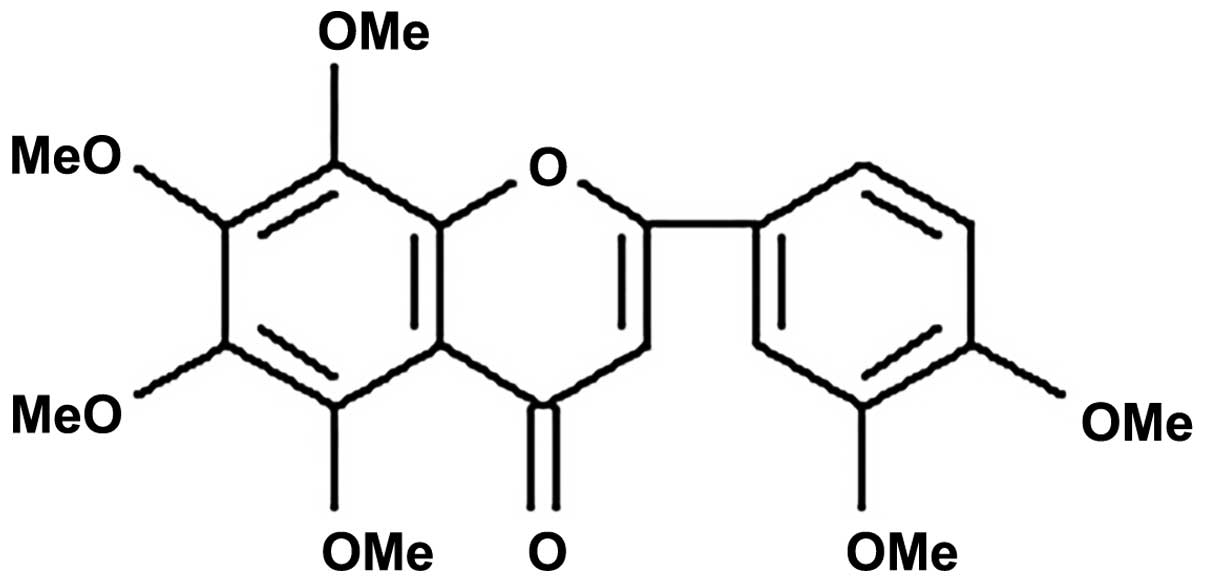
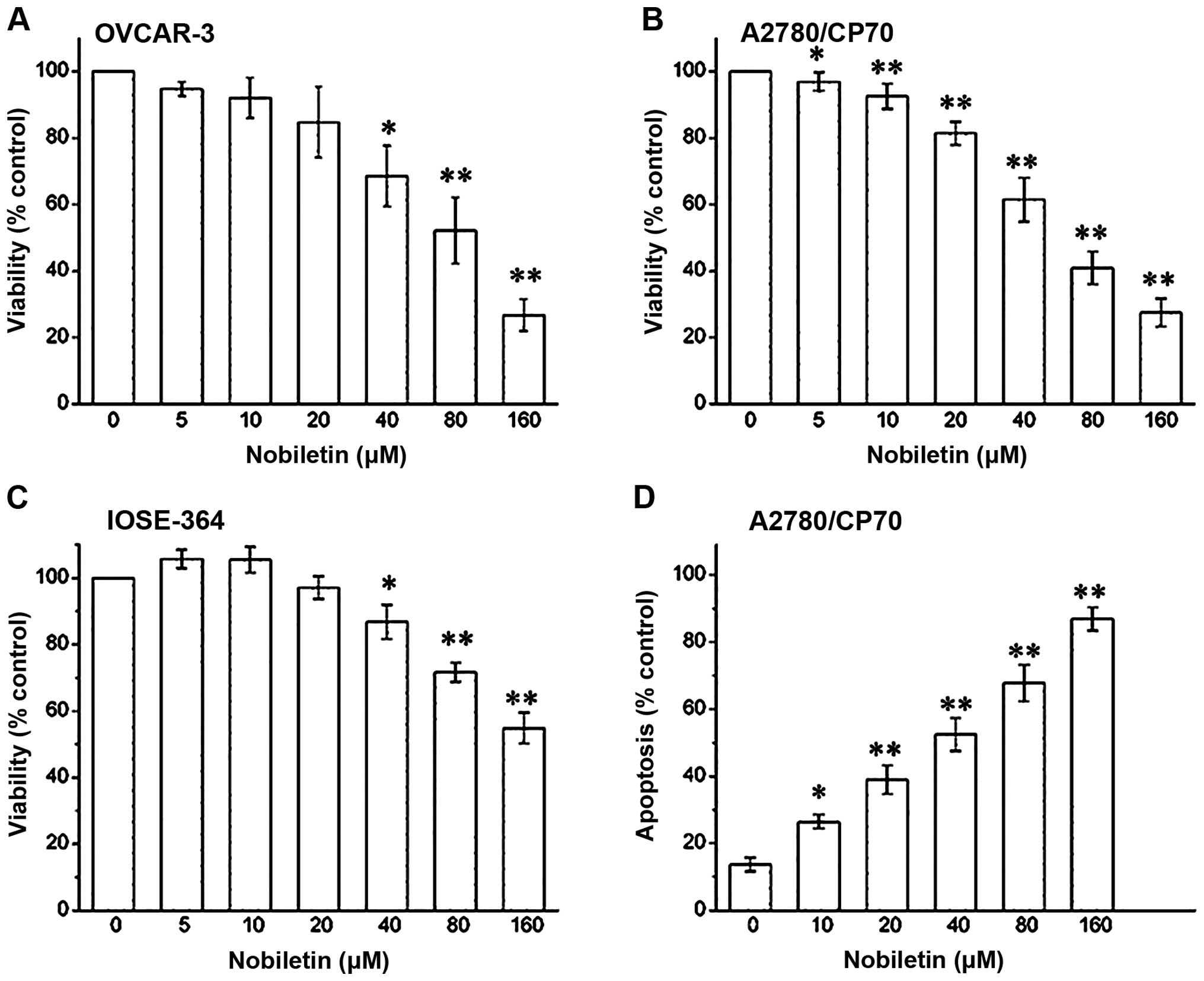
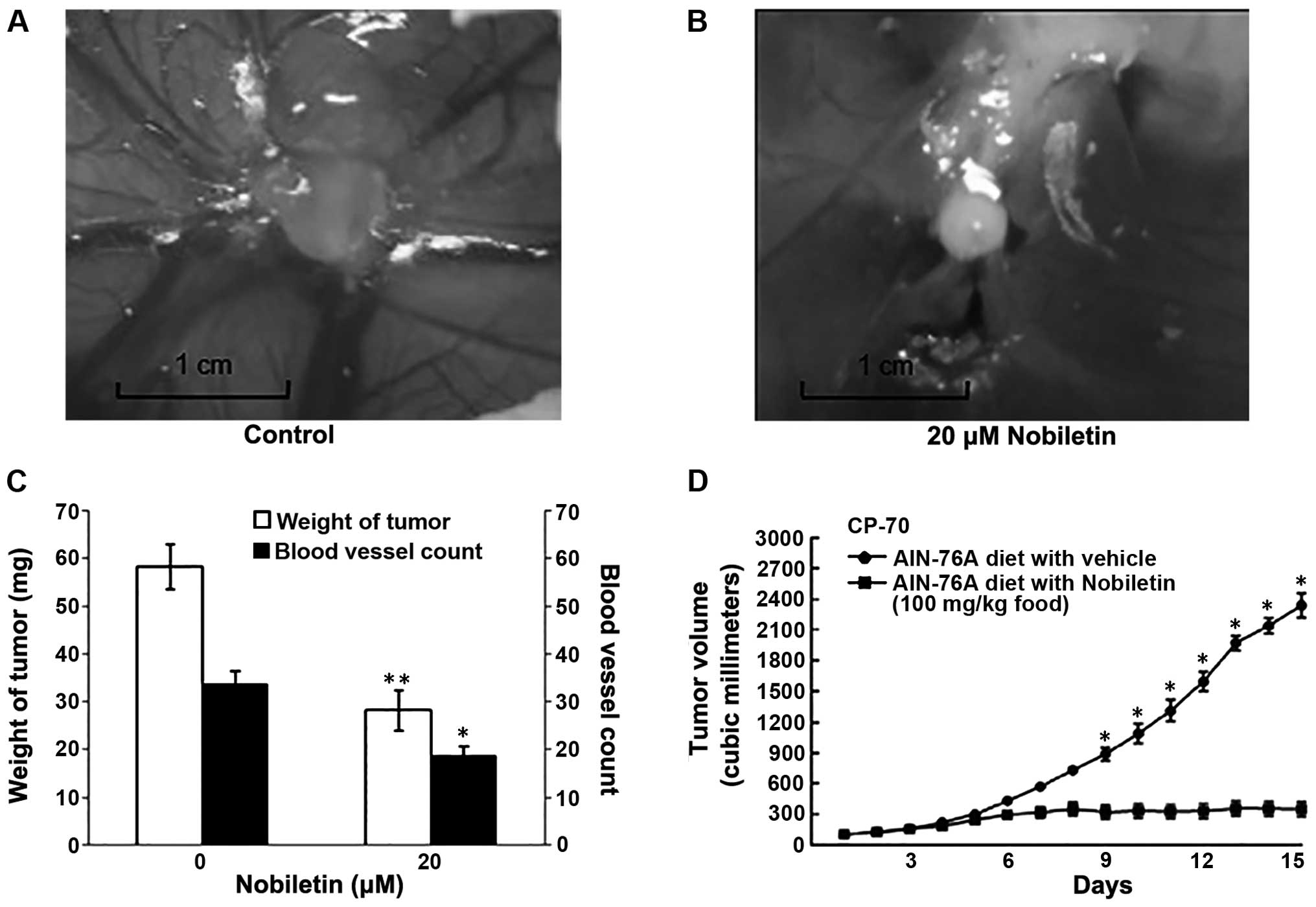
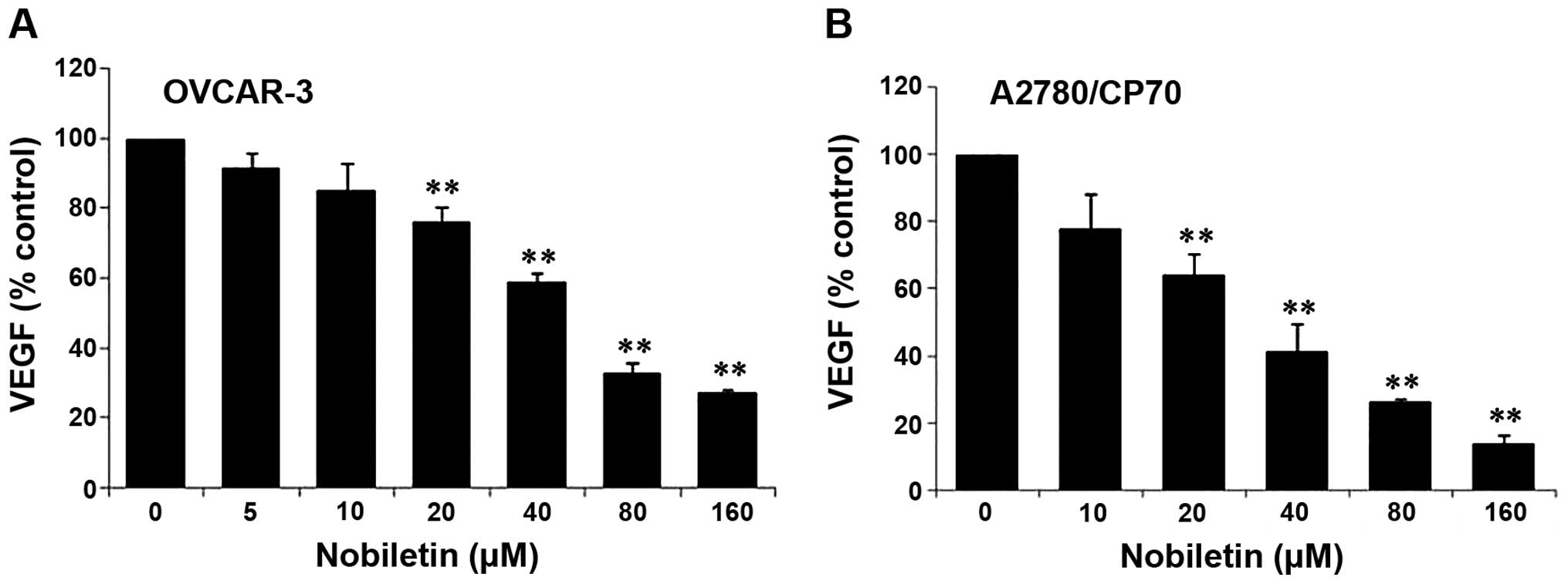
|
1
|
Jemal A, Tiwari RC, Murray T, Ghafoor A,
Samuels A, Ward E, Feuer EJ and Thun MJ: American Cancer Society:
Cancer statistics, 2004. CA Cancer J Clin. 54:8–29. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bast RC Jr, Xu FJ, Yu YH, Barnhill S,
Zhang Z and Mills GB: CA 125: The past and the future. Int J Biol
Markers. 13:179–187. 1998.
|
|
4
|
Winstead ER: Ovarian cancer study raises
questions about developing markers for early detection. NCI cancer
bulletin [On-line serial]. 8(5): Available simplencicancerbulletin@mail.nih.gov
Message: NCI Cancer Bulletin. March 8–2011
|
|
5
|
Fishman DA and Schwartz PE: Current
approaches to diagnosis and treatment of ovarian germ cell
malignancies. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 6:98–104. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Greenlee RT, Hill-Harmon MB, Murray T and
Thun M: Cancer statistics, 2001. CA Cancer J Clin. 51:15–36. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bosetti C, Rossi M, McLaughlin JK, Negri
E, Talamini R, Lagiou P, Montella M, Ramazzotti V, Franceschi S and
LaVecchia C: Flavonoids and the risk of renal cell carcinoma.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 16:98–101. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bosetti C, Bravi F, Talamini R, Parpinel
M, Gnagnarella P, Negri E, Montella M, Lagiou P, Franceschi S and
La Vecchia C: Flavonoids and prostate cancer risk: A study in
Italy. Nutr Cancer. 56:123–127. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Theodoratou E, Kyle J, Cetnarskyj R,
Farrington SM, Tenesa A, Barnetson R, Porteous M, Dunlop M and
Campbell H: Dietary flavonoids and the risk of colorectal cancer.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 16:684–693. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Adhami VM, Malik A, Zaman N, Sarfaraz S,
Siddiqui IA, Syed DN, Afaq F, Pasha FS, Saleem M and Mukhtar H:
Combined inhibitory effects of green tea polyphenols and selective
cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors on the growth of human prostate cancer
cells both in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 13:1611–1619.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Choi EJ, Kim T and Lee MS: Pro-apoptotic
effect and cytotoxicity of genistein and genistin in human ovarian
cancer SK-OV-3 cells. Life Sci. 80:1403–1408. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Seo HS, DeNardo DG, Jacquot Y, Laïos I,
Vidal DS, Zambrana CR, Leclercq G and Brown PH: Stimulatory effect
of genistein and apigenin on the growth of breast cancer cells
correlates with their ability to activate ER alpha. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 99:121–134. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fang J, Zhou Q, Liu LZ, Xia C, Hu X, Shi X
and Jiang BH: Apigenin inhibits tumor angiogenesis through
decreasing HIF-1alpha and VEGF expression. Carcinogenesis.
28:858–864. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Birt DF, Hendrich S and Wang W: Dietary
agents in cancer prevention: Flavonoids and isoflavonoids.
Pharmacol Ther. 90:157–177. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gossner G, Choi M, Tan L, Fogoros S,
Griffith KA, Kuenker M and Liu JR: Genistein-induced apoptosis and
autophagocytosis in ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 105:23–30.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Spinella F, Rosanò L, Di Castro V,
Decandia S, Albini A, Nicotra MR, Natali PG and Bagnato A: Green
tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits the endothelin
axis and downstream signaling pathways in ovarian carcinoma. Mol
Cancer Ther. 5:1483–1492. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Brusselmans K, Vrolix R, Verhoeven G and
Swinnen JV: Induction of cancer cell apoptosis by flavonoids is
associated with their ability to inhibit fatty acid synthase
activity. J Biol Chem. 280:5636–5645. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Nogata Y, Sakamoto K, Shiratsuchi H, Ishii
T, Yano M and Ohta H: Flavonoid composition of fruit tissues of
citrus species. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 70:178–192. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Murakami A, Nakamura Y, Torikai K, Tanaka
T, Koshiba T, Koshimizu K, Kuwahara S, Takahashi Y, Ogawa K, Yano
M, et al: Inhibitory effect of citrus nobiletin on phorbol
ester-induced skin inflammation, oxidative stress, and tumor
promotion in mice. Cancer Res. 60:5059–5066. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kohno H, Yoshitani S, Tsukio Y, Murakami
A, Koshimizu K, Yano M, Tokuda H, Nishino H, Ohigashi H and Tanaka
T: Dietary administration of citrus nobiletin inhibits
azoxymethane-induced colonic aberrant crypt foci in rats. Life Sci.
69:901–913. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Suzuki R, Kohno H, Murakami A, Koshimizu
K, Ohigashi H, Yano M, Tokuda H, Nishino H and Tanaka T: Citrus
nobiletin inhibits azoxymethane-induced large bowel carcinogenesis
in rats. Biofactors. 22:111–114. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lam KH, Alex D, Lam IK, Tsui SK, Yang ZF
and Lee SM: Nobiletin, a polymethoxylated flavonoid from citrus,
shows anti-angiogenic activity in a zebrafish in vivo model and
HUVEC in vitro model. J Cell Biochem. 112:3313–3321. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kunimasa K, Ikekita M, Sato M, Ohta T,
Yamori Y, Ikeda M, Kuranuki S and Oikawa T: Nobiletin, a citrus
polymethoxyflavonoid, suppresses multiple angiogenesis-related
endothelial cell functions and angiogenesis in vivo. Cancer Sci.
101:2462–2469. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kunimasa K, Kuranuki S, Matsuura N,
Iwasaki N, Ikeda M, Ito A, Sashida Y, Mimaki Y, Yano M, Sato M, et
al: Identification of nobiletin, a polymethoxyflavonoid, as an
enhancer of adiponectin secretion. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
19:2062–2064. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Saito T, Abe D and Sekiya K: Nobiletin
enhances differentiation and lipolysis of 3T3-L1 adipocytes.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 357:371–376. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Miyata Y, Sato T, Yano M and Ito A:
Activation of protein kinase C βII/ɛ-c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase
pathway and inhibition of mitogen-activated protein/extracellular
signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation in antitumor invasive
activity induced by the polymethoxy flavonoid, nobiletin. Mol
Cancer Ther. 3:839–847. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Miyata Y, Sato T, Imada K, Dobashi A, Yano
M and Ito A: A citrus polymethoxyflavonoid, nobiletin, is a novel
MEK inhibitor that exhibits antitumor metastasis in human
fibrosarcoma HT-1080 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
366:168–173. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Luo H, Li B, Li Z, Cutler SJ, Rankin GO
and Chen YC: Chaetoglobosin K inhibits tumor angiogenesis through
downregulation of vascular epithelial growth factor-binding
hypoxia-inducible factor 1α. Anticancer Drugs. 24:715–724. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fang J, Cao Z, Chen YC, Reed E and Jiang
BH: 9-β-D-Arabinofuranosyl-2-fluoroadenine inhibits expression of
vascular endothelial growth factor through hypoxia-inducible
factor-1 in human ovarian cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol. 66:178–186.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Blancher C, Moore JW, Robertson N and
Harris AL: Effects of ras and von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) gene
mutations on hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α, HIF-2α, and
vascular endothelial growth factor expression and their regulation
by the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Cancer
Res. 61:7349–7355. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Laughner E, Taghavi P, Chiles K, Mahon PC
and Semenza GL: HER2 (neu) signaling increases the rate of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) synthesis: Novel mechanism for
HIF-1-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor expression. Mol
Cell Biol. 21:3995–4004. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Stiehl DP, Jelkmann W, Wenger RH and
Hellwig-Bürgel T: Normoxic induction of the hypoxia-inducible
factor 1alpha by insulin and interleukin-1beta involves the
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. FEBS Lett. 512:157–162.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Miura T, Chiba M, Kasai K, Nozaka H,
Nakamura T, Shoji T, Kanda T, Ohtake Y and Sato T: Apple
procyanidins induce tumor cell apoptosis through mitochondrial
pathway activation of caspase-3. Carcinogenesis. 29:585–593. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Jeong WS and Kong ANT: Biological
properties of monomeric and polymeric catechins: Green tea
catechins and procyanidins. Pharm Biol. 42(s1): 84–93. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Luo H, Rankin GO, Juliano N, Jiang BH and
Chen YC: Kaempferol inhibits VEGF expression and in vitro
angiogenesis through a novel ERK-NFκB-c-Myc-p21 pathway. Food Chem.
130:321–328. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chu EC and Tarnawski AS: PTEN regulatory
functions in tumor suppression and cell biology. Med Sci Monit.
10:RA235–RA241. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hay N and Sonenberg N: Upstream and
downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev. 18:1926–1945. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ferrara N: Vascular endothelial growth
factor as a target for anticancer therapy. Oncologist. 9(Suppl 1):
2–10. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ramakrishnan S, Subramanian IV, Yokoyama Y
and Geller M: Angiogenesis in normal and neoplastic ovaries.
Angiogenesis. 8:169–182. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hazelton D, Nicosia RF and Nicosia SV:
Vascular endothelial growth factor levels in ovarian cyst fluid
correlate with malignancy. Clin Cancer Res. 5:823–829.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Alvarez AA, Krigman HR, Whitaker RS, Dodge
RK and Rodriguez GC: The prognostic significance of angiogenesis in
epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 5:587–591.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Duyndam MC, Hilhorst MC, Schlüper HM,
Verheul HM, van Diest PJ, Kraal G, Pinedo HM and Boven E: Vascular
endothelial growth factor-165 overexpression stimulates
angiogenesis and induces cyst formation and macrophage infiltration
in human ovarian cancer xenografts. Am J Pathol. 160:537–548. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hefler LA, Mustea A, Könsgen D, Concin N,
Tanner B, Strick R, Heinze G, Grimm C, Schuster E, Tempfer C, et
al: Vascular endothelial growth factor gene polymorphisms are
associated with prognosis in ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
13:898–901. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Forsythe JA, Jiang BH, Iyer NV, Agani F,
Leung SW, Koos RD and Semenza GL: Activation of vascular
endothelial growth factor gene transcription by hypoxia-inducible
factor 1. Mol Cell Biol. 16:4604–4613. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lam IK, Alex D, Wang YH, Liu P, Liu AL, Du
GH and Lee SM: In vitro and in vivo structure and activity
relationship analysis of polymethoxylated flavonoids: Identifying
sinensetin as a novel antiangiogenesis agent. Mol Nutr Food Res.
56:945–956. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Luo H, Rankin GO, Liu L, Daddysman MK,
Jiang BH and Chen YC: Kaempferol inhibits angiogenesis and VEGF
expression through both HIF dependent and independent pathways in
human ovarian cancer cells. Nutr Cancer. 61:554–563. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Jiang BH and Liu LZ: AKT signaling in
regulating angiogenesis. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:19–26. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hu L, Hofmann J and Jaffe RB:
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase mediates angiogenesis and vascular
permeability associated with ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
11:8208–8212. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Shi MD, Liao YC, Shih YW and Tsai LY:
Nobiletin attenuates metastasis via both ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways
in HGF-treated liver cancer HepG2 cells. Phytomedicine. 20:743–752.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lee YC, Cheng TH, Lee JS, Chen JH, Liao
YC, Fong Y, Wu CH and Shih YW: Nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid,
suppresses invasion and migration involving FAK/PI3K/Akt and small
GTPase signals in human gastric adenocarcinoma AGS cells. Mol Cell
Biochem. 347:103–115. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Kar S, Palit S, Ball WB and Das PK:
Carnosic acid modulates Akt/IKK/NF-κB signaling by PP2A and induces
intrinsic and extrinsic pathway mediated apoptosis in human
prostate carcinoma PC-3 cells. Apoptosis. 17:735–747. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kim MO, Moon DO, Heo MS, Lee JD, Jung JH,
Kim SK, Choi YH and Kim GY: Pectenotoxin-2 abolishes constitutively
activated NF-κB, leading to suppression of NF-κB related gene
products and potentiation of apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 271:25–33.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ozes ON, Mayo LD, Gustin JA, Pfeffer SR,
Pfeffer LM and Donner DB: NF-κB activation by tumour necrosis
factor requires the Akt serine-threonine kinase. Nature. 401:82–85.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
van Uden P, Kenneth NS and Rocha S:
Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α by NF-kappaB. Biochem J.
412:477–484. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Karin M: Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer
development and progression. Nature. 441:431–436. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lin YG, Kunnumakkara AB, Nair A, Merritt
WM, Han LY, Armaiz-Pena GN, Kamat AA, Spannuth WA, Gershenson DM,
Lutgendorf SK, et al: Curcumin inhibits tumor growth and
angiogenesis in ovarian carcinoma by targeting the nuclear
factor-kappaB pathway. Clin Cancer Res. 13:3423–3430. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Gonzalez-Perez RR, Xu Y, Guo S, Watters A,
Zhou W and Leibovich SJ: Leptin upregulates VEGF in breast cancer
via canonic and non-canonical signalling pathways and
NFkappaB/HIF-1alpha activation. Cell Signal. 22:1350–1362. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Testa JR and Bellacosa A: AKT plays a
central role in tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:10983–10985. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Cain K, Langlais C, Sun XM, Brown DG and
Cohen GM: Physiological concentrations of K+ inhibit
cytochrome c-dependent formation of the apoptosome. J Biol Chem.
276:41985–41990. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Arafa SA, Zhu Q, Barakat BM, Wani G, Zhao
Q, El-Mahdy MA and Wani AA: Tangeretin sensitizes
cisplatin-resistant human ovarian cancer cells through
downregulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway.
Cancer Res. 69:8910–8917. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Luo H, Daddysman MK, Rankin GO, Jiang BH
and Chen YC: Kaempferol enhances cisplatin’s effect on ovarian
cancer cells through promoting apoptosis caused by down regulation
of c-Myc. Cancer Cell Int. 10:162010. View Article : Google Scholar
|