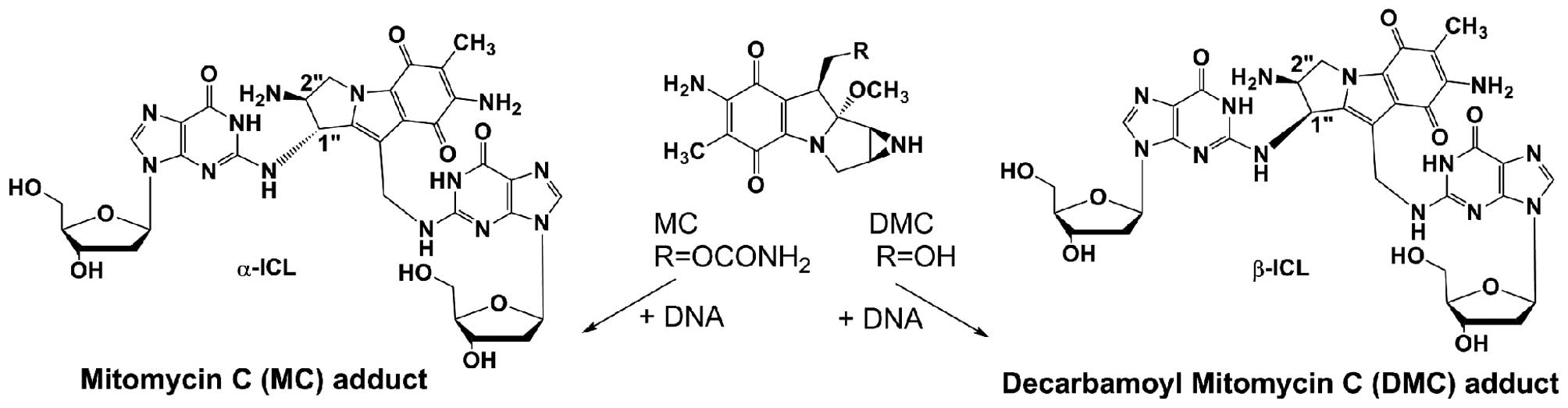
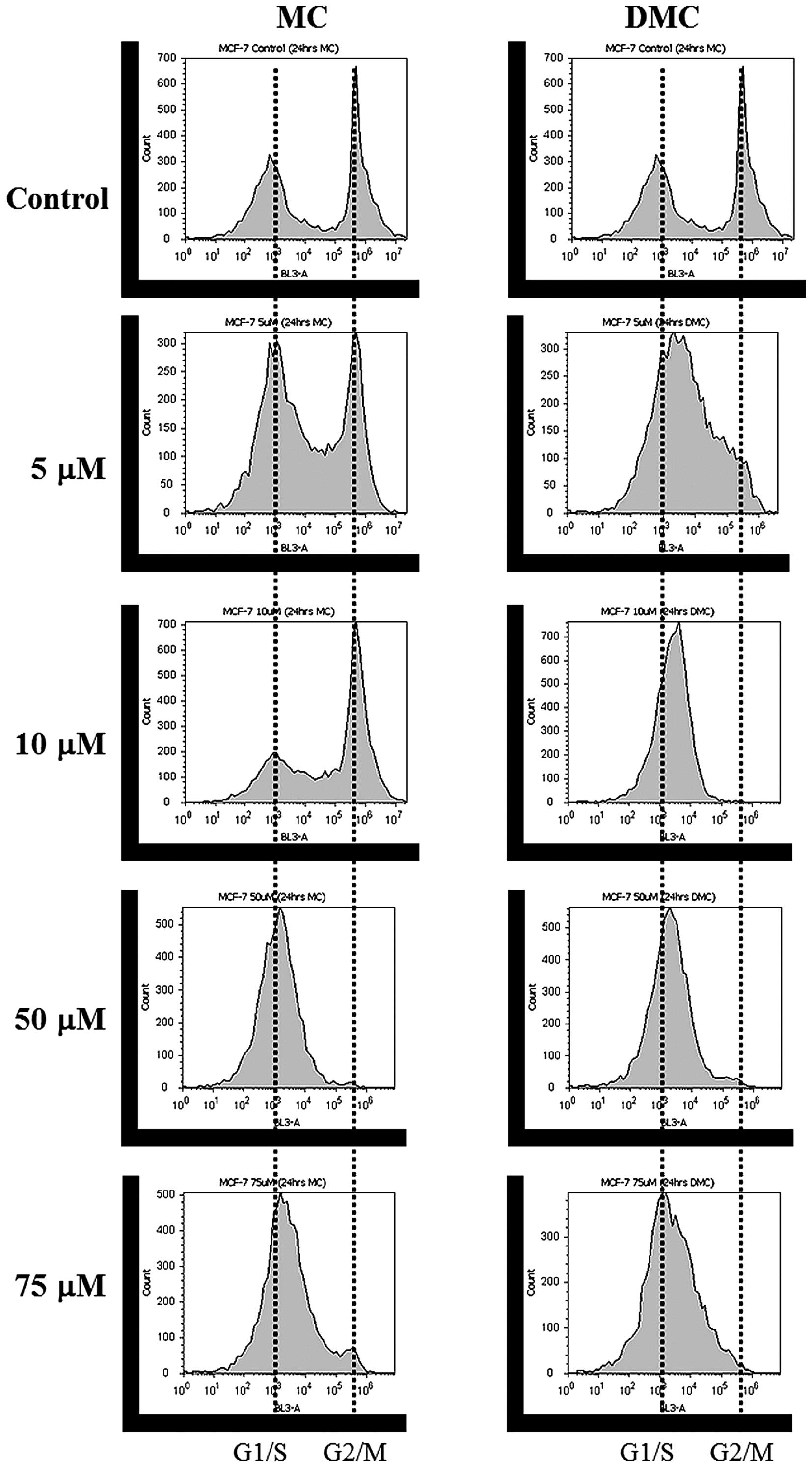
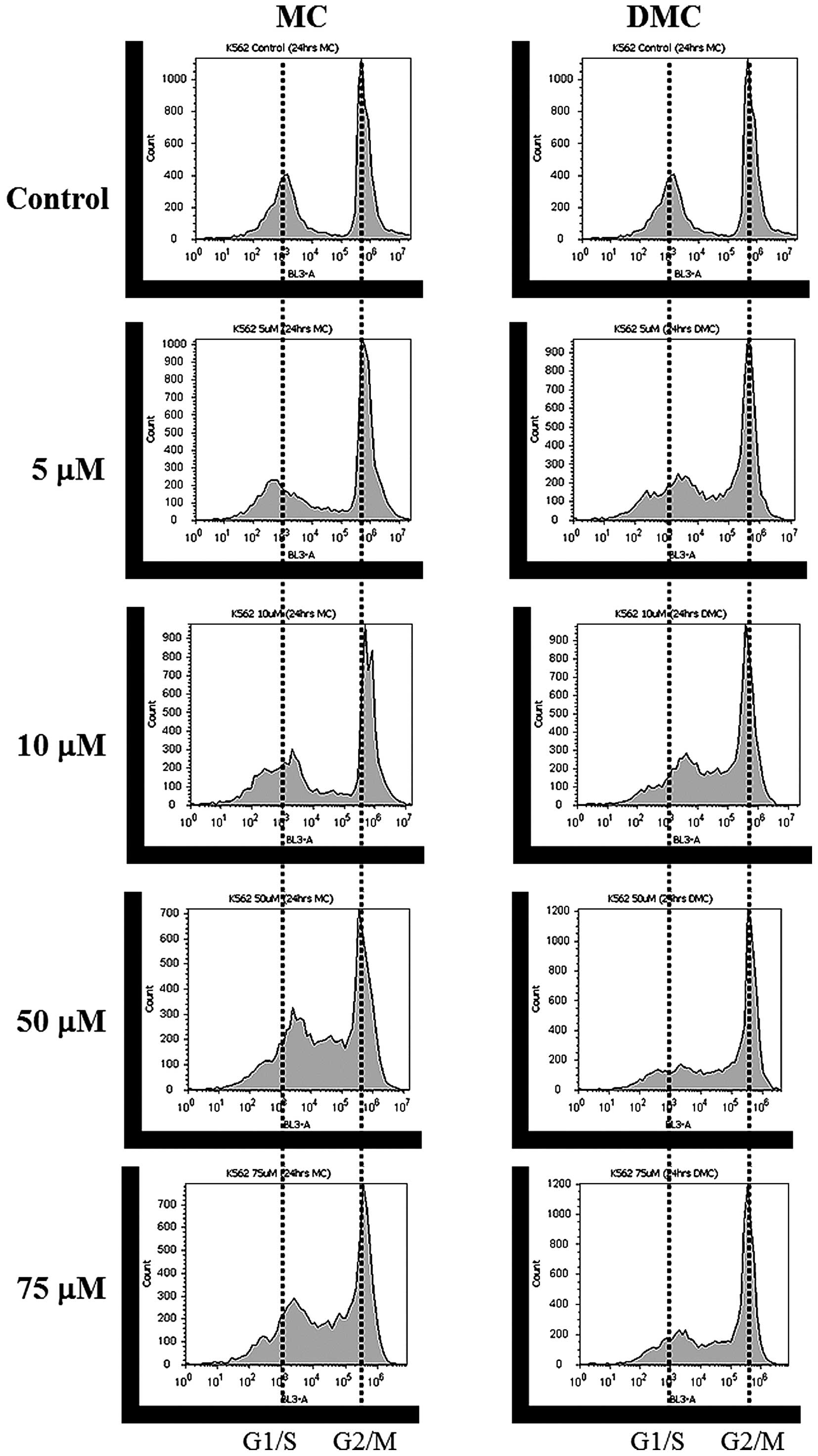
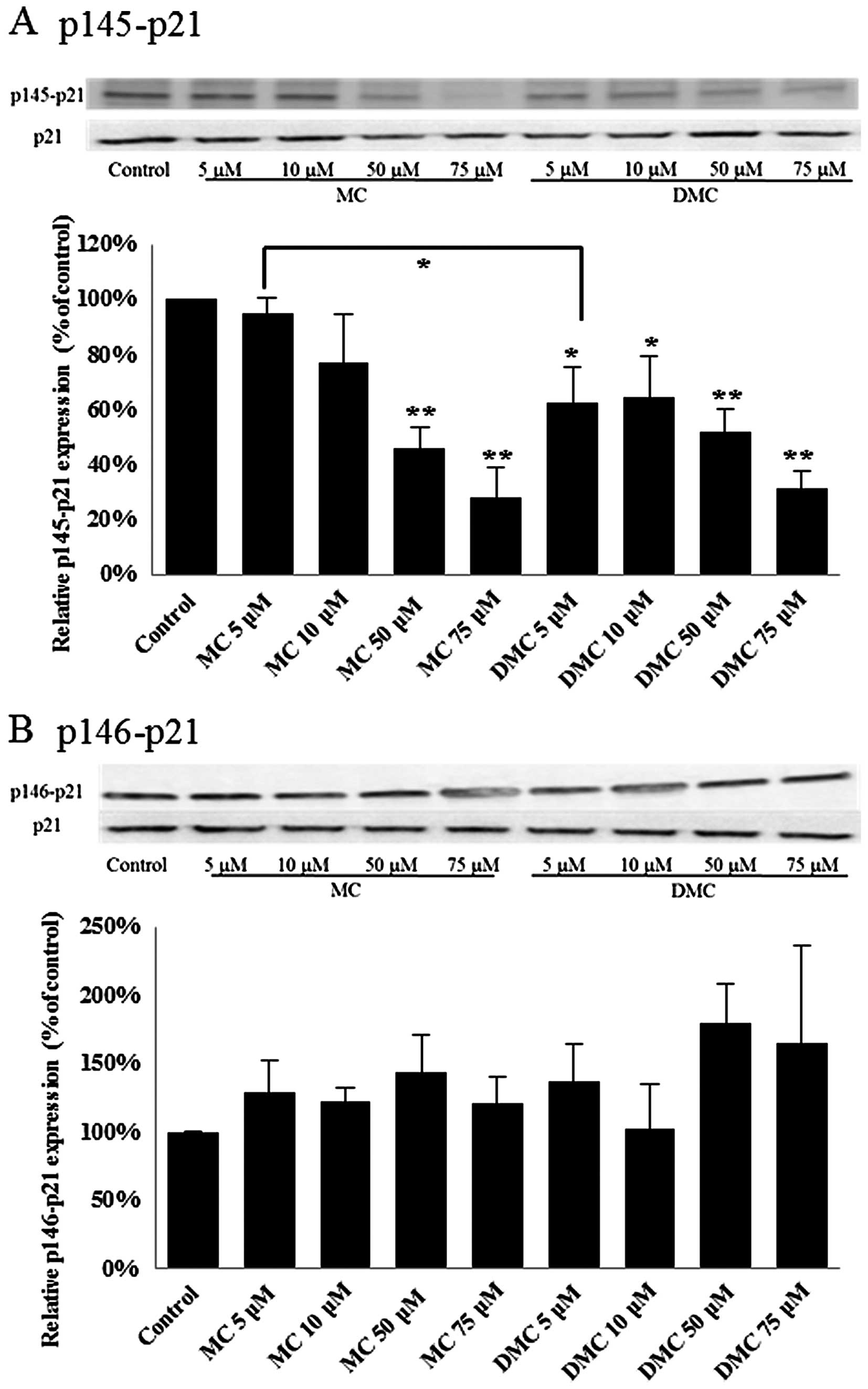
|
1
|
Hata T, Hoshi T, Kanamori K, Matsumae A,
Sano Y, Shima T and Sugawara R: Mitomycin, a new antibiotic from
Streptomyces. I. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 9:141–146. 1956.
|
|
2
|
Sartorelli AC, Hodnick WF, Belcourt MF,
Tomasz M, Haffty B, Fischer JJ and Rockwell S: Mitomycin C: A
prototype bioreductive agent. Oncol Res. 6:501–508. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Verweij J and Pinedo H: Cancer
Chemotherapy and Biological Response Modifiers. Annual 11. Pinedo
HM, Chabner BA and Longo DL: 67. Elsevier Science Publishers B.V;
Amsterdam: 1990
|
|
4
|
Bradner WT: Mitomycin C: A clinical
update. Cancer Treat Rev. 27:35–50. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Borowy-Borowski H, Lipman R and Tomasz M:
Recognition between mitomycin C and specific DNA sequences for
cross-link formation. Biochemistry. 29:2999–3006. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Boamah EK, White DE, Talbott KE, Arva NC,
Berman D, Tomasz M and Bargonetti J: Mitomycin-DNA adducts induce
p53-dependent and p53-independent cell death pathways. ACS Chem
Biol. 2:399–407. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Abbas T, Olivier M, Lopez J, Houser S,
Xiao G, Kumar GS, Tomasz M and Bargonetti J: Differential
activation of p53 by the various adducts of mitomycin C. J Biol
Chem. 277:40513–40519. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ben-Yehoyada M, Wang LC, Kozekov ID, Rizzo
CJ, Gottesman ME and Gautier J: Checkpoint signaling from a single
DNA interstrand crosslink. Mol Cell. 35:704–715. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Räschle M, Knipscheer P, Enoiu M, Angelov
T, Sun J, Griffith JD, Ellenberger TE, Schärer OD and Walter JC:
Mechanism of replication-coupled DNA interstrand crosslink repair.
Cell. 134:969–980. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Weng MW, Zheng Y, Jasti VP, Champeil E,
Tomasz M, Wang Y, Basu AK and Tang MS: Repair of mitomycin C mono-
and inter-strand cross-linked DNA adducts by UvrABC: A new model.
Nucleic Acids Res. 38:6976–6984. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shinohara K, Bando T, Sasaki S, Sakakibara
Y, Minoshima M and Sugiyama H: Antitumor activity of
sequence-specific alkylating agents: Pyrolle-imidazole CBI
conjugates with indole linker. Cancer Sci. 97:219–225. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Palom Y, Suresh Kumar G, Tang LQ, Paz MM,
Musser SM, Rockwell S and Tomasz M: Relative toxicities of DNA
cross-links and monoadducts: New insights from studies of
decarbamoyl mitomycin C and mitomycin C. Chem Res Toxicol.
15:1398–1406. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kaspárková J and Brabec V: Recognition of
DNA interstrand cross-links of cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) and
its trans isomer by DNA-binding proteins. Biochemistry.
34:12379–12387. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Patrick SM, Tillison K and Horn JM:
Recognition of cisplatin-DNA interstrand cross-links by replication
protein A. Biochemistry. 47:10188–10196. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xiao G, Kue P, Bhosle R and Bargonetti J:
Decarbamoyl mitomycin C (DMC) activates p53-independent ataxia
telangiectasia and rad3 related protein (ATR) chromatin eviction.
Cell Cycle. 14:744–754. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Esposito D, Crescenzi E, Sagar V, Loreni
F, Russo A and Russo G: Human rpL3 plays a crucial role in cell
response to nucleolar stress induced by 5-FU and L-OHP. Oncotarget.
5:11737–11751. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Russo A, Esposito D, Catillo M,
Pietropaolo C, Crescenzi E and Russo G: Human rpL3 induces G1/S
arrest or apoptosis by modulating p21 (waf1/cip1) levels in a
p53-independent manner. Cell Cycle. 12:76–87. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Resnitzky D, Gossen M, Bujard H and Reed
SI: Acceleration of the G1/S phase transition by expression of
cyclins D1 and E with an inducible system. Mol Cell Biol.
14:1669–1679. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
He G, Kuang J, Huang Z, Koomen J,
Kobayashi R, Khokhar AR and Siddik ZH: Upregulation of p27 and its
inhibition of CDK2/cyclin E activity following DNA damage by a
novel platinum agent are dependent on the expression of p21. Br J
Cancer. 95:1514–1524. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Choi SY, Shen YN, Woo SR, Yun M, Park JE,
Ju YJ, Jeong J, Shin HJ, Joo HY, Park ER, et al: Mitomycin C and
doxorubicin elicit conflicting signals by causing accumulation of
cyclin E prior to p21WAF1/CIP1 elevation in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 40:277–286. 2012.
|
|
21
|
Willers H, Dahm-Daphi J and Powell SN:
Repair of radiation damage to DNA. Br J Cancer. 90:1297–1301. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Harris SL and Levine AJ: The p53 pathway:
Positive and negative feedback loops. Oncogene. 24:2899–2908. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Petitjean A, Achatz MI, Borresen-Dale AL,
Hainaut P and Olivier M: TP53 mutations in human cancers:
Functional selection and impact on cancer prognosis and outcomes.
Oncogene. 26:2157–2165. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Faulhaber O and Bristow RG: Basis of cell
kill following clinical radiotherapy. Application of Apoptosis to
Cancer Treatment. Sluyser M: Springer; Amsterdam: pp. 293–320.
2005, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Fang L, Igarashi M, Leung J, Sugrue MM,
Lee SW and Aaronson SA: p21Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1 induces permanent growth
arrest with markers of replicative senescence in human tumor cells
lacking functional p53. Oncogene. 18:2789–2797. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sugiyama K, Shimizu M, Akiyama T, Tamaoki
T, Yamaguchi K, Takahashi R, Eastman A and Akinaga S: UCN-01
selectively enhances mitomycin C cytotoxicity in p53 defective
cells which is mediated through S and/or G(2) checkpoint
abrogation. Int J Cancer. 85:703–709. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Law JC, Ritke MK, Yalowich JC, Leder GH
and Ferrell RE: Mutational inactivation of the p53 gene in the
human erythroid leukemic K562 cell line. Leuk Res. 17:1045–1050.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kinoshita S, Uzu K, Nakano K and Takahashi
T: Mitomycin derivatives. 2. Derivatives of decarbamoylmitosane and
decar-bamoylmitosene. J Med Chem. 14:109–112. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Summer H, Grämer R and Dröge P: Denaturing
urea polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (Urea PAGE). J Vis Exp.
32:e14852009.
|
|
30
|
Zhou QM, Wang XF, Liu XJ, Zhang H, Lu YY
and Su SB: Curcumin enhanced antiproliferative effect of mitomycin
C in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells in vitro and in vivo. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 32:1402–1410. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yu J, Zhao L, Li Y, Li N, He M, Bai X, Yu
Z, Zheng Z, Mi X, Wang E, et al: Silencing of Fanconi anemia
complementation group F exhibits potent chemosensitization of
mitomycin C activity in breast cancer cells. J Breast Cancer.
16:291–299. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rössig L, Jadidi AS, Urbich C, Badorff C,
Zeiher AM and Dimmeler S: Akt-dependent phosphorylation of
p21(Cip1) regulates PCNA binding and proliferation of endothelial
cells. Mol Cell Biol. 21:5644–5657. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li Y, Dowbenko D and Lasky LA: AKT/PKB
phosphorylation of p21Cip/WAF1 enhances protein
stability of p21Cip/WAF1 and promotes cell survival. J
Biol Chem. 277:11352–11361. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Boamah EK, Brekman A, Tomasz M, Myeku N,
Figueiredo-Pereira M, Hunter S, Meyer J, Bhosle RC and Bargonetti
J: DNA adducts of decarbamoyl mitomycin C efficiently kill cells
without wild-type p53 resulting from proteasome-mediated
degradation of checkpoint protein 1. Chem Res Toxicol.
23:1151–1162. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Di Leonardo A, Linke SP, Clarkin K and
Wahl GM: DNA damage triggers a prolonged p53-dependent G1 arrest
and long-term induction of Cip1 in normal human fibroblasts. Genes
Dev. 8:2540–2551. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Macleod KF, Sherry N, Hannon G, Beach D,
Tokino T, Kinzler K, Vogelstein B and Jacks T: p53-dependent and
independent expression of p21 during cell growth, differentiation,
and DNA damage. Genes Dev. 9:935–944. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lawley PD and Phillips DH: DNA adducts
from chemotherapeutic agents. Mutat Res. 355:13–40. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bargonetti J, Champeil E and Tomasz M:
Differential toxicity of DNA adducts of mitomycin C. J Nucleic
Acids. 2010:6989602010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tomasz M: Mitomycin C: Small, fast and
deadly (but very selective). Chem Biol. 2:575–579. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rao S, Lowe M, Herliczek TW and Keyomarsi
K: Lovastatin mediated G1 arrest in normal and tumor breast cells
is through inhibition of CDK2 activity and redistribution of p21
and p27, independent of p53. Oncogene. 17:2393–2402. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|