|
1
|
Poon D, Anderson BO, Chen LT, Tanaka K,
Lau WY, Van Cutsem E, Singh H, Chow WC, Ooi LL, Chow P, et al Asian
Oncology Summit: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma in Asia:
Consensus statement from the Asian Oncology Summit 2009. Lancet
Oncol. 10:1111–1118. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McGlynn KA, Petrick JL and London WT:
Global epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: An emphasis on
demographic and regional variability. Clin Liver Dis. 19:223–238.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thorgeirsson SS and Grisham JW: Molecular
pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet.
31:339–346. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chaffer CL and Weinberg RA: A perspective
on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 331:1559–1564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thompson EW, Newgreen DF and Tarin D:
Carcinoma invasion and metastasis: A role for
epithelial-mesenchymal transition? Cancer Res. 65:5991–5995;
discussion 5995. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
van Zijl F, Krupitza G and Mikulits W:
Initial steps of metastasis: Cell invasion and endothelial
transmigration. Mutat Res. 728:23–34. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yamada S, Okumura N, Wei L, Fuchs BC,
Fujii T, Sugimoto H, Nomoto S, Takeda S, Tanabe KK and Kodera Y:
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is associated with shorter
disease-free survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol.
21:3882–3890. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Micalizzi DS, Farabaugh SM and Ford HL:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer: Parallels between
normal development and tumor progression. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 15:117–134. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gujral TS, Chan M, Peshkin L, Sorger PK,
Kirschner MW and MacBeath G: A noncanonical Frizzled2 pathway
regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Cell.
159:844–856. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Willert K, Brown JD, Danenberg E, Duncan
AW, Weissman IL, Reya T, Yates JR III and Nusse R: Wnt proteins are
lipid-modified and can act as stem cell growth factors. Nature.
423:448–452. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Deka J, Wiedemann N, Anderle P,
Murphy-Seiler F, Bultinck J, Eyckerman S, Stehle JC, André S,
Vilain N, Zilian O, et al: Bcl9/Bcl9l are critical for Wnt-mediated
regulation of stem cell traits in colon epithelium and
adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 70:6619–6628. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gupta S, Iljin K, Sara H, Mpindi JP,
Mirtti T, Vainio P, Rantala J, Alanen K, Nees M and Kallioniemi O:
FZD4 as a mediator of ERG oncogene-induced WNT signaling and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human prostate cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 70:6735–6745. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu ZQ, Brabletz T, Fearon E, Willis AL, Hu
CY, Li XY and Weiss SJ: Canonical Wnt suppressor, Axin2, promotes
colon carcinoma oncogenic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:11312–11317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee TK, Poon RT, Yuen AP, Ling MT, Kwok
WK, Wang XH, Wong YC, Guan XY, Man K, Chau KL, et al: Twist
overexpression correlates with hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis
through induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Clin Cancer
Res. 12:5369–5376. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Giannelli G, Bergamini C, Fransvea E,
Sgarra C and Antonaci S: Laminin-5 with transforming growth
factor-β1 induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 129:1375–1383. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee TK, Man K, Poon RT, Lo CM, Yuen AP, Ng
IO, Ng KT, Leonard W and Fan ST: Signal transducers and activators
of transcription 5b activation enhances hepatocellular carcinoma
aggressiveness through induction of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Cancer Res. 66:9948–9956. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen CL, Hsieh FC, Lieblein JC, Brown J,
Chan C, Wallace JA, Cheng G, Hall BM and Lin J: Stat3 activation in
human endometrial and cervical cancers. Br J Cancer. 96:591–599.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kusaba T, Nakayama T, Yamazumi K, Yakata
Y, Yoshizaki A, Nagayasu T and Sekine I: Expression of p-STAT3 in
human colorectal adenocarcinoma and adenoma; correlation with
clinicopathological factors. J Clin Pathol. 58:833–838. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Suiqing C, Min Z and Lirong C:
Overexpression of phosphorylated-STAT3 correlated with the invasion
and metastasis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Dermatol.
32:354–360. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tomizawa M, Shinozaki F, Motoyoshi Y,
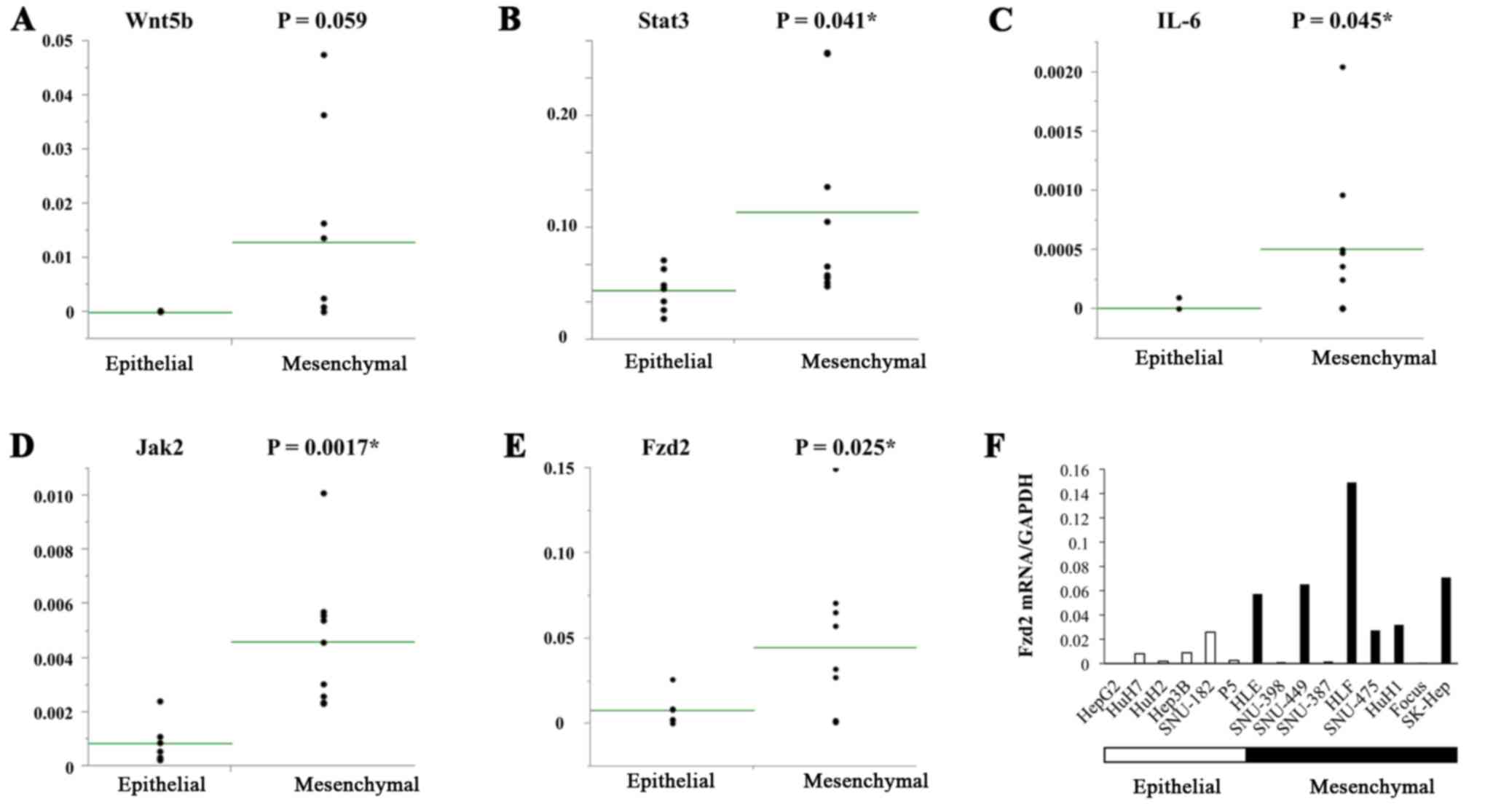
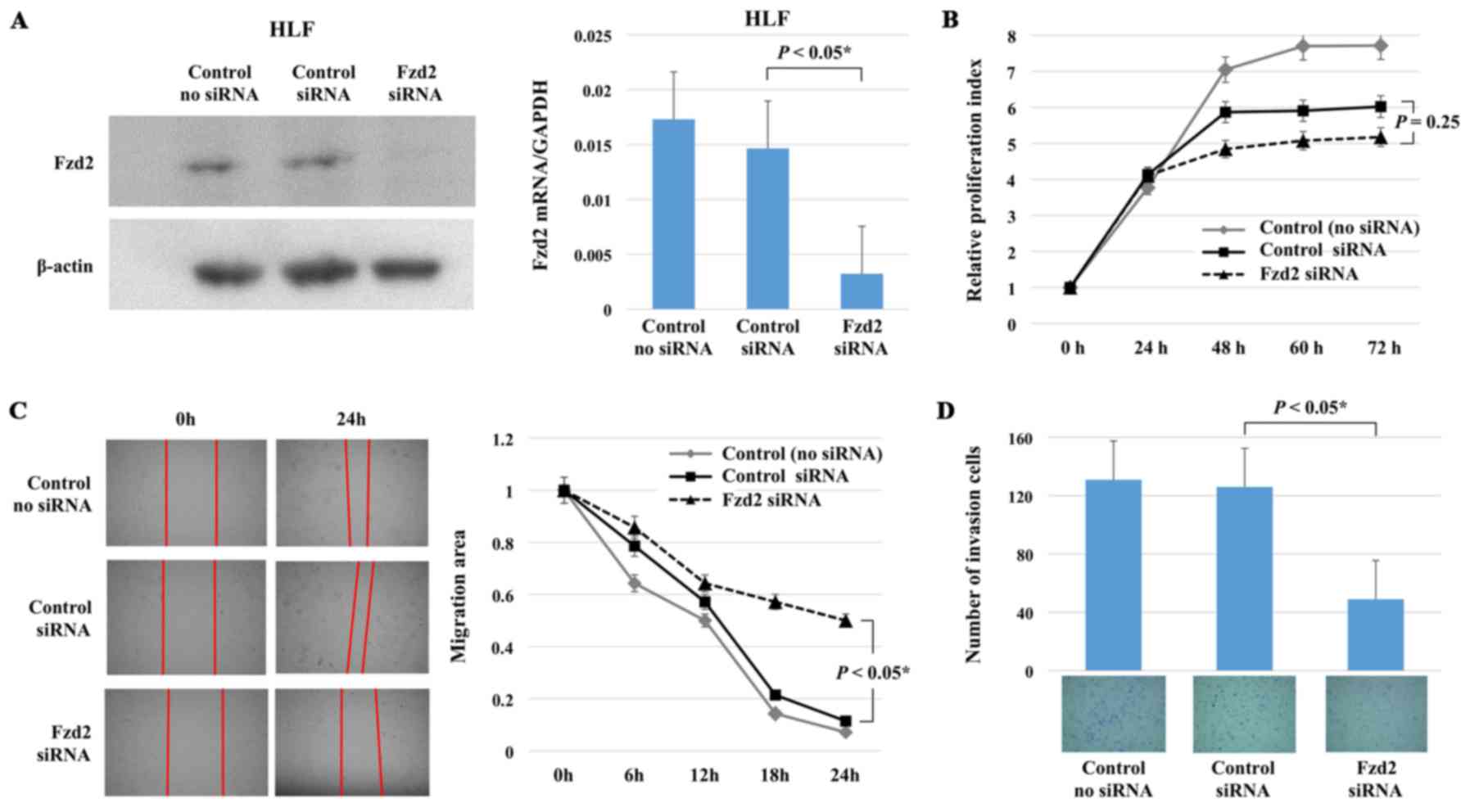
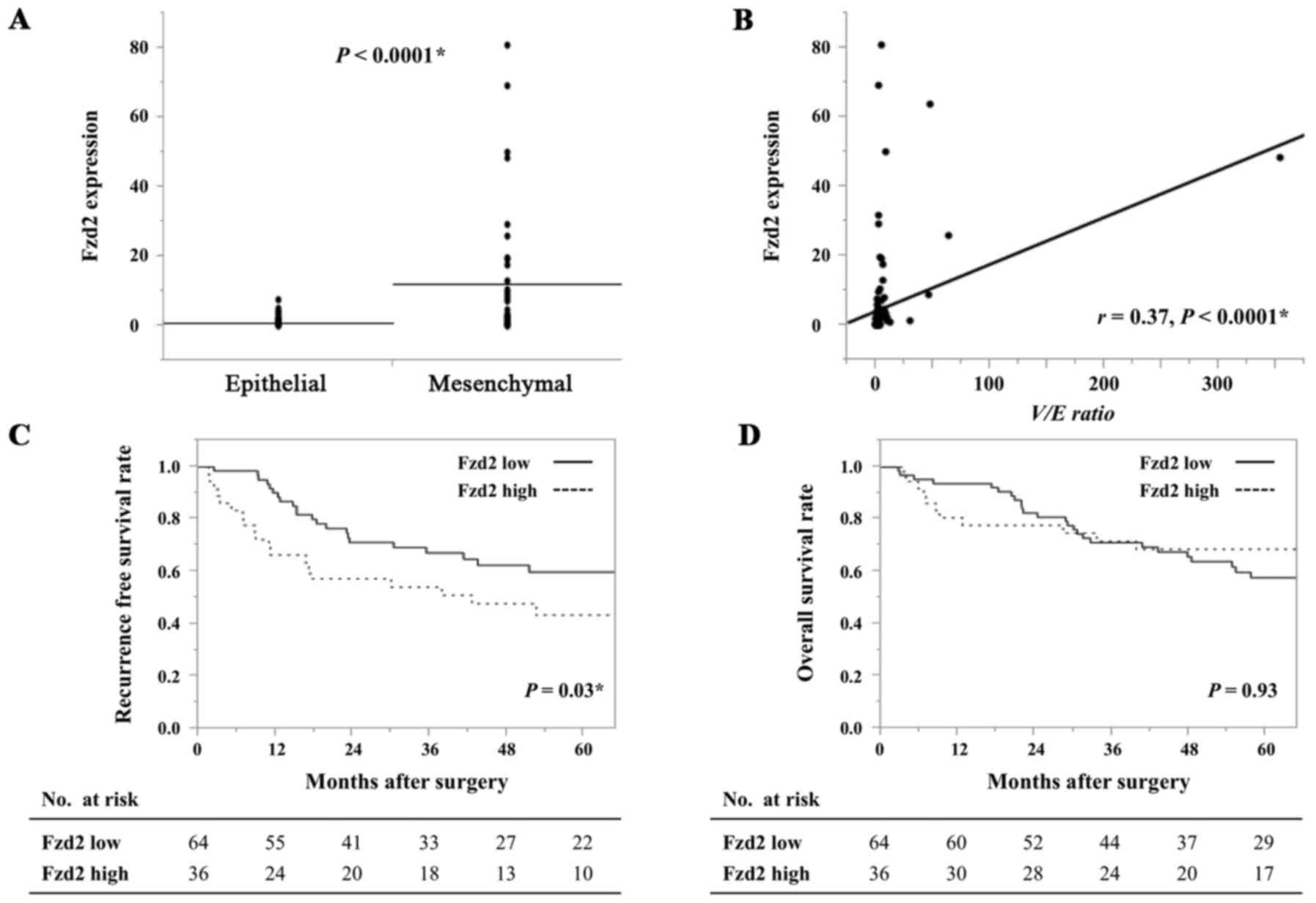
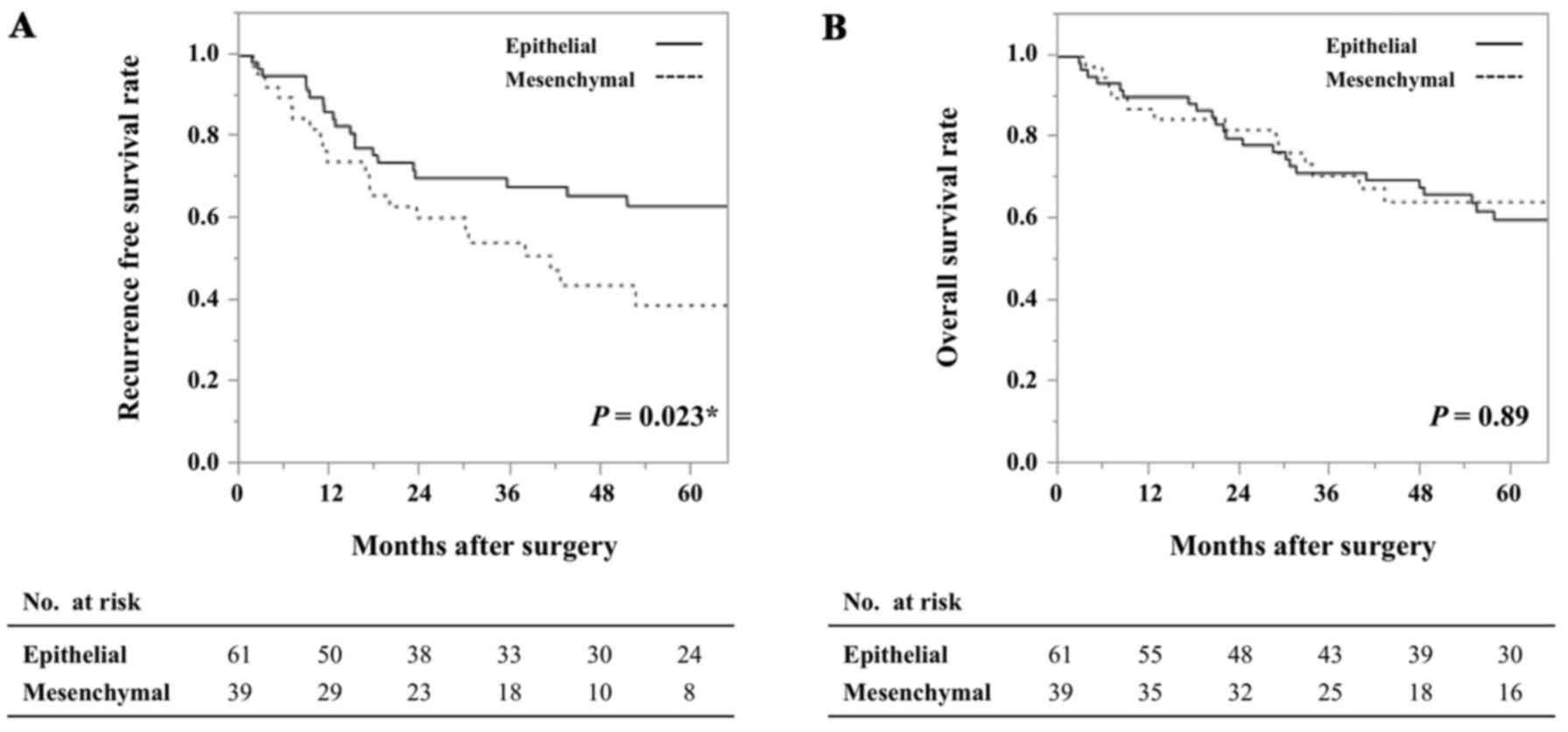
Sugiyama T, Yamamoto S and Ishige N: Suppression of hepatocellular
carcinoma cell proliferation by short hairpin RNA of frizzled 2
with Sonazoid-enhanced irradiation. Int J Oncol. 48:123–129.
2016.
|
|
25
|
Won C, Kim BH, Yi EH, Choi KJ, Kim EK,
Jeong JM, Lee JH, Jang JJ, Yoon JH, Jeong WI, et al: Signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3-mediated CD133
up-regulation contributes to promotion of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 62:1160–1173. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wan S, Zhao E, Kryczek I, Vatan L,
Sadovskaya A, Ludema G, Simeone DM, Zou W and Welling TH:
Tumor-associated macrophages produce interleukin 6 and signal via
STAT3 to promote expansion of human hepatocellular carcinoma stem
cells. Gastroenterology. 147:1393–1404. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ghoshal S, Fuchs BC and Tanabe KK: STAT3
is a key transcriptional regulator of cancer stem cell marker CD133
in HCC. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 5:201–203. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|