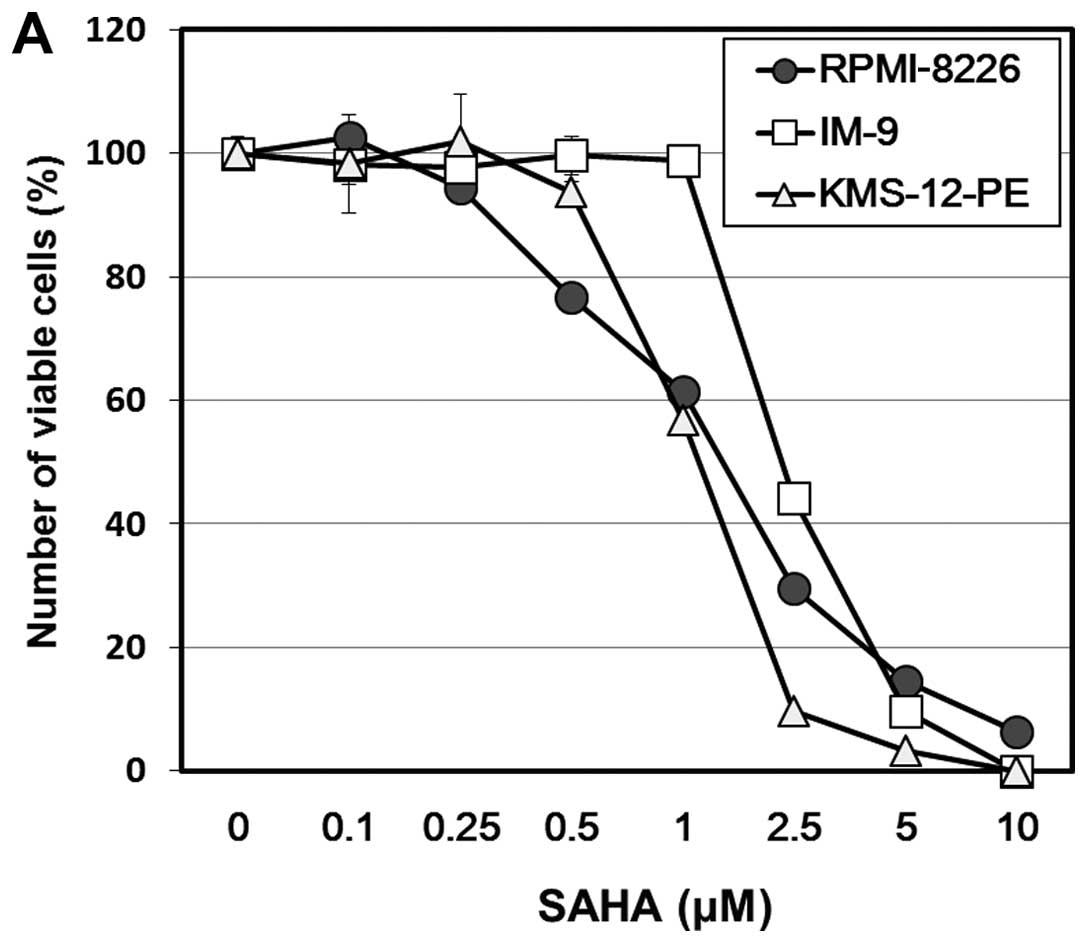
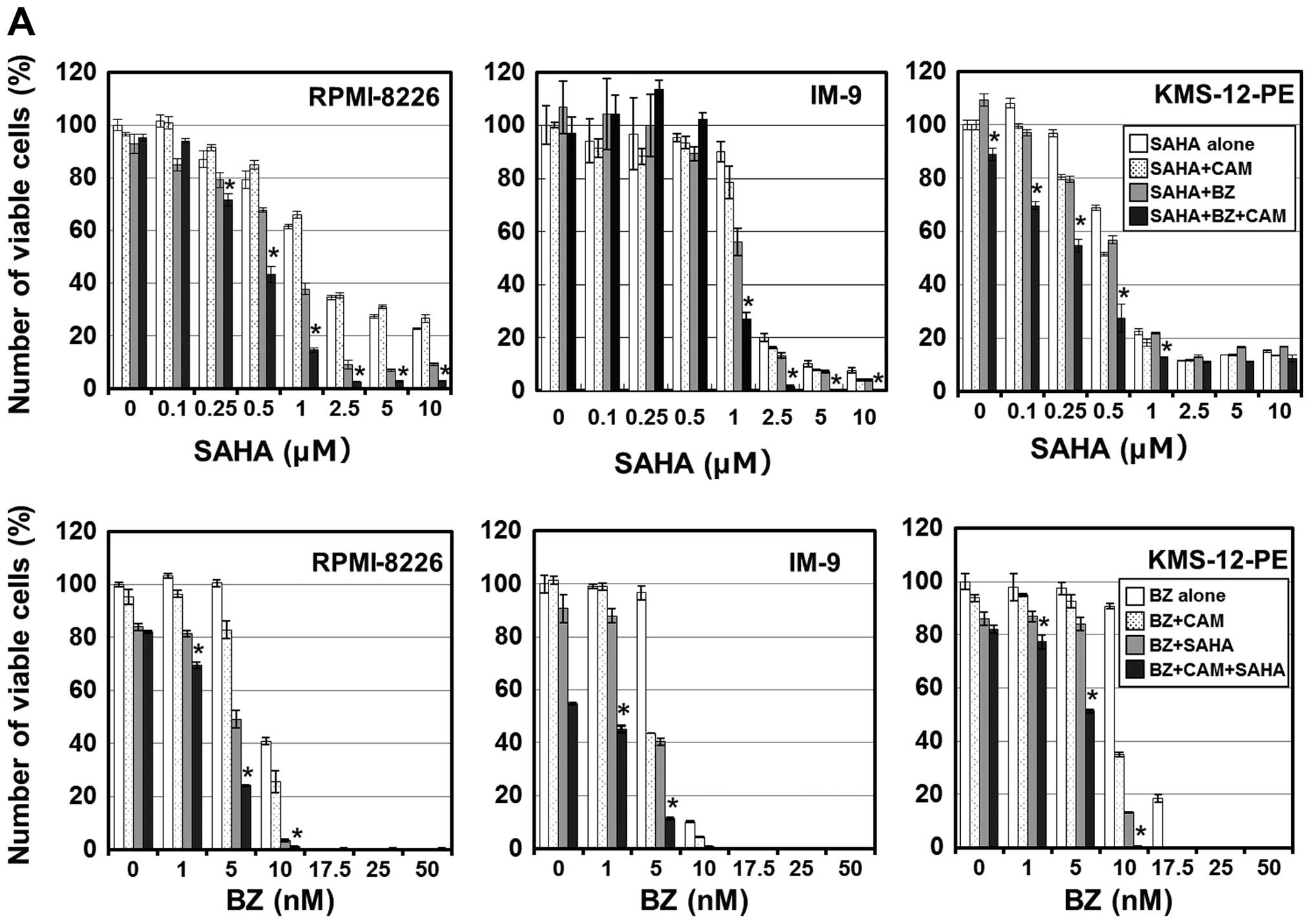
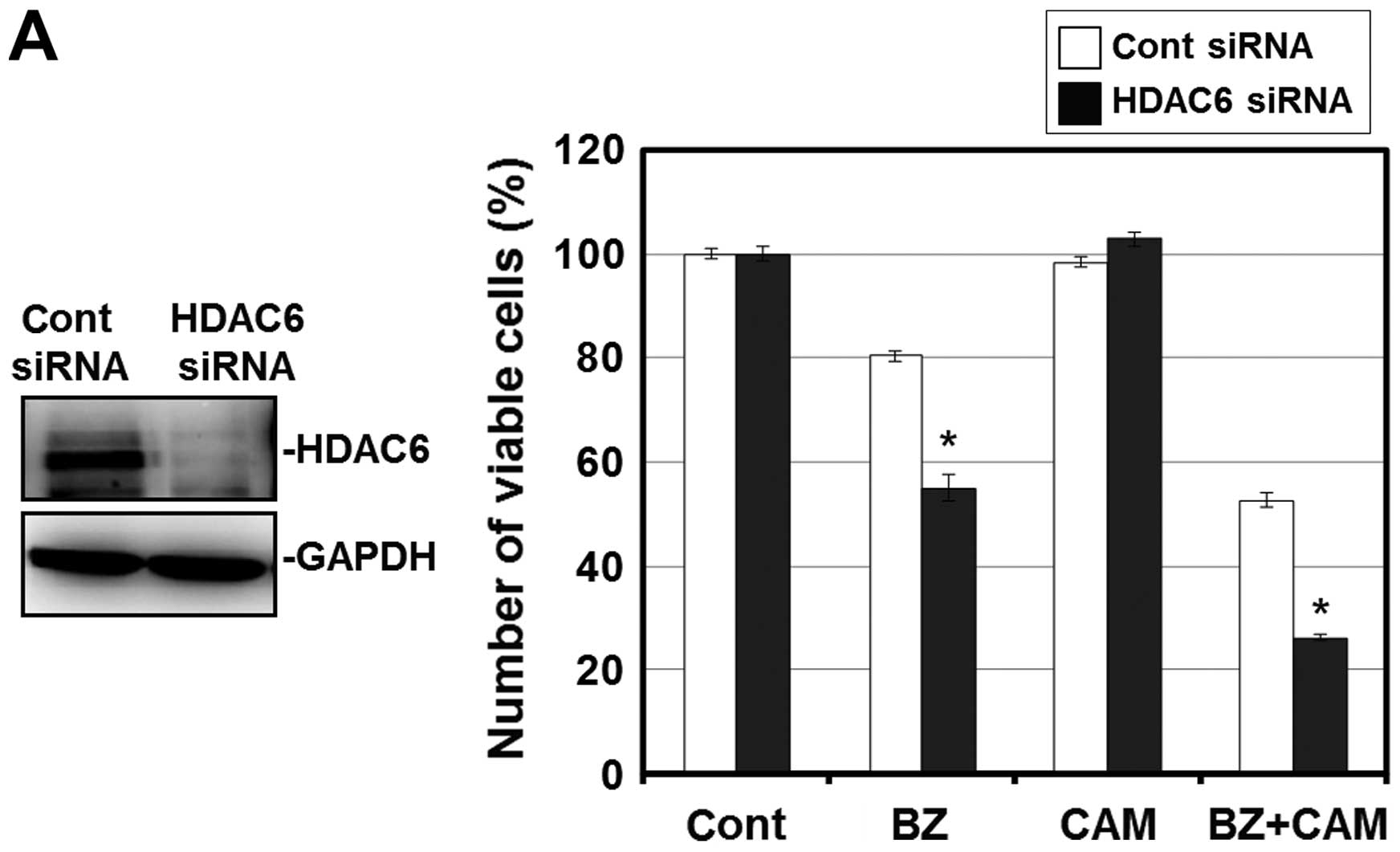
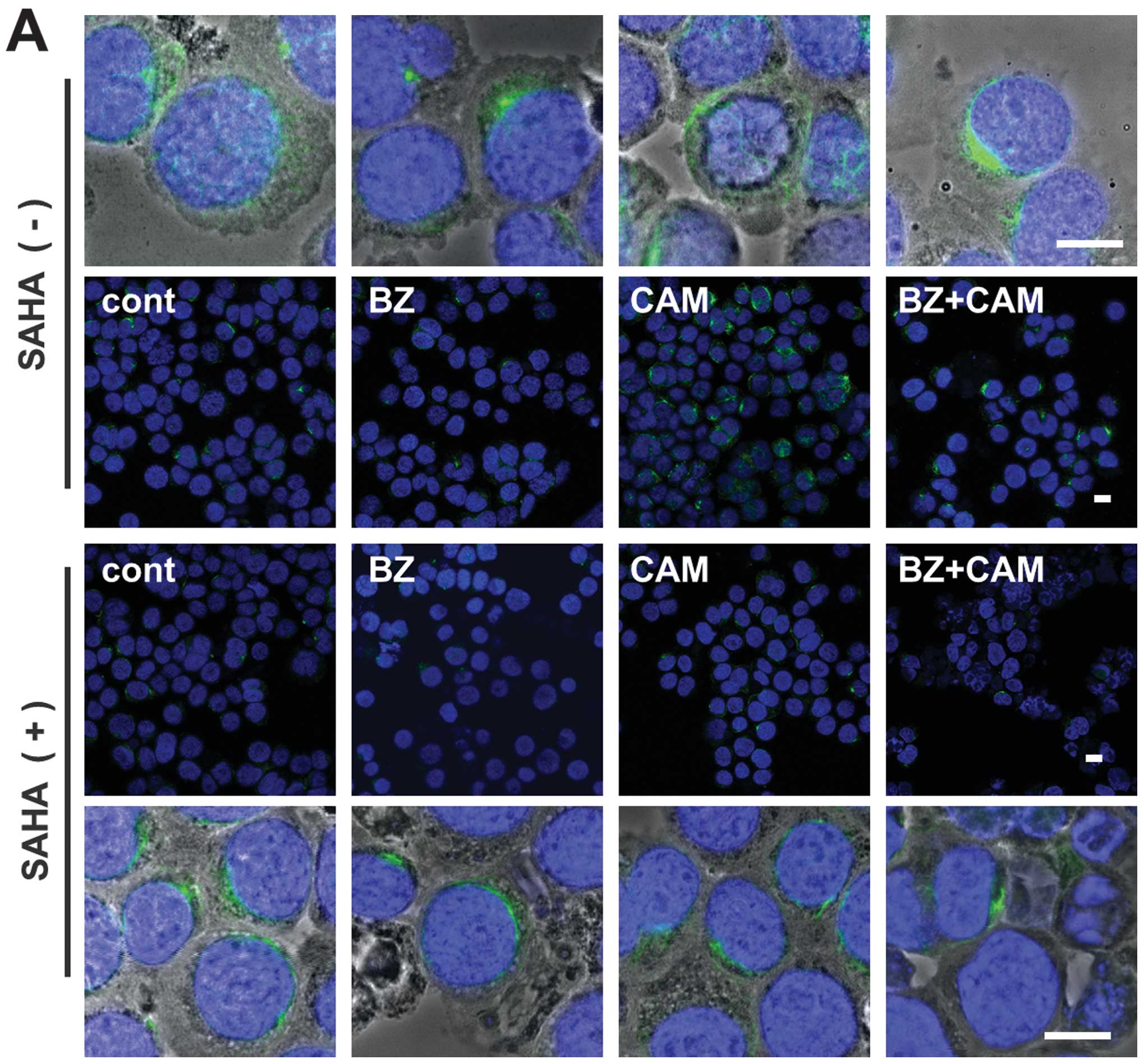
|
1
|
Richardson PG, Barlogie B, Berenson J, et
al: A phase 2 study of bortezomib in relapsed, refractory myeloma.
N Engl J Med. 348:2609–2617. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
San Miguel JF, Schlag R, Khuageva NK, et
al: Bortezomib plus melphalan and prednisone for initial treatment
of multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 359:906–917. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Richardson PG, Xie W, Jagannath S, et al:
A phase 2 trial of lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone in
patients with relapsed and relapsed/refractory myeloma. Blood.
123:1461–1469. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siegel DS, Martin T, Wang M, et al: A
phase 2 study of single-agent carfilzomib (PX-171–003-A1) in
patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. Blood.
120:2817–2825. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dimopoulos M, Siegel DS, Lonial S, et al:
Vorinostat or placebo in combination with bortezomib in patients
with multiple myeloma (VANTAGE 088): a multicentre, randomised,
double-blind study. Lancet Oncol. 14:1129–1140. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Orlowski RZ: Novel agents for multiple
myeloma to overcome resistance in phase III clinical trials. Semin
Oncol. 40:634–651. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Martinon F: Targeting endoplasmic
reticulum signaling pathways in cancer. Acta Oncol. 51:822–830.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hetz C, Chevet E and Harding HP: Targeting
the unfolded protein response in disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
12:703–719. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tabas I and Ron D: Integrating the
mechanisms of apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Nat Cell Biol. 13:184–190. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Verfaillie T, Salazar M, Velasco G and
Agostinis P: Linking ER stress to autophagy: potential implications
for cancer therapy. Int J Cell Biol. 2010:9305092010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mizushima N: Autophagy in protein and
organelle turnover. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 76:397–402.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kirkin V, McEwan DG, Novak I and Dikic I:
A role for ubiquitin in selective autophagy. Mol Cell. 34:259–269.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Korolchuk VI, Menzies FM and Rubinsztein
DC: Mechanisms of cross-talk between the ubiquitin-proteasome and
autophagy-lysosome systems. FEBS Lett. 584:1393–1398. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kawaguchi T, Miyazawa K, Moriya S, Ohtomo
T, Che XF, Naito M, Itoh M and Tomoda A: Combined treatment with
bortezomib plus bafilomycin A1 enhances the cytocidal
effect and induces endoplasmic reticulum stress in U266 myeloma
cells: Crosstalk among proteasome, autophagy-lysosome and ER
stress. Int J Oncol. 38:643–654. 2011.
|
|
16
|
Moriya S, Che XF, Komatsu S, Abe A,
Kawaguchi T, Gotoh A, Inazu M, Tomoda A and Miyazawa K: Macrolide
antibiotics block autophagy flux and sensitize to bortezomib via
endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated CHOP induction in myeloma
cells. Int J Oncol. 42:1541–1550. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Komatsu S, Miyazawa K, Moriya S, Takase A,
Naito M, Inazu M, Kohno N, Itoh M and Tomoda A: Clarithromycin
enhances bortezomib-induced cytotoxicity via endoplasmic reticulum
stress-mediated CHOP (GADD153) induction and autophagy in breast
cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 40:1029–1039. 2012.
|
|
18
|
Simms-Waldrip T, Rodriguez-Gonzalez A, Lin
T, Ikeda AK, Fu C and Sakamoto KM: The aggresome pathway as a
target for therapy in hematologic malignancies. Mol Genet Metab.
94:283–286. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kawaguchi Y, Kovacs JJ, McLaurin A, Vance
JM, Ito A and Yao TP: The deacetylase HDAC6 regulates aggresome
formation and cell viability in response to misfolded protein
stress. Cell. 115:727–738. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ouyang H, Ali YO, Ravichandran M, Dong A,
Qiu W, MacKenzie F, Dhe-Paganon S, Arrowsmith CH and Zhai RG:
Protein aggregates are recruited to aggresome by histone
deacetylase 6 via unanchored ubiquitin C termini. J Biol Chem.
287:2317–2327. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Lee JY, Koga H, Kawaguchi Y, et al: HDAC6
controls autophagosome maturation essential for ubiquitin-selective
quality-control autophagy. EMBO J. 29:969–980. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fusco C, Micale L, Egorov M, et al: The
E3-ubiquitin ligase TRIM50 interacts with HDAC6 and p62, and
promotes the sequestration and clearance of ubiquitinated proteins
into the aggresome. PLoS One. 7:e404402012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yan J, Seibenhener ML, Calderilla-Barbosa
L, Diaz-Meco MT, Moscat J, Jiang J, Wooten MW and Wooten MC:
SQSTM1/p62 interacts with HDAC6 and regulates deacetylase activity.
PLoS One. 8:e760162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Komatsu S, Moriya S, Che XF, Yokoyama T,
Kohno N and Miyazawa K: Combined treatment with SAHA, bortezomib,
and clarithromycin for concomitant targeting of aggresome formation
and intracellular proteolytic pathways enhances ER stress-mediated
cell death in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
437:41–47. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Olsen EA, Kim YH, Kuzel TM, et al: Phase
IIb multicenter trial of vorinostat in patients with persistent,
progressive, or treatment refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J
Clin Oncol. 25:3109–3115. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kavanaugh SM, White LA and Kolesar JM:
Vorinostat: a novel therapy for the treatment of cutaneous T-cell
lymphoma. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 67:793–797. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hubbert C, Guardiola A, Shao R, Kawaguchi
Y, Ito A, Nixon A, Yoshida M, Wang XF and Yao TP: HDAC6 is a
microtubule-associated deacetylase. Nature. 417:455–458. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Haggarty SJ, Koeller KM, Wong JC,
Grozinger CM and Schreiber SL: Domain-selective small-molecule
inhibitor of histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6)-mediated tubulin
deacetylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:4389–4394. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Garcia-Mata R, Bebök Z, Sorscher EJ and
Sztul ES: Characterization and dynamics of aggresome formation by a
cytosolic GFP-chimera. J Cell Biol. 146:1239–1254. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Johnston JA, Ward CL and Kopito RR:
Aggresomes: a cellular response to misfolded proteins. J Cell Biol.
143:1883–1898. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hung YH, Chen LM, Yang JY and Yang WY:
Spatiotemporally controlled induction of autophagy-mediated
lysosome turnover. Nat Commun. 4:21112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Richter-Landsberg C and Leyk J: Inclusion
body formation, macroautophagy, and the role of HDAC6 in
neurodegeneration. Acta Neuropathol. 126:793–807. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hol EM, Fischer DF, Ovaa H and Scheper W:
Ubiquitin proteasome system as a pharmacological target in
neurodegeneration. Expert Rev Neurother. 6:1337–1347. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nawrocki ST, Carew JS, Maclean KH, Courage
JF, Huang P, Houghton JA, Cleveland JL, Giles FJ and McConkey DJ:
Myc regulates aggresome formation, the induction of Noxa, and
apoptosis in response to the combination of bortezomib and SAHA.
Blood. 112:2917–2926. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zaarur N, Meriin AB, Bejarano E, Xu X,
Gabai VL, Cuervo AM and Sherman MY: Proteasome failure promotes
positioning of lysosomes around the aggresome via local block of
microtubule-dependent transport. Mol Cell Biol. 34:1336–1348. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nakamura M, Kikukawa Y, Takeya M, Mitsuya
H and Hata H: Clarithromycin attenuates autophagy in myeloma cells.
Int J Oncol. 37:815–820. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yamamoto A, Tagawa Y, Yoshimori T,
Moriyama Y, Masaki R and Tashiro Y: Bafilomycin A1
prevents maturation of autophagic vacuoles by inhibiting fusion
between autophagosomes and lysosomes in rat hepatoma cell line,
H-4-II-E cells. Cell Struct Funct. 23:33–42. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Renna M, Schaffner C, Brown K, et al:
Azithromycin blocks autophagy and may predispose cystic fibrosis
patients to mycobacterial infection. J Clin Invest. 121:3554–3563.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Maejima I, Takahashi A, Omori H, et al:
Autophagy sequesters damaged lysosomes to control lysosomal
biogenesis and kidney injury. EMBO J. 32:2336–2347. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|