|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Steelman LS, Stadelman KM, Chappell WH,
Horn S, Bäsecke J, Cervello M, Nicoletti F, Libra M, Stivala F,
Martelli AM, et al: Akt as a therapeutic target in cancer. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 12:1139–1165. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bellacosa A, Kumar CC, Di Cristofano A and
Testa JR: Activation of AKT kinases in cancer: Implications for
therapeutic targeting. Adv Cancer Res. 94:29–86. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Arcaro A and Guerreiro AS: The
phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in human cancer: Genetic
alterations and therapeutic implications. Curr Genomics. 8:271–306.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades N and Koutsilieris
M: The Akt pathway: Molecular targets for anti-cancer drug
development. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 4:235–256. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Altomare DA and Testa JR: Perturbations of
the AKT signaling pathway in human cancer. Oncogene. 24:7455–7464.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Song G, Ouyang G and Bao S: The activation
of Akt/PKB signaling pathway and cell survival. J Cell Mol Med.
9:59–71. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Martelli AM, Tabellini G, Bressanin D,
Ognibene A, Goto K, Cocco L and Evangelisti C: The emerging
multiple roles of nuclear Akt. Biochim Biophys Acta - Mol Cell Res.
1823.2168–2178. 2012.
|
|
10
|
Arencibia JM, Pastor-Flores D, Bauer AF,
Schulze JO and Biondi RM: AGC protein kinases: From structural
mechanism of regulation to allosteric drug development for the
treatment of human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1834.1302–1321.
2013.
|
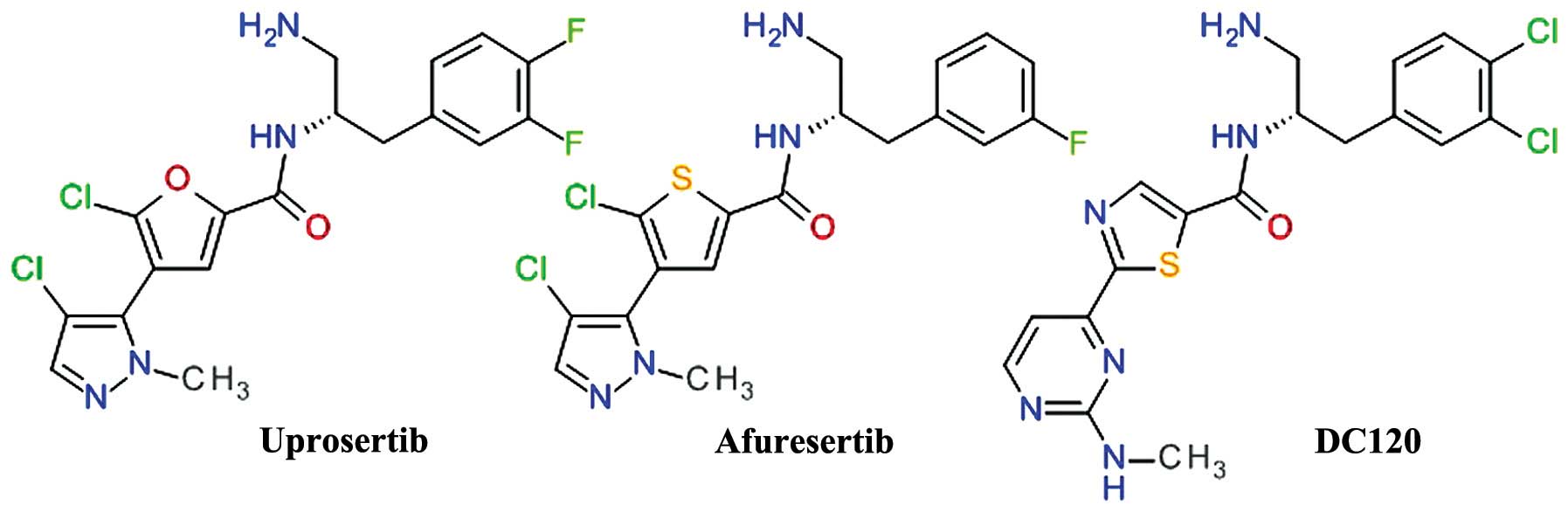
|
11
|
Davis WJ, Lehmann PZ and Li W: Nuclear
PI3K signaling in cell growth and tumorigenesis. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 3:242015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
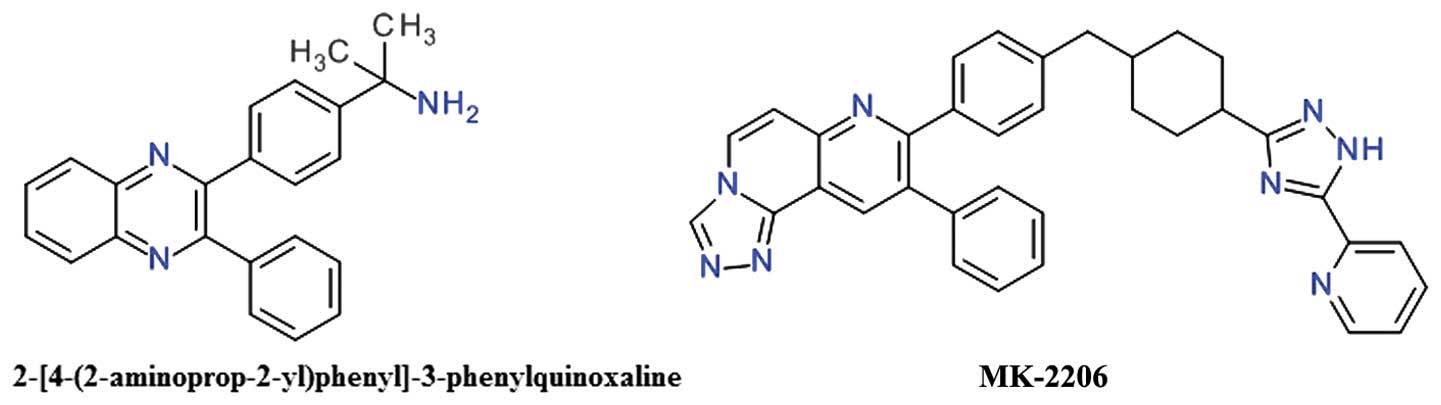
12
|
Sasaki T, Yamashita Y and Kuniyasu H: AKT
plays a crucial role in gastric cancer (Review). Oncol Lett.
10:607–611. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
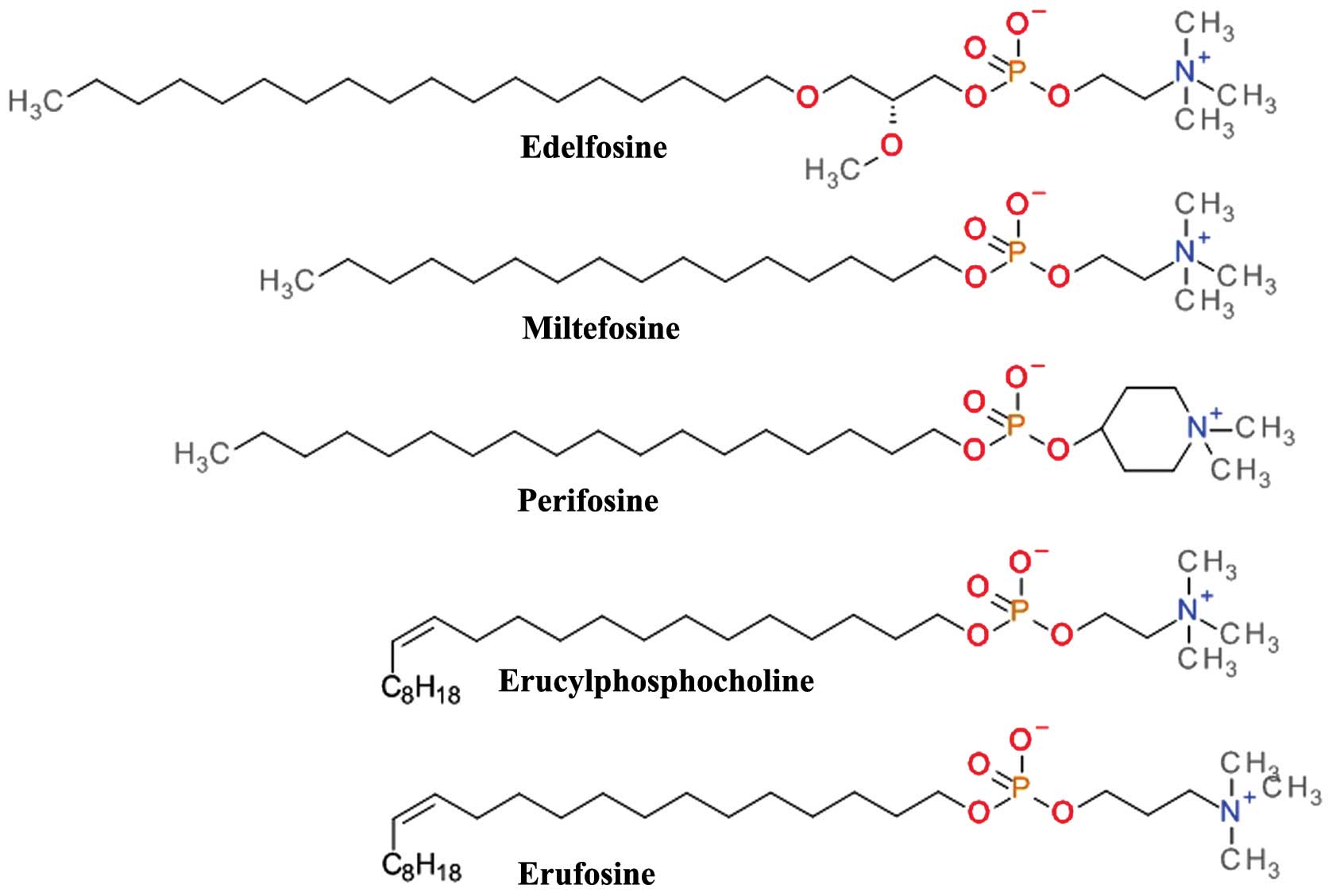
Shayesteh L, Lu Y, Kuo W-L, Baldocchi R,
Godfrey T, Collins C, Pinkel D, Powell B, Mills GB and Gray JW:
PIK3CA is implicated as an oncogene in ovarian cancer. Nat Genet.
21:99–102. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Levine DA, Bogomolniy F, Yee CJ, Lash A,
Barakat RR, Borgen PI and Boyd J: Frequent mutation of the PIK3CA
gene in ovarian and breast cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 11:2875–2878.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Andjelković M, Alessi DR, Meier R,
Fernandez A, Lamb NJ, Frech M, Cron P, Cohen P, Lucocq JM and
Hemmings BA: Role of translocation in the activation and function
of protein kinase B. J Biol Chem. 272:31515–31524. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
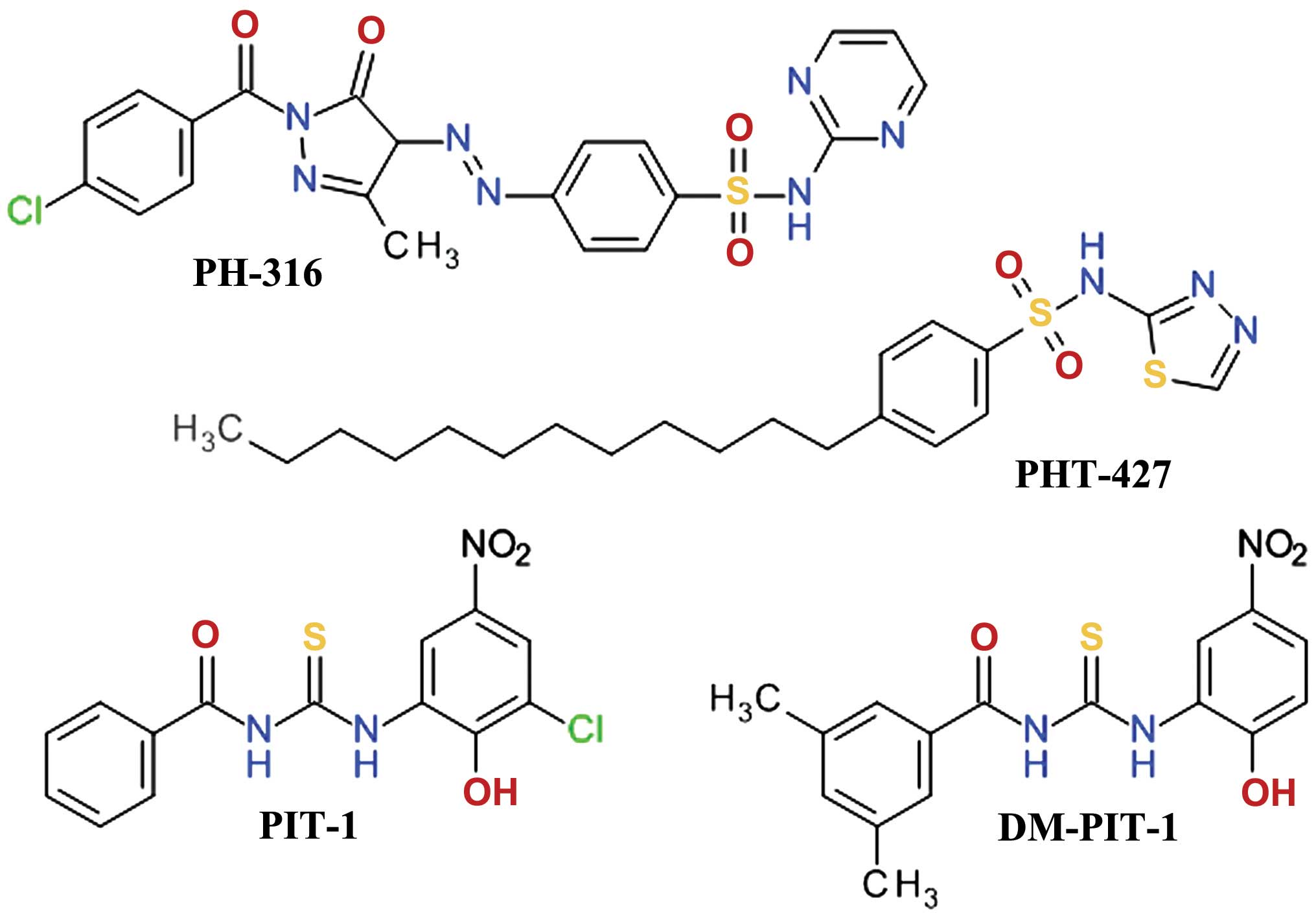
16
|
Carnero A and Paramio JM: The
PTEN/PI3K/AKT Pathway in vivo, Cancer Mouse Models. Front Oncol.
4:2522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Conus NM, Hannan KM, Cristiano BE,
Hemmings BA and Pearson RB: Direct identification of tyrosine 474
as a regulatory phosphorylation site for the Akt protein kinase. J
Biol Chem. 277:38021–38028. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Legate KR, Montañez E, Kudlacek O and
Fässler R: ILK, PINCH and parvin: The tIPP of integrin signalling.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:20–31. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jhaveri K and Modi S: Ganetespib: Research
and clinical development. Onco Targets Ther. 8:1849–1858.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
O‘Neill AK, Niederst MJ and Newton AC:
Suppression of survival signalling pathways by the phosphatase
PHLPP. FEBS J. 280:572–583. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Fresno Vara JA, Casado E, de Castro J,
Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C and González-Barón M: PI3K/Akt signalling
pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 30:193–204. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Altomare DA and Khaled AR: Homeostasis and
the importance for a balance between AKT/mTOR activity and
intracellular signaling. Curr Med Chem. 19:3748–3762. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cohen MM Jr: The AKT genes and their roles
in various disorders. Am J Med Genet A. 161A:2931–2937. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Emamian ES: AKT/GSK3 signaling pathway and
schizophrenia. Front Mol Neurosci. 5:332012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mackenzie RWA and Elliott BT: Akt/PKB
activation and insulin signaling: A novel insulin signaling pathway
in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes.
7:55–64. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Osorio-Fuentealba C and Klip A: Dissecting
signalling by individual Akt/PKB isoforms, three steps at once.
Biochem J. 470:e13–e16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Easton RM, Cho H, Roovers K, Shineman DW,
Mizrahi M, Forman MS, Lee VM, Szabolcs M, de Jong R, Oltersdorf T,
et al: Role for Akt3/protein kinase Bgamma in attainment of normal
brain size. Mol Cell Biol. 25:1869–1878. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
West KA, Castillo SS and Dennis PA:
Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway and chemotherapeutic resistance.
Drug Resist Updat. 5:234–248. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Candido S, Rapisarda V, Marconi A,
Malaponte G, Bevelacqua V, Gangemi P, Scalisi A, McCubrey JA,
Maestro R, Spandidos DA, et al: Analysis of the
B-RafV600E mutation in cutaneous melanoma patients with
occupational sun exposure. Oncol Rep. 31:1079–1082. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shi Y, Liu X, Han EK, Guan R, Shoemaker
AR, Oleksijew A, Woods KW, Fisher JP, Klinghofer V, Lasko L, et al:
Optimal classes of chemotherapeutic agents sensitized by specific
small-molecule inhibitors of akt in vitro and in vivo. Neoplasia.
7:992–1000. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hafsi S, Pezzino FM, Candido S, Ligresti
G, Spandidos DA, Soua Z, McCubrey JA, Travali S and Libra M: Gene
alterations in the PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathway as a mechanism of
drug-resistance (Review). Int J Oncol. 40:639–644. 2012.
|
|
32
|
Carnero A: The PKB/AKT pathway in cancer.
Curr Pharm Des. 16:34–44. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nagata Y, Lan K-H, Zhou X, Tan M, Esteva
FJ, Sahin AA, Klos KS, Li P, Monia BP, Nguyen NT, et al: PTEN
activation contributes to tumor inhibition by trastuzumab, and loss
of PTEN predicts trastuzumab resistance in patients. Cancer Cell.
6:117–127. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fujita T, Doihara H, Washio K, Kawasaki K,
Takabatake D, Takahashi H, Tsukuda K, Ogasawara Y and Shimizu N:
Proteasome inhibitor bortezomib increases PTEN expression and
enhances trastuzumab-induced growth inhibition in
trastuzumab-resistant cells. Anticancer Drugs. 17:455–462. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Olaru OT, Niţulescu GM, Orţan A and
Dinu-Pîrvu CE: Ethnomedicinal, Phytochemical and Pharmacological
Profile of Anthriscus sylvestris as an Alternative Source for
Anticancer Lignans. Molecules. 20:15003–15022. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Peuhu E, Rivero-Müller A, Stykki H,
Torvaldson E, Holmbom T, Eklund P, Unkila M, Sjöholm R and Eriksson
JE: Inhibition of Akt signaling by the lignan matairesinol
sensitizes prostate cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis.
Oncogene. 29:898–908. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Shoji K, Oda K, Nakagawa S, Hosokawa S,
Nagae G, Uehara Y, Sone K, Miyamoto Y, Hiraike H, Hiraike-Wada O,
et al: The oncogenic mutation in the pleckstrin homology domain of
AKT1 in endometrial carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 101:145–148. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rychahou PG, Kang J, Gulhati P, Doan HQ,
Chen LA, Xiao SY, Chung DH and Evers BM: Akt2 overexpression plays
a critical role in the establishment of colorectal cancer
metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:20315–20320. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Graff JR, Konicek BW, McNulty AM, Wang Z,
Houck K, Allen S, Paul JD, Hbaiu A, Goode RG, Sandusky GE, et al:
Increased AKT activity contributes to prostate cancer progression
by dramatically accelerating prostate tumor growth and diminishing
p27Kip1 expression. J Biol Chem. 275:24500–24505. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Altomare DA, Tanno S, De Rienzo A,
Klein-Szanto AJ, Tanno S, Skele KL, Hoffman JP and Testa JR:
Frequent activation of AKT2 kinase in human pancreatic carcinomas.
J Cell Biochem. 87:470–476. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Lin HP, Lin CY, Huo C, Jan YJ, Tseng JC,
Jiang SS, Kuo YY, Chen SC, Wang CT, Chan TM, et al: AKT3 promotes
prostate cancer proliferation cells through regulation of Akt,
B-Raf, and TSC1/TSC2. Oncotarget. 6:27097–27112. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cristiano BE, Chan JC, Hannan KM, Lundie
NA, Marmy-Conus NJ, Campbell IG, Phillips WA, Robbie M, Hannan RD
and Pearson RB: A specific role for AKT3 in the genesis of ovarian
cancer through modulation of G(2)-M phase transition. Cancer Res.
66:11718–11725. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mattmann ME, Stoops SL and Lindsley CW:
Inhibition of Akt with small molecules and biologics: Historical
perspective and current status of the patent landscape. Expert Opin
Ther Pat. 21:1309–1338. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kumar CC and Madison V: AKT crystal
structure and AKT-specific inhibitors. Oncogene. 24:7493–7501.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Böckmann S and Nebe B: The in vitro
effects of H-89, a specific inhibitor of protein kinase A, in the
human colonic carcinoma cell line Caco-2. Eur J Cancer Prev.
12:469–478. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Reuveni H, Livnah N, Geiger T, Klein S,
Ohne O, Cohen I, Benhar M, Gellerman G and Levitzki A: Toward a PKB
inhibitor: Modification of a selective PKA inhibitor by rational
design. Biochemistry. 41:10304–10314. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Breitenlechner CB, Wegge T, Berillon L,
Graul K, Marzenell K, Friebe WG, Thomas U, Schumacher R, Huber R,
Engh RA, et al: Structure-based optimization of novel azepane
derivatives as PKB inhibitors. J Med Chem. 47:1375–1390. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Murray AJ: Pharmacological PKA inhibition:
All may not be what it seems. Sci Signal. 1:re4-re42008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Heerding DA, Rhodes N, Leber JD, Clark TJ,
Keenan RM, Lafrance LV, Li M, Safonov IG, Takata DT, Venslavsky JW,
et al: Identification of
4-(2-(4-amino-1,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl)-1-ethyl-7-{[(3S)-3-piperidinylmethyl]oxy}-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-4-yl)-2-methyl-3-butyn-2-ol
(GSK690693), a novel inhibitor of AKT kinase. J Med Chem.
51:5663–5679. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Levy DS, Kahana JA and Kumar R: AKT
inhibitor, GSK690693, induces growth inhibition and apoptosis in
acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines. Blood. 113:1723–1729.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Carol H, Morton CL, Gorlick R, Kolb EA,
Keir ST, Reynolds CP, Kang MH, Maris JM, Billups C, Smith MA, et
al: Initial testing (stage 1) of the Akt inhibitor GSK690693 by the
pediatric preclinical testing program. Pediatr Blood Cancer.
55:1329–1337. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Crouthamel MC, Kahana JA, Korenchuk S,
Zhang SY, Sundaresan G, Eberwein DJ, Brown KK and Kumar R:
Mechanism and management of AKT inhibitor-induced hyperglycemia.
Clin Cancer Res. 15:217–225. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Donald A, McHardy T, Rowlands MG, Hunter
LJ, Davies TG, Berdini V, Boyle RG, Aherne GW, Garrett MD and
Collins I: Rapid evolution of 6-phenylpurine inhibitors of protein
kinase B through structure-based design. J Med Chem. 50:2289–2292.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Caldwell JJ, Davies TG, Donald A, McHardy
T, Rowlands MG, Aherne GW, Hunter LK, Taylor K, Ruddle R, Raynaud
FI, et al: Identification of
4-(4-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d] pyrimidines as
selective inhibitors of protein kinase B through fragment
elaboration. J Med Chem. 51:2147–2157. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yap TA, Walton MI, Hunter L-JK, Valenti M,
de Haven Brandon A, Eve PD, Ruddle R, Heaton SP, Henley A, Pickard
L, et al: Preclinical pharmacology, antitumor activity, and
development of pharmacodynamic markers for the novel, potent AKT
inhibitor CCT128930. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:360–371. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Freeman-Cook KD, Autry C, Borzillo G,
Gordon D, Barbacci-Tobin E, Bernardo V, Briere D, Clark T, Corbett
M, Jakubczak J, et al: Design of selective, ATP-competitive
inhibitors of Akt. J Med Chem. 53:4615–4622. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Lippa B, Pan G, Corbett M, Li C, Kauffman
GS, Pandit J, Robinson S, Wei L, Kozina E, Marr ES, et al:
Synthesis and structure based optimization of novel Akt inhibitors.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 18:3359–3363. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
McHardy T, Caldwell JJ, Cheung KM, Hunter
LJ, Taylor K, Rowlands M, Ruddle R, Henley A, de Haven Brandon A,
Valenti M, et al: Discovery of 4-amino-1-(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]
pyrimidin-4-yl)piperidine-4-carboxamides as selective, orally
active inhibitors of protein kinase B (Akt). J Med Chem.
53:2239–2249. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Addie M, Ballard P, Buttar D, et al:
Discovery of
4-amino-N-[(1S)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl]-1-(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]
pyrimidin-4-yl)piperidine-4-carboxamide (AZD5363), an orally
bioavailable, potent inhibitor of Akt kinases. J Med Chem.
56:2059–2073. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Crafter C, Vincent JP, Tang E, Dudley P,
James NH, Klinowska T and Davies BR: Combining AZD8931, a novel
EGFR/HER2/HER3 signalling inhibitor, with AZD5363 limits AKT
inhibitor induced feedback and enhances antitumour efficacy in
HER2-amplified breast cancer models. Int J Oncol. 47:446–454.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lamoureux F and Zoubeidi A: Dual
inhibition of autophagy and the AKT pathway in prostate cancer.
Autophagy. 9:1119–1120. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Blake JF, Xu R, Bencsik JR, Xiao D, Kallan
NC, Schlachter S, Mitchell IS, Spencer KL, Banka AL, Wallace EM, et
al: Discovery and preclinical pharmacology of a selective
ATP-competitive Akt inhibitor (GDC-0068) for the treatment of human
tumors. J Med Chem. 55:8110–8127. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Lin J, Sampath D, Nannini MA, Lee BB,
Degtyarev M, Oeh J, Savage H, Guan Z, Hong R, Kassees R, et al:
Targeting activated Akt with GDC-0068, a novel selective Akt
inhibitor that is efficacious in multiple tumor models. Clin Cancer
Res. 19:1760–1772. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Kim S, Tan AR, Im S, Villanueva R, Valero
V, Saura C, Oliveira M, Isakoff SJ, Singel SM and Dent RA: LOTUS: A
randomized, phase II, multicenter, placebo-controlled study of
ipatasertib (Ipat, GDC-0068), an inhibitor of Akt, in combination
with paclitaxel (Pac) as front-line treatment for patients (pts)
with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). ASCO Meet
Abstr. 33:TPS11112015.
|
|
65
|
Luo Y, Shoemaker AR, Liu X, Woods KW,
Thomas SA, de Jong R, Han EK, Li T, Stoll VS, Powlas JA, et al:
Potent and selective inhibitors of Akt kinases slow the progress of
tumors in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:977–986. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Woods KW, Fischer JP, Claiborne A, Li T,
Thomas SA, Zhu GD, Diebold RB, Liu X, Shi Y, Klinghofer V, et al:
Synthesis and SAR of indazole-pyridine based protein kinase B/Akt
inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem. 14:6832–6846. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Lin H, Yamashita DS, Xie R, Zeng J, Wang
W, Leber J, Safonov IG, Verma S, Li M, Lafrance L, et al:
Tetrasubstituted pyridines as potent and selective AKT inhibitors:
Reduced CYP450 and hERG inhibition of aminopyridines. Bioorg Med
Chem Lett. 20:684–688. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Ko JH, Yeon SW, Ryu JS, Kim TY, Song EH,
You HJ, Park RE and Ryu CK: Synthesis and biological evaluation of
5-arylamino-6-chloro-1H-indazole-4,7-diones as inhibitors of
protein kinase B/Akt. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 16:6001–6005. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Bencsik JR, Xiao D, Blake JF, Kallan NC,
Mitchell IS, Spencer KL, Xu R, Gloor SL, Martinson M, Risom T, et
al: Discovery of dihydrothieno- and dihydrofuropyrimidines as
potent pan Akt inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 20:7037–7041.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Saxty G, Woodhead SJ, Berdini V, Davies
TG, Verdonk ML, Wyatt PG, Boyle RG, Barford D, Downham R, Garrett
MD, et al: Identification of inhibitors of protein kinase B using
fragment-based lead discovery. J Med Chem. 50:2293–2296. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Grimshaw KM, Hunter L-JK, Yap TA, Heaton
SP, Walton MI, Woodhead SJ, Fazal L, Reule M, Davies TG, Seavers
LC, et al: AT7867 is a potent and oral inhibitor of AKT and p70 S6
kinase that induces pharmacodynamic changes and inhibits human
tumor xenograft growth. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:1100–1110. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yap TA, Walton MI, Grimshaw KM, Te Poele
RH, Eve PD, Valenti MR, de Haven Brandon AK, Martins V, Zetterlund
A, Heaton SP, et al: AT13148 is a novel, oral multi-AGC kinase
inhibitor with potent pharmacodynamic and antitumor activity. Clin
Cancer Res. 18:3912–3923. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Lin X, Murray JM, Rico AC, Wang MX, Chu
DT, Zhou Y, Del Rosario M, Kaufman S, Ma S, Fang E, et al:
Discovery of 2-pyrimidyl-5-amidothiophenes as potent inhibitors for
AKT: Synthesis and SAR studies. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 16:4163–4168.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Dumble M, Crouthamel MC, Zhang SY, Schaber
M, Levy D, Robell K, Liu Q, Figueroa DJ, Minthorn EA, Seefeld MA,
et al: Discovery of novel AKT inhibitors with enhanced anti-tumor
effects in combination with the MEK inhibitor. PLoS One.
9:e1008802014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Chang S, Zhang Z, Zhuang X, Luo J, Cao X,
Li H, Tu Z, Lu X, Ren X and Ding K: New thiazole carboxamides as
potent inhibitors of Akt kinases. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
22:1208–1212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Deng R, Yang F, Chang SH, Tang J, Qin J,
Feng GK, Ding K and Zhu XF: DC120, a novel and potent inhibitor of
AKT kinase, induces tumor cell apoptosis and suppresses tumor
growth. Mol Pharmacol. 82:189–198. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Spencer A, Yoon SS, Harrison SJ, Morris
SR, Smith DA, Brigandi RA, Gauvin J, Kumar R, Opalinska JB and Chen
C: The novel AKT inhibitor afuresertib shows favorable safety,
pharmacokinetics, and clinical activity in multiple myeloma. Blood.
124:2190–2195. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Faiman B and Richards T: Innovative agents
in multiple myeloma. J Adv Pract Oncol. 5:193–202. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Wu WI, Voegtli WC, Sturgis HL, Dizon FP,
Vigers GPA and Brandhuber BJ: Crystal structure of human AKT1 with
an allosteric inhibitor reveals a new mode of kinase inhibition.
PLoS One. 5:e129132010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Lu S, Li S and Zhang J: Harnessing
allostery: A novel approach to drug discovery. Med Res Rev.
34:1242–1285. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Lindsley CW, Zhao Z, Leister WH, Robinson
RG, Barnett SF, Defeo-Jones D, Jones RE, Hartman GD, Huff JR, Huber
HE, et al: Allosteric Akt (PKB) inhibitors: Discovery and SAR of
isozyme selective inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 15:761–764.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Bilodeau MT, Balitza AE, Hoffman JM,
Manley PJ, Barnett SF, Defeo-Jones D, Haskell K, Jones RE, Leander
K, Robinson RG, et al: Allosteric inhibitors of Akt1 and Akt2: A
naphthyridinone with efficacy in an A2780 tumor xenograft model.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 18:3178–3182. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Li Y, Liang J, Siu T, Hu E, Rossi MA,
Barnett SF, Defeo-Jones D, Jones RE, Robinson RG, Leander K, et al:
Allosteric inhibitors of Akt1 and Akt2: Discovery of
[1,2,4]triazolo[3,4-f][1,6]naphthyridines with potent and balanced
activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 19:834–836. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Hirai H, Sootome H, Nakatsuru Y, Miyama K,
Taguchi S, Tsujioka K, Ueno Y, Hatch H, Majumder PK, Pan BS, et al:
MK-2206, an allosteric Akt inhibitor, enhances antitumor efficacy
by standard chemotherapeutic agents or molecular targeted drugs in
vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:1956–1967. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Fang Z, Simard JR, Plenker D, Nguyen HD,
Phan T, Wolle P, Baumeister S and Rauh D: Discovery of inter-domain
stabilizers-a novel assay system for allosteric akt inhibitors. ACS
Chem Biol. 10:279–288. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Jiao P, Zhou YS, Yang JX, Zhao YL, Liu QQ,
Yuan C and Wang FZ: MK-2206 induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
in HepG2 cells and sensitizes TRAIL-mediated cell death. Mol Cell
Biochem. 382:217–224. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Molife LR, Yan L, Vitfell-Rasmussen J,
Zernhelt AM, Sullivan DM, Cassier PA, Chen E, Biondo A, Tetteh E,
Siu LL, et al: Phase 1 trial of the oral AKT inhibitor MK-2206 plus
carboplatin/paclitaxel, docetaxel, or erlotinib in patients with
advanced solid tumors. J Hematol Oncol. 7:12014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Kümler I, Tuxen MK and Nielsen DL: A
systematic review of dual targeting in HER2-positive breast cancer.
Cancer Treat Rev. 40:259–270. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Konopleva MY, Walter RB, Faderl SH,
Jabbour EJ, Zeng Z, Borthakur G, Huang X, Kadia TM, Ruvolo PP,
Feliu JB, et al: Preclinical and early clinical evaluation of the
oral AKT inhibitor, MK-2206, for the treatment of acute myelogenous
leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 20:2226–2235. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Do K, Speranza G, Bishop R, Khin S,
Rubinstein L, Kinders RJ, Datiles M, Eugeni M, Lam MH, Doyle LA, et
al: Biomarker-driven phase 2 study of MK-2206 and selumetinib
(AZD6244, ARRY-142886) in patients with colorectal cancer. Invest
New Drugs. 33:720–728. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Meuillet EJ: Novel inhibitors of AKT:
Assessment of a different approach targeting the pleckstrin
homology domain. Curr Med Chem. 18:2727–2742. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Gills JJ and Dennis PA: Perifosine: Update
on a novel Akt inhibitor. Curr Oncol Rep. 11:102–110. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
van Blitterswijk WJ and Verheij M:
Anticancer mechanisms and clinical application of
alkylphospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1831.663–674. 2013.
|
|
94
|
van der Luit AH, Vink SR, Klarenbeek JB,
Perrissoud D, Solary E, Verheij M and van Blitterswijk WJ: A new
class of anticancer alkylphospholipids uses lipid rafts as membrane
gateways to induce apoptosis in lymphoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
6:2337–2345. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Reis-Sobreiro M, Roué G, Moros A, Gajate
C, de la Iglesia-Vicente J, Colomer D and Mollinedo F: Lipid
raft-mediated Akt signaling as a therapeutic target in mantle cell
lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 3:e1182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
de Pachioni JA, Magalhães JG, Lima EJC, de
Bueno LM, Barbosa JF, de Sá MM and Rangel-Yagui CO:
Alkylphospholipids - a promising class of chemotherapeutic agents
with a broad pharmacological spectrum. J Pharm Pharm Sci.
16:742–759. 2013.
|
|
97
|
Giantonio BJ, Derry C, McAleer C,
McPhillips JJ and O‘Dwyer PJ: Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of
the cytotoxic ether lipid ilmofosine administered by weekly
two-hour infusion in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin
Cancer Res. 10:1282–1288. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Verweij J, Krzemieniecki K, Kok T, Poveda
A, van Pottelsberghe C, van Glabbeke M and Mouridsen H: Phase II
study of miltefosine (hexadecylphosphocholine) in advanced soft
tissue sarcomas of the adult - an EORTC Soft Tissue and Bone
Sarcoma Group Study. Eur J Cancer. 29A:208–209. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Becher R, Kloke K, Füger A, Bremer K,
Drozd A, Kleeberg UR, Fritze D, Rieche K and Sindermann H: Phase II
Trial of Orally Administered Miltefosine in Advanced Colorectal
Cancer. Onkologie. 16:11–15. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Clive S, Gardiner J and Leonard RCF:
Miltefosine as a topical treatment for cutaneous metastases in
breast carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol Suppl. 44:2000.
|
|
101
|
Dorlo TPC, Balasegaram M, Beijnen JH and
de Vries PJ: Miltefosine: A review of its pharmacology and
therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of leishmaniasis. J
Antimicrob Chemother. 67:2576–2597. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Orlowski RZ: Novel agents for multiple
myeloma to overcome resistance in phase III clinical trials. Semin
Oncol. 40:634–651. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Henke G, Lindner LH, Vogeser M, Eibl HJ,
Wörner J, Müller AC, Bamberg M, Wachholz K, Belka C and Jendrossek
V: Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of Erufosine in nude mice -
implications for combination with radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol.
4:462009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
104
|
Rübel A, Handrick R, Lindner LH, Steiger
M, Eibl H, Budach W, Belka C and Jendrossek V: The membrane
targeted apoptosis modulators erucylphosphocholine and
erucylphosphohomocholine increase the radiation response of human
glioblastoma cell lines in vitro. Radiat Oncol. 1:62006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Kaleağasıoğlu F and Berger MR:
Differential effects of erufosine on proliferation, wound healing
and apoptosis in colorectal cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep.
31:1407–1416. 2014.
|
|
106
|
Rudner J, Ruiner CE, Handrick R, Eibl HJ,
Belka C and Jendrossek V: The Akt-inhibitor Erufosine induces
apoptotic cell death in prostate cancer cells and increases the
short term effects of ionizing radiation. Radiat Oncol. 5:1082010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Chinni SR and Sarkar FH: Akt inactivation
is a key event in indole-3-carbinol-induced apoptosis in PC-3
cells. Clin Cancer Res. 8:1228–1236. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Aggarwal BB and Ichikawa H: Molecular
targets and anticancer potential of indole-3-carbinol and its
derivatives. Cell Cycle. 4:1201–1215. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Kim DJ, Reddy K, Kim MO, Li Y, Nadas J,
Cho YY, Kim JE, Shim JH, Song NR, Carper A, et al:
(3-Chloroacetyl)-indole, a novel allosteric AKT inhibitor,
suppresses colon cancer growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Prev
Res (Phila). 4:1842–1851. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Chao WR, Yean D, Amin K, Green C and Jong
L: Computer-aided rational drug design: A novel agent (SR13668)
designed to mimic the unique anticancer mechanisms of dietary
indole-3-carbinol to block Akt signaling. J Med Chem. 50:3412–3415.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Kapetanovic IM, Muzzio M, Hu S-C, Crowell
JA, Rajewski RA, Haslam JL, Jong L and McCormick DL:
Pharmacokinetics and enhanced bioavailability of candidate cancer
preventative agent, SR13668 in dogs and monkeys. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 65:1109–1116. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Reid JM, Walden CA, Qin R, Ziegler KL,
Haslam JL, Rajewski RA, Warndahl R, Fitting CL, Boring D, Szabo E,
et al; Cancer Prevention Network. Phase 0 clinical chemoprevention
trial of the Akt inhibitor SR13668. Cancer Prev Res (Phila).
4:347–353. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Weng JR, Tsai CH, Omar HA, Sargeant AM,
Wang D, Kulp SK, Shapiro CL and Chen CS: OSU-A9, a potent
indole-3-carbinol derivative, suppresses breast tumor growth by
targeting the Akt-NF-kappaB pathway and stress response signaling.
Carcinogenesis. 30:1702–1709. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Mahadevan D, Powis G, Mash EA, George B,
Gokhale VM, Zhang S, Shakalya K, Du-Cuny L, Berggren M, Ali MA, et
al: Discovery of a novel class of AKT pleckstrin homology domain
inhibitors. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:2621–2632. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Moses SA, Ali MA, Zuohe S, Du-Cuny L, Zhou
LL, Lemos R, Ihle N, Skillman AG, Zhang S, Mash EA, et al: In vitro
and in vivo activity of novel small-molecule inhibitors targeting
the pleckstrin homology domain of protein kinase B/AKT. Cancer Res.
69:5073–5081. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Meuillet EJ, Zuohe S, Lemos R, Ihle N,
Kingston J, Watkins R, Moses SA, Zhang S, Du-Cuny L and Herbst R:
Molecular pharmacology and antitumor activity of PHT-427, a novel
Akt/phosphatidylinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 pleckstrin
homology domain inhibitor. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:706–717. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Miao B, Skidan I, Yang J, Lugovskoy A,
Reibarkh M, Long K, Brazell T, Durugkar KA, Maki J, Ramana CV, et
al: Small molecule inhibition of
phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3) binding to
pleckstrin homology domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:20126–20131. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Kommagalla Y, Cornea S, Riehle R,
Torchilin V, Degterev A and Ramana CV: Optimization of the
anti-cancer activity of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase pathway
inhibitor PITENIN-1: Switching a thiourea with 1,2,3-triazole.
MedChemComm. 5:1359–1363. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Nitulescu GM, Draghici C, Olaru OT, Matei
L, Ioana A, Dragu LD and Bleotu C: Synthesis and apoptotic activity
of new pyrazole derivatives in cancer cell lines. Bioorg Med Chem.
23:5799–5808. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Yang L, Dan HC, Sun M, Liu Q, Sun XM,
Feldman RI, Hamilton AD, Polokoff M, Nicosia SV, Herlyn M, et al:
Akt/protein kinase B signaling inhibitor-2, a selective small
molecule inhibitor of Akt signaling with antitumor activity in
cancer cells overexpressing Akt. Cancer Res. 64:4394–4399. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Sampath D, Malik A, Plunkett W, Nowak B,
Williams B, Burton M, Verstovsek S, Faderl S, Garcia-Manero G, List
AF, et al: Phase I clinical, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic
study of the Akt-inhibitor triciribine phosphate monohydrate in
patients with advanced hematologic malignancies. Leuk Res.
37:1461–1467. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Berndt N, Yang H, Trinczek B, Betzi S,
Zhang Z, Wu B, Lawrence NJ, Pellecchia M, Schönbrunn E, Cheng JQ,
et al: The Akt activation inhibitor TCN-P inhibits Akt
phosphorylation by binding to the PH domain of Akt and blocking its
recruitment to the plasma membrane. Cell Death Differ.
17:1795–1804. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Evangelisti C, Ricci F, Tazzari P,
Chiarini F, Battistelli M, Falcieri E, Ognibene A, Pagliaro P,
Cocco L, McCubrey JA, et al: Preclinical testing of the Akt
inhibitor triciribine in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J
Cell Physiol. 226:822–831. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Dieterle A, Orth R, Daubrawa M, Grotemeier
A, Alers S, Ullrich S, Lammers R, Wesselborg S and Stork B: The Akt
inhibitor triciribine sensitizes prostate carcinoma cells to
TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Int J Cancer. 125:932–941. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Kim R, Yamauchi T, Husain K, Sebti S and
Malafa M: Triciribine Phosphate Monohydrate, an AKT Inhibitor,
Enhances Gemcitabine Activity in Pancreatic Cancer Cells.
Anticancer Res. 35:4599–4604. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Kim D, Sun M, He L, Zhou QH, Chen J, Sun
XM, Bepler G, Sebti SM and Cheng JQ: A small molecule inhibits Akt
through direct binding to Akt and preventing Akt membrane
translocation. J Biol Chem. 285:8383–8394. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
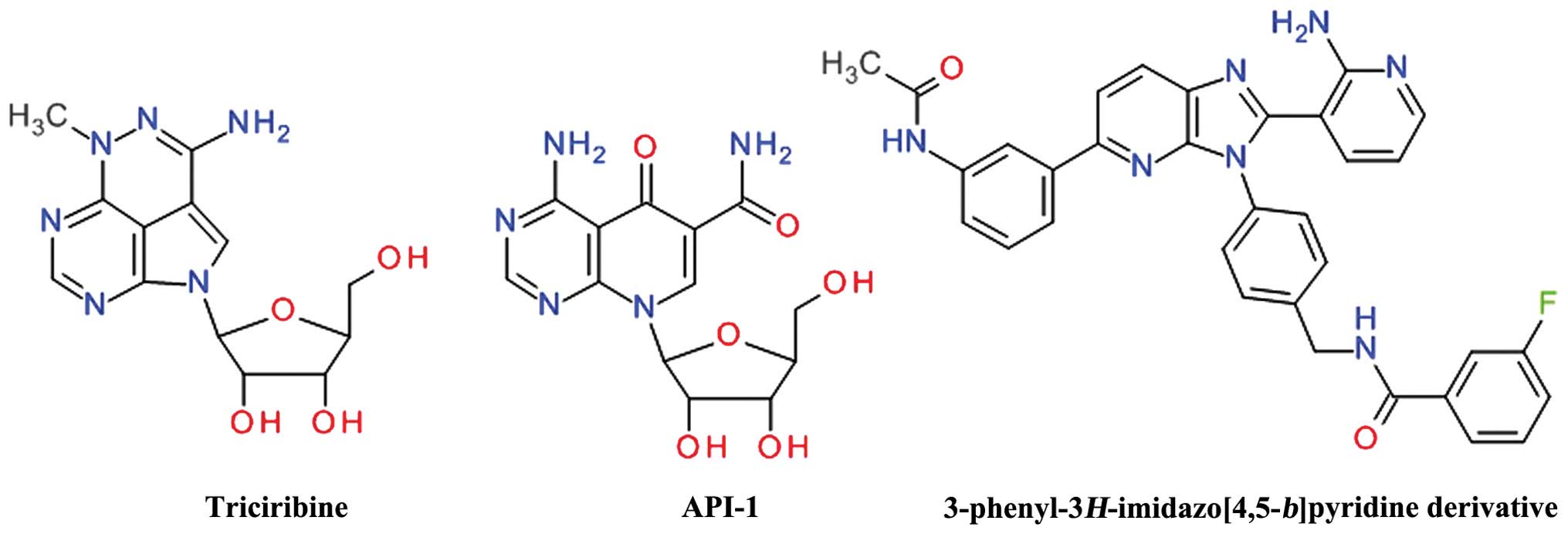
127
|
Li B, Ren H, Yue P, Chen M, Khuri FR and
Sun SY: The novel Akt inhibitor API-1 induces c-FLIP degradation
and synergizes with TRAIL to augment apoptosis independent of Akt
inhibition. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 5:612–620. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Ashwell MA, Lapierre J-M, Brassard C,
Bresciano K, Bull C, Cornell-Kennon S, Eathiraj S, France DS, Hall
T, Hill J, et al: Discovery and optimization of a series of
3-(3-phenyl-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-2-yl)pyridin-2-amines: Orally
bioavailable, selective, and potent ATP-independent Akt inhibitors.
J Med Chem. 55:5291–5310. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Chan TCK, Lapierre JM, Ashwell MA, France
DS, Chen CR, Cornell-Kennon S, Bull C, Eathiraj S, Palma R, Liu Y,
et al: Abstract A230: Discovery and characterization of ARQ 092, an
ATP-independent, potent and selective inhibitor of AKT kinases. Mol
Cancer Ther. 10(Suppl 1): A230. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Yu Y, Savage RE, Eathiraj S, Meade J, Wick
MJ, Hall T, Abbadessa G and Schwartz B: Targeting AKT1-E17K and the
PI3K/AKT pathway with an allosteric AKT inhibitor, ARQ 092. PLoS
One. 10:e01404792015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Politz O, Scholz A, Haegebarth A, Liu N,
Baerfacker L, Ince S, Neuhaus R, Boemer U, Michels M and Mumberg D:
Abstract 3685: BAY 1125976, is a selective allosteric AKT1/2
inhibitor with high efficacy in AKT1-mutated cancers. Cancer Res.
74(Suppl 19): 36852014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Yilmaz OG, Olmez EO and Ulgen KO:
Targeting the Akt1 allosteric site to identify novel scaffolds
through virtual screening. Comput Biol Chem. 48:1–13. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Estrada AC, Syrovets T, Pitterle K, Lunov
O, Büchele B, Schimana-Pfeifer J, Schmidt T, Morad SA and Simmet T:
Tirucallic acids are novel pleckstrin homology domain-dependent Akt
inhibitors inducing apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Mol
Pharmacol. 77:378–387. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Morrow JK, Du-Cuny L, Chen L, Meuillet EJ,
Mash EA, Powis G and Zhang S: Recent development of anticancer
therapeutics targeting Akt. Recent Patents Anticancer Drug Discov.
6:146–159. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
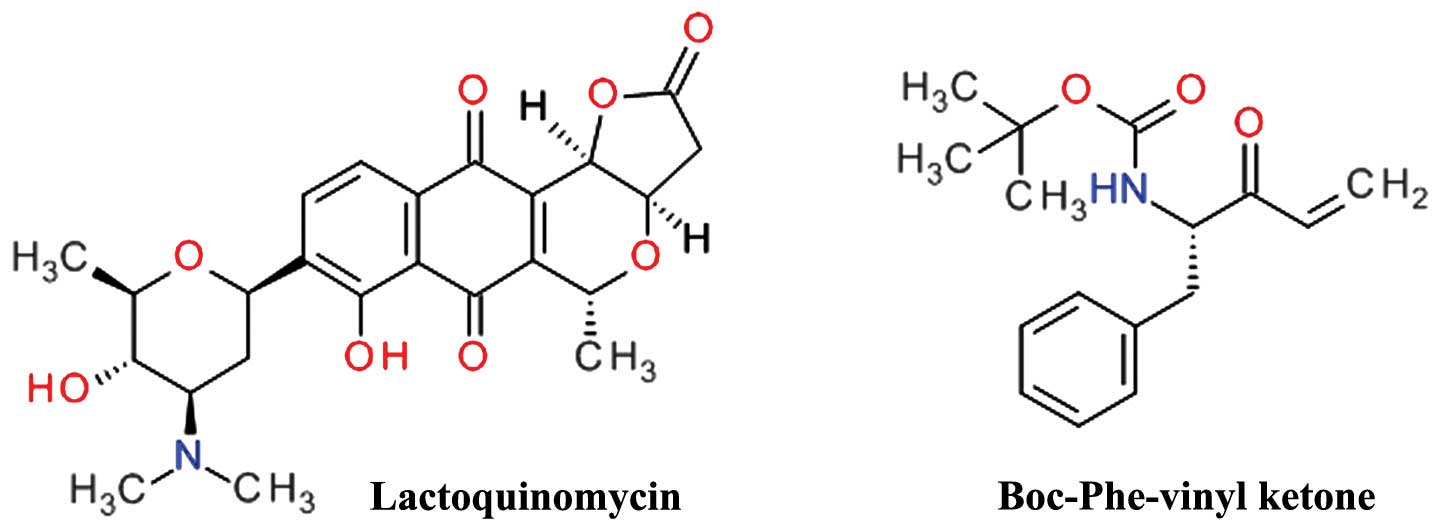
|
135
|
Toral-Barza L, Zhang WG, Huang X, McDonald
LA, Salaski EJ, Barbieri LR, Ding WD, Krishnamurthy G, Hu YB, Lucas
J, et al: Discovery of lactoquinomycin and related
pyranonaphthoquinones as potent and allosteric inhibitors of
AKT/PKB: Mechanistic involvement of AKT catalytic activation loop
cysteines. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:3028–3038. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Salaski EJ, Krishnamurthy G, Ding WD, Yu
K, Insaf SS, Eid C, Shim J, Levin JI, Tabei K, Toral-Barza L, et
al: Pyranonaphthoquinone lactones: A new class of AKT selective
kinase inhibitors alkylate a regulatory loop cysteine. J Med Chem.
52:2181–2184. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Nguyen T, Coover RA, Verghese J, Moran RG
and Ellis KC: Phenylalanine-Based Inactivator of AKT Kinase:
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation. ACS Med Chem Lett.
5:462–467. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Shearn CT, Reigan P and Petersen DR:
Inhibition of hydrogen peroxide signaling by 4-hydroxynonenal due
to differential regulation of Akt1 and Akt2 contributes to
decreases in cell survival and proliferation in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 53:1–11. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Weisner J, Gontla R, van der Westhuizen L,
Oeck S, Ketzer J, Janning P, Richters A, Mühlenberg T, Fang Z,
Taher A, et al: Covalent-allosteric kinase inhibitors. Angew Chem
Int Ed Engl. 54:10313–10316. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
She QB, Chandarlapaty S, Ye Q, Lobo J,
Haskell KM, Leander KR, DeFeo-Jones D, Huber HE and Rosen N: Breast
tumor cells with PI3K mutation or HER2 amplification are
selectively addicted to Akt signaling. PLoS One. 3:e30652008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Sangai T, Akcakanat A, Chen H, Tarco E, Wu
Y, Do KA, Miller TW, Arteaga CL, Mills GB, Gonzalez-Angulo AM and
Meric-Bernstam F: Biomarkers of response to Akt inhibitor MK-2206
in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 18:5816–5828. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Davies BR, Greenwood H, Dudley P, Crafter
C, Yu DH, Zhang J, Li J, Gao B, Ji Q, Maynard J, et al: Preclinical
pharmacology of AZD5363, an inhibitor of AKT: pharmacodynamics,
antitumor activity, and correlation of monotherapy activity with
genetic background. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:873–887. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Yap TA, Yan L, Patnaik A, Fearen I, Olmos
D, Papadopoulos K, Baird RD, Delgado L, Taylor A, Lupinacci L, et
al: First-in-man clinical trial of the oral pan-AKT inhibitor
MK-2206 in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol.
29:4688–4695. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Saura C, Jones S, Mateo J, Hollebecque A,
Cleary JM, Perez DR, Zhu J, Musib LC, Patel PH, Cervantes-Ruiperez
A, et al: A phase Ib study of the Akt inhibitor GDC-0068 with
docetaxel (D) or mFOLFOX-6 (F) in patients (pts) with advanced
solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 30:Suppl; abstr 3021. 2012.
|
|
145
|
Yan Y, Wagle M, Punnoose E, Musib L, Budha
N, Nannini M, Lin K, Liederer BM, Murli S, Ramakrishnan V, et al: A
first-inhuman trial of GDC-0068: A novel, oral, ATP-competitive Akt
inhibitor, demonstrates robust suppression of the Akt pathway in
surrogate and tumor tissues. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:abstr B154. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Banerji U, Ranson M, Schellens J,
Schellens JH, Esaki T, Dean EJ and Zivi A: Results of two phase I
multicenter trials of AZD5363, an inhibitor of AKT1, 2 and 3:
Biomarker and early clinical evaluation in Western and Japanese
patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Res. 73:abstr LB-66.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Dienstmann R, Rodon J, Serra V and
Tabernero J: Picking the point of inhibition: A comparative review
of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibitors. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:1021–1031.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|