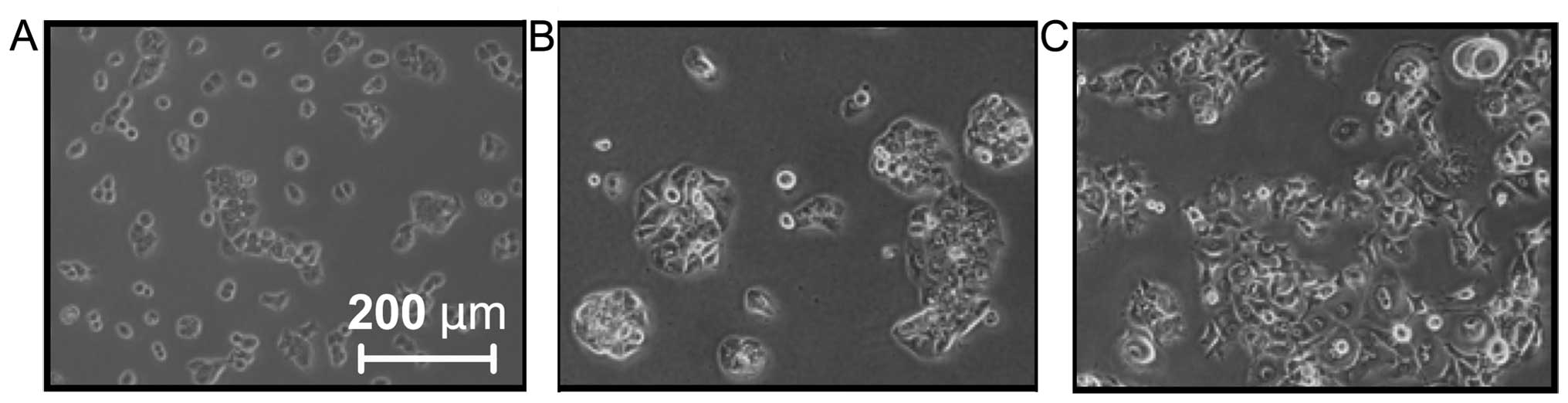
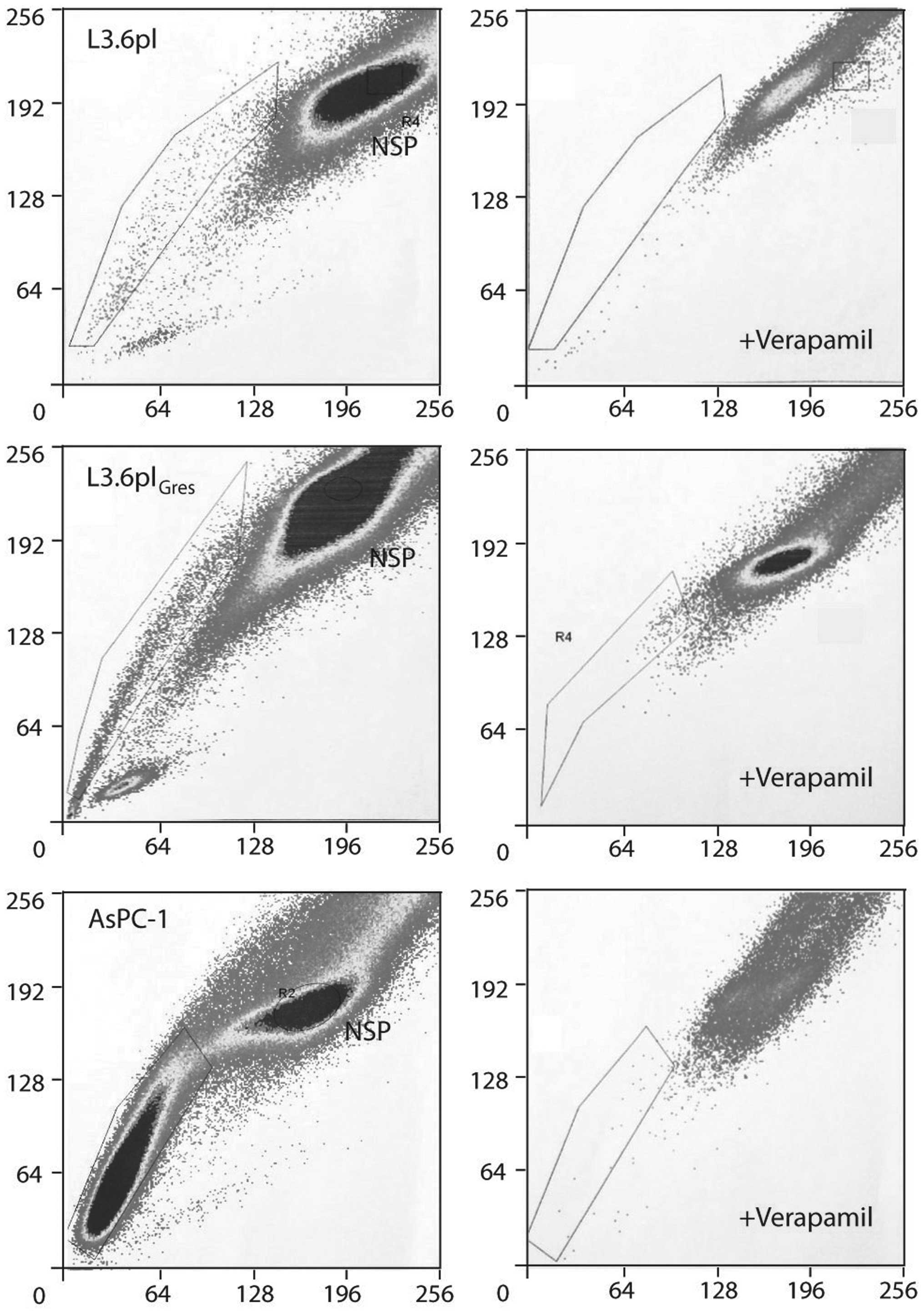
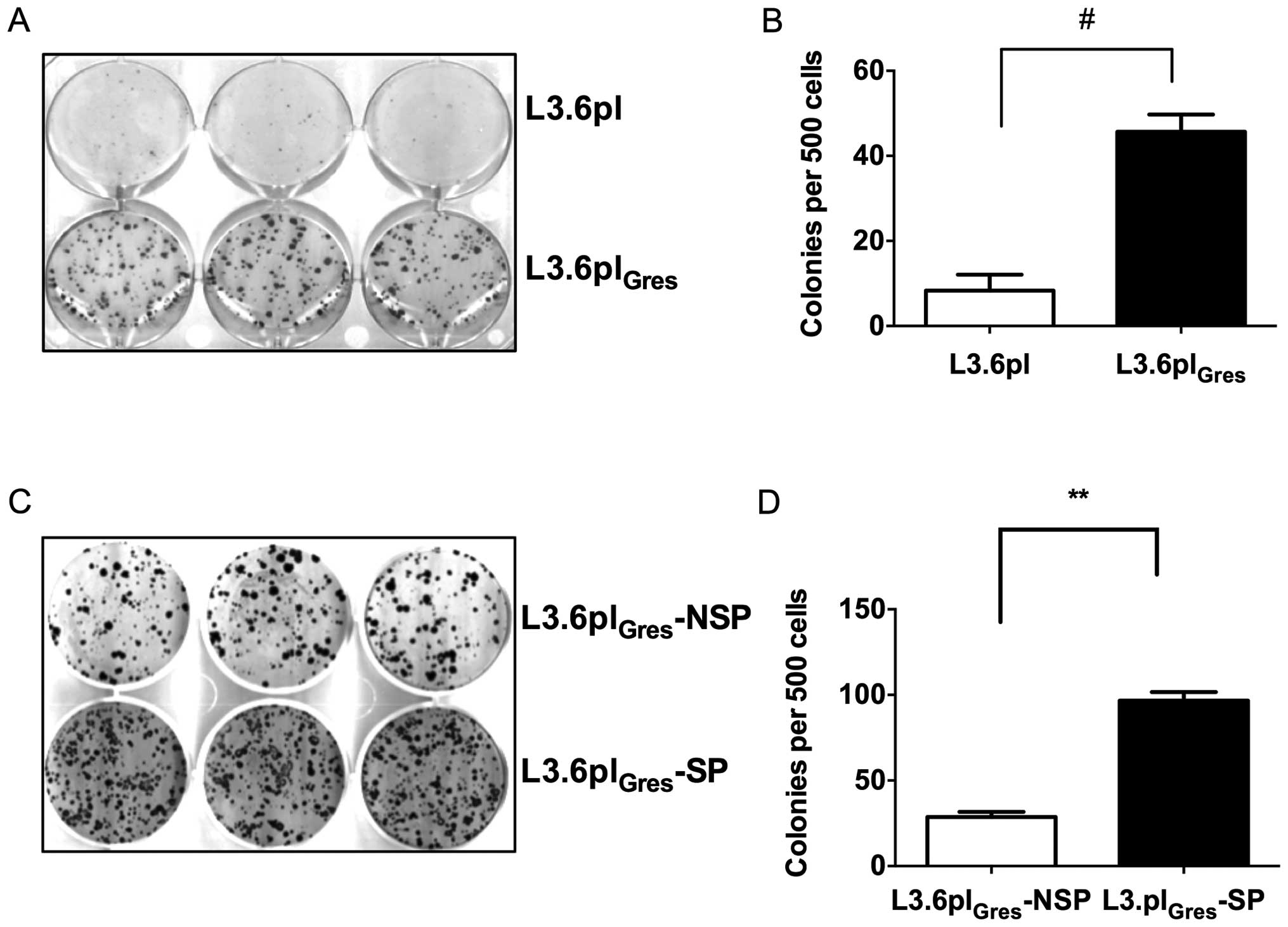
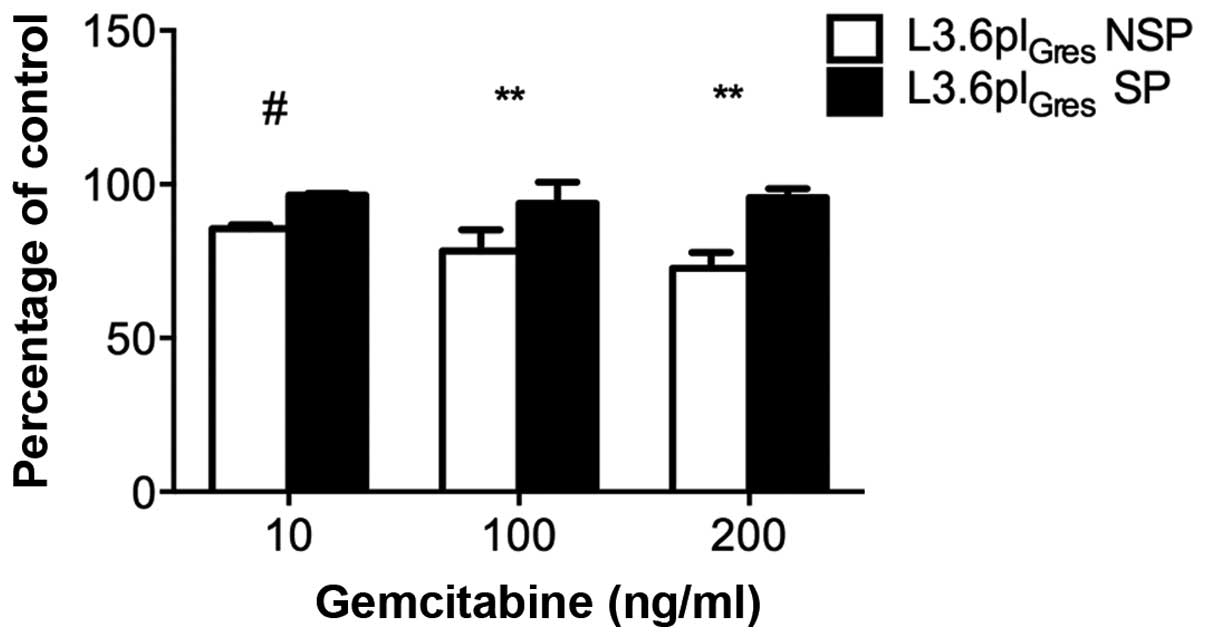
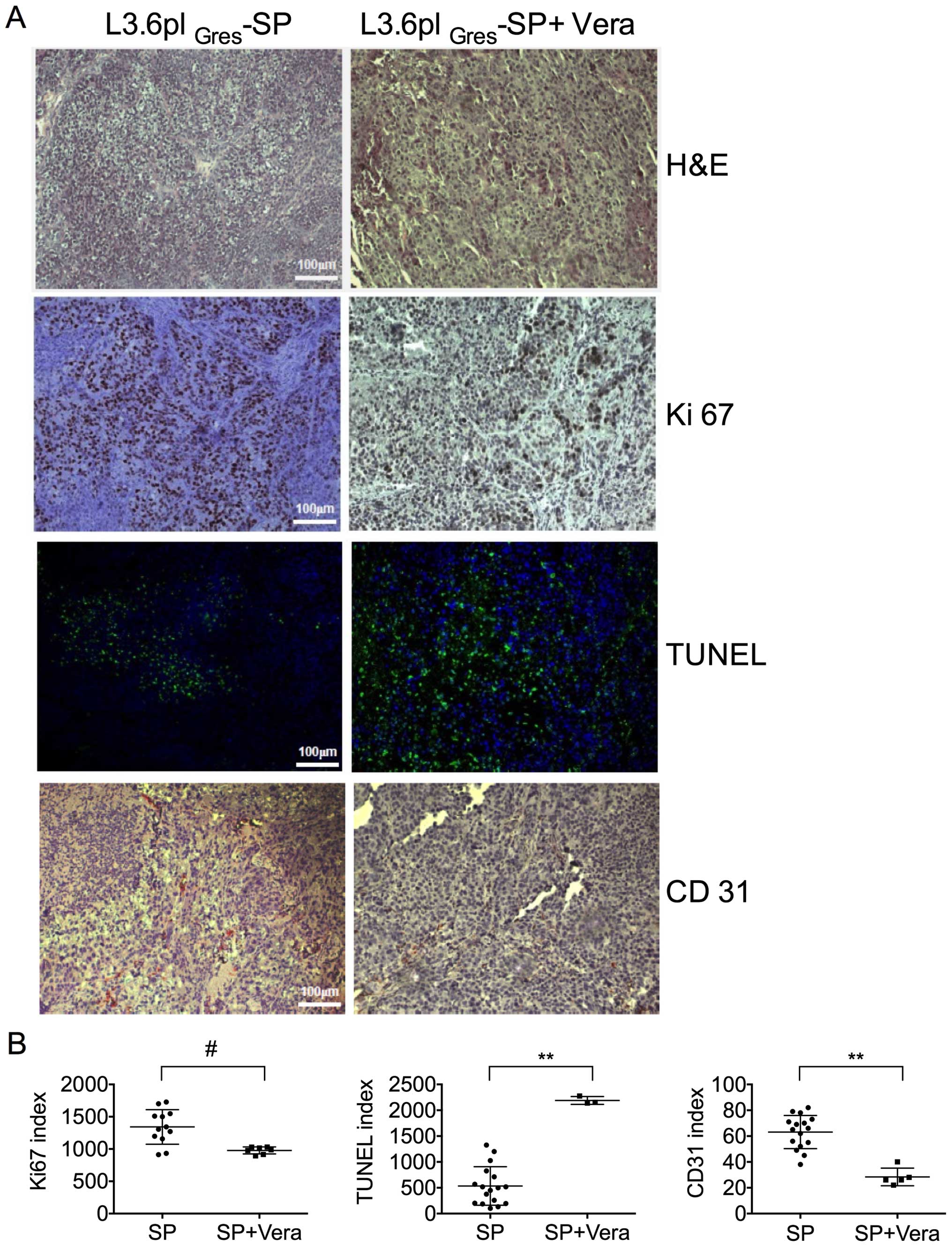
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fernandez E, La Vecchia C, Porta M, Negri
E, Lucchini F and Levi F: Trends in pancreatic cancer mortality in
Europe, 1955–1989. Int J Cancer. 57:786–792. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen M, Xue X, Wang F, An Y, Tang D, Xu Y,
Wang H, Yuan Z, Gao W, Wei J, et al: Expression and promoter
methylation analysis of ATP-binding cassette genes in pancreatic
cancer. Oncol Rep. 27:265–269. 2012.
|
|
4
|
Arbuck SG: Overview of chemotherapy for
pancreatic cancer. Int J Pancreatol. 7:209–222. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Suwa H, Ohshio G, Arao S, Imamura T,
Yamaki K, Manabe T, Imamura M, Hiai H and Fukumoto M:
Immunohistochemical localization of P-glycoprotein and expression
of the multidrug resistance-1 gene in human pancreatic cancer:
Relevance to indicator of better prognosis. Jpn J Cancer Res.
87:641–649. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Grant CE, Valdimarsson G, Hipfner DR,
Almquist KC, Cole SP and Deeley RG: Overexpression of multidrug
resistance-associated protein (MRP) increases resistance to natural
product drugs. Cancer Res. 54:357–361. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Germann UA, Chambers TC, Ambudkar SV,
Licht T, Cardarelli CO, Pastan I and Gottesman MM: Characterization
of phosphorylation-defective mutants of human P-glycoprotein
expressed in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 271:1708–1716. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Childs S and Ling V: The MDR superfamily
of genes and its biological implications. Important Adv Oncol.
21–36. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chin KV, Pastan I and Gottesman MM:
Function and regulation of the human multidrug resistance gene. Adv
Cancer Res. 60:157–180. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Thomas H and Coley HM: Overcoming
multidrug resistance in cancer: an update on the clinical strategy
of inhibiting P-glycoprotein. Cancer Control. 10:159–165.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hagmann W, Jesnowski R and Löhr JM:
Interdependence of gemcitabine treatment, transporter expression,
and resistance in human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Neoplasia.
12:740–747. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mackey JR, Mani RS, Selner M, Mowles D,
Young JD, Belt JA, Crawford CR and Cass CE: Functional nucleoside
transporters are required for gemcitabine influx and manifestation
of toxicity in cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 58:4349–4357.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ritzel MW, Ng AM, Yao SY, Graham K, Loewen
SK, Smith KM, Ritzel RG, Mowles DA, Carpenter P, Chen XZ, et al:
Molecular identification and characterization of novel human and
mouse concentrative Na+-nucleoside cotransporter
proteins (hCNT3 and mCNT3) broadly selective for purine and
pyrimidine nucleosides (system cib). J Biol Chem. 276:2914–2927.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Garcia-Manteiga J, Molina-Arcas M, Casado
FJ, Mazo A and Pastor-Anglada M: Nucleoside transporter profiles in
human pancreatic cancer cells: Role of hCNT1 in
2′,2′-difluorodeoxy-cytidine- induced cytotoxicity. Clin Cancer
Res. 9:5000–5008. 2003.
|
|
15
|
Al-Hajj M and Clarke MF: Self-renewal and
solid tumor stem cells. Oncogene. 23:7274–7282. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Goodell MA, Brose K, Paradis G, Conner AS
and Mulligan RC: Isolation and functional properties of murine
hematopoietic stem cells that are replicating in vivo. J Exp Med.
183:1797–1806. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bunting KD, Zhou S, Lu T and Sorrentino
BP: Enforced P-glycoprotein pump function in murine bone marrow
cells results in expansion of side population stem cells in vitro
and repopulating cells in vivo. Blood. 96:902–909. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou S, Schuetz JD, Bunting KD, Colapietro
AM, Sampath J, Morris JJ, Lagutina I, Grosveld GC, Osawa M,
Nakauchi H, et al: The ABC transporter Bcrp1/ABCG2 is expressed in
a wide variety of stem cells and is a molecular determinant of the
side-population phenotype. Nat Med. 7:1028–1034. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hirschmann-Jax C, Foster AE, Wulf GG,
Nuchtern JG, Jax TW, Gobel U, Goodell MA and Brenner MK: A distinct
‘side population’ of cells with high drug efflux capacity in human
tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:14228–14233. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Benchaouir R, Rameau P, Decraene C,
Dreyfus P, Israeli D, Piétu G, Danos O and Garcia L: Evidence for a
resident subset of cells with SP phenotype in the C2C12 myogenic
line: A tool to explore muscle stem cell biology. Exp Cell Res.
294:254–268. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ambudkar SV, Dey S, Hrycyna CA,
Ramachandra M, Pastan I and Gottesman MM: Biochemical, cellular,
and pharmacological aspects of the multidrug transporter. Annu Rev
Pharmacol Toxicol. 39:361–398. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yao J, Cai HH, Wei JS, An Y, Ji ZL, Lu ZP,
Wu JL, Chen P, Jiang KR, Dai CC, et al: Side population in the
pancreatic cancer cell lines SW1990 and CFPAC-1 is enriched with
cancer stem-like cells. Oncol Rep. 23:1375–1382. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang SN, Huang FT, Huang YJ, Zhong W and
Yu Z: Characterization of a cancer stem cell-like side population
derived from human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Tumori.
96:985–992. 2010.
|
|
24
|
Vohra J: Verapamil in cardiac arrhythmias:
An overview. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol Suppl. 6:129–134.
1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bellamy WT: P-glycoproteins and multidrug
resistance. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 36:161–183. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Broxterman HJ, Lankelma J and Pinedo HM:
How to probe clinical tumour samples for P-glycoprotein and
multidrug resistance-associated protein. Eur J Cancer.
32A:1024–1033. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ince P, Appleton DR, Finney KJ, Sunter JP
and Watson AJ: Verapamil increases the sensitivity of primary human
colorectal carcinoma tissue to vincristine. Br J Cancer.
53:137–139. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Merry S, Fetherston CA, Kaye SB, Freshney
RI and Plumb JA: Resistance of human glioma to adriamycin in vitro:
The role of membrane transport and its circumvention with
verapamil. Br J Cancer. 53:129–135. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Morrow M, Wait RB, Rosenthal RA and
Gamelli RL: Verapamil enhances antitumor activity without
increasing myeloid toxicity. Surgery. 101:63–68. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tsuruo T, Iida H, Tsukagoshi S and Sakurai
Y: Overcoming of vincristine resistance in P388 leukemia in vivo
and in vitro through enhanced cytotoxicity of vincristine and
vinblastine by verapamil. Cancer Res. 41:1967–1972. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bruns CJ, Harbison MT, Kuniyasu H, Eue I
and Fidler IJ: In vivo selection and characterization of metastatic
variants from human pancreatic adenocarcinoma by using orthotopic
implantation in nude mice. Neoplasia. 1:50–62. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Guillermet-Guibert J, Davenne L,
Pchejetski D, Saint-Laurent N, Brizuela L, Guilbeau-Frugier C,
Delisle MB, Cuvillier O, Susini C and Bousquet C: Targeting the
sphingolipid metabolism to defeat pancreatic cancer cell resistance
to the chemotherapeutic gemcitabine drug. Mol Cancer Ther.
8:809–820. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Reddy KL, Zullo JM, Bertolino E and Singh
H: Transcriptional repression mediated by repositioning of genes to
the nuclear lamina. Nature. 452:243–247. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Georges E, Bradley G, Gariepy J and Ling
V: Detection of P-glycoprotein isoforms by gene-specific monoclonal
antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 87:152–156. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dalerba P, Dylla SJ, Park IK, Liu R, Wang
X, Cho RW, Hoey T, Gurney A, Huang EH, Simeone DM, et al:
Phenotypic characterization of human colorectal cancer stem cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:10158–10163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Clayton S and Mousa SA: Therapeutics
formulated to target cancer stem cells: Is it in our future? Cancer
Cell Int. 11:72011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gibbs CP, Kukekov VG, Reith JD,
Tchigrinova O, Suslov ON, Scott EW, Ghivizzani SC, Ignatova TN and
Steindler DA: Stem-like cells in bone sarcomas: Implications for
tumorigenesis. Neoplasia. 7:967–976. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Challen GA and Little MH: A side order of
stem cells: The SP phenotype. Stem Cells. 24:3–12. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wulf GG, Wang RY, Kuehnle I, Weidner D,
Marini F, Brenner MK, Andreeff M and Goodell MA: A leukemic stem
cell with intrinsic drug efflux capacity in acute myeloid leukemia.
Blood. 98:1166–1173. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Grichnik JM, Burch JA, Schulteis RD, Shan
S, Liu J, Darrow TL, Vervaert CE and Seigler HF: Melanoma, a tumor
based on a mutant stem cell? J Invest Dermatol. 126:142–153. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Szotek PP, Pieretti-Vanmarcke R, Masiakos
PT, Dinulescu DM, Connolly D, Foster R, Dombkowski D, Preffer F,
Maclaughlin DT and Donahoe PK: Ovarian cancer side population
defines cells with stem cell-like characteristics and Mullerian
inhibiting substance responsiveness. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:11154–11159. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kondo T, Setoguchi T and Taga T:
Persistence of a small subpopulation of cancer stem-like cells in
the C6 glioma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:781–786. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Haraguchi N, Utsunomiya T, Inoue H, Tanaka
F, Mimori K, Barnard GF and Mori M: Characterization of a side
population of cancer cells from human gastrointestinal system. Stem
Cells. 24:506–513. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Asuthkar S, Stepanova V, Lebedeva T,
Holterman AL, Estes N, Cines DB, Rao JS and Gondi CS:
Multifunctional roles of urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) in
cancer stemness and chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer. Mol Biol
Cell. 24:2620–2632. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhou J, Wang CY, Liu T, Wu B, Zhou F,
Xiong JX, Wu HS, Tao J, Zhao G, Yang M, et al: Persistence of side
population cells with high drug efflux capacity in pancreatic
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 14:925–930. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kabashima A, Higuchi H, Takaishi H,
Matsuzaki Y, Suzuki S, Izumiya M, Iizuka H, Sakai G, Hozawa S,
Azuma T, et al: Side population of pancreatic cancer cells
predominates in TGF-beta-mediated epithelial to mesenchymal
transition and invasion. Int J Cancer. 124:2771–2779. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yang AD, Fan F, Camp ER, van Buren G, Liu
W, Somcio R, Gray MJ, Cheng H, Hoff PM and Ellis LM: Chronic
oxaliplatin resistance induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
in colorectal cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res. 12:4147–4153.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Okano M, Konno M, Kano Y, Kim H, Kawamoto
K, Ohkuma M, Haraguchi N, Yokobori T, Mimori K, Yamamoto H, et al:
Human colorectal CD24+ cancer stem cells are susceptible
to epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Oncol. 45:575–580.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhao Y, Bao Q, Schwarz B, Zhao L,
Mysliwietz J, Ellwart J, Renner A, Hirner H, Niess H, Camaj P, et
al: Stem cell-like side populations in esophageal cancer: A source
of chemotherapy resistance and metastases. Stem Cells Dev.
23:180–192. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Doyle L and Ross DD: Multidrug resistance
mediated by the breast cancer resistance protein BCRP (ABCG2).
Oncogene. 22:7340–7358. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jensen RL, Lee YS, Guijrati M, Origitano
TC, Wurster RD and Reichman OH: Inhibition of in vitro meningioma
proliferation after growth factor stimulation by calcium channel
antagonists: Part II - Additional growth factors, growth factor
receptor immunohistochemistry, and intracellular calcium
measurements. Neurosurgery. 37:937–946; discussion 946-937. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Zhao Y, Zhao L, Ischenko I, Bao Q, Schwarz
B, Nieß H, Wang Y, Renner A, Mysliwietz J, Jauch KW, et al:
Antisense inhibition of microRNA-21 and microRNA-221 in
tumor-initiating stem-like cells modulates tumorigenesis,
metastasis, and chemotherapy resistance in pancreatic cancer.
Target Oncol. 10:535–548. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Jensen RL, Petr M and Wurster RD: Calcium
channel antagonist effect on in vitro meningioma signal
transduction pathways after growth factor stimulation.
Neurosurgery. 46:692–702; discussion 702-693. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Berridge MJ, Lipp P and Bootman MD: Signal
transduction. The calcium entry pas de deux. Science.
287:1604–1605. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hajnóczky G, Csordás G, Madesh M and
Pacher P: Control of apoptosis by IP(3) and ryanodine receptor
driven calcium signals. Cell Calcium. 28:349–363. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Cao QZ, Niu G and Tan HR: In vitro growth
inhibition of human colonic tumor cells by Verapamil. World J
Gastroenterol. 11:2255–2259. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Trompier D, Chang XB, Barattin R, du
Moulinet D'Hardemare A, Di Pietro A and Baubichon-Cortay H:
Verapamil and its derivative trigger apoptosis through glutathione
extrusion by multidrug resistance protein MRP1. Cancer Res.
64:4950–4956. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ghibelli L, Coppola S, Rotilio G, Lafavia
E, Maresca V and Ciriolo MR: Non-oxidative loss of glutathione in
apoptosis via GSH extrusion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
216:313–320. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wang F, Zhang D, Zhang Q, Chen Y, Zheng D,
Hao L, Duan C, Jia L, Liu G and Liu Y: Synergistic effect of
folate-mediated targeting and verapamil-mediated P-gp inhibition
with paclitaxel-polymer micelles to overcome multi-drug resistance.
Biomaterials. 32:9444–9456. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yalowich JC and Ross WE: Verapamil-induced
augmentation of etoposide accumulation in L1210 cells in vitro.
Cancer Res. 45:1651–1656. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Robinson BA, Clutterbuck RD, Millar JL and
McElwain TJ: Verapamil potentiation of melphalan cytotoxicity and
cellular uptake in murine fibrosarcoma and bone marrow. Br J
Cancer. 52:813–822. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Spratlin J, Sangha R, Glubrecht D, Dabbagh
L, Young JD, Dumontet C, Cass C, Lai R and Mackey JR: The absence
of human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 is associated with
reduced survival in patients with gemcitabine-treated pancreas
adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 10:6956–6961. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|