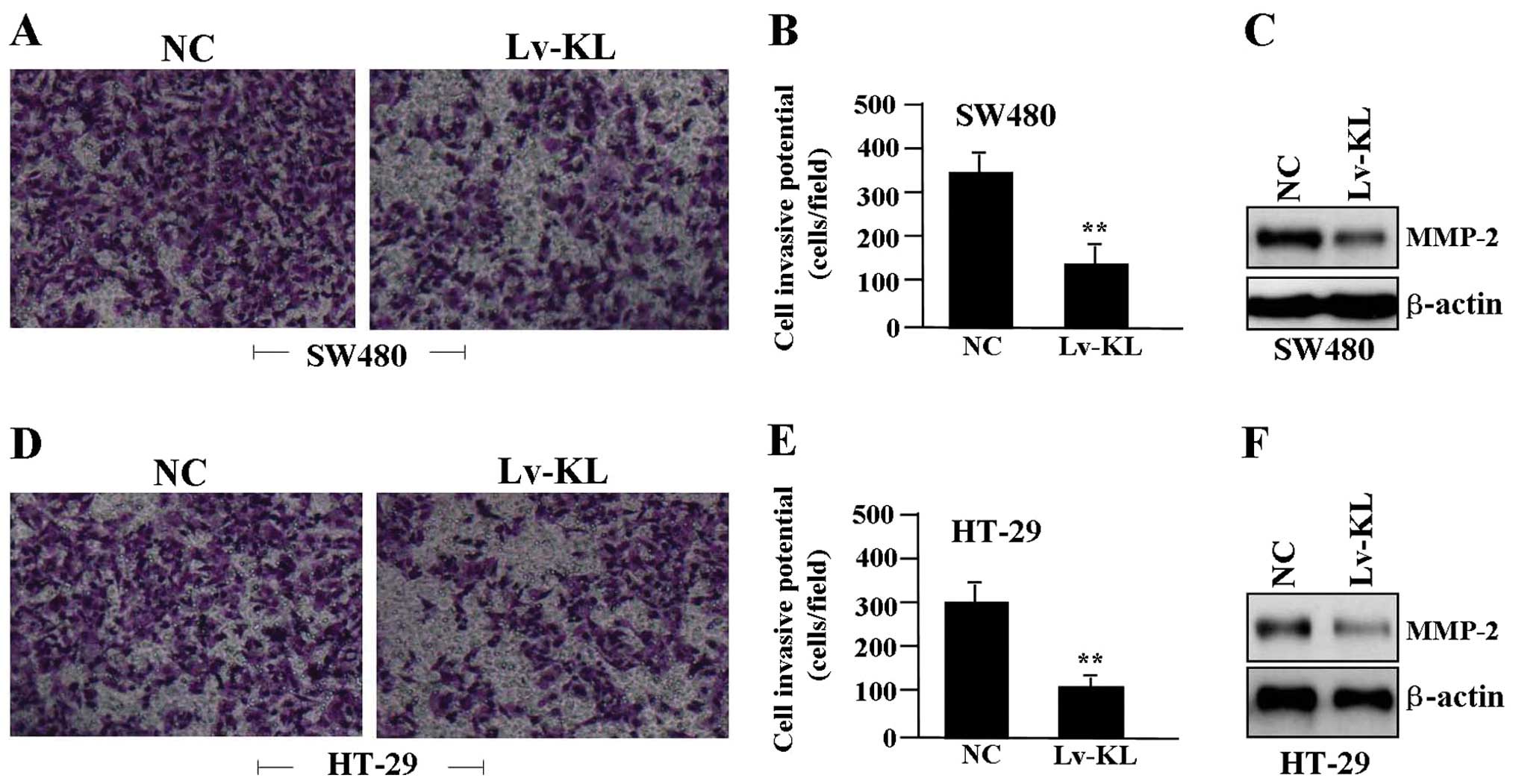
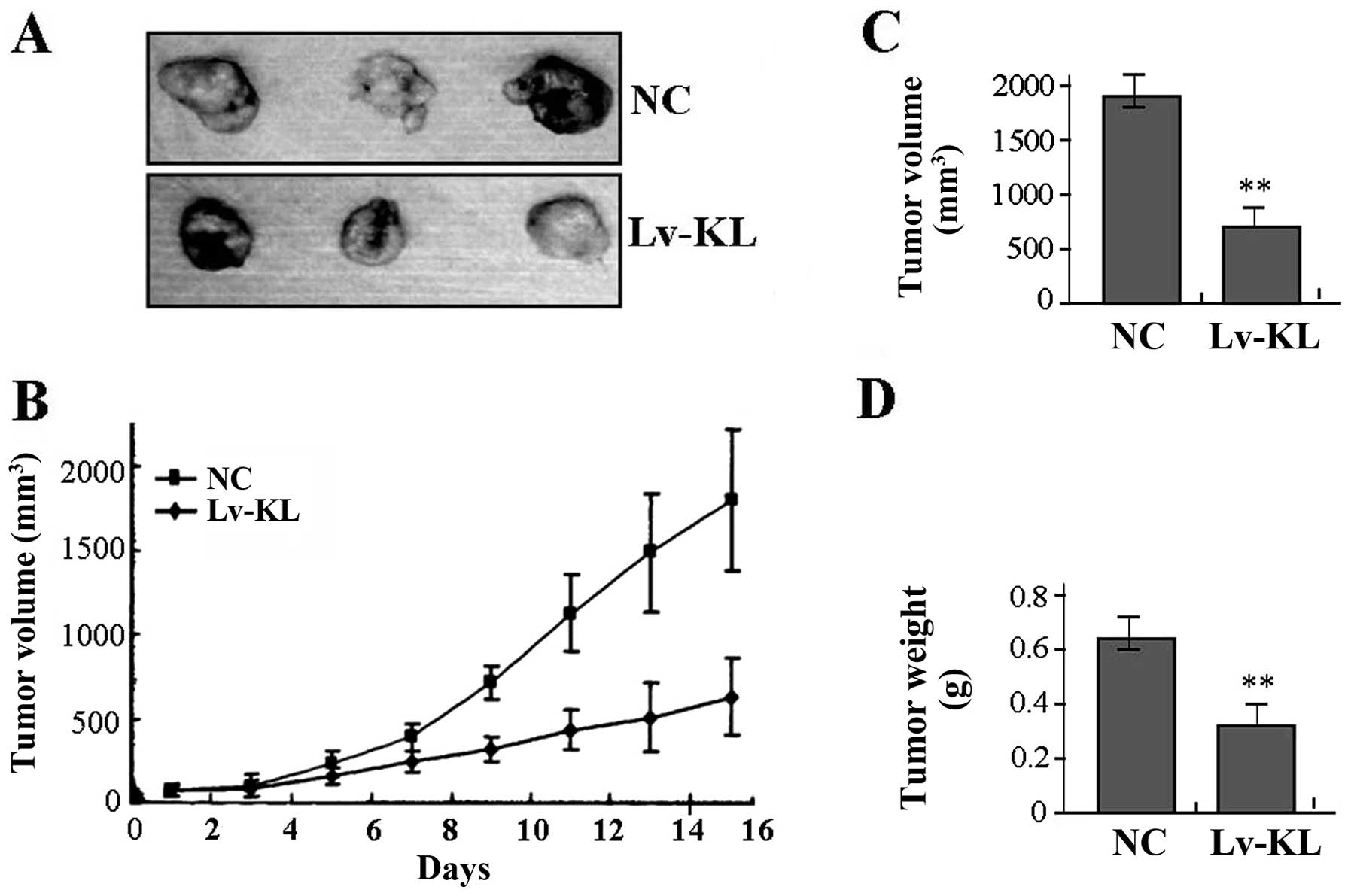
|
1
|
Antonic V, Stojadinovic A, Kester KE, et
al: Significance of infectious agents in colorectal cancer
development. J Cancer. 4:227–240. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Young PE and Womeldorph CM: Colonoscopy
for colorectal cancer screening. J Cancer. 4:217–226. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kuro-o M: Klotho as a regulator of
oxidative stress and senescence. Biol Chem. 38:233–241. 2008.
|
|
4
|
Xie B, Chen J, Liu B, et al: Klotho acts
as a tumor suppressor in cancers. Pathol Oncol Res. 19:611–617.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang L, Wang X, Wang X, et al: Klotho is
silenced through promoter hypermethylation in gastric cancer. Am J
Cancer Res. 1:111–119. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pan J, Zhong J, Gan LH, et al: Klotho, an
anti-senescence related gene, is frequently inactivated through
promoter hypermethylation in colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol.
32:729–735. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rubinek T, Shulman M, Israeli S, et al:
Epigenetic silencing of the tumor suppressor klotho in human breast
cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 133:649–657. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Usuda J, Ichinose S, Ishizumi T, et al:
Klotho predicts good clinical outcome in patients with
limited-disease small cell lung cancer who received surgery. Lung
Cancer. 74:332–337. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Xie B, Zhou J, Yuan L, et al: Epigenetic
silencing of Klotho expression correlates with poor prognosis of
human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 44:795–801. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Doi S, Zou Y, Togao O, et al: Klotho
inhibits transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) signaling and
suppresses renal fibrosis and cancer metastasis in mice. J Biol
Chem. 286:8655–8665. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Camilli TC, Xu M, O’Connell MP, et al:
Loss of Klotho during melanoma progression leads to increased
filamin cleavage, increased Wnt5A expression, and enhanced melanoma
cell motility. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 24:175–186. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Abramovitz L, Rubinek T, Ligumsky H, et
al: KL1 internal repeat mediates klotho tumor suppressor activities
and inhibits bFGF and IGF-I signaling in pancreatic cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 17:4254–4266. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen B, Ma X, Liu S, et al: Inhibition of
lung cancer cells growth, motility and induction of apoptosis by
Klotho, a novel secreted Wnt antagonist, in a dose-dependent
manner. Cancer Biol Ther. 13:1221–1228. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen B, Wang X, Zhao W, et al: Klotho
inhibits growth and promotes apoptosis in human lung cancer cell
line A549. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 29:992010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chang B, Kim J, Jeong D, et al: Klotho
inhibits the capacity of cell migration and invasion in cervical
cancer. Oncol Rep. 28:1022–1028. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu L, Katsaros D, Wiley A, et al: Klotho
expression in epithelial ovarian cancer and its association with
insulin-like growth factors and disease progression. Cancer Invest.
26:185–192. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Poh W, Wong W, Ong H, et al: Klotho-beta
overexpression as a novel target for suppressing proliferation and
fibroblast growth factor receptor-4 signaling in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 11:142012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kuro-o M: Klotho in health and disease.
Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 21:362–368. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yahata K, Mori K, Arai H, et al: Molecular
cloning and expression of a novel klotho-related protein. J Mol Med
(Berl). 78:389–394. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Usuda J, Ichinose S, Ishizumi T, et al:
Klotho is a novel biomarker for good survival in resected large
cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung. Lung Cancer. 72:355–359.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dërmaku-Sopjani M, Kolgeci S, Abazi S, et
al: Significance of the anti-aging protein Klotho. Mol Membr Biol.
30:369–385. 2013.
|
|
23
|
Shu G, Xie B, Ren F, et al: Restoration of
klotho expression induces apoptosis and autophagy in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 36:121–129. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ye X, Guo Y, Zhang Q, et al: βKlotho
suppresses tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating
Akt/GSK-3β/cyclin D1 signaling pathway. PLoS One. 8:e556152013.
|
|
25
|
Xie B, Zhou J, Shu G, et al: Restoration
of klotho gene expression induces apoptosis and autophagy in
gastric cancer cells: tumor suppressive role of klotho in gastric
cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 13:182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen L, Liu H, Liu J, et al: Klotho endows
hepatoma cells with resistance to anoikis via VEGFR2/PAK1
activation in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e584132013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu Y, Xu L, Zhang J, et al: Klotho
suppresses tumor progression via inhibiting PI3K/Akt/GSK3β/Snail
signaling in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 104:663–671.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Y, Chen L, Huang G, et al: Klotho
sensitizes human lung cancer cell line to cisplatin via PI3k/Akt
pathway. PLoS One. 8:e573912013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
do Lim Y, Cho HJ, Kim J, et al: Luteolin
decreases IGF-II production and downregulates insulin-like growth
factor-I receptor signaling in HT-29 human colon cancer cells. BMC
Gastroenterol. 12:92012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Risio M: Cell proliferation in colorectal
tumor progression: an immunohistochemical approach to intermediate
biomarkers. J Cell Biochem (Suppl). 16G:79–87. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liabakk NB, Talbot I, Smith RA, et al:
Matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) and matrix metalloproteinase 9
(MMP-9) type IV collagenases in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res.
56:190–196. 1996.
|
|
32
|
Fu Y, Zhang Q, Kang C, et al: Inhibitory
effects of adenovirus mediated Akt1 and PIK3R1 shRNA on the growth
of malignant tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biol Ther.
8:1002–1009. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|