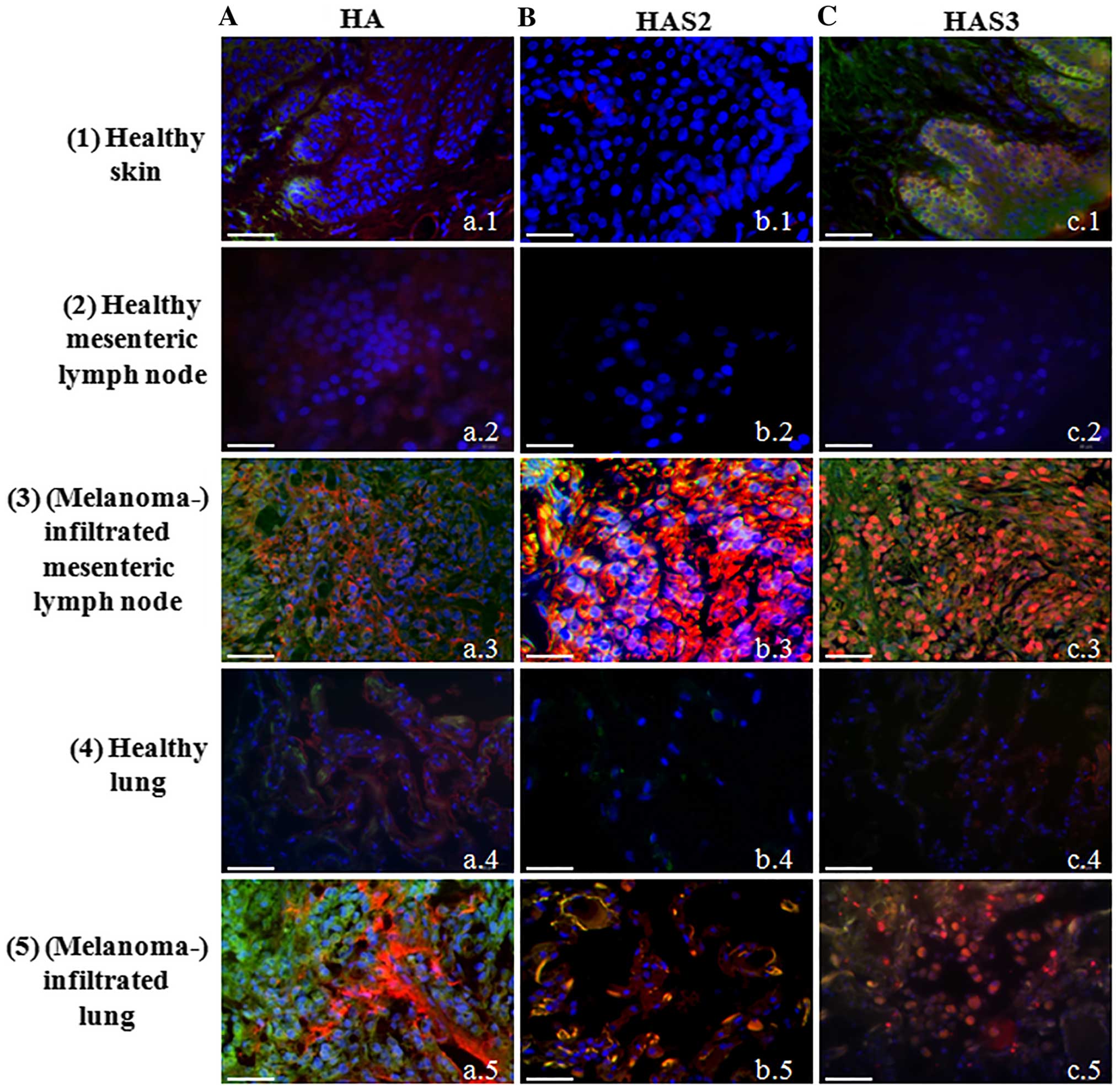
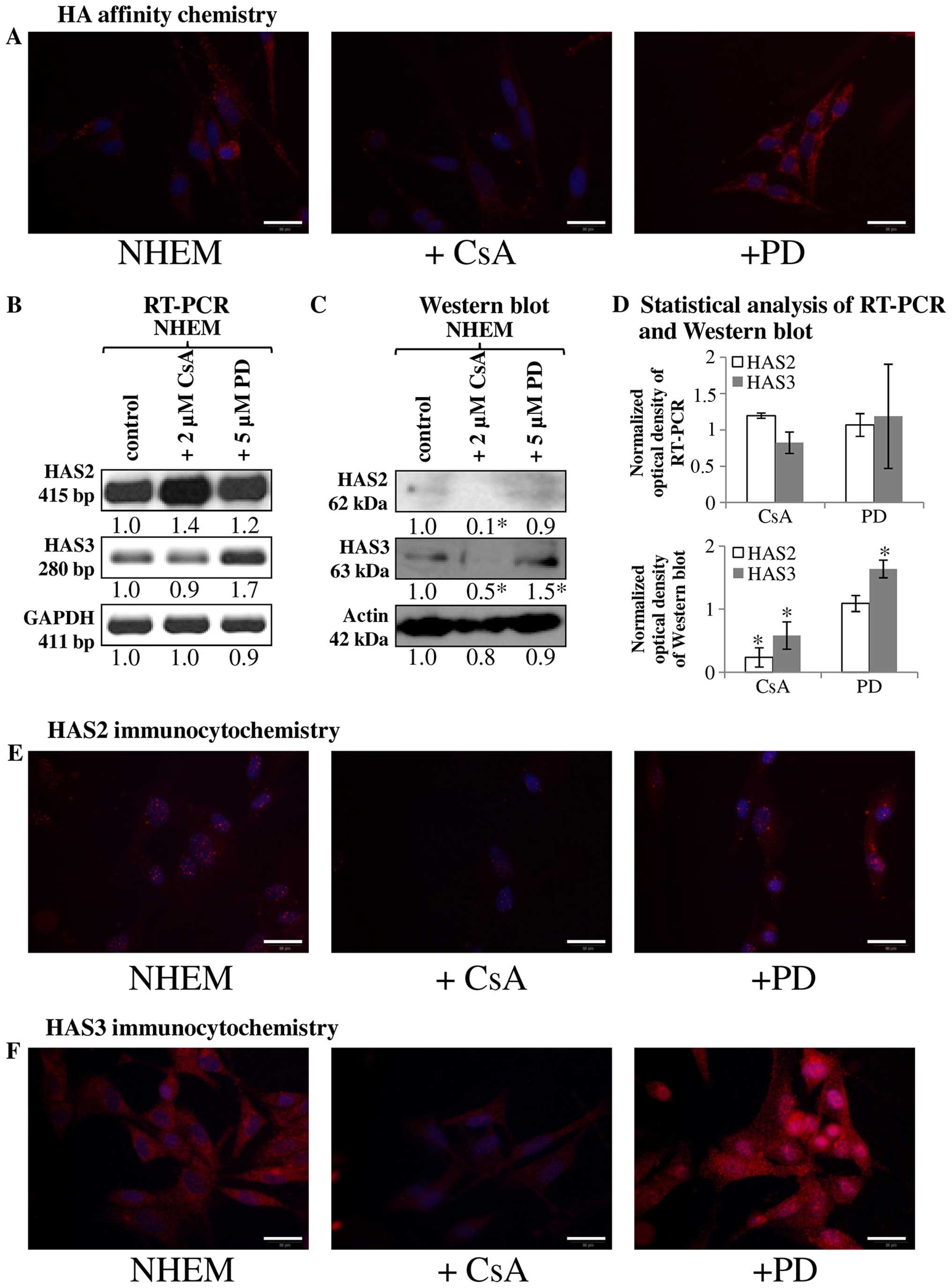
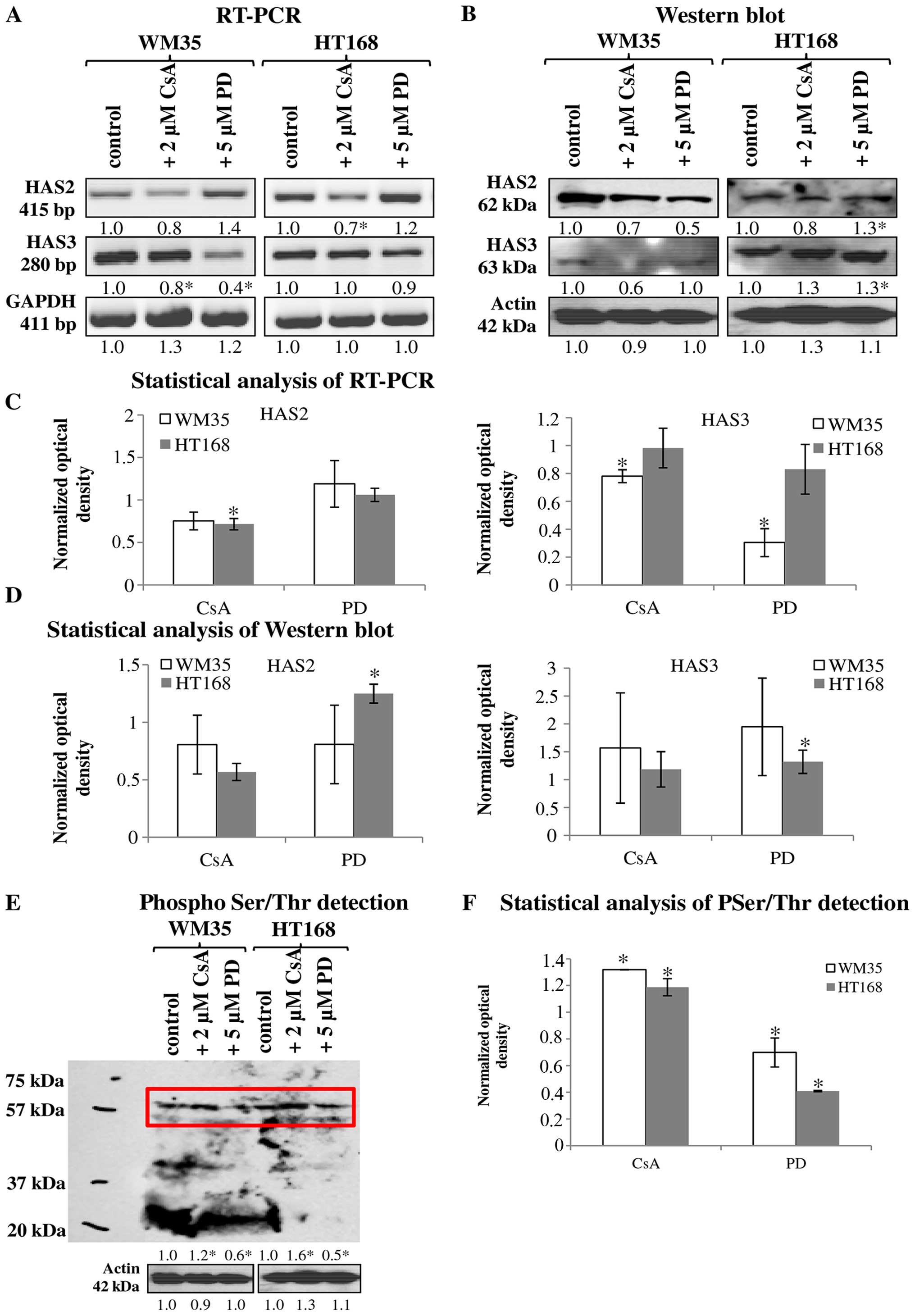
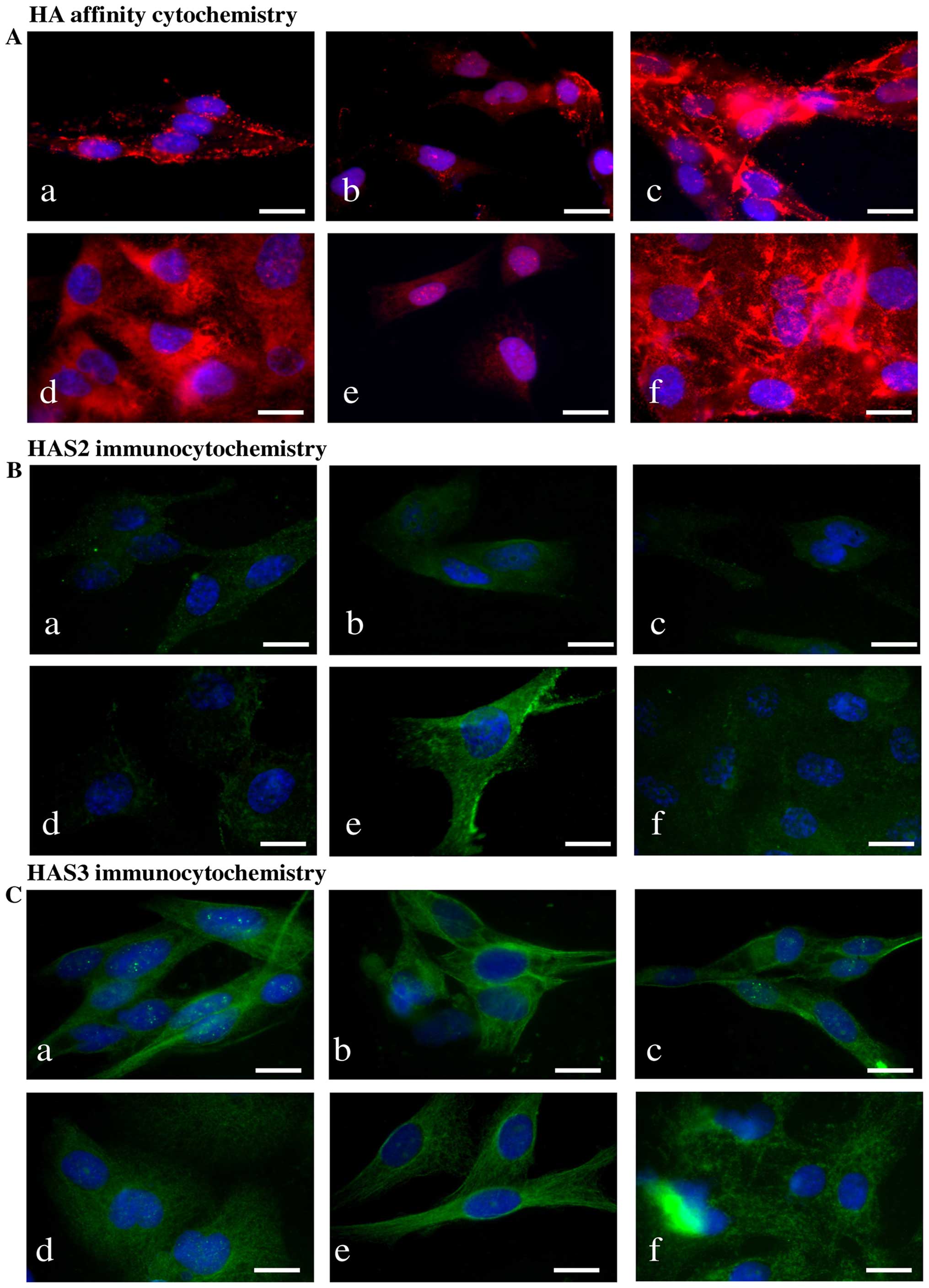
|
1
|
Tsao H, Chin L, Garraway LA and Fisher DE:
Melanoma: From mutations to medicine. Genes Dev. 26:1131–1155.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mandalà M, Merelli B and Massi D: Nras in
melanoma: Targeting the undruggable target. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
92:107–122. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Marshall JF, Nesbitt SA, Helfrich MH,
Horton MA, Polakova K and Hart IR: Integrin expression in human
melanoma cell lines: Heterogeneity of vitronectin receptor
composition and function. Int J Cancer. 49:924–931. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pocheć E, Janik M, Hoja-Łukowicz D,
Link-Lenczowski P, Przybyło M and Lityńska A: Expression of
integrins α3β1 and α5β1 and GlcNAc β1,6 glycan branching influences
metastatic melanoma cell migration on fibronectin. Eur J Cell Biol.
92:355–362. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ahrens T, Assmann V, Fieber C, Termeer C,
Herrlich P, Hofmann M and Simon JC: CD44 is the principal mediator
of hyaluronic-acid-induced melanoma cell proliferation. J Invest
Dermatol. 116:93–101. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Itano N, Atsumi F, Sawai T, Yamada Y,
Miyaishi O, Senga T, Hamaguchi M and Kimata K: Abnormal
accumulation of hyaluronan matrix diminishes contact inhibition of
cell growth and promotes cell migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:3609–3614. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Prehm P: Hyaluronate is synthesized at
plasma membranes. Biochem J. 220:597–600. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brinck J and Heldin P: Expression of
recombinant hyaluronan synthase (HAS) isoforms in CHO cells reduces
cell migration and cell surface CD44. Exp Cell Res. 252:342–351.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Itano N, Sawai T, Yoshida M, Lenas P,
Yamada Y, Imagawa M, Shinomura T, Hamaguchi M, Yoshida Y, Ohnuki Y,
et al: Three isoforms of mammalian hyaluronan synthases have
distinct enzymatic properties. J Biol Chem. 274:25085–25092. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Weigel PH, Hascall VC and Tammi M:
Hyaluronan synthases. J Biol Chem. 272:13997–14000. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Goentzel BJ, Weigel PH and Steinberg RA:
Recombinant human hyaluronan synthase 3 is phosphorylated in
mammalian cells. Biochem J. 396:347–354. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kuroda Y, Kasai K, Nanashima N, Nozaka H,
Nakano M, Chiba M, Yoneda M and Nakamura T: 4-Methylumbelliferone
inhibits the phosphorylation of hyaluronan synthase 2 induced by
12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate. Biomed Res. 34:97–103. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sironen RK, Tammi M, Tammi R, Auvinen PK,
Anttila M and Kosma VM: Hyaluronan in human malignancies. Exp Cell
Res. 317:383–391. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Turley EA, Noble PW and Bourguignon LY:
Signaling properties of hyaluronan receptors. J Biol Chem.
277:4589–4592. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Maxwell CA, McCarthy J and Turley E:
Cell-surface and mitotic-spindle RHAMM: Moonlighting or dual
oncogenic functions? J Cell Sci. 121:925–932. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Telmer PG, Tolg C, McCarthy JB and Turley
EA: How does a protein with dual mitotic spindle and extracellular
matrix receptor functions affect tumor susceptibility and
progression? Commun Integr Biol. 4:182–185. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qiu L, Li Z, Qiao M, Long M, Wang M, Zhang
X, Tian C and Chen D: Self-assembled pH-responsive hyaluronic
acid-g-poly((L)-histidine) copolymer micelles for targeted
intracellular delivery of doxorubicin. Acta Biomater. 10:2024–2035.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Adamia S, Pilarski PM, Belch AR and
Pilarski LM: Aberrant splicing, hyaluronan synthases and
intracellular hyaluronan as drivers of oncogenesis and potential
drug targets. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 13:347–361. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee JY and Spicer AP: Hyaluronan: A
multifunctional, mega-Dalton, stealth molecule. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 12:581–586. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Voelcker V, Gebhardt C, Averbeck M,
Saalbach A, Wolf V, Weih F, Sleeman J, Anderegg U and Simon J:
Hyaluronan fragments induce cytokine and metalloprotease
upregulation in human melanoma cells in part by signalling via
TLR4. Exp Dermatol. 17:100–107. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hatano H, Shigeishi H, Kudo Y, Higashikawa
K, Tobiume K, Takata T and Kamata N: RHAMM/ERK interaction induces
proliferative activities of cementifying fibroma cells through a
mechanism based on the CD44-EGFR. Lab Invest. 91:379–391. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Soares AS, Costa VM, Diniz C and Fresco P:
Inosine strongly enhances proliferation of human C32 melanoma cells
through PLC-PKC-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 and PI3K pathways. Basic Clin
Pharmacol Toxicol. 116:25–36. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Haydn JM, Hufnagel A, Grimm J, Maurus K,
Schartl M and Meierjohann S: The MAPK pathway as an apoptosis
enhancer in melanoma. Oncotarget. 5:5040–5053. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rusnak F and Mertz P: Calcineurin: Form
and function. Physiol Rev. 80:1483–1521. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dotto GP: Calcineurin signaling as a
negative determinant of keratinocyte cancer stem cell potential and
carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 71:2029–2033. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Smit NP, Van Rossum HH, Romijn FP, Sellar
KJ, Breetveld M, Gibbs S and Van Pelt J: Calcineurin activity and
inhibition in skin and (epi)dermal cell cultures. J Invest
Dermatol. 128:1686–1690. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Breuer K, Werfel T and Kapp A: Allergic
manifestations of skin diseases--atopic dermatitis. Chem Immunol
Allergy. 91:76–86. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Juhász T, Matta C, Veress G, Nagy G,
Szíjgyártó Z, Molnár Z, Fodor J, Zákány R and Gergely P: Inhibition
of calcineurin by cyclosporine A exerts multiple effects on human
melanoma cell lines HT168 and WM35. Int J Oncol. 34:995–1003.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ladányi A, Tímár J, Paku S, Molnár G and
Lapis K: Selection and characterization of human melanoma lines
with different liver-colonizing capacity. Int J Cancer. 46:456–461.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Herlyn M: Human melanoma: Development and
progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 9:101–112. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tammi R, Pasonen-Seppänen S, Kolehmainen E
and Tammi M: Hyaluronan synthase induction and hyaluronan
accumulation in mouse epidermis following skin injury. J Invest
Dermatol. 124:898–905. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sugiyama Y, Shimada A, Sayo T, Sakai S and
Inoue S: Putative hyaluronan synthase mRNA are expressed in mouse
skin and TGF-beta upregulates their expression in cultured human
skin cells. J Invest Dermatol. 110:116–121. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tammi R, Ripellino JA, Margolis RU and
Tammi M: Localization of epidermal hyaluronic acid using the
hyaluronate binding region of cartilage proteoglycan as a specific
probe. J Invest Dermatol. 90:412–414. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schmaus A, Klusmeier S, Rothley M, Dimmler
A, Sipos B, Faller G, Thiele W, Allgayer H, Hohenberger P, Post S,
et al: Accumulation of small hyaluronan oligosaccharides in tumour
interstitial fluid correlates with lymphatic invasion and lymph
node metastasis. Br J Cancer. 111:559–567. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Raso-Barnett L, Banky B, Barbai T, Becsagh
P, Timar J and Raso E: Demonstration of a melanoma-specific CD44
alternative splicing pattern that remains qualitatively stable, but
shows quantitative changes during tumour progression. PLoS One.
8:e538832013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Malaisse J, Bourguignon V, De Vuyst E,
Lambert de Rouvroit C, Nikkels AF, Flamion B and Poumay Y:
Hyaluronan metabolism in human keratinocytes and atopic dermatitis
skin is driven by a balance of hyaluronan synthases 1 and 3. J
Invest Dermatol. 134:2174–2182. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Siiskonen H, Poukka M, Tyynelä-Korhonen K,
Sironen R and Pasonen-Seppänen S: Inverse expression of
hyaluronidase 2 and hyaluronan synthases 1-3 is associated with
reduced hyaluronan content in malignant cutaneous melanoma. BMC
Cancer. 13:1812013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Karvinen S, Pasonen-Seppänen S, Hyttinen
JM, Pienimäki JP, Törrönen K, Jokela TA, Tammi MI and Tammi R:
Keratinocyte growth factor stimulates migration and hyaluronan
synthesis in the epidermis by activation of keratinocyte hyaluronan
synthases 2 and 3. J Biol Chem. 278:49495–49504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ichikawa T, Itano N, Sawai T, Kimata K,
Koganehira Y, Saida T and Taniguchi S: Increased synthesis of
hyaluronate enhances motility of human melanoma cells. J Invest
Dermatol. 113:935–939. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rilla K, Oikari S, Jokela TA, Hyttinen JM,
Kärnä R, Tammi RH and Tammi MI: Hyaluronan synthase 1 (HAS1)
requires higher cellular UDP-GlcNAc concentration than HAS2 and
HAS3. J Biol Chem. 288:5973–5983. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Auvinen P, Rilla K, Tumelius R, Tammi M,
Sironen R, Soini Y, Kosma VM, Mannermaa A, Viikari J and Tammi R:
Hyaluronan synthases (HAS1-3) in stromal and malignant cells
correlate with breast cancer grade and predict patient survival.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 143:277–286. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Edward M, Quinn JA, Pasonen-Seppänen SM,
McCann BA and Tammi RH: 4-Methylumbelliferone inhibits tumour cell
growth and the activation of stromal hyaluronan synthesis by
melanoma cell-derived factors. Br J Dermatol. 162:1224–1232. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu N, Gao F, Han Z, Xu X, Underhill CB
and Zhang L: Hyaluronan synthase 3 overexpression promotes the
growth of TSU prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 61:5207–5214.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Savani RC, Cao G, Pooler PM, Zaman A, Zhou
Z and DeLisser HM: Differential involvement of the hyaluronan (HA)
receptors CD44 and receptor for HA-mediated motility in endothelial
cell function and angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 276:36770–36778. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Thomas L, Byers HR, Vink J and Stamenkovic
I: CD44H regulates tumor cell migration on hyaluronate-coated
substrate. J Cell Biol. 118:971–977. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Turley EA, Austen L, Vandeligt K and Clary
C: Hyaluronan and a cell-associated hyaluronan binding protein
regulate the locomotion of ras-transformed cells. J Cell Biol.
112:1041–1047. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Du YC, Chou CK, Klimstra DS and Varmus H:
Receptor for hyaluronan-mediated motility isoform B promotes liver
metastasis in a mouse model of multistep tumorigenesis and a tail
vein assay for metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:16753–16758.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hall CL, Lange LA, Prober DA, Zhang S and
Turley EA: pp60(c-src) is required for cell locomotion regulated by
the hyaluronanreceptor RHAMM. Oncogene. 13:2213–2224.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kouvidi K, Berdiaki A, Nikitovic D,
Katonis P, Afratis N, Hascall VC, Karamanos NK and Tzanakakis GN:
Role of receptor for hyaluronic acid-mediated motility (RHAMM) in
low molecular weight hyaluronan (LMWHA)-mediated fibrosarcoma cell
adhesion. J Biol Chem. 286:38509–38520. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Park D, Kim Y, Kim H, Kim K, Lee YS, Choe
J, Hahn JH, Lee H, Jeon J, Choi C, et al: Hyaluronic acid promotes
angiogenesis by inducing RHAMM-TGFβ receptor interaction via
CD44-PKCδ. Mol Cells. 33:563–574. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang S, Chang MC, Zylka D, Turley S,
Harrison R and Turley EA: The hyaluronan receptor RHAMM regulates
extra-cellular-regulated kinase. J Biol Chem. 273:11342–11348.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hanagiri T, Shinohara S, Takenaka M,
Shigematsu Y, Yasuda M, Shimokawa H, Nagata Y, Nakagawa M, Uramoto
H, So T, et al: Effects of hyaluronic acid and CD44 interaction on
the proliferation and invasiveness of malignant pleural
mesothelioma. Tumour Biol. 33:2135–2141. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ohta S, Yoshida J, Iwata H and Hamaguchi
M: Hyaluronate activates tyrosine phosphorylation of cellular
proteins including focal adhesion kinase via CD44 in human glioma
cells. Int J Oncol. 10:561–564. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Okamoto I, Kawano Y, Murakami D, Sasayama
T, Araki N, Miki T, Wong AJ and Saya H: Proteolytic release of CD44
intracellular domain and its role in the CD44 signaling pathway. J
Cell Biol. 155:755–762. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Fecher LA, Amaravadi RK and Flaherty KT:
The MAPK pathway in melanoma. Curr Opin Oncol. 20:183–189. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kohno M, Tanimura S and Ozaki K: Targeting
the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway in cancer
therapy. Biol Pharm Bull. 34:1781–1784. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Vigetti D, Viola M, Karousou E, De Luca G
and Passi A: Metabolic control of hyaluronan synthases. Matrix
Biol. 35:8–13. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Li L, Asteriou T, Bernert B, Heldin CH and
Heldin P: Growth factor regulation of hyaluronan synthesis and
degradation in human dermal fibroblasts: Importance of hyaluronan
for the mitogenic response of PDGF-BB. Biochem J. 404:327–336.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
David-Raoudi M, Deschrevel B, Leclercq S,
Galéra P, Boumediene K and Pujol JP: Chondroitin sulfate increases
hyaluronan production by human synoviocytes through differential
regulation of hyaluronan synthases: Role of p38 and Akt. Arthritis
Rheum. 60:760–770. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Törrönen K, Nikunen K, Kärnä R, Tammi M,
Tammi R and Rilla K: Tissue distribution and subcellular
localization of hyaluronan synthase isoenzymes. Histochem Cell
Biol. 141:17–31. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Vigetti D, Clerici M, Deleonibus S,
Karousou E, Viola M, Moretto P, Heldin P, Hascall VC, De Luca G and
Passi A: Hyaluronan synthesis is inhibited by adenosine
monophosphate-activated protein kinase through the regulation of
HAS2 activity in human aortic smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem.
286:7917–7924. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Bourguignon LY, Gilad E and Peyrollier K:
Heregulin-mediated ErbB2-ERK signaling activates hyaluronan
synthases leading to CD44-dependent ovarian tumor cell growth and
migration. J Biol Chem. 282:19426–19441. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Herbold KW, Zhou J, Haggerty JG and
Milstone LM: CD44 expression on epidermal melanocytes. J Invest
Dermatol. 106:1230–1235. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Tolg C, Hamilton SR, Morningstar L, Zhang
J, Zhang S, Esguerra KV, Telmer PG, Luyt LG, Harrison R, McCarthy
JB, et al: RHAMM promotes interphase microtubule instability and
mitotic spindle integrity through MEK1/ERK1/2 activity. J Biol
Chem. 285:26461–26474. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Tofuku K, Yokouchi M, Murayama T, Minami S
and Komiya S: HAS3-related hyaluronan enhances biological
activities necessary for metastasis of osteosarcoma cells. Int J
Oncol. 29:175–183. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|