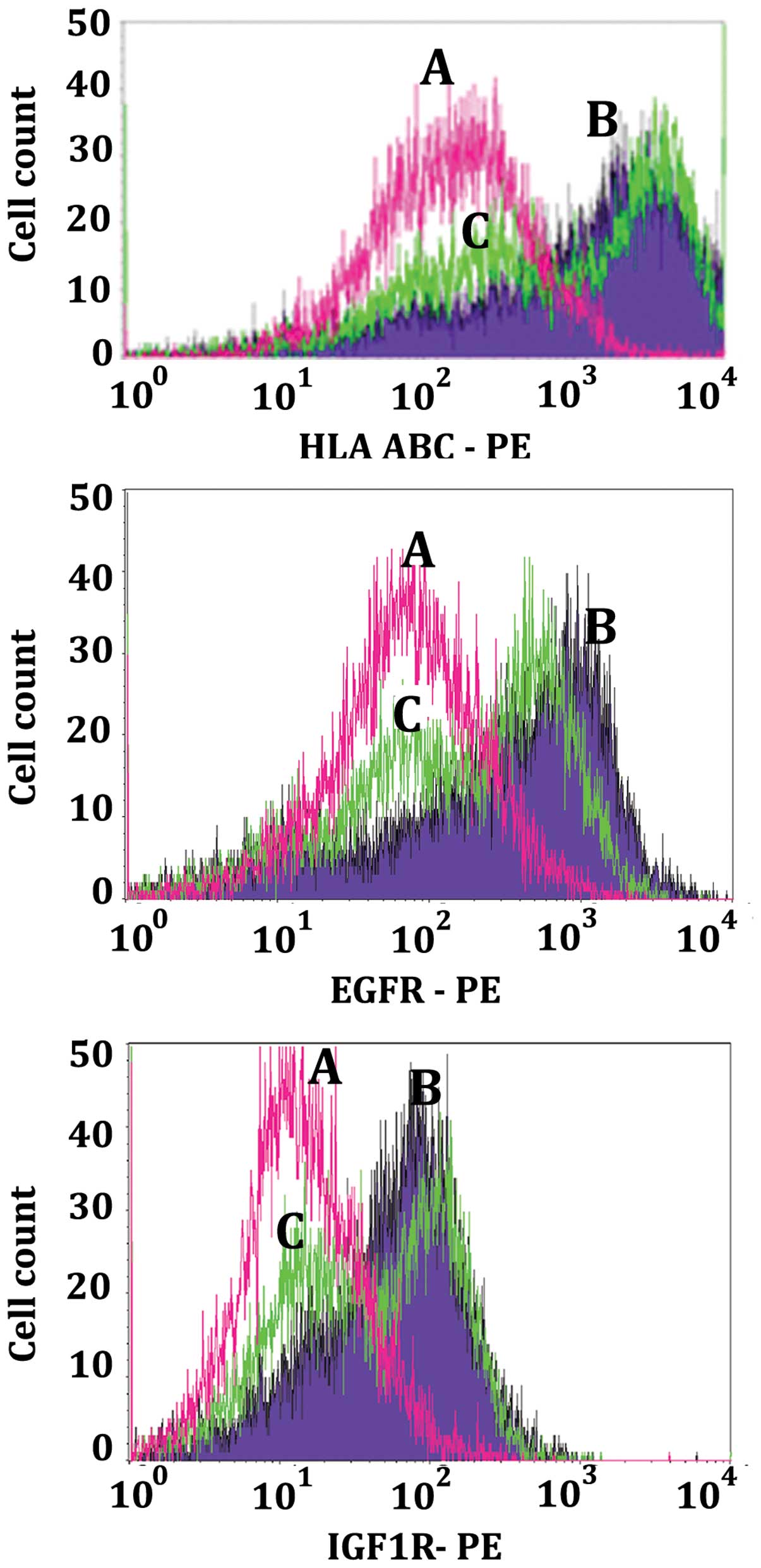
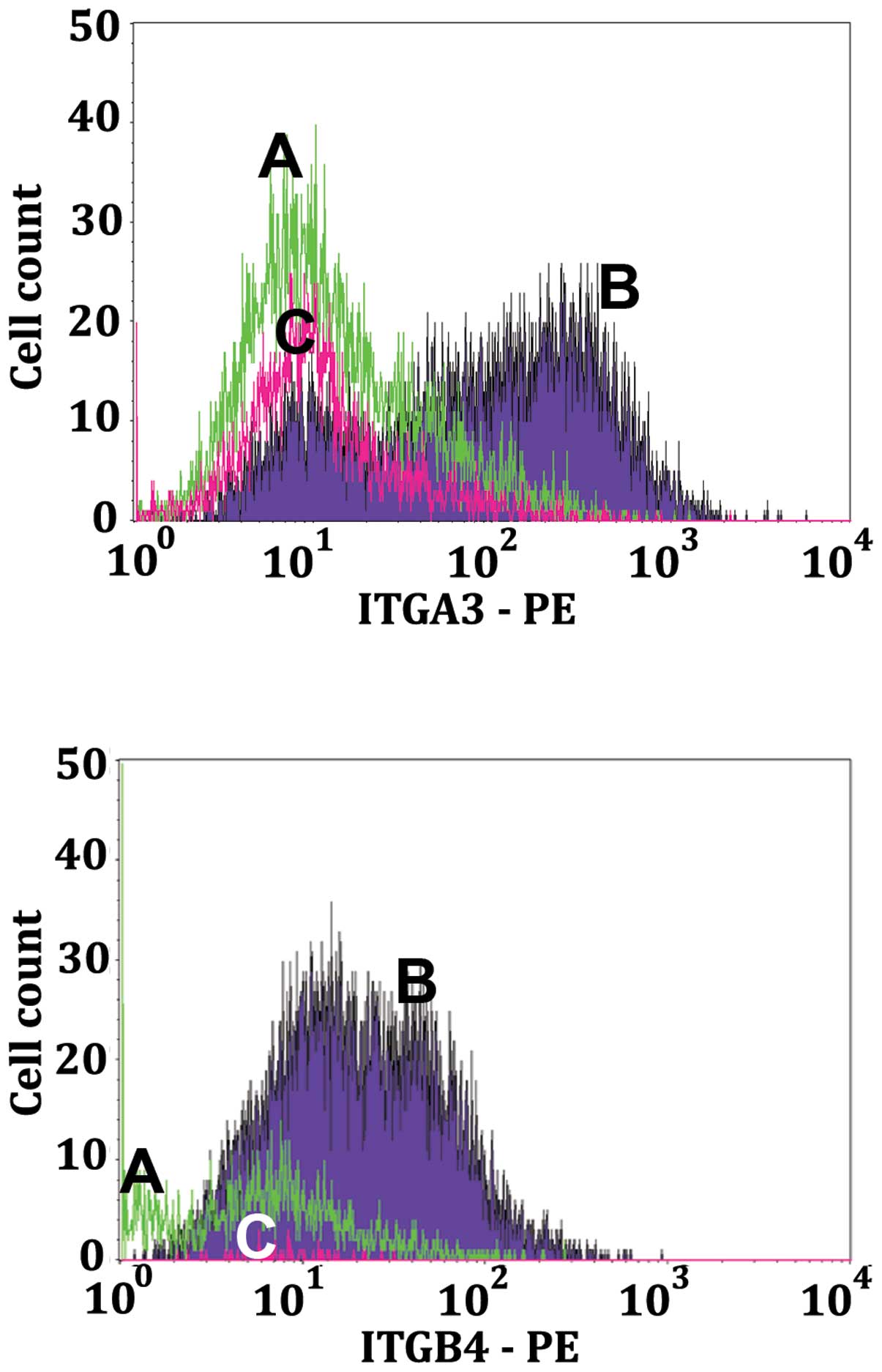
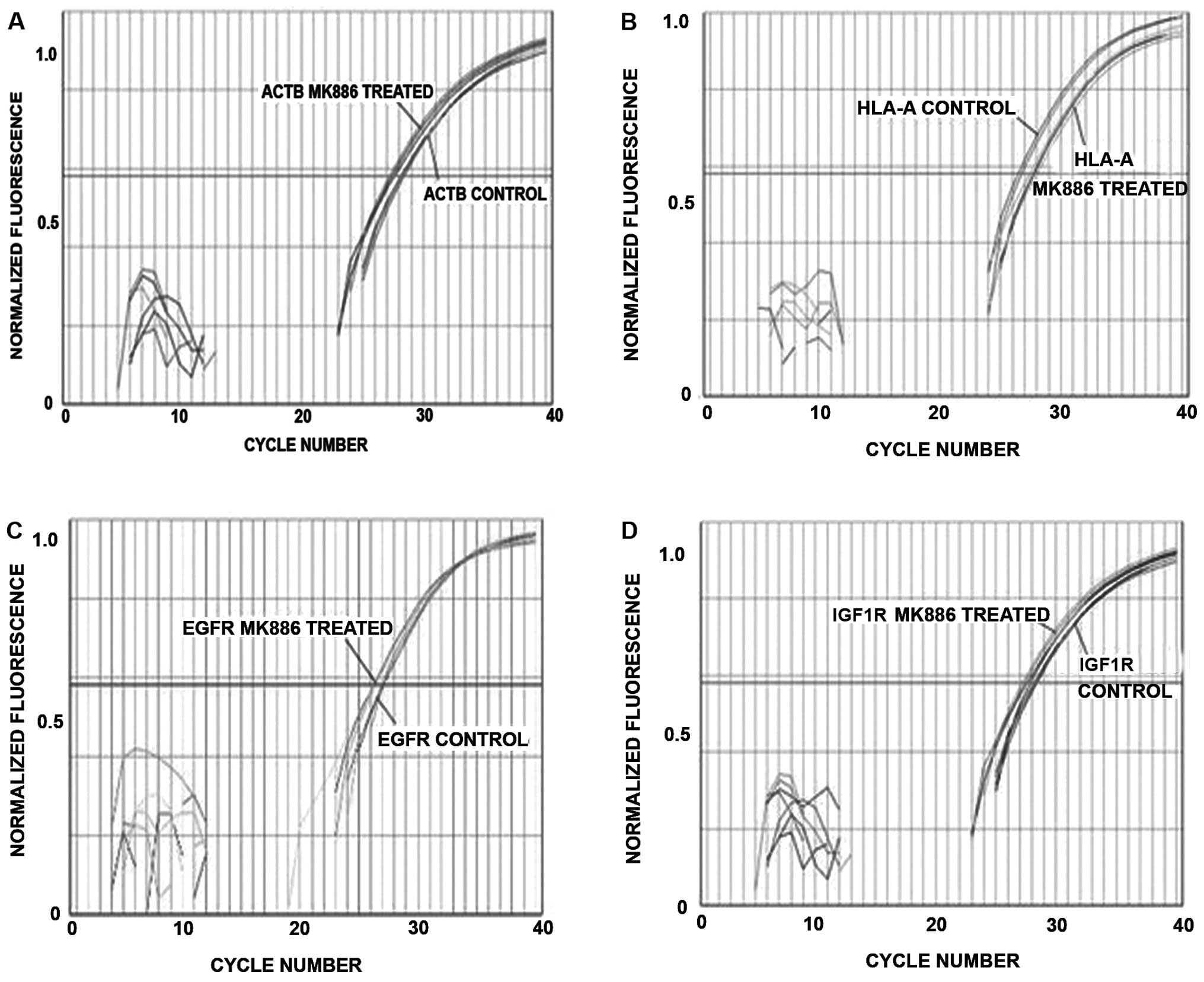
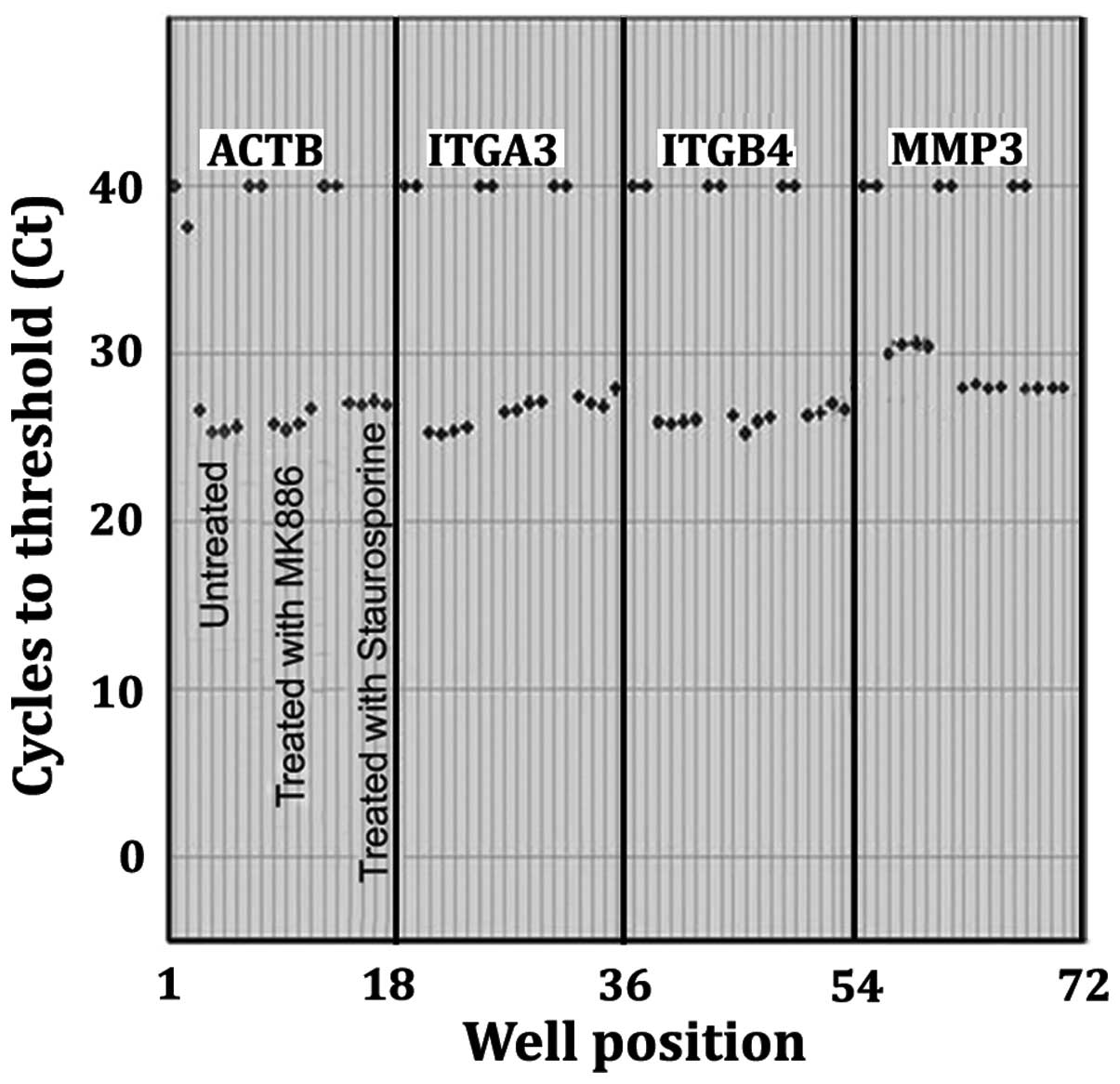
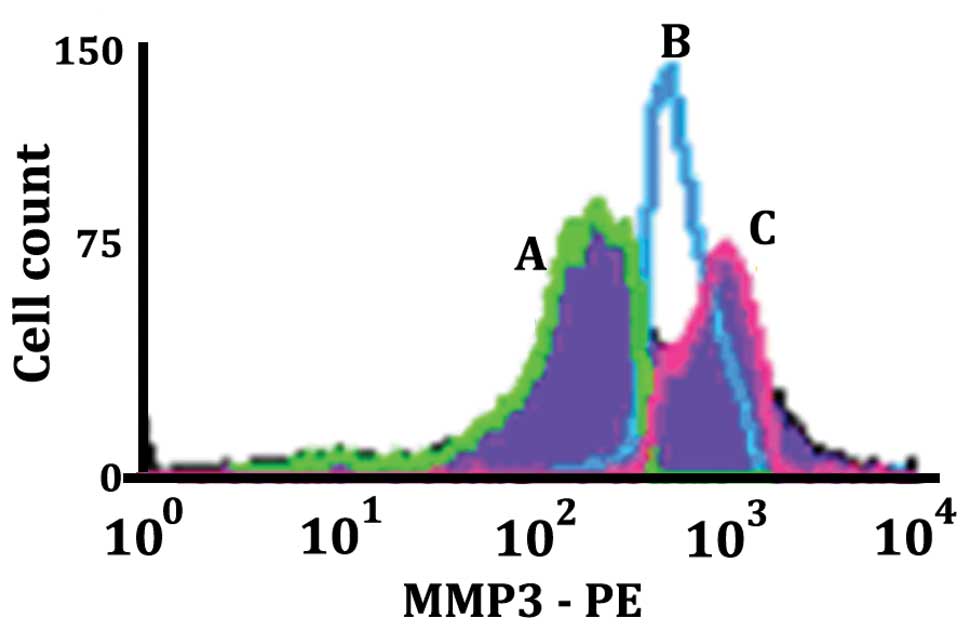
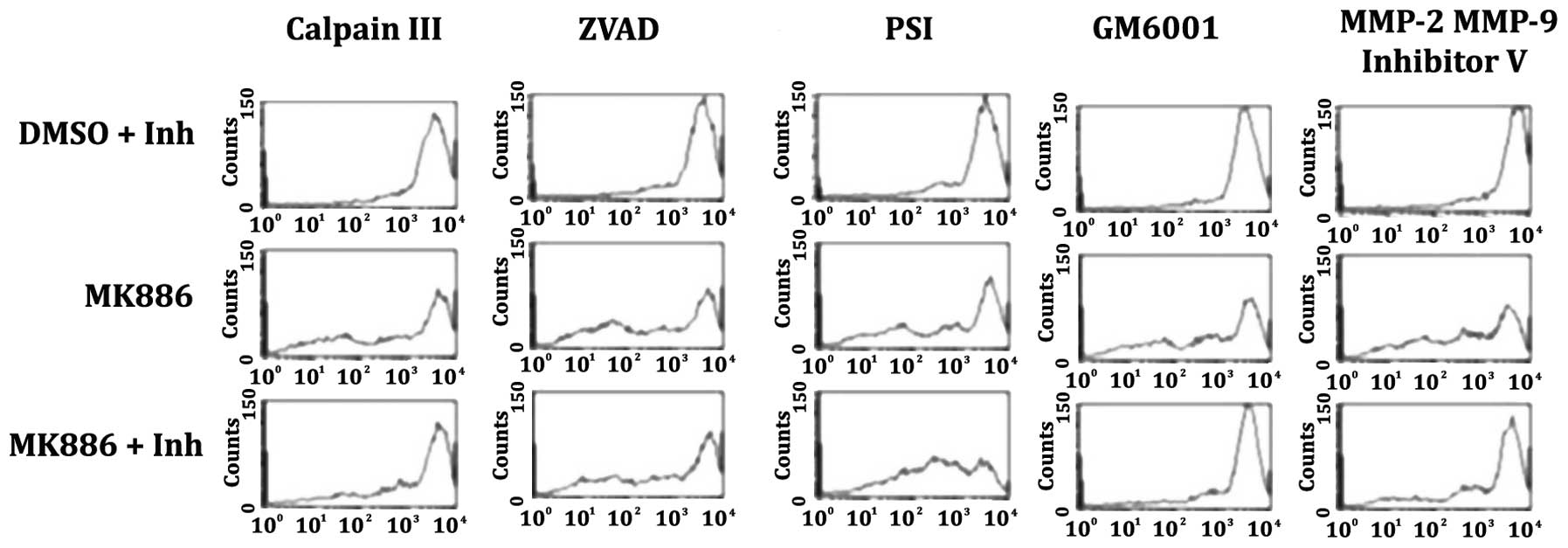
|
1.
|
Lockshin RA and Williams CM: Programmed
cell death-II. Endocrine potentiation of the breakdown of the
intersegmental muscles of silkmoths. J Insect Physiol. 10:643–649.
1964. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Sulston J and Brenner S: The DNA of
Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 77:95–104. 1974.
|
|
3.
|
Sulston JE and Horvitz HR: Post-embryonic
cell lineages of the nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev
Biol. 56:110–156. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Jacobson MD, Weil M and Raff MC:
Programmed cell death in animal development. Cell. 88:347–354.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Horvitz HR: Genetic control of programmed
cell death in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Cancer
Res. 59(Suppl 7): 1701–1706. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Li Y, Fengyi W, Sudeshna D, et al:
Autophagic programmed cell death by selective catalase degradation.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:4952–4957. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: a review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Taddei ML, Giannoni E, Fiaschi T and
Chiarugi P: Anoikis: an emerging hallmark in health and diseases. J
Pathol. 226:380–393. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Hirsch T, Marchetti P, Susin SA, et al:
The apoptosis-necrosis paradox. Apoptogenic proteases activated
after mitochondrial permeability transition determine the mode of
cell death. Oncogene. 15:1573–1581. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Proskuryakov SY, Konoplyannikov A and
Gabai VL: Necrosis: a specific form of programmed cell death. Exp
Cell Res. 283:1–16. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Gilmore AP, Metcalfe AD, Romer LH and
Streuli CH: Integrin-mediated survival signals regulate the
apoptotic function of bax through its conformation and subcellular
localization. J Cell Biol. 149:431–445. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
LeRoith D, Werner H, Beitner-Johnson D and
Roberts CT Jr: Molecular and cellular aspects of the insulin-like
growth factor I receptor. Endocr Rev. 16:143–163. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
|
Jorissen RN, Walker F, Pouliot N, Garrett
TPJ, Ward CW and Burgessa AW: Epidermal growth factor receptor:
mechanisms of activation and signaling. Exp Cell Res. 284:31–53.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Adams TE, McKern NM and Ward CW:
Signalling by the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor:
interplay with the epidermal growth factor receptor. Growth
Factors. 22:89–95. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
van der Veeken J, Oliveira S, Schiffelers
RM, Storm G, van Bergen En Henegouwen PM and Roovers RC: Crosstalk
between epidermal growth factor receptor- and insulin-like growth
factor-1 receptor signaling: implications for cancer therapy. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 9:748–760. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH and Currie AR:
Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging
implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 26:239–257. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17.
|
Frisch SM and Francis H: Disruption of
epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol.
124:619–626. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Ruoslahti E and Pierschbacher MD: New
perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science.
238:491–497. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Ruoslahti E: Integrins. J Clin Invest.
87:1–5. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Ruoslahti E and Reed JC: Anchorange
independence, integrins, and apoptosis. Cell. 77:477–478. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Frisch SM and Ruoslahti E: Integrins and
anoikis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 9:701–706. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Reed JC: Apoptosis-targeted therapies for
cancer. Cancer Cell. 3:17–22. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23.
|
Zhong X and Rescorla FJ: Cell surface
adhesion molecules and adhesion-initiated signaling: understanding
of anoikis resistance mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities.
Cell Signal. 24:393–401. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Baguley BC: Multiple drug resistance
mechanisms in cancer. Mol Biotechnol. 46:308–316. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Zahreddine H and Borden KL: Mechanisms and
insights into drug resistance in cancer. Front Pharmacol. 4:282013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Beier D, Schulz JP and Beier CP:
Chemoresistance of glioblastoma cancer stem cells-much more complex
than expected. Mol Cancer. 10:1282011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Zeiss CJ: The apoptosis-necrosis
continuum: insights from genetically altered mice. Vet Pathol.
40:481–495. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Hacker G: The morphology of apoptosis.
Cell Tissue Res. 301:5–17. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Diserens AC, de Tribolet N, Martin-Achard
A, et al: Characterization of an established human malignant glioma
cell line: LN-18. Acta Neuorpathol. 53:21–28. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Anderson KM, Seed T, Jajeh A, et al: An in
vivo inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase, MK886, at micormolar
concentration induces apoptosis in U937 and CML cells. Anticancer
Res. 16:2589–2599. 1966.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Ghosh J and Myers CE: Inhibition of
arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase triggers massive apoptosis in human
prostate cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:13182–13187.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32.
|
Ghosh J and Myers CE: Arachidonic acid
stimulates prostate cancer cell growth: critical role of
5-lipoxygenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 235:418–423. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Tong WG, Ding XZ and Adrian TE: The
mechanisms of lipoxygenase inhibitor-induced apoptosis in human
breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 296:942–948. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Dixon RAF, Diehl RE, Opas E, et al:
Requirement of a 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein for leukotriene
synthesis. Nature. 343:282–284. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Miller DK, Gillard JW, Vickers PJ, et al:
Identification and isolation of a membrane protein necessary for
leukotriene production. Nature. 343:278–281. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Ford-Hutchinson AW: FLAP: a novel drug
target for inhibiting the synthesis of leukotrienes. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 12:68–70. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Vegesna RV, Wu HL, Mong S and Crooke ST:
Staurosporine inhibits protein kinase C and prevents phorbol
ester-mediated leukotriene D4 receptor desensitization in RBL-1
cells. Mol Pharmacol. 33:537–542. 1998.
|
|
38.
|
Belmokhtar CA, Hillion J and
Ségal-Bendirdjian E: Staurosporine induces apoptosis through both
caspase-dependent and caspase-independent mechanisms. Oncogene.
20:3354–3362. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Kabir J, Lobo M and Zachary I:
Staurosporine induces endothelial cell apoptosis via focal adhesion
kinase dephosphorylation and focal adhesion disassembly independent
of focal adhesion kinase proteolysis. Biochem J. 367:145–155. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40.
|
Yang E, Zha J, Jockel J, Boise LH,
Thompson CB and Korsmeyer SJ: Bad, a heterodimeric partner for
Bcl-XL and Bcl-2, displaces Bax and promotes cell death. Cell.
80:285–291. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Hetz C, Vitte PA, Bombrun A, et al: Bax
channel inhibitors prevent mitochondrion-mediated apoptosis and
protect neurons in a model of global brain ischemia. J Biol Chem.
280:42960–42970. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Narita M, Shimizu S, Ito T, et al: Bax
interacts with the permeability transition pore to induce
permeability transition and cytochrome c release in isolated
mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:14681–14686. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Zamzami N, Marchetti P, Castedo M, et al:
Sequential reduction of mitochondrial transmembrane potential and
generation of reactive oxygen species in early programmed cell
death. J Exp Med. 182:367–377. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR and
Newmeyer DD: The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: a
primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science.
275:1132–1136. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Adrain C, Creagh EM and Martin SJ:
Apoptosis-associated release of Smac/DIABLO from mitochondria
requires active caspases and is blocked by Bcl-2. EMBO J.
20:6627–6636. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Hill MM, Adrain C, Duriez PJ, Creagh EM
and Martin SJ: Analysis of the composition, assembly kinetics and
activity of native Apaf-1 apoptosomes. EMBO J. 23:2134–2145. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Zou H, Li Y, Liu X and Wang X: An APAF-1
cytochrome c multimeric complex is a function apoptosome that
activates procaspase-9. J Biol Chem. 274:11549–11556. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L and Wang X: Smac,
a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent
caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell. 102:33–42.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, et al:
Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9
complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 91:479–489.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
McIlwain DR, Berger T and Mak TW: Caspase
functions in cell death and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Biol. 5:a0086562013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51.
|
Martin SJ and Green DR: Protease
activation during apoptosis: death by a thousand cuts? Cell.
82:349–352. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Earnshaw WC, Martins LM and Kaufmann SH:
Mammalian caspases: structure, activation, substrates, and
functions during apoptosis. Annu Rev. 68:383–424. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Zhang JH and Xu M: DNA fragmentation in
apoptosis. Cell Res. 10:205–211. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54.
|
Okayama H: Cell cycle control by anchorage
signaling. Cell Signal. 24:1599–1609. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55.
|
Aplin AE, Howe A, Alahari SK and Juliano
RL: Signal transduction and signal modulation by cell adhesion
receptors: the role of integrins, cadherins, immunoglobulin-cell
adhesion molecules, and selectins. Pharmacol Rev. 50:197–263.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
Schwartz MA and Baron V: Interactions
between mitogenic stimuli, or, a thousand and one connections. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 11:197–202. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57.
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Abrams SL, et
al: Roles of the RAF/ MEK/ERK and P13K/PTEN/AKT pathways in
malignant transformation and drug resistance. Adv Enzyme Regul.
46:249–279. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58.
|
Chitnis MM, Yuen JS, Protheroe AS, Pollak
M and Macaulay VM: The type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor
pathway. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6364–6370. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59.
|
Ivaska J and Heino J: Cooperation between
integrins and growth factor receptors in signaling and endocytosis.
Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol. 27:291–320. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60.
|
Werb Z: ECM and cell surface proteolysis:
regulating cellular ecology. Cell. 91:439–442. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61.
|
Mott JD and Werb Z: Regulation of matrix
biology by matrix metalloproteinases. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
16:558–564. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62.
|
Massova I, Kotra LP, Fridman R and
Mobashery S: Matrix metalloproteinases: structures, evolution, and
diversification. FASEB J. 12:1075–1095. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63.
|
Nagase H and Woessner JF Jr: Matrix
metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem. 274:21491–21494. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64.
|
Seiki M: Membrane-type 1 matrix
metalloproteinase: a key enzyme for tumor invasion. Cancer Lett.
194:1–11. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65.
|
Sohail A, Sun Q, Zhao H, Bernardo MM, Cho
JA and Fridman R: MT4-(MMP17) and MT6-MMP (MMP25), a unique set of
membrane-anchored matrix metalloproteinases: properties and
expression in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 27:289–302. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66.
|
Edwards DR, Handsley MM and Pennington CJ:
The ADAM metalloproteinases. Mol Aspects Med. 5:258–289. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67.
|
Tang BL: ADAMTS: a novel family of
extracellular matrix proteases. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 33:33–44.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68.
|
Kang T, Nagase H and Pei D: Activation of
membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase 3 zymogen by the proprotein
convertase furin in the trans-Golgi network. Cancer Res.
62:675–681. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69.
|
Kang T, Zhao YG, Pei D, Sucic JF and Sang
QX: Intracellular activation of human adamalysin 19/disintegrin and
metalloproteinase 19 by furin occurs via one of the two consecutive
recognition sites. J Biol Chem. 277:25583–25591. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70.
|
Stawowy P, Meyborg H, Stibenz D, et al:
Furin-like proprotein convertases are central regulators of the
membrane type matrix metalloproteinase-pro-matrix
metalloproteinase-2 proteolytic cascade in atherosclerosis. Circ.
111:2820–2827. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71.
|
Dubois CM, Laprise M-H, Blanchette F,
Gentry LE and Leduc R: Processing of transforming growth factor β1
precursor by human furin convertase. J Biol Chem. 270:10618–10624.
1995.
|
|
72.
|
Dubois CM, Blanchette F, Laprise MH, Leduc
R, Grondin F and Seidah NG: Evidence that furin is an authentic
transforming growth factor-beta1-converting enzyme. Am J Pathol.
158:305–316. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73.
|
Letterio JJ and Roberts AB: Regulation of
immune responses by TGF-beta. Annu Rev Immunol. 16:137–161. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74.
|
Mantel PY and Schmidt-Weber CB:
Transforming growth factor-beta: recent advances on its role in
immune tolerance. Methods Mol Biol. 677:303–338. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75.
|
Bommireddy R and Doetschman T: TGFβ1 and
Treg cells: alliance for tolerance Trends. Mol Med.
11:492–501. 2007.
|
|
76.
|
Gomez GG and Kruse CA: Mechanisms of
malignant glioma resistance and sources of immunosuppression. Gene
Ther Mol Biol. 10:133–146. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77.
|
Avril T, Vauleon E, Tanguy-Royer S, Mosser
J and Quillien V: Mechanisms of immunomodulation in human
glioblastoma. Immunotherapy. 3(Suppl 4): 42–44. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78.
|
Leitlein J, Aulwurm S, Waltereit R, et al:
Processing of immunosuppressive pro-TGF-beta 1,2 by human
glioblastoma cells involves cytoplasmic and secreted furin-like
proteases. J Immunol. 166:7238–7243. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79.
|
Mercapide J, Lopez De Cicco R, Bassi DE,
Castresana JS, Thomas G and Klein-Szanto AJ: Inhibition of
furin-mediated processing results in suppression of astrocytoma
cell growth and invasiveness. Clin Cancer Res. 8:1740–1746.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80.
|
Poli A, Kmiecik J, Domingues O, et al: NK
cells in central nervous system disorders. J Immunol.
190:5355–5362. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81.
|
Lodoen MB and Lanier LL: Viral modulation
of NK cell immunity. Nat Rev Microbiol. 3:59–69. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82.
|
Vivier E, Raulet DH, Moretta A, et al:
Innate or adaptive immunity? The example of natural killer cells.
Science. 331:44–49. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83.
|
Daga A, Bottino C, Castriconi R, Gangemi R
and Ferrini S: New perspectives in glioma immunotherapy. Curr Pharm
Des. 17:2439–2467. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84.
|
Hegi ME, Rajakannu P and Weller M:
Epidermal growth factor receptor: a re-emerging target in
glioblastoma. Curr Opin Neurol. 25:774–779. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85.
|
Pala A, Karpel-Massler G, Kast RE, Wirtz
CR and Halatsch ME: Epidermal to mesenchymal transition and failure
of EGFR-targeted therapy in glioblastoma. Cancers. 4:523–530. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|