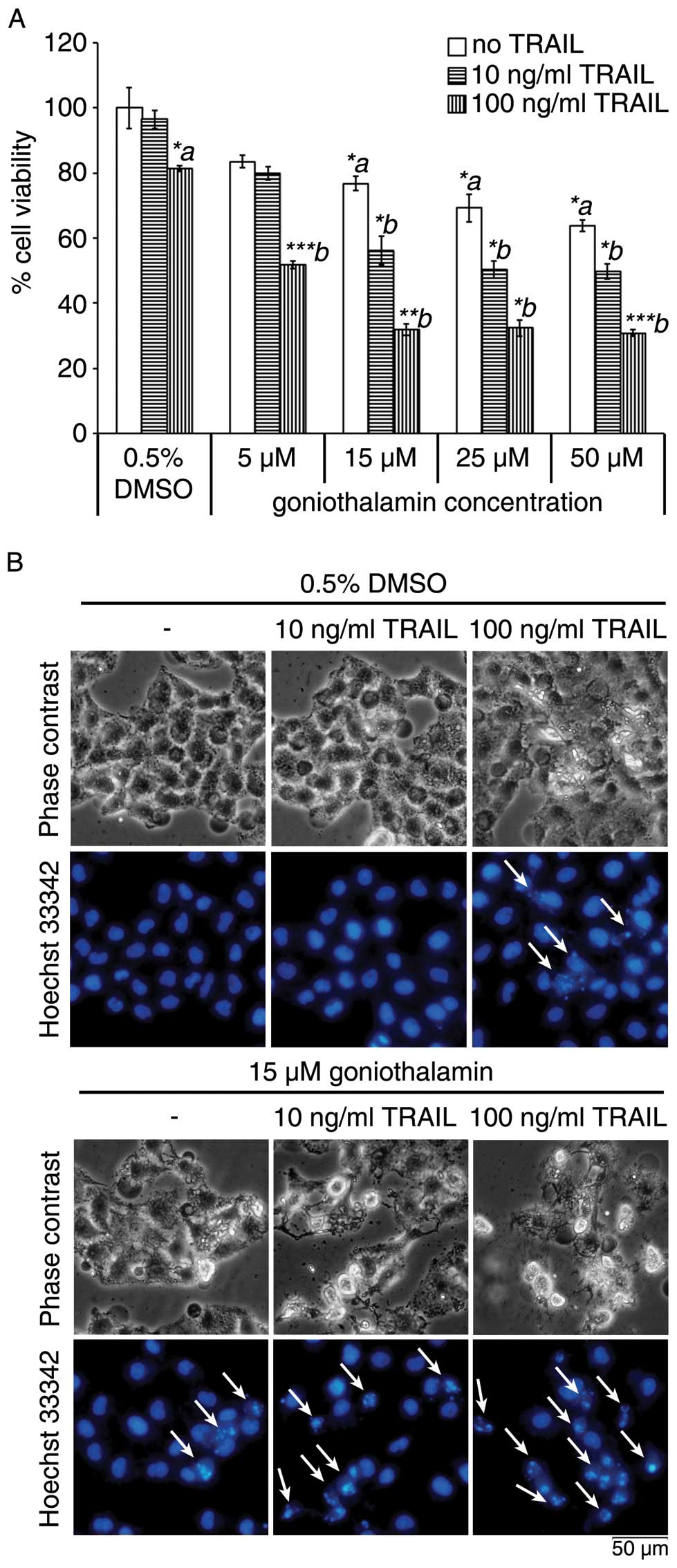
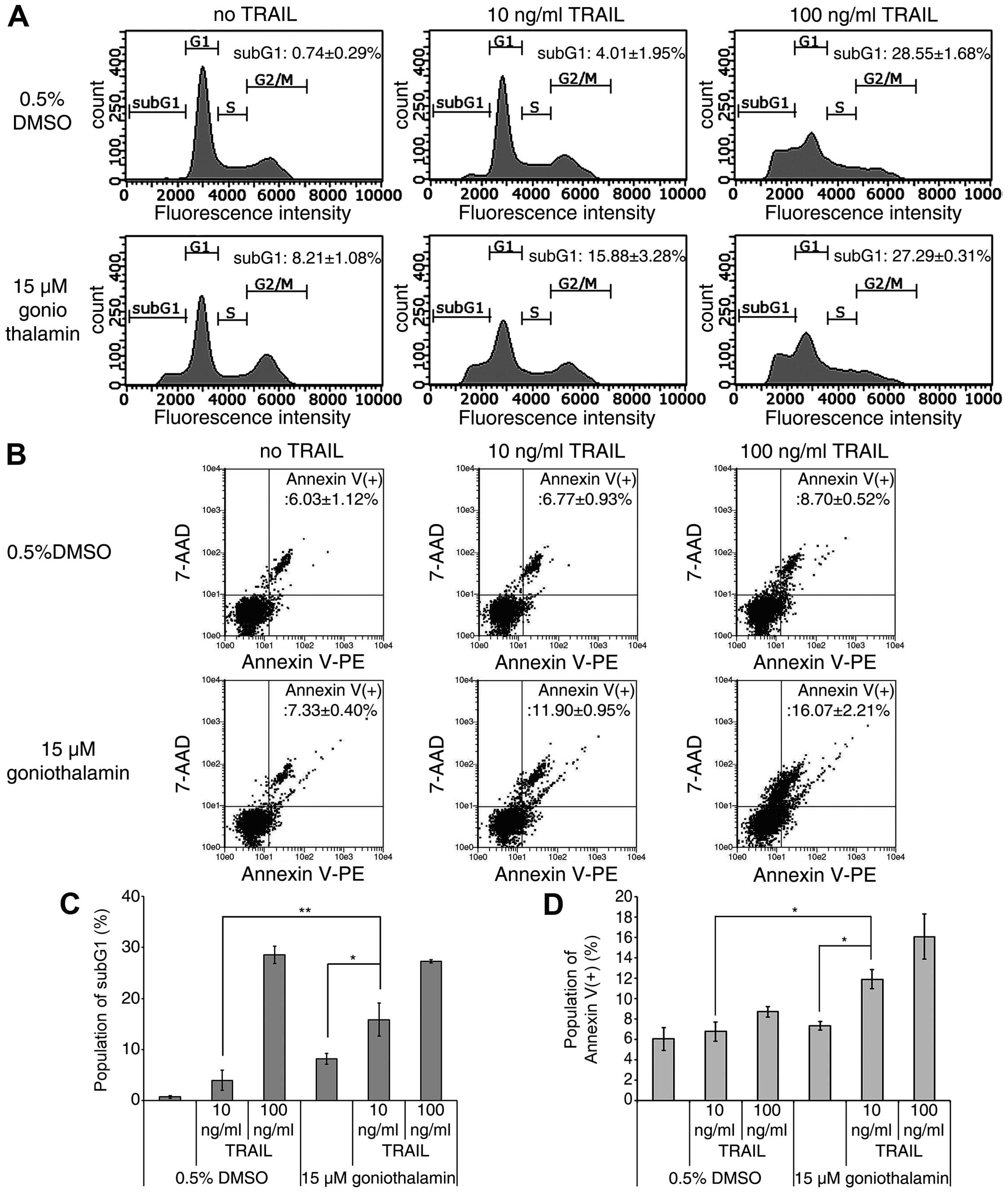
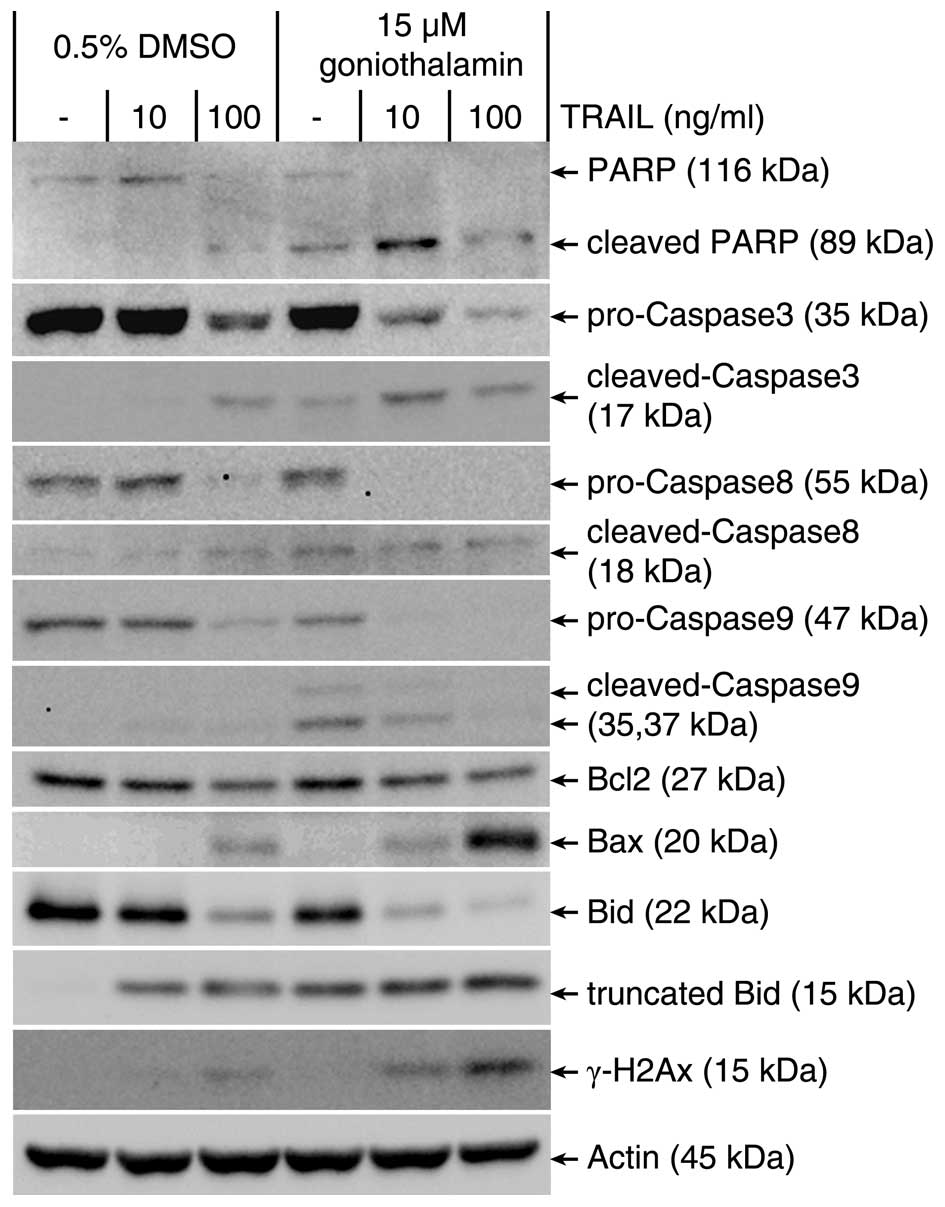
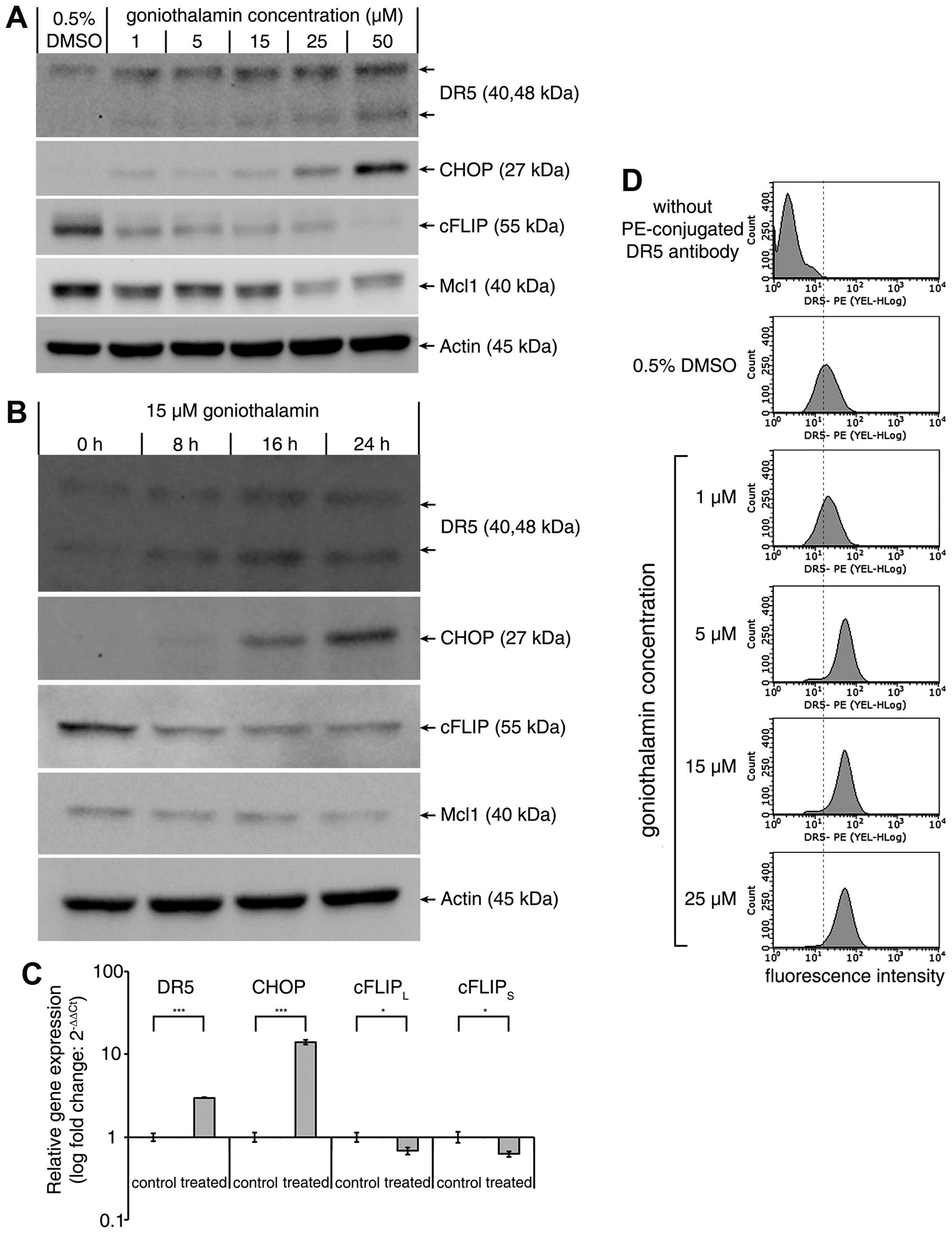
|
1
|
Fukuda M, Hamao A, Tanaka A, Kitada M,
Suzuki S, Kusama K and Sakashita H: Tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL/APO2L) and its receptors
expression in human squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity.
Oncol Rep. 10:1113–1119. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kichev A, Rousset CI, Baburamani AA,
Levison SW, Wood TL, Gressens P, Thornton C and Hagberg H: Tumor
necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) signaling
and cell death in the immature central nervous system after
hypoxia-ischemia and inflammation. J Biol Chem. 289:9430–9439.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, Gliniak B,
Griffith TS, Kubin M, Chin W, Jones J, Woodward A, Le T, et al:
Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med. 5:157–163. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ and Yuan J: Cleavage of
BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas
pathway of apoptosis. Cell. 94:491–501. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gross A, McDonnell JM and Korsmeyer SJ:
BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev.
13:1899–1911. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schug ZT, Gonzalvez F, Houtkooper RH, Vaz
FM and Gottlieb E: BID is cleaved by caspase-8 within a native
complex on the mitochondrial membrane. Cell Death Differ.
18:538–548. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Kantari C and Walczak H: Caspase-8 and
bid: Caught in the act between death receptors and mitochondria.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:558–563. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Galligan L, Longley DB, McEwan M, Wilson
TR, McLaughlin K and Johnston PG: Chemotherapy and TRAIL-mediated
colon cancer cell death: The roles of p53, TRAIL receptors, and
c-FLIP. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:2026–2036. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang L and Fang B: Mechanisms of
resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in cancer. Cancer Gene Ther.
12:228–237. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lemke J, von Karstedt S, Zinngrebe J and
Walczak H: Getting TRAIL back on track for cancer therapy. Cell
Death Differ. 21:1350–1364. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Grambihler A, Higuchi H, Bronk SF and
Gores GJ: cFLIP-L inhibits p38 MAPK activation: An additional
anti-apoptotic mechanism in bile acid-mediated apoptosis. J Biol
Chem. 278:26831–26837. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nagane M, Pan G, Weddle JJ, Dixit VM,
Cavenee WK and Huang HJ: Increased death receptor 5 expression by
chemotherapeutic agents in human gliomas causes synergistic
cytotoxicity with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 60:847–853.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sheikh MS, Burns TF, Huang Y, Wu GS,
Amundson S, Brooks KS, Fornace AJ Jr and el-Deiry WS: p53-dependent
and -independent regulation of the death receptor KILLER/DR5 gene
expression in response to genotoxic stress and tumor necrosis
factor alpha. Cancer Res. 58:1593–1598. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu X, Yue P, Chen S, Hu L, Lonial S,
Khuri FR and Sun SY: The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 (bortezomib)
up-regulates DR5 expression leading to induction of apoptosis and
enhancement of TRAIL-induced apoptosis despite up-regulation of
c-FLIP and survivin expression in human NSCLC cells. Cancer Res.
67:4981–4988. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shiraishi T, Yoshida T, Nakata S, Horinaka
M, Wakada M, Mizutani Y, Miki T and Sakai T: Tunicamycin enhances
tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced
apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 65:6364–6370.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lim JH, Park JW, Choi KS, Park YB and Kwon
TK: Rottlerin induces apoptosis via death receptor 5 (DR5)
upregulation through CHOP-dependent and PKC delta-independent
mechanism in human malignant tumor cells. Carcinogenesis.
30:729–736. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kikuchi H, Ohtsuki T, Koyano T,
Kowithayakorn T, Sakai T and Ishibashi M: Brandisianins A-F,
isoflavonoids isolated from Millettia brandisiana in a screening
program for death-receptor expression enhancement activity. J Nat
Prod. 70:1910–1914. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim YH, Park JW, Lee JY and Kwon TK:
Sodium butyrate sensitizes TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by induction of
transcription from the DR5 gene promoter through Sp1 sites in colon
cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 25:1813–1820. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yamamoto K, Makino M, Watanapokasin R,
Tashiro E and Imoto M: Inostamycin enhanced TRAIL-induced apoptosis
through DR5 upregulation on the cell surface. J Antibiot (Tokyo).
65:295–300. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhou W, Cao A, Wang L and Wu D: Kurarinone
synergizes TRAIL-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. Cell
Biochem Biophys. 72:241–249. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Han H, Xu B, Hou P, Jiang C, Liu L, Tang
M, Yang X, Zhang Y and Liu Y: Icaritin sensitizes human
glioblastoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 72:533–542. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Henrich CJ, Brooks AD, Erickson KL, Thomas
CL, Bokesch HR, Tewary P, Thompson CR, Pompei RJ, Gustafson KR,
McMahon JB and Sayers TJ: Withanolide E sensitizes renal carcinoma
cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by increasing cFLIP degradation.
Cell Death Dis. 6:e16662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Son YG, Kim EH, Kim JY, Kim SU, Kwon TK,
Yoon AR, Yun CO and Choi KS: Silibinin sensitizes human glioma
cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis via DR5 up-regulation and
down-regulation of c-FLIP and survivin. Cancer Res. 67:8274–8284.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee DH, Kim DW, Jung CH, Lee YJ and Park
D: Gingerol sensitizes TRAIL-induced apoptotic cell death of
glioblastoma cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 279:253–265. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tse AK, Cao HH, Cheng CY, Kwan HY, Yu H,
Fong WF and Yu ZL: Indomethacin sensitizes TRAIL-resistant melanoma
cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through ROS-mediated upregulation
of death receptor 5 and downregulation of survivin. J Invest
Dermatol. 134:1397–1407. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ahmed D, Eide PW, Eilertsen IA, Danielsen
SA, Eknæs M, Hektoen M, Lind GE and Lothe RA: Epigenetic and
genetic features of 24 colon cancer cell lines. Oncogenesis.
2:e712013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wattanapiromsakul C, Wangsintaweekul B,
Sangprapan P, Itharat A and Keawpradub N: Goniothalamin, a
cytotoxic compound, isolated from Goniothalamus macrophyllus
(Blume) Hook. f & Thomson var macrophyllus Songklanakarin. J
Sci Technol. 27:479–487. 2005.
|
|
29
|
Inayat-Hussain SH, Annuar BO, Din LB, Ali
AM and Ross D: Loss of mitochondrial transmembrane potential and
caspase-9 activation during apoptosis induced by the novel
styryl-lactone goniothalamin in HL-60 leukemia cells. Toxicol In
Vitro. 17:433–439. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chan KM, Rajab NF, Ishak MH, Ali AM,
Yusoff K, Din LB and Inayat-Hussain SH: Goniothalamin induces
apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Chem Biol Interact.
159:129–140. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chen WY, Wu CC, Lan YH, Chang FR, Teng CM
and Wu YC: Goniothalamin induces cell cycle-specific apoptosis by
modulating the redox status in MDA-MB-231 cells. Eur J Pharmacol.
522:20–29. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
de Fátima A, Kohn LK, Antônio MA, de
Carvalho JE and Pilli RA: (R)-Goniothalamin: Total syntheses and
cytotoxic activity against cancer cell lines. Bioorg Med Chem.
13:2927–2933. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Alabsi AM, Ali R, Ali AM, Al-Dubai SA,
Harun H, Abu Kasim NH and Alsalahi A: Apoptosis induction, cell
cycle arrest and in vitro anticancer activity of gonothalamin in a
cancer cell lines. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:5131–5136. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Petsophonsakul P, Pompimon W and
Banjerdpongchai R: Apoptosis induction in human leukemic
promyelocytic HL-60 and monocytic U937 cell lines by goniothalamin.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:2885–2889. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Denizot F and Lang R: Rapid colorimetric
assay for cell growth and survival. Modifications to the
tetrazolium dye procedure giving improved sensitivity and
reliability. J Immunol Methods. 89:271–277. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Oberhammer FA, Hochegger K, Fröschl G,
Tiefenbacher R and Pavelka M: Chromatin condensation during
apoptosis is accompanied by degradation of lamin A+B, without
enhanced activation of cdc2 kinase. J Cell Biol. 126:827–837. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shi J, Zheng D, Man K, Fan ST and Xu R:
TRAIL: A potential agent for cancer therapy. Curr Mol Med.
3:727–736. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nagane M, Huang HJ and Cavenee WK: The
potential of TRAIL for cancer chemotherapy. Apoptosis. 6:191–197.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shankar S and Srivastava RK: Enhancement
of therapeutic potential of TRAIL by cancer chemotherapy and
irradiation: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Drug Resist
Updat. 7:139–156. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Buchsbaum DJ, Forero-Torres A and LoBuglio
AF: TRAIL-receptor antibodies as a potential cancer treatment.
Future Oncol. 3:405–409. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Krajarng A, Imoto M, Tashiro E, Fujimaki
T, Shinjo S and Watanapokasin R: Apoptosis induction associated
with the ER stress response through up-regulation of JNK in HeLa
cells by gambogic acid. BMC Complement Altern Med. 15:262015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Trivedi R, Maurya R and Mishra DP:
Medicarpin, a legume phytoalexin sensitizes myeloid leukemia cells
to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through the induction of DR5 and
activation of the ROS-JNK-CHOP pathway. Cell Death Dis.
5:e14652014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pennati M, Sbarra S, De Cesare M,
Lopergolo A, Locatelli SL, Campi E, Daidone MG, Carlo-Stella C,
Gianni AM and Zaffaroni N: YM155 sensitizes triple-negative breast
cancer to membrane-bound TRAIL through p38 MAPK- and CHOP-mediated
DR5 upregulation. Int J Cancer. 136:299–309. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Yi L, Zongyuan Y, Cheng G, Lingyun Z,
Guilian Y and Wei G: Quercetin enhances apoptotic effect of tumor
necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) in
ovarian cancer cells through reactive oxygen species (ROS) mediated
CCAAT enhancer-binding protein homologous protein (CHOP)-death
receptor 5 pathway. Cancer Sci. 105:520–527. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yoon MJ, Kang YJ, Kim IY, Kim EH, Lee JA,
Lim JH, Kwon TK and Choi KS: Monensin, a polyether ionophore
antibiotic, overcomes TRAIL resistance in glioma cells via
endoplasmic reticulum stress, DR5 upregulation and c-FLIP
downregulation. Carcinogenesis. 34:1918–1928. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang S, Shen HM and Ong CN:
Down-regulation of c-FLIP contributes to the sensitization effect
of 3,3′-diindolylmethane on TRAIL-induced apoptosis in cancer
cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:1972–1981. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
García-García C, Fumarola C, Navaratnam N,
Carling D and López-Rivas A: AMPK-independent down-regulation of
cFLIP and sensitization to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by AMPK
activators. Biochem Pharmacol. 79:853–863. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Lin Y, Liu X, Yue P, Benbrook DM, Berlin
KD, Khuri FR and Sun SY: Involvement of c-FLIP and survivin
down-regulation in flexible heteroarotinoid-induced apoptosis and
enhancement of TRAIL-initiated apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 7:3556–3565. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Day TW, Huang S and Safa AR: c-FLIP
knockdown induces ligand-independent DR5-, FADD-, caspase-8-, and
caspase-9-dependent apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Biochem
Pharmacol. 76:1694–1704. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Safa AR and Pollok KE: Targeting the
anti-apoptotic protein c-FLIP for cancer therapy. Cancers (Basel).
3:1639–1671. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Safa AR: c-FLIP, a master anti-apoptotic
regulator. Exp Oncol. 34:176–184. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Safa AR: Roles of c-FLIP in apoptosis,
necroptosis, and autophagy. J Carcinog Mutagen. (Suppl 6): pii:
003. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wilson TR, McLaughlin KM, McEwan M, Sakai
H, Rogers KM, Redmond KM, Johnston PG and Longley DB: c-FLIP: A key
regulator of colorectal cancer cell death. Cancer Res.
67:5754–5762. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lee SJ, Noh HJ, Sung EG, Song IH, Kim JY,
Kwon TK and Lee TJ: Berberine sensitizes TRAIL-induced apoptosis
through proteasome-mediated downregulation of c-FLIP and Mcl-1
proteins. Int J Oncol. 38:485–492. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Murphy AC, Weyhenmeyer B, Noonan J,
Kilbride SM, Schimansky S, Loh KP, Kögel D, Letai AG, Prehn JH and
Murphy BM: Modulation of Mcl-1 sensitizes glioblastoma to
TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis. 19:629–642. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
56
|
Kim SH, Ricci MS and El-Deiry WS: Mcl-1: A
gateway to TRAIL sensitization. Cancer Res. 68:2062–2064. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Clohessy JG, Zhuang J, de Boer J,
Gil-Gómez G and Brady HJ: Mcl-1 interacts with truncated Bid and
inhibits its induction of cytochrome c release and its role in
receptor-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 281:5750–5759. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Ozören N and El-Deiry WS: Cell surface
death receptor signaling in normal and cancer cells. Semin Cancer
Biol. 13:135–147. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chen JJ, Mikelis CM, Zhang Y, Gutkind JS
and Zhang B: TRAIL induces apoptosis in oral squamous carcinoma
cells - a crosstalk with oncogenic Ras regulated cell surface
expression of death receptor 5. Oncotarget. 4:206–217. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ren YG, Wagner KW, Knee DA, Aza-Blanc P,
Nasoff M and Deveraux QL: Differential regulation of the TRAIL
death receptors DR4 and DR5 by the signal recognition particle. Mol
Biol Cell. 15:5064–5074. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wei MC, Lindsten T, Mootha VK, Weiler S,
Gross A, Ashiya M, Thompson CB and Korsmeyer SJ: tBID, a
membrane-targeted death ligand, oligomerizes BAK to release
cytochrome c. Genes Dev. 14:2060–2071. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Pietenpol JA and Stewart ZA: Cell cycle
checkpoint signaling: Cell cycle arrest versus apoptosis.
Toxicology. 181–182:475–481. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
van Engeland M, Nieland LJ, Ramaekers FC,
Schutte B and Reutelingsperger CP: Annexin V-affinity assay: A
review on an apoptosis detection system based on phosphatidylserine
exposure. Cytometry. 31:1–9. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Kuo LJ and Yang LX: Gamma-H2AX - a novel
biomarker for DNA double-strand breaks. In Vivo. 22:305–309.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Rogakou EP, Nieves-Neira W, Boon C,
Pommier Y and Bonner WM: Initiation of DNA fragmentation during
apoptosis induces phosphorylation of H2AX histone at serine 139. J
Biol Chem. 275:9390–9395. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ko H, Jeong MH, Jeon H, Sung GJ, So Y, Kim
I, Son J, Lee SW, Yoon HG and Choi KC: Delphinidin sensitizes
prostate cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis, by inducing DR5
and causing caspase-mediated HDAC3 cleavage. Oncotarget.
6:9970–9984. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Trang KT, Kim SL, Park SB, Seo SY, Choi
CH, Park JK, Moon JC, Lee ST and Kim SW: Parthenolide sensitizes
human colorectal cancer cells to tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand through mitochondrial and caspase
dependent pathway. Intest Res. 12:34–41. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|