|
1
|
Nucifora G, Laricchia-Robbio L and Senyuk
V: EVI1 and hematopoietic disorders: History and perspectives.
Gene. 368:1–11. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Haladyna JN, Yamauchi T, Neff T and Bernt
KM: Epigenetic modifiers in normal and malignant hematopoiesis.
Epigenomics. 7:301–320. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yamazaki H, Suzuki M, Otsuki A, Shimizu R,
Bresnick EH, Engel JD and Yamamoto M: A remote GATA2 hematopoietic
enhancer drives leukemogenesis in inv(3)(q21;q26) by activating
EVI-1 expression. Cancer Cell. 25:415–427. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ney Garcia DR, Liehr T, Emerenciano M,
Meyer C, Marschalek R, Pombo-de-Oliveira MS, Ribeiro RC, Poirot
Land MG and Macedo Silva ML: Molecular studies reveal a MLL-MLLT3
gene fusion displaced in a case of childhood acute lymphoblastic
leukemia with complex karyotype. Cancer Genet. 208:143–147. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
De Braekeleer M, Le Bris MJ, De Braekeleer
E, Basinko A, Morel F and Douet-Guilbert N: 3q26/EVI-1
rearrangements in myeloid hemopathies: A cytogenetic review. Future
Oncol. 11:1675–1686. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Su G, Lian X, Tan D, Tao H, Liu H, Chen S,
Yin H, Wu D and Yin B: Aberrant expression of ecotropic viral
integration site-1 in acute myeloid leukemia and acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 56:472–479. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Glass C, Wilson M, Gonzalez R, Zhang Y and
Perkins AS: The role of EVI1 in myeloid malignancies. Blood Cells
Mol Dis. 53:67–76. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Koos B, Bender S, Witt H, Mertsch S,
Felsberg J, Beschorner R, Korshunov A, Riesmeier B, Pfister S,
Paulus W, et al: The transcription factor evi-1 is overexpressed,
promotes proliferation, and is prognostically unfavorable in
infratentorial ependymomas. Clin Cancer Res. 17:3631–3637. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jazaeri AA, Ferriss JS, Bryant JL, Dalton
MS and Dutta A: Evaluation of EVI-1 and EVI-1s (Delta324) as
potential therapeutic targets in ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
118:189–195. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Balgobind BV, Lugthart S, Hollink IH,
Arentsen-Peters ST, van Wering ER, de Graaf SS, Reinhardt D,
Creutzig U, Kaspers GJ, de Bont ES, et al: EVI-1 overexpression in
distinct subtypes of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia.
24:942–949. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yasui K, Konishi C, Gen Y, Endo M, Dohi O,
Tomie A, Kitaichi T, Yamada N, Iwai N, Nishikawa T, et al: EVI-1, a
target gene for amplification at 3q26, antagonizes transforming
growth factor-β-mediated growth inhibition in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 106:929–937. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bindels EMJ, Havermans M, Lugthart S,
Erpelinck C, Wocjtowicz E, Krivtsov AV, Rombouts E, Armstrong SA,
Taskesen E, Haanstra JR, et al: EVI-1 is critical for the
pathogenesis of a subset of MLL-AF9-rearranged AMLs. Blood.
119:5838–5849. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mucenski ML, Taylor BA, Ihle JN, Hartley
JW, Morse HC III, Jenkins NA and Copeland NG: Identification of a
common ecotropic viral integration site, EVI-1, in the DNA of AKXD
murine myeloid tumors. Mol Cell Biol. 8:301–308. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu K, Wang L and Hao Y: Advances in the
study of EVI-1 and mds1 genes. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi.
20:331–333. 1999.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Aytekin M, Vinatzer U, Musteanu M, Raynaud
S and Wieser R: Regulation of the expression of the oncogene EVI-1
through the use of alternative mRNA 5′-ends. Gene. 356:160–168.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fears S, Mathieu C, Zeleznik-Le N, Huang
S, Rowley JD and Nucifora G: Intergenic splicing of MDS1 and EVI-1
occurs in normal tissues as well as in myeloid leukemia and
produces a new member of the PR domain family. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 93:1642–1647. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Soderholm J, Kobayashi H, Mathieu C,
Rowley JD and Nucifora G: The leukemia-associated gene MDS1/EVI-1
is a new type of GATA-binding transactivator. Leukemia. 11:352–358.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
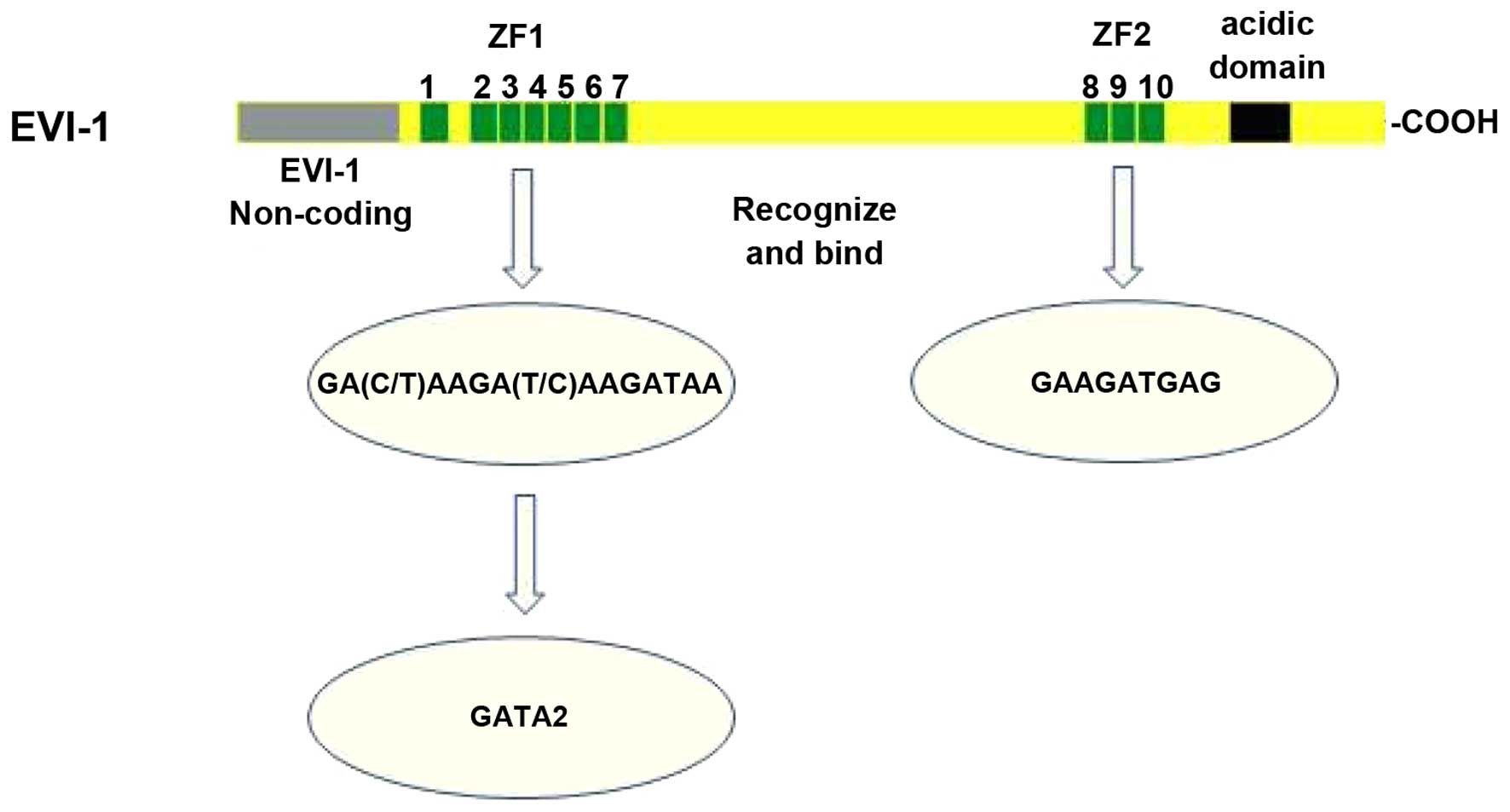
Delwel R, Funabiki T, Kreider BL,
Morishita K and Ihle JN: Four of the seven zinc fingers of the
EVI-1 myeloid-transforming gene are required for sequence-specific
binding to GA(C/T) AAGA(T/C)AAGATAA. Mol Cell Biol. 13:4291–4300.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Funabiki T, Kreider BL and Ihle JN: The
carboxyl domain of zinc fingers of the EVI-1 myeloid transforming
gene binds a consensus sequence of GAAGATGAG. Oncogene.
9:1575–1581. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lopingco MC and Perkins AS: Molecular
analysis of EVI-1, a zinc finger oncogene involved in myeloid
leukemia. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 211:211–222. 1996.
|
|
21
|
Saito Y and Morishita K: Maintenance of
leukemic and normal hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow niches
by EVI-1-regulated GPR56. Rinsho Ketsueki. 56:375–383. 2015.(In
Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fukuda S, Hoggatt J, Singh P, Abe M, Speth
JM, Hu P, Conway EM, Nucifora G, Yamaguchi S and Pelus LM: Survivin
modulates genes with divergent molecular functions and regulates
proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells through EVI-1. Leukemia.
29:433–440. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Goyama S, Yamamoto G, Shimabe M, Sato T,
Ichikawa M, Ogawa S, Chiba S and Kurokawa M: EVI-1 is a critical
regulator for hematopoietic stem cells and transformed leukemic
cells. Cell Stem Cell. 3:207–220. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yuasa H, Oike Y, Iwama A, Nishikata I,
Sugiyama D, Perkins A, Mucenski ML, Suda T and Morishita K:
Oncogenic transcription factor EVI-1 regulates hematopoietic stem
cell proliferation through GATA-2 expression. EMBO J. 24:1976–1987.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Matsugi T, Kreider BL, Delwel R, Cleveland
JL, Askew DS and Ihle JN: The EVI-1 zinc finger myeloid
transforming protein binds to genomic fragments containing (GATA)n
sequences. Oncogene. 11:191–198. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kreider BL, Orkin SH and Ihle JN: Loss of
erythropoietin responsiveness in erythroid progenitors due to
expression of the EVI-1 myeloid-transforming gene. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 90:6454–6458. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Laricchia-Robbio L, Fazzina R, Li D,
Rinaldi CR, Sinha KK, Chakraborty S and Nucifora G: Point mutations
in two EVI-1 Zn fingers abolish EVI-1-GATA1 interaction and allow
erythroid differentiation of murine bone marrow cells. Mol Cell
Biol. 26:7658–7666. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Louz D, van den Broek M, Verbakel S,
Vankan Y, van Lom K, Joosten M, Meijer D, Löwenberg B and Delwel R:
Erythroid defects and increased retrovirally-induced tumor
formation in EVI-1 transgenic mice. Leukemia. 14:1876–1884. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Morishita K, Parganas E, Matsugi T and
Ihle JN: Expression of the EVI-1 zinc finger gene in 32Dc13 myeloid
cells blocks granulocytic differentiation in response to
granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Mol Cell Biol. 12:183–189.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Boyd KE, Xiao YY, Fan K, Poholek A,
Copeland NG, Jenkins NA and Perkins AS: Sox4 cooperates with EVI-1
in AKXD-23 myeloid tumors via transactivation of proviral LTR.
Blood. 107:733–741. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Laricchia-Robbio L, Premanand K, Rinaldi
CR and Nucifora G: EVI-1 Impairs myelopoiesis by deregulation of
PU.1 function. Cancer Res. 69:1633–1642. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shimizu S, Nagasawa T, Katoh O, Komatsu N,
Yokota J and Morishita K: EVI-1 is expressed in megakaryocyte cell
lineage and enforced expression of EVI-1 in UT-7/GM cells induces
megakaryocyte differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
292:609–616. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kilbey A, Alzuherri H, McColl J, Calés C,
Frampton J and Bartholomew C: The EVI-1 proto-oncoprotein blocks
endomitosis in megakaryocytes by inhibiting sustained
cyclin-dependent kinase 2 catalytic activity. Br J Haematol.
130:902–911. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gröschel S, Sanders MA, Hoogenboezem R, de
Wit E, Bouwman BA, Erpelinck C, van der Velden VH, Havermans M,
Avellino R, van Lom K, et al: A single oncogenic enhancer
rearrangement causes concomitant EVI-1 and GATA2 deregulation in
leukemia. Cell. 157:369–381. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lahortiga I, Vázquez I, Agirre X, Larrayoz
MJ, Vizmanos JL, Gozzetti A, Calasanz MJ and Odero MD: Molecular
heterogeneity in AML/MDS patients with 3q21q26 rearrangements.
Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 40:179–189. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Matsuo H, Kajihara M, Tomizawa D, Watanabe
T, Saito AM, Fujimoto J, Horibe K, Kodama K, Tokumasu M, Itoh H, et
al: EVI-1 overexpression is a poor prognostic factor in pediatric
patients with mixed lineage leukemia-AF9 rearranged acute myeloid
leukemia. Haematologica. 99:e225–e227. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Goyama S and Kurokawa M: EVI-1 as a
critical regulator of leukemic cells. Int J Hematol. 91:753–757.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ito Y: Oncogenic potential of the RUNX
gene family: ‘overview’. Oncogene. 23:4198–4208. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
van Wijnen AJ, Stein GS, Gergen JP, Groner
Y, Hiebert SW, Ito Y, Liu P, Neil JC, Ohki M and Speck N:
Nomenclature for Runt-related (RUNX) proteins. Oncogene.
23:4209–4210. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Levanon D and Groner Y: Structure and
regulated expression of mammalian RUNX genes. Oncogene.
23:4211–4219. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Durst KL and Hiebert SW: Role of RUNX
family members in transcriptional repression and gene silencing.
Oncogene. 23:4220–4224. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cameron ER and Neil JC: The Runx genes:
Lineage-specific oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Oncogene.
23:4308–4314. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
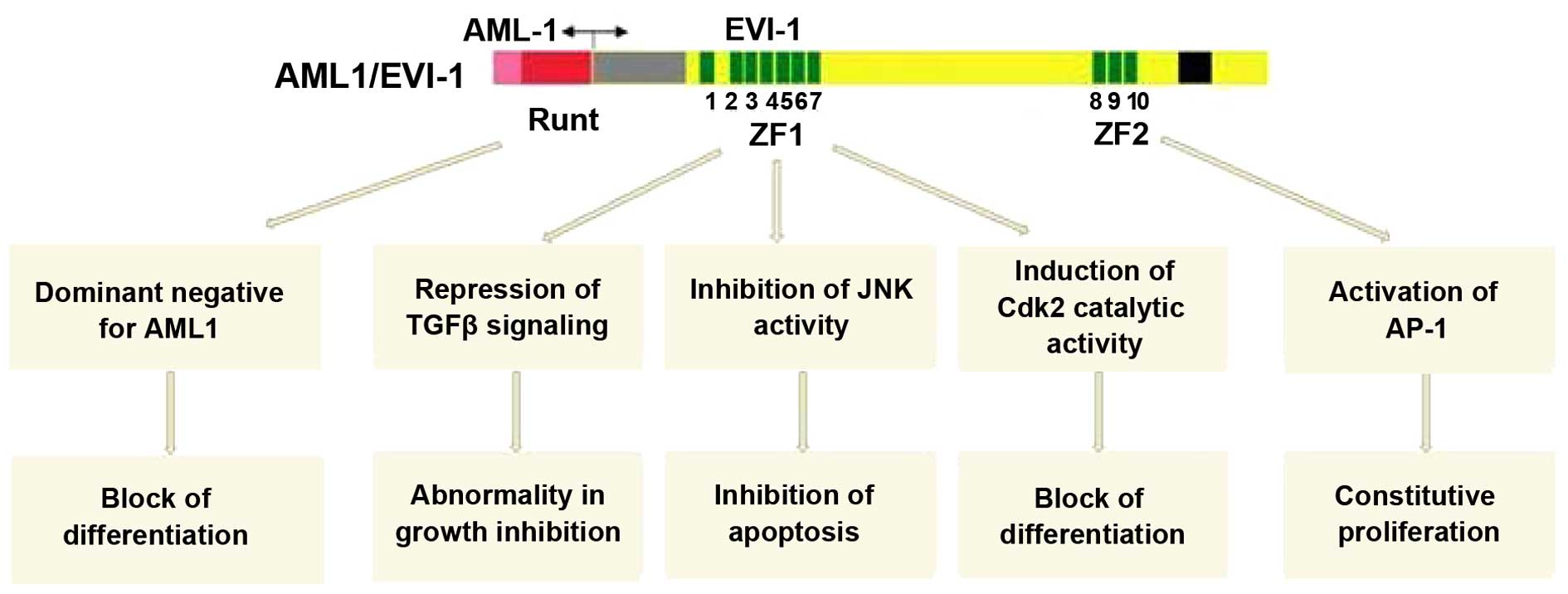
Mitani K: Molecular mechanisms of
leukemogenesis by AML1/ EVI-1. Oncogene. 23:4263–4269. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Palmer S, Brouillet JP, Kilbey A, Fulton
R, Walker M, Crossley M and Bartholomew C: EVI-1 transforming and
repressor activities are mediated by CtBP co-repressor proteins. J
Biol Chem. 276:25834–25840. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Senyuk V, Chakraborty S, Mikhail FM, Zhao
R, Chi Y and Nucifora G: The leukemia-associated transcription
repressor AML1/MDS1/EVI-1 requires CtBP to induce abnormal growth
and differentiation of murine hematopoietic cells. Oncogene.
21:3232–3240. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chinnadurai G: CtBP, an unconventional
transcriptional corepressor in development and oncogenesis. Mol
Cell. 9:213–224. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kahata K, Asaka M and Miyazono K: TGF-beta
signaling and carcinogenesis. Nihon Rinsho. 63(Suppl 4): 549–554.
2005.(In Japanese).
|
|
48
|
Hirai H, Izutsu K, Kurokawa M and Mitani
K: Oncogenic mechanisms of EVI-1 protein. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 48(Suppl 1): S35–S40. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Alliston T, Ko TC, Cao Y, Liang YY, Feng
XH, Chang C and Derynck R: Repression of bone morphogenetic protein
and activin-inducible transcription by EVI-1. J Biol Chem.
280:24227–24237. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Izutsu K, Kurokawa M, Imai Y, Maki K,
Mitani K and Hirai H: The corepressor CtBP interacts with EVI-1 to
repress transforming growth factor β signaling. Blood.
97:2815–2822. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Vinatzer U, Taplick J, Seiser C, Fonatsch
C and Wieser R: The leukaemia-associated transcription factors
EVI-1 and MDS1/ EVI-1 repress transcription and interact with
histone deacetylase. Br J Haematol. 114:566–573. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Liu Y, Chen L, Ko TC, Fields AP and
Thompson EA: EVI-1 is a survival factor which conveys resistance to
both TGFbeta-and taxol-mediated cell death via PI3K/AKT. Oncogene.
25:3565–3575. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kurokawa M, Mitani K, Yamagata T,
Takahashi T, Izutsu K, Ogawa S, Moriguchi T, Nishida E, Yazaki Y
and Hirai H: The EVI-1 oncoprotein inhibits c-Jun N-terminal kinase
and prevents stress-induced cell death. EMBO J. 19:2958–2968. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Tanaka T, Nishida J, Mitani K, Ogawa S,
Yazaki Y and Hirai H: EVI-1 raises AP-1 activity and stimulates
c-fos promoter transactivation with dependence on the second zinc
finger domain. J Biol Chem. 269:24020–24026. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhang Y, Sicot G, Cui X, Vogel M, Wuertzer
CA, Lezon-Geyda K, Wheeler J, Harki DA, Muzikar KA, Stolper DA, et
al: Targeting a DNA binding motif of the EVI-1 protein by a
pyrrole-imidazole polyamide. Biochemistry. 50:10431–10441. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kilbey A, Stephens V and Bartholomew C:
Loss of cell cycle control by deregulation of cyclin-dependent
kinase 2 kinase activity in EVI-1 transformed fibroblasts. Cell
Growth Differ. 10:601–610. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Karakaya K, Herbst F, Ball C, Glimm H,
Krämer A and Löffler H: Overexpression of EVI-1 interferes with
cytokinesis and leads to accumulation of cells with supernumerary
centrosomes in G0/1 phase. Cell Cycle. 11:3492–3503. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Pradhan AK, Mohapatra AD, Nayak KB and
Chakraborty S: Acetylation of the proto-oncogene EVI-1 abrogates
Bcl-xL promoter binding and induces apoptosis. PLoS One.
6:e253702011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Vázquez I, Maicas M, Cervera J, Agirre X,
Marin-Béjar O, Marcotegui N, Vicente C, Lahortiga I, Gomez-Benito
M, Carranza C, et al: Down-regulation of EVI-1 is associated with
epigenetic alterations and good prognosis in patients with acute
myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 96:1448–1456. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
White DJ, Unwin RD, Bindels E, Pierce A,
Teng HY, Muter J, Greystoke B, Somerville TD, Griffiths J, Lovell
S, et al: Phosphorylation of the leukemic oncoprotein EVI-1 on
serine 196 modulates DNA binding, transcriptional repression and
transforming ability. PLoS One. 8:e665102013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Volkert S, Schnittger S, Zenger M, Kern W,
Haferlach T and Haferlach C: Amplification of EVI-1 on
cytogenetically cryptic double minutes as new mechanism for
increased expression of EVI-1. Cancer Genet. 207:103–108. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lugthart S, Figueroa ME, Bindels E,
Skrabanek L, Valk PJ, Li Y, Meyer S, Erpelinck-Verschueren C,
Greally J, Löwenberg B, et al: Aberrant DNA hypermethylation
signature in acute myeloid leukemia directed by EVI-1. Blood.
117:234–241. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
63
|
Yoshimi A and Kurokawa M: EVI-1 forms a
bridge between the epigenetic machinery and signaling pathways.
Oncotarget. 2:575–586. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Maicas M, Vázquez I, Vicente C,
García-Sánchez MA, Marcotegui N, Urquiza L, Calasanz MJ and Odero
MD: Functional characterization of the promoter region of the human
EVI-1 gene in acute myeloid leukemia: RUNX1 and ELK1 directly
regulate its transcription. Oncogene. 32:2069–2078. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Vasyutina E, Boucas JM, Bloehdorn J, Aszyk
C, Crispatzu G, Stiefelhagen M, Breuer A, Mayer P, Lengerke C,
Döhner H, et al: The regulatory interaction of EVI-1 with the TCL1A
oncogene impacts cell survival and clinical outcome in CLL.
Leukemia. 10:10382015.
|
|
66
|
Matsuo H, Goyama S, Kamikubo Y and Adachi
S: The subtype-specific features of EVI-1 and PRDM16 in acute
myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 100:e116–e117. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Takahashi S: Epigenetic aberrations in
myeloid malignancies (Review). Int J Mol Med. 32:532–538.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Jo A, Mitani S, Shiba N, Hayashi Y, Hara
Y, Takahashi H, Tsukimoto I, Tawa A, Horibe K, Tomizawa D, et al:
High expression of EVI-1 and MEL1 is a compelling poor prognostic
marker of pediatric AML. Leukemia. 29:1076–1083. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Lavallée VP, Gendron P, Lemieux S,
D'Angelo G, Hébert J and Sauvageau G: EVI-1-rearranged acute
myeloid leukemias are characterized by distinct molecular
alterations. Blood. 125:140–143. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|