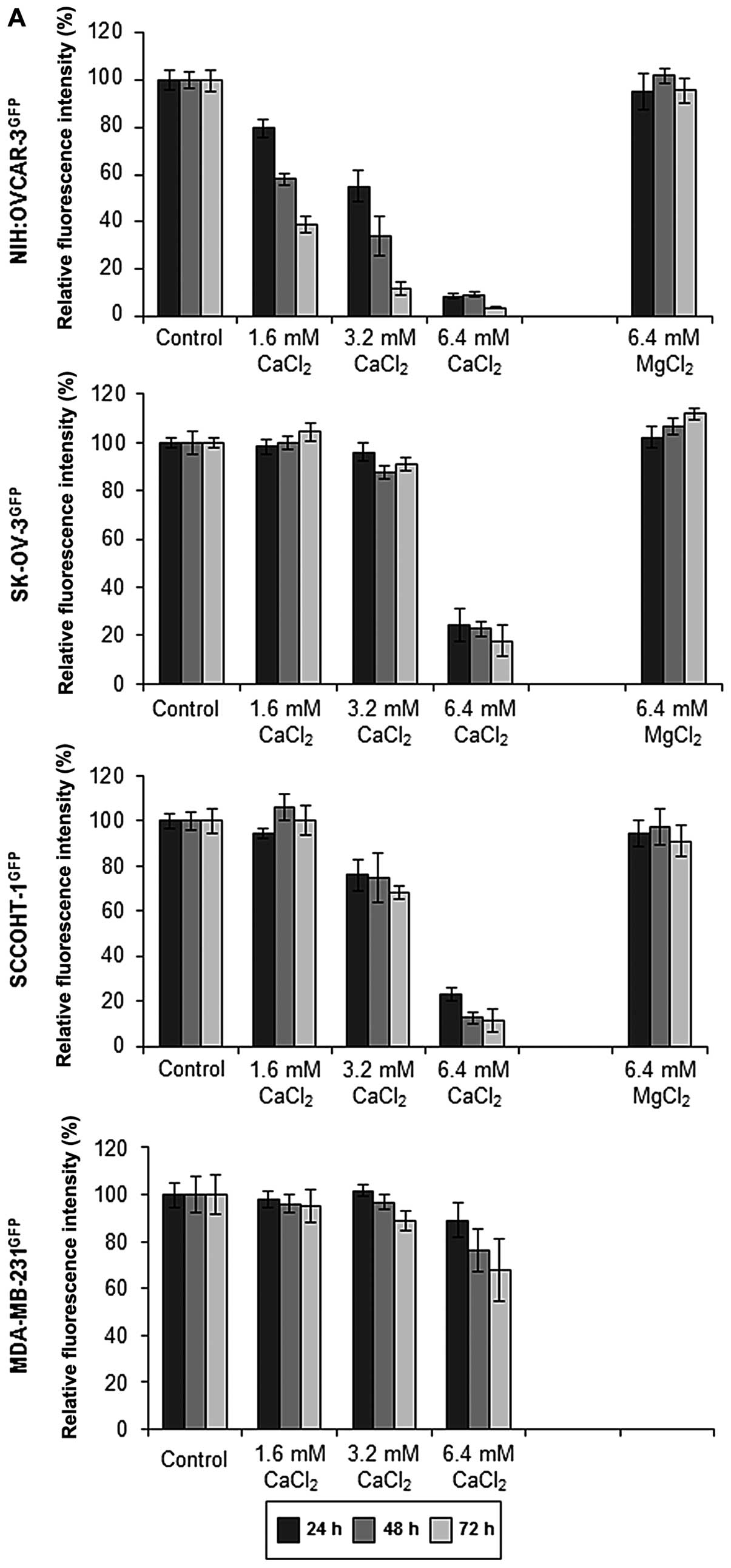
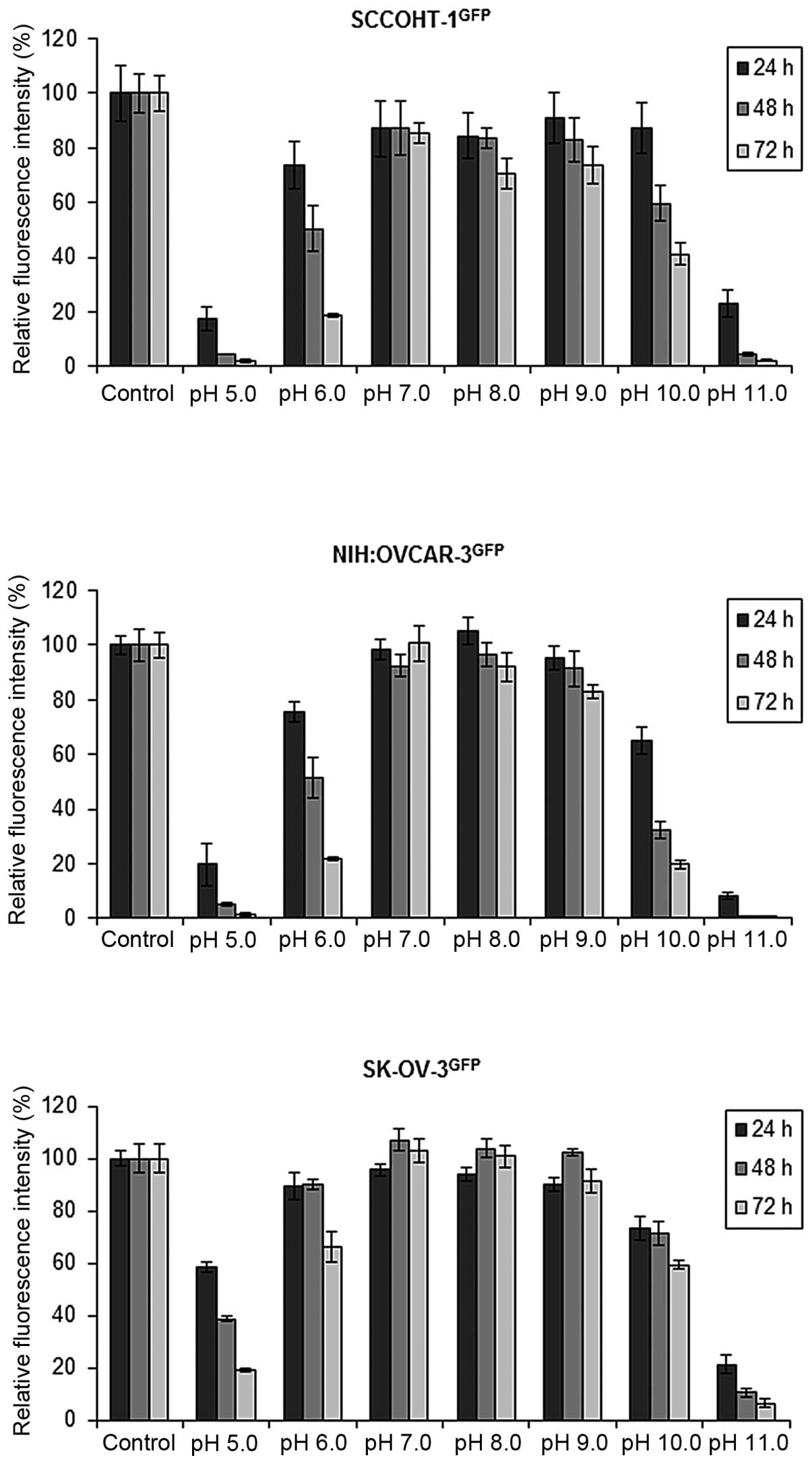
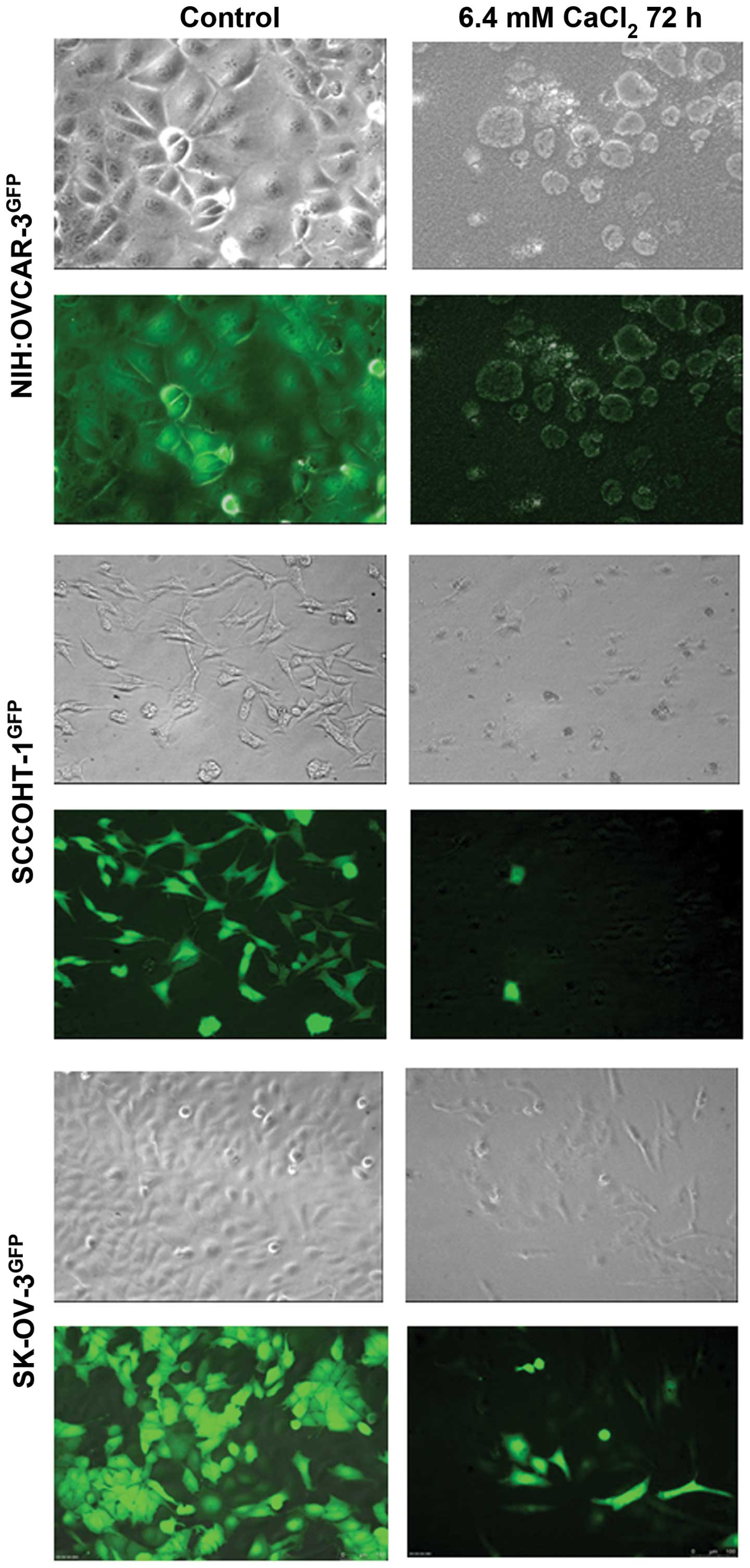
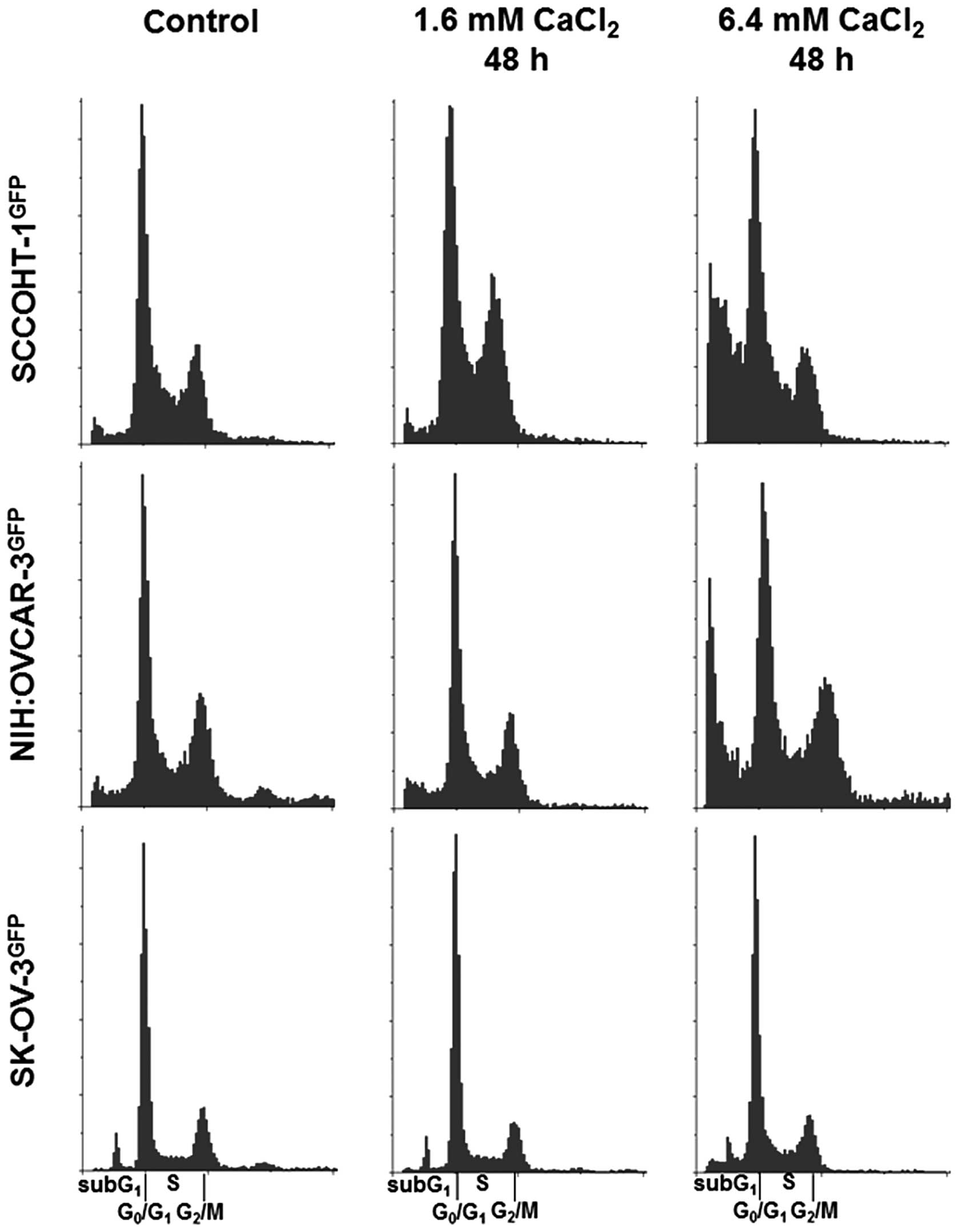
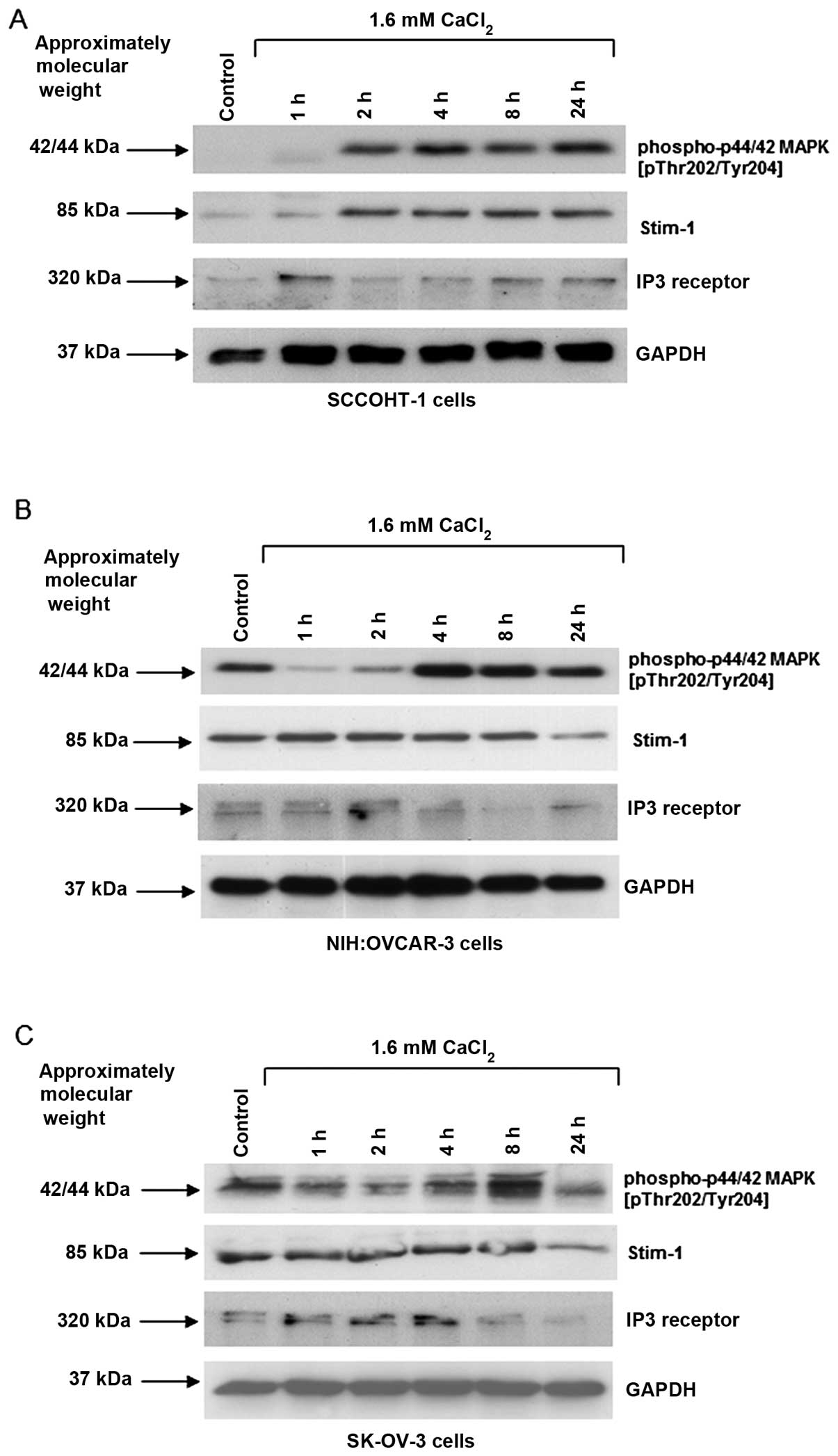
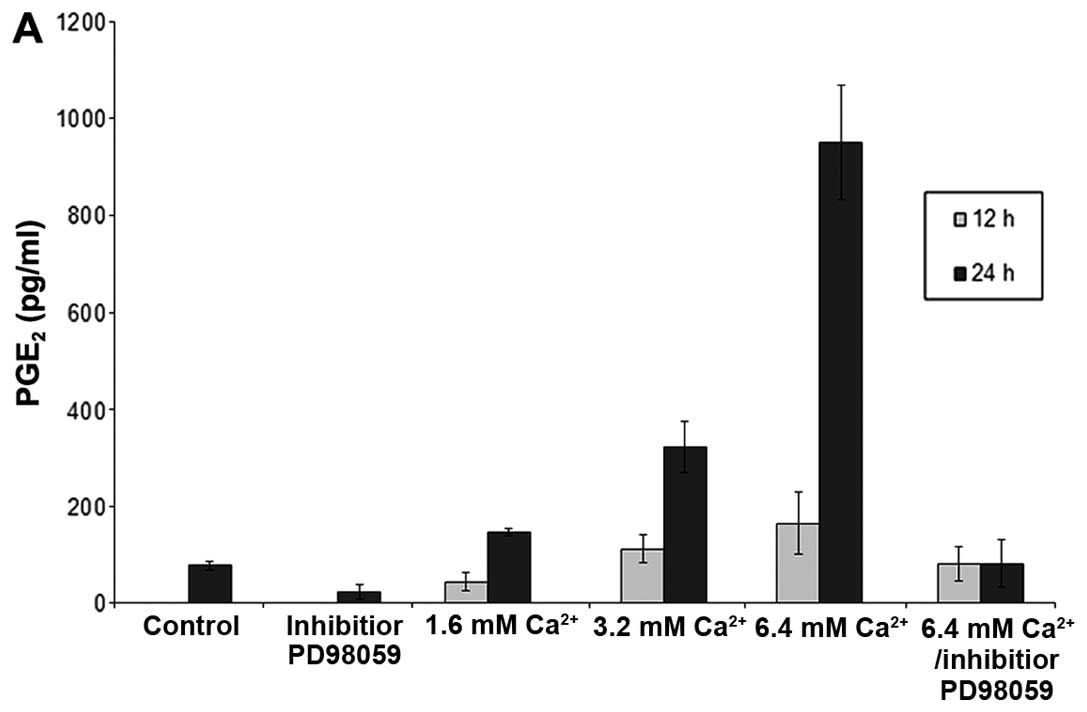
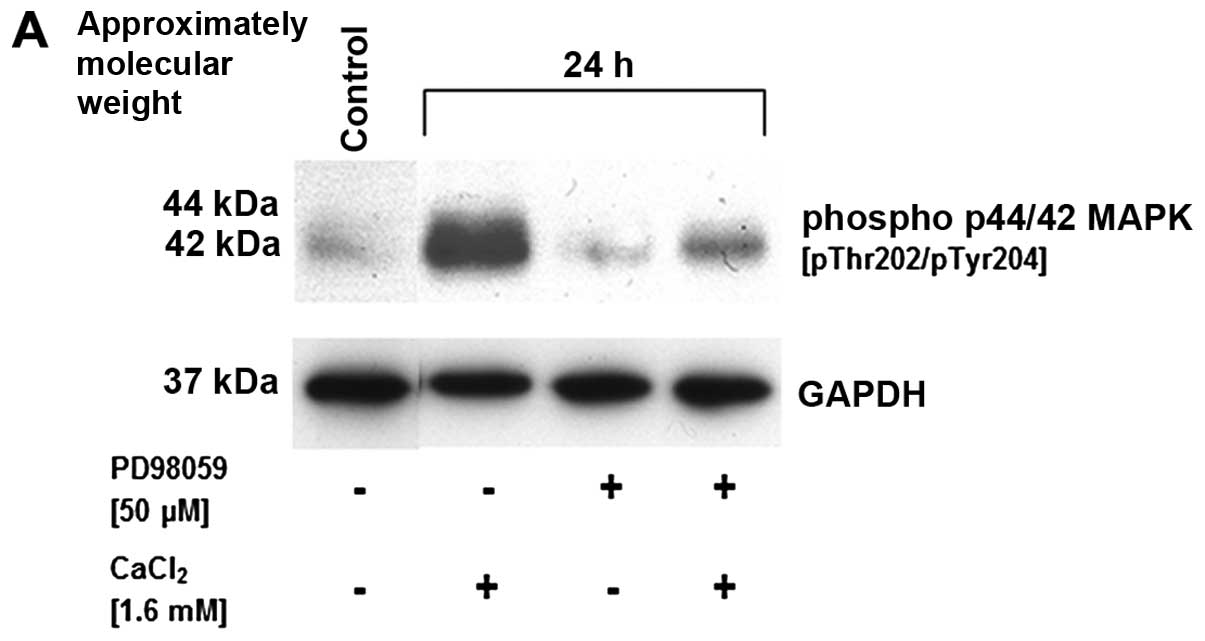
|
1
|
Otte A, Gohring G, Steinemann D, et al: A
tumor-derived population (SCCOHT-1) as cellular model for a small
cell ovarian carcinoma of the hypercalcemic type. Int J Oncol.
41:765–775. 2012.
|
|
2
|
Dickersin GR, Kline IW and Scully RE:
Small cell carcinoma of the ovary with hypercalcemia: a report of
eleven cases. Cancer. 49:188–197. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Young RH, Oliva E and Scully RE: Small
cell carcinoma of the hypercalcemic type in the ovary. Gynecol
Oncol. 57:7–8. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jelinic P, Mueller JJ, Olvera N, et al:
Recurrent SMARCA4 mutations in small cell carcinoma of the ovary.
Nat Genet. 46:424–426. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Witkowski L, Carrot-Zhang J, Albrecht S,
et al: Germline and somatic SMARCA4 mutations characterize small
cell carcinoma of the ovary, hypercalcemic type. Nat Genet.
46:438–443. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ramos P, Karnezis AN, Craig DW, et al:
Small cell carcinoma of the ovary, hypercalcemic type, displays
frequent inactivating germline and somatic mutations in SMARCA4.
Nat Genet. 46:427–429. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Scully RE: Atlas of Tumor Pathology:
Tumors of the Ovary and Maldeveloped Gonads. Armed Forces Institute
of Pathology; Washington, DC: 1979
|
|
8
|
Ulbright TM, Roth LM, Stehman FB, Talerman
A and Senekjian EK: Poorly differentiated (small cell) carcinoma of
the ovary in young women: evidence supporting a germ cell origin.
Hum Pathol. 18:175–184. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aguirre P, Thor AD and Scully RE: Ovarian
small cell carcinoma. Histogenetic considerations based on
immunohistochemical and other findings. Am J Clin Pathol.
92:140–149. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Walt H, Hornung R, Fink D, et al:
Hypercalcemic-type of small cell carcinoma of the ovary:
characterization of a new tumor line. Anticancer Res. 21:3253–3259.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
McCluggage WG, Oliva E, Connolly LE,
McBride HA and Young RH: An immunohistochemical analysis of ovarian
small cell carcinoma of hypercalcemic type. Int J Gynecol Pathol.
23:330–336. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Harrison ML, Hoskins P, du Bois A, et al:
Small cell of the ovary, hypercalcemic type - analysis of combined
experience and recommendation for management. A GCIG study. Gynecol
Oncol. 100:233–238. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shrimali RK, Correa PD and Reed NS:
Dose-dense and dose-intense chemotherapy for small cell ovarian
cancer: 2 cases and review of literature. Med Oncol. 28:766–770.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Benrubi GI, Pitel P and Lammert N: Small
cell carcinoma of the ovary with hypercalcemia responsive to
sequencing chemotherapy. South Med J. 86:247–248. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Reed WC: Small cell carcinoma of the ovary
with hypercalcemia: report of a case of survival without recurrence
5 years after surgery and chemotherapy. Gynecol Oncol. 56:452–455.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dykgraaf RH, de Jong D, van Veen M,
Ewing-Graham PC, Helmerhorst TJ and van der Burg ME: Clinical
management of ovarian small-cell carcinoma of the hypercalcemic
type: a proposal for conservative surgery in an advanced stage of
disease. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 19:348–353. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Barondeau J, Rodgers M, Braun L, Azarow K,
Forouhar M and Faucette K: Small cell ovarian carcinoma: a rare,
aggressive tumor masquerading as constipation in a teenager with a
fatal outcome. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 32:e139–e141. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Mandel K, Yang Y, Schambach A, Glage S,
Otte A and Hass R: Mesenchymal stem cells directly interact with
breast cancer cells and promote tumor cell growth in vitro and in
vivo. Stem Cells Dev. 22:3114–3127. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bertram C and Hass R: Cellular senescence
of human mammary epithelial cells (HMEC) is associated with an
altered MMP-7/HB-EGF signaling and increased formation of
elastin-like structures. Mech Ageing Dev. 130:657–669. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Putney JW: Capacitative calcium entry:
from concept to molecules. Immunol Rev. 231:10–22. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Schwartz GG and Skinner HG: Prospective
studies of total and ionized serum calcium in relation to incident
and fatal ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 129:169–172. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Trump BF and Berezesky IK:
Calcium-mediated cell injury and cell death. FASEB J. 9:219–228.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nomura M, Ueno A, Saga K, Fukuzawa M and
Kaneda Y: Accumulation of cytosolic calcium induces necroptotic
cell death in human neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 74:1056–1066. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ungefroren H, Sebens S, Seidl D, Lehnert H
and Hass R: Interaction of tumor cells with the microenvironment.
Cell Commun Signal. 9:182011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hass R and Otte A: Mesenchymal stem cells
as all-round supporters in a normal and neoplastic
microenvironment. Cell Commun Signal. 10:262012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Van Rossum GS, Klooster R, van den Bosch
H, Verkleij AJ and Boonstra J: Phosphorylation of p42/44(MAPK) by
various signal transduction pathways activates cytosolic
phospholipase A(2) to variable degrees. J Biol Chem.
276:28976–28983. 2001.
|
|
28
|
Koehler L, Hass R, DeWitt DL, Resch K and
Goppelt-Struebe M: Glucocorticoid-induced reduction of prostanoid
synthesis in TPA-differentiated U937 cells is mainly due to a
reduced cyclooxygenase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 40:1307–1316.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Rehfeldt W, Hass R and Goppelt-Struebe M:
Characterization of phospholipase A2 in monocytic cell lines.
Functional and biochemical aspects of membrane association. Biochem
J. 276:631–636. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rask K, Zhu Y, Wang W, Hedin L and
Sundfeldt K: Ovarian epithelial cancer: a role for PGE2-synthesis
and signalling in malignant transformation and progression. Mol
Cancer. 5:622006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Medeiros A, Peres-Buzalaf C, Fortino
Verdan F and Serezani CH: Prostaglandin E2 and the suppression of
phagocyte innate immune responses in different organs. Mediators
Inflamm. 2012:3275682012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|