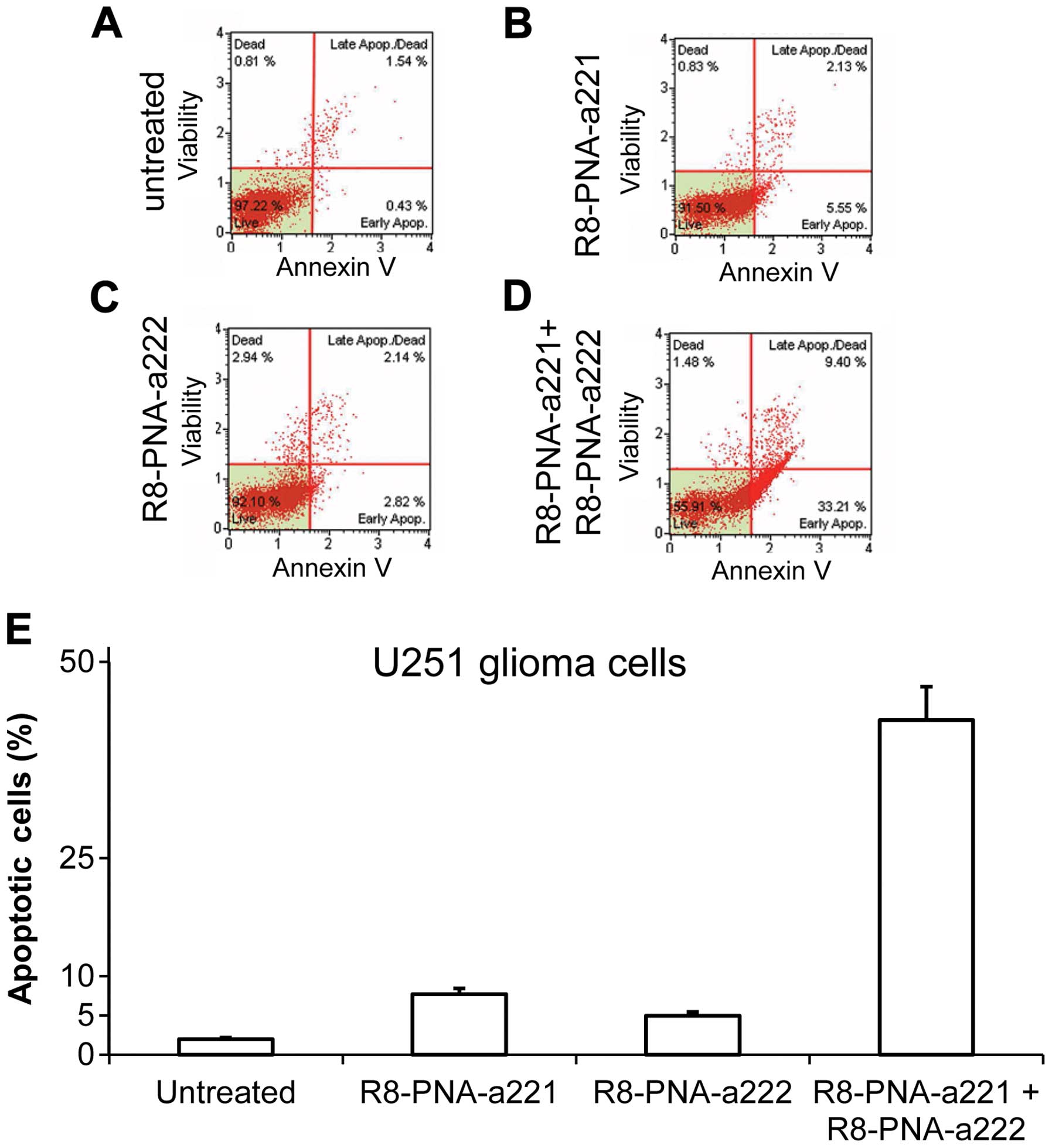
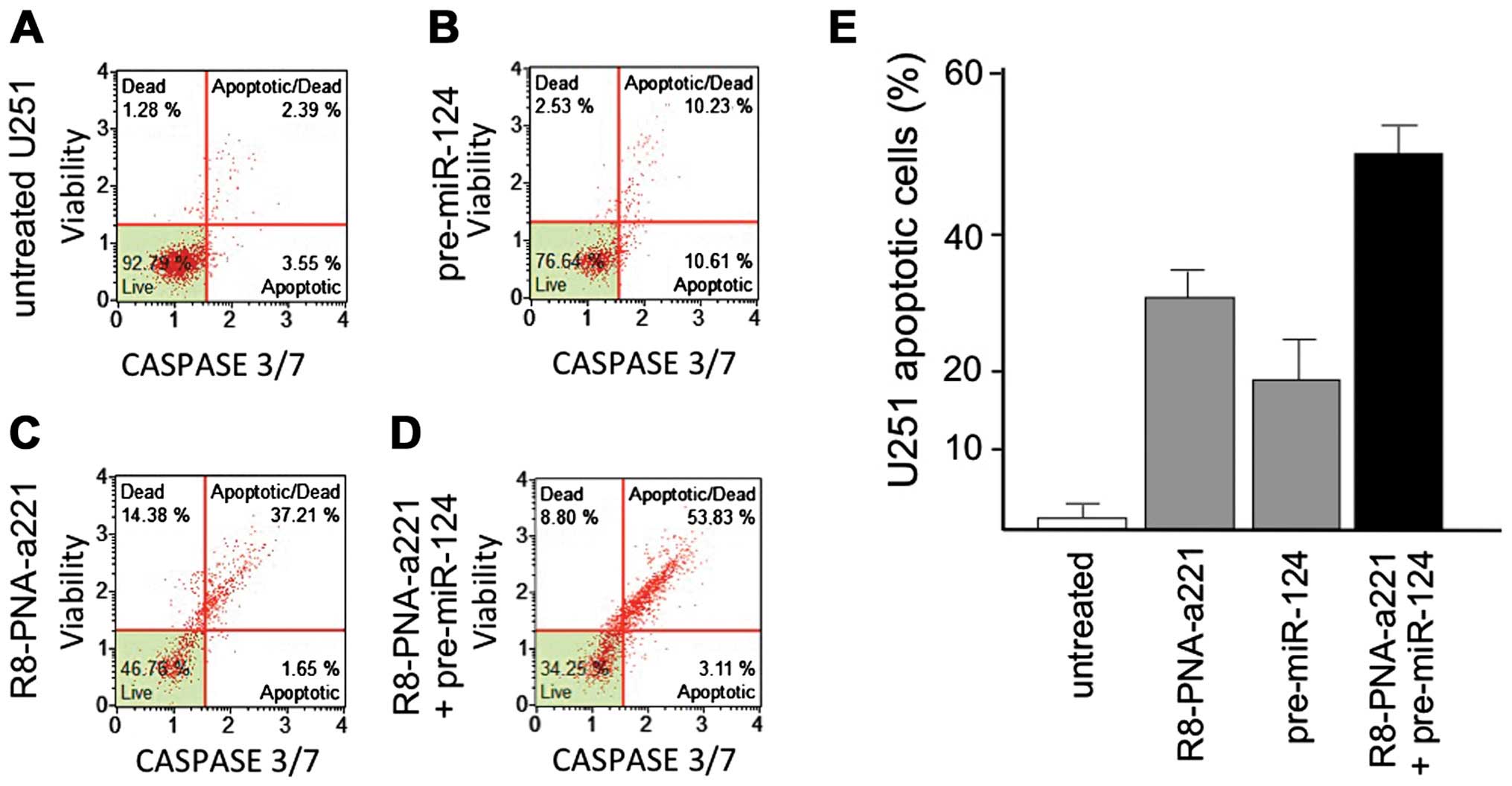
|
1
|
Mazière P and Enright AJ: Prediction of
microRNA targets. Drug Discov Today. 12:452–458. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Witkos TM, Koscianska E and Krzyzosiak WJ:
Practical aspects of microRNA target prediction. Curr Mol Med.
11:93–109. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ghelani HS, Rachchh MA and Gokani RH:
MicroRNAs as newer therapeutic targets: A big hope from a tiny
player. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 3:217–227. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun K and Lai EC: Adult-specific functions
of animal microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 14:535–548. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chekulaeva M and Filipowicz W: Mechanisms
of miRNA-mediated post-transcriptional regulation in animal cells.
Curr Opin Cell Biol. 21:452–460. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS and Bartel
DP: Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA
levels. Nature. 466:835–840. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cammaerts S, Strazisar M, De Rijk P and
Del Favero J: Genetic variants in microRNA genes: Impact on
microRNA expression, function, and disease. Front Genet. 6:1862015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Friedländer MR, Lizano E, Houben AJS,
Bezdan D, Báñez-Coronel M, Kudla G, Mateu-Huertas E, Kagerbauer B,
González J, Chen KC, et al: Evidence for the biogenesis of more
than 1,000 novel human microRNAs. Genome Biol. 15:R572014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheng WC, Chung IF, Tsai CF, Huang TS,
Chen CY, Wang SC, Chang TY, Sun HJ, Chao JY, Cheng CC, et al:
YM500v2: a small RNA sequencing (smRNA-seq) database for human
cancer miRNome research. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:D862–D867. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Londin E, Loher P, Telonis AG, Quann K,
Clark P, Jing Y, Hatzimichael E, Kirino Y, Honda S, Lally M, et al:
Analysis of 13 cell types reveals evidence for the expression of
numerous novel primate- and tissue-specific microRNAs. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 112:E1106–E1115. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Griffiths-Jones S, Grocock RJ, van Dongen
S, Bateman A and Enright AJ: miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets
and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:D140–D144. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Kozomara A and Griffiths-Jones S: miRBase:
Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42:D68–D73. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Taccioli C, Fabbri E, Visone R, Volinia S,
Calin GA, Fong LY, Gambari R, Bottoni A, Acunzo M, Hagan J, et al:
UCbase and miRfunc: A database of ultraconserved sequences and
microRNA function. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:D41–D48. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Witwer KW: Data submission and quality in
microarray-based microRNA profiling. Clin Chem. 59:392–400. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xie B, Ding Q, Han H and Wu D: miRCancer:
A microRNA-cancer association database constructed by text mining
on literature. Bioinformatics. 29:638–644. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson
A, Schelter JM, Castle J, Bartel DP, Linsley PS and Johnson JM:
Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large
numbers of target mRNAs. Nature. 433:769–773. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Peter ME: Targeting of mRNAs by multiple
miRNAs: The next step. Oncogene. 29:2161–2164. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bianchi N, Finotti A, Ferracin M,
Lampronti I, Zuccato C, Breveglieri G, Brognara E, Fabbri E,
Borgatti M, Negrini M, et al: Increase of microRNA-210, decrease of
raptor gene expression and alteration of mammalian target of
rapamycin regulated proteins following mithramycin treatment of
human erythroid cells. PLoS One. 10:e01215672015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Subramanian S and Steer CJ: MicroRNAs as
gatekeepers of apoptosis. J Cell Physiol. 223:289–298.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Y and Blelloch R: Cell cycle
regulation by MicroRNAs in embryonic stem cells. Cancer Res.
69:4093–4096. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fabbri E, Borgatti M, Montagner G, Bianchi
N, Finotti A, Lampronti I, Bezzerri V, Dechecchi MC, Cabrini G and
Gambari R: Expression of microRNA-93 and Interleukin-8 during
Pseudomonas aeruginosa-mediated induction of proinflammatory
responses. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 50:1144–1155. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Faruq O and Vecchione A: microRNA:
Diagnostic perspective. Front Med Lausanne. 2:512015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shalaby T, Fiaschetti G, Baumgartner M and
Grotzer MA: Significance and therapeutic value of miRNAs in
embryonal neural tumors. Molecules. 19:5821–5862. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M,
et al: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites
and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Palmero EI, de Campos SG, Campos M, de
Souza NC, Guerreiro ID, Carvalho AL and Marques MM: Mechanisms and
role of microRNA deregulation in cancer onset and progression.
Genet Mol Biol. 34:363–370. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Weber JA, Baxter DH, Zhang S, Huang DY,
Huang KH, Lee MJ, Galas DJ and Wang K: The microRNA spectrum in 12
body fluids. Clin Chem. 56:1733–1741. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fayyad-Kazan H, Bitar N, Najar M, Lewalle
P, Fayyad-Kazan M, Badran R, Hamade E, Daher A, Hussein N, ElDirani
R, et al: Circulating miR-150 and miR-342 in plasma are novel
potential biomarkers for acute myeloid leukemia. J Transl Med.
11:312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Neviani P and Fabbri M: Exosomic microRNAs
in the tumor microenvironment. Front Med Lausanne.
2:472015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Köberle V, Kronenberger B, Pleli T, Trojan
J, Imelmann E, Peveling-Oberhag J, Welker MW, Elhendawy M, Zeuzem
S, Piiper A, et al: Serum microRNA-1 and microRNA-122 are
prognostic markers in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J
Cancer. 49:3442–3449. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
He Y, Lin J, Kong D, Huang M, Xu C, Kim
TK, Etheridge A, Luo Y, Ding Y and Wang K: Current state of
circulating MicroRNAs as cancer biomarkers. Clin Chem.
61:1138–1155. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Westphal M and Lamszus K: Circulating
biomarkers for gliomas. Nat Rev Neurol. 11:556–566. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yau TO, Wu CW, Dong Y, Tang CM, Ng SS,
Chan FK, Sung JJ and Yu J: microRNA-221 and microRNA-18a
identification in stool as potential biomarkers for the
non-invasive diagnosis of colorectal carcinoma. Br J Cancer.
111:1765–1771. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cheng H, Zhang L, Cogdell DE, Zheng H,
Schetter AJ, Nykter M, Harris CC, Chen K, Hamilton SR and Zhang W:
Circulating plasma MiR-141 is a novel biomarker for metastatic
colon cancer and predicts poor prognosis. PLoS One. 6:e177452011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Czech MP: MicroRNAs as therapeutic
targets. N Engl J Med. 354:1194–1195. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Brown BD and Naldini L: Exploiting and
antagonizing microRNA regulation for therapeutic and experimental
applications. Nat Rev Genet. 10:578–585. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kota SK and Balasubramanian S: Cancer
therapy via modulation of micro RNA levels: A promising future.
Drug Discov Today. 15:733–740. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Small EM and Olson EN: Pervasive roles of
microRNAs in cardiovascular biology. Nature. 469:336–342. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bader AG and Lammers P: The Therapeutic
Potential of microRNAs. Discovery Technology. 2011.
|
|
40
|
Rothschild SI: microRNA therapies in
cancer. Mol Cell Ther. 2:72014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
van Rooij E and Kauppinen S: Development
of microRNA therapeutics is coming of age. EMBO Mol Med. 6:851–864.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Orellana EA and Kasinski AL: MicroRNAs in
cancer: A historical perspective on the path from discovery to
therapy. Cancers (Basel). 7:1388–1405. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Berindan-Neagoe I, Monroig PC, Pasculli B
and Calin GA: MicroRNAome genome: A treasure for cancer diagnosis
and therapy. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:311–336. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bernardo BC, Ooi JY, Lin RC and McMullen
JR: miRNA therapeutics: A new class of drugs with potential
therapeutic applications in the heart. Future Med Chem.
7:1771–1792. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Weiler J, Hunziker J and Hall J:
Anti-miRNA oligonucleotides (AMOs): Ammunition to target miRNAs
implicated in human disease? Gene Ther. 13:496–502. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lu Y, Xiao J, Lin H, Bai Y, Luo X, Wang Z
and Yang B: A single anti-microRNA antisense
oligodeoxyribonucleotide (AMO) targeting multiple microRNAs offers
an improved approach for microRNA interference. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:e242009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lennox KA and Behlke MA: Chemical
modification and design of anti-miRNA oligonucleotides. Gene Ther.
18:1111–1120. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Obad S, dos Santos CO, Petri A, Heidenblad
M, Broom O, Ruse C, Fu C, Lindow M, Stenvang J, Straarup EM, et al:
Silencing of microRNA families by seed-targeting tiny LNAs. Nat
Genet. 43:371–378. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Elmén J, Lindow M, Schütz S, Lawrence M,
Petri A, Obad S, Lindholm M, Hedtjärn M, Hansen HF, Berger U, et
al: LNA-mediated microRNA silencing in non-human primates. Nature.
452:896–899. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Stenvang J, Silahtaroglu AN, Lindow M,
Elmen J and Kauppinen S: The utility of LNA in microRNA-based
cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. Semin Cancer Biol. 18:89–102.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chabot S, Teissié J and Golzio M: Targeted
electro-delivery of oligonucleotides for RNA interference: siRNA
and antimiR. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 81:161–168. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Lundin KE, Højland T, Hansen BR, Persson
R, Bramsen JB, Kjems J, Koch T, Wengel J and Smith CI: Biological
activity and biotechnological aspects of locked nucleic acids. Adv
Genet. 82:47–107. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Staedel C, Varon C, Nguyen PH, Vialet B,
Chambonnier L, Rousseau B, Soubeyran I, Evrard S, Couillaud F and
Darfeuille F: Inhibition of gastric tumor cell growth using
seed-targeting LNA as specific, long-lasting MicroRNA inhibitors.
Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 4:e2462015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Avitabile C, Accardo A, Ringhieri P,
Morelli G, Saviano M, Montagner G, Fabbri E, Gallerani E, Gambari R
and Romanelli A: Incorporation of naked peptide nucleic acids into
liposomes leads to fast and efficient delivery. Bioconjug Chem.
26:1533–1541. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Fabbri E, Manicardi A, Tedeschi T, Sforza
S, Bianchi N, Brognara E, Finotti A, Breveglieri G, Borgatti M,
Corradini R, et al: Modulation of the biological activity of
microRNA-210 with peptide nucleic acids (PNAs). ChemMedChem.
6:2192–2202. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Brognara E, Fabbri E, Bazzoli E, Montagner
G, Ghimenton C, Eccher A, Cantù C, Manicardi A, Bianchi N, Finotti
A, et al: Uptake by human glioma cell lines and biological effects
of a peptide-nucleic acids targeting miR-221. J Neurooncol.
118:19–28. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Cheng CJ, Bahal R, Babar IA, Pincus Z,
Barrera F, Liu C, Svoronos A, Braddock DT, Glazer PM, Engelman DM,
et al: MicroRNA silencing for cancer therapy targeted to the tumour
microenvironment. Nature. 518:107–110. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Morris JK, Chomyk A, Song P, Parker N,
Deckard S, Trapp BD, Pimplikar SW and Dutta R: Decrease in levels
of the evolutionarily conserved microRNA miR-124 affects
oligodendrocyte numbers in Zebrafish, Danio rerio. Invert Neurosci.
15:42015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Conte I, Hadfield KD, Barbato S, Carrella
S, Pizzo M, Bhat RS, Carissimo A, Karali M, Porter LF, Urquhart J,
et al: MiR-204 is responsible for inherited retinal dystrophy
associated with ocular coloboma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
112:E3236–E3245. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ristori E, Lopez-Ramirez MA, Narayanan A,
Hill-Teran G, Moro A, Calvo CF, Thomas JL and Nicoli S: A
Dicer-miR-107 interaction regulates biogenesis of specific miRNAs
crucial for neurogenesis. Dev Cell. 32:546–560. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ebert MS, Neilson JR and Sharp PA:
MicroRNA sponges: Competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian
cells. Nat Methods. 4:721–726. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ebert MS and Sharp PA: MicroRNA sponges:
Progress and possibilities. RNA. 16:2043–2050. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kluiver J, Gibcus JH, Hettinga C, Adema A,
Richter MK, Halsema N, Slezak-Prochazka I, Ding Y, Kroesen BJ and
van den Berg A: Rapid generation of microRNA sponges for microRNA
inhibition. PLoS One. 7:e292752012a. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Kluiver J, Slezak-Prochazka I,
Smigielska-Czepiel K, Halsema N, Kroesen BJ and van den Berg A:
Generation of miRNA sponge constructs. Methods. 58:113–117. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Li KC, Chang YH, Yeh CL and Hu YC: Healing
of osteoporotic bone defects by baculovirus-engineered bone
marrow-derived MSCs expressing MicroRNA sponges. Biomaterials.
74:155–166. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
de Melo Maia B, Ling H, Monroig P, Ciccone
M, Soares FA, Calin GA and Rocha RM: Design of a miRNA sponge for
the miR-17 miRNA family as a therapeutic strategy against vulvar
carcinoma. Mol Cell Probes. 29:420–426. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Tay FC, Lim JK, Zhu H, Hin LC and Wang S:
Using artificial microRNA sponges to achieve microRNA
loss-of-function in cancer cells. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 81:117–127.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Liu Y, Han Y, Zhang H, Nie L, Jiang Z, Fa
P, Gui Y and Cai Z: Synthetic miRNA-mowers targeting miR-183-96-182
cluster or miR-210 inhibit growth and migration and induce
apoptosis in bladder cancer cells. PLoS One. 7:e522802012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Choi WY, Giraldez AJ and Schier AF: Target
protectors reveal dampening and balancing of Nodal agonist and
antagonist by miR-430. Science. 318:271–274. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Haraguchi T, Ozaki Y and Iba H: Vectors
expressing efficient RNA decoys achieve the long-term suppression
of specific microRNA activity in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids
Res. 37:e432009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Krol J, Busskamp V, Markiewicz I, Stadler
MB, Ribi S, Richter J, Duebel J, Bicker S, Fehling HJ, Schübeler D,
et al: Characterizing light-regulated retinal microRNAs reveals
rapid turnover as a common property of neuronal microRNAs. Cell.
141:618–631. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Cassidy JJ, Straughan AJ and Carthew RW:
Differential masking of natural genetic variation by miR-9a in
Drosophila. Genetics. 202:675–687. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Wang Z: The principles of MiRNA-masking
antisense oligonucleotides technology. Methods Mol Biol. 676:43–49.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Bak RO, Hollensen AK and Mikkelsen JG:
Managing microRNAs with vector-encoded decoy-type inhibitors. Mol
Ther. 21:1478–1485. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Murakami K and Miyagishi M: Tiny masking
locked nucleic acids effectively bind to mRNA and inhibit binding
of microRNAs in relation to thermodynamic stability. Biomed Rep.
2:509–512. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Shin KJ, Wall EA, Zavzavadjian JR, Santat
LA, Liu J, Hwang JI, Rebres R, Roach T, Seaman W, Simon MI, et al:
A single lentiviral vector platform for microRNA-based conditional
RNA interference and coordinated transgene expression. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 103:13759–13764. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Askou AL, Aagaard L, Kostic C, Arsenijevic
Y, Hollensen AK, Bek T, Jensen TG, Mikkelsen JG and Corydon TJ:
Multigenic lentiviral vectors for combined and tissue-specific
expression of miRNA- and protein-based antiangiogenic factors. Mol
Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2:140642015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Winbanks CE, Beyer C, Hagg A, Qian H,
Sepulveda PV and Gregorevic P: miR-206 represses hypertrophy of
myogenic cells but not muscle fibers via inhibition of HDAC4. PLoS
One. 8:e735892013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Montgomery RL, Yu G, Latimer PA, Stack C,
Robinson K, Dalby CM, Kaminski N and van Rooij E: MicroRNA mimicry
blocks pulmonary fibrosis. EMBO Mol Med. 6:1347–1356. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Bader AG: miR-34 - a microRNA replacement
therapy is headed to the clinic. Front Genet. 3:1202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Kwekkeboom RF, Lei Z, Doevendans PA,
Musters RJ and Sluijter JP: Targeted delivery of miRNA therapeutics
for cardiovascular diseases: Opportunities and challenges. Clin Sci
(Lond). 127:351–365. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Sherr CJ: Principles of tumor suppression.
Cell. 116:235–246. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Lee YS and Dutta A: The tumor suppressor
microRNA let-7 represses the HMGA2 oncogene. Genes Dev.
21:1025–1030. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Mayr C, Hemann MT and Bartel DP:
Disrupting the pairing between let-7 and Hmga2 enhances oncogenic
transformation. Science. 315:1576–1579. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Park SM, Shell S, Radjabi AR, Schickel R,
Feig C, Boyerinas B, Dinulescu DM, Lengyel E and Peter ME: Let-7
prevents early cancer progression by suppressing expression of the
embryonic gene HMGA2. Cell Cycle. 6:2585–2590. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Sampson VB, Rong NH, Han J, Yang Q, Aris
V, Soteropoulos P, Petrelli NJ, Dunn SP and Krueger LJ: MicroRNA
let-7a down-regulates MYC and reverts MYC-induced growth in Burkitt
lymphoma cells. Cancer Res. 67:9762–9770. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Müller DW and Bosserhoff AK: Integrin beta
3 expression is regulated by let-7a miRNA in malignant melanoma.
Oncogene. 27:6698–6706. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Peng Y, Laser J, Shi G, Mittal K, Melamed
J, Lee P and Wei JJ: Antiproliferative effects by Let-7 repression
of high-mobility group A2 in uterine leiomyoma. Mol Cancer Res.
6:663–673. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Bader AG, Brown D and Winkler M: The
promise of microRNA replacement therapy. Cancer Res. 70:7027–7030.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Wiggins JF, Ruffino L, Kelnar K, Omotola
M, Patrawala L, Brown D and Bader AG: Development of a lung cancer
therapeutic based on the tumor suppressor microRNA-34. Cancer Res.
70:5923–5930. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Ibrahim AF, Weirauch U, Thomas M,
Grünweller A, Hartmann RK and Aigner A: MicroRNA replacement
therapy for miR-145 and miR-33a is efficacious in a model of colon
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 71:5214–5224. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Trang P, Wiggins JF, Daige CL, Cho C,
Omotola M, Brown D, Weidhaas JB, Bader AG and Slack FJ: Systemic
delivery of tumor suppressor microRNA mimics using a neutral lipid
emulsion inhibits lung tumors in mice. Mol Ther. 19:1116–1122.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Buechner J, Tømte E, Haug BH, Henriksen
JR, Løkke C, Flægstad T and Einvik C: Tumour-suppressor microRNAs
let-7 and miR-101 target the proto-oncogene MYCN and inhibit cell
proliferation in MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma. Br J Cancer.
105:296–303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Scheibner KA, Teaboldt B, Hauer MC, Chen
X, Cherukuri S, Guo Y, Kelley SM, Liu Z, Baer MR, Heimfeld S, et
al: MiR-27a functions as a tumor suppressor in acute leukemia by
regulating 14-3-3θ. PLoS One. 7:e508952012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Thomas M, Lange-Grünweller K, Weirauch U,
Gutsch D, Aigner A, Grünweller A and Hartmann RK: The
proto-oncogene Pim-1 is a target of miR-33a. Oncogene. 31:918–928.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Endo H, Muramatsu T, Furuta M, Uzawa N,
Pimkhaokham A, Amagasa T, Inazawa J and Kozaki K: Potential of
tumor-suppressive miR-596 targeting LGALS3BP as a therapeutic agent
in oral cancer. Carcinogenesis. 34:560–569. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Wu Y, Crawford M, Mao Y, Lee RJ, Davis IC,
Elton TS, Lee LJ and Nana-Sinkam SP: Therapeutic delivery of
microRNA-29b by cationic lipoplexes for lung cancer. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 2:e842013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Huang X, Schwind S, Yu B, Santhanam R,
Wang H, Hoellerbauer P, Mims A, Klisovic R, Walker AR, Chan KK, et
al: Targeted delivery of microRNA-29b by transferrin-conjugated
anionic lipopolyplex nanoparticles: A novel therapeutic strategy in
acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 19:2355–2367.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Liang Z, Ahn J, Guo D, Votaw JR and Shim
H: MicroRNA-302 replacement therapy sensitizes breast cancer cells
to ionizing radiation. Pharm Res. 30:1008–1016. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
100
|
Møller HG, Rasmussen AP, Andersen HH,
Johnsen KB, Henriksen M and Duroux M: A systematic review of
microRNA in glioblastoma multiforme: Micro-modulators in the
mesenchymal mode of migration and invasion. Mol Neurobiol.
47:131–144. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
101
|
Hershkovitz-Rokah O, Modai S,
Pasmanik-Chor M, Toren A, Shomron N, Raanani P, Shpilberg O and
Granot G: Restoration of miR-424 suppresses BCR-ABL activity and
sensitizes CML cells to imatinib treatment. Cancer Lett.
360:245–256. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Lee YM, Lee JY, Ho CC, Hong QS, Yu SL,
Tzeng CR, Yang PC and Chen HW: miRNA-34b as a tumor suppressor in
estrogen-dependent growth of breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer
Res. 13:R1162011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Huang P, Ye B, Yang Y, Shi J and Zhao H:
MicroRNA-181 functions as a tumor suppressor in non-small cell lung
cancer (NSCLC) by targeting Bcl-2. Tumour Biol. 36:3381–3387. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Su R, Lin HS, Zhang XH, Yin XL, Ning HM,
Liu B, Zhai PF, Gong JN, Shen C, Song L, et al: MiR-181 family:
Regulators of myeloid differentiation and acute myeloid leukemia as
well as potential therapeutic targets. Oncogene. 34:3226–3239.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Bachetti T, Di Zanni E, Ravazzolo R and
Ceccherini I: miR-204 mediates post-transcriptional down-regulation
of PHOX2B gene expression in neuroblastoma cells. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1849.1057–1065. 2015.
|
|
106
|
Fernandez S, Risolino M, Mandia N, Talotta
F, Soini Y, Incoronato M, Condorelli G, Banfi S and Verde P:
miR-340 inhibits tumor cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by
targeting multiple negative regulators of p27 in non-small cell
lung cancer. Oncogene. 34:3240–3250. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Liu G, Liu Y, Yang Z, Wang J, Li D and
Zhang X: Tumor suppressor microRNA-18a regulates tumor
proliferation and invasion by targeting TBPL1 in colorectal cancer
cells. Mol Med Rep. 12:7643–7648. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Xishan Z, Ziying L, Jing D and Gang L:
MicroRNA-320a acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting BCR/ABL
oncogene in chronic myeloid leukemia. Sci Rep. 5:124602015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Zhao Z, Ma X, Sung D, Li M, Kosti A, Lin
G, Chen Y, Pertsemlidis A, Hsiao TH and Du L: microRNA-449a
functions as a tumor suppressor in neuroblastoma through inducing
cell differentiation and cell cycle arrest. RNA Biol. 12:538–554.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Kalinowski FC, Brown RA, Ganda C, Giles
KM, Epis MR, Horsham J and Leedman PJ: microRNA-7: A tumor
suppressor miRNA with therapeutic potential. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 54:312–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Gu DN, Huang Q and Tian L: The molecular
mechanisms and therapeutic potential of microRNA-7 in cancer.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 19:415–426. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Nohata N, Hanazawa T, Enokida H and Seki
N: microRNA-1/133a and microRNA-206/133b clusters: Dysregulation
and functional roles in human cancers. Oncotarget. 3:9–21.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Hudson RS, Yi M, Esposito D, Watkins SK,
Hurwitz AA, Yfantis HG, Lee DH, Borin JF, Naslund MJ, Alexander RB,
et al: MicroRNA-1 is a candidate tumor suppressor and prognostic
marker in human prostate cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:3689–3703.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Chang YS, Chen WY, Yin JJ,
Sheppard-Tillman H, Huang J and Liu YN: EGF receptor pomotes
prostate cancer bone metastasis by downregulating miR-1 and
activating TWIST1. Cancer Res. 75:3077–3086. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Zhang H, Cai K, Wang J, Wang X, Cheng K,
Shi F, Jiang L, Zhang Y and Dou J: MiR-7, inhibited indirectly by
lincRNA HOTAIR, directly inhibits SETDB1 and reverses the EMT of
breast cancer stem cells by downregulating the STAT3 pathway. Stem
Cells. 32:2858–2868. 2014a. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Okuda H, Xing F, Pandey PR, Sharma S,
Watabe M, Pai SK, Mo YY, Iiizumi-Gairani M, Hirota S, Liu Y, et al:
miR-7 suppresses brain metastasis of breast cancer stem-like cells
by modulating KLF4. Cancer Res. 73:1434–1444. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Zhou X, Hu Y, Dai L, Wang Y, Zhou J, Wang
W, Di W and Qiu L: MicroRNA-7 inhibits tumor metastasis and
reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition through AKT/ERK1/2
inactivation by targeting EGFR in epithelial ovarian cancer. PLoS
One. 9:e967182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Dangi-Garimella S, Yun J, Eves EM, Newman
M, Erkeland SJ, Hammond SM, Minn AJ and Rosner MR: Raf kinase
inhibitory protein suppresses a metastasis signalling cascade
involving LIN28 and let-7. EMBO J. 28:347–358. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Takamizawa J, Konishi H, Yanagisawa K,
Tomida S, Osada H, Endoh H, Harano T, Yatabe Y, Nagino M, Nimura Y,
et al: Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung
cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival.
Cancer Res. 64:3753–3756. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Shi XB, Tepper CG and deVere White RW:
Cancerous miRNAs and their regulation. Cell Cycle. 7:1529–1538.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, Byrom
M, Jarvis R, Cheng A, Labourier E, Reinert KL, Brown D and Slack
FJ: RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell.
120:635–647. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Zheng L, Qi T, Yang D, Qi M, Li D, Xiang
X, Huang K and Tong Q: microRNA-9 suppresses the proliferation,
invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells through targeting
cyclin D1 and Ets1. PLoS One. 8:e557192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Aqeilan RI, Calin GA and Croce CM: miR-15a
and miR-16-1 in cancer: Discovery, function and future
perspectives. Cell Death Differ. 17:215–220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R,
Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, et al:
Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and
miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:15524–15529. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Pekarsky Y and Croce CM: Role of miR-15/16
in CLL. Cell Death Differ. 22:6–11. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Bonci D, Coppola V, Musumeci M, Addario A,
Giuffrida R, Memeo L, D'Urso L, Pagliuca A, Biffoni M, Labbaye C,
et al: The miR-15a-miR-16-1 cluster controls prostate cancer by
targeting multiple oncogenic activities. Nat Med. 14:1271–1277.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Kang W, Tong JH, Lung RW, Dong Y, Zhao J,
Liang Q, Zhang L, Pan Y, Yang W, Pang JC, et al: Targeting of YAP1
by microRNA-15a and microRNA-16-1 exerts tumor suppressor function
in gastric adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer. 14:522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Chen F, Chen L, He H, Huang W, Zhang R, Li
P, et al: Up-regulation of microRNA-16 in glioblastoma inhibits the
function of endothelial cells and tumor angiogenesis by targeting
Bmi-1. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2015.
|
|
129
|
Humphreys KJ, McKinnon RA and Michael MZ:
miR-18a inhibits CDC42 and plays a tumour suppressor role in
colorectal cancer cells. PLoS One. 9:e1122882014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Zoni E, van der Horst G, van de Merbel AF,
Chen L, Rane JK, Pelger RC, Collins AT, Visakorpi T, Snaar-Jagalska
BE, Maitland NJ, et al: miR-25 modulates invasiveness and
dissemination of human prostate cancer cells via regulation of αv-
and α6 integrin expression. Cancer Res. 75:2326–2336. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Sengupta S, den Boon JA, Chen IH, Newton
MA, Stanhope SA, Cheng YJ, Chen CJ, Hildesheim A, Sugden B and
Ahlquist P: MicroRNA 29c is down-regulated in nasopharyngeal
carcinomas, up-regulating mRNAs encoding extracellular matrix
proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:5874–5878. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Ugalde AP, Ramsay AJ, de la Rosa J, Varela
I, Mariño G, Cadiñanos J, Lu J, Freije JM and López-Otín C: Aging
and chronic DNA damage response activate a regulatory pathway
involving miR-29 and p53. EMBO J. 30:2219–2232. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Garzon R, Heaphy CE, Havelange V, Fabbri
M, Volinia S, Tsao T, Zanesi N, Kornblau SM, Marcucci G, Calin GA,
et al: MicroRNA 29b functions in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood.
114:5331–5341. 2009a. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Garzon R, Liu S, Fabbri M, Liu Z, Heaphy
CE, Callegari E, Schwind S, Pang J, Yu J, Muthusamy N, et al:
MicroRNA-29b induces global DNA hypomethylation and tumor
suppressor gene reexpression in acute myeloid leukemia by targeting
directly DNMT3A and 3B and indirectly DNMT1. Blood. 113:6411–6418.
2009b. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Kapinas K, Kessler CB and Delany AM:
miR-29 suppression of osteonectin in osteoblasts: Regulation during
differentiation and by canonical Wnt signaling. J Cell Biochem.
108:216–224. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Mott JL, Kobayashi S, Bronk SF and Gores
GJ: miR-29 regulates Mcl-1 protein expression and apoptosis.
Oncogene. 26:6133–6140. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Fabbri M, Garzon R, Cimmino A, Liu Z,
Zanesi N, Callegari E, Liu S, Alder H, Costinean S,
Fernandez-Cymering C, et al: MicroRNA-29 family reverts aberrant
methylation in lung cancer by targeting DNA methyltransferases 3A
and 3B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:15805–15810. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Xiong Y, Fang JH, Yun JP, Yang J, Zhang Y,
Jia WH and Zhuang SM: Effects of microRNA-29 on apoptosis,
tumorigenicity, and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 51:836–845. 2010.
|
|
139
|
Filkowski JN, Ilnytskyy Y, Tamminga J,
Koturbash I, Golubov A, Bagnyukova T, Pogribny IP and Kovalchuk O:
Hypomethylation and genome instability in the germline of exposed
parents and their progeny is associated with altered miRNA
expression. Carcinogenesis. 31:1110–1115. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Wang Y, Zhang X, Li H, Yu J and Ren X: The
role of miRNA-29 family in cancer. Eur J Cell Biol. 92:123–128.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Hu W, Dooley J, Chung SS, Chandramohan D,
Cimmino L, Mukherjee S, Mason CE, de Strooper B, Liston A and Park
CY: miR-29a maintains mouse hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal by
regulating Dnmt3a. Blood. 125:2206–2216. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Li L and Wang B: Overexpression of
microRNA-30b improves adenovirus-mediated p53 cancer gene therapy
for laryngeal carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 15:19729–19740. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Hou C, Sun B, Jiang Y, Zheng J, Yang N, Ji
C, Liang Z, Shi J, Zhang R, Liu Y, et al: MicroRNA-31 inhibits lung
adenocarcinoma stem-like cells via down-regulation of MET-PI3K-Akt
signaling pathway. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 16:501–518. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Valastyan S, Reinhardt F, Benaich N,
Calogrias D, Szász AM, Wang ZC, Brock JE, Richardson AL and
Weinberg RA: A pleiotropically acting microRNA, miR-31, inhibits
breast cancer metastasis. Cell. 137:1032–1046. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Sossey-Alaoui K, Downs-Kelly E, Das M,
Izem L, Tubbs R and Plow EF: WAVE3, an actin remodeling protein, is
regulated by the metastasis suppressor microRNA, miR-31, during the
invasion-metastasis cascade. Int J Cancer. 129:1331–1343. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
146
|
Lin Y, Liu AY, Fan C, Zheng H, Li Y, Zhang
C, Wu S, Yu D, Huang Z, Liu F, et al: MicroRNA-33b inhibits breast
cancer metastasis by targeting HMGA2, SALL4 and Twist1. Sci Rep.
5:99952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Xu N, Li Z, Yu Z, Yan F, Liu Y, Lu X and
Yang W: MicroRNA-33b suppresses migration and invasion by targeting
c-Myc in osteosarcoma cells. PLoS One. 9:e1153002014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
He L, He X, Lim LP, de Stanchina E, Xuan
Z, Liang Y, Xue W, Zender L, Magnus J, Ridzon D, et al: A microRNA
component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature.
447:1130–1134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Bommer GT, Gerin I, Feng Y, Kaczorowski
AJ, Kuick R, Love RE, Zhai Y, Giordano TJ, Qin ZS, Moore BB, et al:
p53-mediated activation of miRNA34 candidate tumorsuppressor genes.
Curr Biol. 17:1298–1307. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Fujita Y, Kojima K, Hamada N, Ohhashi R,
Akao Y, Nozawa Y, Deguchi T and Ito M: Effects of miR-34a on cell
growth and chemoresistance in prostate cancer PC3 cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 377:114–119. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Leucci E, Cocco M, Onnis A, De Falco G,
van Cleef P, Bellan C, van Rijk A, Nyagol J, Byakika B, Lazzi S, et
al: MYC translocation-negative classical Burkitt lymphoma cases: An
alternative pathogenetic mechanism involving miRNA deregulation. J
Pathol. 216:440–450. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Saito Y, Nakaoka T and Saito H:
microRNA-34a as a therapeutic agent against human cancer. J Clin
Med. 4:1951–1959. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Wei JS, Song YK, Durinck S, Chen QR, Cheuk
AT, Tsang P, Zhang Q, Thiele CJ, Slack A, Shohet J, et al: The MYCN
oncogene is a direct target of miR-34a. Oncogene. 27:5204–5213.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M and Lowenstein CJ:
miR-34a repression of SIRT1 regulates apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:13421–13426. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Lodygin D, Tarasov V, Epanchintsev A,
Berking C, Knyazeva T, Körner H, Knyazev P, Diebold J and Hermeking
H: Inactivation of miR-34a by aberrant CpG methylation in multiple
types of cancer. Cell Cycle. 7:2591–2600. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Yang S, Li Y, Gao J, Zhang T, Li S, Luo A,
Chen H, Ding F, Wang X and Liu Z: MicroRNA-34 suppresses breast
cancer invasion and metastasis by directly targeting Fra-1.
Oncogene. 32:4294–4303. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
157
|
Yang P, Li QJ, Feng Y, Zhang Y, Markowitz
GJ, Ning S, Deng Y, Zhao J, Jiang S, Yuan Y, et al:
TGF-β-miR-34a-CCL22 signaling-induced Treg cell recruitment
promotes venous metastases of HBV-positive hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 22:291–303. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Liu C, Kelnar K, Liu B, Chen X,
Calhoun-Davis T, Li H, Patrawala L, Yan H, Jeter C, Honorio S, et
al: The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and
metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat Med. 17:211–215. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Krzeszinski JY, Wei W, Huynh H, Jin Z,
Wang X, Chang TC, Xie XJ, He L, Mangala LS, Lopez-Berestein G, et
al: miR-34a blocks osteoporosis and bone metastasis by inhibiting
osteoclastogenesis and Tgif2. Nature. 512:431–435. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Wang LG, Ni Y, Su BH, Mu XR, Shen HC and
Du JJ: MicroRNA-34b functions as a tumor suppressor and acts as a
nodal point in the feedback loop with Met. Int J Oncol. 42:957–962.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Yu Z, Kim J, He L, Creighton CJ, Gunaratne
PH, Hawkins SM and Matzuk MM: Functional analysis of miR-34c as a
putative tumor suppressor in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Biol
Reprod. 91:1132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Liu XY, Liu ZJ, He H, Zhang C and Wang YL:
MicroRNA-101-3p suppresses cell proliferation, invasion and
enhances chemotherapeutic sensitivity in salivary gland adenoid
cystic carcinoma by targeting Pim-1. Am J Cancer Res. 5:3015–3029.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Tsai WC, Hsu SD, Hsu CS, Lai TC, Chen SJ,
Shen R, Huang Y, Chen HC, Lee CH, Tsai TF, et al: MicroRNA-122
plays a critical role in liver homeostasis and
hepatocarcinogenesis. J Clin Invest. 122:2884–2897. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Taniguchi K, Sugito N, Kumazaki M,
Shinohara H, Yamada N, Nakagawa Y, Ito Y, Otsuki Y, Uno B, Uchiyama
K, et al: MicroRNA-124 inhibits cancer cell growth through
PTB1/PKM1/PKM2 feedback cascade in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett.
363:17–27. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Huang TC, Chang HY, Chen CY, Wu PY, Lee H,
Liao YF, Hsu WM, Huang HC and Juan HF: Silencing of miR-124 induces
neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cell differentiation, cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis through promoting AHR. FEBS Lett. 585:3582–3586. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Kato T, Enomoto A, Watanabe T, Haga H,
Ishida S, Kondo Y, Furukawa K, Urano T, Mii S, Weng L, et al:
TRIM27/MRTF-B-dependent integrin β1 expression defines leading
cells in cancer cell collectives. Cell Rep. 7:1156–1167. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Zheng F, Liao YJ, Cai MY, Liu YH, Liu TH,
Chen SP, Bian XW, Guan XY, Lin MC, Zeng YX, et al: The putative
tumour suppressor microRNA-124 modulates hepatocellular carcinoma
cell aggressiveness by repressing ROCK2 and EZH2. Gut. 61:278–289.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
168
|
Wang X, Wu Q, Xu B, Wang P, Fan W, Cai Y,
Gu X and Meng F: miR-124 exerts tumor suppressive functions on the
cell proliferation, motility and angiogenesis of bladder cancer by
fine-tuning UHRF1. FEBS J. 282:4376–4388. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Zhang C, Hu Y, Wan J and He H:
MicroRNA-124 suppresses the migration and invasion of osteosarcoma
cells via targeting ROR2-mediated non-canonical Wnt signaling.
Oncol Rep. 34:2195–2201. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Sun Y, Ai X, Shen S and Lu S:
NF-κB-mediated miR-124 suppresses metastasis of non-small-cell lung
cancer by targeting MYO10. Oncotarget. 6:8244–8254. 2015a.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
171
|
Sun Y, Luo ZM, Guo XM, Su DF and Liu X: An
updated role of microRNA-124 in central nervous system disorders: A
review. Front Cell Neurosci. 9:1932015b. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
172
|
Chen Z, Liu S, Tian L, Wu M, Ai F, Tang W,
Zhao L, Ding J, Zhang L and Tang A: miR-124 and miR-506 inhibit
colorectal cancer progression by targeting DNMT3B and DNMT1.
Oncotarget. 6:38139–38150. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Zhang Y, Li H, Han J and Zhang Y:
Down-regulation of microRNA-124 is correlated with tumor metastasis
and poor prognosis in patients with lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:1967–1972. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Cowden Dahl KD, Dahl R, Kruichak JN and
Hudson LG: The epidermal growth factor receptor responsive miR-125a
represses mesenchymal morphology in ovarian cancer cells.
Neoplasia. 11:1208–1215. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Fan Z, Cui H, Xu X, Lin Z, Zhang X, Kang
L, Han B, Meng J, Yan Z, Yan X, et al: MiR-125a suppresses tumor
growth, invasion and metastasis in cervical cancer by targeting
STAT3. Oncotarget. 6:25266–25280. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Sun Y, Bai Y, Zhang F, Wang Y, Guo Y and
Guo L: miR-126 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cells
proliferation by targeting EGFL7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
391:1483–1489. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
177
|
Xiong Y, Kotian S, Zeiger MA, Zhang L and
Kebebew E: miR-126-3p inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth and
metastasis, and is associated with aggressive thyroid cancer. PLoS
One. 10:e01304962015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Wang CZ, Yuan P and Li Y: MiR-126
regulated breast cancer cell invasion by targeting ADAM9. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:6547–6553. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Wen Q, Zhao J, Bai L, Wang T, Zhang H and
Ma Q: miR-126 inhibits papillary thyroid carcinoma growth by
targeting LRP6. Oncol Rep. 34:2202–2210. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Jiang L, He A, Zhang Q and Tao C: miR-126
inhibits cell growth, invasion, and migration of osteosarcoma cells
by downregulating ADAM-9. Tumour Biol. 35:12645–12654. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Du C, Lv Z, Cao L, Ding C, Gyabaah OA, Xie
H, Zhou L, Wu J and Zheng S: MiR-126-3p suppresses tumor metastasis
and angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting LRP6 and
PIK3R2. J Transl Med. 12:2592014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Zhang Y, Wang X, Xu B, Wang B, Wang Z,
Liang Y, Zhou J, Hu J and Jiang B: Epigenetic silencing of miR-126
contributes to tumor invasion and angiogenesis in colorectal
cancer. Oncol Rep. 30:1976–1984. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Png KJ, Halberg N, Yoshida M and Tavazoie
SF: A microRNA regulon that mediates endothelial recruitment and
metastasis by cancer cells. Nature. 481:190–194. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Shi ZM, Wang J, Yan Z, You YP, Li CY, Qian
X, Yin Y, Zhao P, Wang YY, Wang XF, et al: MiR-128 inhibits tumor
growth and angiogenesis by targeting p70S6K1. PLoS One.
7:e327092012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Wuchty S, Arjona D, Li A, Kotliarov Y,
Walling J, Ahn S, Zhang A, Maric D, Anolik R, Zenklusen JC, et al:
Prediction of associations between microRNAs and gene expression in
glioma biology. PLoS One. 6:e146812011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Zhang Y, Chao T, Li R, Liu W, Chen Y, Yan
X, Gong Y, Yin B, Liu W, Qiang B, et al: MicroRNA-128 inhibits
glioma cells proliferation by targeting transcription factor E2F3a.
J Mol Med Berl. 87:43–51. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
187
|
Huang CY, Huang XP, Zhu JY, Chen ZG, Li
XJ, Zhang XH, Huang S, He JB, Lian F, Zhao YN, et al: miR-128-3p
suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation by regulating
PIK3R1 and is correlated with the prognosis of HCC patients. Oncol
Rep. 33:2889–2898. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Kano M, Seki N, Kikkawa N, Fujimura L,
Hoshino I, Akutsu Y, Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Nakagawa M and
Matsubara H: miR-145, miR-133a and miR-133b: Tumor-suppressive
miRNAs target FSCN1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 127:2804–2814. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
189
|
Kroiss A, Vincent S, Decaussin-Petrucci M,
Meugnier E, Viallet J, Ruffion A, Chalmel F, Samarut J and Allioli
N: Androgen-regulated microRNA-135a decreases prostate cancer cell
migration and invasion through downregulating ROCK1 and ROCK2.
Oncogene. 34:2846–2855. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
190
|
Liang L, Li X, Zhang X, Lv Z, He G, Zhao
W, Ren X, Li Y, Bian X, Liao W, et al: MicroRNA-137, an HMGA1
target, suppresses colorectal cancer cell invasion and metastasis
in mice by directly targeting FMNL2. Gastroenterology.
144:624–635.e4. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
191
|
Xia H, Sun S, Wang B, Wang T, Liang C, Li
G, Huang C, Qi D and Chu X: miR-143 inhibits NSCLC cell growth and
metastasis by targeting Limk1. Int J Mol Sci. 15:11973–11983. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Gao P, Xing AY, Zhou GY, Zhang TG, Zhang
JP, Gao C, Li H and Shi DB: The molecular mechanism of microRNA-145
to suppress invasion-metastasis cascade in gastric cancer.
Oncogene. 32:491–501. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
193
|
Zhang H, Pu J, Qi T, Qi M, Yang C, Li S,
Huang K, Zheng L and Tong Q: MicroRNA-145 inhibits the growth,
invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis of neuroblastoma cells
through targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 2 alpha. Oncogene.
33:387–397. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
194
|
Bhaumik D, Scott GK, Schokrpur S, Patil
CK, Campisi J and Benz CC: Expression of microRNA-146 suppresses
NF-kappaB activity with reduction of metastatic potential in breast
cancer cells. Oncogene. 27:5643–5647. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Lin SL, Chiang A, Chang D and Ying SY:
Loss of miR-146a function in hormone-refractory prostate cancer.
RNA. 14:417–424. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Zhang JP, Zeng C, Xu L, Gong J, Fang JH
and Zhuang SM: MicroRNA-148a suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and metastasis of hepatoma cells by targeting Met/Snail
signaling. Oncogene. 33:4069–4076. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
197
|
Cimino D, De Pittà C, Orso F, Zampini M,
Casara S, Penna E, Quaglino E, Forni M, Damasco C, Pinatel E, et
al: miR148b is a major coordinator of breast cancer progression in
a relapse-associated microRNA signature by targeting ITGA5, ROCK1,
PIK3CA, NRAS, and CSF1. FASEB J. 27:1223–1235. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
198
|
Bischoff A, Huck B, Keller B, Strotbek M,
Schmid S, Boerries M, Busch H, Müller D and Olayioye MA: miR149
functions as a tumor suppressor by controlling breast epithelial
cell migration and invasion. Cancer Res. 74:5256–5265. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Visone R, Veronese A, Rassenti LZ, Balatti
V, Pearl DK, Acunzo M, Volinia S, Taccioli C, Kipps TJ and Croce
CM: miR-181b is a biomarker of disease progression in chronic
lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 118:3072–3079. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Kouri FM, Hurley LA, Daniel WL, Day ES,
Hua Y, Hao L, Peng CY, Merkel TJ, Queisser MA, Ritner C, et al:
miR-182 integrates apoptosis, growth, and differentiation programs
in glioblastoma. Genes Dev. 29:732–745. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Leivonen SK, Rokka A, Ostling P, Kohonen
P, Corthals GL, Kallioniemi O and Perälä M: Identification of
miR-193b targets in breast cancer cells and systems biological
analysis of their functional impact. Mol Cell Proteomics.
10:M110.0053222011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Yang H, Liu P, Zhang J, Peng X, Lu Z, Yu
S, Meng Y, Tong WM and Chen J: Long noncoding RNA MIR31HG exhibits
oncogenic property in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and is
negatively regulated by miR-193b. Oncogene. Nov 9–2015.(Epub ahead
of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
203
|
Tan S, Li R, Ding K, Lobie PE and Zhu T:
miR-198 inhibits migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma
cells by targeting the HGF/c-MET pathway. FEBS Lett. 585:2229–2234.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Bao W, Wang HH, Tian FJ, He XY, Qiu MT,
Wang JY, Zhang HJ, Wang LH and Wan XP: A TrkB-STAT3-miR-204-5p
regulatory circuitry controls proliferation and invasion of
endometrial carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer. 12:1552013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Xia Z, Liu F, Zhang J and Liu L: Decreased
expression of MiRNA-204-5p contributes to glioma progression and
promotes glioma cell growth, migration and invasion. PLoS One.
10:e01323992015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Gandellini P, Folini M, Longoni N, Pennati
M, Binda M, Colecchia M, Salvioni R, Supino R, Moretti R, Limonta
P, et al: miR-205 exerts tumor-suppressive functions in human
prostate through down-regulation of protein kinase Cepsilon. Cancer
Res. 69:2287–2295. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Chen QY, Jiao DM, Yan L, Wu YQ, Hu HZ,
Song J, Yan J, Wu LJ, Xu LQ and Shi JG: Comprehensive gene and
microRNA expression profiling reveals miR-206 inhibits MET in lung
cancer metastasis. Mol Biosyst. 11:2290–2302. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Chen DL, Wang ZQ, Zeng ZL, Wu WJ, Zhang
DS, Luo HY, Wang F, Qiu MZ, Wang DS, Ren C, et al: Identification
of microRNA-214 as a negative regulator of colorectal cancer liver
metastasis by way of regulation of fibroblast growth factor
receptor 1 expression. Hepatology. 60:598–609. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Tie J, Pan Y, Zhao L, Wu K, Liu J, Sun S,
Guo X, Wang B, Gang Y, Zhang Y, et al: MiR-218 inhibits invasion
and metastasis of gastric cancer by targeting the Robo1 receptor.
PLoS Genet. 6:e10008792010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Wei JJ, Wu X, Peng Y, Shi G, Basturk O,
Yang X, Daniels G, Osman I, Ouyang J, Hernando E, et al: Regulation
of HMGA1 expression by microRNA-296 affects prostate cancer growth
and invasion. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1297–1305. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
211
|
Wang L, Yao J, Shi X, Hu L, Li Z, Song T
and Huang C: MicroRNA-302b suppresses cell proliferation by
targeting EGFR in human hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells.
BMC Cancer. 13:4482013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Tavazoie SF, Alarcón C, Oskarsson T, Padua
D, Wang Q, Bos PD, Gerald WL and Massagué J: Endogenous human
microRNAs that suppress breast cancer metastasis. Nature.
451:147–152. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Hurst DR, Edmonds MD and Welch DR:
Metastamir: The field of metastasis-regulatory microRNA is
spreading. Cancer Res. 69:7495–7498. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Li KK, Pang JC, Lau KM, Zhou L, Mao Y,
Wang Y, Poon WS and Ng HK: MiR-383 is downregulated in
medulloblastoma and targets peroxiredoxin 3 (PRDX3). Brain Pathol.
23:413–425. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
215
|
Bou Kheir T, Futoma-Kazmierczak E,
Jacobsen A, Krogh A, Bardram L, Hother C, Grønbæk K, Federspiel B,
Lund AH and Friis-Hansen L: miR-449 inhibits cell proliferation and
is down-regulated in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 10:292011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Luo W, Huang B, Li Z, Li H, Sun L, Zhang
Q, Qiu X and Wang E: MicroRNA-449a is downregulated in non-small
cell lung cancer and inhibits migration and invasion by targeting
c-Met. PLoS One. 8:e647592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Okamoto K, Ishiguro T, Midorikawa Y, Ohata
H, Izumiya M, Tsuchiya N, Sato A, Sakai H and Nakagama H: miR-493
induction during carcinogenesis blocks metastatic settlement of
colon cancer cells in liver. EMBO J. 31:1752–1763. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Gu Y, Cheng Y, Song Y, Zhang Z, Deng M,
Wang C, Zheng G and He Z: MicroRNA-493 suppresses tumor growth,
invasion and metastasis of lung cancer by regulating E2F1. PLoS
One. 9:e1026022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Sakai H1, Sato A, Aihara Y, Ikarashi Y,
Midorikawa Y, Kracht M, Nakagama H and Okamoto K: MKK7 mediates
miR-493-dependent suppression of liver metastasis of colon cancer
cells. Cancer Sci. 105:425–430. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Kikkawa N, Kinoshita T, Nohata N, Hanazawa
T, Yamamoto N, Fukumoto I, Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Nakagawa M,
Okamoto Y, et al: microRNA-504 inhibits cancer cell proliferation
via targeting CDK6 in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J
Oncol. 44:2085–2092. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Keklikoglou I, Koerner C, Schmidt C, Zhang
JD, Heckmann D, Shavinskaya A, Allgayer H, Gückel B, Fehm T,
Schneeweiss A, et al: MicroRNA-520/373 family functions as a tumor
suppressor in estrogen receptor negative breast cancer by targeting
NF-κB and TGF-β signaling pathways. Oncogene. 31:4150–4163. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
222
|
Song B, Ji W, Guo S, Liu A, Jing W, Shao
C, Li G and Jin G: miR-545 inhibited pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma growth by targeting RIG-I. FEBS Lett. 588:4375–4381.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Bowen D, Zhe W, Xin Z, Shipeng F, Guoxin
W, Jianxing H and Zhang B: MicroRNA-545 suppresses cell
proliferation by targeting cyclin D1 and CDK4 in lung cancer cells.
PLoS. 9:880222014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
224
|
Calin GA, Ferracin M, Cimmino A, Di Leva
G, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Iorio MV, Visone R, Sever NI, Fabbri M, et
al: A MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression
in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 353:1793–1801. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A,
Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M,
et al: MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 65:7065–7070. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Iorio MV, Visone R, Di Leva G, Donati V,
Petrocca F, Casalini P, Taccioli C, Volinia S, Liu CG, Alder H, et
al: MicroRNA signatures in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
67:8699–8707. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Porkka KP, Pfeiffer MJ, Waltering KK,
Vessella RL, Tammela TL and Visakorpi T: MicroRNA expression
profiling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 67:6130–6135. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal
K, Jacob ST and Patel T: MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the
PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer.
Gastroenterology. 133:647–658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Zhu S, Si ML, Wu H and Mo YY: MicroRNA-21
targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J Biol
Chem. 282:14328–14336. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A,
Lindow M, Krogh A and Lund AH: Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is
an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 283:1026–1033. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
232
|
Garzon R, Volinia S, Liu CG,
Fernandez-Cymering C, Palumbo T, Pichiorri F, Fabbri M, Coombes K,
Alder H, Nakamura T, et al: MicroRNA signatures associated with
cytogenetics and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood.
111:3183–3189. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
233
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
White NM, Fatoohi E, Metias M, Jung K,
Stephan C and Yousef GM: Metastamirs: A stepping stone towards
improved cancer management. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 8:75–84. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
235
|
Zhou L, Liu F, Wang X and Ouyang G: The
roles of microRNAs in the regulation of tumor metastasis. Cell
Biosci. 5:322015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
Wang XH, Cai P, Wang MH and Wang Z:
microRNA 25 promotes osteosarcoma cell proliferation by targeting
the cell cycle inhibitor p27. Mol Med Rep. 10:855–859.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
237
|
Siu MK, Tsai YC, Chang YS, Yin JJ, Suau F,
Chen WY and Liu YN: Transforming growth factor-β promotes prostate
bone metastasis through induction of microRNA-96 and activation of
the mTOR pathway. Oncogene. 34:4767–4776. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
238
|
Xia X, Li Y, Wang W, Tang F, Tan J, Sun L,
Li Q, Sun L, Tang B and He S: MicroRNA-1908 functions as a
glioblastoma oncogene by suppressing PTEN tumor suppressor pathway.
Mol Cancer. 14:1542015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
239
|
Sachdeva M, Mito JK, Lee CL, Zhang M, Li
Z, Dodd RD, Cason D, Luo L, Ma Y, Van Mater D, et al: MicroRNA-182
drives metastasis of primary sarcomas by targeting multiple genes.
J Clin Invest. 124:4305–4319. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
240
|
Tian Y, Luo A, Cai Y, Su Q, Ding F, Chen H
and Liu Z: MicroRNA-10b promotes migration and invasion through
KLF4 in human esophageal cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem.
285:7986–7994. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
241
|
Wang YY, Ye ZY, Zhao ZS, Li L, Wang YX,
Tao HQ, Wang HJ and He XJ: Clinicopathologic significance of
miR-10b expression in gastric carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 44:1278–1285.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM and Kosik KS:
MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells.
Cancer Res. 65:6029–6033. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
243
|
Liu W, Zabirnyk O, Wang H, Shiao YH,
Nickerson ML, Khalil S, Anderson LM, Perantoni AO and Phang JM:
miR-23b targets proline oxidase, a novel tumor suppressor protein
in renal cancer. Oncogene. 29:4914–4924. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
244
|
Fletcher CE, Dart DA, Sita-Lumsden A,
Cheng H, Rennie PS and Bevan CL: Androgen-regulated processing of
the oncomir miR-27a, which targets Prohibitin in prostate cancer.
Hum Mol Genet. 21:3112–3127. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
245
|
Ng WL, Yan D, Zhang X, Mo YY and Wang Y:
Over-expression of miR-100 is responsible for the low-expression of
ATM in the human glioma cell line: M059J. DNA Repair (Amst).
9:1170–1175. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
246
|
Zheng YS, Zhang H, Zhang XJ, Feng DD, Luo
XQ, Zeng CW, Lin KY, Zhou H, Qu LH, Zhang P, et al: MiR-100
regulates cell differentiation and survival by targeting RBSP3, a
phosphatase-like tumor suppressor in acute myeloid leukemia.
Oncogene. 31:80–92. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
247
|
Knackmuss U, Lindner SE, Aneichyk T,
Kotkamp B, Knust Z, Villunger A and Herzog S: MAP3K11 is a tumor
suppressor targeted by the oncomiR miR-125b in early B cells. Cell
Death Differ. 23:242–252. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
248
|
Park JK, Henry JC, Jiang J, Esau C, Gusev
Y, Lerner MR, Postier RG, Brackett DJ and Schmittgen TD: miR-132
and miR-212 are increased in pancreatic cancer and target the
retinoblastoma tumor suppressor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
406:518–523. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
249
|
Kong W, He L, Coppola M, Guo J, Esposito
NN, Coppola D and Cheng JQ: MicroRNA-155 regulates cell survival,
growth, and chemosensitivity by targeting FOXO3a in breast cancer.
J Biol Chem. 285:17869–17879. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
250
|
Jiang S, Zhang HW, Lu MH, He XH, Li Y, Gu
H, Liu MF and Wang ED: MicroRNA-155 functions as an OncomiR in
breast cancer by targeting the suppressor of cytokine signaling 1
gene. Cancer Res. 70:3119–3127. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
251
|
Czyzyk-Krzeska MF and Zhang X: MiR-155 at
the heart of oncogenic pathways. Oncogene. 33:677–678. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
252
|
Wang J and Wu J: Role of miR-155 in breast
cancer. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 17:2350–2355. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
253
|
Ling N, Gu J, Lei Z, Li M, Zhao J, Zhang
HT and Li X: microRNA-155 regulates cell proliferation and invasion
by targeting FOXO3a in glioma. Oncol Rep. 30:2111–2118.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
254
|
Musilova K and Mraz M: MicroRNAs in B-cell
lymphomas: How a complex biology gets more complex. Leukemia.
29:1004–1017. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
255
|
Fontana L, Fiori ME, Albini S, Cifaldi L,
Giovinazzi S, Forloni M, Boldrini R, Donfrancesco A, Federici V,
Giacomini P, et al: AntagomiR-17-5p abolishes the growth of
therapy-resistant neuroblastoma through p21 and BIM. PLoS One.
3:e22362008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
256
|
Segura MF, Hanniford D, Menendez S, Reavie
L, Zou X, Alvarez-Diaz S, Zakrzewski J, Blochin E, Rose A,
Bogunovic D, et al: Aberrant miR-182 expression promotes melanoma
metastasis by repressing FOXO3 and microphthalmia-associated
transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:1814–1819. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
257
|
Yang H, Kong W, He L, Zhao JJ, O'Donnell
JD, Wang J, Wenham RM, Coppola D, Kruk PA, Nicosia SV, et al:
MicroRNA expression profiling in human ovarian cancer: miR-214
induces cell survival and cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN.
Cancer Res. 68:425–433. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
258
|
Zhang CZ, Zhang JX, Zhang AL, Shi ZD, Han
L, Jia ZF, Yang WD, Wang GX, Jiang T, You YP, et al: MiR-221 and
miR-222 target PUMA to induce cell survival in glioblastoma. Mol
Cancer. 9:2292010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
259
|
Garofalo M, Quintavalle C, Romano G, Croce
CM and Condorelli G: miR221/222 in cancer: Their role in tumor
progression and response to therapy. Curr Mol Med. 12:27–33. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
260
|
Quintavalle C, Garofalo M, Zanca C, Romano
G, Iaboni M, del Basso De Caro M, Martinez-Montero JC, Incoronato
M, Nuovo G, Croce CM, et al: miR-221/222 overexpession in human
glioblastoma increases invasiveness by targeting the protein
phosphate PTPμ. Oncogene. 31:858–868. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
261
|
Chen WX, Hu Q, Qiu MT, Zhong SL, Xu JJ,
Tang JH and Zhao JH: miR-221/222: Promising biomarkers for breast
cancer. Tumour Biol. 34:1361–1370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
262
|
Matsuzaki J and Suzuki H: Role of
MicroRNAs-221/222 in digestive systems. J Clin Med. 4:1566–1577.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
263
|
Würdinger T, Tannous BA, Saydam O, Skog J,
Grau S, Soutschek J, Weissleder R, Breakefield XO and Krichevsky
AM: miR-296 regulates growth factor receptor overexpression in
angiogenic endothelial cells. Cancer Cell. 14:382–393. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
264
|
Shi W, Gerster K, Alajez NM, Tsang J,
Waldron L, Pintilie M, Hui AB, Sykes J, P'ng C, Miller N, et al:
MicroRNA-301 mediates proliferation and invasion in human breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 71:2926–2937. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
265
|
Voorhoeve PM, le Sage C, Schrier M, Gillis
AJ, Stoop H, Nagel R, Liu YP, van Duijse J, Drost J, Griekspoor A,
et al: A genetic screen implicates miRNA-372 and miRNA-373 as
oncogenes in testicular germ cell tumors. Adv Exp Med Biol.
604:17–46. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
266
|
Xu Y, Jin J, Liu Y, Huang Z, Deng Y, You
T, Zhou T, Si J and Zhuo W: Snail-regulated MiR-375 inhibits
migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by targeting JAK2.
PLoS One. 9:e995162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
267
|
Lee DY, Deng Z, Wang CH and Yang BB:
MicroRNA-378 promotes cell survival, tumor growth, and angiogenesis
by targeting SuFu and Fus-1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:20350–20355. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
268
|
Tu K, Liu Z, Yao B, Han S and Yang W:
MicroRNA-519a promotes tumor growth by targeting PTEN/PI3K/AKT
signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 48:965–974.
2016.
|
|
269
|
Shao J, Cao J, Liu Y, Mei H, Zhang Y and
Xu W: MicroRNA-519a promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis
of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting FOXF2. FEBS Open
Bio. 5:893–899. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
270
|
Ward A, Shukla K, Balwierz A, Soons Z,
König R, Sahin O and Wiemann S: MicroRNA-519a is a novel oncomir
conferring tamoxifen resistance by targeting a network of
tumour-suppressor genes in ER+ breast cancer. J Pathol.
233:368–379. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
271
|
Tsang WP, Ng EK, Ng SS, Jin H, Yu J, Sung
JJ and Kwok TT: Oncofetal H19-derived miR-675 regulates tumor
suppressor RB in human colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis.
31:350–358. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
272
|
Ma L, Young J, Prabhala H, Pan E, Mestdagh
P, Muth D, Teruya-Feldstein J, Reinhardt F, Onder TT, Valastyan S,
et al: miR-9, a MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin
and cancer metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 12:247–256. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
273
|
Chen D, Sun Y, Wei Y, Zhang P, Rezaeian
AH, Teruya-Feldstein J, Gupta S, Liang H, Lin HK, Hung MC, et al:
LIFR is a breast cancer metastasis suppressor upstream of the
Hippo-YAP pathway and a prognostic marker. Nat Med. 18:1511–1517.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
274
|
White RA, Neiman JM, Reddi A, Han G,
Birlea S, Mitra D, Dionne L, Fernandez P, Murao K, Bian L, et al:
Epithelial stem cell mutations that promote squamous cell carcinoma
metastasis. J Clin Invest. 123:4390–4404. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
275
|
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J and Weinberg RA:
Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast
cancer. Nature. 449:682–688. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
276
|
Lin J, Teo S, Lam DH, Jeyaseelan K and
Wang S: MicroRNA-10b pleiotropically regulates invasion,
angiogenicity and apoptosis of tumor cells resembling mesenchymal
subtype of glioblastoma multiforme. Cell Death Dis. 3:e3982012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
277
|
Zhang WL, Zhang JH, Wu XZ, Yan T and Lv W:
miR-15b promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by inhibiting
SMURF2 in pancreatic cancer. Int J Oncol. 47:1043–1053.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
278
|
Wu Q, Yang Z, An Y, Hu H, Yin J, Zhang P,
Nie Y, Wu K, Shi Y and Fan D: MiR-19a/b modulate the metastasis of
gastric cancer cells by targeting the tumour suppressor MXD1. Cell
Death Dis. 5:e11442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
279
|
Chang Y, Liu C, Yang J, Liu G, Feng F,
Tang J, Hu L, Li L, Jiang F, Chen C, et al: MiR-20a triggers
metastasis of gallbladder carcinoma. J Hepatol. 59:518–527. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
280
|
Zhao S, Yao D, Chen J, Ding N and Ren F:
MiR-20a promotes cervical cancer proliferation and metastasis in
vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 10:e01209052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
281
|
Dean ZS, Riahi R and Wong PK:
Spatiotemporal dynamics of microRNA during epithelial collective
cell migration. Biomaterials. 37:156–163. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
282
|
Peacock O, Lee AC, Cameron F, Tarbox R,
Vafadar-Isfahani N, Tufarelli C and Lund JN: Inflammation and
MiR-21 pathways functionally interact to downregulate PDCD4 in
colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 9:e1102672014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
283
|
Xu J, Zhang W, Lv Q and Zhu D:
Overexpression of miR-21 promotes the proliferation and migration
of cervical cancer cells via the inhibition of PTEN. Oncol Rep.
33:3108–3116. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
284
|
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA,
Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S and Allgayer H: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21)
post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and
stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal
cancer. Oncogene. 27:2128–2136. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
285
|
Melnik BC: MiR-21: An environmental driver
of malignant melanoma? J Transl Med. 13:2022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
286
|
Zhou W, Fong MY, Min Y, Somlo G, Liu L,
Palomares MR, Yu Y, Chow A, O'Connor ST, Chin AR, et al:
Cancer-secreted miR-105 destroys vascular endothelial barriers to
promote metastasis. Cancer Cell. 25:501–515. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
287
|
Fong MY, Zhou W, Liu L, Alontaga AY,
Chandra M, Ashby J, Chow A, O'Connor ST, Li S, Chin AR, et al:
Breast-cancer-secreted miR-122 reprograms glucose metabolism in
premetastatic niche to promote metastasis. Nat Cell Biol.
17:183–194. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
288
|
Lin CW, Chang YL, Chang YC, Lin JC, Chen
CC, Pan SH, Wu CT, Chen HY, Yang SC, Hong TM, et al: MicroRNA-135b
promotes lung cancer metastasis by regulating multiple targets in
the Hippo pathway and LZTS1. Nat Commun. 4:18772013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
289
|
Taylor MA, Sossey-Alaoui K, Thompson CL,
Danielpour D and Schiemann WP: TGF-β upregulates miR-181a
expression to promote breast cancer metastasis. J Clin Invest.
123:150–163. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
290
|
Qiu Y, Luo X, Kan T, Zhang Y, Yu W, Wei Y,
Shen N, Yi B and Jiang X: TGF-β upregulates miR-182 expression to
promote gallbladder cancer metastasis by targeting CADM1. Mol
Biosyst. 10:679–685. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
291
|
Ren LH, Chen WX, Li S, He XY, Zhang ZM, Li
M, Cao RS, Hao B, Zhang HJ, Qiu HQ, et al: MicroRNA-183 promotes
proliferation and invasion in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma
by targeting programmed cell death 4. Br J Cancer. 111:2003–2013.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
292
|
Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G and Kang Y: The
miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin
transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem.
283:14910–14914. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
293
|
Korpal M, Ell BJ, Buffa FM, Ibrahim T,
Blanco MA, Celià-Terrassa T, Mercatali L, Khan Z, Goodarzi H, Hua
Y, et al: Direct targeting of Sec23a by miR-200s influences cancer
cell secretome and promotes metastatic colonization. Nat Med.
17:1101–1108. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
294
|
Park SM, Gaur AB, Lengyel E and Peter ME:
The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer
cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes
Dev. 22:894–907. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
295
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry
SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, Vadas MA, Khew-Goodall Y and Goodall GJ:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
296
|
Penna E, Orso F, Cimino D, Tenaglia E,
Lembo A, Quaglino E, Poliseno L, Haimovic A, Osella-Abate S, De
Pittà C, et al: microRNA-214 contributes to melanoma tumour
progression through suppression of TFAP2C. EMBO J. 30:1990–2007.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
297
|
Penna E, Orso F, Cimino D, Vercellino I,
Grassi E, Quaglino E, Turco E and Taverna D: miR-214 coordinates
melanoma progression by upregulating ALCAM through TFAP2 and
miR-148b downmodulation. Cancer Res. 73:4098–4111. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
298
|
Long H, Wang Z, Chen J, Xiang T, Li Q,
Diao X and Zhu B: microRNA-214 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma by targeting the
suppressor-of-fused protein (Sufu). Oncotarget. 6:38705–38718.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
299
|
Liu X, Chen Q, Yan J, Wang Y, Zhu C, Chen
C, Zhao X, Xu M, Sun Q, Deng R, et al: MiRNA-296-3p-ICAM-1 axis
promotes metastasis of prostate cancer by possible enhancing
survival of natural killer cell-resistant circulating tumour cells.
Cell Death Dis. 4:e9282013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
300
|
Vaira V, Faversani A, Martin NM, Garlick
DS, Ferrero S, Nosotti M, Kissil JL, Bosari S and Altieri DC:
Regulation of lung cancer metastasis by Klf4-Numb-like signaling.
Cancer Res. 73:2695–2705. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
301
|
Ni F, Zhao H, Cui H, Wu Z, Chen L, Hu Z,
Guo C, Liu Y, Chen Z, Wang X, et al: MicroRNA-362-5p promotes tumor
growth and metastasis by targeting CYLD in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 356:809–818. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
302
|
Chen D, Dang BL, Huang JZ, Chen M, Wu D,
Xu ML, Li R and Yan GR: MiR-373 drives the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis via the
miR-373-TXNIP-HIF1α-TWIST signaling axis in breast cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:32701–32712. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
303
|
Lu S, Zhu Q, Zhang Y, Song W, Wilson MJ
and Liu P: Dual-functions of miR-373 and miR-520c by differently
regulating the activities of MMP2 and MMP9. J Cell Physiol.
230:1862–1870. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
304
|
Glover AR, Zhao JT, Gill AJ, Weiss J,
Mugridge N, Kim E, Feeney AL, Ip JC, Reid G, Clarke S, et al:
MicroRNA-7 as a tumor suppressor and novel therapeutic for
adrenocortical carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:36675–36688.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
305
|
Babae N, Bourajjaj M, Liu Y, Van Beijnum
JR, Cerisoli F, Scaria PV, Verheul M, Van Berkel MP, Pieters EH,
Van Haastert RJ, et al: Systemic miRNA-7 delivery inhibits tumor
angiogenesis and growth in murine xenograft glioblastoma.
Oncotarget. 5:6687–6700. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
306
|
Wang W, Dai LX, Zhang S, Yang Y, Yan N,
Fan P, Dai L, Tian HW, Cheng L, Zhang XM, et al: Regulation of
epidermal growth factor receptor signaling by plasmid-based
microRNA-7 inhibits human malignant gliomas growth and metastasis
in vivo. Neoplasma. 60:274–283. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
307
|
Cortez MA, Valdecanas D, Zhang X, Zhan Y,
Bhardwaj V, Calin GA, Komaki R, Giri DK, Quini CC, Wolfe T, et al:
Therapeutic delivery of miR-200c enhances radiosensitivity in lung
cancer. Mol Ther. 22:1494–1503. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
308
|
Wu X, Liu T, Fang O, Dong W, Zhang F,
Leach L, Hu X and Luo Z: MicroRNA-708-5p acts as a therapeutic
agent against metastatic lung cancer. Oncotarget. 7:2417–2432.
2016.
|
|
309
|
Ge YF, Sun J, Jin CJ, Cao BQ, Jiang ZF and
Shao JF: AntagomiR-27a targets FOXO3a in glioblastoma and
suppresses U87 cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 14:963–968. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
310
|
Shu M, Zheng X, Wu S, Lu H, Leng T, Zhu W,
Zhou Y, Ou Y, Lin X, Lin Y, et al: Targeting oncogenic miR-335
inhibits growth and invasion of malignant astrocytoma cells. Mol
Cancer. 10:592011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
311
|
Rather MI, Nagashri MN, Swamy SS, Gopinath
KS and Kumar A: Oncogenic microRNA-155 down-regulates tumor
suppressor CDC73 and promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma cell
proliferation: Implications for cancer therapeutics. J Biol Chem.
288:608–618. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
312
|
Haug BH, Henriksen JR, Buechner J, Geerts
D, Tømte E, Kogner P, Martinsson T, Flægstad T, Sveinbjørnsson B
and Einvik C: MYCN-regulated miRNA-92 inhibits secretion of the
tumor suppressor DICKKOPF-3 (DKK3) in neuroblastoma.
Carcinogenesis. 32:1005–1012. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
313
|
Tang H, Liu X, Wang Z, She X, Zeng X, Deng
M, Liao Q, Guo X, Wang R, Li X, et al: Interaction of hsa-miR-381
and glioma suppressor LRRC4 is involved in glioma growth. Brain
Res. 1390:21–32. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
314
|
Ma L, Reinhardt F, Pan E, Soutschek J,
Bhat B, Marcusson EG, Teruya-Feldstein J, Bell GW and Weinberg RA:
Therapeutic silencing of miR-10b inhibits metastasis in a mouse
mammary tumor model. Nat Biotechnol. 28:341–347. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
315
|
Mercatelli N, Coppola V, Bonci D, Miele F,
Costantini A, Guadagnoli M, Bonanno E, Muto G, Frajese GV, De Maria
R, et al: The inhibition of the highly expressed miR-221 and
miR-222 impairs the growth of prostate carcinoma xenografts in
mice. PLoS One. 3:e40292008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
316
|
Zhao Y, Zhao L, Ischenko I, Bao Q, Schwarz
B, Nieß H, Wang Y, Renner A, Mysliwietz J, Jauch KW, et al:
Antisense inhibition of microRNA-21 and microRNA-221 in
tumor-initiating stem-like cells modulates tumorigenesis,
metastasis, and chemotherapy resistance in pancreatic cancer.
Target Oncol. 10:535–548. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
317
|
Wagenaar TR, Zabludoff S, Ahn SM, Allerson
C, Arlt H, Baffa R, Cao H, Davis S, Garcia-Echeverria C, Gaur R, et
al: Anti-miR-21 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma growth via
broad transcriptional network deregulation. Mol Cancer Res.
13:1009–1021. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
318
|
Fabani MM, Abreu-Goodger C, Williams D,
Lyons PA, Torres AG, Smith KG, Enright AJ, Gait MJ and Vigorito E:
Efficient inhibition of miR-155 function in vivo by peptide nucleic
acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 38:4466–4475. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
319
|
Brognara E, Fabbri E, Aimi F, Manicardi A,
Bianchi N, Finotti A, Breveglieri G, Borgatti M, Corradini R,
Marchelli R, et al: Peptide nucleic acids targeting miR-221
modulate p27Kip1 expression in breast cancer MDA-MB-231
cells. Int J Oncol. 41:2119–2127. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
320
|
Yan LX, Wu QN, Zhang Y, Li YY, Liao DZ,
Hou JH, Fu J, Zeng MS, Yun JP, Wu QL, et al: Knockdown of miR-21 in
human breast cancer cell lines inhibits proliferation, in vitro
migration and in vivo tumor growth. Breast Cancer Res. 13:R22011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
321
|
Zhang J and Ma L: MicroRNA control of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 31:653–662. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
322
|
Zaravinos A, Radojicic J, Lambrou GI,
Volanis D, Delakas D, Stathopoulos EN and Spandidos DA: Expression
of miRNAs involved in angiogenesis, tumor cell proliferation, tumor
suppressor inhibition, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
activation of metastasis in bladder cancer. J Urol. 188:615–623.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
323
|
Kiesslich T, Pichler M and Neureiter D:
Epigenetic control of epithelial-mesenchymal-transition in human
cancer. Mol Clin Oncol. 1:3–11. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
324
|
Lei C, Wang Y, Huang Y, Yu H, Huang Y, Wu
L and Huang L: Up-regulated miR155 reverses the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by EGF and increases
chemo-sensitivity to cisplatin in human Caski cervical cancer
cells. PLoS One. 7:e523102012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
325
|
Koutsaki M, Spandidos DA and Zaravinos A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-associated miRNAs in ovarian
carcinoma, with highlight on the miR-200 family: Prognostic value
and prospective role in ovarian cancer therapeutics. Cancer Lett.
351:173–181. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
326
|
Gao H, Teng C, Huang W, Peng J and Wang C:
SOX2 promotes the epithelial to mesenchymal transition of
esophageal squamous cells by modulating Slug expression through the
activation of STAT3/HIF-α signaling.
|
|
327
|
Lambertini E, Lolli A, Vezzali F,
Penolazzi L, Gambari R and Piva R: Correlation between Slug
transcription factor and miR-221 in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells.
BMC Cancer. 12:4452012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
328
|
Qiu G, Lin Y, Zhang H and Wu D: miR-139-5p
inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion
of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 463:315–321. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
329
|
Bezzerri V, Borgatti M, Finotti A,
Tamanini A, Gambari R and Cabrini G: Mapping the transcriptional
machinery of the IL-8 gene in human bronchial epithelial cells. J
Immunol. 187:6069–6081. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
330
|
Raychaudhuri B and Vogelbaum MA: IL-8 is a
mediator of NF-κB induced invasion by gliomas. J Neurooncol.
101:227–235. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
331
|
Xie TX, Xia Z, Zhang N, Gong W and Huang
S: Constitutive NF-κB activity regulates the expression of VEGF and
IL-8 and tumor angiogenesis of human glioblastoma. Oncol Rep.
23:725–732. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
332
|
Sun S, Wang Q, Giang A, Cheng C, Soo C,
Wang CY, Liau LM and Chiu R: Knockdown of CypA inhibits
interleukin-8 (IL-8) and IL-8-mediated proliferation and tumor
growth of glioblastoma cells through down-regulated NF-κB. J
Neurooncol. 101:1–14. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
333
|
Gabellini C, Castellini L, Trisciuoglio D,
Kracht M, Zupi G and Del Bufalo D: Involvement of nuclear
factor-kappa B in bcl-xL-induced interleukin 8 expression in
glioblastoma. J Neurochem. 107:871–882. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
334
|
Yang TQ, Lu XJ, Wu TF, Ding DD, Zhao ZH,
Chen GL, Xie XS, Li B, Wei YX, Guo LC, et al: MicroRNA-16 inhibits
glioma cell growth and invasion through suppression of BCL2 and the
nuclear factor-κB1/MMP9 signaling pathway. Cancer Sci. 105:265–271.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
335
|
Fang L, Deng Z, Shatseva T, Yang J, Peng
C, Du WW, Yee AJ, Ang LC, He C, Shan SW, et al: MicroRNA miR-93
promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting integrin-β8.
Oncogene. 30:806–821. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
336
|
Magge SN, Malik SZ, Royo NC, Chen HI, Yu
L, Snyder EY, O'Rourke DM and Watson DJ: Role of monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1/CCL2) in migration of neural
progenitor cells toward glial tumors. J Neurosci Res. 87:1547–1555.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
337
|
Nazarenko I, Hede SM, He X, Hedrén A,
Thompson J, Lindström MS and Nistér M: PDGF and PDGF receptors in
glioma. Ups J Med Sci. 117:99–112. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
338
|
Cai JJ, Qi ZX, Chen LC, Yao Y, Gong Y and
Mao Y: miR-124 suppresses the migration and invasion of glioma
cells in vitro via Capn4. Oncol Rep. 35:284–290. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
339
|
Cheng Y, Li Y, Nian Y, Liu D, Dai F and
Zhang J: STAT3 is involved in miR-124-mediated suppressive effects
on esophageal cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 15:3062015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
340
|
Dong LL, Chen LM, Wang WM and Zhang LM:
Decreased expression of microRNA-124 is an independent unfavorable
prognostic factor for patients with breast cancer. Diagn Pathol.
10:452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
341
|
Long QZ, Du YF, Liu XG, Li X and He DL:
miR-124 represses FZD5 to attenuate P-glycoprotein-mediated
chemo-resistance in renal cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
36:7017–7026. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
342
|
Lu SH, Jiang XJ, Xiao GL, Liu DY and Yuan
XR: miR-124a restoration inhibits glioma cell proliferation and
invasion by suppressing IQGAP1 and β-catenin. Oncol Rep.
32:2104–2110. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
343
|
Chen SM, Chou WC, Hu LY, Hsiung CN, Chu
HW, Huang YL, Hsu HM, Yu JC and Shen CY: The Effect of MicroRNA-124
overexpression on anti-tumor drug sensitivity. PLoS One.
10:e01284722015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
344
|
Fabbri E, Brognara E, Montagner G,
Ghimenton C, Eccher A, Cantù C, Khalil S, Bezzerri V, Provezza L,
Bianchi N, et al: Regulation of IL-8 gene expression in gliomas by
microRNA miR-93. BMC Cancer. 15:6612015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
345
|
Fabbri E, Montagner G, Bianchi N, Finotti
A, Borgatti M, Lampronti I, Cabrini G and Gambari R: MicroRNA
miR-93-5p regulates expression of IL-8 and VEGF in neuroblastoma
SK-N-AS cells. Oncol Rep. 35:2866–2872. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
346
|
Galardi S, Mercatelli N, Giorda E,
Massalini S, Frajese GV, Ciafrè SA and Farace MG: miR-221 and
miR-222 expression affects the proliferation potential of human
prostate carcinoma cell lines by targeting p27Kip1. J
Biol Chem. 282:23716–23724. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
347
|
Lu X, Zhao P, Zhang C, Fu Z, Chen Y, Lu A,
Liu N, You Y, Pu P and Kang C: Analysis of miR-221 and p27
expression in human gliomas. Mol Med Rep. 2:651–656.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
348
|
Gillies JK and Lorimer IA: Regulation of
p27Kip1 by miRNA 221/222 in glioblastoma. Cell Cycle.
6:2005–2009. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
349
|
Wang Y, Wang X, Zhang J, Sun G, Luo H,
Kang C, Pu P, Jiang T, Liu N and You Y: MicroRNAs involved in the
EGFR/PTEN/AKT pathway in gliomas. J Neurooncol. 106:217–224. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
350
|
Ueda R, Kohanbash G, Sasaki K, Fujita M,
Zhu X, Kastenhuber ER, McDonald HA, Potter DM, Hamilton RL, Lotze
MT, et al: Dicer-regulated microRNAs 222 and 339 promote resistance
of cancer cells to cytotoxic T-lymphocytes by down-regulation of
ICAM-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:10746–10751. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
351
|
Zhang J, Han L, Ge Y, Zhou X, Zhang A,
Zhang C, Zhong Y, You Y, Pu P and Kang C: miR-221/222 promote
malignant progression of glioma through activation of the Akt
pathway. Int J Oncol. 36:913–920. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
352
|
Zhang C, Jiang T, Wang J, Cheng J, Pu P
and Kang C: MiR-221/222 promote the growth of malignant glioma
cells by regulating its target genes, molecular targets of CNS
tumors. Dr Garami Miklos : ISBN: 978-953-307-736-9InTech; pp.
461–482. 2011
|
|
353
|
Sarkar S, Dubaybo H, Ali S, Goncalves P,
Kollepara SL, Sethi S, Philip PA and Li Y: Down-regulation of
miR-221 inhibits proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells through
up-regulation of PTEN, p27(kip1), p57(kip2), and PUMA. Am J Cancer
Res. 3:465–477. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
354
|
Zhang C, Kang C, You Y, Pu P, Yang W, Zhao
P, Wang G, Zhang A, Jia Z, Han L, et al: Co-suppression of
miR-221/222 cluster suppresses human glioma cell growth by
targeting p27Kip1 in vitro and in vivo. Int J Oncol.
34:1653–1660. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
355
|
Zhang R, Pang B, Xin T, Guo H, Xing Y, Xu
S, Feng B, Liu B and Pang Q: Plasma miR-221/222 family as novel
descriptive and prognostic biomarkers for glioma. Mol Neurobiol.
53:1452–1460. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
356
|
Yang Y, Li F, Saha MN, Abdi J, Qiu L and
Chang H: miR-137/197 induce apoptosis and suppress tumorigenicity
by targeting MCL-1 in multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res.
21:2399–2411. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
357
|
Lee SH, Jung YD, Choi YS and Lee YM:
Targeting of RUNX3 by miR-130a and miR-495 cooperatively increases
cell proliferation and tumor angiogenesis in gastric cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 6:33269–33278. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
358
|
Brognara E, Fabbri E, Montagner G,
Gasparello J, Manicardi A, Corradini R, Bianchi N, Finotti A,
Breveglieri G, Borgatti M, et al: High levels of apoptosis are
induced in human glioma cell lines by co-administration of peptide
nucleic acids targeting miR-221 and miR-222. Int J Oncol.
48:1029–1038. 2016.
|
|
359
|
Giunti L, da Ros M, Vinci S, Gelmini S,
Iorio AL, Buccoliero AM, Cardellicchio S, Castiglione F, Genitori
L, de Martino M, et al: Anti-miR21 oligonucleotide enhances
chemosensitivity of T98G cell line to doxorubicin by inducing
apoptosis. Am J Cancer Res. 5:231–242. 2014.
|
|
360
|
Gao C, Peng FH and Peng LK: MiR-200c
sensitizes clear-cell renal cell carcinoma cells to sorafenib and
imatinib by targeting heme oxygenase-1. Neoplasma. 61:680–689.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
361
|
Pogribny IP, Filkowski JN, Tryndyak VP,
Golubov A, Shpyleva SI and Kovalchuk O: Alterations of microRNAs
and their targets are associated with acquired resistance of MCF-7
breast cancer cells to cisplatin. Int J Cancer. 127:1785–1794.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
362
|
Suto T, Yokobori T, Yajima R, Morita H,
Fujii T, Yamaguchi S, Altan B, Tsutsumi S, Asao T and Kuwano H:
MicroRNA-7 expression in colorectal cancer is associated with poor
prognosis and regulates cetuximab sensitivity via EGFR regulation.
Carcinogenesis. 36:338–345. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
363
|
Liu R, Liu X, Zheng Y, Gu J, Xiong S,
Jiang P, Jiang X, Huang E, Yang Y, Ge D, et al: MicroRNA-7
sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to paclitaxel. Oncol
Lett. 8:2193–2200. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
364
|
Gomes SE, Simões AE, Pereira DM, Castro
RE, Rodrigues CM and Borralho PM: miR-143 or miR-145 overexpression
increases cetuximab-mediated antibody-dependent cellular
cytotoxicity in human colon cancer cells. Oncotarget. Jan
25–2016.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
365
|
Costa PM, Cardoso AL, Nóbrega C, Pereira
de Almeida LF, Bruce JN, Canoll P and Pedroso de Lima MC:
MicroRNA-21 silencing enhances the cytotoxic effect of the
antiangiogenic drug sunitinib in glioblastoma. Hum Mol Genet.
22:904–918. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
366
|
Qian X, Ren Y, Shi Z, Long L, Pu P, Sheng
J, Yuan X and Kang C: Sequence-dependent synergistic inhibition of
human glioma cell lines by combined temozolomide and miR-21
inhibitor gene therapy. Mol Pharm. 9:2636–2645. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
367
|
Zhang S, Han L, Wei J, Shi Z, Pu P, Zhang
J, Yuan X and Kang C: Combination treatment with doxorubicin and
microRNA-21 inhibitor synergistically augments anticancer activity
through upregulation of tumor suppressing genes. Int J Oncol.
46:1589–1600. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
368
|
Zhang Q, Ran R, Zhang L, Liu Y, Mei L,
Zhang Z, Gao H and He Q: Simultaneous delivery of therapeutic
antagomirs with paclitaxel for the management of metastatic tumors
by a pH-responsive anti-microbial peptide-mediated liposomal
delivery system. J Control Release. 197:208–218. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
369
|
Fan L, Yang Q, Tan J, Qiao Y, Wang Q, He
J, Wu H and Zhang Y: Dual loading miR-218 mimics and Temozolomide
using AuCOOH@FA-CS drug delivery system: Promising
targeted anti-tumor drug delivery system with sequential release
functions. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:1062015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
370
|
Xue W, Dahlman JE, Tammela T, Khan OF,
Sood S, Dave A, Cai W, Chirino LM, Yang GR, Bronson R, et al: Small
RNA combination therapy for lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:E3553–E3561. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
371
|
Nishimura M, Jung EJ, Shah MY, Lu C,
Spizzo R, Shimizu M, Han HD, Ivan C, Rossi S, Zhang X, et al:
Therapeutic synergy between microRNA and siRNA in ovarian cancer
treatment. Cancer Discov. 3:1302–1315. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
372
|
Hu X, Li W, Liu G, Wu H, Gao Y, Chen S, He
D and Zhang Y: The effect of Bcl-2 siRNA combined with miR-15a
oligonucleotides on the growth of Raji cells. Med Oncol.
30:4302013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|