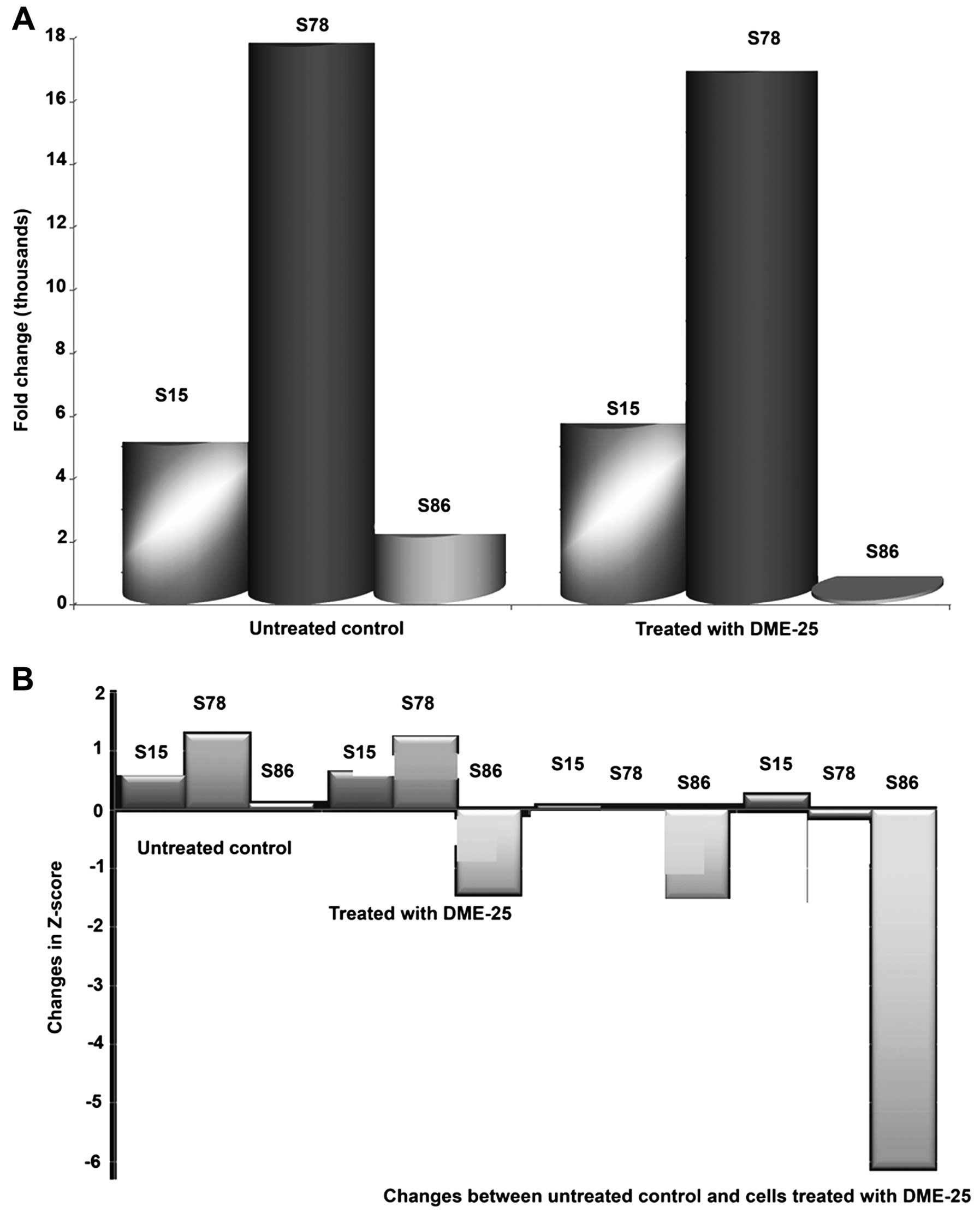
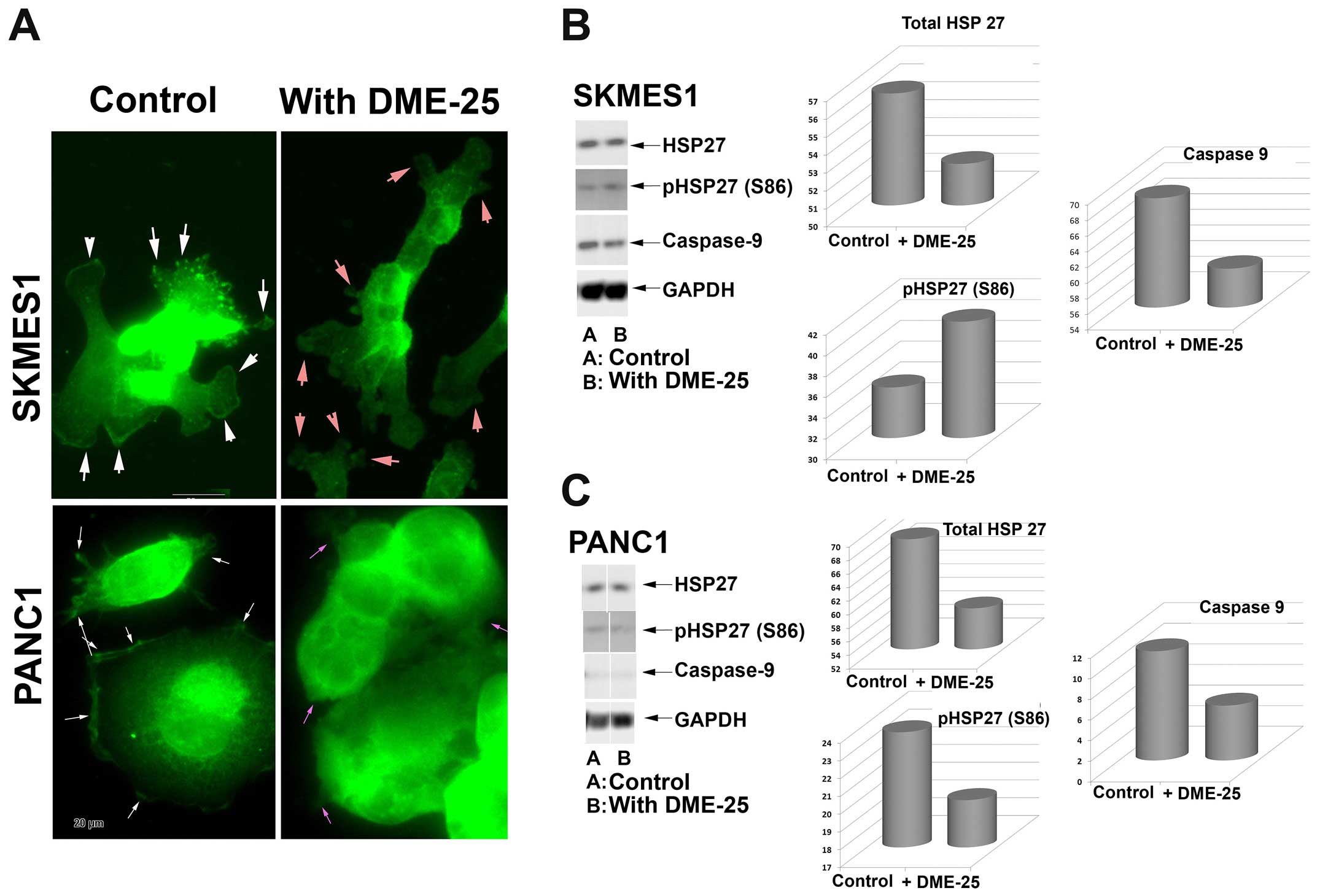
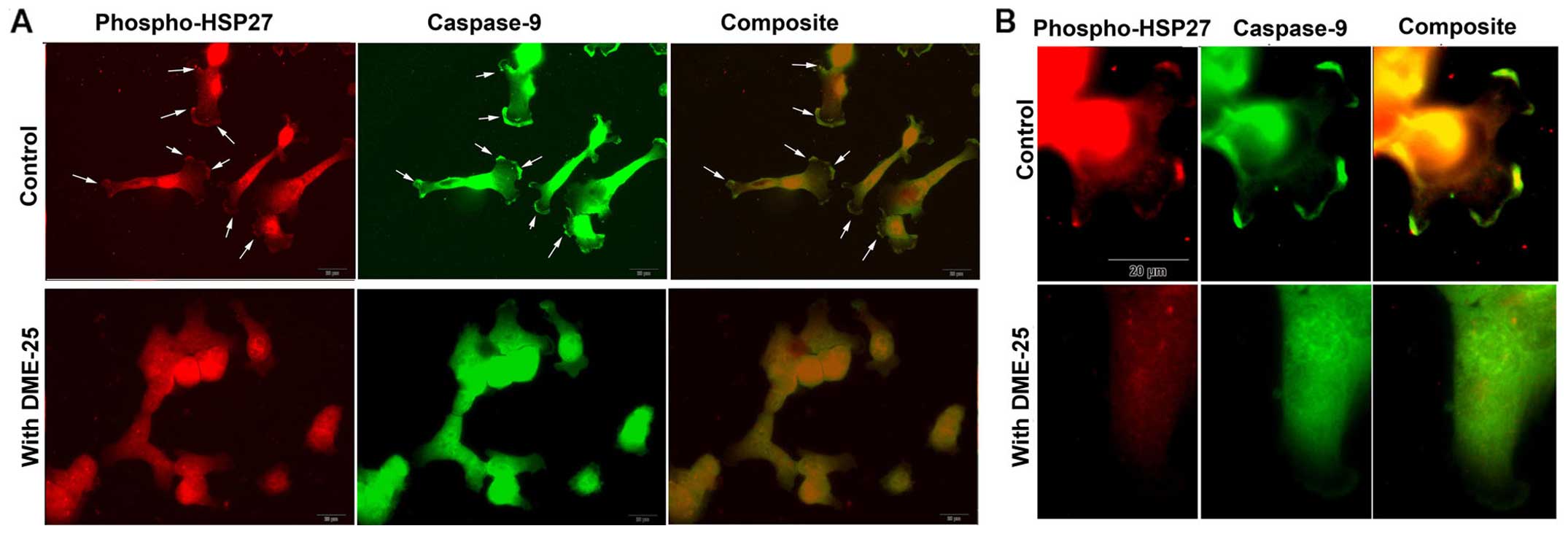
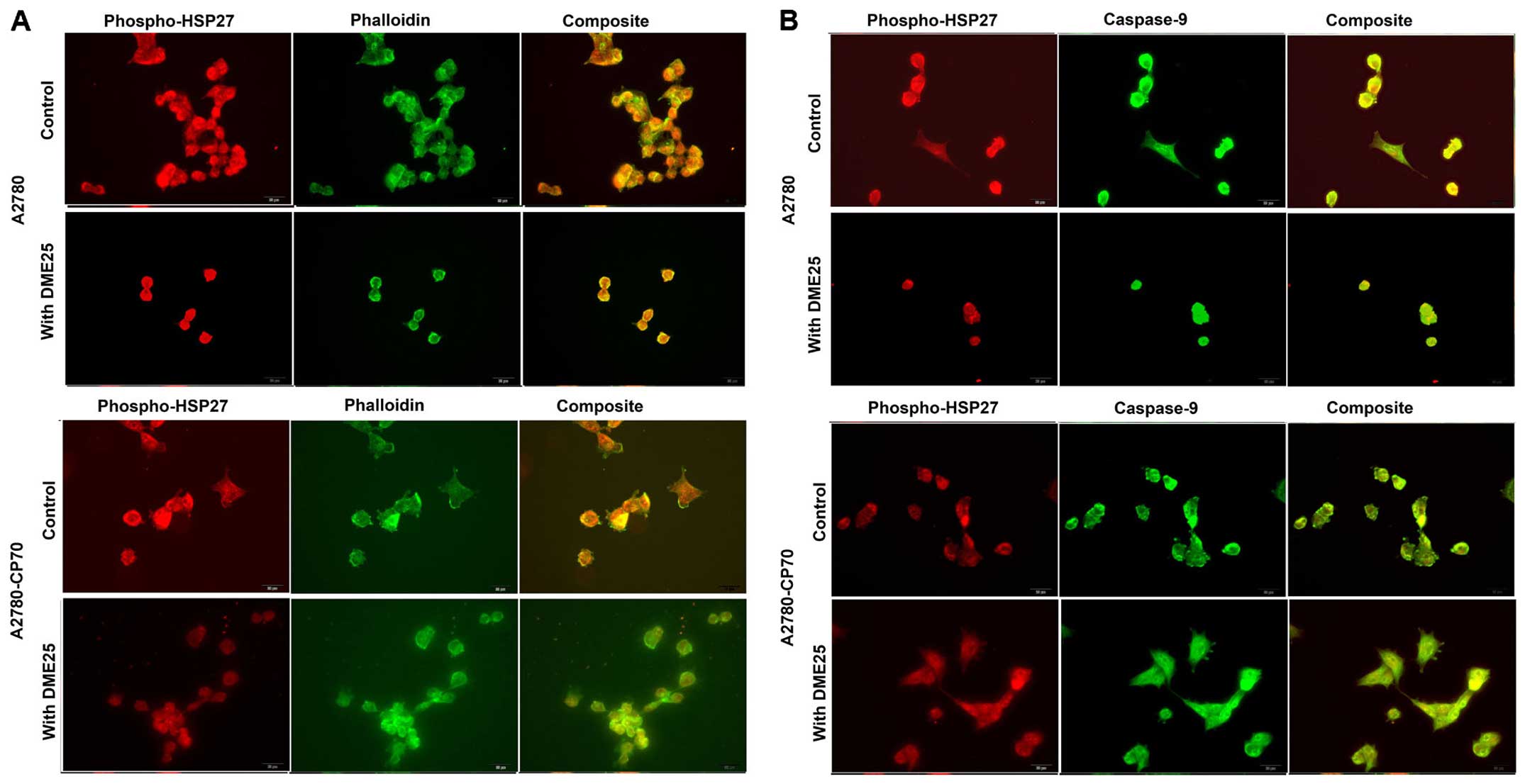
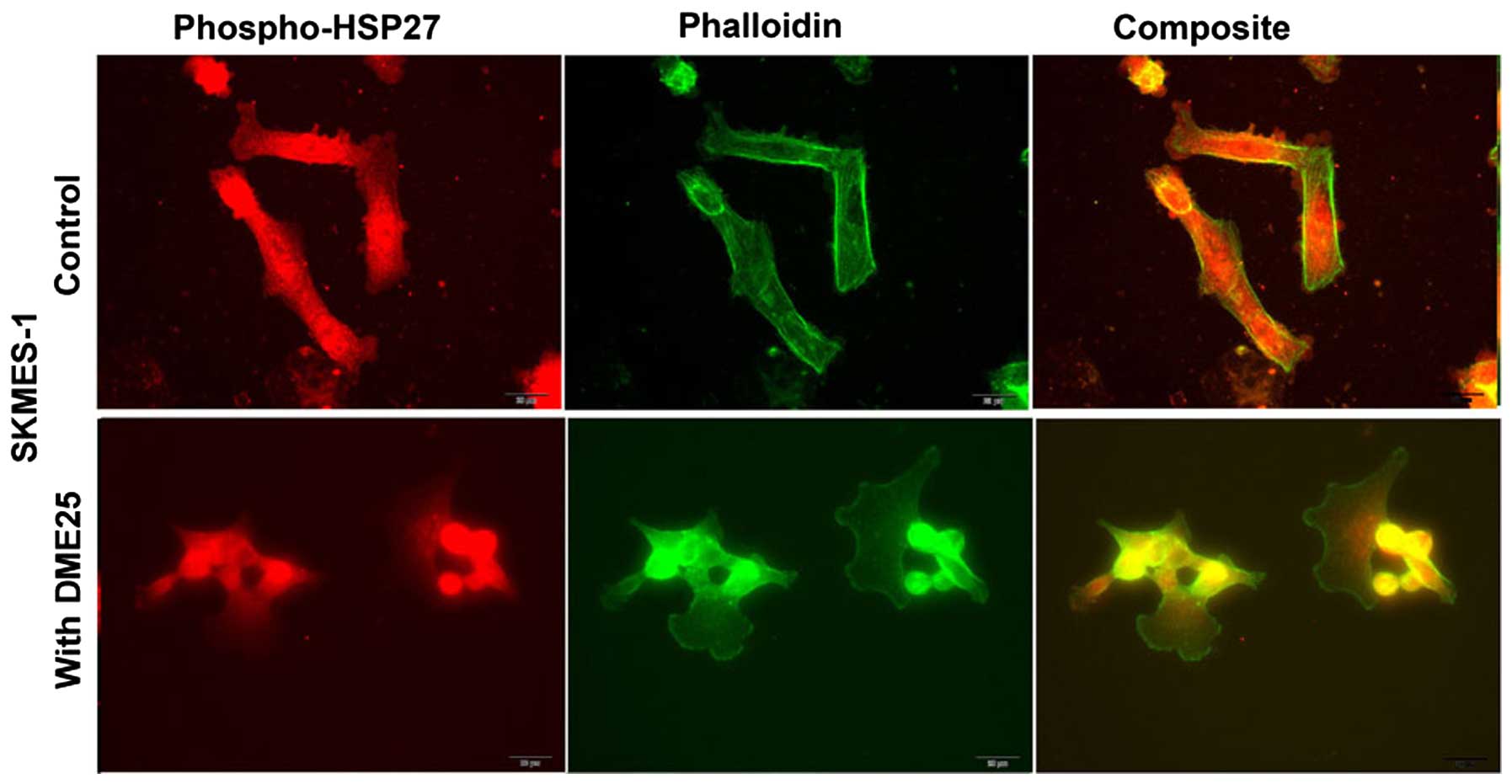
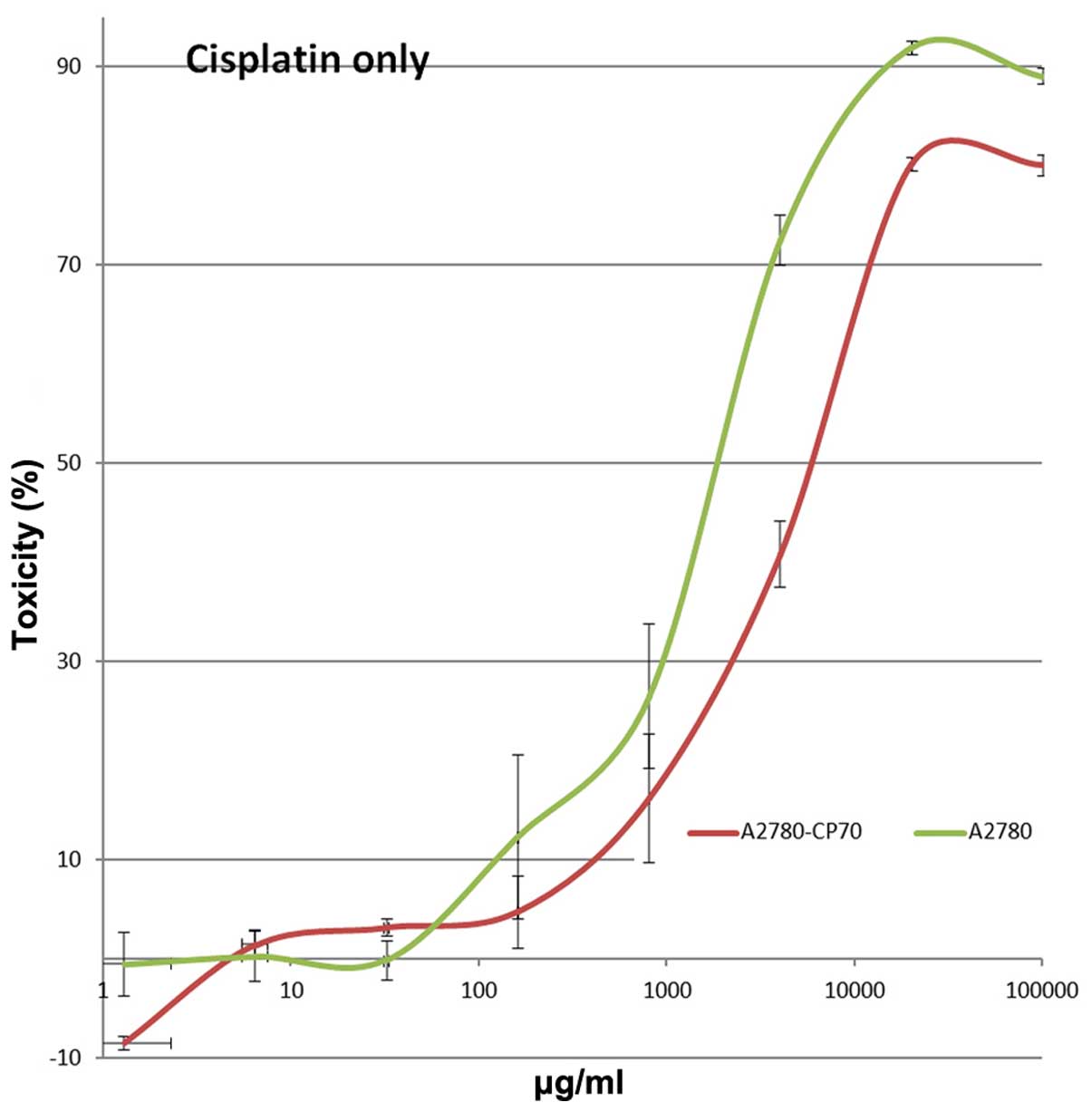
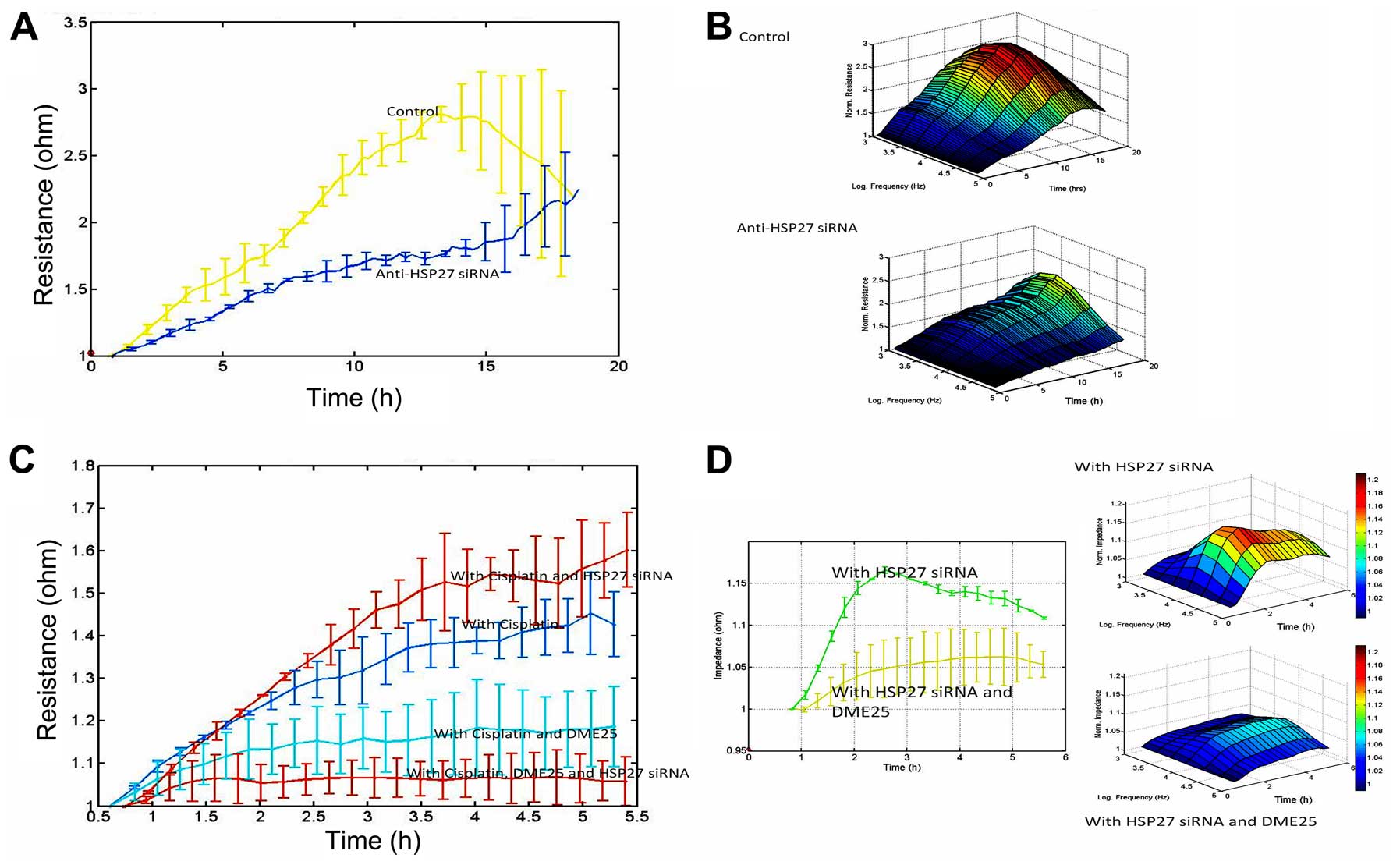
|
1
|
Bonnycastle LL, Yu CE, Hunt CR, Trask BJ,
Clancy KP, Weber JL, Patterson D and Schellenberg GD: Cloning,
sequencing, and mapping of the human chromosome 14 heat shock
protein gene (HSPA2). Genomics. 23:85–93. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dix DJ, Allen JW, Collins BW, Mori C,
Nakamura N, Poorman-Allen P, Goulding EH and Eddy EM: Targeted gene
disruption of Hsp70-2 results in failed meiosis, germ cell
apoptosis, and male infertility. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
93:3264–3268. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bowen-Jones D, Fantes J and Gupta R:
Diabetes and heat shock protein. Nature. 355:119–120. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Keyse SM and Emslie EA: Oxidative stress
and heat shock induce a human gene encoding a protein-tyrosine
phosphatase. Nature. 359:644–647. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ackerley S, James PA, Kalli A, French S,
Davies KE and Talbot K: A mutation in the small heat-shock protein
HSPB1 leading to distal hereditary motor neuronopathy disrupts
neurofilament assembly and the axonal transport of specific
cellular cargoes. Hum Mol Genet. 15:347–354. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Evgrafov OV, Mersiyanova I, Irobi J, Van
Den Bosch L, Dierick I, Leung CL, Schagina O, Verpoorten N, Van
Impe K, Fedotov V, et al: Mutant small heat-shock protein 27 causes
axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and distal hereditary motor
neuropathy. Nat Genet. 36:602–606. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hickey E, Brandon SE, Potter R, Stein G,
Stein J and Weber LA: Sequence and organization of genes encoding
the human 27 kDa heat shock protein. Nucleic Acids Res.
14:4127–4145. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wyttenbach A, Sauvageot O, Carmichael J,
Diaz-Latoud C, Arrigo AP and Rubinsztein DC: Heat shock protein 27
prevents cellular polyglutamine toxicity and suppresses the
increase of reactive oxygen species caused by huntingtin. Hum Mol
Genet. 11:1137–1151. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Erkizan O, Kirkali G, Yörükoğlu K and
Kirkali Z: Significance of heat shock protein-27 expression in
patients with renal cell carcinoma. Urology. 64:474–478. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Langdon SP, Rabiasz GJ, Hirst GL, King RJ,
Hawkins RA, Smyth JF and Miller WR: Expression of the heat shock
protein HSP27 in human ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
1:1603–1609. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Whelan RD and Hill BT: Differential
expression of steroid receptors, hsp27, and pS2 in a series of drug
resistant human breast tumor cell lines derived following exposure
to antitumor drugs or to fractionated X-irradiation. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 26:23–39. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zimmermann M, Nickl S, Lambers C, Hacker
S, Mitterbauer A, Hoetzenecker K, Rozsas A, Ostoros G, Laszlo V,
Hofbauer H, et al: Discrimination of clinical stages in non-small
cell lung cancer patients by serum HSP27 and HSP70: A
multi-institutional case-control study. Clin Chim Acta.
413:1115–1120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Giaginis C, Daskalopoulou SS, Vgenopoulou
S, Sfiniadakis I, Kouraklis G and Theocharis SE: Heat Shock
Protein-27, -60 and -90 expression in gastric cancer: Association
with clinicopathological variables and patient survival. BMC
Gastroenterol. 9:142009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Garrido C, Brunet M, Didelot C, Zermati Y,
Schmitt E and Kroemer G: Heat shock proteins 27 and 70:
Anti-apoptotic proteins with tumorigenic properties. Cell Cycle.
5:2592–2601. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gibert B, Eckel B, Gonin V, Goldschneider
D, Fombonne J, Deux B, Mehlen P, Arrigo AP, Clézardin P and
Diaz-Latoud C: Targeting heat shock protein 27 (HspB1) interferes
with bone metastasis and tumour formation in vivo. Br J Cancer.
107:63–70. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schweiger T, Nikolowsky C, Starlinger P,
Traxler D, Zimmermann M, Birner P, Hegedüs B, Dome B, Bergmann M,
Mildner M, et al: Stromal expression of heat-shock protein 27 is
associated with worse clinical outcome in patients with colorectal
cancer lung metastases. PLoS One. 10:e01207242015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Andrieu C, Taieb D, Baylot V, Ettinger S,
Soubeyran P, De-Thonel A, Nelson C, Garrido C, So A, Fazli L, et
al: Heat shock protein 27 confers resistance to androgen ablation
and chemotherapy in prostate cancer cells through eIF4E. Oncogene.
29:1883–1896. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Musiani D, Konda JD, Pavan S, Torchiaro E,
Sassi F, Noghero A, Erriquez J, Perera T, Olivero M and Di Renzo
MF: Heat-shock protein 27 (HSP27, HSPB1) is up-regulated by MET
kinase inhibitors and confers resistance to MET-targeted therapy.
FASEB J. 28:4055–4067. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yamamoto K, Okamoto A, Isonishi S, Ochiai
K and Ohtake Y: Heat shock protein 27 was up-regulated in cisplatin
resistant human ovarian tumor cell line and associated with the
cisplatin resistance. Cancer Lett. 168:173–181. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kuramitsu Y, Wang Y, Taba K, Suenaga S,
Ryozawa S, Kaino S, Sakaida I and Nakamura K: Heat-shock protein 27
plays the key role in gemcitabine-resistance of pancreatic cancer
cells. Anticancer Res. 32:2295–2299. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rogalla T, Ehrnsperger M, Preville X,
Kotlyarov A, Lutsch G, Ducasse C, Paul C, Wieske M, Arrigo AP,
Buchner J, et al: Regulation of Hsp27 oligomerization, chaperone
function, and protective activity against oxidative stress/tumor
necrosis factor alpha by phosphorylation. J Biol Chem.
274:18947–18956. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Charette SJ and Landry J: The interaction
of HSP27 with Daxx identifies a potential regulatory role of HSP27
in Fas-induced apoptosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 926:126–131. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Charette SJ, Lavoie JN, Lambert H and
Landry J: Inhibition of Daxx-mediated apoptosis by heat shock
protein 27. Mol Cell Biol. 20:7602–7612. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kang D, Choi HJ, Kang S, Kim SY, Hwang YS,
Je S, Han Z, Kim JH and Song JJ: Ratio of phosphorylated HSP27 to
nonphosphorylated HSP27 biphasically acts as a determinant of
cellular fate in gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells.
Cell Signal. 27:807–817. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nakashima M, Adachi S, Yasuda I, Yamauchi
T, Kawaguchi J, Itani M, Yoshioka T, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Hirose
Y, Kozawa O, et al: Phosphorylation status of heat shock protein 27
plays a key role in gemcitabine-induced apoptosis of pancreatic
cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 313:218–225. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ciocca DR and Calderwood SK: Heat shock
proteins in cancer: Diagnostic, prognostic, predictive, and
treatment implications. Cell Stress Chaperones. 10:86–103. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Baylot V, Andrieu C, Katsogiannou M, Taieb
D, Garcia S, Giusiano S, Acunzo J, Iovanna J, Gleave M, Garrido C,
et al: OGX-427 inhibits tumor progression and enhances gemcitabine
chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2:e2212011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kamada M, So A, Muramaki M, Rocchi P,
Beraldi E and Gleave M: Hsp27 knockdown using nucleotide-based
therapies inhibit tumor growth and enhance chemotherapy in human
bladder cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:299–308. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lelj-Garolla B, Kumano M, Beraldi E, Nappi
L, Rocchi P, Ionescu DN, Fazli L, Zoubeidi A and Gleave ME: Hsp27
Inhibition with OGX-427 sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells
to erlotinib and chemotherapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 14:1107–1116. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Matsui Y, Hadaschik BA, Fazli L, Andersen
RJ, Gleave ME and So AI: Intravesical combination treatment with
antisense oligonucleotides targeting heat shock protein-27 and
HTI-286 as a novel strategy for high-grade bladder cancer. Mol
Cancer Ther. 8:2402–2411. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li Sun JR: Yei Tan, Xuedong Gao: Yang
capsule in treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with
interventional chemotherapy random double-blind, multicenter
clinical study. World Chin J. 8:688–691. 2013.
|
|
32
|
Ligan Xing XZ, Li G, Zhang X, Sun X, Guo Q
and Yu J: Controlled clinical studies in the effects of Yang
capsule in advanced lung cancer in combination with chemotherapy.
China J Cancer Prev Treat. 21:384–386. 2014.
|
|
33
|
Xingjun Cui WM and Bi X: Effect of
Yangzheng Xiaoji capsule on cellular immune function in patients
with advanced gastric cancer chemotherapy. Chin J Difficult
Complicated Cases. 10:703–704. 2011.
|
|
34
|
Xue Kan SF and Ji J: Meta-anlaysis of the
safety of Yangzheng Xiaoji capsule for the treatment of cancer and
precancerosis. Chin J Clin Oncol. 40:1318–1323. 2013.
|
|
35
|
Jiang WG, Ye L, Ji K, Frewer N, Ji J and
Mason MD: Inhibitory effects of Yangzheng Xiaoji on angiogenesis
and the role of the focal adhesion kinase pathway. Int J Oncol.
41:1635–1642. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ye L, Ji K, Frewer N, Ji J and Jiang WG:
Impact of Yangzheng Xiaoji on the adhesion and migration of human
cancer cells: The role of the AKT signalling pathway. Anticancer
Res. 32:2537–2543. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Guo Y, Ziesch A, Hocke S, Kampmann E, Ochs
S, De Toni EN, Göke B and Gallmeier E: Overexpression of heat shock
protein 27 (HSP27) increases gemcitabine sensitivity in pancreatic
cancer cells through S-phase arrest and apoptosis. J Cell Mol Med.
19:340–350. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Rocchi P, So A, Kojima S, Signaevsky M,
Beraldi E, Fazli L, Hurtado-Coll A, Yamanaka K and Gleave M: Heat
shock protein 27 increases after androgen ablation and plays a
cytoprotective role in hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer
Res. 64:6595–6602. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Choi DH, Ha JS, Lee WH, Song JK, Kim GY,
Park JH, Cha HJ, Lee BJ and Park JW: Heat shock protein 27 is
associated with irinotecan resistance in human colorectal cancer
cells. FEBS Lett. 581:1649–1656. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rashmi R, Santhosh Kumar TR and
Karunagaran D: Human colon cancer cells differ in their sensitivity
to curcumin-induced apoptosis and heat shock protects them by
inhibiting the release of apoptosis-inducing factor and caspases.
FEBS Lett. 538:19–24. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Belkacemi L and Hebb MO: HSP27 knockdown
produces synergistic induction of apoptosis by HSP90 and kinase
inhibitors in glioblastoma multiforme. Anticancer Res.
34:4915–4927. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jakubowicz-Gil J, Langner E, Bądziul D,
Wertel I and Rzeski W: Silencing of Hsp27 and Hsp72 in glioma cells
as a tool for programmed cell death induction upon temozolomide and
quercetin treatment. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 273:580–589. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jiang WG, Ye L, Ruge F, Owen S, Martin T,
Sun PH, Sanders AJ, Lane J, Satherley L, Weeks HP, et al: Yangzheng
Xiaoji exerts anti-tumour growth effects by antagonising the
effects of HGF and its receptor, cMET, in human lung cancer cells.
J Transl Med. 13:2802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shiota M, Bishop JL, Nip KM, Zardan A,
Takeuchi A, Cordonnier T, Beraldi E, Bazov J, Fazli L, Chi K, et
al: Hsp27 regulates epithelial mesenchymal transition, metastasis,
and circulating tumor cells in prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
73:3109–3119. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wettstein G, Bellaye PS, Kolb M, Hammann
A, Crestani B, Soler P, Marchal-Somme J, Hazoume A, Gauldie J,
Gunther A, et al: Inhibition of HSP27 blocks fibrosis development
and EMT features by promoting Snail degradation. FASEB J.
27:1549–1560. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cordonnier T, Bishop JL, Shiota M, Nip KM,
Thaper D, Vahid S, Heroux D, Gleave M and Zoubeidi A: Hsp27
regulates EGF/β-catenin mediated epithelial to mesenchymal
transition in prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 136:E496–E507. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Voll EA, Ogden IM, Pavese JM, Huang X, Xu
L, Jovanovic BD and Bergan RC: Heat shock protein 27 regulates
human prostate cancer cell motility and metastatic progression.
Oncotarget. 5:2648–2663. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Thuringer D, Jego G, Wettstein G, Terrier
O, Cronier L, Yousfi N, Hébrard S, Bouchot A, Hazoumé A, Joly AL,
et al: Extracellular HSP27 mediates angiogenesis through Toll-like
receptor 3. FASEB J. 27:4169–4183. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|