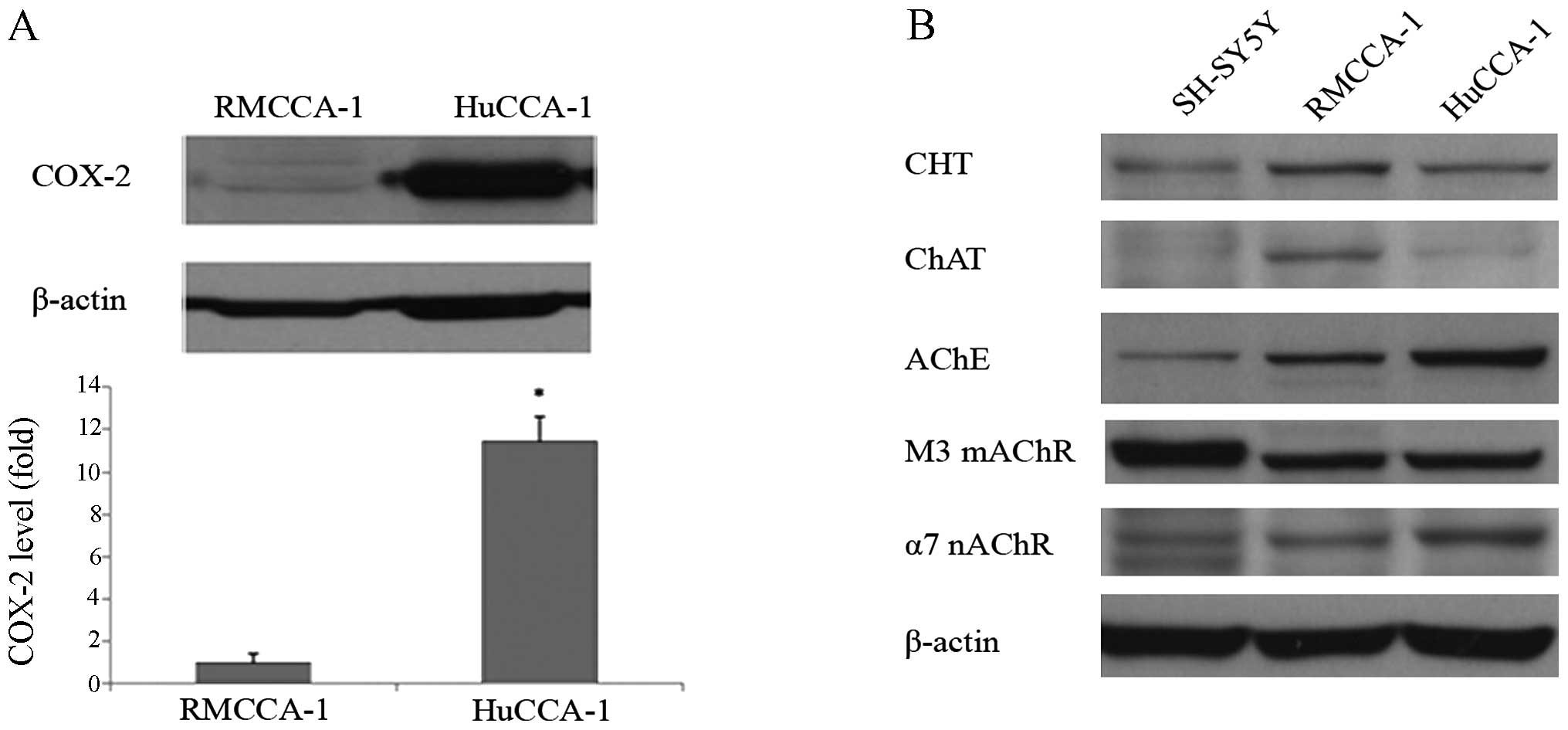
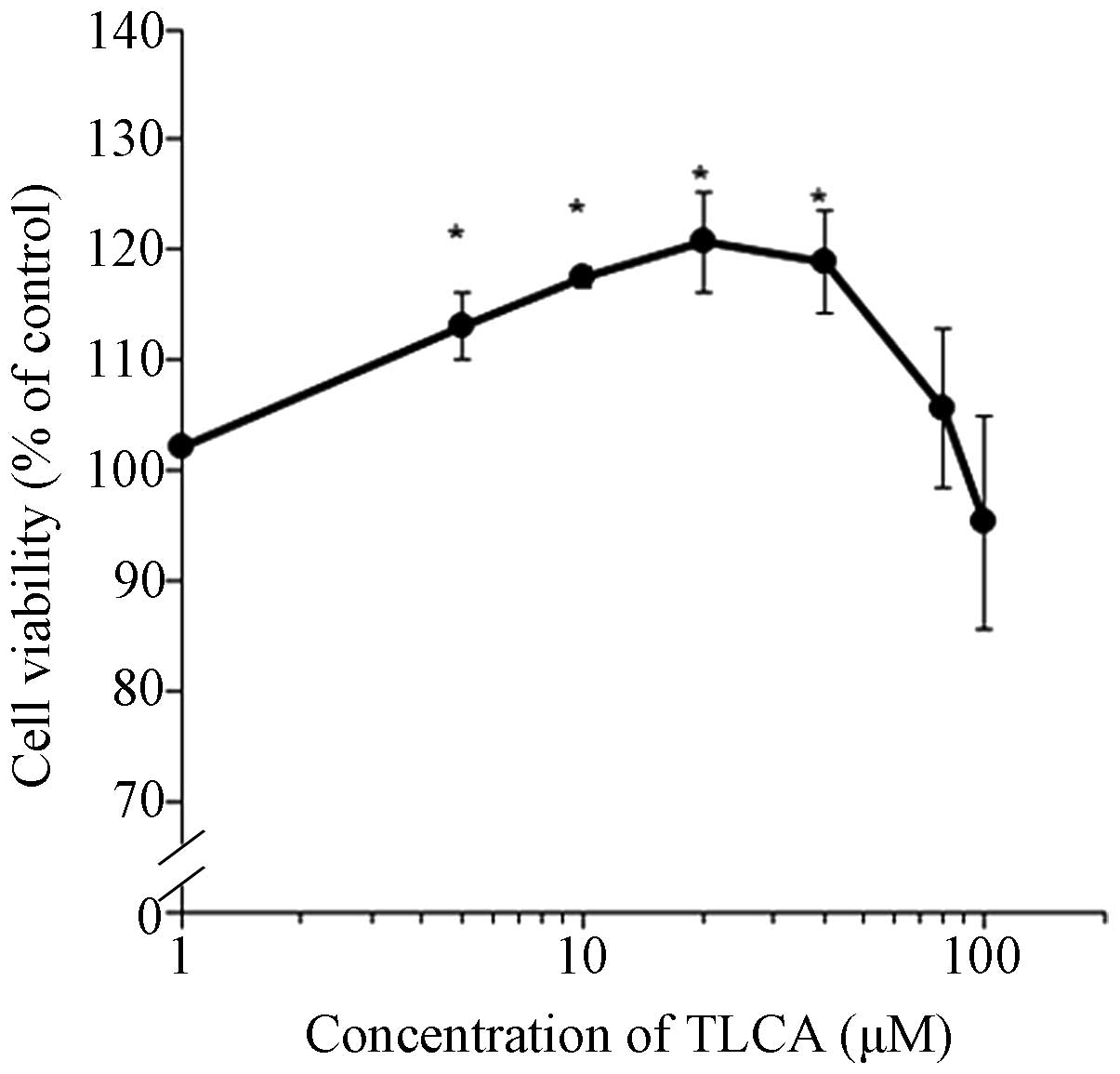
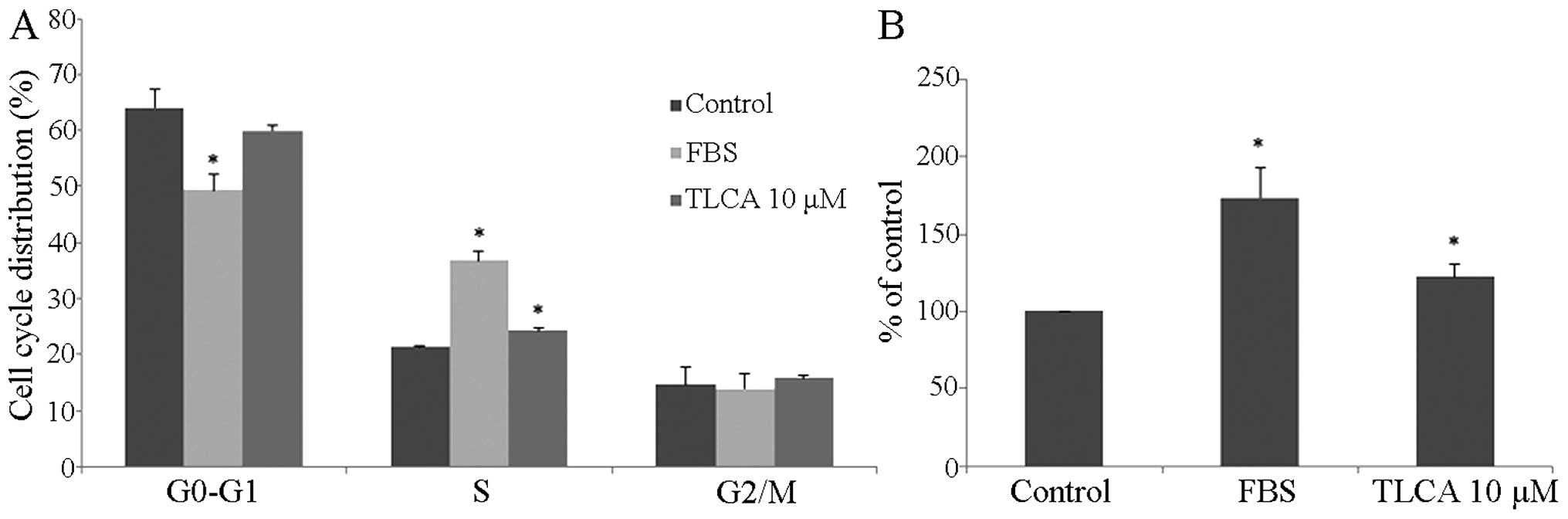
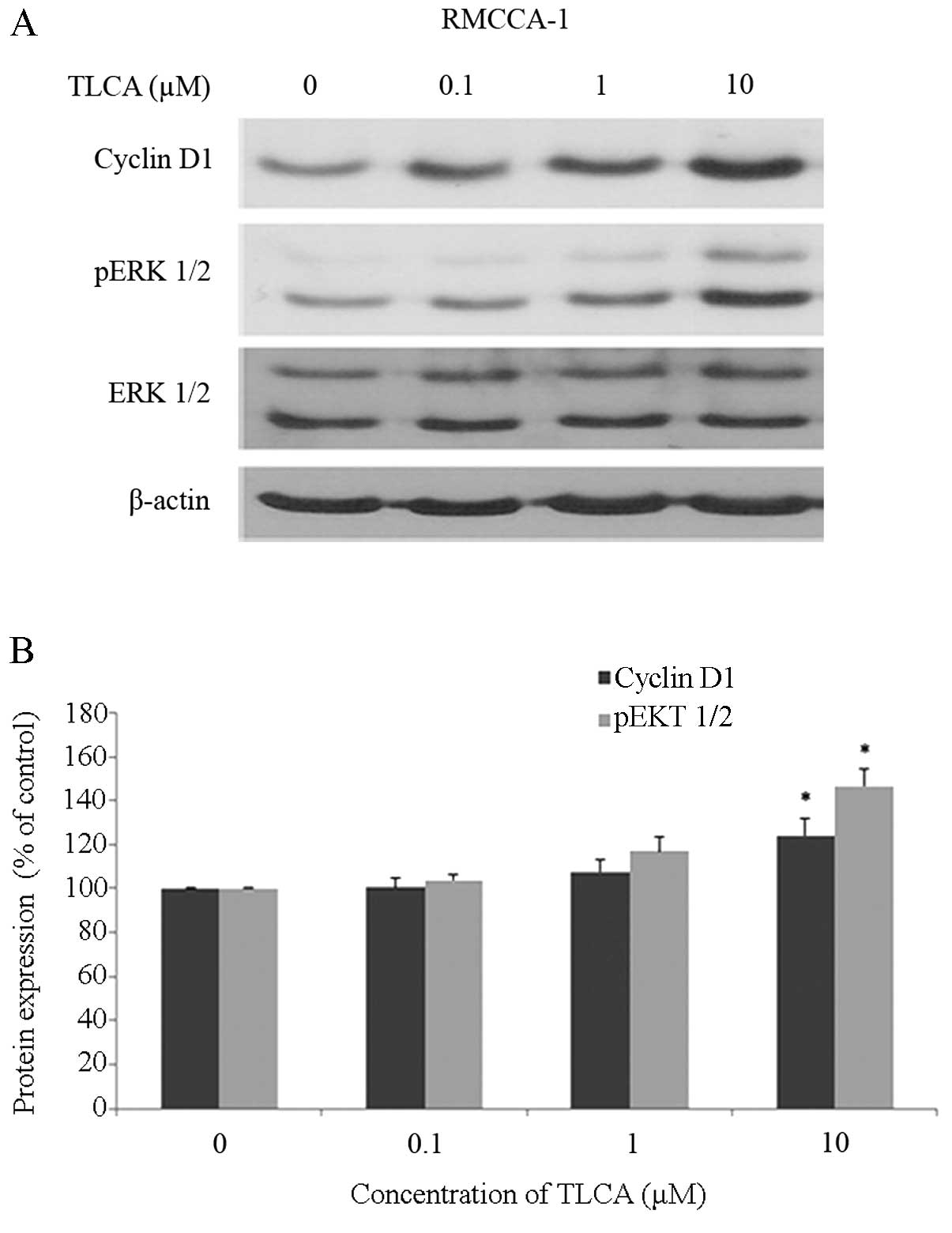
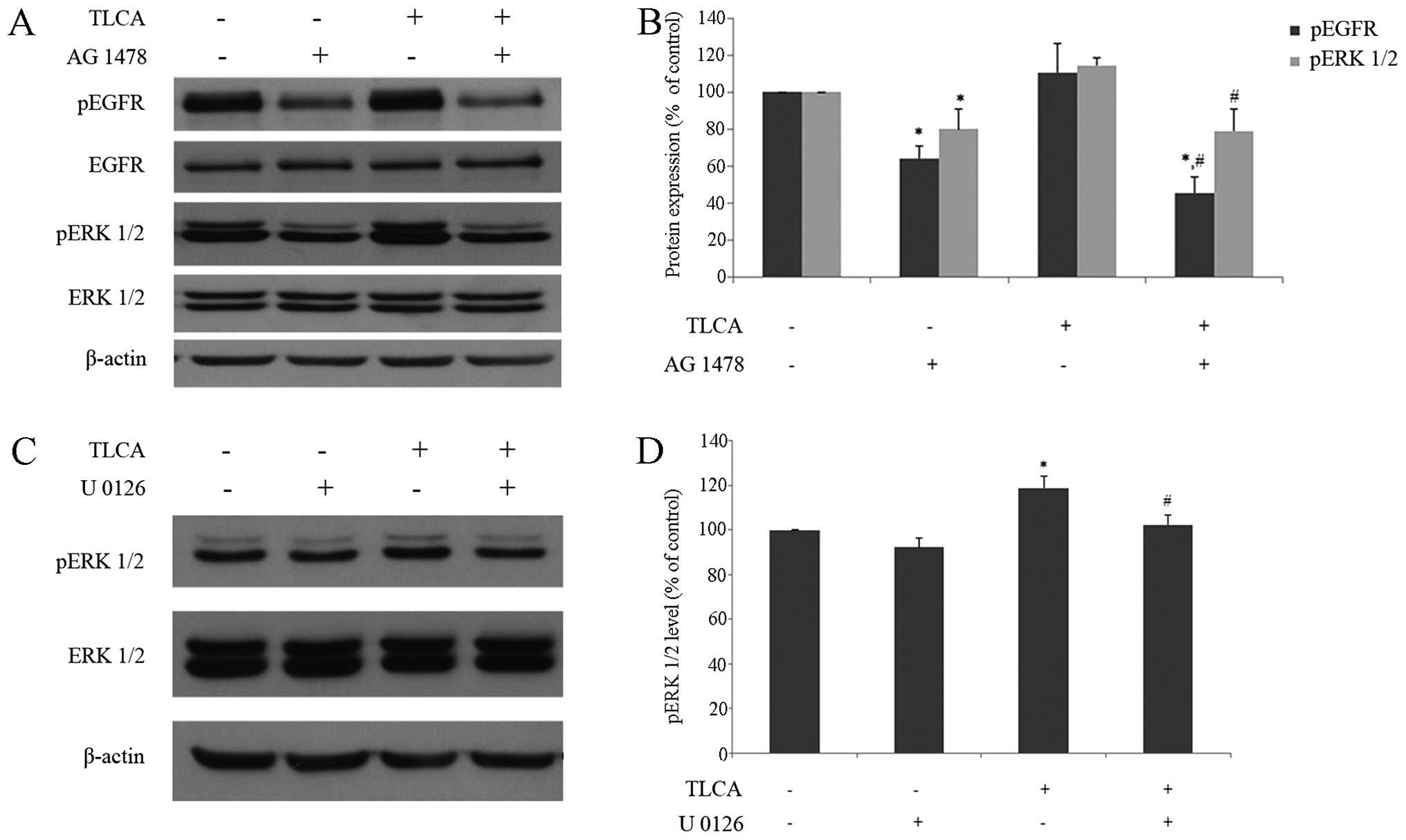
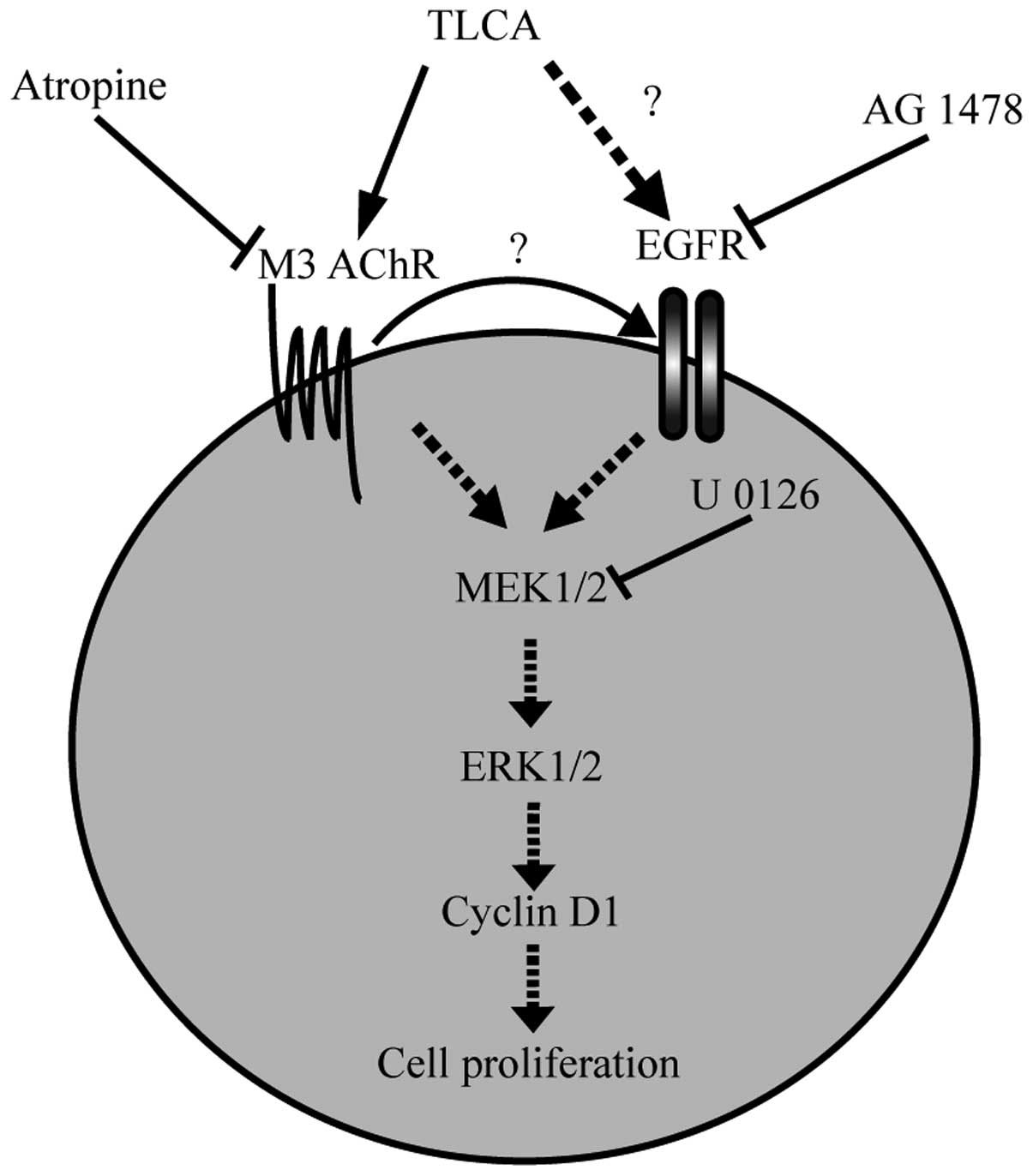
|
1
|
Patel T: Cholangiocarcinoma -
controversies and challenges. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
8:189–200. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Raufman JP, Cheng K and Zimniak P:
Activation of muscarinic receptor signaling by bile acids:
Physiological and medical implications. Dig Dis Sci. 48:1431–1444.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bernstein H, Bernstein C, Payne CM,
Dvorakova K and Garewal H: Bile acids as carcinogens in human
gastrointestinal cancers. Mutat Res. 589:47–65. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cheng K and Raufman JP: Bile acid-induced
proliferation of a human colon cancer cell line is mediated by
transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptors. Biochem
Pharmacol. 70:1035–1047. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fujino T, Takeuchi A, Maruko-Ohtake A,
Ohtake Y, Satoh J, Kobayashi T, Tanaka T, Ito H, Sakamaki R,
Kashimura R, et al: Critical role of farnesoid X receptor for
hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation. J Biochem.
152:577–586. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu R, Zhao R, Zhou X, Liang X, Campbell
DJ, Zhang X, Zhang L, Shi R, Wang G, Pandak WM, et al: Conjugated
bile acids promote cholangiocarcinoma cell invasive growth via
activation of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 2. Hepatology.
60:908–918. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Casaburi I, Avena P, Lanzino M, Sisci D,
Giordano F, Maris P, Catalano S, Morelli C and Andò S:
Chenodeoxycholic acid through a TGR5-dependent CREB signaling
activation enhances cyclin D1 expression and promotes human
endometrial cancer cell proliferation. Cell Cycle. 11:2699–2710.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cheng K, Chen Y, Zimniak P, Raufman JP,
Xiao Y and Frucht H: Functional interaction of lithocholic acid
conjugates with M3 muscarinic receptors on a human colon cancer
cell line. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1588:48–55. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Raufman JP, Chen Y, Cheng K, Compadre C,
Compadre L and Zimniak P: Selective interaction of bile acids with
muscarinic receptors: A case of molecular mimicry. Eur J Pharmacol.
457:77–84. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shah N, Khurana S, Cheng K and Raufman JP:
Muscarinic receptors and ligands in cancer. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 296:C221–C232. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Trombino S, Bisio A, Catassi A, Cesario A,
Falugi C and Russo P: Role of the non-neuronal human cholinergic
system in lung cancer and mesothelioma: Possibility of new
therapeutic strategies. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 4:535–542.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Español AJ, de la Torre E, Fiszman GL and
Sales ME: Role of non-neuronal cholinergic system in breast cancer
progression. Life Sci. 80:2281–2285. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Belo A, Cheng K, Chahdi A, Shant J, Xie G,
Khurana S and Raufman JP: Muscarinic receptor agonists stimulate
human colon cancer cell migration and invasion. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 300:G749–G760. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Parnell EA, Calleja-Macias IE, Kalantari
M, Grando SA and Bernard HU: Muscarinic cholinergic signaling in
cervical cancer cells affects cell motility via ERK1/2 signaling.
Life Sci. 91:1093–1098. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rayford W, Noble MJ, Austenfeld MA, Weigel
J, Mebust WK and Shah GV: Muscarinic cholinergic receptors promote
growth of human prostate cancer cells. Prostate. 30:160–166. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Paleari L, Grozio A, Cesario A and Russo
P: The cholinergic system and cancer. Semin Cancer Biol.
18:211–217. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schuller HM: Is cancer triggered by
altered signalling of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors? Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:195–205. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Feng YJ, Zhang BY, Yao RY and Lu Y:
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3 in proliferation and
perineural invasion of cholangiocarcinoma cells. Hepatobiliary
Pancreat Dis Int. 11:418–423. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fava G, Marzioni M, Francis H, Glaser S,
Demorrrow S, Ueno Y, Benedetti A and Alpini G: Novel interaction of
bile acid and neural signaling in the regulation of cholangiocyte
function. Hepatol Res. 37(Suppl 3): S420–S429. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sirisinha S, Tengchaisri T, Boonpucknavig
S, Prempracha N, Ratanarapee S and Pausawasdi A: Establishment and
characterization of a cholangiocarcinoma cell line from a Thai
patient with intrahepatic bile duct cancer. Asian Pac J Allergy
Immunol. 9:153–157. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rattanasinganchan P, Leelawat K,
Treepongkaruna SA, Tocharoentanaphol C, Subwongcharoen S,
Suthiphongchai T and Tohtong R: Establishment and characterization
of a cholangiocarcinoma cell line (RMCCA-1) from a Thai patient.
World J Gastroenterol. 12:6500–6506. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
LeSage G, Alvaro D, Benedetti A, Glaser S,
Marucci L, Baiocchi L, Eisel W, Caligiuri A, Phinizy JL, Rodgers R,
et al: Cholinergic system modulates growth, apoptosis, and
secretion of cholangiocytes from bile duct-ligated rats.
Gastroenterology. 117:191–199. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dai J, Wang H, Dong Y, Zhang Y and Wang J:
Bile acids affect the growth of human cholangiocarcinoma via NF-κB
pathway. Cancer Invest. 31:111–120. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Werneburg NW, Yoon JH, Higuchi H and Gores
GJ: Bile acids activate EGF receptor via a TGF-alpha-dependent
mechanism in human cholangiocyte cell lines. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 285:G31–G36. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Degirolamo C, Modica S, Palasciano G and
Moschetta A: Bile acids and colon cancer: Solving the puzzle with
nuclear receptors. Trends Mol Med. 17:564–572. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Renga B, Mencarelli A, Cipriani S, D’Amore
C, Carino A, Bruno A, Francisci D, Zampella A, Distrutti E and
Fiorucci S: The bile acid sensor FXR is required for
immune-regulatory activities of TLR-9 in intestinal inflammation.
PLoS One. 8:e544722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Y, Hong JY, Rockwell CE, Copple BL,
Jaeschke H and Klaassen CD: Effect of bile duct ligation on bile
acid composition in mouse serum and liver. Liver Int. 32:58–69.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Tribe RM, Dann AT, Kenyon AP, Seed P,
Shennan AH and Mallet A: Longitudinal profiles of 15 serum bile
acids in patients with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Am J
Gastroenterol. 105:585–595. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sharif AW, Williams HR, Lampejo T, Khan
SA, Bansi DS, Westaby D, Thillainayagam AV, Thomas HC, Cox IJ and
Taylor-Robinson SD: Metabolic profiling of bile in
cholangiocarcinoma using in vitro magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
HPB (Oxford). 12:396–402. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bobeldijk I, Hekman M, de Vries-van der
Weij J, Coulier L, Ramaker R, Kleemann R, Kooistra T, Rubingh C,
Freidig A and Verheij E: Quantitative profiling of bile acids in
biofluids and tissues based on accurate mass high resolution
LC-FT-MS: Compound class targeting in a metabolomics workflow. J
Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 871:306–313. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Greco AV and Mingrone G: Serum bile acid
concentrations in mild liver cirrhosis. Clin Chim Acta.
221:183–189. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xu ZP, Yang K, Xu GN, Zhu L, Hou LN, Zhang
WH, Chen HZ and Cui YY: Role of M3 mAChR in in vivo and in vitro
models of LPS-induced inflammatory response. Int Immunopharmacol.
14:320–327. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sales ME: Muscarinic receptors as targets
for anti-inflammatory therapy. Curr Opin Investig Drugs.
11:1239–1245. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Avissar NE, Toia L, Hu Y, Watson TJ, Jones
C, Raymond DP, Matousek A and Peters JH: Bile acid alone, or in
combination with acid, induces CDX2 expression through activation
of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). J Gastrointest
Surg. 13:212–222. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|