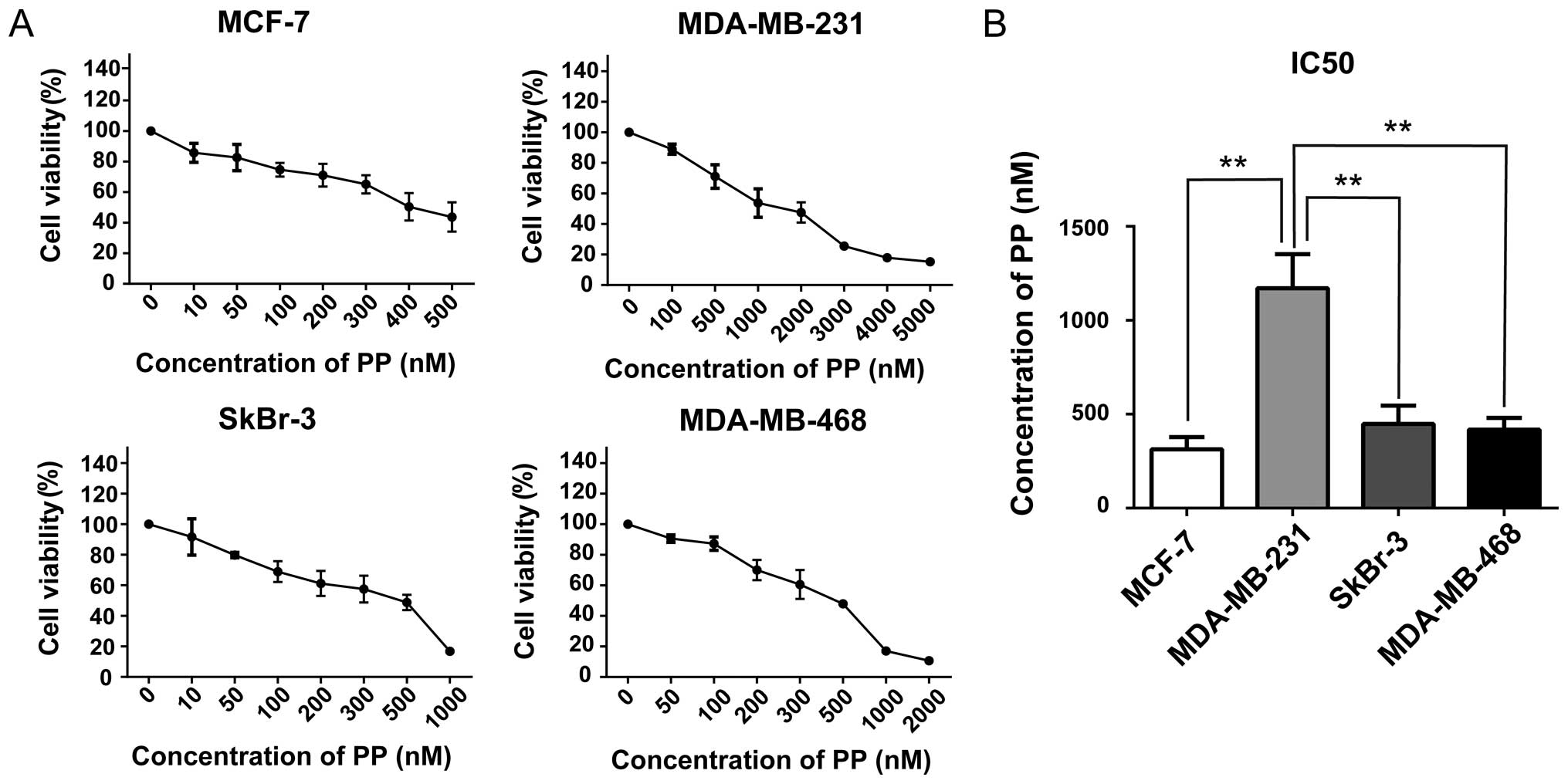
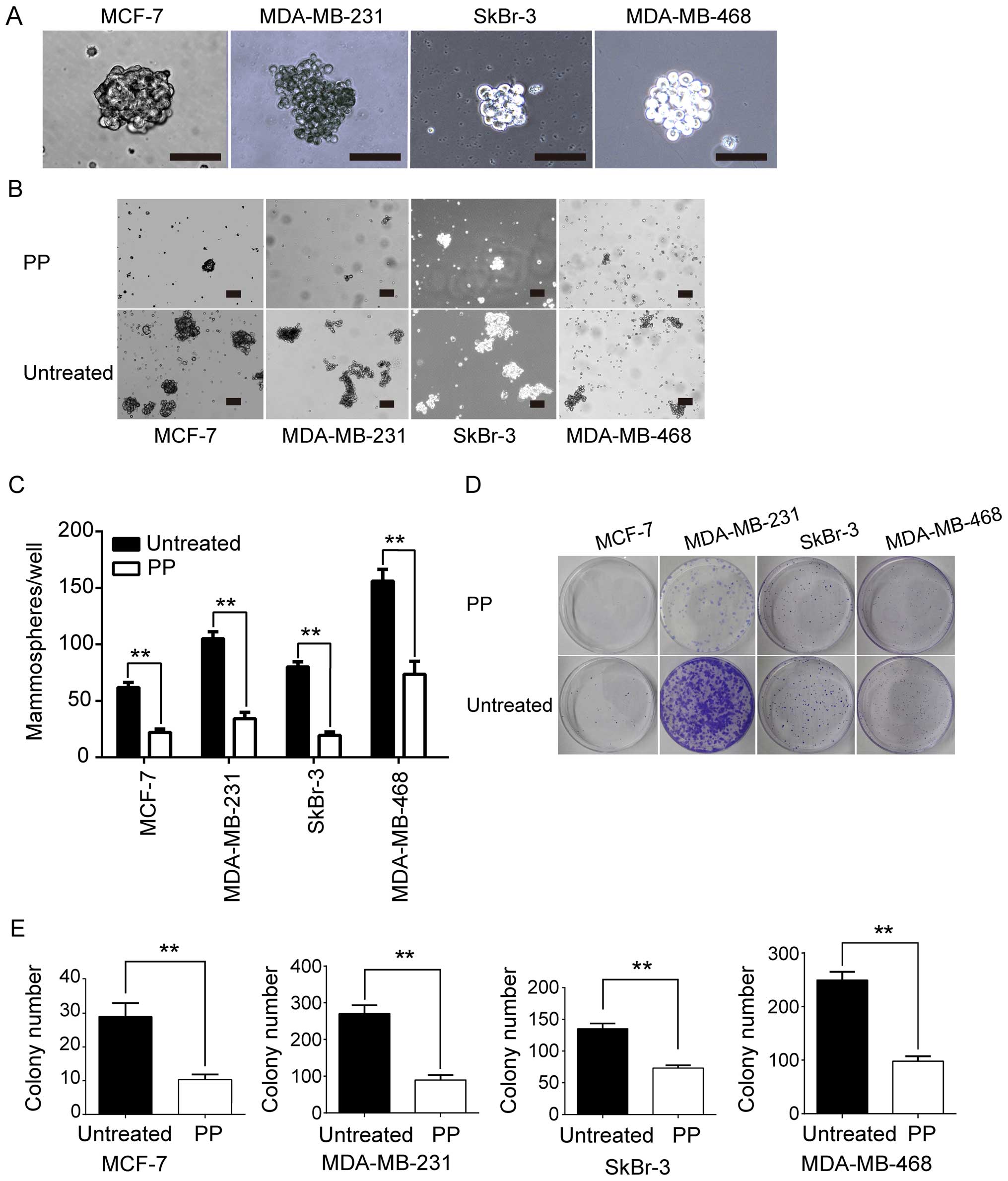
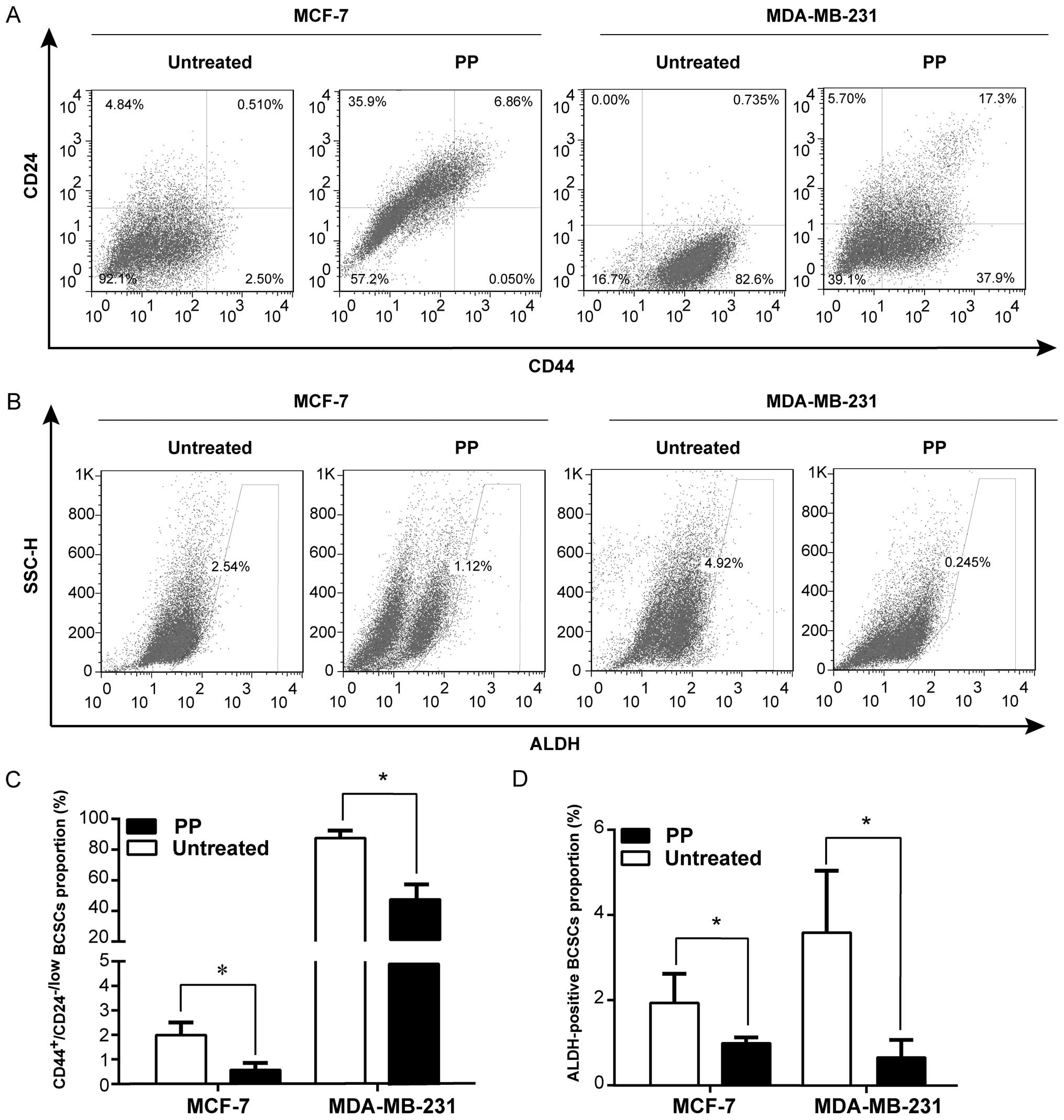
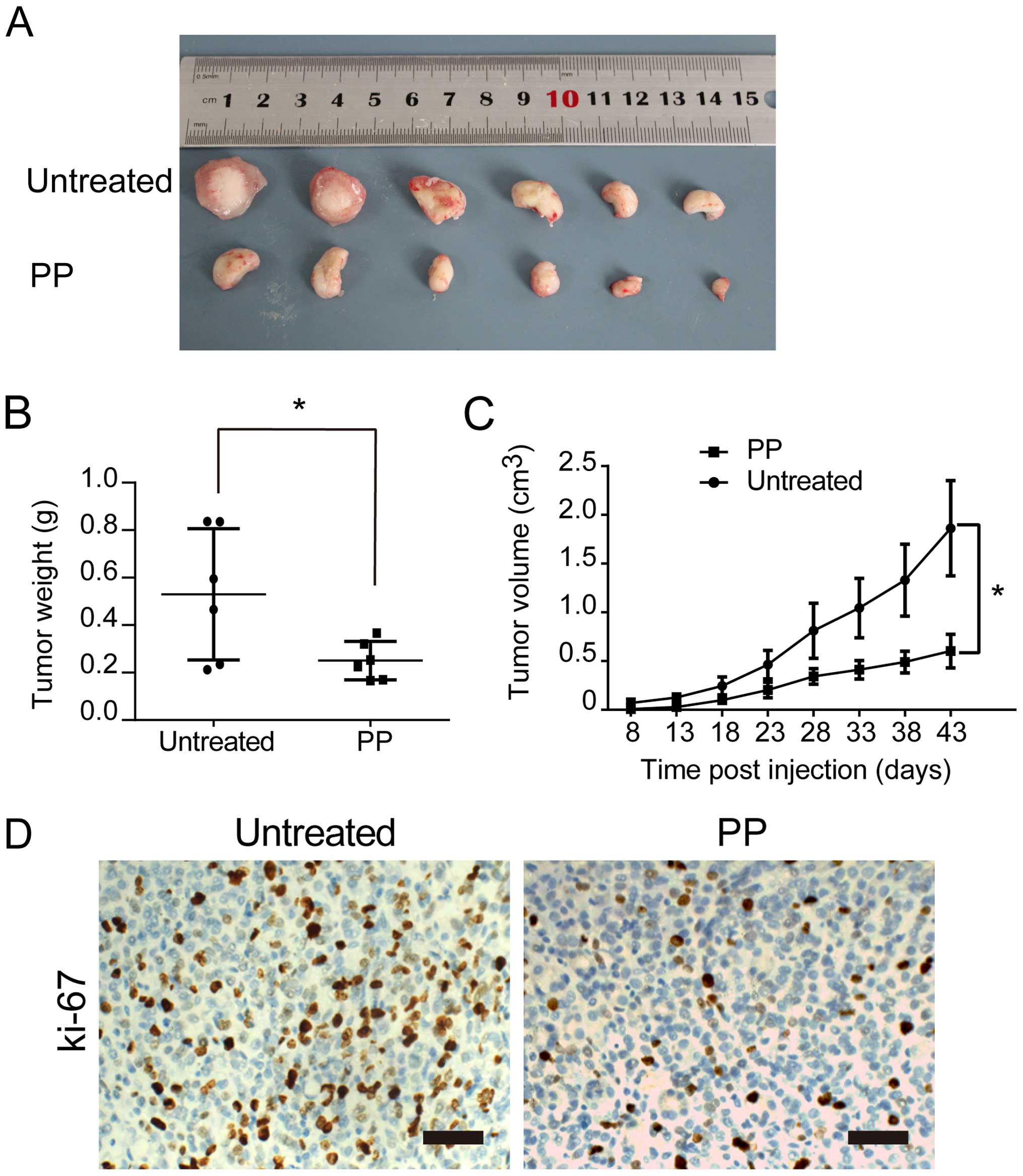
|
1
|
Chiba T, Kita K, Zheng YW, Yokosuka O,
Saisho H, Iwama A, Nakauchi H and Taniguchi H: Side population
purified from hepatocellular carcinoma cells harbors cancer stem
cell-like properties. Hepatology. 44:240–251. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ricardo S, Vieira AF, Gerhard R, Leitão D,
Pinto R, Cameselle-Teijeiro JF, Milanezi F, Schmitt F and Paredes
J: Breast cancer stem cell markers CD44, CD24 and ALDH1: Expression
distribution within intrinsic molecular subtype. J Clin Pathol.
64:937–946. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
O'Brien CA, Kreso A and Jamieson CH:
Cancer stem cells and self-renewal. Clin Cancer Res. 16:3113–3120.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lou H and Dean M: Targeted therapy for
cancer stem cells: The patched pathway and ABC transporters.
Oncogene. 26:1357–1360. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ishii H, Iwatsuki M, Ieta K, Ohta D,
Haraguchi N, Mimori K and Mori M: Cancer stem cells and
chemoradiation resistance. Cancer Sci. 99:1871–1877. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chuthapisith S, Eremin J, El-Sheemey M and
Eremin O: Breast cancer chemoresistance: Emerging importance of
cancer stem cells. Surg Oncol. 19:27–32. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Saadin K and White IM: Breast cancer stem
cell enrichment and isolation by mammosphere culture and its
potential diagnostic applications. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 13:49–60.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sehl ME, Sinsheimer JS, Zhou H and Lange
KL: Differential destruction of stem cells: Implications for
targeted cancer stem cell therapy. Cancer Res. 69:9481–9489. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Malhotra GK, Zhao X, Band H and Band V:
Shared signaling pathways in normal and breast cancer stem cells. J
Carcinog. 10:382011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Harrison H, Farnie G, Howell SJ, Rock RE,
Stylianou S, Brennan KR, Bundred NJ and Clarke RB: Regulation of
breast cancer stem cell activity by signaling through the Notch4
receptor. Cancer Res. 70:709–718. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Farnie G and Clarke RB: Mammary stem cells
and breast cancer - role of Notch signalling. Stem Cell Rev.
3:169–175. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Czerwinska P and Kaminska B: Regulation of
breast cancer stem cell features. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 19A:A7–A15.
2015.
|
|
13
|
Zhao C, Chen A, Jamieson CH, Fereshteh M,
Abrahamsson A, Blum J, Kwon HY, Kim J, Chute JP, Rizzieri D, et al:
Hedgehog signalling is essential for maintenance of cancer stem
cells in myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 458:776–779. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tomasetti C and Vogelstein B: Cancer
etiology. Variation in cancer risk among tissues can be explained
by the number of stem cell divisions. Science. 347:78–81. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Venugopal C, Hallett R, Vora P, Manoranjan
B, Mahendram S, Qazi MA, McFarlane N, Subapanditha M, Nolte SM,
Singh M, et al: Pyrvinium targets CD133 in human glioblastoma brain
tumor-initiating cells. Clin Cancer Res. 21:5324–5337. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Abetov D, Mustapova Z, Saliev T, Bulanin
D, Batyrbekov K and Gilman CP: Novel small molecule inhibitors of
cancer stem cell signaling pathways. Stem Cell Rev. 11:909–918.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Harada Y, Ishii I, Hatake K and Kasahara
T: Pyrvinium pamoate inhibits proliferation of
myeloma/erythroleukemia cells by suppressing mitochondrial
respiratory complex I and STAT3. Cancer Lett. 319:83–88. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wiegering A, Uthe FW, Hüttenrauch M,
Mühling B, Linnebacher M, Krummenast F, Germer CT, Thalheimer A and
Otto C: The impact of pyrvinium pamoate on colon cancer cell
viability. Int J Colorectal Dis. 29:1189–1198. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang X, Lou Y, Zheng X, Wang H, Sun J,
Dong Q and Han B: Wnt blockers inhibit the proliferation of lung
cancer stem cells. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:2399–2407.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Reya T and Clevers H: Wnt signalling in
stem cells and cancer. Nature. 434:843–850. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Polyak K: Heterogeneity in breast cancer.
J Clin Invest. 121:3786–3788. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sorlie T, Tibshirani R, Parker J, Hastie
T, Marron JS, Nobel A, Deng S, Johnsen H, Pesich R, Geisler S, et
al: Repeated observation of breast tumor subtypes in independent
gene expression data sets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:8418–8423.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lorico A and Rappa G: Phenotypic
heterogeneity of breast cancer stem cells. J Oncol.
2011:1350392011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang A, Chen L, Li C and Zhu Y:
Heterogeneity in cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett. 357:63–68. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chen J, Li Y, Yu TS, McKay RM, Burns DK,
Kernie SG and Parada LF: A restricted cell population propagates
glioblastoma growth after chemotherapy. Nature. 488:522–526. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q,
Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD and Rich JN: Glioma stem
cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA
damage response. Nature. 444:756–760. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu Y, Nenutil R, Appleyard MV, Murray K,
Boylan M, Thompson AM and Coates PJ: Lack of correlation of stem
cell markers in breast cancer stem cells. Br J Cancer.
110:2063–2071. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bozkulak EC and Weinmaster G: Selective
use of ADAM10 and ADAM17 in activation of Notch1 signaling. Mol
Cell Biol. 29:5679–5695. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Appleyard MV, Murray KE, Coates PJ,
Wullschleger S, Bray SE, Kernohan NM, Fleming S, Alessi DR and
Thompson AM: Phenformin as prophylaxis and therapy in breast cancer
xenografts. Br J Cancer. 106:1117–1122. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Reynolds BA and Weiss S: Generation of
neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian
central nervous system. Science. 255:1707–1710. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lu S and Labhasetwar V: Drug resistant
breast cancer cell line displays cancer stem cell phenotype and
responds sensitively to epigenetic drug SAHA. Drug Deliv Transl
Res. 3:183–194. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lombardo Y, de Giorgio A, Coombes CR,
Stebbing J and Castellano L: Mammosphere formation assay from human
breast cancer tissues and cell lines. J Vis Exp. Mar 22–2015.(Epub
ahead of print). View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hwang-Verslues WW, Lee WH and Lee EY:
Biomarkers to target heterogeneous breast cancer stem cells. J Mol
Biomark Diagn. (Suppl 8): 62012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Luo M, Brooks M and Wicha MS:
Epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity of breast cancer stem cells:
Implications for metastasis and therapeutic resistance. Curr Pharm
Des. 21:1301–1310. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Li B, Fei DL, Flaveny CA, Dahmane N,
Baubet V, Wang Z, Bai F, Pei XH, Rodriguez-Blanco J, Hang B, et al:
Pyrvinium attenuates Hedgehog signaling downstream of smoothened.
Cancer Res. 74:4811–4821. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bourguignon LY, Wong G, Earle C and Chen
L: Hyaluronan-CD44v3 interaction with Oct4-Sox2-Nanog promotes
miR-302 expression leading to self-renewal, clonal formation, and
cisplatin resistance in cancer stem cells from head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. J Biol Chem. 287:32800–32824. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Peifer M and Polakis P: Wnt signaling in
oncogenesis and embryogenesis - a look outside the nucleus.
Science. 287:1606–1609. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Anastas JN and Moon RT: WNT signalling
pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
13:11–26. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Dihlmann S and von Knebel Doeberitz M:
Wnt/beta-catenin-pathway as a molecular target for future
anti-cancer therapeutics. Int J Cancer. 113:515–524. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Deng L, Lei Y, Liu R, Li J, Yuan K, Li Y,
Chen Y, Liu Y, Lu Y, Edwards CK III, et al: Pyrvinium targets
autophagy addiction to promote cancer cell death. Cell Death Dis.
4:e6142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gangopadhyay S, Nandy A, Hor P and
Mukhopadhyay A: Breast cancer stem cells: A novel therapeutic
target. Clin Breast Cancer. 13:7–15. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Prat A, Parker JS, Karginova O, Fan C,
Livasy C, Herschkowitz JI, He X and Perou CM: Phenotypic and
molecular characterization of the claudin-low intrinsic subtype of
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 12:R682010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Asiedu MK, Ingle JN, Behrens MD, Radisky
DC and Knutson KL: TGFbeta/TNF(alpha)-mediated
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates breast cancer stem
cells with a claudin-low phenotype. Cancer Res. 71:4707–4719. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Creighton CJ, Li X, Landis M, Dixon JM,
Neumeister VM, Sjolund A, Rimm DL, Wong H, Rodriguez A,
Herschkowitz JI, et al: Residual breast cancers after conventional
therapy display mesenchymal as well as tumor-initiating features.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:13820–13825. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xu W, Lacerda L, Debeb BG, Atkinson RL,
Solley TN, Li L, Orton D, McMurray JS, Hang BI, Lee E, et al: The
antihelmintic drug pyrvinium pamoate targets aggressive breast
cancer. PLoS One. 8:e715082013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Swanton C, Burrell RA and Futreal PA:
Breast cancer genome heterogeneity: A challenge to personalised
medicine? Breast Cancer Res. 13:1042011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E,
Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M, Jacquemier J, Viens P, Kleer CG,
Liu S, et al: ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human
mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell
Stem Cell. 1:555–567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
de Beça FF, Caetano P, Gerhard R,
Alvarenga CA, Gomes M, Paredes J and Schmitt F: Cancer stem cells
markers CD44, CD24 and ALDH1 in breast cancer special histological
types. J Clin Pathol. 66:187–191. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Bill R and Christofori G: The relevance of
EMT in breast cancer metastasis: Correlation or causality? FEBS
Lett. 589:1577–1587. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Thorne CA, Hanson AJ, Schneider J, Tahinci
E, Orton D, Cselenyi CS, Jernigan KK, Meyers KC, Hang BI, Waterson
AG, et al: Small-molecule inhibition of Wnt signaling through
activation of casein kinase 1α. Nat Chem Biol. 6:829–836. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Saraswati S, Alfaro MP, Thorne CA,
Atkinson J, Lee E and Young PP: Pyrvinium, a potent small molecule
Wnt inhibitor, promotes wound repair and post-MI cardiac
remodeling. PLoS One. 5:e155212010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Venerando A, Girardi C, Ruzzene M and
Pinna LA: Pyrvinium pamoate does not activate protein kinase CK1,
but promotes Akt/PKB down-regulation and GSK3 activation. Biochem
J. 452:131–137. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Song L, Li ZY, Liu WP and Zhao MR:
Crosstalk between Wnt/β-catenin and Hedgehog/Gli signaling pathways
in colon cancer and implications for therapy. Cancer Biol Ther.
16:1–7. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Yanai K, Nakamura M, Akiyoshi T, Nagai S,
Wada J, Koga K, Noshiro H, Nagai E, Tsuneyoshi M, Tanaka M, et al:
Crosstalk of hedgehog and Wnt pathways in gastric cancer. Cancer
Lett. 263:145–156. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Smith TC, Kinkel AW, Gryczko CM and Goulet
JR: Absorption of pyrvinium pamoate. Clin Pharmacol Ther.
19:802–806. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Bartucci M, Dattilo R, Moriconi C,
Pagliuca A, Mottolese M, Federici G, Benedetto AD, Todaro M, Stassi
G, Sperati F, et al: TAZ is required for metastatic activity and
chemoresistance of breast cancer stem cells. Oncogene. 34:681–690.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|