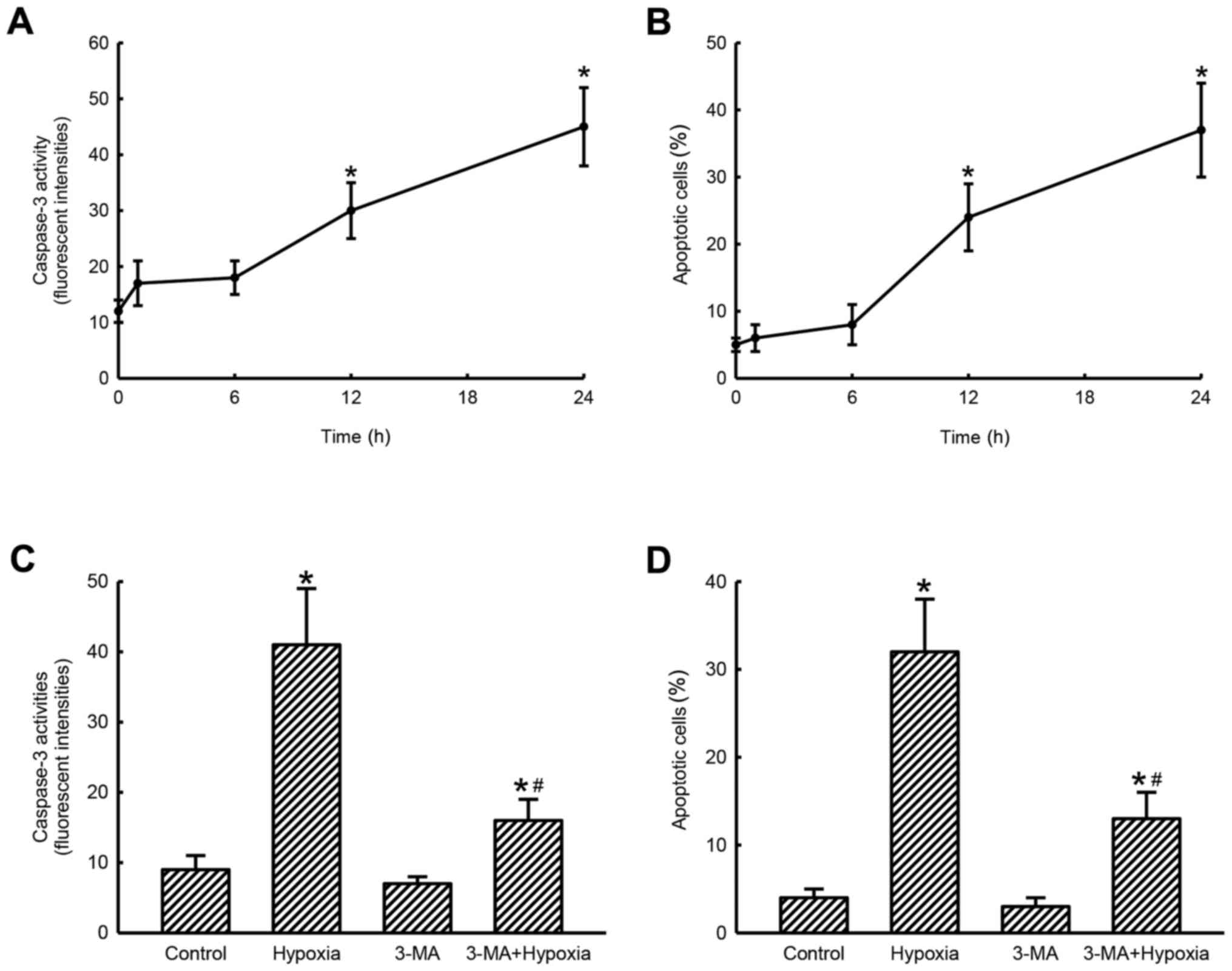
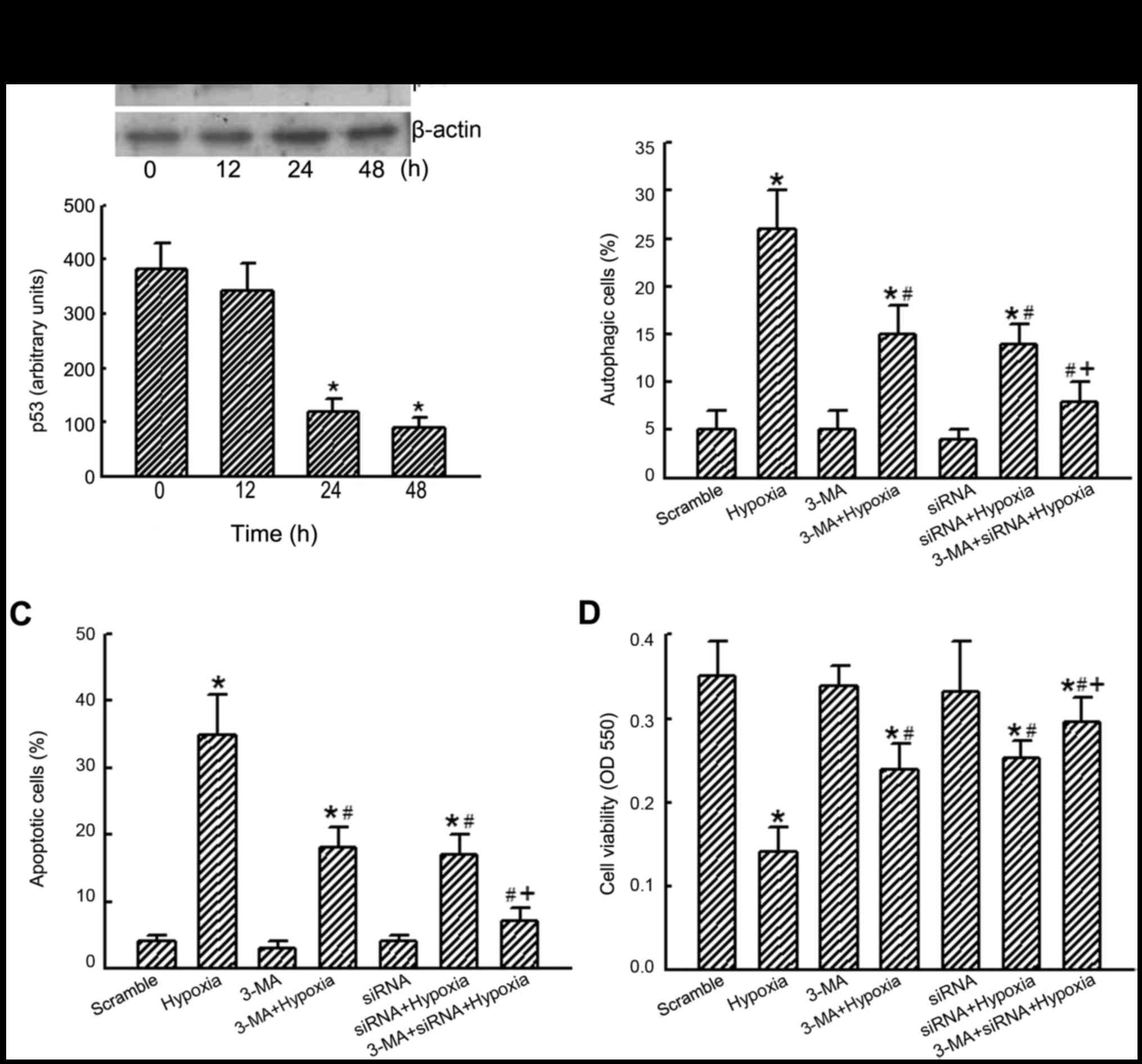
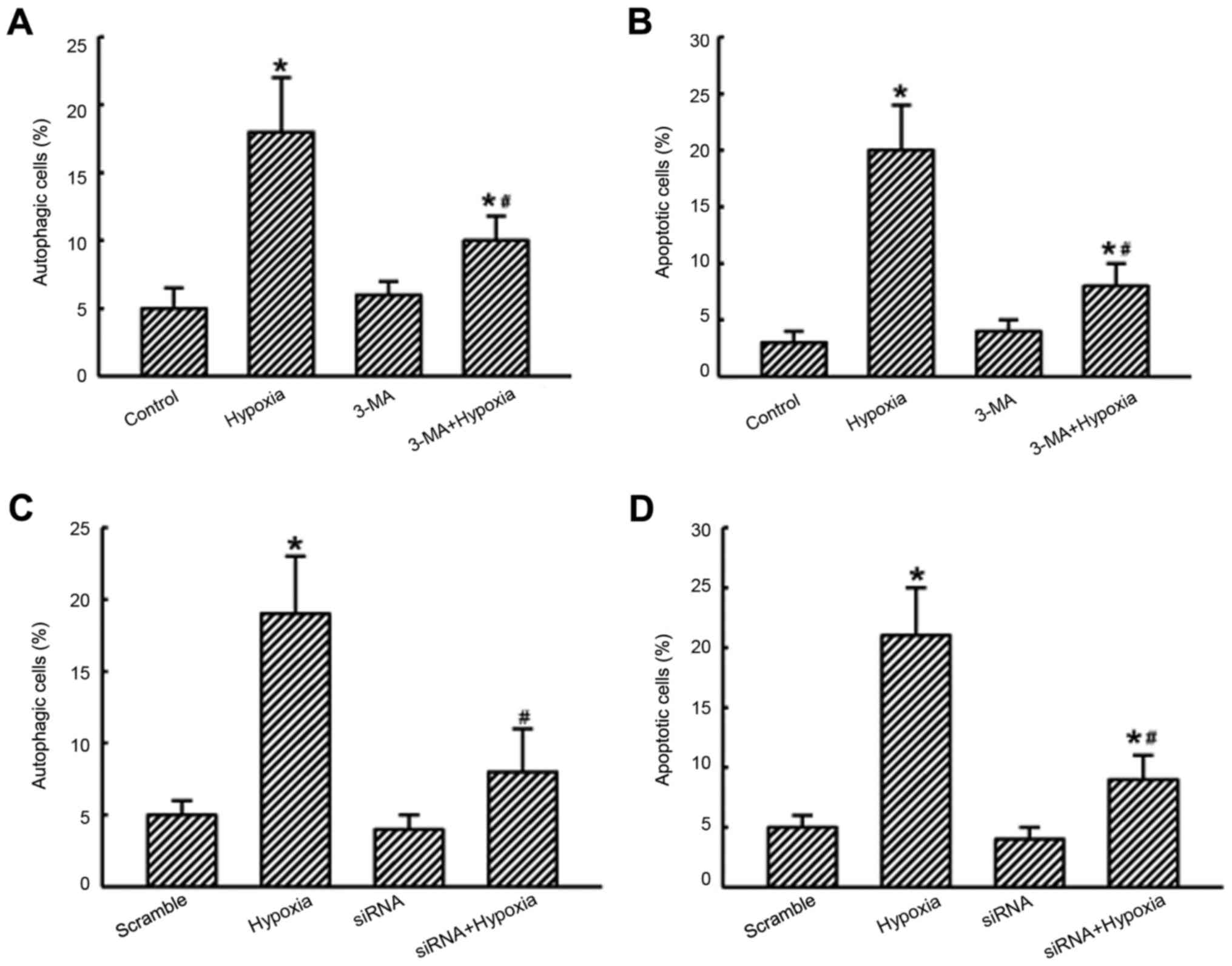
|
1
|
Wacker MR, Hoshino T, Ahn DK, Davis RL and
Prados MD: The prognostic implications of histologic classification
and bromodeoxyuridine labeling index of mixed gliomas. J
Neurooncol. 19:113–122. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jordan JT, Gerstner ER, Batchelor TT,
Cahill DP and Plotkin SR: Glioblastoma care in the elderly. Cancer.
122:189–197. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kalkan R: Hypoxia is the driving force
behind GBM and could be a new tool in GBM treatment. Crit Rev
Eukaryot Gene Expr. 25:363–369. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Preusser M, Lim M, Hafler DA, Reardon DA
and Sampson JH: Prospects of immune checkpoint modulators in the
treatment of glioblastoma. Nat Rev Neurol. 11:504–514. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Curtin JF, Liu N, Candolfi M, Xiong W,
Assi H, Yagiz K, Edwards MR, Michelsen KS, Kroeger KM, Liu C, et
al: HMGB1 mediates endogenous TLR2 activation and brain tumor
regression. PLoS Med. 6:e102009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gerstner ER, Duda DG, di Tomaso E, Ryg PA,
Loeffler JS, Sorensen AG, Ivy P, Jain RK and Batchelor TT: VEGF
inhibitors in the treatment of cerebral edema in patients with
brain cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 6:229–236. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Freese KE, Kokai L, Edwards RP, Philips
BJ, Sheikh MA, Kelley J, Comerci J, Marra KG, Rubin JP and Linkov
F: Adipose-derived stems cells and their role in human cancer
development, growth, progression, and metastasis: A systematic
review. Cancer Res. 75:1161–1168. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lingsma HF, Roozenbeek B, Steyerberg EW,
Murray GD and Maas AI: Early prognosis in traumatic brain injury:
From prophecies to predictions. Lancet Neurol. 9:543–554. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Semenza GL: Surviving ischemia: Adaptive
responses mediated by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Clin Invest.
106:809–812. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin CJ, Lin YL, Luh F, Yen Y and Chen RM:
Preclinical effects of CRLX101, an investigational
camptothecin-containing nanoparticle drug conjugate, on treating
glioblastoma multiforme via apoptosis and antiangiogenesis.
Oncotarget. 7:42408–42421. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chan DA, Krieg AJ, Turcotte S and Giaccia
AJ: HIF gene expression in cancer therapy. Methods Enzymol.
435:323–345. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chio CC, Lin JW, Cheng HA, Chiu WT, Wang
YH, Wang JJ, Hsing CH and Chen RM: MicroRNA-210 targets
antiapoptotic Bcl-2 expression and mediates hypoxia-induced
apoptosis of neuroblastoma cells. Arch Toxicol. 87:459–468. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Joseph JV, Conroy S, Pavlov K, Sontakke P,
Tomar T, Eggens-Meijer E, Balasubramaniyan V, Wagemakers M, den
Dunnen WF and Kruyt FA: Hypoxia enhances migration and invasion in
glioblastoma by promoting a mesenchymal shift mediated by the
HIF1α-ZEB1 axis. Cancer Lett. 359:107–116. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun W, Jelkmann W and Depping R:
Prolyl-4-hydroxylase 2 enhances hypoxia-induced glioblastoma cell
death by regulating the gene expression of hypoxia-inducible
factor-α. Cell Death Dis. 5:e13222014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Codogno P, Mehrpour M and Proikas-Cezanne
T: Canonical and non-canonical autophagy: Variations on a common
theme of self-eating? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:7–12.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kaur J and Debnath J: Autophagy at the
crossroads of catabolism and anabolism. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
16:461–472. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yoshimori T: Autophagy: A regulated bulk
degradation process inside cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
313:453–458. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kondo Y, Kanzawa T, Sawaya R and Kondo S:
The role of autophagy in cancer development and response to
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:726–734. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nanegrungsunk D, Onchan W, Chattipakorn N
and Chattipakorn SC: Current evidence of temozolomide and
bevacizumab in treatment of gliomas. Neurol Res. 37:167–183. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Dolma S, Selvadurai HJ, Lan X, Lee L,
Kushida M, Voisin V, Whetstone H, So M, Aviv T, Park N, et al:
Inhibition of dopamine receptor D4 impedes autophagic flux,
proliferation, and survival of glioblastoma stem cells. Cancer
Cell. 29:859–873. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lin CJ, Chen TL, Tseng YY, Wu GJ, Hsieh
MH, Lin YW and Chen RM: Honokiol induces autophagic cell death in
malignant glioma through reactive oxygen species-mediated
regulation of the p53/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 304:59–69. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bota DA, Alexandru D, Keir ST, Bigner D,
Vredenburgh J and Friedman HS: Proteasome inhibition with
bortezomib induces cell death in GBM stem-like cells and
temozolomide-resistant glioma cell lines, but stimulates GBM
stem-like cells' VEGF production and angiogenesis. J Neurosurg.
119:1415–1423. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hu YL, DeLay M, Jahangiri A, Molinaro AM,
Rose SD, Carbonell WS and Aghi MK: Hypoxia-induced autophagy
promotes tumor cell survival and adaptation to antiangiogenic
treatment in glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 72:1773–1783. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xue H, Yuan G, Guo X, Liu Q, Zhang J, Gao
X, Guo X, Xu S, Li T, Shao Q, et al: A novel tumor-promoting
mechanism of IL6 and the therapeutic efficacy of tocilizumab:
Hypoxia-induced IL6 is a potent autophagy initiator in glioblastoma
via the p-STAT3-MIR155-3p-CREBRF pathway. Autophagy. 12:1129–1152.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yeh PS, Wang W, Chang YA, Lin CJ, Wang JJ
and Chen RM: Honokiol induces autophagy of neuroblastoma cells
through activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR and endoplasmic reticular
stress/ERK1/2 signaling pathways and suppressing cell migration.
Cancer Lett. 370:66–77. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Vousden KH and Lu X: Live or let die: The
cell's response to p53. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:594–604. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ho MH, Liao MH, Lin YL, Lai CH, Lin PI and
Chen RM: Improving effects of chitosan nanofiber scaffolds on
osteoblast proliferation and maturation. Int J Nanomed.
9:4293–4304. 2014.
|
|
28
|
Chang CY, Lui TN, Lin JW, Lin YL, Hsing
CH, Wang JJ and Chen RM: Roles of microRNA-1 in hypoxia-induced
apoptotic insults to neuronal cells. Arch Toxicol. 90:191–202.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lee YE, Hong CY, Lin YL and Chen RM:
MicroRNA-1 participates in nitric oxide-induced apoptotic insults
to MC3T3-E1 cells by targeting heat-shock protein-70. Int J Biol
Sci. 11:246–255. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu GJ, Wang W, Lin YL, Liu SH and Chen RM:
Oxidative stress-induced apoptotic insults to rat osteoblasts are
attenuated by nitric oxide pretreatment via GATA-5-involved
regulation of Bcl-X L gene expression and protein translocation.
Arch Toxicol. 90:905–916. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wu TT, Tai YT, Cherng YG, Chen TG, Lin CJ,
Chen TL, Chang HC and Chen RM: GATA-2 transduces LPS-induced il-1β
gene expression in macrophages via a toll-like receptor
4/MD88/MAPK-dependent mechanism. PLoS One. 8:e724042013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Messaoudi K, Clavreul A and Lagarce F:
Toward an effective strategy in glioblastoma treatment. Part II:
RNA interference as a promising way to sensitize glioblastomas to
temozolomide. Drug Discov Today. 20:772–779. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kaelin WG Jr and Ratcliffe PJ: Oxygen
sensing by metazoans: The central role of the HIF hydroxylase
pathway. Mol Cell. 30:393–402. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mamlouk S and Wielockx B:
Hypoxia-inducible factors as key regulators of tumor inflammation.
Int J Cancer. 132:2721–2729. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kajita K, Mori I, Kitada Y, Taguchi K,
Kajita T, Hanamoto T, Ikeda T, Fujioka K, Yamauchi M, Okada H, et
al: Small proliferative adipocytes: Identification of proliferative
cells expressing adipocyte markers. Endocr J. 60:931–939. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li W, Winters A, Poteet E, Ryou MG, Lin S,
Hao S, Wu Z, Yuan F, Hatanpaa KJ, Simpkins JW, et al: Involvement
of estrogen receptor β5 in the progression of glioma. Brain Res.
1503:97–107. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T and Levine B:
Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell. 140:313–326. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdelmohsen K, Abe A, Abedin
MJ, Abeliovich H, Acevedo Arozena A, Adachi H, Adams CM, Adams PD,
Adeli K, et al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays
for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy. 12:1–222. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wu YT, Tan HL, Shui G, Bauvy C, Huang Q,
Wenk MR, Ong CN, Codogno P and Shen HM: Dual role of
3-methyladenine in modulation of autophagy via different temporal
patterns of inhibition on class I and III phosphoinositide
3-kinase. J Biol Chem. 285:10850–10861. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen N and Karantza-Wadsworth V: Role and
regulation of autophagy in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1793:1516–1523. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Galluzzi L, Kepp O and Kroemer G:
Caspase-3 and prostaglandins signal for tumor regrowth in cancer
therapy. Oncogene. 31:2805–2808. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Mariño G, Niso-Santano M, Baehrecke EH and
Kroemer G: Self-consumption: The interplay of autophagy and
apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:81–94. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sui X, Chen R, Wang Z, Huang Z, Kong N,
Zhang M, Han W, Lou F, Yang J, Zhang Q, et al: Autophagy and
chemotherapy resistance: A promising therapeutic target for cancer
treatment. Cell Death Dis. 4:e8382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Feng Z, Zhang H, Levine AJ and Jin S: The
coordinate regulation of the p53 and mTOR pathways in cells. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:8204–8209. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Crighton D, Wilkinson S, O'Prey J, Syed N,
Smith P, Harrison PR, Gasco M, Garrone O, Crook T and Ryan KM:
DRAM, a p53-induced modulator of autophagy, is critical for
apoptosis. Cell. 126:121–134. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|