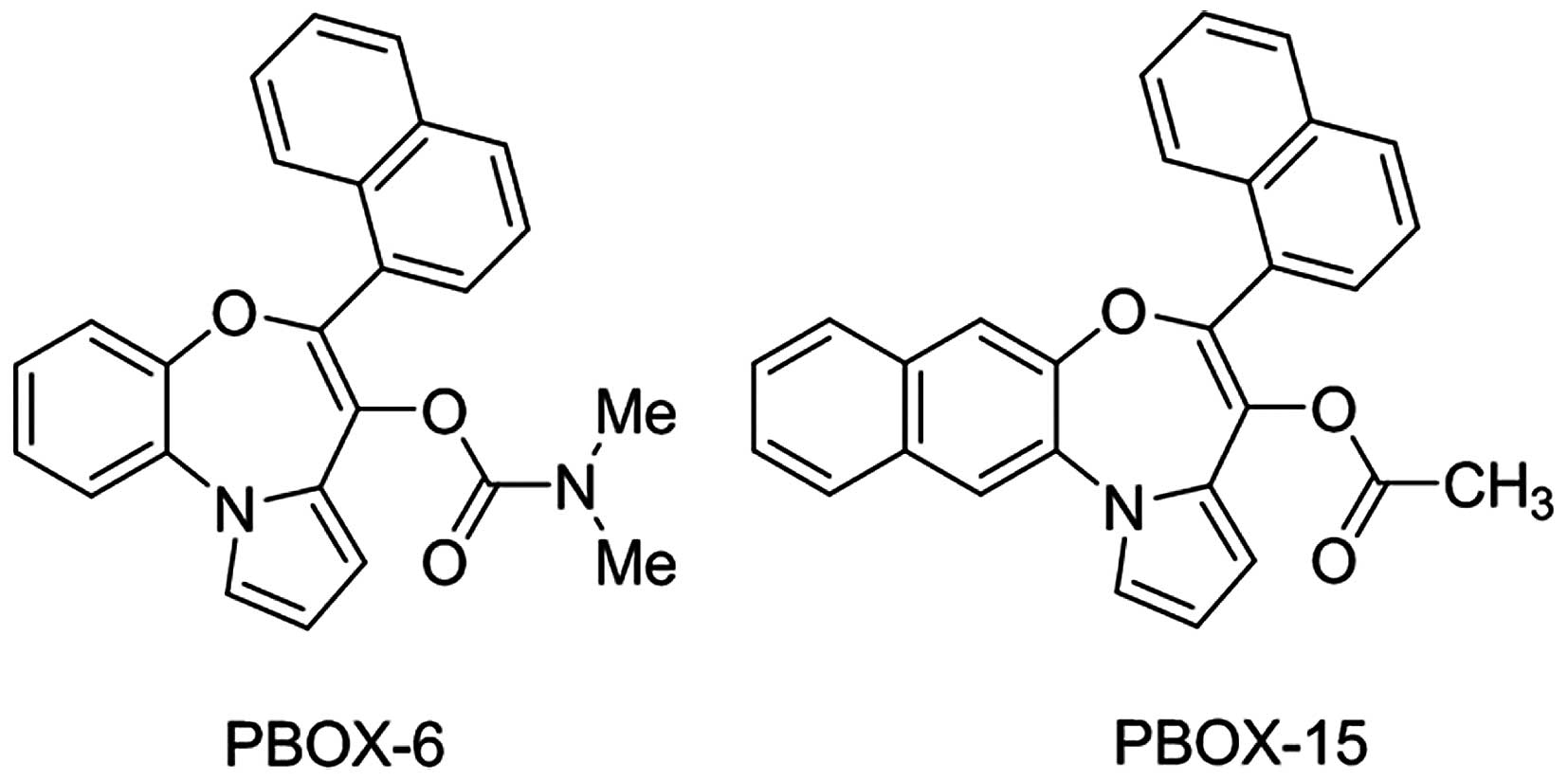
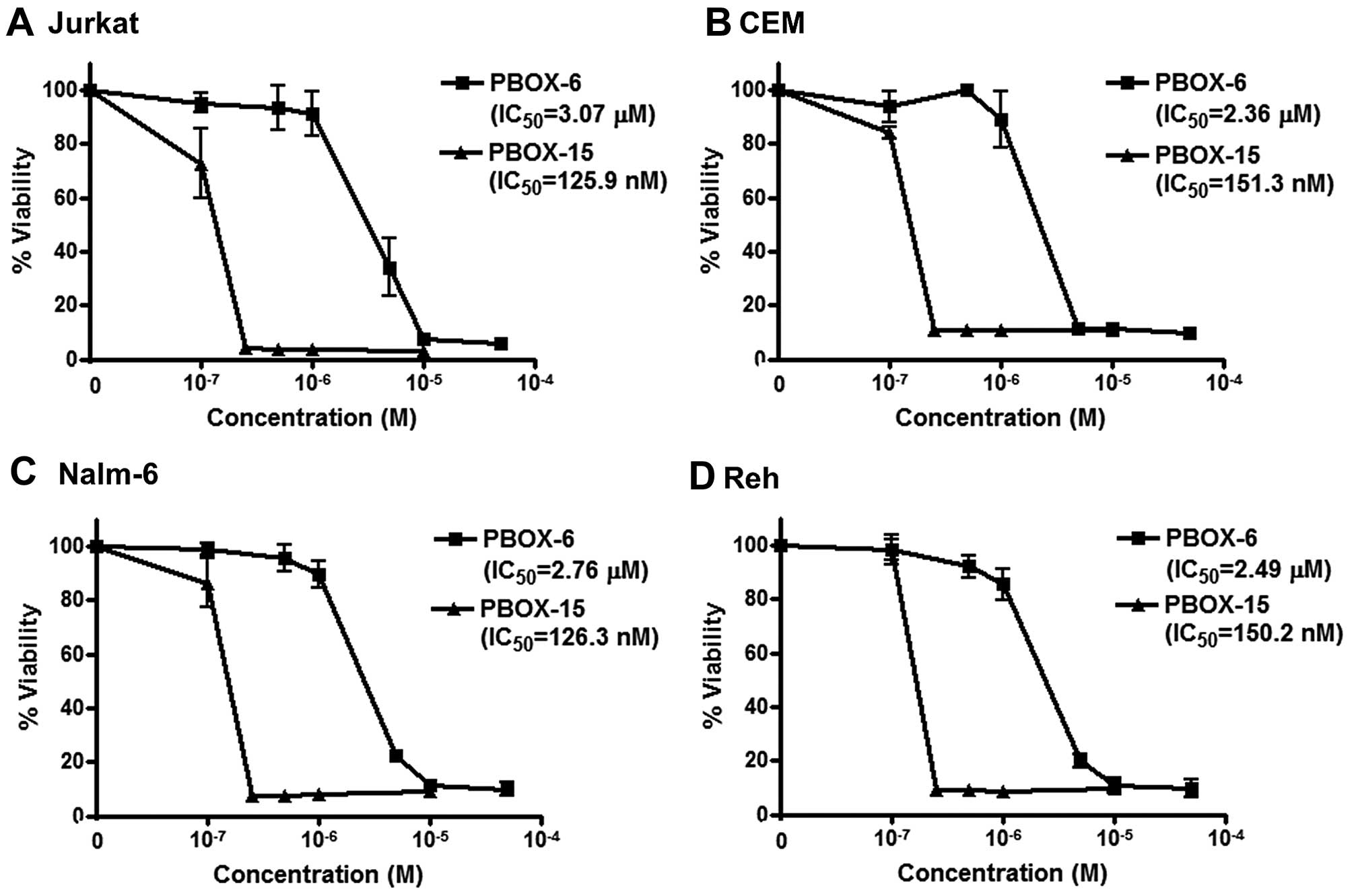
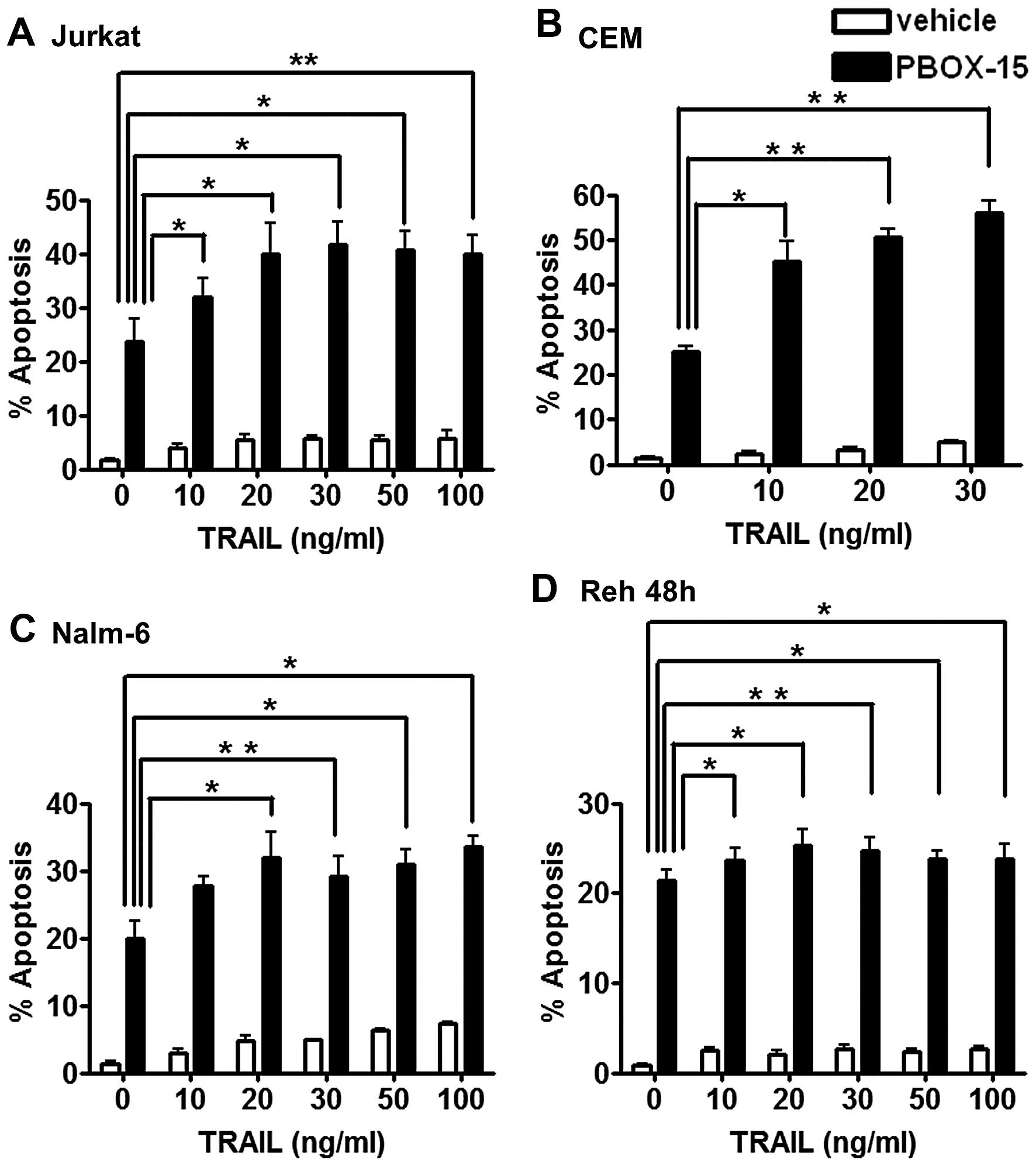
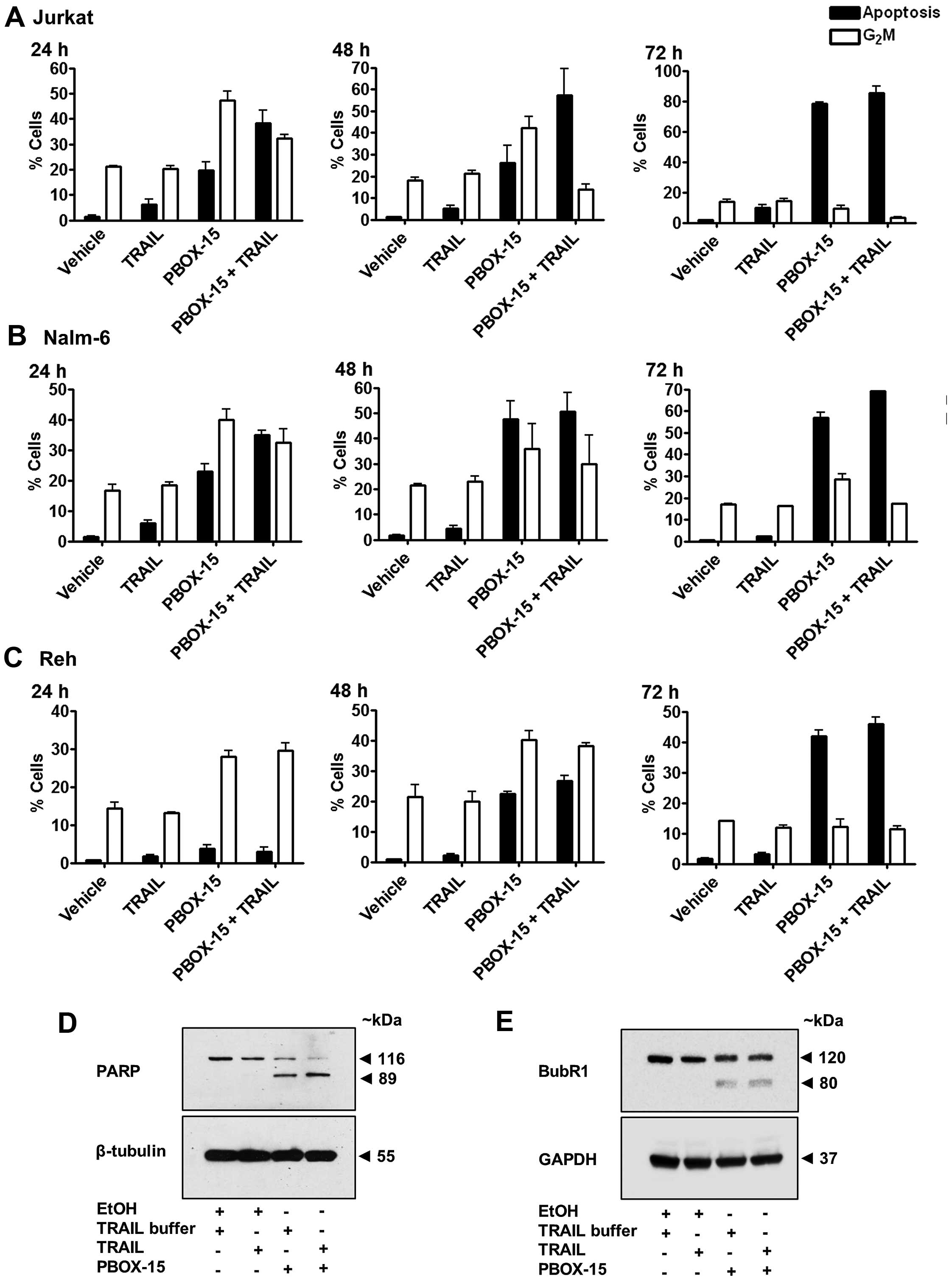
|
1
|
Inaba H, Greaves M and Mullighan CG: Acute
lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet. 381:1943–1955. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Banihashem A, Ghasemi A, Ghaemi N, Moazzen
N and Amirabadi A: Prevalence of transient hyperglycemia and
diabetes mellitus in pediatric patients with acute leukemia. Iran J
Ped Hematol Oncol. 4:5–10. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Woo JS, Alberti MO and Tirado CA:
Childhood B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A genetic update. Exp
Hematol Oncol. 3:162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guicciardi ME and Gores GJ: Life and death
by death receptors. FASEB J. 23:1625–1637. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
French LE and Tschopp J: Protein-based
therapeutic approaches targeting death receptors. Cell Death
Differ. 10:117–123. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Prasad S, Kim JH, Gupta SC and Aggarwal
BB: Targeting death receptors for TRAIL by agents designed by
Mother Nature. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 35:520–536. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Daniels RA, Turley H, Kimberley FC, Liu
XS, Mongkolsapaya J, Ch'En P, Xu XN, Jin BQ, Pezzella F and
Screaton GR: Expression of TRAIL and TRAIL receptors in normal and
malignant tissues. Cell Res. 15:430–438. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang S and El-Deiry WS: TRAIL and
apoptosis induction by TNF-family death receptors. Oncogene.
22:8628–8633. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stuckey DW and Shah K: TRAIL on trial:
Preclinical advances in cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med. 19:685–694.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bellail AC, Qi L, Mulligan P, Chhabra V
and Hao C: TRAIL agonists on clinical trials for cancer therapy:
The promises and the challenges. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 4:34–41.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mahalingam D, Szegezdi E, Keane M, de Jong
S and Samali A: TRAIL receptor signalling and modulation: Are we on
the right TRAIL? Cancer Treat Rev. 35:280–288. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ashkenazi A, Holland P and Eckhardt SG:
Ligand-based targeting of apoptosis in cancer: The potential of
recombinant human apoptosis ligand 2/Tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand (rhApo2L/TRAIL). J Clin Oncol.
26:3621–3630. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ehrhardt H, Fulda S, Schmid I, Hiscott J,
Debatin KM and Jeremias I: TRAIL induced survival and proliferation
in cancer cells resistant towards TRAIL-induced apoptosis mediated
by NF-kappaB. Oncogene. 22:3842–3852. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fakler M, Loeder S, Vogler M, Schneider K,
Jeremias I, Debatin KM and Fulda S: Small molecule XIAP inhibitors
cooperate with TRAIL to induce apoptosis in childhood acute
leukemia cells and overcome Bcl-2-mediated resistance. Blood.
113:1710–1722. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hellwig CT and Rehm M: TRAIL signaling and
synergy mechanisms used in TRAIL-based combination therapies. Mol
Cancer Ther. 11:3–13. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Leong S, Cohen RB, Gustafson DL, Langer
CJ, Camidge DR, Padavic K, Gore L, Smith M, Chow LQ, von Mehren M,
et al: Mapatumumab, an antibody targeting TRAIL-R1, in combination
with paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with advanced solid
malignancies: Results of a phase I and pharmacokinetic study. J
Clin Oncol. 27:4413–4421. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Maginn EN, Browne PV, Hayden P,
Vandenberghe E, MacDonagh B, Evans P, Goodyer M, Tewari P, Campiani
G, Butini S, et al: PBOX-15, a novel microtubule targeting agent,
induces apoptosis, upregulates death receptors, and potentiates
TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells. Br J Cancer.
104:281–289. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Mulligan JM, Greene LM, Cloonan S, Mc Gee
MM, Onnis V, Campiani G, Fattorusso C, Lawler M, Williams DC and
Zisterer DM: Identification of tubulin as the molecular target of
proapoptotic pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepines. Mol Pharmacol. 70:60–70.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lysaght J, Verma NK, Maginn EN, Ryan JM,
Campiani G, Zisterer DM, Williams DC, Browne PV, Lawler MP and
McElligott AM: The microtubule targeting agent PBOX-15 inhibits
integrin-mediated cell adhesion and induces apoptosis in acute
lymphoblastic leukaemia cells. Int J Oncol. 42:239–246. 2013.
|
|
20
|
McElligott AM, Maginn EN, Greene LM,
McGuckin S, Hayat A, Browne PV, Butini S, Campiani G, Catherwood
MA, Vandenberghe E, et al: The novel tubulin-targeting agent
pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepine-15 induces apoptosis in poor prognostic
subgroups of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Res.
69:8366–8375. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Greene LM, Kelly L, Onnis V, Campiani G,
Lawler M, Williams DC and Zisterer DM: STI-571 (imatinib mesylate)
enhances the apoptotic efficacy of pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepine-6, a
novel microtubule-targeting agent, in both STI-571-sensitive and
-resistant Bcr-Abl-positive human chronic myeloid leukemia cells. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 321:288–297. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zisterer DM, McGee MM, Campiani G, Ramunno
A, Fattorusso C, Nacci V, Lawler M and Williams DC:
Pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepines: A new class of apoptotic agents.
Biochem Soc Trans. 29:704–706. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nathwani SM, Butler S, Fayne D, McGovern
NN, Sarkadi B, Meegan MJ, Lloyd DG, Campiani G, Lawler M, Williams
DC, et al: Novel microtubule-targeting agents,
pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepines, induce apoptosis in
multi-drug-resistant cancer cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
66:585–596. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Bright SA, McElligott AM, O'Connell JW,
O'Connor L, Carroll P, Campiani G, Deininger MW, Conneally E,
Lawler M, Williams DC, et al: Novel pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepine
compounds display significant activity against resistant chronic
myeloid leukaemia cells in vitro, in ex vivo patient samples and in
vivo. Br J Cancer. 102:1474–1482. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mc Gee MM, Gemma S, Butini S, Ramunno A,
Zisterer DM, Fattorusso C, Catalanotti B, Kukreja G, Fiorini I,
Pisano C, et al: Pyrrolo[1,5]benzoxa(thia)zepines as a new class of
potent apoptotic agents. Biological studies and identification of
an intracellular location of their drug target. J Med Chem.
48:4367–4377. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
van der Sloot AM, Mullally MM,
Fernandez-Ballester G, Serrano L and Quax WJ: Stabilization of
TRAIL, an all-beta-sheet multimeric protein, using computational
redesign. Protein Eng Des Sel. 17:673–680. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
van der Sloot AM, Tur V, Szegezdi E,
Mullally MM, Cool RH, Samali A, Serrano L and Quax WJ: Designed
tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand variants
initiating apoptosis exclusively via the DR5 receptor. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 103:8634–8639. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Greene LM, Campiani G, Lawler M, Williams
DC and Zisterer DM: BubR1 is required for a sustained mitotic
spindle checkpoint arrest in human cancer cells treated with
tubulin-targeting pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepines. Mol Pharmacol.
73:419–430. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Nathwani SM, Cloonan SM, Stronach M,
Campiani G, Lawler M, Williams DC and Zisterer DM: Novel
microtubule-targeting agents, pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepines, induce
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Oncol
Rep. 24:1499–1507. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sung B, Park B, Yadav VR and Aggarwal BB:
Celastrol, a triterpene, enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis through
the down-regulation of cell survival proteins and up-regulation of
death receptors. J Biol Chem. 285:11498–11507. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nimmanapalli R, Perkins CL, Orlando M,
O'Bryan E, Nguyen D and Bhalla KN: Pretreatment with paclitaxel
enhances apo-2 ligand/tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis of prostate cancer
cells by inducing death receptors 4 and 5 protein levels. Cancer
Res. 61:759–763. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hunter TB, Manimala NJ, Luddy KA, Catlin T
and Antonia SJ: Paclitaxel and TRAIL synergize to kill
paclitaxel-resistant small cell lung cancer cells through a
caspase-independent mechanism mediated through AIF. Anticancer Res.
31:3193–3204. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M, Schneider P,
Hofmann K, Steiner V, Bodmer JL, Schröter M, Burns K, Mattmann C,
et al: Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP.
Nature. 388:190–195. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fulda S: Inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP)
proteins in hematological malignancies: Molecular mechanisms and
therapeutic opportunities. Leukemia. 28:1414–1422. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen D and Zhou Q: Caspase cleavage of
BimEL triggers a positive feedback amplification of apoptotic
signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:1235–1240. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tabellini G, Tazzari PL, Bortul R,
Evangelisti C, Billi AM, Grafone T, Martinelli G, Baccarani M and
Martelli AM: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt inhibition increases
arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis of acute promyelocytic and
T-cell leukaemias. Br J Haematol. 130:716–725. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Franke TF: PI3K/Akt: Getting it right
matters. Oncogene. 27:6473–6488. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mérino D, Lalaoui N, Morizot A, Solary E
and Micheau O: TRAIL in cancer therapy: Present and future
challenges. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 11:1299–1314. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Akahane K, Inukai T, Zhang X, Hirose K,
Kuroda I, Goi K, Honna H, Kagami K, Nakazawa S, Endo K, et al:
Resistance of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia to tumor necrosis
factor--related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis. Exp
Hematol. 38:885–895. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zheng T, Fu JJ, Hu L, Qiu F, Hu M, Zhu JJ,
Hua ZC and Wang H: Nanoarchitectured electrochemical cytosensors
for selective detection of leukemia cells and quantitative
evaluation of death receptor expression on cell surfaces. Anal
Chem. 85:5609–5616. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim K, Fisher MJ, Xu SQ and el-Deiry WS:
Molecular determinants of response to TRAIL in killing of normal
and cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 6:335–346. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang Y and Zhang B: TRAIL resistance of
breast cancer cells is associated with constitutive endocytosis of
death receptors 4 and 5. Mol Cancer Res. 6:1861–1871. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
McDonald ER III, Chui PC, Martelli PF,
Dicker DT and El-Deiry WS: Death domain mutagenesis of KILLER/DR5
reveals residues critical for apoptotic signaling. J Biol Chem.
276:14939–14945. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kojima Y, Nakayama M, Nishina T, Nakano H,
Koyanagi M, Takeda K, Okumura K and Yagita H: Importin β1
protein-mediated nuclear localization of death receptor 5 (DR5)
limits DR5/tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand (TRAIL)-induced cell death of human tumor cells. J Biol
Chem. 286:43383–43393. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sheridan JP, Marsters SA, Pitti RM, Gurney
A, Skubatch M, Baldwin D, Ramakrishnan L, Gray CL, Baker K, Wood
WI, et al: Control of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by a family of
signaling and decoy receptors. Science. 277:818–821. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tong HX, Lu CW, Wang QS and Ma LY:
Combination of IFNγ and chemotherapeutic agents increase TRAIL
sensitivity of neuroblastoma cell lines. Eur J Pediatr Surg.
21:304–309. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kim HR, Lee MW, Kim DS, Jo HY, Lee SH,
Chueh HW, Jung HL, Yoo KH, Sung KW and Koo HH: Etoposide sensitizes
neuroblastoma cells expressing caspase 8 to TRAIL. Cell Biol Int
Rep 2010. 19:e000172012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Timur M, Cort A, Ozdemir E, Sarikcioglu
SB, Sanlioglu S, Sanlioglu AD and Ozben T: Bleomycin induced
sensitivity to TRAIL/Apo-2L-mediated apoptosis in human
seminomatous testicular cancer cells is correlated with
upregulation of death receptors. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
15:99–106. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Venza I, Visalli M, Oteri R, Teti D and
Venza M: Class I-specific histone deacetylase inhibitor MS-275
overrides TRAIL-resistance in melanoma cells by downregulating
c-FLIP. Int Immunopharmacol. 21:439–446. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Green DR: Apoptotic pathways: Paper wraps
stone blunts scissors. Cell. 102:1–4. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Schug ZT, Gonzalvez F, Houtkooper RH, Vaz
FM and Gottlieb E: BID is cleaved by caspase-8 within a native
complex on the mitochondrial membrane. Cell Death Differ.
18:538–548. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
52
|
Safa AR: c-FLIP, a master anti-apoptotic
regulator. Exp Oncol. 34:176–184. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Safa AR: Roles of c-FLIP in apoptosis,
necroptosis, and autophagy. J Carcinog Mutagen (Suppl).
6:0032013.
|
|
54
|
Zang F, Wei X, Leng X, Yu M and Sun B:
C-FLIP(L) contributes to TRAIL resistance in HER2-positive breast
cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 450:267–273. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ding L, Yuan C, Wei F, Wang G, Zhang J,
Bellail AC, Zhang Z, Olson JJ and Hao C: Cisplatin restores TRAIL
apoptotic pathway in glioblastoma-derived stem cells through
up-regulation of DR5 and down-regulation of c-FLIP. Cancer Invest.
29:511–520. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ding J, Polier G, Köhler R, Giaisi M,
Krammer PH and Li-Weber M: Wogonin and related natural flavones
overcome tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
(TRAIL) protein resistance of tumors by down-regulation of c-FLIP
protein and up-regulation of TRAIL receptor 2 expression. J Biol
Chem. 287:641–649. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
57
|
Li LC, Jayaram S, Ganesh L, Qian L,
Rotmensch J, Maker AV and Prabhakar BS: Knockdown of MADD and
c-FLIP overcomes resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in ovarian
cancer cells. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 205:362.e12–362.e25. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Bose P and Grant S: Mcl-1 as a therapeutic
target in acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). Leuk Res Rep. 2:12–14.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Scarfò L and Ghia P: Reprogramming cell
death: BCL2 family inhibition in hematological malignancies.
Immunol Lett. 155:36–39. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
McGee MM, Greene LM, Ledwidge S, Campiani
G, Nacci V, Lawler M, Williams DC and Zisterer DM: Selective
induction of apoptosis by the pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepine
7-[[dimethylcarbamoyl] oxy]-6-(2-naphthyl)pyrrolo-[2,1-d]
(1,5)-benzoxazepine (PBOX-6) in Leukemia cells occurs via the c-Jun
NH2-terminal kinase-dependent phosphorylation and inactivation of
Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 310:1084–1095. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Lennon JC, Bright SA, Carroll E, Butini S,
Campiani G, O'Meara A, Williams DC and Zisterer DM: The novel
pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepine, PBOX-6, synergistically enhances the
apoptotic effects of carboplatin in drug sensitive and multidrug
resistant neuroblastoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 87:611–624. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Greene LM, Nolan DP, Regan-Komito D,
Campiani G, Williams DC and Zisterer DM: Inhibition of late-stage
autophagy synergistically enhances
pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepine-6-induced apoptotic cell death in human
colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 43:927–935. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Gill C, Dowling C, O'Neill AJ and Watson
RW: Effects of cIAP-1, cIAP-2 and XIAP triple knockdown on prostate
cancer cell susceptibility to apoptosis, cell survival and
proliferation. Mol Cancer. 8:392009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Finlay D, Vamos M, González-López M,
Ardecky RJ, Ganji SR, Yuan H, Su Y, Cooley TR, Hauser CT, Welsh K,
et al: Small-molecule IAP antagonists sensitize cancer cells to
TRAIL-induced apoptosis: Roles of XIAP and cIAPs. Mol Cancer Ther.
13:5–15. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
65
|
Guicciardi ME, Mott JL, Bronk SF, Kurita
S, Fingas CD and Gores GJ: Cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 1
(cIAP-1) degradation by caspase 8 during TNF-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis. Exp Cell Res.
317:107–116. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Lanuti P, Bertagnolo V, Pierdomenico L,
Bascelli A, Santavenere E, Alinari L, Capitani S, Miscia S and
Marchisio M: Enhancement of TRAIL cytotoxicity by AG-490 in human
ALL cells is characterized by downregulation of cIAP-1 and cIAP-2
through inhibition of Jak2/Stat3. Cell Res. 19:1079–1089. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Osaki M, Oshimura M and Ito H: PI3K-Akt
pathway: Its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis.
9:667–676. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Gomes AM, Soares MV, Ribeiro P, Caldas J,
Póvoa V, Martins LR, Melão A, Serra-Caetano A, de Sousa AB, Lacerda
JF, et al: Adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells display
decreased PTEN activity and constitutive hyperactivation of
PI3K/Akt pathway despite high PTEN protein levels. Haematologica.
99:1062–1068. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Badura S, Tesanovic T, Pfeifer H, Wystub
S, Nijmeijer BA, Liebermann M, Falkenburg JH, Ruthardt M and
Ottmann OG: Differential effects of selective inhibitors targeting
the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. PLoS
One. 8:e800702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|