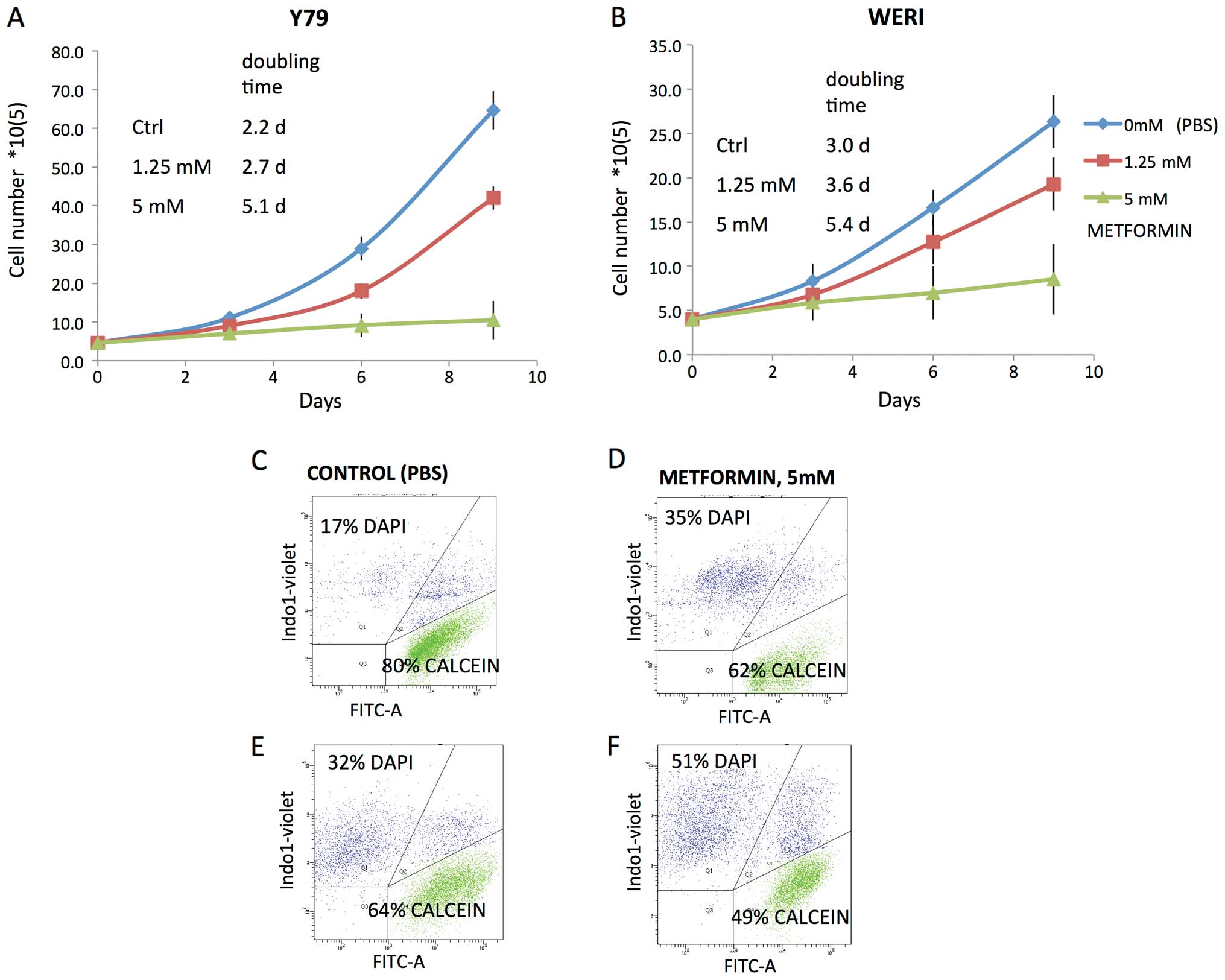
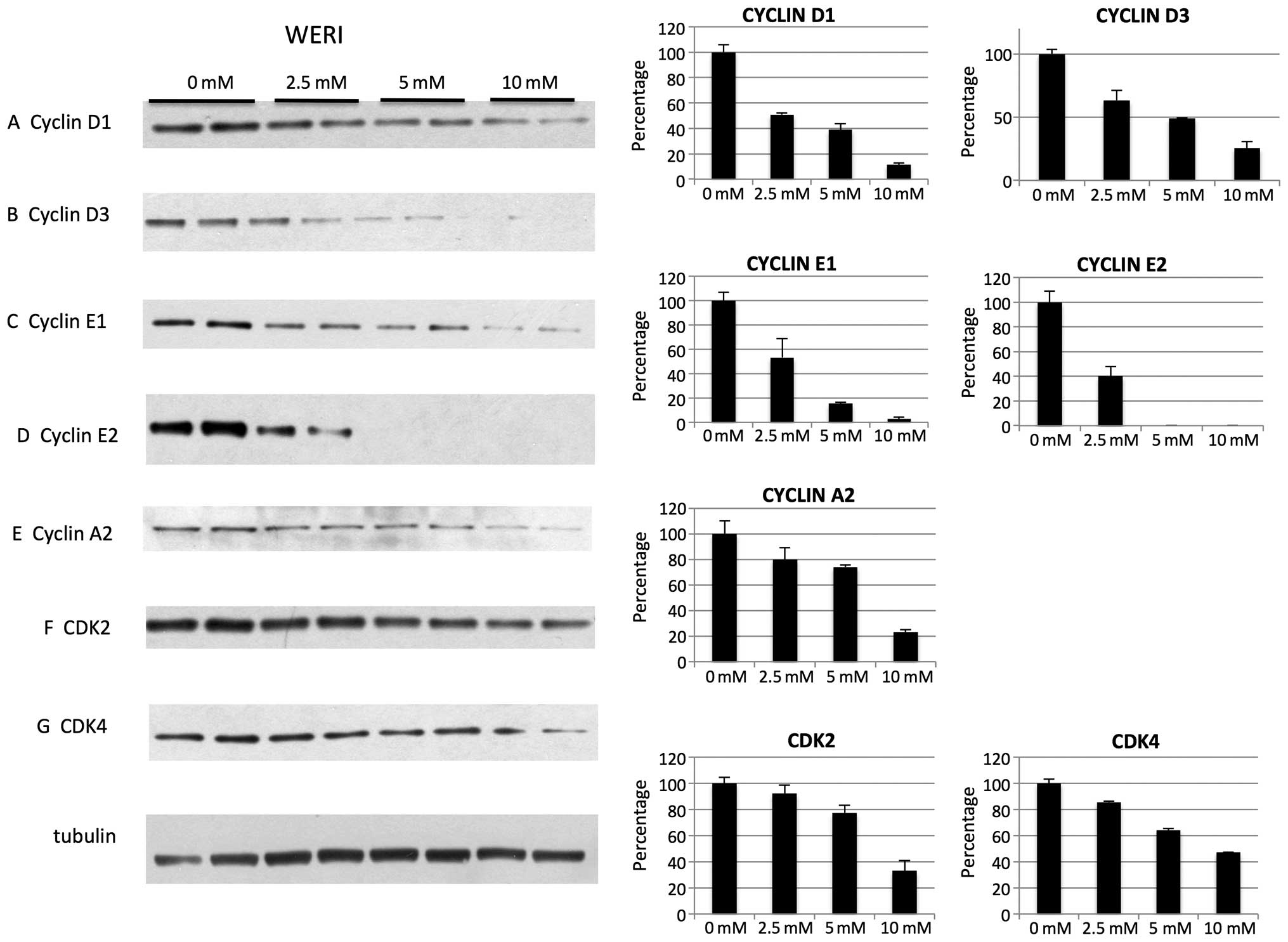
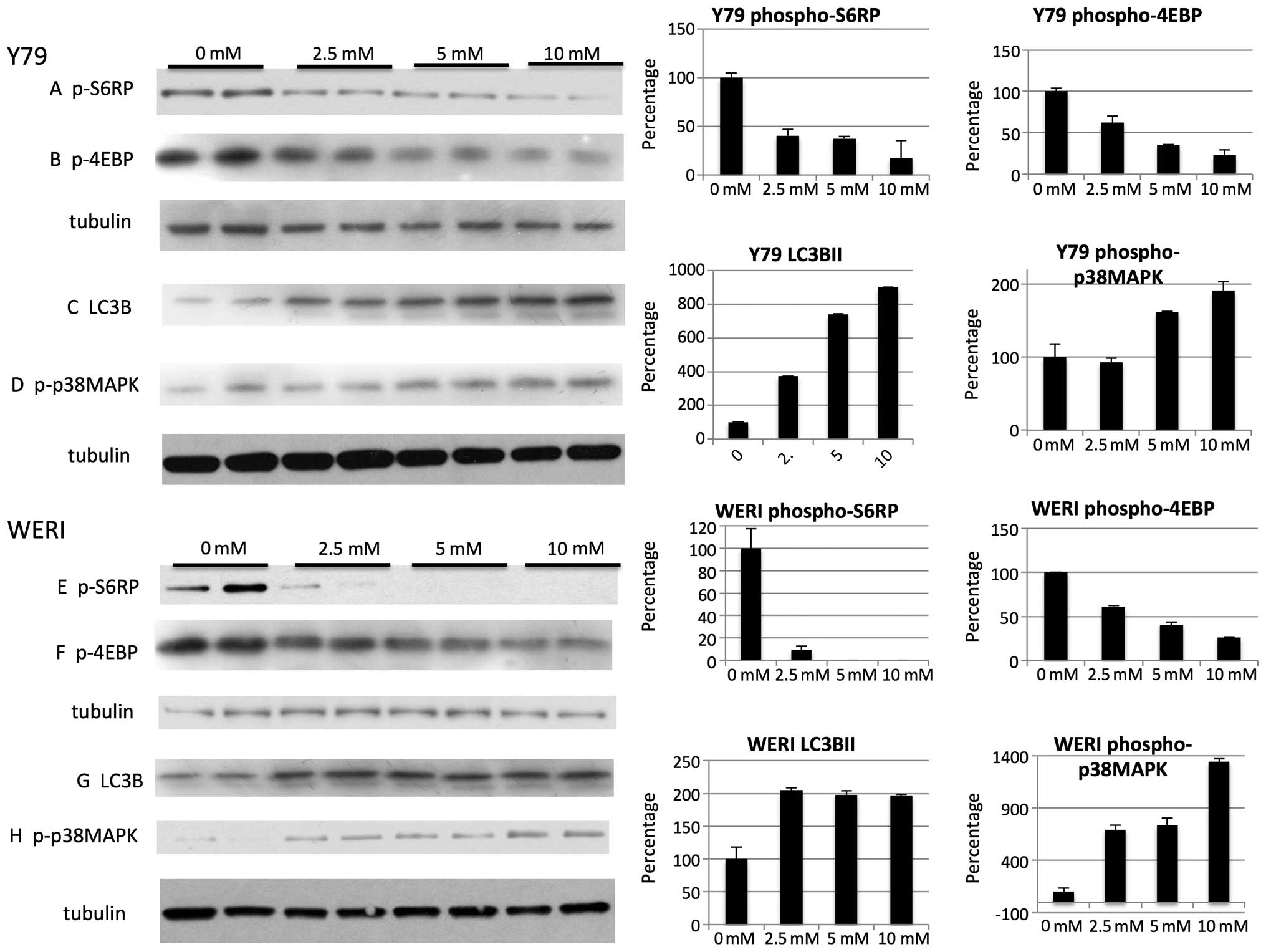
|
1
|
Broaddus E, Topham A and Singh AD:
Incidence of retinoblastoma in the USA: 1975–2004. Br J Ophthalmol.
93:21–23. 2009.
|
|
2
|
Rodriguez-Galindo CC, Wilson MWM, Haik
BGB, et al: Treatment of metastatic retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology.
110:1237–1240. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Roarty JD, McLean IW and Zimmerman LE:
Incidence of second neoplasms in patients with bilateral
retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology. 95:1583–1587. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shaw RJ, Lamia KA, Vasquez D, et al: The
kinase LKB1 mediates glucose homeostasis in liver and therapeutic
effects of metformin. Science. 310:1642–1646. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marr BP, Hung C, Gobin YP, Dunkel IJ,
Brodie SE and Abramson DH: Success of intra-arterial chemotherapy
(chemo-surgery) for retinoblastoma: effect of orbitovascular
anatomy. Arch Ophthalmol. 130:180–185. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu J, Li M, Song B, et al: Metformin
inhibits renal cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo xenograft. Urol
Oncol. 31:264–270. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bianciotto C, Shields CL, Iturralde JC,
Sarici A, Jabbour P and Shields JA: Fluorescein angiographic
findings after intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma.
Ophthalmology. 119:843–849. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Muen WJ, Kingston JE, Robertson F, Brew S,
Sagoo MS and Reddy MA: Efficacy and complications of
super-selective intra-ophthalmic artery melphalan for the treatment
of refractory retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology. 119:611–616. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Miyano-Kurosaki N, Kurosaki K, Hayashi M,
et al: 2-amino-phenoxazine-3-one suppresses the growth of mouse
malignant melanoma B16 cells transplanted into C57BL/6Cr Slc mice.
Biol Pharm Bull. 29:2197–2201. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ghassemi F and Shields CL: Intravitreal
melphalan for refractory or recurrent vitreous seeding from
retinoblastoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 130:1268–1271. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qu Z, Zhang Y, Liao M, Chen Y, Zhao J and
Pan Y: In vitro and in vivo antitumoral action of metformin on
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 42:922–933. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Munier FL, Gaillard M-C, Balmer A, et al:
Intravitreal chemotherapy for vitreous disease in retinoblastoma
revisited: from prohibition to conditional indications. Br J
Ophthalmol. 96:1078–1083. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shields CLC, Honavar SGS, Shields JAJ,
Demirci HH, Meadows ATA and Naduvilath TJT: Factors predictive of
recurrence of retinal tumors, vitreous seeds, and subretinal seeds
following chemoreduction for retinoblastoma. Arch Ophthalmol.
120:460–464. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shields CL, Shelil A, Cater J, Meadows AT
and Shields JA: Development of new retinoblastomas after 6 cycles
of chemo-reduction for retinoblastoma in 162 eyes of 106
consecutive patients. Arch Ophthalmol. 121:1571–1576. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sussman DA, Escalona-Benz E, Benz MS, et
al: Comparison of retinoblastoma reduction for chemotherapy vs
external beam radiotherapy. Arch Ophthalmol. 121:979–984. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schefler AC, Cicciarelli N, Feuer W,
Toledano S and Murray TG: Macular retinoblastoma: evaluation of
tumor control, local complications, and visual outcomes for eyes
treated with chemotherapy and repetitive foveal laser ablation.
Opthalmology. 114:162–169. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Shields CL: Forget-me-nots in the care of
children with retinoblastoma. Semin Ophthalmol. 23:324–334. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shields CL, Palamar M, Sharma P, et al:
Retinoblastoma regression patterns following chemoreduction and
adjuvant therapy in 557 tumors. Arch Ophthalmol. 127:282–290. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Benz MS, Scott IU, Murray TG, Kramer D and
Toledano S: Complications of systemic chemotherapy as treatment of
retinoblastoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 118:577–578. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nishimura S, Sato T, Ueda H and Ueda K:
Acute myeloblastic leukemia as a second malignancy in a patient
with hereditary retinoblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 19:4182–4183.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stumvoll M, Nurjhan N, Perriello G, Dailey
G and Gerich JE: Metabolic effects of metformin in
non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 333:550–554.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, et al: Role of
AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J
Clin Invest. 108:1167–1174. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hundal HS, Ramlal T, Reyes R, Leiter LA
and Klip A: Cellular mechanism of metformin action involves glucose
transporter translocation from an intracellular pool to the plasma
membrane in L6 muscle cells. Endocrinology. 131:1165–1173.
1992.
|
|
24
|
Sahra IB, Laurent K, Loubat A, et al: The
antidiabetic drug metformin exerts an antitumoral effect in vitro
and in vivo through a decrease of cyclin D1 level. Oncogene.
27:3576–3586. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Buzzai M, Jones RG, Amaravadi RK, et al:
Systemic treatment with the antidiabetic drug metformin selectively
impairs p53-deficient tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 67:6745–6752.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cufi S, Corominas-Faja B, Vazquez-Martin
A, et al: Metformin-induced preferential killing of breast cancer
initiating CD44+CD24−/low cells is sufficient
to overcome primary resistance to trastuzumab in HER2+
human breast cancer xenografts. Oncotarget. 3:395–398.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tomic T, Botton T, Cerezo M, et al:
Metformin inhibits melanoma development through autophagy and
apoptosis mechanisms. Cell Death Dis. 2:e1992011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kato K, Gong J, Iwama H, et al: The
antidiabetic drug metformin inhibits gastric cancer cell
proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:549–560.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Martin MJ, Hayward R, Viros A and Marais
R: Metformin accelerates the growth of BRAF V600E-driven melanoma
by upregulating VEGF-A. Cancer Discov. 2:344–355. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Phoenix KN, Vumbaca F and Claffey KP:
Therapeutic metformin/AMPK activation promotes the angiogenic
phenotype in the ERalpha negative MDA-MB-435 breast cancer model.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 113:101–111. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zakikhani M, Dowling R, Fantus IG,
Sonenberg N and Pollak M: Metformin is an AMP kinase-dependent
growth inhibitor for breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
66:10269–10273. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhuang Y and Miskimins WK: Cell cycle
arrest in metformin treated breast cancer cells involves activation
of AMPK, down-regulation of cyclin D1, and requires p27Kip1 or
p21Cip1. J Mol Signal. 3:182008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Towler MC and Hardie DG: AMP-activated
protein kinase in metabolic control and insulin signaling. Circ
Res. 100:328–341. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vijg J and Campisi J: Puzzles, promises
and a cure for ageing. Nature. 454:1065–1071. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Moruno-Manchón JF, Pérez-Jiménez E and
Knecht E: Glucose induces autophagy under starvation conditions by
a p38 MAPK-dependent pathway. Biochem J. 449:497–506.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hardie DG: The LKB1-AMPK pathway-friend or
foe in cancer? Cancer Cell. 23:131–142. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Doyle A, Zhang G, Abdel Fattah EA, Eissa
NT and Li YP: Toll-like receptor 4 mediates
lipopolysaccharide-induced muscle catabolism via coordinate
activation of ubiquitin-proteasome and autophagy-lysosome pathways.
FASEB J. 25:99–110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Matsuzawa T, Kim B-H, Shenoy AR, Kamitani
S, Miyake M and Macmicking JD: IFN-γ elicits macrophage autophagy
via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. J Immunol. 189:813–818.
2012.
|
|
39
|
Webber JL and Tooze SA: Coordinated
regulation of autophagy by p38alpha MAPK through mAtg9 and p38IP.
EMBO J. 29:27–40. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Thyagarajan A, Jedinak A, Nguyen H, et al:
Triterpenes from Ganoderma Lucidum induce autophagy in colon cancer
through the inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated kinase (p38 MAPK).
Nutr Cancer. 62:630–640. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Osborne CK, Bolan G, Monaco ME and Lippman
ME: Hormone responsive human breast cancer in long-term tissue
culture: effect of insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 73:4536–4540.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Metformin insert 1–6, 2009. Distributed
by: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; Princeton, NJ 08543, USA:
http://packagein-serts.bms.com/pi/pi_glucophage_xr.pdf.
|
|
43
|
Quinn BJ, Kitagawa H, Memmott RM, Gills JJ
and Dennis PA: Repositioning metformin for cancer prevention and
treatment. Trends Endocrinol Metabol. 24:469–480. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Janjetovic K, Harhaji-Trajkovic L,
Misirkic-Marjanovic M, et al: In vitro and in vivo anti-melanoma
action of metformin. Eur J Pharmacol. 668:373–382. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hadad SM, Appleyard V and Thompson AM:
Therapeutic metformin/AMPK activation promotes the angiogenic
phenotype in the ERα negative MDA-MB-435 breast cancer model.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 114:391–399. 2009.
|
|
46
|
Dool CJ, Mashhedi H, Zakikhani M, et al:
IGF1/insulin receptor kinase inhibition by BMS-536924 is better
tolerated than alloxan-induced hypoinsulinemia and more effective
than metformin in the treatment of experimental insulin-responsive
breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 18:699–709. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Wilcock C and Bailey CJ: Accumulation of
metformin by tissues of the normal and diabetic mouse. Xenobiotica.
24:49–57. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Evans JM, Donnelly LA, Emslie-Smith AM,
Alessi DR and Morris AD: Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in
diabetic patients. BMJ. 330:1304–1305. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cazzaniga M, Bonanni B, Guerrieri-Gonzaga
A and Decensi A: Is it time to test metformin in breast cancer
clinical trials? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 18:701–705.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Noto H, Goto A, Tsujimoto T and Noda M:
Cancer risk in diabetic patients treated with metformin: a
systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 7:e334112012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Becker C, Meier CR, Jick SS and Bodmer M:
Case-control analysis on metformin and cancer of the esophagus.
Cancer Causes Control. 24:1763–1770. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Becker C, Jick SS, Meier CR and Bodmer M:
Metformin and the risk of endometrial cancer: a case-control
analysis. Gynecol Oncol. 129:565–569. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Bodmer M, Becker C, Jick SS and Meier CR:
Metformin does not alter the risk of lung cancer: a case-control
analysis. Lung Cancer. 78:133–137. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Bodmer M, Becker C, Meier C, Jick SS and
Meier CR: Use of metformin is not associated with a decreased risk
of colorectal cancer: a case-control analysis. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 21:280–286. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kaushik D, Karnes RJ, Eisenberg MS, Rangel
LJ, Carlson RE and Bergstralh EJ: Effect of metformin on prostate
cancer outcomes after radical prostatectomy. Urol Oncol.
32:43.e1–7. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bodmer M, Becker C, Meier C, Jick SS and
Meier CR: Use of antidiabetic agents and the risk of pancreatic
cancer: a case-control analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 107:620–626.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Mazzone PJ, Rai H, Beukemann M, Xu M, Jain
A and Sasidhar M: The effect of metformin and thiazolidinedione use
on lung cancer in diabetics. BMC Cancer. 12:4102012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Bodmer M, Becker C, Meier C, Jick SS and
Meier CR: Use of metformin and the risk of ovarian cancer: a
case-control analysis. Gynecol Oncol. 123:200–204. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Bodmer M, Meier C, Krähenbühl S, Jick SS
and Meier CR: Long-term metformin use is associated with decreased
risk of breast cancer. Diabetes Care. 33:1304–1308. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Tomimoto A, Endo H, Sugiyama M, et al:
Metformin suppresses intestinal polyp growth in ApcMin/+
mice. Cancer Science. 99:2136–2141. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Theodoropoulou S, Kolovou PE, Morizane Y,
et al: Retinoblastoma cells are inhibited by aminoimidazole
carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR) partially through activation of
AMP-dependent kinase. FASEB J. 24:2620–2630. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Rattan R, Giri S, Singh AK and Singh I:
5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-D-ribofuranoside inhibits
cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo via AMP-activated
protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 280:39582–39593. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Inoki KK, Zhu TT and Guan K-LK: TSC2
mediates cellular energy response to control cell growth and
survival. Cell. 115:577–590. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Cheng SWY, Fryer LGD, Carling D and
Shepherd PR: Thr2446 is a novel mammalian target of rapamycin
(mTOR) phosphorylation site regulated by nutrient status. J Biol
Chem. 279:15719–15722. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sarbassov DD, Ali SM and Sabatini DM:
Growing roles for the mTOR pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
17:596–603. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kondo Y, Kanzawa T, Sawaya R and Kondo S:
The role of autophagy in cancer development and response to
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:726–734. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hawley SA, Gadalla AE, Olsen GS and Hardie
DG: The antidiabetic drug metformin activates the AMP-activated
protein kinase cascade via an adenine nucleotide-independent
mechanism. Diabetes. 51:2420–2425. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Kalender A, Selvaraj A, Kim SY, et al:
Metformin, independent of AMPK, inhibits mTORC1 in a rag
GTPase-dependent manner. Cell Metab. 11:390–401. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Liu B, Fan Z, Edgerton SM, et al:
Metformin induces unique biological and molecular responses in
triple negative breast cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 8:2031–2040. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Li C, Liu VWS, Chan DW, Yao KM and Ngan
HYS: LY294002 and metformin cooperatively enhance the inhibition of
growth and the induction of apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells. Int
J Gynecol Cancer. 22:15–22. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Capano M and Crompton M: Bax translocates
to mitochondria of heart cells during simulated ischaemia:
involvement of AMP-activated and p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinases. Biochem J. 395:57–64. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Xi X, Han J and Zhang JZ: Stimulation of
glucose transport by AMP-activated protein kinase via activation of
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 276:41029–41034.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Würth R, Pattarozzi A, Gatti M, et al:
Metformin selectively affects human glioblastoma tumor-initiating
cell viability: A role for metformin-induced inhibition of Akt.
Cell Cycle. 12:145–156. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Bao B, Wang Z, Ali S, et al: Metformin
inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion by attenuating
CSC function mediated by deregulating miRNAs in pancreatic cancer
cells. Cancer Prevent Res. 5:355–364. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Ben Sahra I, Regazzetti C, Robert G, et
al: Metformin, independent of AMPK, induces mTOR inhibition and
cell-cycle arrest through REDD1. Cancer Res. 71:4366–4372.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Soranna D, Scotti L, Zambon A, et al:
Cancer risk associated with use of metformin and sulfonylurea in
type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Oncologist. 17:813–822. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Bost F, Sahra IB, Le Marchand-Brustel Y
and Tanti JF: Metformin and cancer therapy. Curr Opin Oncol.
24:103–108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Iliopoulos D, Hirsch HA and Struhl K:
Metformin decreases the dose of chemotherapy for prolonging tumor
remission in mouse xenografts involving multiple cancer cell types.
Cancer Res. 71:3196–3201. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Hirsch HA, Iliopoulos D, Tsichlis PN and
Struhl K: Metformin selectively targets cancer stem cells, and acts
together with chemotherapy to block tumor growth and prolong
remission. Cancer Res. 69:7507–7511. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Martin-Castillo B, Vazquez-Martin A,
Oliveras-Ferraros C and Menendez JA: Metformin and cancer: doses,
mechanisms and the dandelion and hormetic phenomena. Cell Cycle.
9:1057–1064. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|