Introduction
Colorectal cancer is currently the most common
gastrointestinal malignancy and remains the third most common form
of cancer and second most common cause of cancer-related death in
developed countries (1). Although
surgical resection is the first choice of treatment for colorectal
cancer, radiation therapy and chemotherapy are also essential
interventions. In addition, many patients with local recurrence are
not eligible for surgical resection and are frequently referred for
radiotherapy. However, the results of conventional photon
radiotherapy remain far from satisfactory, with many studies in the
literature reporting 1- and 3-year survival rates of 50 and 10%,
respectively (2,3). Several reports have revealed that
C-ion irradiation offers advantages over conventional photon
irradiation, such as accurate dose distribution, and enhanced
biological effects due to higher LET (4,5).
Thus, C-ion radiotherapy is expected to be promising alternative to
surgery for colorectal cancer.
The RBE of C-ion irradiation with respect to
reference photon radiation sources, such as X-ray- or
γ-ray-irradiation, as assessed by biological endpoints such as cell
death, DNA damage, and chromosomal aberrations, is known to be
~2–3-fold (5–7). However, it is not known how the
effects of C-ion irradiation on cellular proteins, such as protein
stability or degradation compare to the effects of photon
irradiation. Protein ubiquitylation has crucial role in protein
function through the modulation of its stability or its activity
(8–10). Proteins destined for degradation
are labeled with poly-ubiquitin chains by the sequential activity
of a multi-enzymatic system, and the poly-ubiquitin chains then
serve as a recognition signal for protein degradation via
proteasomes (11). It is known
that proteasomes are located in the cell cytosol, endoplasmic
reticulum, and nucleus, and are thought to have a significant role
in degrading the majority of endogeneous cellular proteins, which
can have a marked effect on cell behavior (12). The role of the ubiquitin proteasome
pathway on the classical effects of photon irradiation, such as DNA
repair, chromosome instability, cell cycle arrest, and cell death,
have been studied (12,13). During DSB repair, a series of
phosphorylation events such as γ-H2AX are initiated, which leads to
the ubiquitylation of histon H2A and other unknown proteins which
elicits the chromatin association of BRCA1 as well as TP53BP1
(14,15).
Interestingly, we have previously reported that
C-ion irradiation at a dose of 2 Gy induced a greater amount of
ubiquitylated proteins than X-ray irradiation at a dose of 4 Gy in
a human pancreatic cancer cell line (MIAPaCa-2) (16). The RBE of C-ion irradiation with
respect to the X-ray irradiation of MIAPaCa-2 was 2.0, as assessed
by cell death, thus C-ion irradiation at 2 Gy and X-ray irradiation
at 4 Gy could have a similar cell killing effect. However, an
increase in the formation of ubiquitylated proteins was observed in
C-ion-irradiated MIAPaCa-2 cells. It would be intriguing to study
whether this accumulation of ubiquitylated proteins represents one
of the unique effects of C-ion radiation on cells. Thus far,
however, no studies have focused on the accumulation of
ubiquitylated proteins to examine the characteristics of C-ion
irradiation in comparison to photon irradiation. In this study, we
used two human colon cancer cell lines, SW620 and SW480, and
examined the effects of C-ion and X-ray irradiation on the
accumulation of ubiquitylated proteins.
Materials and methods
Cell culture and reagents
The two human colon cancer cell lines, SW620 and
SW480, were purchased from ATCC (Manassas, VA, USA) and cultured in
DMEM (Nissui, Tokyo, Japan) supplemented with 10% FBS (Hyclone, UT,
USA), 1% L-glutamine (Gibco, CA, USA), and 1%
penicillin/streptomycin (Gibco). RAW264.7, the mouse macrophage
cell line, was purchased from ATCC. The cells were maintained in
DMEM. The cells were incubated with or without LPS (100 ng/ml) for
24 h.
Irradiation
Cells were subjected to C-ion (1, 2, 3 or 4) or
X-ray irradiation (2, 4, 6 or 8 Gy). The C-ions were accelerated by
HIMAC, and X-rays were produced by a PANTAK HF-320S generator
(Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) at NIRS, Japan, as described previously
(17).
Immunofluorescence labeling and image
acquisition
Immunofluorescence labeling and image acquisition
was performed as described previously (18). The primary antibodies against
multi-ubiquitin, which recognizes K29-, K48-, K63-linked
poly-ubiquitylated and mono-ubiquitylated protein purified from
hybridoma, clone FK2 (MBL, Nagoya, Japan), γ-H2AX (Cell Signaling
Technology, MA, USA), and TP53BP1 (Cell Signaling Technology), were
suspended with Can Get Signal solution 1 (Toyobo, Tokyo, Japan) at
1:250 and used for the assay. Cells were then treated with Alexa
Flour 555- or 488-labeled anti-mouse IgG or anti-rabbit IgG
secondary antibodies (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The slides
were mounted with ProLong Gold Antifade Reagent containing the
nuclear counterstain DAPI (Invitrogen).
Cellular ubiquitylated proteins were visualized and
photographed with a BZ-9000 fluorescence microscope (Keyence,
Osaka, Japan) using a 20X Plan fluorescence lens (N.A 0.45) with BZ
filters for Tritc and DAPI.
To examine the co-localization of proteins, a
DSU-IX70 fluorescence microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) with
MetaMorph's 3D Deconvolution module (Molecular Devices, CA, USA)
was used (19). Representative
images were uniformly processed in Adobe Photoshop using the
brightness and contrast tools.
The measurement of ubiquitylated protein
accumulation levels in each of the cell types
To compare the accumulation levels of ubiquitylated
proteins within non-irradiated, X-ray-irradiated or
C-ion-irradiated cells, we used immunofluorescence-labeled images
stained with anti-multi-ubiquitin antibody and DAPI, and analyzed
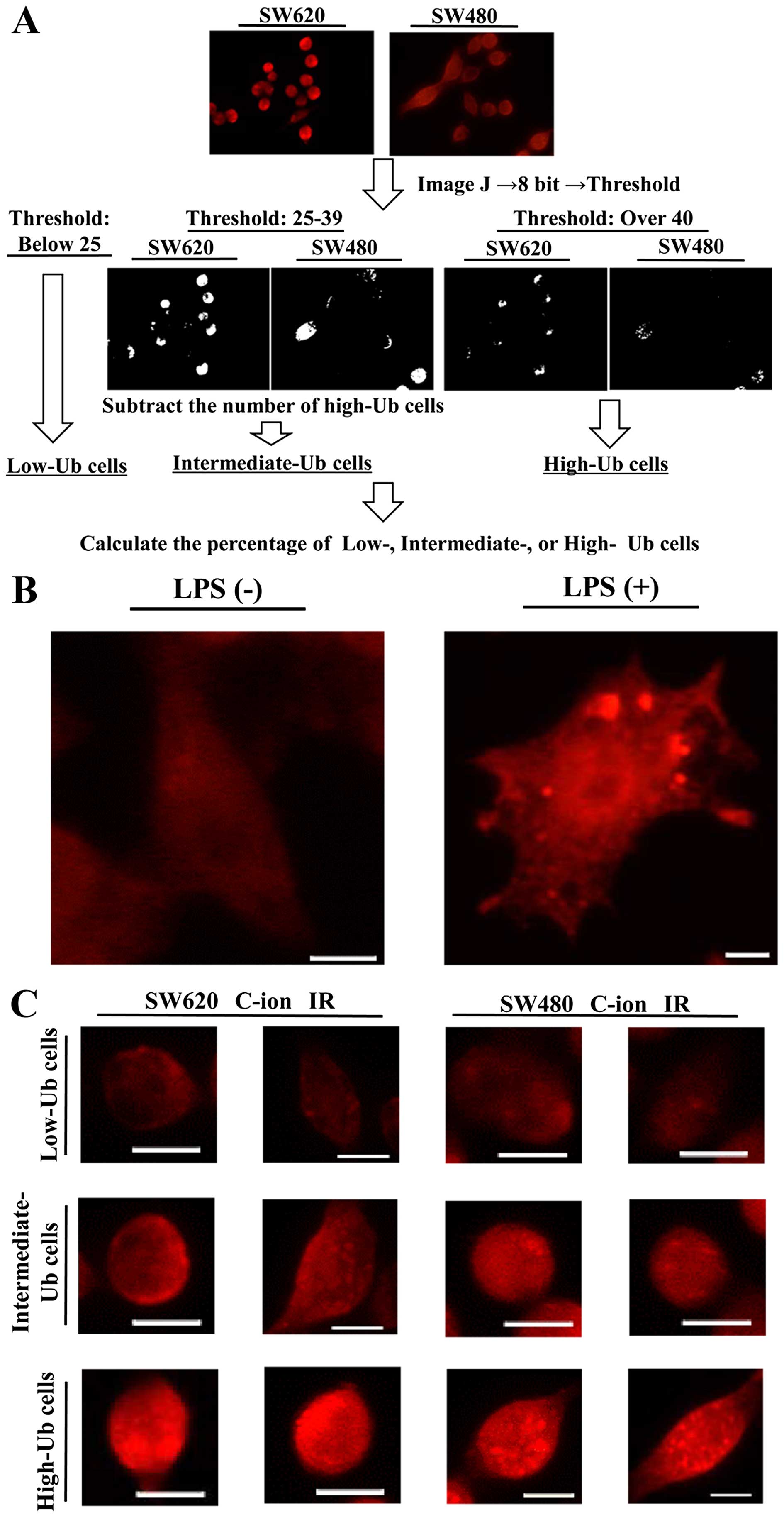
the images with the ImageJ software program (Fig. 1A). We first used DAPI images and
counted the number of cell nuclei per image, which represents the
total number of cells per image. Next, the anti-multi-ubiquitin
antibody-stained images were converted into 8 bit grayscale images.
The thresholding tool of the ImageJ software program, which can
separate the pixels that fall within a desired range of intensity
values from those which do not, was used to separate the cells with
low, intermediate or high accumulation of ubiquitylated proteins.
The criteria for the cells containing low, intermediate or high
ubiquitylated protein accumulation were stated as follows: the
cells in which the distribution of pixel intensity was <25 was
classified as Low-Ub, the cells with the pixel intensity ≥40 was
classified High-Ub, and the cells with the pixel intensity between
25 and 39 and the High-Ub cells were subtracted was classified as
the Intermediate-Ub cells. The numbers of Low-Ub, Intermediate-Ub,
and High-Ub cells were counted for each image, and divided by the
total number of cells per image to evaluate the percentage of
Low-Ub, Intermediate-Ub or High-Ub cells within the total cell
population. Three images per group were used for the analysis. The
number of cells ranged from 18 to 78 per group. The cell numbers
tended to be lower at 5 days after irradiation because cell death
continued in the period after irradiation.
Cell viability assays
The cells were grown to ~60% confluence in a 12-well
plate and used for the irradiation. The conditioning medium was
replaced with fresh medium, and the cells were incubated for 51 h
in a CO2 incubator. The cells were then fixed and
stained with Diff-Quick (Sysmex, Kobe, Japan). Six random fields
were photographed and cell numbers were counted. For the proteasome
inhibitor treatment, 5, 10, 15 or 20 nM epoxomicin was added to the
conditioning medium at 3 h after irradiation, and the cells were
fixed and stained at 51 h after the irradiation, and used for the
count.
Western blotting
Primary antibodies against LC3 (MBL) or GAPDH
(Trevigen, MD, USA) were suspended with Can Get Signal solution 1
at 1:2,500 or 1:10,000, respectively. The membranes were then
washed and incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated
anti-mouse or -rabbit IgG (Amersham Biosciences, Buckinghamshire,
UK) suspended with Can Get Signal solution 2 (Toyobo) at 1:10,000.
Protein bands were detected by enhanced chemiluminescence and
imaged with an LAS 4000 Lumino image analyzer (Fujifilm, Tokyo,
Japan). siRNA targeting Atg5 and negative control siRNA were
purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MS, USA). Cells
were grown to ~60% confluence in a 6-well plate and then incubated
with a transfection mixture containing LipoTrust Ex Oligo (Hokkaido
System Science Co., Ltd., Hokkaido, Japan) and 50 nmol siRNA for 40
h. Primary antibodies against Atg5 (Cell Signaling Technology), and
GAPDH were suspended with Can Get Signal solution 1 at 1:2,500 and
1:10,000, respectively.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analyses were performed using an
unpaired Student's t-test, and the differences between groups were
assessed with a two-tailed test. P-values of <0.05 were
considered to indicate statistical significance. Each experiment
was performed in triplicate and independently repeated at least
twice on different days.
Results
The high accumulation of ubiquitylated
proteins was observed in C-ion-irradiated SW620 cells
First, we used RAW264.7 treated with 100 ng/ml LPS
for 24 h, and confirmed the immunofluorescence staining of
ubiquitylated protein accumulation as reported in a previous report
(Fig. 1B) (20). Next, we examined the effects of
C-ion and X-ray irradiation on the accumulation of ubiquitylated
protein. A summary of the criteria for the Low-Ub, Intermediate-Ub,
and High-Ub cells, is shown in Fig.
1A, representative images of the cells are show in Fig. 1C.
The percentages of Low-Ub, Intermediate-Ub or
High-Ub cells were determined in SW620 and SW480 cells at 6 h after
C-ion irradiation (1, 2, 3 or 4 Gy) or X-ray irradiation (2, 4, 6
or 8 Gy). Increased percentages of High-Ub cells were observed in
the C-ion-irradiated-SW620 with a peak at 3 Gy, 73% within total
cells, whereas, the numbers of High-Ub cells in the
X-ray-irradiated SW620 were lower, even at higher doses (Fig. 2A–C). The peak number of High-Ub
cells in the C-ion-irradiated SW620 was also higher than that
detected in the C-ion or X-ray-irradiated SW480, which was 49% in 4
Gy C-ion-irradiated SW480 or 46% in 8 Gy X-ray irradiated SW480,
respectively (Fig. 2D–F).
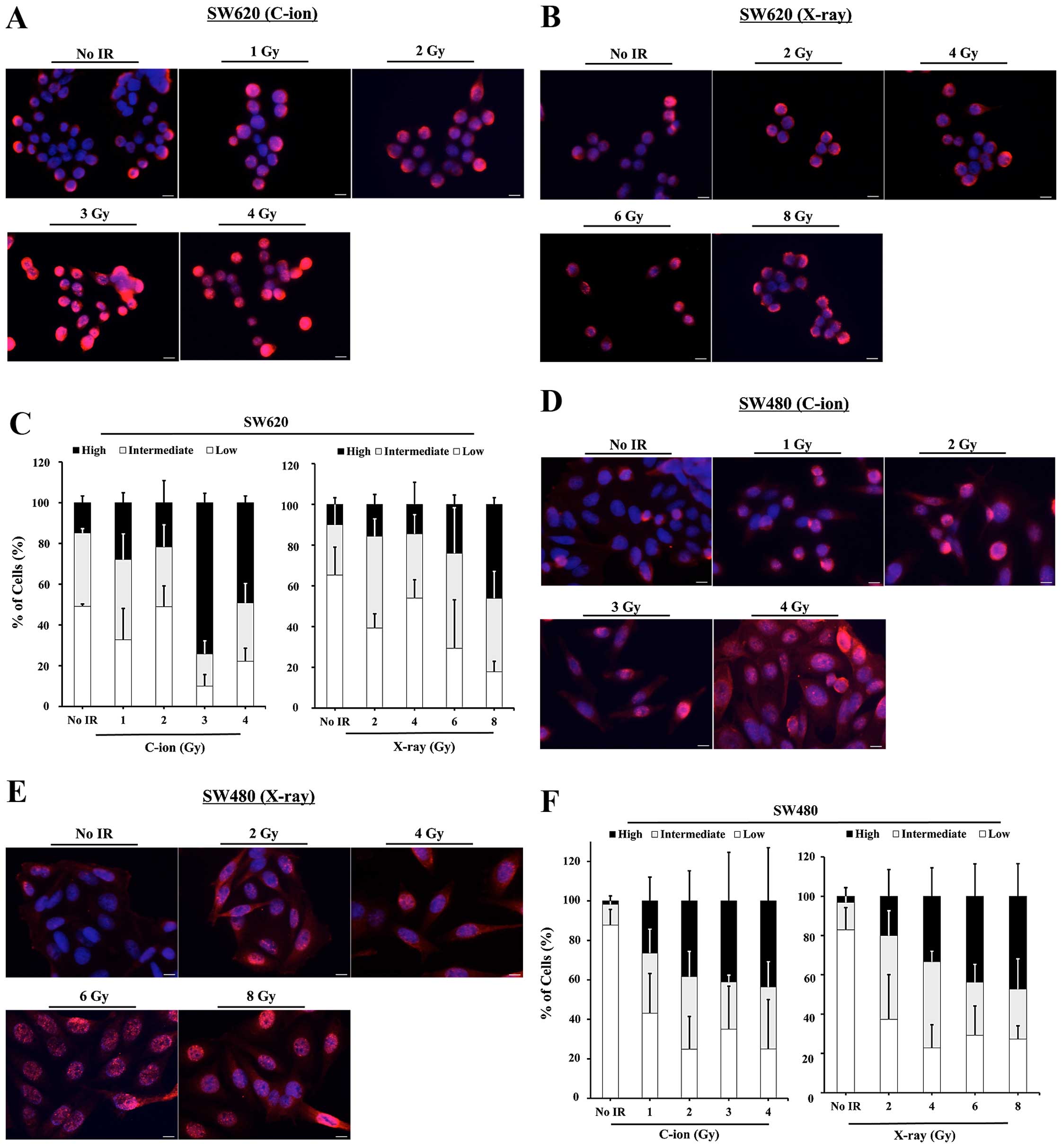 | Figure 2The dose-dependency of ubiquitylated
protein accumulation in C-ion- or X-ray-irradiated SW620 and SW480
cells. The cells were irradiated and fixed at 6 h after
irradiation, then used for immunofluorescence staining with
anti-multi-ubiquitin antibody. The representative images of the
cellular accumulation of ubiquitylated protein in SW620 and SW480
cells after C-ion irradiation (1, 2, 3 or 4 Gy) (A and D), and
X-ray irradiation (2, 4, 6 and 8 Gy) (B and E) are shown. Red,
ubiquitylated proteins. Blue, DAPI. Scale bar, 10 μm. The numbers
of Low-Ub, Intermediate-Ub, and High-Ub cells were counted using
the ImageJ software program. The percentages of Low-Ub,
Intermediate-Ub, and High-Ub cells are shown in the graph (C and
F). The data represent the mean ± SD, n=3 images, 28–71 cells per
image. |
We further examined the time-dependency of
ubiquitylated protein accumulation in 3 Gy C-ion-irradiated cells
and 6 Gy X-ray-irradiated cells. An increased number of High-Ub
cells was already observed at 1 h after C-ion or X-ray irradiation.
In SW620, the number of High-Ub cells peaked at 6 h after C-ion
irradiation, 69% within total cells, at which point the number of
High-Ub cells was higher than that in the X-ray irradiated cells at
any time (Fig. 3A–C). In SW480,
the number of High-Ub cells peaked at 6 h in both C-ion or X-ray
irradiated cells, at 41 or 43%, which were both lower than the peak
value observed in the C-ion-irradiated SW620 (Fig. 3D–F). The difference in the peak
values of the High-Ub cells that were detected in C-ion-irradiated
cells versus X-ray-irradiated cells was greater in the SW620 cells
than it was in the SW480 cells. In addition, ubiquitylated protein
accumulation was decreased at 5 days after irradiation, indicating
that ubiquitylated proteins may be degraded over time after
radiation treatment.
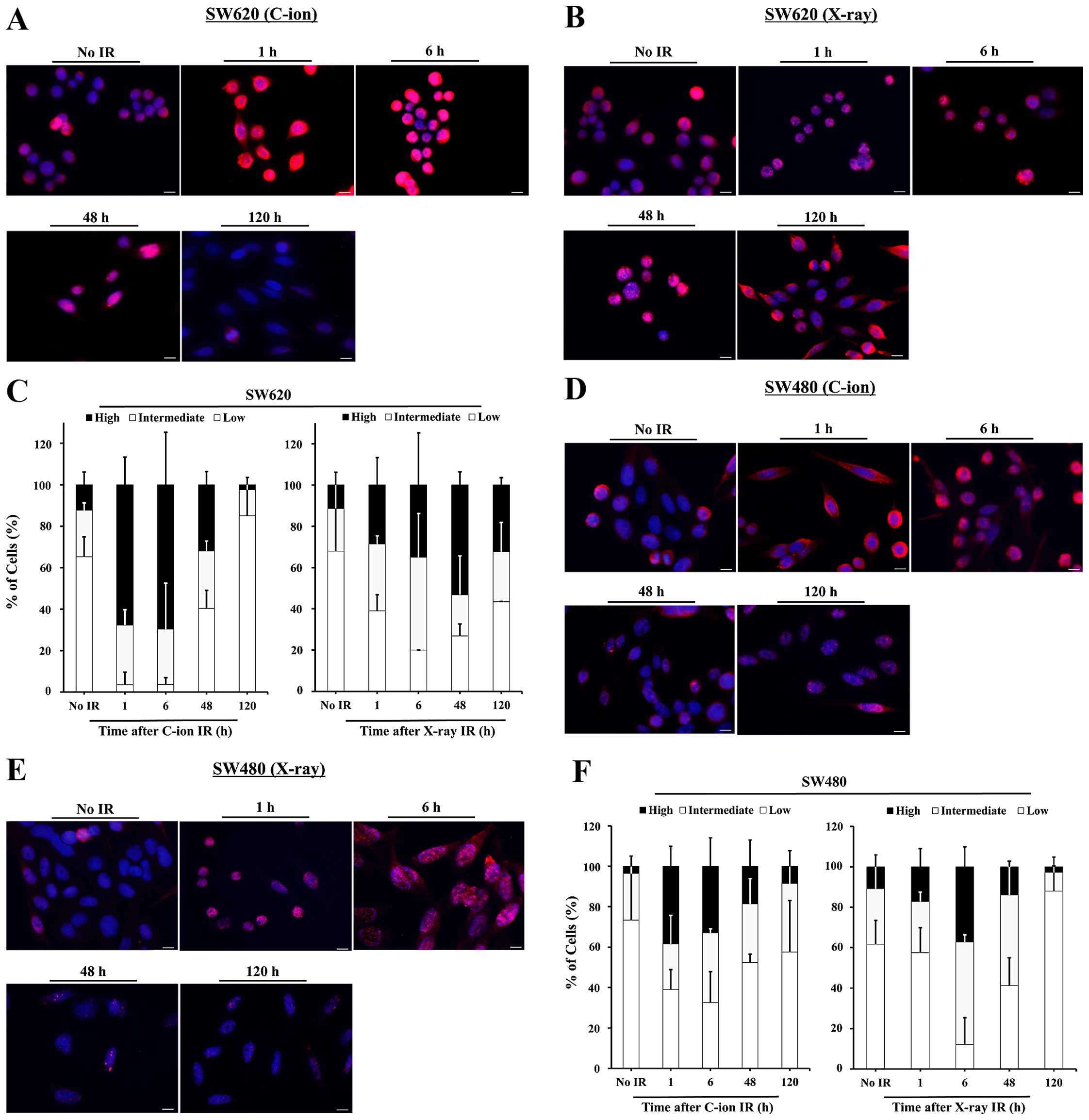 | Figure 3The time-dependency of ubiquitylated
protein accumulation in C-ion- or X-ray-irradiated SW620 and SW480
cells. The cells were irradiated and fixed at 1, 6, 48 or 120 h
after irradiation, then used for immunofluorescence staining with
anti-multi ubiquitin antibody. Representative images of the changes
of cellular ubiquitylated proteins over time in C-ion-irradiated (A
and D) or X-ray-irradiated SW620 and SW480 cells (B and E) are
shown. Red, ubiquitylated proteins. Blue, DAPI. Scale bar, 10 μm.
The number of Low-Ub, Intermediate-Ub, and High-Ub cells was gained
by ImageJ software program. The percentages of Low-Ub,
Intermediate-Ub, and High-Ub cells are shown in the graph (C and
F). The data represent the mean ± SD, n=3 images, 18–78 cells per
image. |
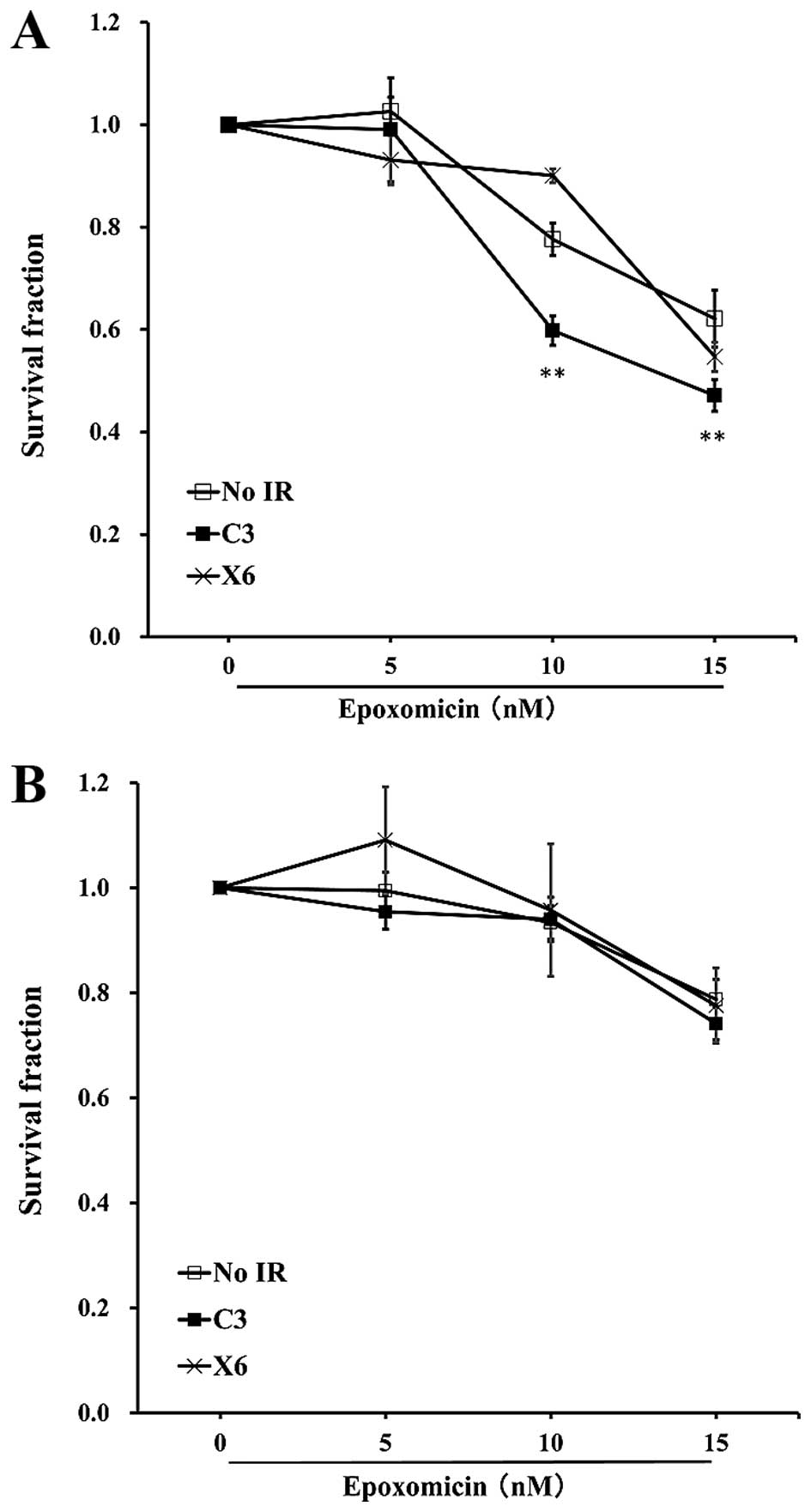
The treatment of SW620 cells with a
proteasome inhibitor enhances cellular sensitivity to C-ion
irradiation
It is well known that damaged proteins are toxic to
cells (21), the proteins were
therefore ubiquitylated and degraded through proteasomes or
autophagy (22,23). It would be intriguing to see
whether blocking the clearance of ubiquitylated proteins enhances
the radiosensitivity to radiation. To clarify this, we irradiated
SW620 and SW480 cells with C-ion at 3 Gy or X-ray at 6 Gy, and
treated the cells with epoxomicin at 3 h after irradiation and the
cells were incubated for another 48 h. The treatment of SW620 with
10 or 15 nM epoxomicin significantly reduced the numbers of
surviving cells and increased the radiosensitivity to C-ion
radiation. A reduction in the number of surviving cells was not
observed in X-ray-irradiated SW620 cells; 10 nM epoxomicin even
enhanced the cell survival after X-ray irradiation (Fig. 4A). In the case of SW480 cells, none
of the doses of epoxomicin enhanced radiosensitivity to C-ion or
X-ray irradiation (Fig. 4B).
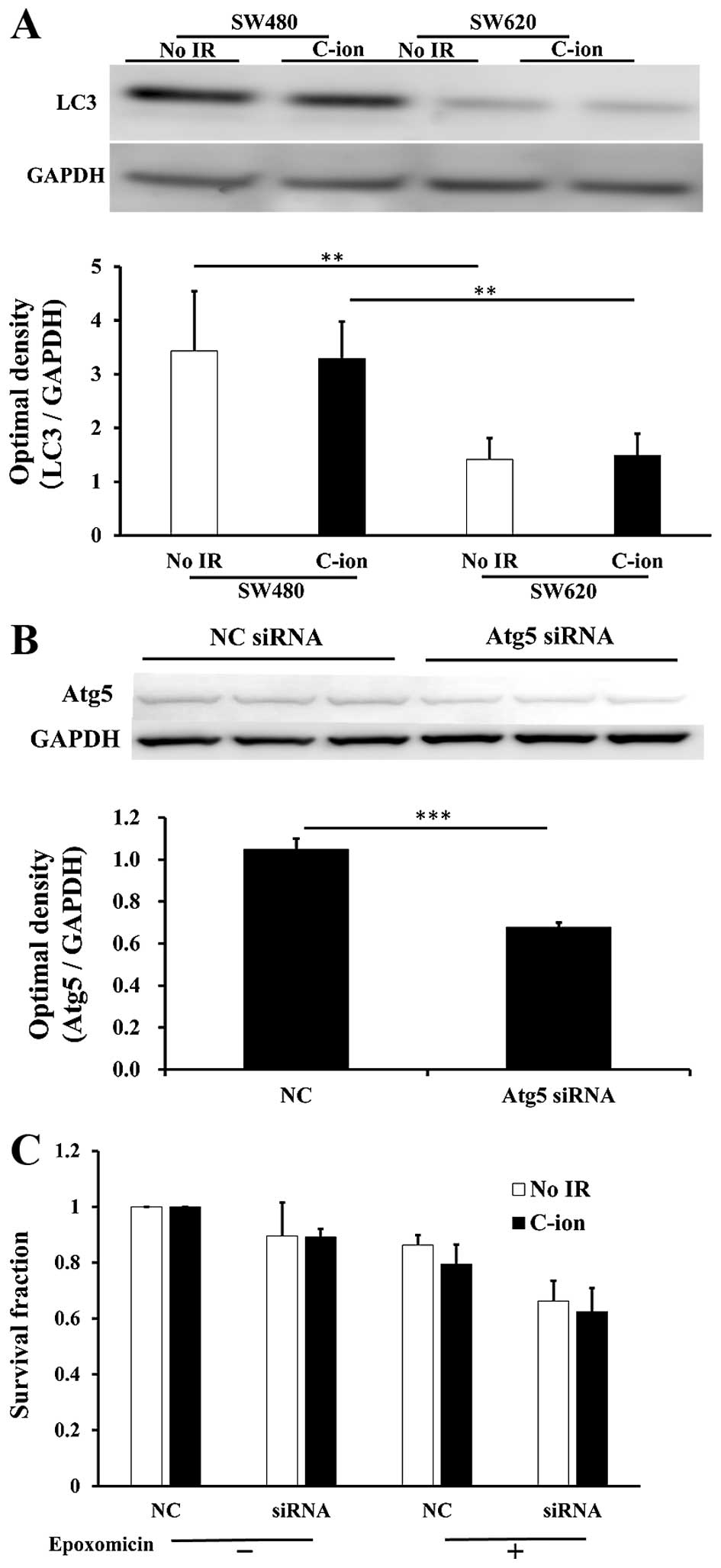
The protein levels of LC3, a component of autophagy,
were much higher in SW480 cells than in SW620 cells (Fig. 5A). We therefore hypothesized that
ubiquitylated proteins might be degraded by autophagy rather than
by proteasomes in SW480 cells, and the blocking of autophagy or the
blocking of both autophagy and proteasomes may increase the
radiosensitivity to radiation. Thus, we next treated SW480 cells
with siRNA specific for Atg5, which is the functional component of
autophagy, with or without treatment with 10 nM epoxomicin, in
order to examine cellular survival in C-ion-irradiated cells. The
reduction of Atg5 protein expression was confirmed in SW480 cells
that were treated with Atg5 siRNA (Fig. 5B). However, Atg5 siRNA treatment
(with or without epoxomicin) did not enhance the radiosensitivity
of C-ion-irradiated SW480 cells (Fig.
5C).
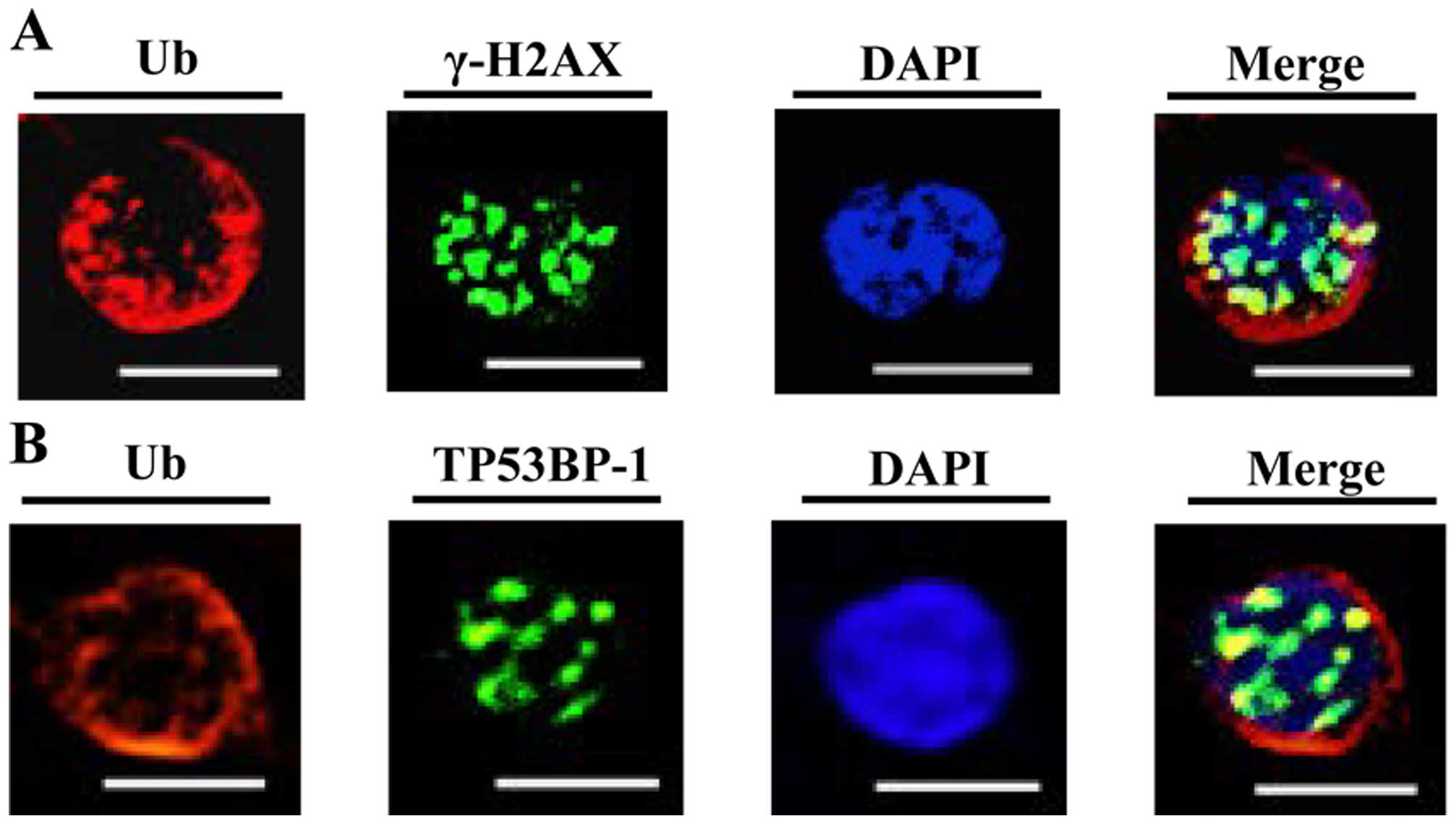
Ubiquitylated proteins were co-localized
with γ-H2AX and TP53BP1 in C-ion-irradiated SW620 cells
C-ion irradiation is known to induce greater amount
of DNA damage such as DSBs (5).
During DSBs repair, DNA damage-induced ubiquitylation cascade was
fundamental for eliciting the chromatin association of TP53BP1
(14,15). To examine the relation of
ubiquitylated proteins and DNA repair system after the C-ion
irradiation, we used 3 Gy C-ion-irradiated SW620 cells, which were
fixed at 6 h after irradiation, and stained the cells with
anti-multi-ubiquitylated chain antibody with anti-γ-H2AX antibody,
the marker of DSBs or anti-TP53BP1 antibody. We found that some of
the ubiquitylated proteins were partially co-localized with γ-H2AX
(Fig. 6A) or TP53BP1 (Fig. 6B) in C-ion-irradiated SW620 cells,
indicated that C-ion induced ubiquitylated proteins may have some
function in DNA repair system.
Discussion
In this study, we compared the effects of
irradiation with C-ions and X-rays, focusing on the cellular
accumulation of ubiquitylated protein. We found the greatest
accumulation of ubiquitylated proteins, occurred in
C-ion-irradiated SW620. Higher levels of ubiquitylated proteins
were also reported in C-ion-irradiated pancreatic cancer cell line,
MIAPaCa-2 in comparison to those detected in non-irradiated or
X-ray-irradiated MIAPaCa-2 (16).
Thus, the induction of a great amount of ubiquitylated proteins in
cells may be a unique property of C-ion radiation in several cell
lines. The treatment of SW620 with a proteasome inhibitor enhanced
the cell killing of C-ion-irradiated SW620 cells. Thus, blocking
the clearance of ubiquitylated proteins may be promising candidate
treatment for enhancing the radiosensitivity of tumor cells to
C-ion radiation.
Since heavy ions, such as C-ions, have a higher
ionization density in the track of individual particles, they can
induce greater DNA damage and cytotoxicity in tumor cells (24–26).
Thus, it can be hypothesized that C-ion irradiation may also induce
greater effects on cellular proteins. Radiation-induced
ubiquitylated proteins may represent the sum of the effects of
irradiation on cellular proteins, such as the damage of proteins
via radiation stress, which leads to their elimination (27), and functional proteins, which are
involved such as in the DNA repair system (14,15).
There have been a number of studies showing ubiquitin accumulation
at DSB sites (28,29); ubiquitylated proteins were detected
as foci in the nucleus of irradiated cells, which were colocalized
with Rad51 (29). In this study,
we only examined the co-localization of C-ion-induced ubiquitylated
proteins involved in DNA repair system, γ-H2AX and TP53BP1.
However, it would be intriguing to examine the relationship between
ubiquitylated proteins and other proteins that are involved in the
cellular stress responses, since some of the ubiquitylated proteins
were detected in the periphery of the nuclear or in the
cytoplasm.
Classically, it has been reported that
proteasome-mediated protein degradation requires the ubiquitylation
of proteins, which is then recognized by 26S proteasomes, whereas
autophagy is considered to be a random cytoplasmic degradation
system. However, several studies have suggested that ubiquitylated
proteins are also degraded by autophagy, and there is crosstalk
between the proteasome- and autophagy-mediated protein degradation
(22,30,31).
In this study, blocking the clearance of ubiquitylated proteins by
treatment with a proteasome inhibitor enhanced the cell killing of
C-ion-irradiated SW620 cells. However, the proteasome inhibitor
treatment did not enhance the radiosensitivity of SW480 cells to
C-ions. It may be because of less accumulation of ubiquitylated
proteins in C-ion irradiated SW480, however, we also detected the
protein levels of LC3, an autophagy marker, were much higher in
SW480 cells than in SW620 cells. We therefore hypothesized that
SW480 cells may use autophagy-mediated protein degradation more
dominantly than proteasome-mediated degradation or use both systems
to degrade ubiquitylated proteins. However, the treatment of siRNA
specific for Atg5, a functional component of autophagy or Atg5
siRNA with a proteasome inhibitor did not increase cell killing in
C-ion-irradiated SW480 cells. Thus, another system seemed to be
involved in reducing the ubiquitylated proteins in SW480 cells.
Further studies will be required to clarify the mechanism by which
the clearance of ubiquitylated proteins is blocked in this type of
cells.
Blocking the clearance system of aggregated proteins
with the use of a proteasome inhibitor has already been used in
clinical studies, and it has also been reported in combination with
photon radiotherapy (32–35). The potential of proteasome
inhibitor, bortezomib, in combination with radiotherapy has been
shown in several types of tumors, however, increase of side effects
was also reported (33–35). C-ion radiotherapy has the advantage
over photon radiation with accurate dose distribution to the target
tumor (4–7), thus the accumulation of ubiquitylated
proteins may largely occur in tumor cells, while smaller amounts
accumulate in normal tissues. It is still challenging to use
radiation on colorectal cancer treatment, because the intestines
are a highly radiosensitive organ. Thus, blocking the clearance of
ubiquitylated proteins is expected to greatly impact on the
increase of therapeutic ratio of C-ion radiation for colorectal
cancer, which can induce cell death, especially in tumors without
side effects in normal tissues.
Acknowledgements
This study was performed as Research Project with
Heavy Ions at the NIRS-HIMAC.
Abbreviations:
|
C-ion
|
carbon ion
|
|
LET
|
linear energy transfer
|
|
RBE
|
relative biological effectiveness
|
|
DSB
|
DNA double-strand break
|
|
γ-H2AX
|
phosphorylation of the histone variant
H2AX
|
|
DMEM
|
Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium
|
|
HIMAC
|
heavy-ion medical accelerator in
Chiba
|
|
NIRS
|
National Institute of Radiological
Sciences
|
|
DAPI
|
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenyllindole
|
|
Tritc
|
tetramethylrhodamine
isothiocyanate
|
|
LPS
|
lipopolysaccharide
|
References
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yamada S, Shinoto M and Endo S: Carbon ion
radiotherapy for patients with locally recurrent cancer. In:
Proceedings of NIRS-IMP Joint Symposium on Carbon Ion Therapy and
Radiation Emergency Medicine; pp. 42–47. 2012
|
|
3
|
Lingareddy V, Ahmad NR and Mohiuddin M:
Palliative reirradiation for recurrent rectal cancer. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 38:785–790. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kamada T, Tsujii H, Blakely EA, Debus J,
De Neve W, Durante M, Jäkel O, Mayer R, Orecchia R, Pötter R, et
al: Carbon ion radiotherapy in Japan: An assessment of 20 years of
clinical experience. Lancet Oncol. 16:e93–e100. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fokas E, Kraft G, An H and
Engenhart-Cabillic R: Ion beam radiobiology and cancer: Time to
update ourselves. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1796:216–229.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Uzawa A, Ando K, Koike S, Furusawa Y,
Matsumoto Y, Takai N, Hirayama R, Watanabe M, Scholz M, Elsässer T,
et al: Comparison of biological effectiveness of carbon-ion beams
in Japan and Germany. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 73:1545–1551.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schulz-Ertner D, Jäkel O and Schlegel W:
Radiation therapy with charged particles. Semin Radiat Oncol.
16:249–259. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Micel LN, Tentler JJ, Smith PG and
Eckhardt GS: Role of ubiquitin ligases and the proteasome in
oncogenesis: Novel targets for anticancer therapies. J Clin Oncol.
31:1231–1238. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Brown JS and Jackson SP: Ubiquitylation,
neddylation and the DNA damage response. Open Biol. 5:1500182015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sadowski M, Suryadinata R, Tan AR, Roesley
SN and Sarcevic B: Protein monoubiquitination and
polyubiquitination generate structural diversity to control
distinct biological processes. IUBMB Life. 64:136–142. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Deshaies RJ and Joazeiro CAP: RING domain
E3 ubiquitin ligases. Annu Rev Biochem. 78:399–434. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
McBride WH, Iwamoto KS, Syljuasen R,
Pervan M and Pajonk F: The role of the ubiquitin/proteasome system
in cellular responses to radiation. Oncogene. 22:5755–5773. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pajonk F and McBride WH: The proteasome in
cancer biology and treatment. Radiat Res. 156:447–459. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tu Y, Chen C, Pan J, Xu J, Zhou ZG and
Wang CY: The Ubiquitin Proteasome Pathway (UPP) in the regulation
of cell cycle control and DNA damage repair and its implication in
tumorigenesis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 5:726–738. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ulrich HD: Ubiquitin and SUMO in DNA
repair at a glance. J Cell Sci. 125:249–254. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fujita M, Imadome K, Shoji Y, Isozaki T,
Endo S, Yamada S and Imai T: Carbon-ion irradiation suppresses
migration and invasiveness of human pancreatic carcinoma cells
MIAPaCa-2 via Rac1 and RhoA degradation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 93:173–180. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fujita M, Otsuka Y, Imadome K, Endo S,
Yamada S and Imai T: Carbon-ion radiation enhances migration
ability and invasiveness of the pancreatic cancer cell, PANC-1, in
vitro. Cancer Sci. 103:677–683. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Fujita M, Imadome K, Endo S, Shoji Y,
Yamada S and Imai T: Nitric oxide increases the invasion of
pancreatic cancer cells via activation of the PI3K-AKT and RhoA
pathways after carbon ion irradiation. FEBS Lett. 588:3240–3250.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Landmann L: Deconvolution improves
colocalization analysis of multiple fluorochromes in 3D confocal
data sets more than filtering techniques. J Microsc. 208:134–147.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu XD, Ko S, Xu Y, Fattah EA, Xiang Q,
Jagannath C, Ishii T, Komatsu M and Eissa NT: Transient aggregation
of ubiquitinated proteins is a cytosolic unfolded protein response
to inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Biol Chem.
287:19687–19698. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mogk A, Kummer E and Bukau B: Cooperation
of Hsp70 and Hsp100 chaperone machines in protein disaggregation.
Front Mol Biosci. 2:222015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Szeto J, Kaniuk NA, Canadien V, Nisman R,
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, Bazett-Jones DP and Brumell JH: ALIS are
stress-induced protein storage compartments for substrates of the
proteasome and autophagy. Autophagy. 2:189–199. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lilienbaum A: Relationship between the
proteasomal system and autophagy. Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 4:1–26.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hill MA: Radiation damage to DNA: The
importance of track structure. Radiat Meas. 31:15–23. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Nikjoo H, Uehara S, Wilson WE, Hoshi M and
Goodhead DT: Track structure in radiation biology: Theory and
applications. Int J Radiat Biol. 73:355–364. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Goodhead DT: Initial events in the
cellular effects of ionizing radiations: Clustered damage in DNA.
Int J Radiat Biol. 65:7–17. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fulda S, Gorman AM, Hori O and Samali A:
Cellular stress responses: Cell survival and cell death. Int J Cell
Biol. 2010:2140742010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Polanowska J, Martin JS, Garcia-Muse T,
Petalcorin MI and Boulton SJ: A conserved pathway to activate
BRCA1-dependent ubiquitylation at DNA damage sites. EMBO J.
25:2178–2188. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao GY, Sonoda E, Barber LJ, Oka H,
Murakawa Y, Yamada K, Ikura T, Wang X, Kobayashi M, Yamamoto K, et
al: A critical role for the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Ubc13 in
initiating homologous recombination. Mol Cell. 25:663–675. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kraft C, Peter M and Hofmann K: Selective
autophagy: Ubiquitin-mediated recognition and beyond. Nat Cell
Biol. 12:836–841. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nedelsky NB, Todd PK and Taylor JP:
Autophagy and the ubiquitin-proteasome system: Collaborators in
neuroprotection. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1782:691–699. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cui H, Qin Q, Yang M, Zhang H, Liu Z, Yang
Y, Chen X, Zhu H, Wang D, Meng C, et al: Bortezomib enhances the
radiosensitivity of hypoxic cervical cancer cells by inhibiting
HIF-1α expression. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:9032–9041. 2015.
|
|
33
|
Zhao Y, Foster NR, Meyers JP, Thomas SP,
Northfelt DW, Rowland KM Jr, Mattar BI, Johnson DB, Molina JR,
Mandrekar SJ, et al: A phase I/II study of bortezomib in
combination with paclitaxel, carboplatin, and concurrent thoracic
radiation therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer: North Central
Cancer Treatment Group (NCCTG)-N0321. J Thorac Oncol. 10:172–180.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Lao CD, Friedman J, Tsien CI, Normolle DP,
Chapman C, Cao Y, Lee O, Schipper M, Van Poznak C, Hamstra D, et
al: Concurrent whole brain radiotherapy and bortezomib for brain
metastasis. Radiat Oncol. 8:2042013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
O'Neil BH, Raftery L, Calvo BF,
Chakravarthy AB, Ivanova A, Myers MO, Kim HJ, Chan E, Wise PE,
Caskey LS, et al: A phase I study of bortezomib in combination with
standard 5-fluorouracil and external-beam radiation therapy for the
treatment of locally advanced or metastatic rectal cancer. Clin
Colorectal Cancer. 9:119–125. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|