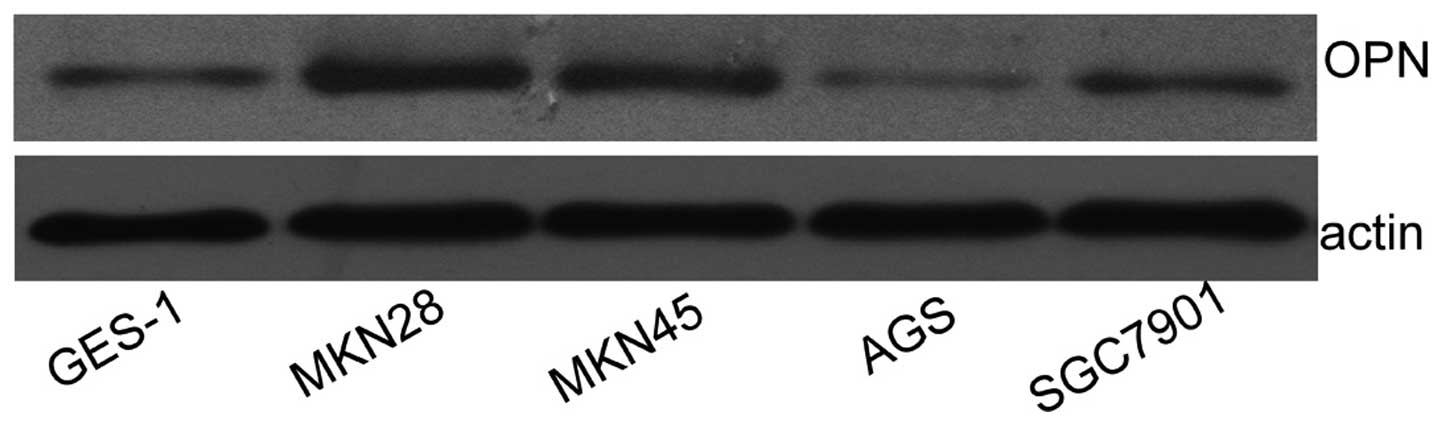
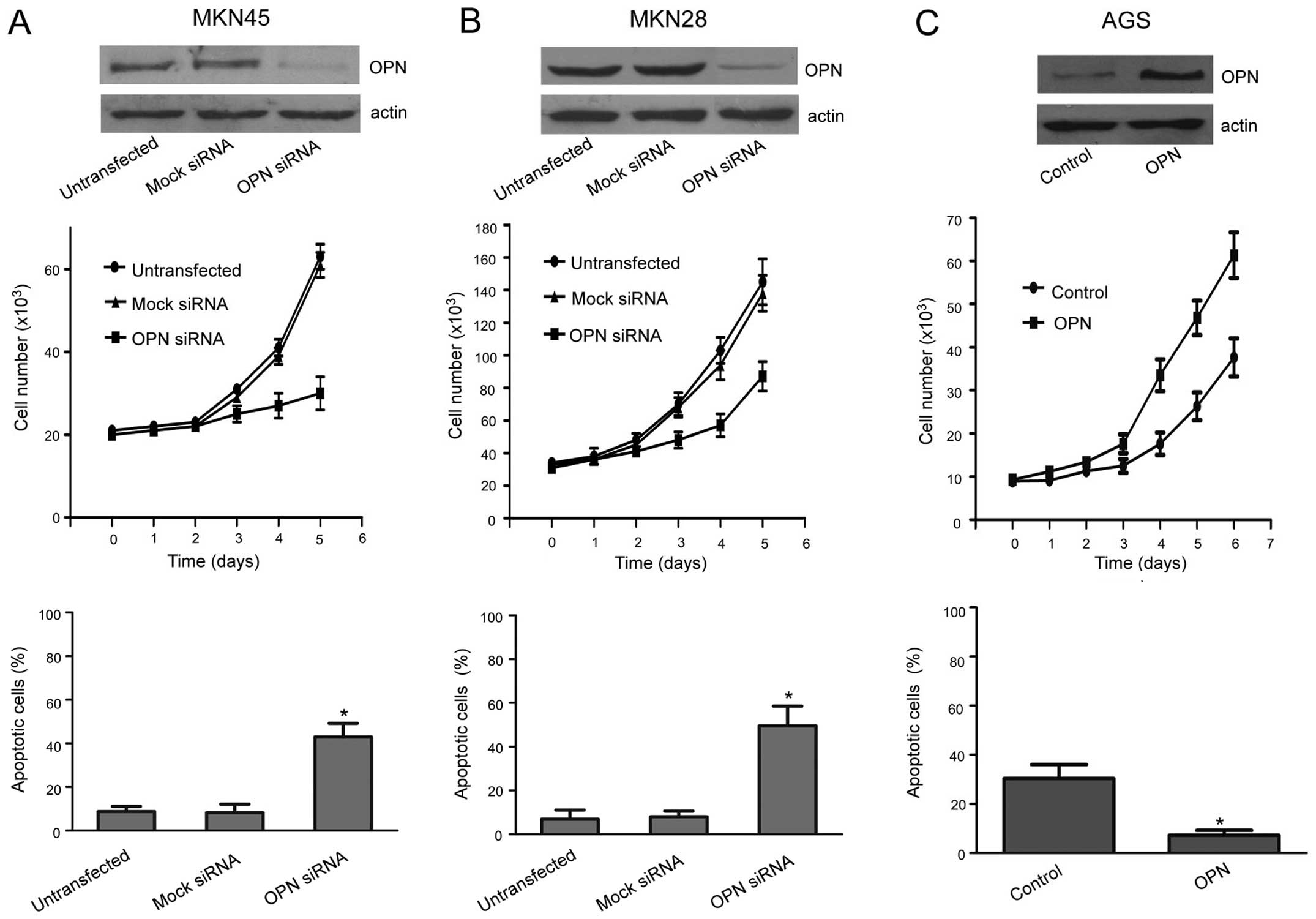
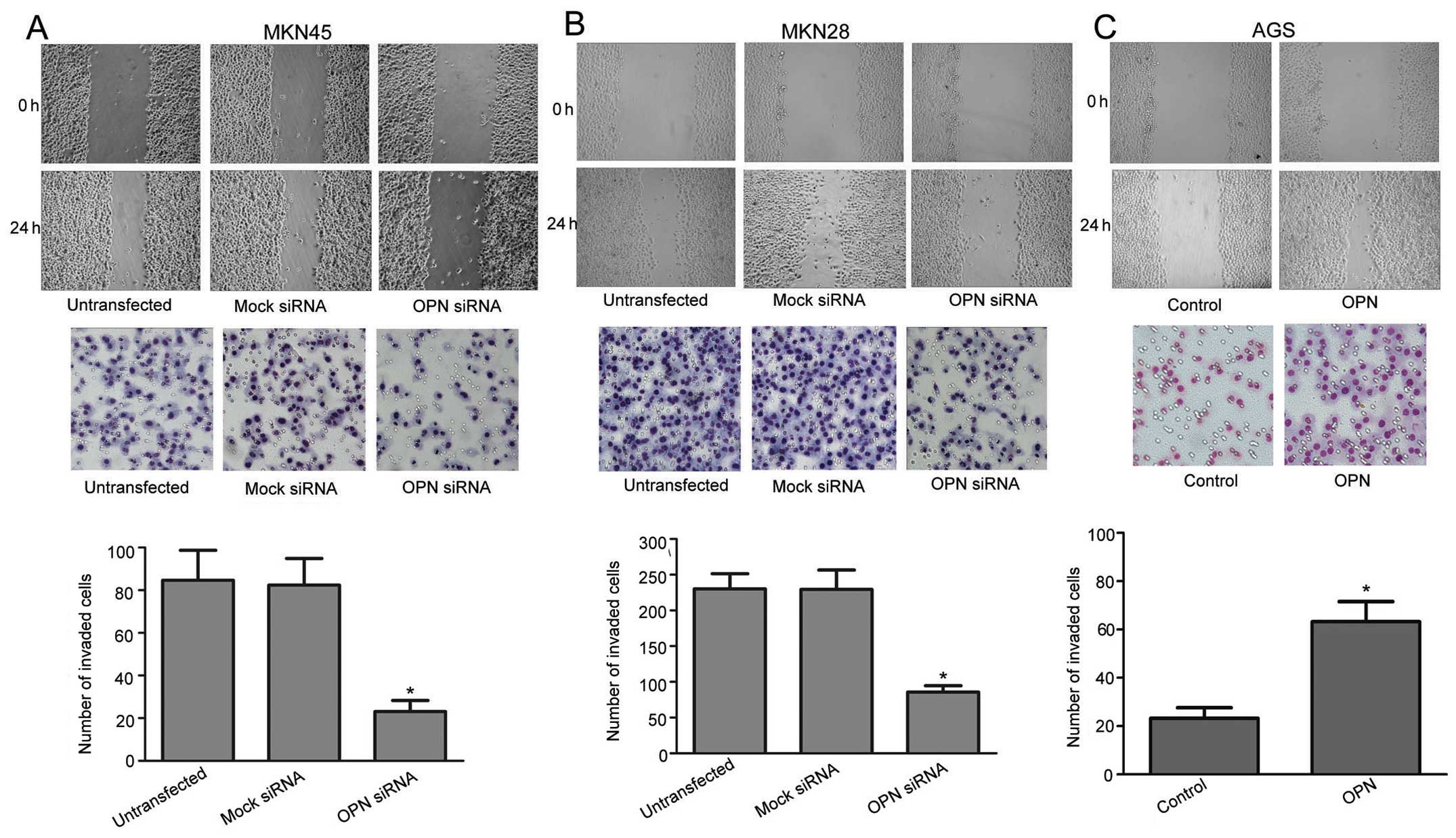
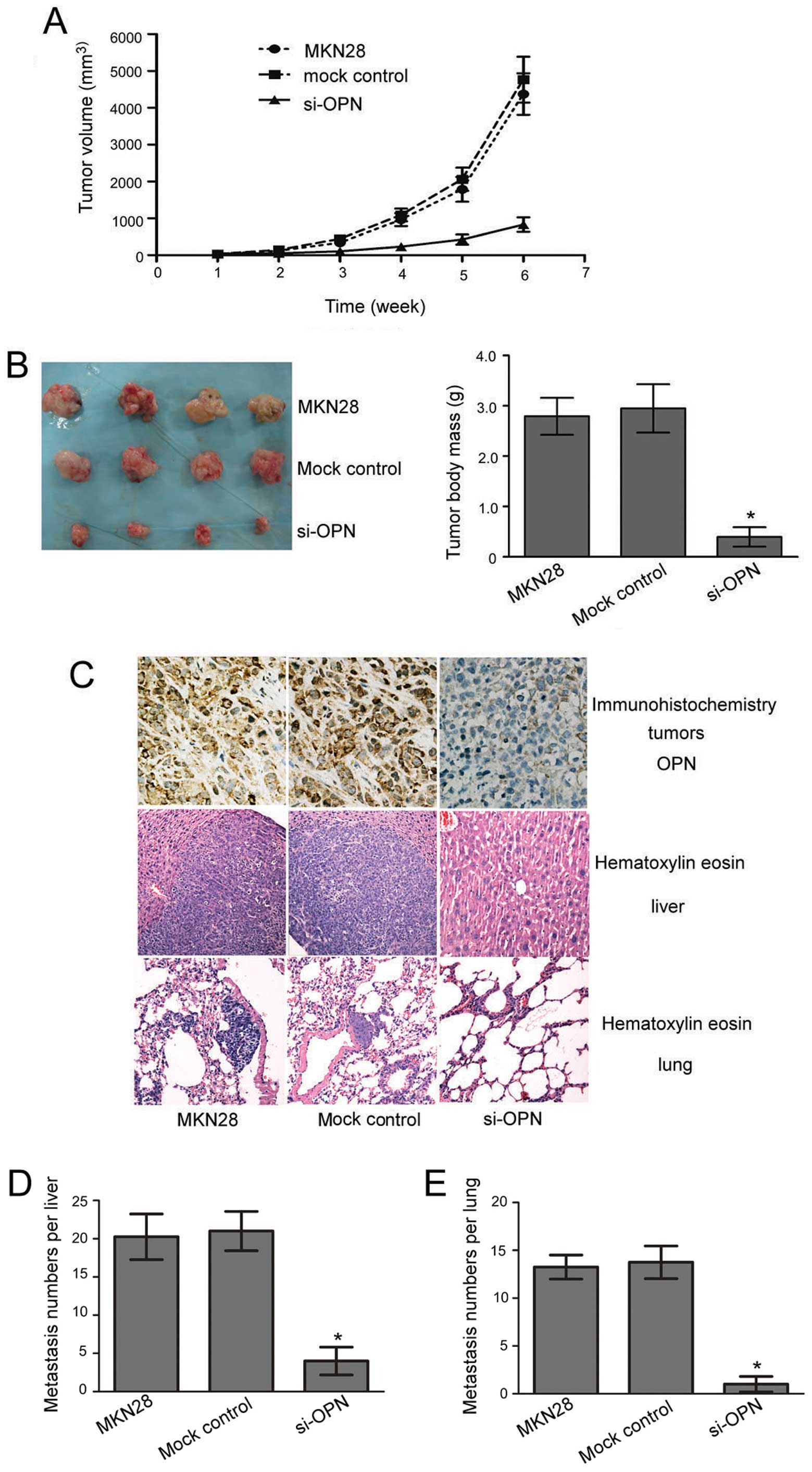
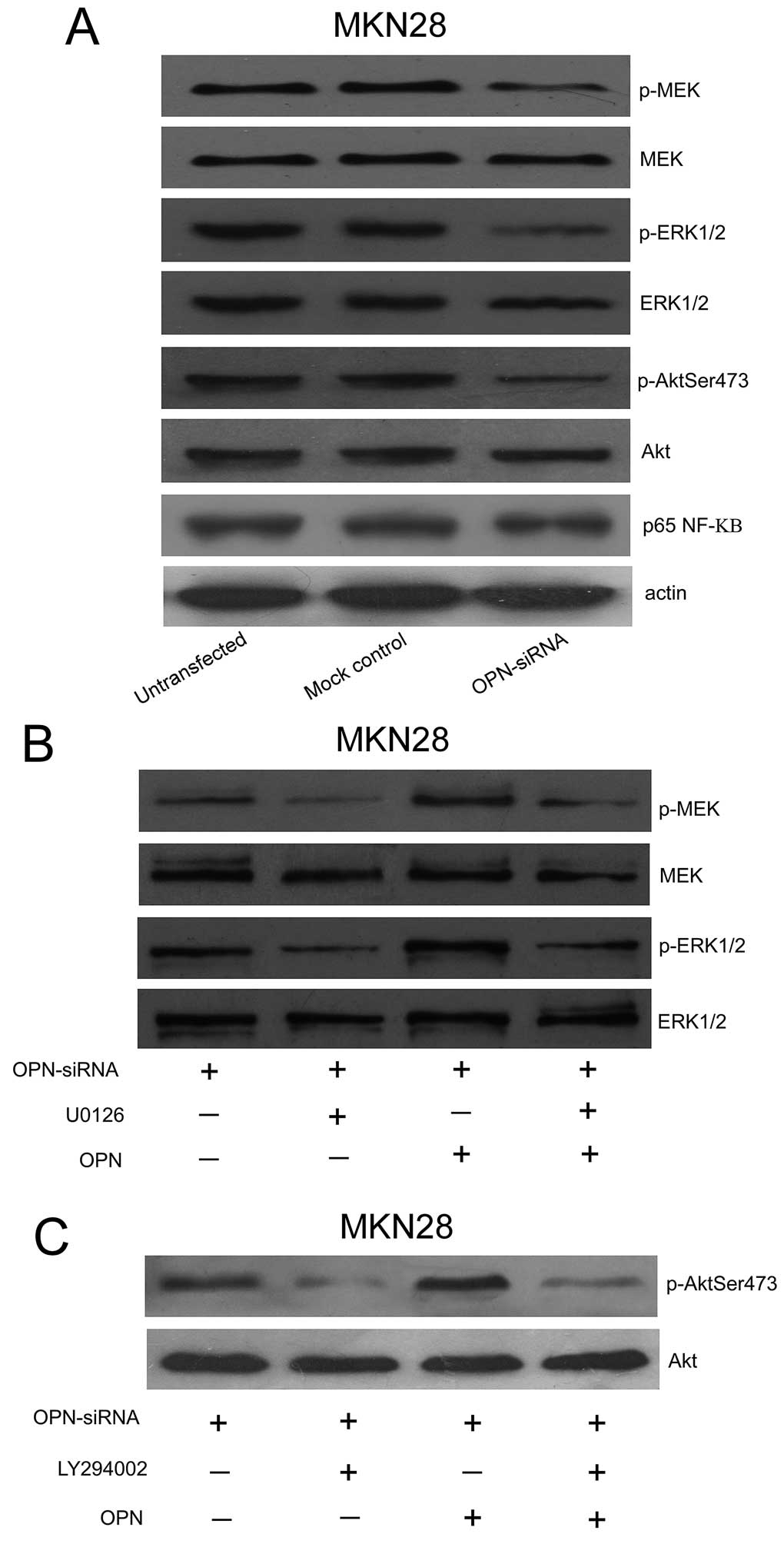
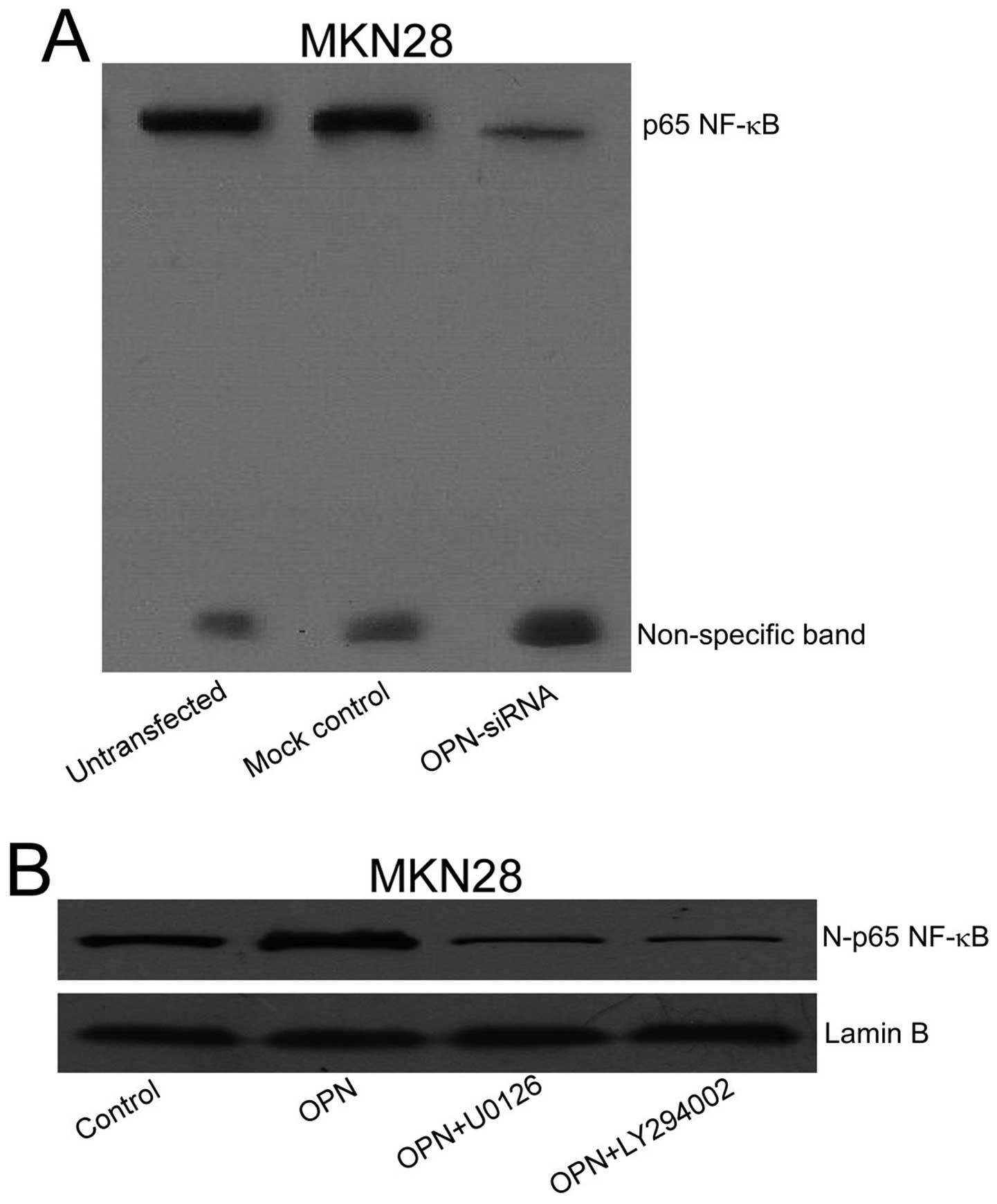
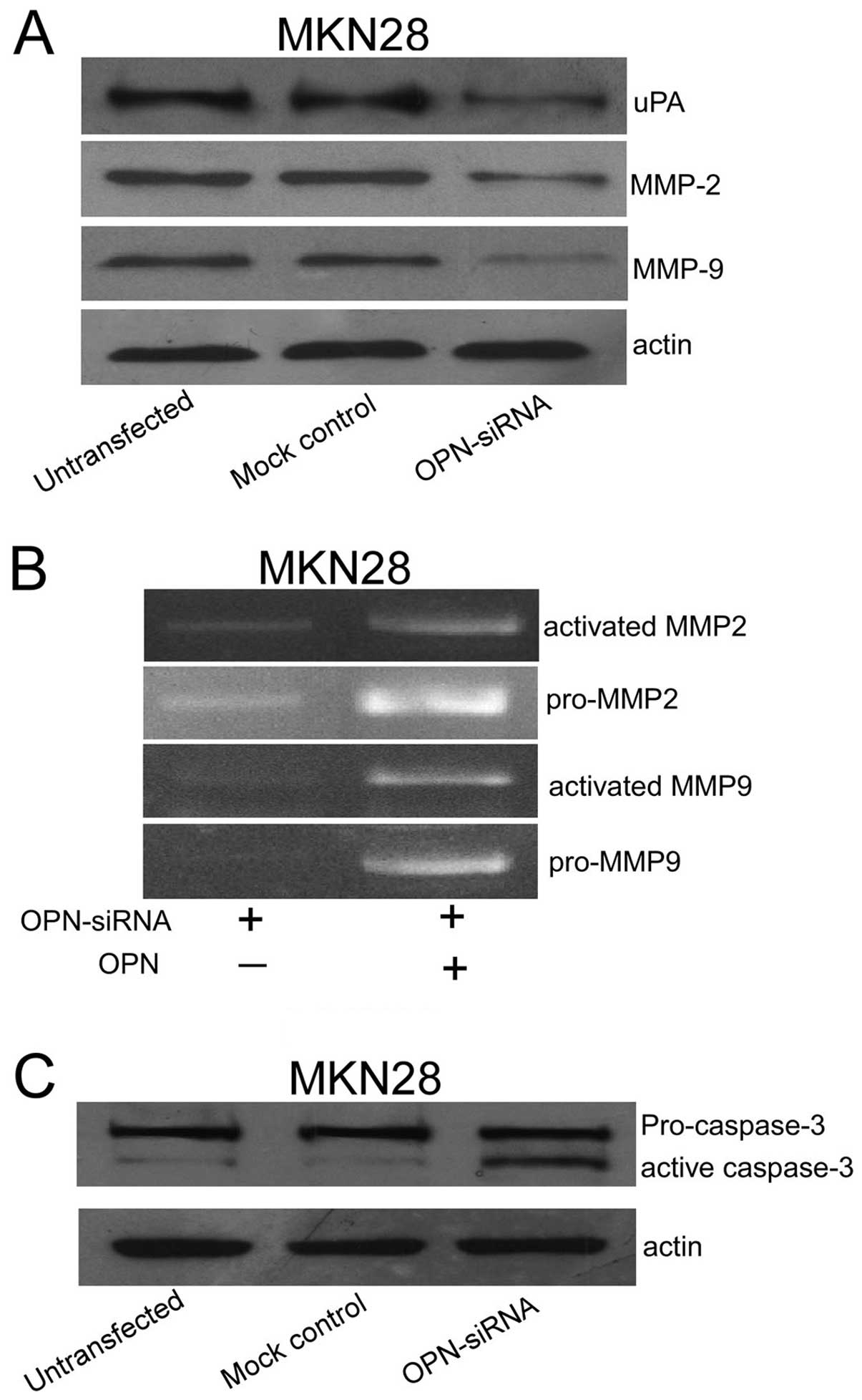
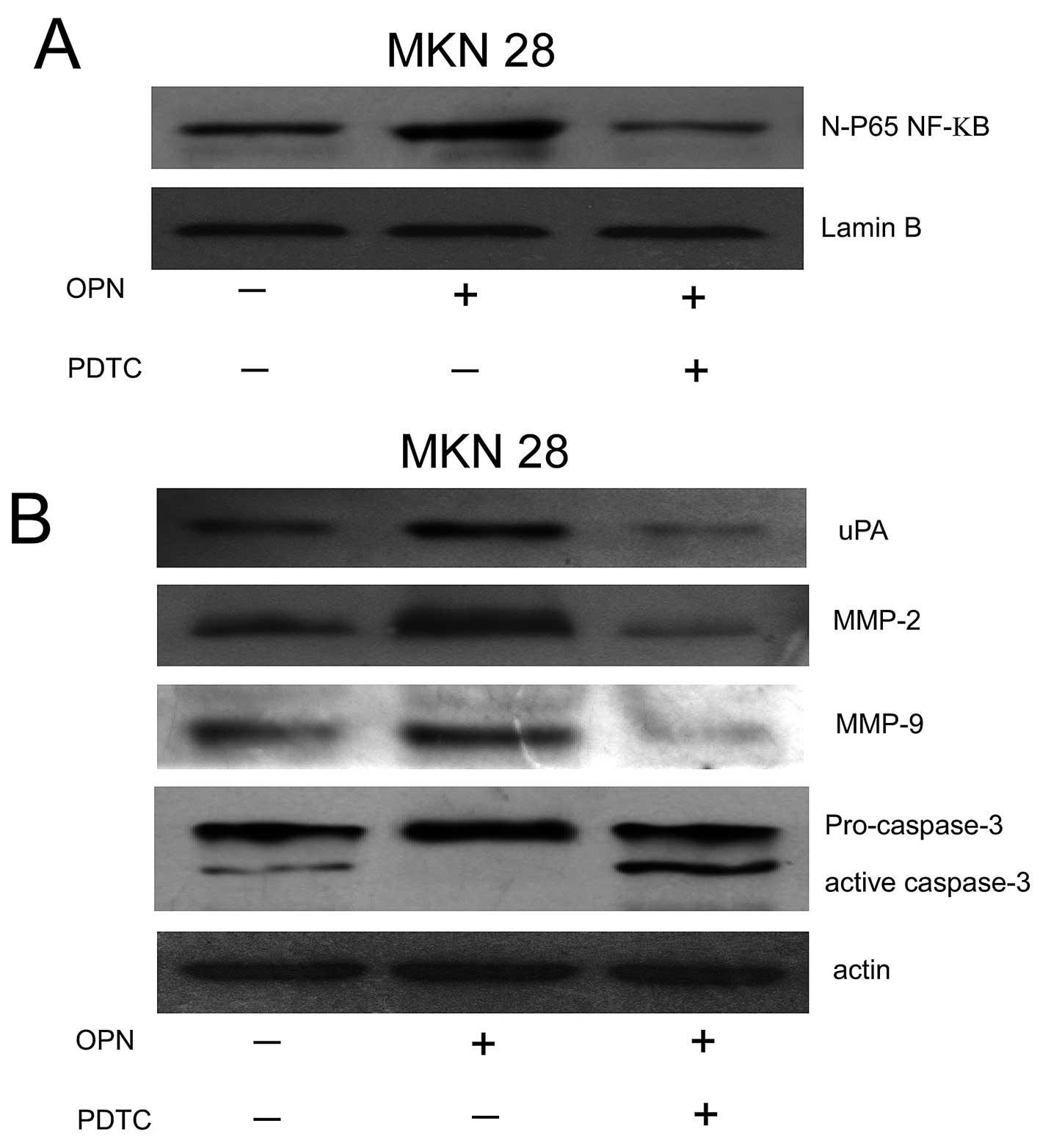
|
1.
|
Prince CW, Oosawa T, Butler WT, et al:
Isolation, characterization, and biosynthesis of a phosphorylated
glycoprotein from rat bone. J Biol Chem. 262:2900–2907.
1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Ramaiah SK and Rittling S:
Pathophysiological role of osteo-pontin in hepatic inflammation,
toxicity, and cancer. Toxicol Sci. 103:4–13. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Rangaswami H, Bulbule A and Kundu GC:
Osteopontin: role in cell signaling and cancer progression. Trends
Cell Biol. 16:79–87. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Higashiyama M, Ito T, Tanaka E and Shimada
Y: Prognostic significance of osteopontin expression in human
gastric carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 14:3419–3427. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Imano M, Satou T, Itoh T, et al:
Immunohistochemical expression of osteopontin in gastric cancer. J
Gastrointest Surg. 13:1577–1582. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Junnila S, Kokkola A, Mizuguchi T, et al:
Gene expression analysis identifies over-expression of CXCL1,
SPARC, SPP1, and SULF1 in gastric cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer.
49:28–39. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Wu CY, Wu MS, Chiang EP, et al: Elevated
plasma osteopontin associated with gastric cancer development,
invasion and survival. Gut. 56:782–789. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Tang H, Wang J, Bai F, et al: Inhibition
of osteopontin would suppress angiogenesis in gastric cancer.
Biochem Cell Biol. 85:103–110. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Gong M, Lu Z, Fang G, Bi J and Xue X: A
small interfering RNA targeting osteopontin as gastric cancer
therapeutics. Cancer Lett. 272:148–159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Wang ZM, Cui YH, Li W, Chen SY and Liu TS:
Lentiviral-mediated siRNA targeted against osteopontin suppresses
the growth and metastasis of gastric cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
25:997–1003. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Ue T, Yokozaki H, Kitadai Y, et al:
Co-expression of osteopontin and CD44v9 in gastric cancer. Int J
Cancer. 79:127–132. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Dai N, Bao Q, Lu A and Li J: Protein
expression of osteopontin in tumor tissues is an independent
prognostic indicator in gastric cancer. Oncology. 72:89–96. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Zhang X, Tsukamoto T, Mizoshita T, et al:
Expression of osteopontin and CDX2: indications of phenotypes and
prognosis in advanced gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 21:609–613.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Bellahcene A, Castronovo V, Ogbureke KU,
Fisher LW and Fedarko NS: Small integrin-binding ligand N-linked
glycoproteins (SIBLINGs): multifunctional proteins in cancer. Nat
Rev Cancer. 8:212–226. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Scatena M, Almeida M, Chaisson ML, Fausto
N, Nicosia RF and Giachelli CM: NF-kappaB mediates alphavbeta3
integrin-induced endothelial cell survival. J Cell Biol.
141:1083–1093. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Rangaswami H, Bulbule A and Kundu GC:
Nuclear factor-inducing kinase plays a crucial role in
osteopontin-induced MAPK/IkappaBalpha kinase-dependent nuclear
factor kappaB-mediated promatrix metalloproteinase-9 activation. J
Biol Chem. 279:38921–38935. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17.
|
Rittling SR and Chambers AF: Role of
osteopontin in tumour progression. Br J Cancer. 90:1877–1881. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Philip S and Kundu GC: Osteopontin induces
nuclear factor kappa B-mediated promatrix metalloproteinase-2
activation through I kappa B alpha/IKK signaling pathways, and
curcumin (diferulolylmethane) down-regulates these pathways. J Biol
Chem. 278:14487–14497. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19.
|
Das R, Mahabeleshwar GH and Kundu GC:
Osteopontin stimulates cell motility and nuclear factor
kappaB-mediated secretion of urokinase type plasminogen activator
through phosphati-dylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathways in
breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 278:28593–28606. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Jain S, Chakraborty G and Kundu GC: The
crucial role of cyclooxygenase-2 in osteopontin-induced protein
kinase C alpha/c-Src/IkappaB kinase alpha/beta-dependent prostate
tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 66:6638–6648. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Mi Z, Guo H, Wai PY, Gao C and Kuo PC:
Integrin-linked kinase regulates osteopontin-dependent MMP-2 and
uPA expression to convey metastatic function in murine mammary
epithelial cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 27:1134–1145. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22.
|
Shaulian E and Karin M: AP-1 as a
regulator of cell life and death. Nat Cell Biol. 4:E131–E136. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Lin YH and Yang-Yen HF: The
osteopontin-CD44 survival signal involves activation of the
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. J Biol Chem.
276:46024–46030. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Lee KW, Kim SG, Kim HP, et al:
Enzastaurin, a protein kinase C beta inhibitor, suppresses
signaling through the ribosomal S6 kinase and bad pathways and
induces apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells. Cancer Res.
68:1916–1926. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Chae S, Jun HO, Lee EG, et al: Osteopontin
splice variants differentially modulate the migratory activity of
hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Int J Oncol. 35:1409–1416.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
He B, Mirza M and Weber GF: An osteopontin
splice variant induces anchorage independence in human breast
cancer cells. Oncogene. 25:2192–2202. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Zhao B, Sun T, Meng F, et al: Osteopontin
as a potential biomarker of proliferation and invasiveness for lung
cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:1061–1070. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Tang X, Li J, Yu B, et al: Osteopontin
splice variants differentially exert clinicopathological features
and biological functions in gastric cancer. Int J Biol Sci.
9:55–66. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|