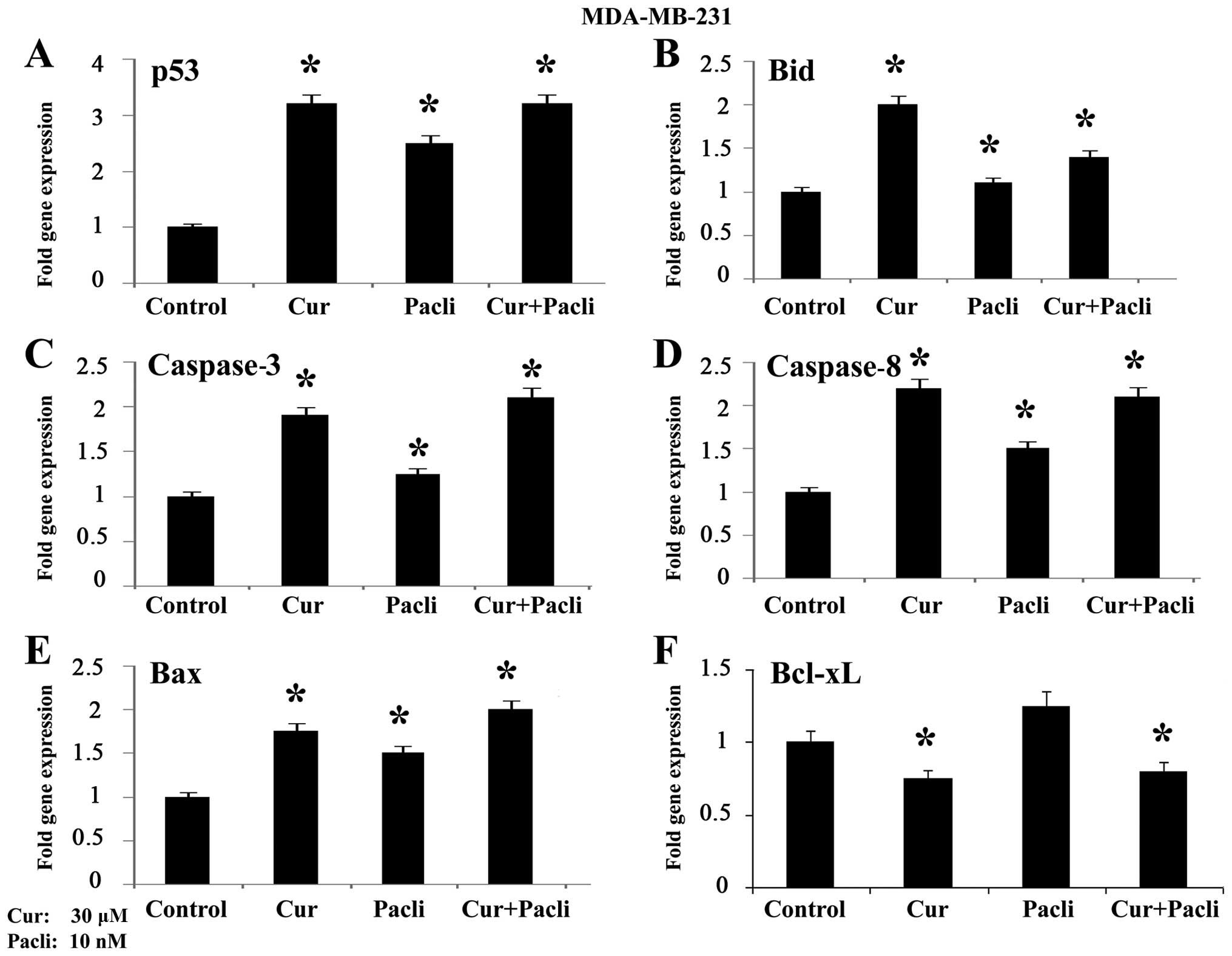
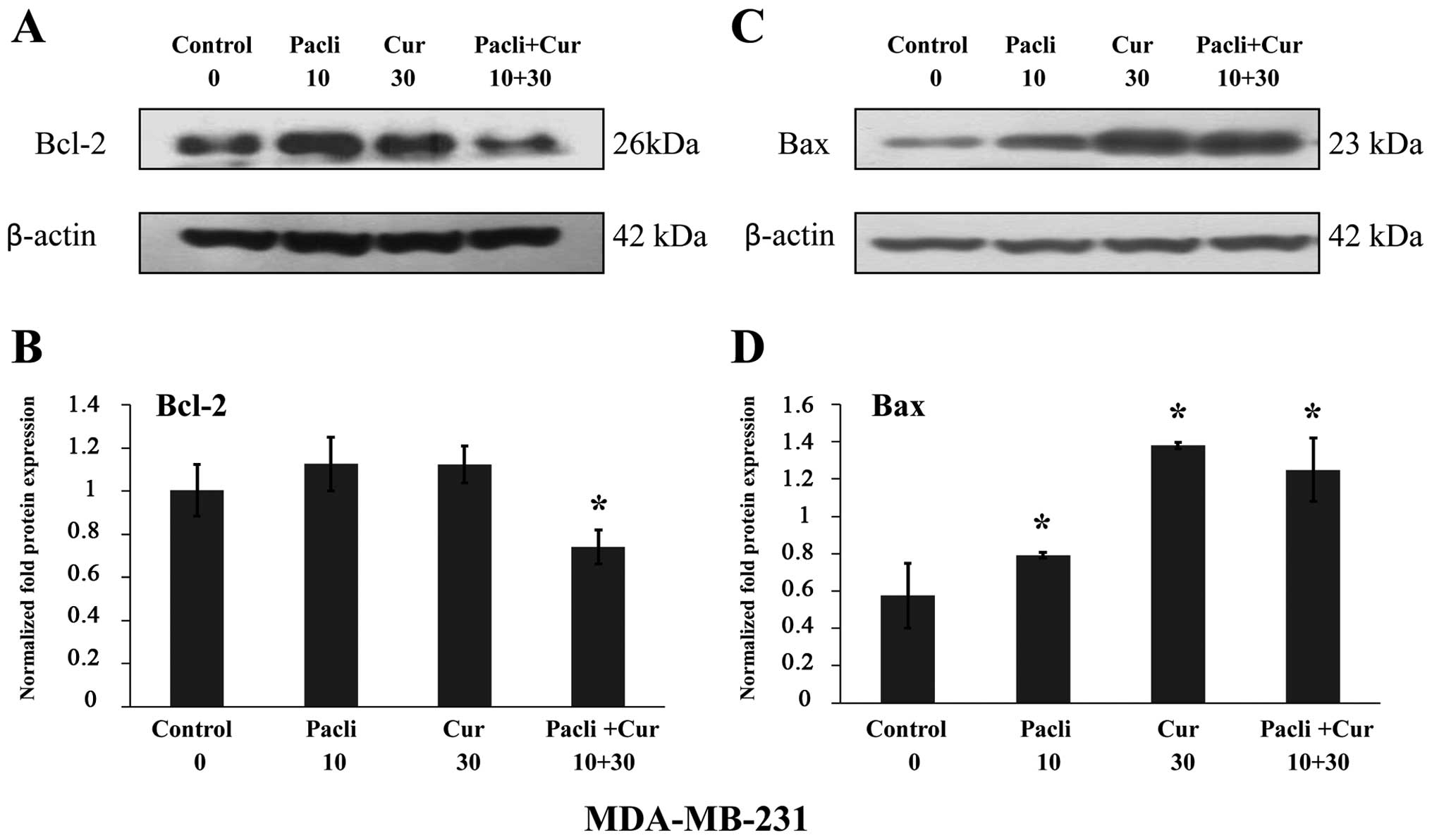
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E,
Lortet-Tieulent J, Rosso S, Coebergh JW, Comber H, Forman D and
Bray F: Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe:
Estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer. 49:1374–1403.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Calaf GM, Echiburú-Chau C, Roy D, Chai Y,
Wen G and Balajee AS: Protective role of curcumin in oxidative
stress of breast cells. Oncol Rep. 26:1029–1035. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Calaf GM, Echiburú-Chau C, Wen G, Balajee
AS and Roy D: Effect of curcumin on irradiated and
estrogen-transformed human breast cell lines. Int J Oncol.
40:436–442. 2012.
|
|
4
|
Joe B, Vijaykumar M and Lokesh BR:
Biological properties of curcumin-cellular and molecular mechanisms
of action. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 44:97–111. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gabizon A, Price DC, Huberty J, Bresalier
RS and Papahadjopoulos D: Effect of liposome composition and other
factors on the targeting of liposomes to experimental tumors:
Biodistribution and imaging studies. Cancer Res. 50:6371–6378.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fu Y, Li S, Zu Y, Yang G, Yang Z, Luo M,
Jiang S, Wink M and Efferth T: Medicinal chemistry of paclitaxel
and its analogues. Curr Med Chem. 16:3966–3985. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Okano J and Rustgi AK: Paclitaxel induces
prolonged activation of the Ras/MEK/ERK pathway independently of
activating the programmed cell death machinery. J Biol Chem.
276:19555–19564. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
McGrogan BT, Gilmartin B, Carney DN and
McCann A: Taxanes, microtubules and chemoresistant breast cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1785:96–132. 2008.
|
|
9
|
Jin C, Wu H, Liu J, Bai L and Guo G: The
effect of paclitaxel-loaded nanoparticles with radiation on hypoxic
MCF-7 cells. J Clin Pharm Ther. 32:41–47. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Barbacid M: ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem.
56:779–827. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kasid A, Lippman ME, Papageorge AG, Lowy
DR and Gelmann EP: Transfection of v-rasH DNA into MCF-7 human
breast cancer cells bypasses dependence on estrogen for
tumorigenicity. Science. 228:725–728. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yu LLG and Gu JY: Advances in the role of
Rho sub-family in tumor invasion. Fudan Univ J Med Sci. 37:617–619.
2010.
|
|
13
|
Hall A: Rho GTPases and the actin
cytoskeleton. Science. 279:509–514. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
DerMardirossian C and Bokoch GM: GDIs:
Central regulatory molecules in Rho GTPase activation. Trends Cell
Biol. 15:356–363. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Olofsson B: Rho guanine dissociation
inhibitors: Pivotal molecules in cellular signalling. Cell Signal.
11:545–554. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schmitt CA, Fridman JS, Yang M, Lee S,
Baranov E, Hoffman RM and Lowe SW: A senescence program controlled
by p53 and p16INK4a contributes to the outcome of cancer therapy.
Cell. 109:335–346. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vogelstein B, Lane D and Levine AJ:
Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 408:307–310. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hengartner MO: The biochemistry of
apoptosis. Nature. 407:770–776. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yonish-Rouach E, Grunwald D, Wilder S,
Kimchi A, May E, Lawrence JJ, May P and Oren M: p53-mediated cell
death: Relationship to cell cycle control. Mol Cell Biol.
13:1415–1423. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Miyashita T, Krajewski S, Krajewska M,
Wang HG, Lin HK, Liebermann DA, Hoffman B and Reed JC: Tumor
suppressor p53 is a regulator of bcl-2 and bax gene expression in
vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 9:1799–1805. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Miyashita T and Reed JC: Tumor suppressor
p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene.
Cell. 80:293–299. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cory S and Adams JM: The Bcl2 family:
Regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:647–656. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
García-Sáez AJ: The secrets of the Bcl-2
family. Cell Death Differ. 19:1733–1740. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
González de Aguilar JL, Gordon JW, René F,
de Tapia M, Lutz-Bucher B, Gaiddon C and Loeffler JP: Alteration of
the Bcl-x/Bax ratio in a transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic
lateral sclerosis: Evidence for the implication of the p53
signaling pathway. Neurobiol Dis. 7:406–415. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
van Delft MF and Huang DC: How the Bcl-2
family of proteins interact to regulate apoptosis. Cell Res.
16:203–213. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jürgensmeier JM, Xie Z, Deveraux Q,
Ellerby L, Bredesen D and Reed JC: Bax directly induces release of
cytochrome c from isolated mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:4997–5002. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Placzek WJ, Wei J, Kitada S, Zhai D, Reed
JC and Pellecchia M: A survey of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 subfamily
expression in cancer types provides a platform to predict the
efficacy of Bcl-2 antagonists in cancer therapy. Cell Death Dis.
1:e402010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Davids MS and Letai A: Targeting the
B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 2 family in cancer. J Clin Oncol.
30:3127–3135. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Walensky LD: From mitochondrial biology to
magic bullet: Navitoclax disarms BCL-2 in chronic lymphocytic
leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 30:554–557. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Dai Y, Lawrence TS and Xu L: Overcoming
cancer therapy resistance by targeting inhibitors of apoptosis
proteins and nuclear factor-kappa B. Am J Transl Res. 1:1–15.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Han J, Sun M, Cui Y, Wang T, Zhang W, Guo
M, Zhou Y, Liu W, Zhang M, Duan J, et al: Kushen flavonoids induce
apoptosis in tumor cells by inhibition of NF-kappaB activation and
multiple receptor tyrosine kinase activities. Phytother Res.
21:262–268. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wulczyn FG, Naumann M and Scheidereit C:
Candidate proto-oncogene bcl-3 encodes a subunit-specific inhibitor
of transcription factor NF-kappa B. Nature. 358:597–599. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bours V, Franzoso G, Azarenko V, Park S,
Kanno T, Brown K and Siebenlist U: The oncoprotein Bcl-3 directly
transactivates through kappa B motifs via association with
DNA-binding p50B homodimers. Cell. 72:729–739. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dobrzanski P, Ryseck RP and Bravo R:
Differential interactions of Rel-NF-kappa B complexes with I kappa
B alpha determine pools of constitutive and inducible NF-kappa B
activity. EMBO J. 13:4608–4616. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Baldwin AS Jr: The NF-kappa B and I kappa
B proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol.
14:649–683. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cheng JD, Ryseck RP, Attar RM, Dambach D
and Bravo R: Functional redundancy of the nuclear factor kappa B
inhibitors I kappa B alpha and I kappa B beta. J Exp Med.
188:1055–1062. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Huxford T, Huang DB, Malek S and Ghosh G:
The crystal structure of the IkappaBalpha/NF-kappaB complex reveals
mechanisms of NF-kappaB inactivation. Cell. 95:759–770. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tam WF and Sen R: IkappaB family members
function by different mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 276:7701–7704. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hoffmann A, Levchenko A, Scott ML and
Baltimore D: The IkappaB-NF-kappaB signaling module: Temporal
control and selective gene activation. Science. 298:1241–1245.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Anest V, Hanson JL, Cogswell PC,
Steinbrecher KA, Strahl BD and Baldwin AS: A nucleosomal function
for IkappaB kinase-alpha in NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression.
Nature. 423:659–663. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Calaf G and Russo J: Transformation of
human breast epithelial cells by chemical carcinogens.
Carcinogenesis. 14:483–492. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhan Y, Chen Y, Liu R, Zhang H and Zhang
Y: Potentiation of paclitaxel activity by curcumin in human breast
cancer cell by modulating apoptosis and inhibiting EGFR signaling.
Arch Pharm Res. 37:1086–1095. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Aggarwal BB, Shishodia S, Takada Y,
Banerjee S, Newman RA, Bueso-Ramos CE and Price JE: Curcumin
suppresses the paclitaxel-induced nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in
breast cancer cells and inhibits lung metastasis of human breast
cancer in nude mice. Clin Cancer Res. 11:7490–7498. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kang HJ, Lee SH, Price JE and Kim LS:
Curcumin suppresses the paclitaxel-induced nuclear factor-kappaB in
breast cancer cells and potentiates the growth inhibitory effect of
paclitaxel in a breast cancer nude mice model. Breast J.
15:223–229. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Choudhuri T, Pal S, Agwarwal ML, Das T and
Sa G: Curcumin induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells
through p53-dependent Bax induction. FEBS Lett. 512:334–340. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Masuelli L, Benvenuto M, Fantini M,
Marzocchella L, Sacchetti P, Di Stefano E, Tresoldi I, Izzi V,
Bernardini R, Palumbo C, et al: Curcumin induces apoptosis in
breast cancer cell lines and delays the growth of mammary tumors in
neu transgenic mice. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 27:105–119.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Siddiqui RA, Harvey KA, Walker C,
Altenburg J, Xu Z, Terry C, Camarillo I, Jones-Hall Y and Mariash
C: Characterization of synergistic anti-cancer effects of
docosahexaenoic acid and curcumin on DMBA-induced mammary
tumorigenesis in mice. BMC Cancer. 13:4182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lu WD, Qin Y, Yang C, Li L and Fu ZX:
Effect of curcumin on human colon cancer multidrug resistance in
vitro and in vivo. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 68:694–701. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Thiyagarajan S, Thirumalai K, Nirmala S,
Biswas J and Krishnakumar S: Effect of curcumin on lung
resistance-related protein (LRP) in retinoblastoma cells. Curr Eye
Res. 34:845–851. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Gallardo M and Calaf GM: Curcumin and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells
transformed by low doses of radiation and estrogen. Int J Oncol.
48:2534–2542. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gallardo M and Calaf GM: Curcumin inhibits
invasive capabilities through epithelial mesenchymal transition in
breast cancer cell lines. Int J Oncol. 49:1019–1027.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|