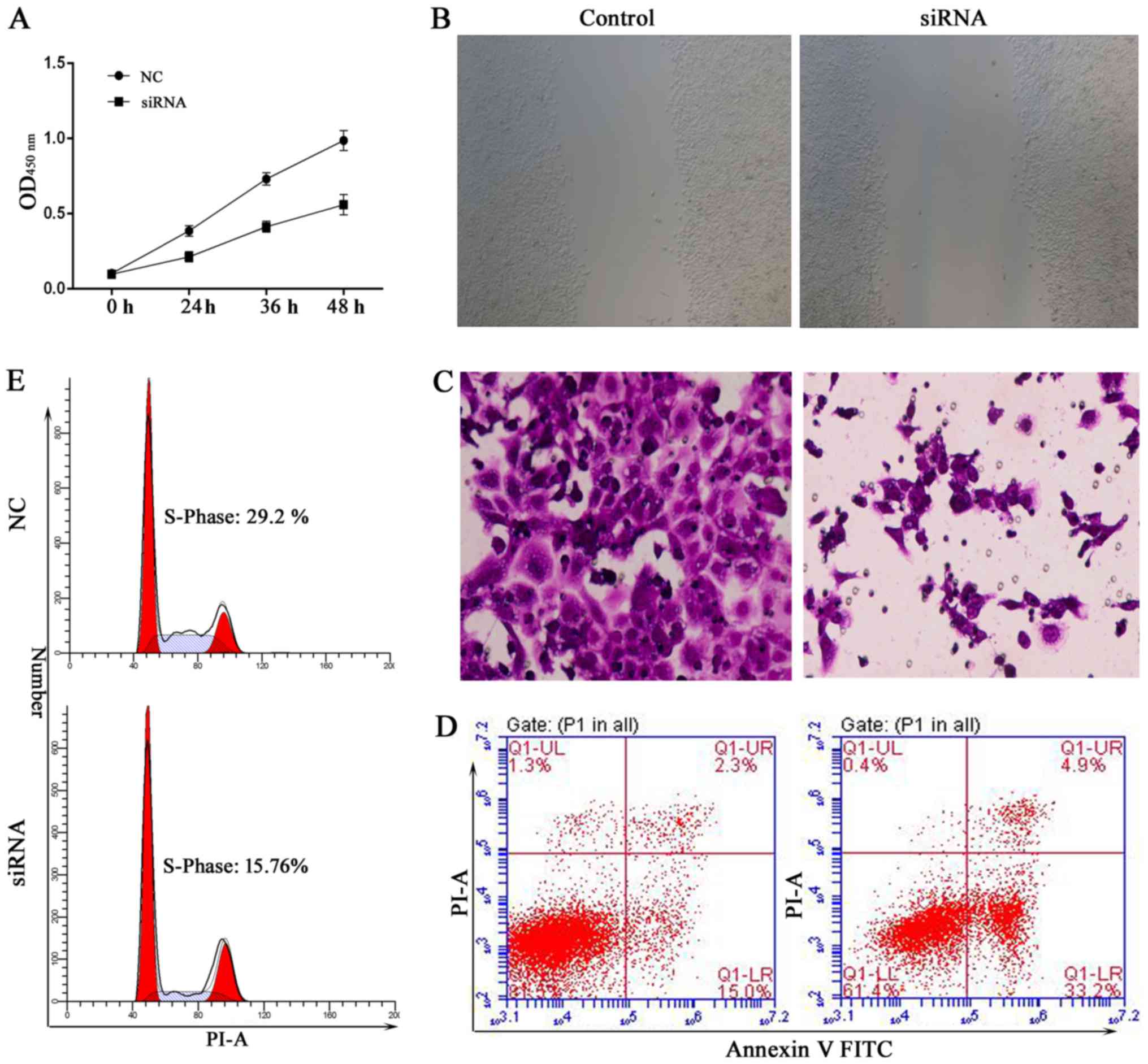
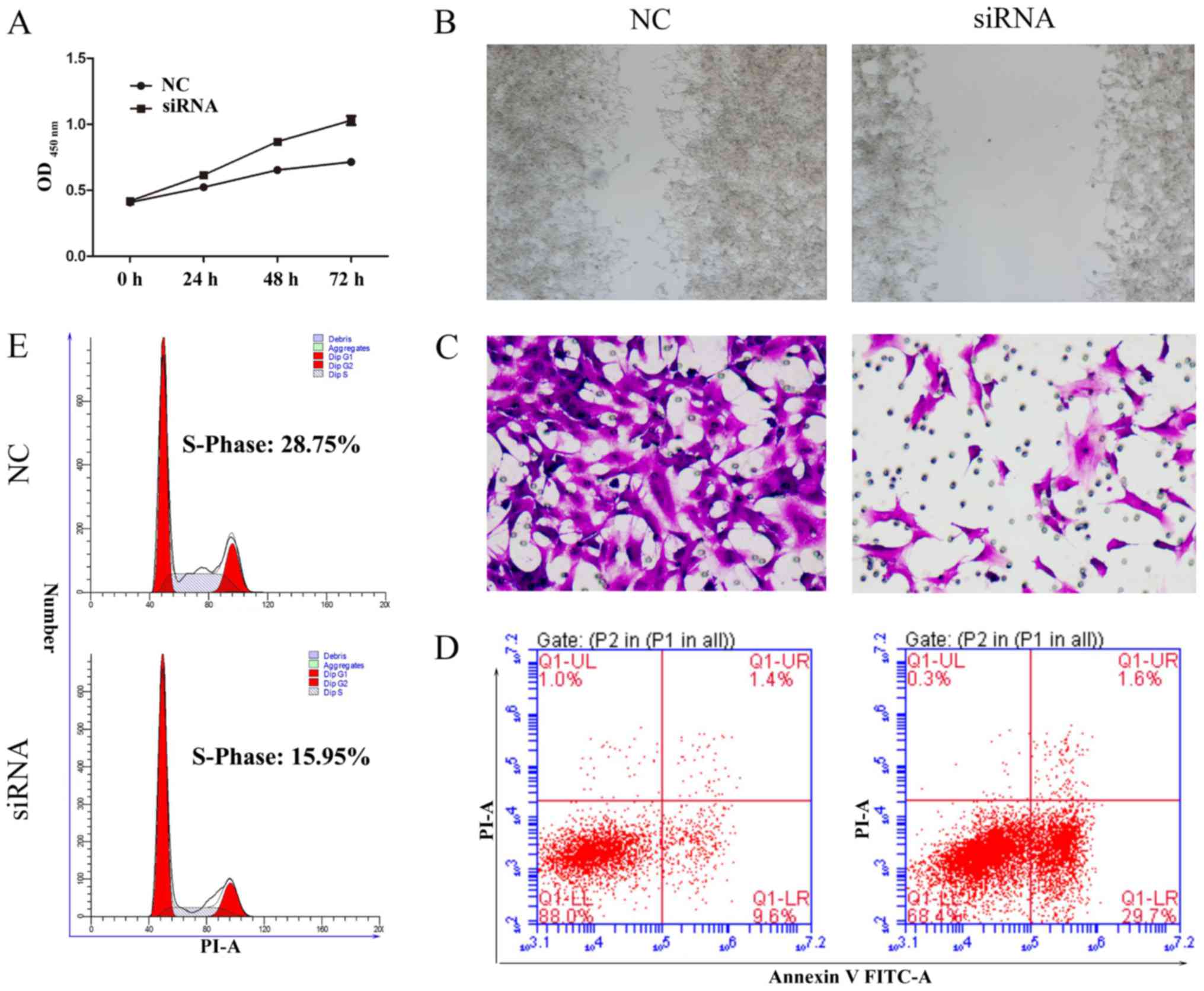
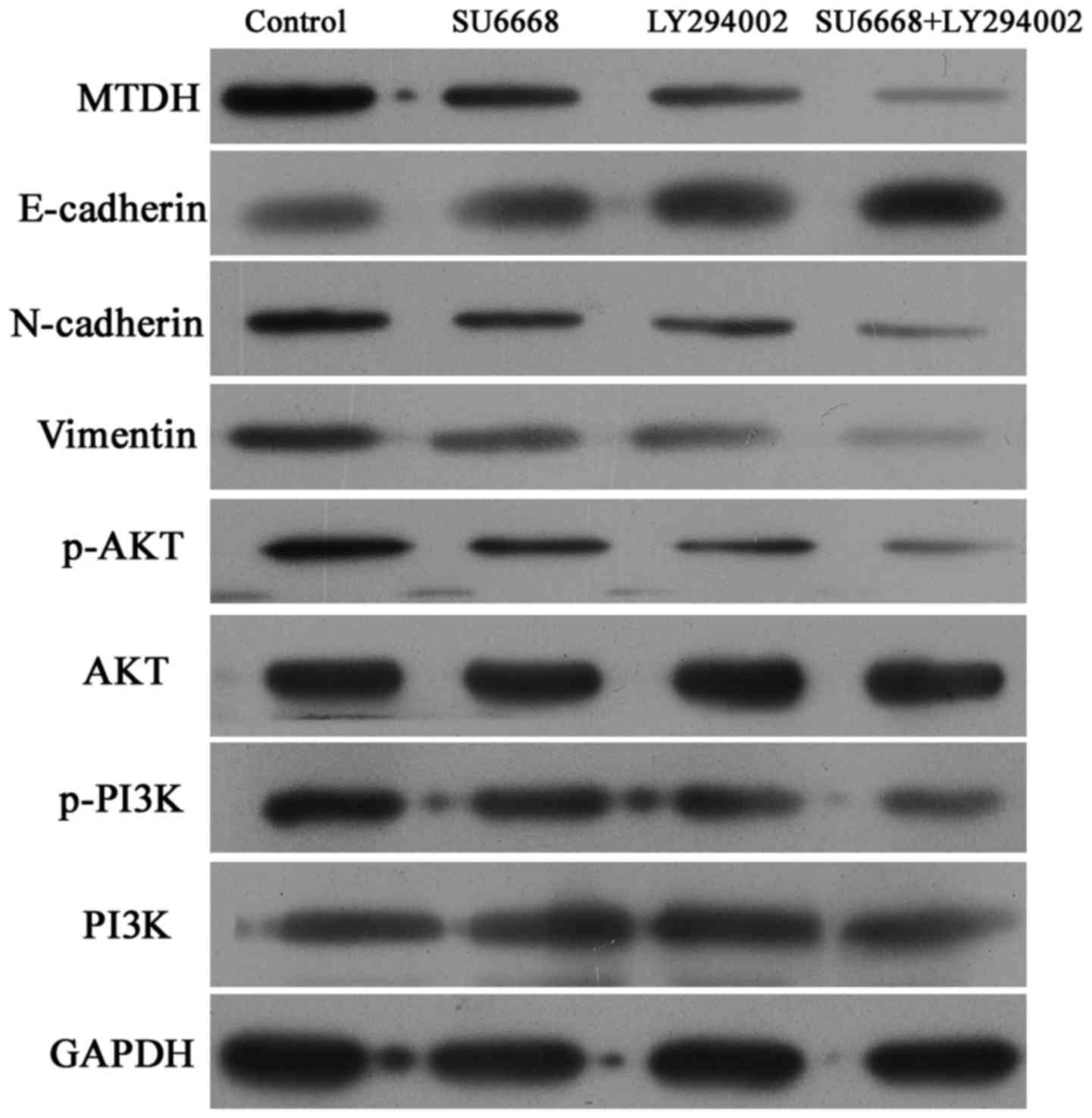
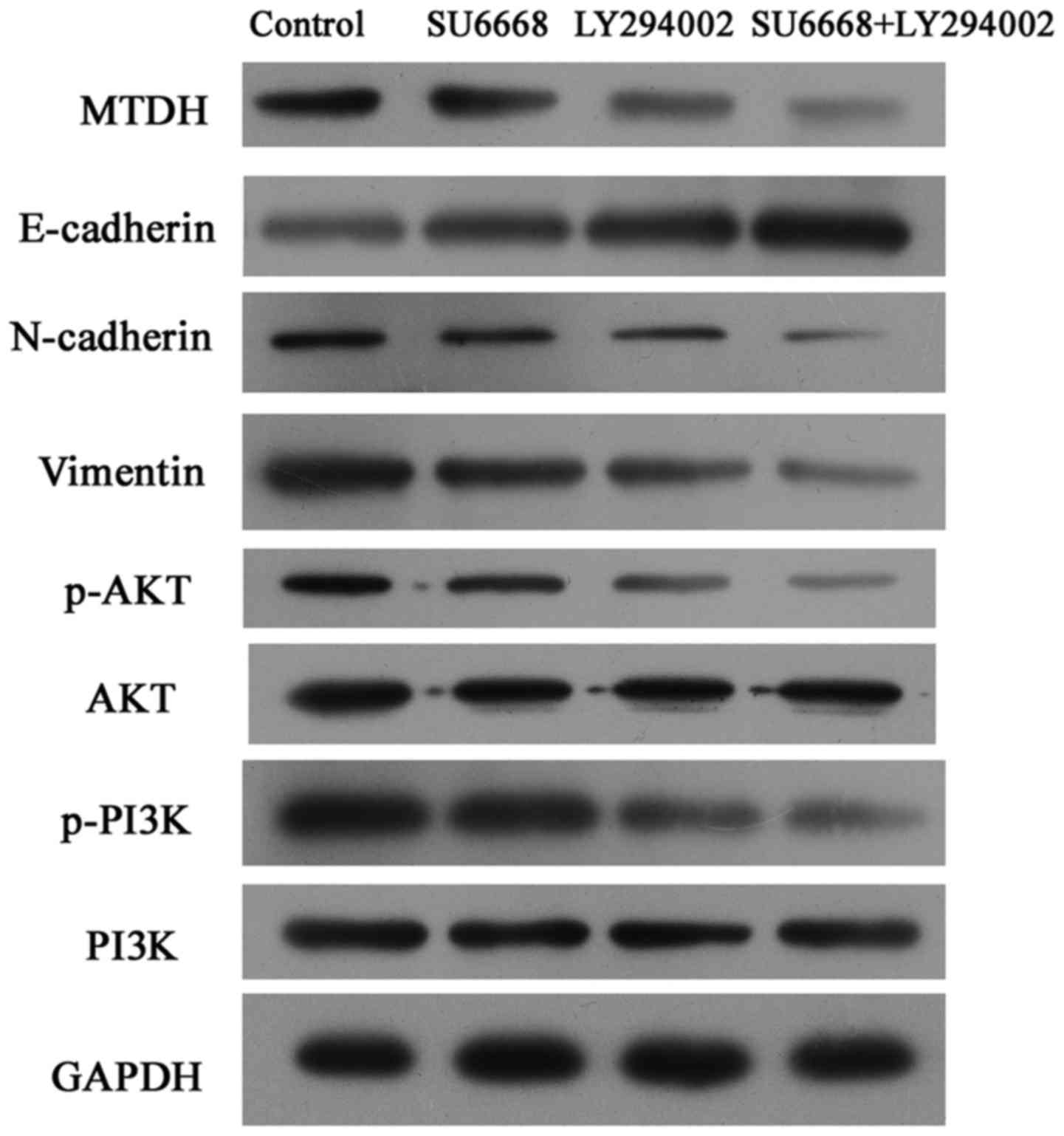
|
1
|
Castillejos-Molina RA and
Gabilondo-Navarro FB: Prostate cancer. Salud Publica Mex.
58:279–284. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
El-Shami K, Oeffinger KC, Erb L, Willis A,
Bretsch JK, Pratt-Chapman ML, Cannady RS, Wong SL, Rose J, Barbour
AL, et al: American Cancer Society Colorectal Cancer Survivorship
Care Guidelines. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:428–455. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Roehl KA, Antenor JA and Catalona WJ:
Serial biopsy results in prostate cancer screening study. J Urol.
167:2435–2439. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Walsh PC: Re: The natural history of
metastatic progression in men with prostate-specific antigen
recurrence after radical prostatectomy: long-term follow-up. J
Urol. 188:8092012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Antonarakis ES, Feng Z, Trock BJ,
Humphreys EB, Carducci MA, Partin AW, Walsh PC and Eisenberger MA:
The natural history of metastatic progression in men with
prostate-specific antigen recurrence after radical prostatectomy:
Long-term follow-up. BJU Int. 109:32–39. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sweeney CJ, Chen YH, Carducci M, Liu G,
Jarrard DF, Eisenberger M, Wong YN, Hahn N, Kohli M, Cooney MM, et
al: Chemohormonal therapy in metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate
cancer. N Engl J Med. 373:737–746. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gale NW and Yancopoulos GD: Growth factors
acting via endothelial cell-specific receptor tyrosine kinases:
VEGFs, angiopoietins, and ephrins in vascular development. Genes
Dev. 13:1055–1066. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hoekman K: SU6668, a multitargeted
angiogenesis inhibitor. Cancer J. 7(Suppl 3): S134–S138. 2001.
|
|
9
|
Laird AD, Vajkoczy P, Shawver LK, Thurnher
A, Liang C, Mohammadi M, Schlessinger J, Ullrich A, Hubbard SR,
Blake RA, et al: SU6668 is a potent antiangiogenic and antitumor
agent that induces regression of established tumors. Cancer Res.
60:4152–4160. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Laird AD, Christensen JG, Li G, Carver J,
Smith K, Xin X, Moss KG, Louie SG, Mendel DB and Cherrington JM:
SU6668 inhibits Flk-1/KDR and PDGFRbeta in vivo, resulting in rapid
apoptosis of tumor vasculature and tumor regression in mice. FASEB
J. 16:681–690. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang L, Liu Z, Ma D, Piao Y, Guo F, Han Y
and Xie X: SU6668 suppresses proliferation of triple negative
breast cancer cells through down-regulating MTDH expression. Cancer
Cell Int. 13:882013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang X, Raskovalova T, Lokshin A,
Krasinskas A, Devlin J, Watkins S, Wolf SF and Gorelik E: Combined
antiangiogenic and immune therapy of prostate cancer. Angiogenesis.
8:13–23. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Figg WD, Kruger EA, Price DK, Kim S and
Dahut WD: Inhibition of angiogenesis: Treatment options for
patients with metastatic prostate cancer. Invest New Drugs.
20:183–194. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Timke C, Zieher H, Roth A, Hauser K,
Lipson KE, Weber KJ, Debus J, Abdollahi A and Huber PE: Combination
of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor/platelet-derived
growth factor receptor inhibition markedly improves radiation tumor
therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2210–2219. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Abdollahi A, Lipson KE, Han X, Krempien R,
Trinh T, Weber KJ, Hahnfeldt P, Hlatky L, Debus J, Howlett AR, et
al: SU5416 and SU6668 attenuate the angiogenic effects of
radiation-induced tumor cell growth factor production and amplify
the direct anti-endothelial action of radiation in vitro. Cancer
Res. 63:3755–3763. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Su ZZ, Kang DC, Chen Y, Pekarskaya O, Chao
W, Volsky DJ and Fisher PB: Identification and cloning of human
astrocyte genes displaying elevated expression after infection with
HIV-1 or exposure to HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein by rapid
subtraction hybridization, RaSH. Oncogene. 21:3592–3602. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Z, Wei YB, Gao YL, Yan B, Yang JR and
Guo Q: Metadherin in prostate, bladder, and kidney cancer: A
systematic review. Mol Clin Oncol. 2:1139–1144. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu X, Wang D, Liu H, Feng Y, Zhu T, Zhang
L, Zhu B and Zhang Y: Knockdown of astrocyte elevated gene-1
(AEG-1) in cervical cancer cells decreases their invasiveness,
epithelial to mesenchymal transition, and chemoresistance. Cell
Cycle. 13:1702–1707. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dong L, Qin S, Li Y, Zhao L, Dong S, Wang
Y, Zhang C and Han S: High expression of astrocyte elevated gene-1
is associated with clinical staging, metastasis, and unfavorable
prognosis in gastric carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 36:2169–2178. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hu G, Wei Y and Kang Y: The multifaceted
role of MTDH/AEG-1 in cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res.
15:5615–5620. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Z, Tang ZY, Yin Z, Wei YB, Liu LF,
Yan B, Zhou KQ, Nian YQ, Gao YL and Yang JR: Metadherin regulates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther.
9:2429–2436. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li J, Zhang N, Song LB, Liao WT, Jiang LL,
Gong LY, Wu J, Yuan J, Zhang HZ, Zeng MS, et al: Astrocyte elevated
gene-1 is a novel prognostic marker for breast cancer progression
and overall patient survival. Clin Cancer Res. 14:3319–3326. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Noch E, Bookland M and Khalili K:
Astrocyte-elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) induction by hypoxia and glucose
deprivation in glioblastoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 11:32–39. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Sun W, Fan YZ, Xi H, Lu XS, Ye C and Zhang
JT: Astrocyte elevated gene-1 overexpression in human primary
gallbladder carcinomas: An unfavorable and independent prognostic
factor. Oncol Rep. 26:1133–1142. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu JB, Wu H, He YL, Zhang CH, Zang LJ, Cai
SR and Zhang WH: Astrocyte-elevated gene-1 overexpression is
associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Med Oncol.
28:455–462. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kikuno N, Shiina H, Urakami S, Kawamoto K,
Hirata H, Tanaka Y, Place RF, Pookot D, Majid S, Igawa M, et al:
Knockdown of astrocyte-elevated gene-1 inhibits prostate cancer
progression through upregulation of FOXO3a activity. Oncogene.
26:7647–7655. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Acloque H, Adams MS, Fishwick K,
Bronner-Fraser M and Nieto MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions:
The importance of changing cell state in development and disease. J
Clin Invest. 119:1438–1449. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nieto MA, Huang RY, Jackson RA and Thiery
JP: Emt: 2016. Cell. 166:21–45. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chaffer CL and Weinberg RA: A perspective
on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 331:1559–1564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Emdad L, Lee SG, Su ZZ, Jeon HY, Boukerche
H, Sarkar D and Fisher PB: Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1)
functions as an oncogene and regulates angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 106:21300–21305. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yoo BK, Emdad L, Su ZZ, Villanueva A,
Chiang DY, Mukhopadhyay ND, Mills AS, Waxman S, Fisher RA, Llovet
JM, et al: Astrocyte elevated gene-1 regulates hepatocellular
carcinoma development and progression. J Clin Invest. 119:465–477.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sarkar D, Emdad L, Lee SG, Yoo BK, Su ZZ
and Fisher PB: Astrocyte elevated gene-1: Far more than just a gene
regulated in astrocytes. Cancer Res. 69:8529–8535. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Godl K, Gruss OJ, Eickhoff J, Wissing J,
Blencke S, Weber M, Degen H, Brehmer D, Orfi L, Horváth Z, et al:
Proteomic characterization of the angiogenesis inhibitor SU6668
reveals multiple impacts on cellular kinase signaling. Cancer Res.
65:6919–6926. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Guo X, Ying W, Wan J, Hu Z, Qian X, Zhang
H and He F: Proteomic characterization of early-stage
differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells into neural cells
induced by all-trans retinoic acid in vitro. Electrophoresis.
22:3067–3075. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shi X and Wang X: The role of MTDH/AEG-1
in the progression of cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:4795–4807.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chang L, Graham PH, Ni J, Hao J, Bucci J,
Cozzi PJ and Li Y: Targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in the
treatment of prostate cancer radioresistance. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 96:507–517. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Taylor BS, Schultz N, Hieronymus H,
Gopalan A, Xiao Y, Carver BS, Arora VK, Kaushik P, Cerami E, Reva
B, et al: Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer.
Cancer Cell. 18:11–22. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Edlind MP and Hsieh AC: PI3K-AKT-mTOR
signaling in prostate cancer progression and androgen deprivation
therapy resistance. Asian J Androl. 16:378–386. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee SG, Su ZZ, Emdad L, Sarkar D and
Fisher PB: Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) is a target gene of
oncogenic Ha-ras requiring phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and c-Myc.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:17390–17395. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|