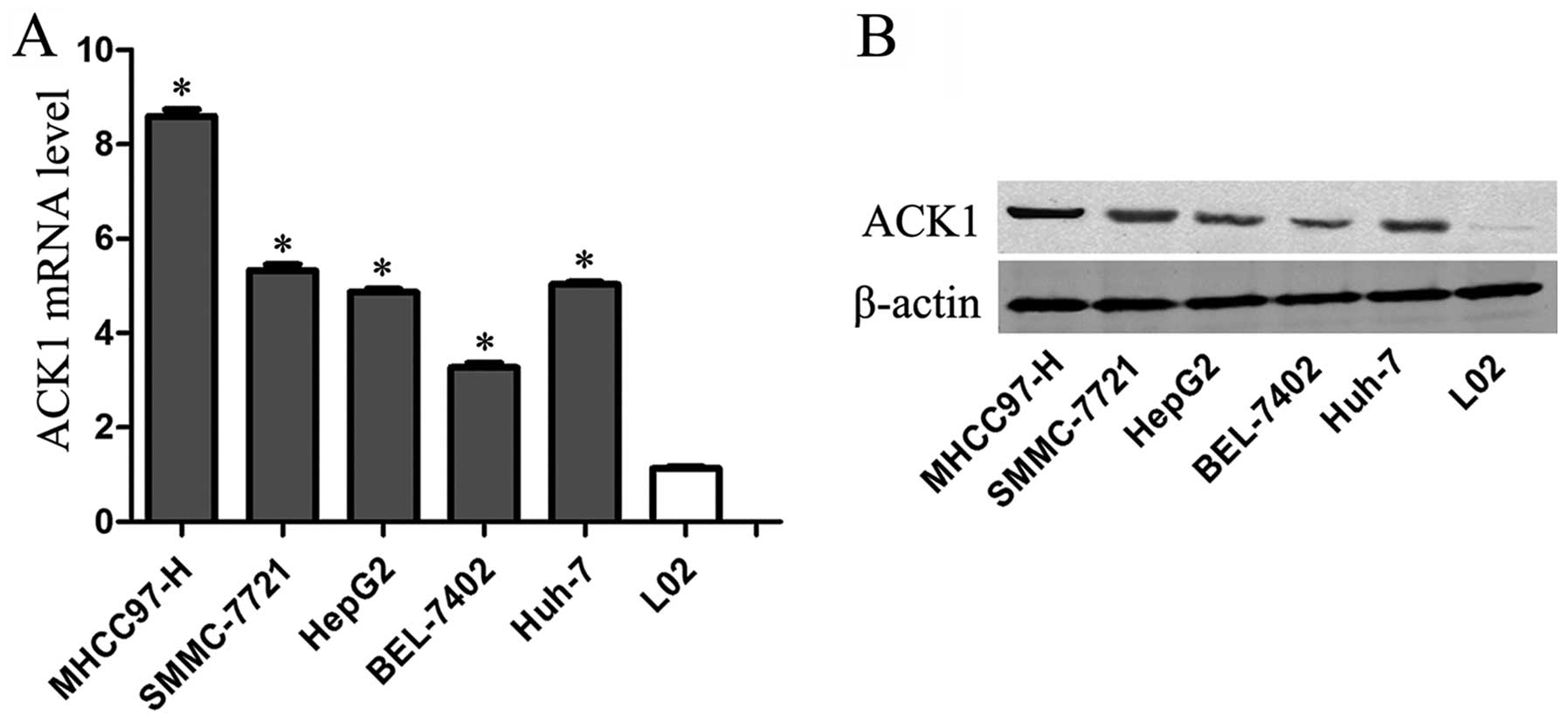
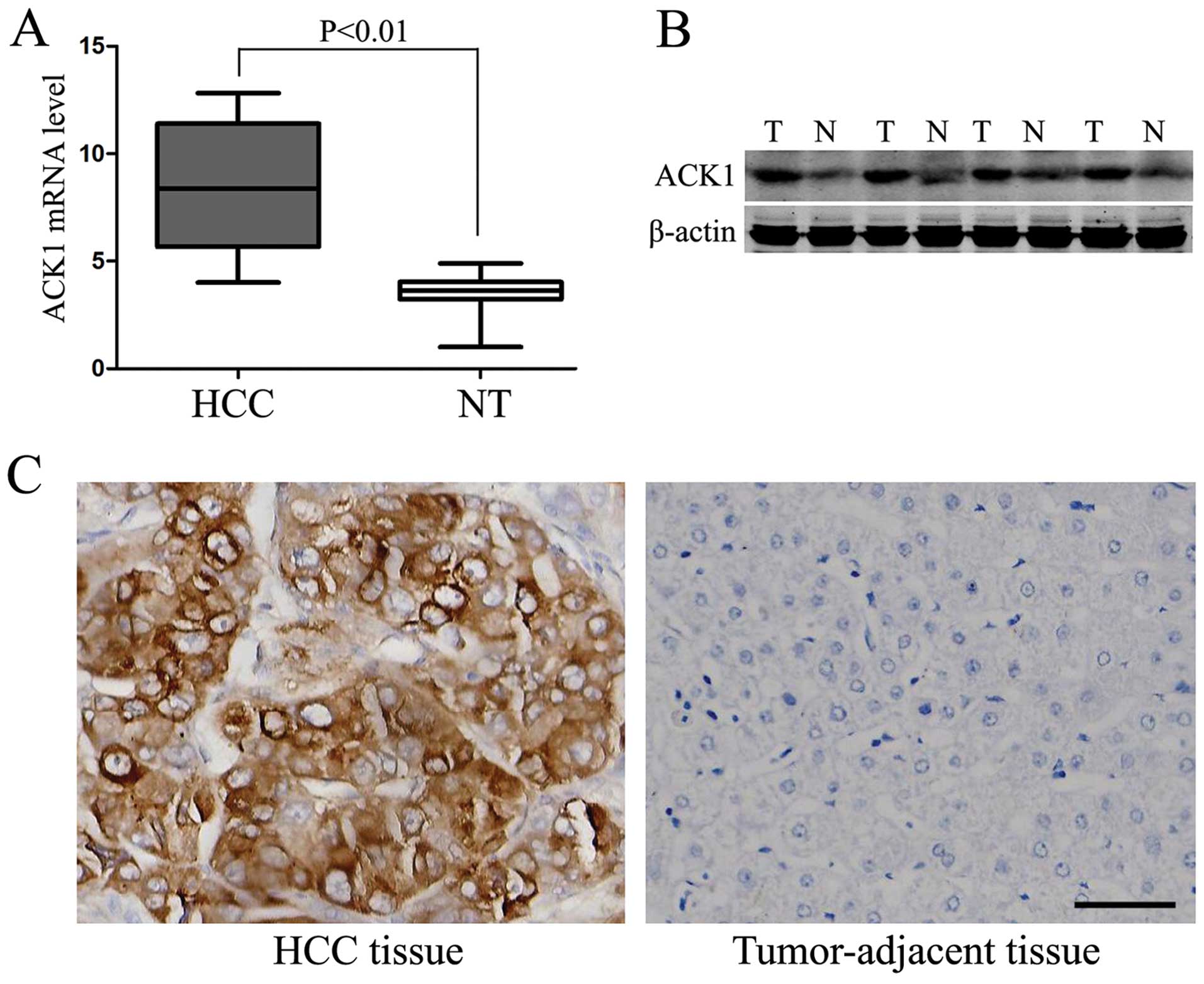
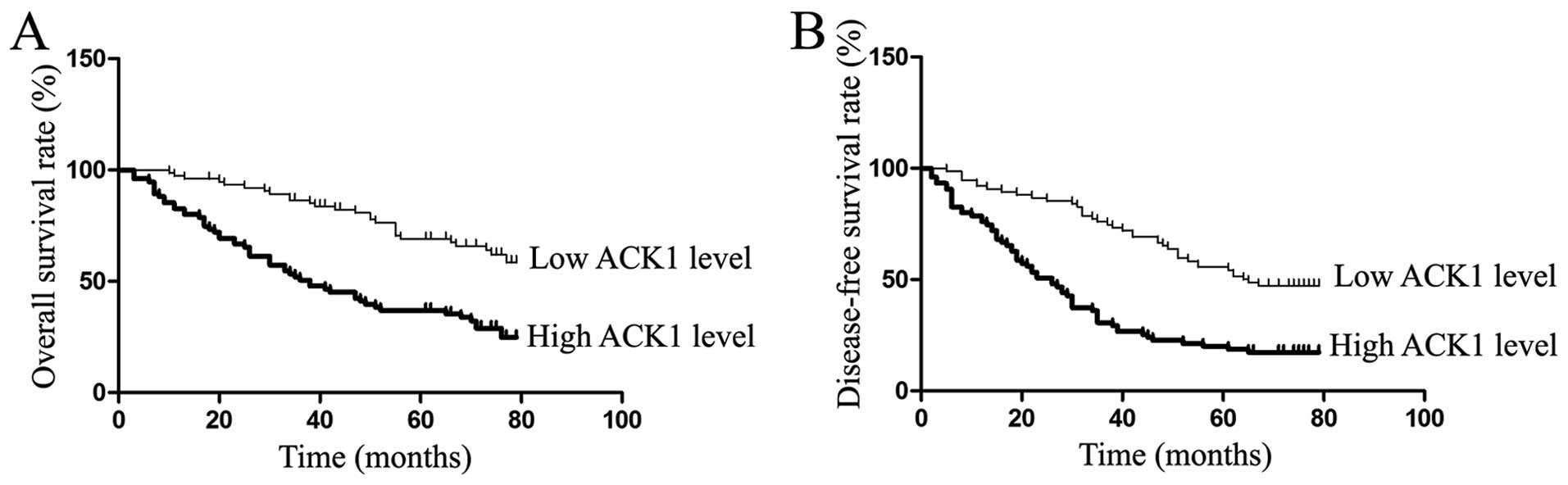
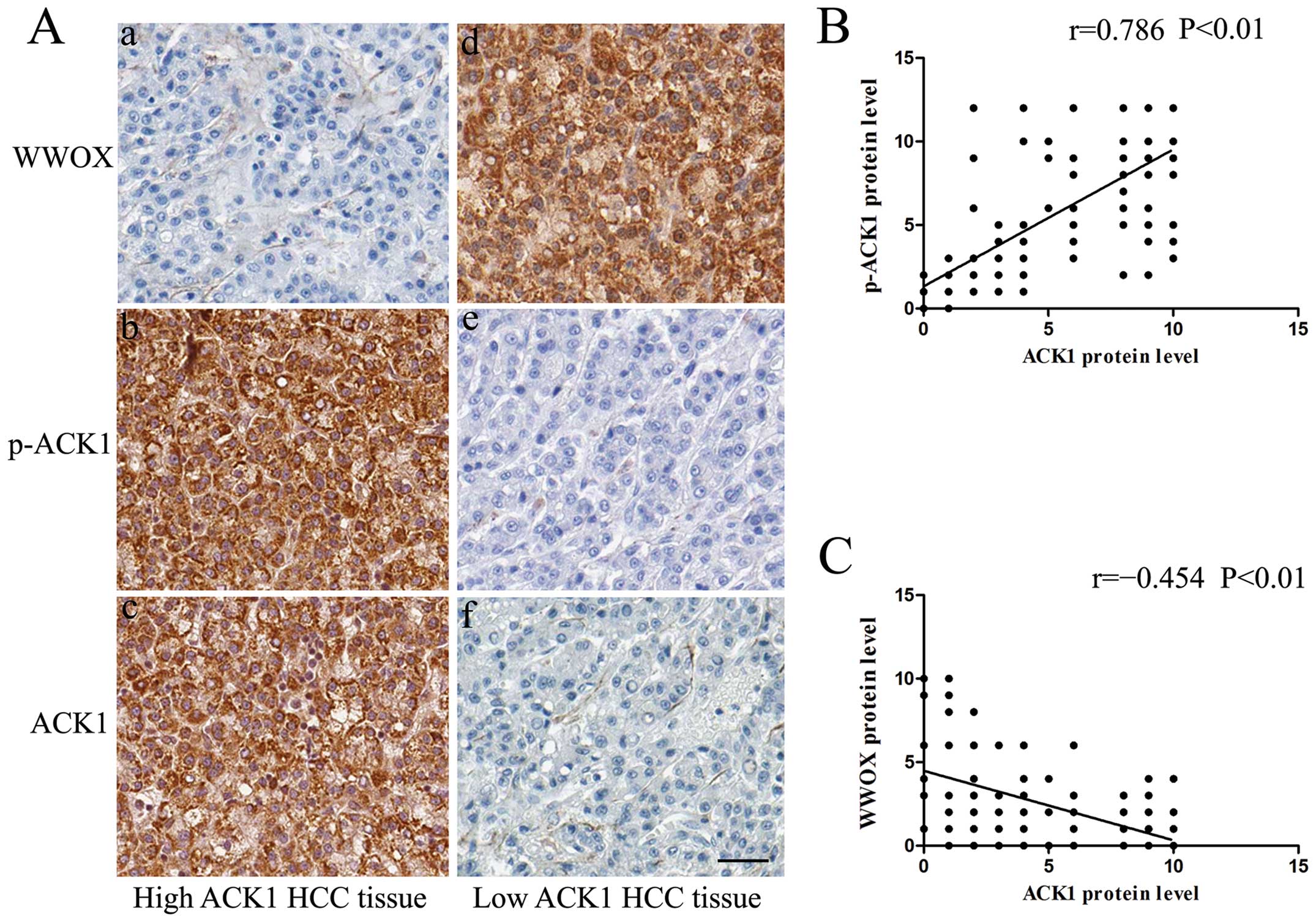
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen WQ, Zeng HM, Zheng RS, Zhang SW and
He J: Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2007. Chin J Cancer
Res. 24:1–8. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Nishikawa H, Osaki Y, Endo M, et al:
Japanese Red Cross Liver Study Group: Comparison of standard-dose
and half-dose sorafenib therapy on clinical outcome in patients
with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in field practice: A
propensity score matching analysis. Int J Oncol. 45:2295–2302.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Venook AP, Papandreou C, Furuse J and de
Guevara LL: The incidence and epidemiology of hepatocellular
carcinoma: A global and regional perspective. Oncologist. 15(Suppl
4): 5–13. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alazawi W, Cunningham M, Dearden J and
Foster GR: Systematic review: Outcome of compensated cirrhosis due
to chronic hepatitis C infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
32:344–355. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu Q, Tu K, Zhang H, Zheng X, Yao Y and
Liu Q: TPX2 as a novel prognostic biomarker for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatol Res. Sep 29–2014.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bruix J and Sherman M; American
Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology. 53:1020–1022.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Han S, Han L, Yao Y, Sun H, Zan X and Liu
Q: Activated hepatic stellate cells promote hepatocellular
carcinoma cell migration and invasion via the activation of
FAK-MMP9 signaling. Oncol Rep. 31:641–648. 2014.
|
|
9
|
Nur-E-Kamal MS, Kamal JM, Qureshi MM and
Maruta H: The CDC42-specific inhibitor derived from ACK-1 blocks
v-Ha-Ras-induced transformation. Oncogene. 18:7787–7793. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Prieto-Echagüe V, Gucwa A, Craddock BP,
Brown DA and Miller WT: Cancer-associated mutations activate the
nonreceptor tyrosine kinase Ack1. J Biol Chem. 285:10605–10615.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chan W, Tian R, Lee YF, Sit ST, Lim L and
Manser E: Down-regulation of active ACK1 is mediated by association
with the E3 ubiquitin ligase Nedd4–2. J Biol Chem. 284:8185–8194.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Grøvdal LM, Johannessen LE, Rødland MS,
Madshus IH and Stang E: Dysregulation of Ack1 inhibits
down-regulation of the EGF receptor. Exp Cell Res. 314:1292–1300.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kelley LC and Weed SA: Cortactin is a
substrate of activated Cdc42-associated kinase 1 (ACK1) during
ligand-induced epidermal growth factor receptor downregulation.
PLoS One. 7:e443632012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gajiwala KS, Maegley K, Ferre R, He YA and
Yu X: Ack1: Activation and regulation by allostery. PLoS One.
8:e539942013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shinmura K, Kiyose S, Nagura K, Igarashi
H, Inoue Y, Nakamura S, Maeda M, Baba M, Konno H and Sugimura H:
TNK2 gene amplification is a novel predictor of a poor prognosis in
patients with gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 109:189–197. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Howlin J, Rosenkvist J and Andersson T:
TNK2 preserves epidermal growth factor receptor expression on the
cell surface and enhances migration and invasion of human breast
cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 10:R362008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mahajan K, Coppola D, Challa S, et al:
Ack1 mediated AKT/PKB tyrosine 176 phosphorylation regulates its
activation. PLoS One. 5:e96462010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mahajan K and Mahajan NP: ACK1 tyrosine
kinase: Targeted inhibition to block cancer cell proliferation.
Cancer Lett. 338:185–192. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li YP, Wu CC, Chen WT, Huang YC and Chai
CY: The expression and significance of WWOX and β-catenin in
hepatocellular carcinoma. APMIS. 121:120–126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Salah Z, Aqeilan R and Huebner K: WWOX
gene and gene product: Tumor suppression through specific protein
interactions. Future Oncol. 6:249–259. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang J and Zhang W: WWOX tumor suppressor
gene. Histol Histopathol. 23:877–882. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lewandowska U, Zelazowski M, Seta K,
Byczewska M, Pluciennik E and Bednarek AK: WWOX, the tumour
suppressor gene affected in multiple cancers. J Physiol Pharmacol.
60(Suppl 1): 47–56. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mahajan K and Mahajan NP: Shepherding AKT
and androgen receptor by Ack1 tyrosine kinase. J Cell Physiol.
224:327–333. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zheng X, Gai X, Ding F, Lu Z, Tu K, Yao Y
and Liu Q: Histone acetyltransferase PCAF up-regulated cell
apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma via acetylating histone H4
and inactivating AKT signaling. Mol Cancer. 12:962013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu Q, Yang P, Tu K, Zhang H, Zheng X, Yao
Y and Liu Q: TPX2 knockdown suppressed hepatocellular carcinoma
cell invasion via inactivating AKT signaling and inhibiting MMP2
and MMP9 expression. Chin J Cancer Res. 26:410–417. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mahajan K and Mahajan NP: PI3K-independent
AKT activation in cancers: a treasure trove for novel therapeutics.
J Cell Physiol. 227:3178–3184. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tan DS, Haaland B, Gan JM, et al:
Bosutinib inhibits migration and invasion via ACK1 in KRAS mutant
non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer. 13:132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
van der Horst EH, Degenhardt YY, Strelow
A, et al: Metastatic properties and genomic amplification of the
tyrosine kinase gene ACK1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15901–15906.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mahajan K, Coppola D, Rawal B, Chen YA,
Lawrence HR, Engelman RW, Lawrence NJ and Mahajan NP: Ack1-mediated
androgen receptor phosphorylation modulates radiation resistance in
castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Biol Chem. 287:22112–22122.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chua BT, Lim SJ, Tham SC, Poh WJ and
Ullrich A: Somatic mutation in the ACK1 ubiquitin association
domain enhances oncogenic signaling through EGFR regulation in
renal cancer derived cells. Mol Oncol. 4:323–334. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mahajan K, Coppola D, Chen YA, Zhu W,
Lawrence HR, Lawrence NJ and Mahajan NP: Ack1 tyrosine kinase
activation correlates with pancreatic cancer progression. Am J
Pathol. 180:1386–1393. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cheng CH, Lee CF, Wu TH, Chan KM, Chou HS,
Wu TJ, Yu MC, Chen TC, Lee WC and Chen MF: Evaluation of the new
AJCC staging system for resectable hepatocellular carcinoma. World
J Surg Oncol. 9:1142011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mahajan K, Challa S, Coppola D, Lawrence
H, Luo Y, Gevariya H, Zhu W, Chen YA, Lawrence NJ and Mahajan NP:
Effect of Ack1 tyrosine kinase inhibitor on ligand-independent
androgen receptor activity. Prostate. 70:1274–1285. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell.
141:52–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|