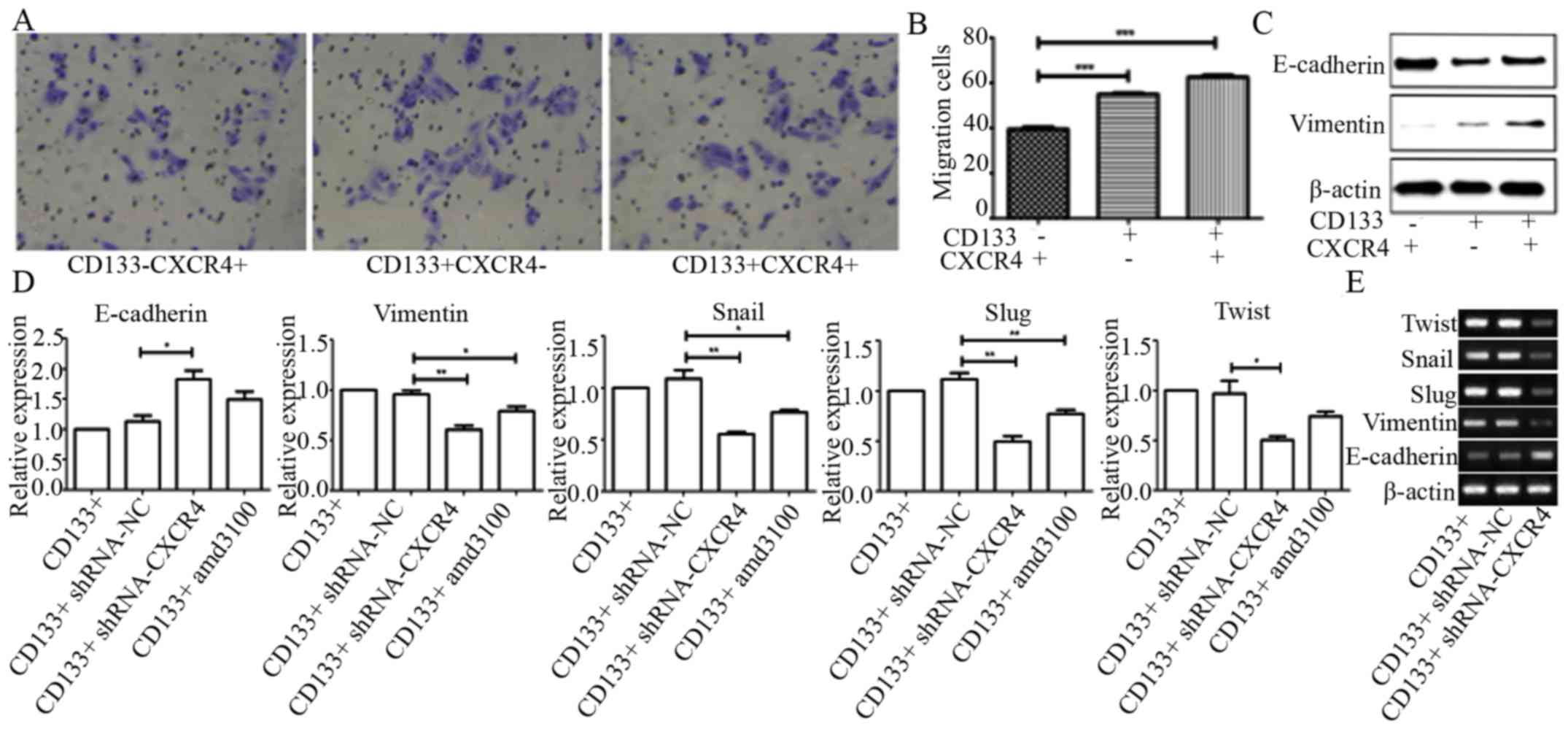
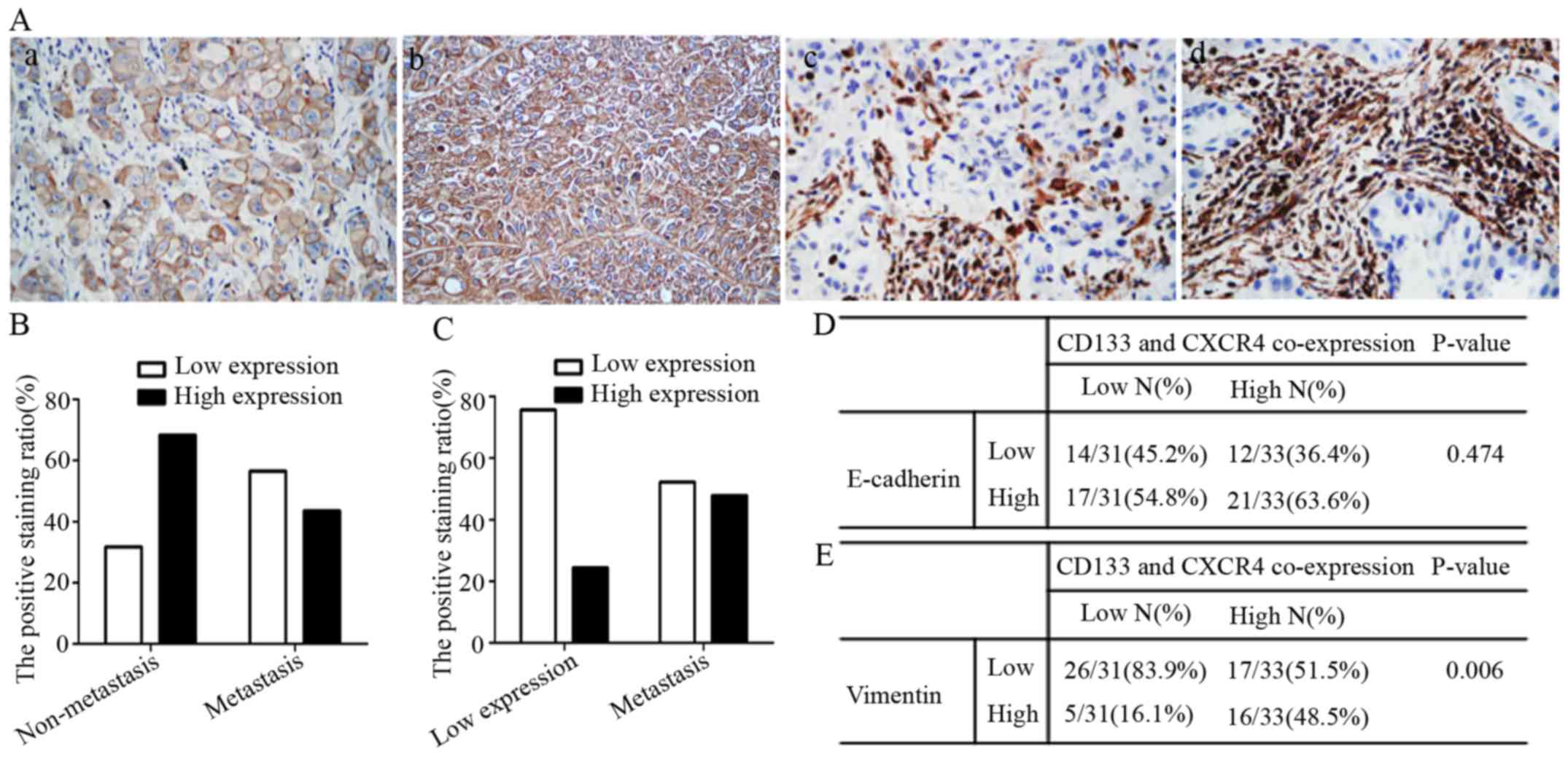
|
1
|
Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, Mariotto AB,
Kramer JL, Rowland JH, Stein KD, Alteri R and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin.
66:271–289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chaffer CL and Weinberg RA: A perspective
on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 331:1559–1564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cai C, Yu JW, Wu JG, Lu RQ, Ni XC, Wang SL
and Jiang BJ: CD133 promotes the invasion and metastasis of gastric
cancer via epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Zhonghua Wei Chang
Wai Ke Za Zhi. 16:662–667. 2013.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bock C, Kuhn C, Ditsch N, Krebold R,
Heublein S, Mayr D, Doisneau-Sixou S and Jeschke U: Strong
correlation between N-cadherin and CD133 in breast cancer: Role of
both markers in metastatic events. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
140:1873–1881. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ding Q, Miyazaki Y, Tsukasa K, Matsubara
S, Yoshimitsu M and Takao S: CD133 facilitates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through interaction with the ERK
pathway in pancreatic cancer metastasis. Mol Cancer. 13:152014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nomura A, Banerjee S, Chugh R, Dudeja V,
Yamamoto M, Vickers SM and Saluja AK: CD133 initiates tumors,
induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and increases metastasis
in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget. 6:8313–8322. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Long H, Xiang T, Qi W, Huang J, Chen J, He
L, Liang Z, Guo B, Li Y, Xie R, et al: CD133+ ovarian
cancer stem-like cells promote non-stem cancer cell metastasis via
CCL5 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget.
6:5846–5859. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Koren A, Rijavec M, Kern I, Sodja E,
Korosec P and Cufer T: BMI1, ALDH1A1, and CD133 transcripts connect
epithelial-mesenchymal transition to cancer stem cells in lung
carcinoma. Stem Cells Int. 2016:97143152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Latorre E, Carelli S, Raimondi I,
D'Agostino V, Castiglioni I, Zucal C, Moro G, Luciani A, Ghilardi
G, Monti E, et al: The ribonucleic complex HuR-MALAT1 represses
CD133 expression and suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 76:2626–2636. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee SO, Yang X, Duan S, Tsai Y, Strojny
LR, Keng P and Chen Y: IL-6 promotes growth and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of CD133+ cells of
non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 7:6626–6638. 2016.
|
|
15
|
Moon Y, Kim D, Sohn H and Lim W: Effect of
CD133 overexpression on the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
oral cancer cell lines. Clin Exp Metastasis. 33:487–496. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fargeas CA, Florek M, Huttner WB and
Corbeil D: Characterization of prominin-2, a new member of the
prominin family of pentaspan membrane glycoproteins. J Biol Chem.
278:8586–8596. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sowa T, Menju T, Sonobe M, Nakanishi T,
Shikuma K, Imamura N, Motoyama H, Hijiya K, Aoyama A, Chen F, et
al: Association between epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
cancer stemness and their effect on the prognosis of lung
adenocarcinoma. Cancer Med. 4:1853–1862. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bertolini G, D'Amico L, Moro M, Landoni E,
Perego P, Miceli R, Gatti L, Andriani F, Wong D, Caserini R, et al:
Microenvironment-modulated metastatic
CD133+/CXCR4+/EpCAM− lung
cancer-initiating cells sustain tumor dissemination and correlate
with poor prognosis. Cancer Res. 75:3636–3649. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Teicher BA and Fricker SP: CXCL12
(SDF-1)/CXCR4 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2927–2931.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dai X, Mao Z, Huang J, Xie S and Zhang H:
The CXCL12/CXCR4 autocrine loop increases the metastatic potential
of non-small cell lung cancer in vitro. Oncol Lett. 5:277–282.
2013.
|
|
21
|
Xie S, Zeng W, Fan G, Huang J, Kang G,
Geng Q, Cheng B, Wang W and Dong P: Effect of CXCL12/CXCR4 on
increasing the metastatic potential of non-small cell lung cancer
in vitro is inhibited through the downregulation of CXCR4 chemokine
receptor expression. Oncol Lett. 7:941–947. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nikzaban M, Hakhamaneshi MS, Fakhari S,
Sheikhesmaili F, Roshani D, Ahsan B, Kamali F and Jalili A: The
chemokine receptor CXCR4 is associated with the staging of gastric
cancer. Adv Biomed Res. 3:162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Okuyama Kishima M, de Oliveira CE,
Banin-Hirata BK, Losi-Guembarovski R, Brajão de Oliveira K,
Amarante MK and Watanabe MA: Immunohistochemical expression of
CXCR4 on breast cancer and its clinical significance. Anal Cell
Pathol (Amst). 2015:8910202015.
|
|
24
|
Teng F, Tian WY, Wang YM, Zhang YF, Guo F,
Zhao J, Gao C and Xue FX: Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote the
progression of endometrial cancer via the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis. J
Hematol Oncol. 9:82016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hu TH, Yao Y, Yu S, Han LL, Wang WJ, Guo
H, Tian T, Ruan ZP, Kang XM, Wang J, et al: SDF-1/CXCR4 promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and progression of colorectal
cancer by activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer
Lett. 354:417–426. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li X, Li P, Chang Y, Xu Q, Wu Z, Ma Q and
Wang Z: The SDF-1/CXCR4 axis induces epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem.
392:77–84. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lv B, Yang X, Lv S, Wang L, Fan K, Shi R,
Wang F, Song H, Ma X, Tan X, et al: CXCR4 signaling induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition by PI3K/AKT and ERK pathways in
glioblastoma. Mol Neurobiol. 52:1263–1268. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yang P, Wang G, Huo H, Li Q, Zhao Y and
Liu Y: SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling up-regulates survivin to regulate
human sacral chondrosarcoma cell cycle and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition via ERK and PI3K/AKT pathway. Med Oncol. 32:3772015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Liao A, Shi R, Jiang Y, Tian S, Li P, Song
F, Qu Y, Li J, Yun H and Yang X: SDF-1/CXCR4 axis regulates cell
cycle progression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via
up-regulation of survivin in glioblastoma. Mol Neurobiol.
53:210–215. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhang SS, Han ZP, Jing YY, Tao SF, Li TJ,
Wang H, Wang Y, Li R, Yang Y, Zhao X, et al: CD133(+)CXCR4(+) colon
cancer cells exhibit metastatic potential and predict poor
prognosis of patients. BMC Med. 10:852012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Silinsky J, Grimes C, Driscoll T, Green H,
Cordova J, Davis NK, Li L and Margolin DA: CD 133+ and
CXCR4+ colon cancer cells as a marker for lymph node
metastasis. J Surg Res. 185:113–118. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li XF, Guo XG, Yang YY and Liu AY: Effect
of CXCR4 and CD133 co-expression on the prognosis of patients with
stage II–III colon cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:1073–1076.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lu C, Xu F, Gu J, Yuan Y, Zhao G, Yu X and
Ge D: Clinical and biological significance of stem-like
CD133(+)CXCR4(+) cells in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J
Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 150:386–395. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Siegel
RL, Stein KD, Kramer JL, Alteri R, Robbins AS and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin.
64:252–271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sun Y and Ma L: The emerging molecular
machinery and therapeutic targets of metastasis. Trends Pharmacol
Sci. 36:349–359. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kakarala M and Wicha MS: Implications of
the cancer stem-cell hypothesis for breast cancer prevention and
therapy. J Clin Oncol. 26:2813–2820. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen Y, Zhang F, Tsai Y, Yang X, Yang L,
Duan S, Wang X, Keng P and Lee SO: IL-6 signaling promotes DNA
repair and prevents apoptosis in CD133+ stem-like cells
of lung cancer after radiation. Radiat Oncol. 10:2272015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Roudi R, Korourian A, Shariftabrizi A and
Madjd Z: Differential expression of cancer stem cell markers ALDH1
and CD133 in various lung cancer subtypes. Cancer Invest.
33:294–302. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu QF, Zhang ZF, Hou GJ, Yang GY and He
Y: Polymorphisms of the stem cell marker gene CD133 and the risk of
lung cancer in Chinese population. Lung. 194:393–400. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nian WQ, Chen FL, Ao XJ and Chen ZT: CXCR4
positive cells from Lewis lung carcinoma cell line have cancer
metastatic stem cell characteristics. Mol Cell Biochem.
355:241–248. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jung MJ, Rho JK, Kim YM, Jung JE, Jin YB,
Ko YG, Lee JS, Lee SJ, Lee JC and Park MJ: Upregulation of CXCR4 is
functionally crucial for maintenance of stemness in drug-resistant
non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncogene. 32:209–221. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wang Z, Sun J, Feng Y, Tian X, Wang B and
Zhou Y: Oncogenic roles and drug target of CXCR4/CXCL12 axis in
lung cancer and cancer stem cell. Tumour Biol. 37:8515–8528. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jiang YX, Yang SW, Li PA, Luo X, Li ZY,
Hao YX and Yu PW: The promotion of the transformation of quiescent
gastric cancer stem cells by IL-17 and the underlying mechanisms.
Oncogene. Aug 15–2016.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Fish KM: Mesenchymal stem cells drive
cardiac stem cell chemotaxis, proliferation, and phenotype via
CXCR4 and ckit signaling. Circ Res. 119:891–892. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang C, Zhou C, Wu XJ, Yang M, Yang ZH,
Xiong HZ, Zhou CP, Lu YX, Li Y and Li XN: Human CD133-positive
hematopoietic progenitor cells initiate growth and metastasis of
colorectal cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 35:2771–2777. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Won C, Kim BH, Yi EH, Choi KJ, Kim EK,
Jeong JM, Lee JH, Jang JJ, Yoon JH, Jeong WI, et al: Signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3-mediated CD133
up-regulation contributes to promotion of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 62:1160–1173. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhao W, Luo Y, Li B and Zhang T:
Tumorigenic lung tumorospheres exhibit stem-like features with
significantly increased expression of CD133 and ABCG2. Mol Med Rep.
14:2598–2606. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yuan X, Wu H, Han N, Xu H, Chu Q, Yu S,
Chen Y and Wu K: Notch signaling and EMT in non-small cell lung
cancer: Biological significance and therapeutic application. J
Hematol Oncol. 7:872014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Knapp CF, Sayegh Z, Schell MJ, Rawal B,
Ochoa T, Sondak VK and Messina JL: Expression of CXCR4, E-cadherin,
Bcl-2, and survivin in Merkel cell carcinoma: An
immunohistochemical study using a tissue microarray. Am J
Dermatopathol. 34:592–596. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Havel LS, Kline ER, Salgueiro AM and
Marcus AI: Vimentin regulates lung cancer cell adhesion through a
VAV2-Rac1 pathway to control focal adhesion kinase activity.
Oncogene. 34:1979–1990. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|