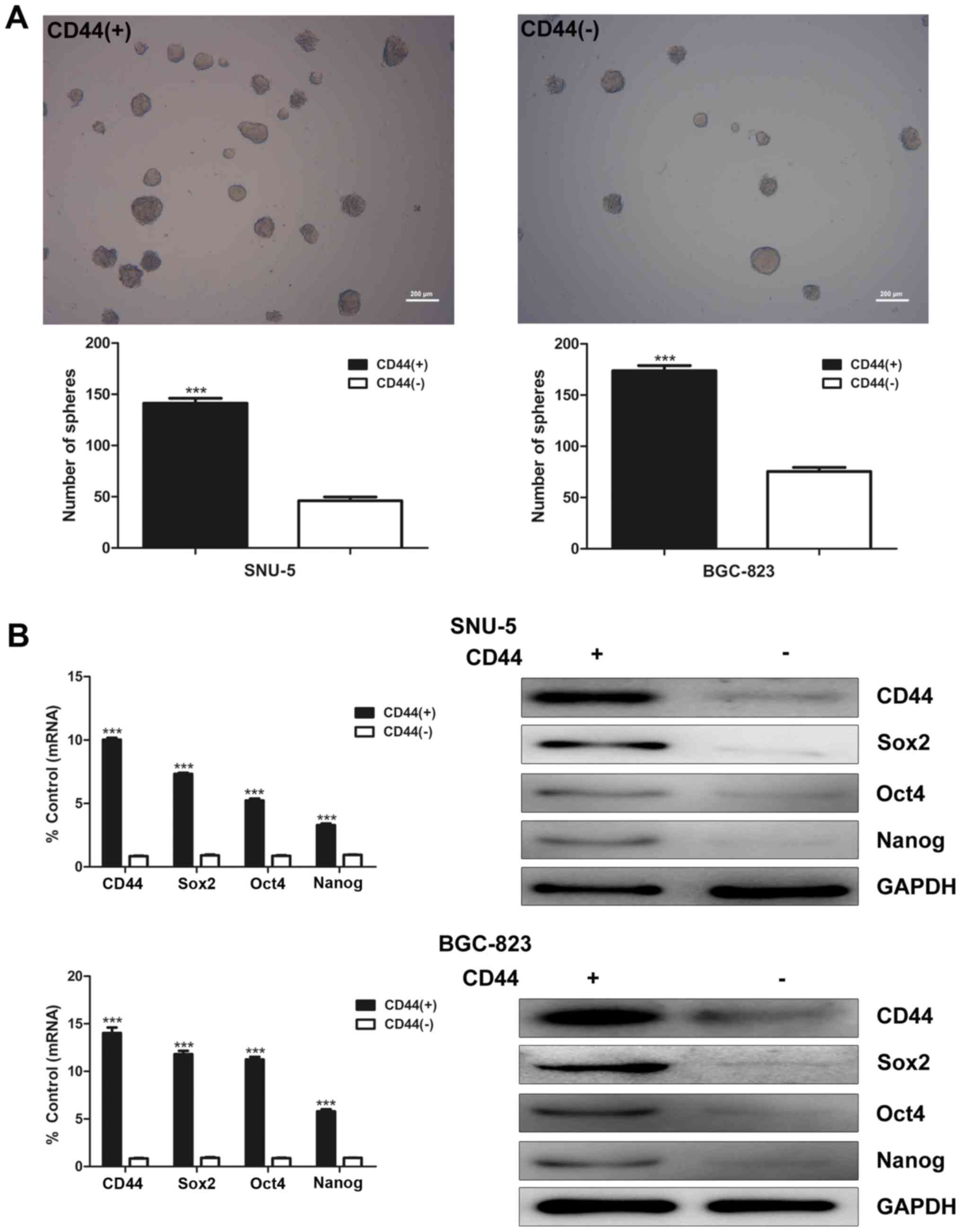
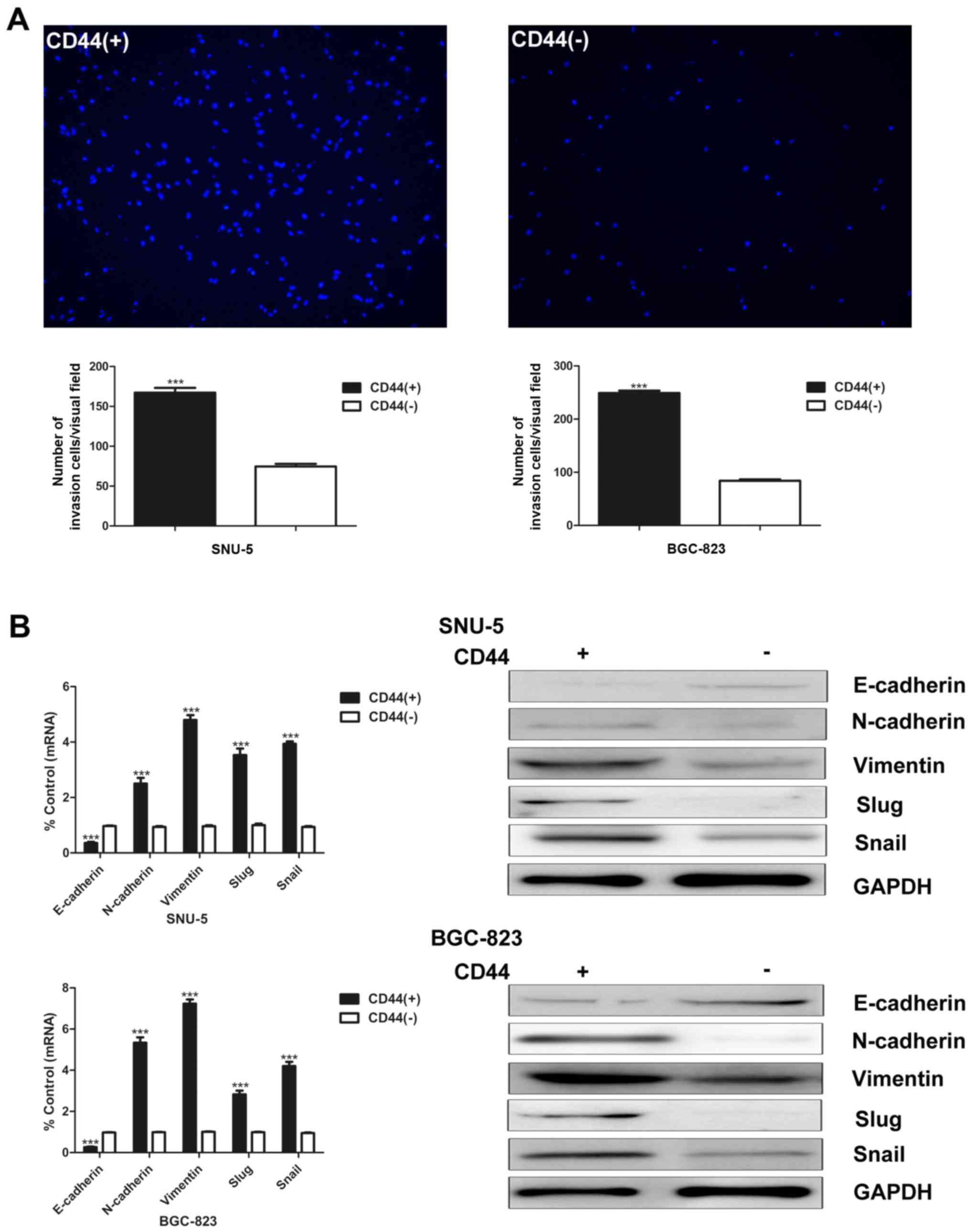
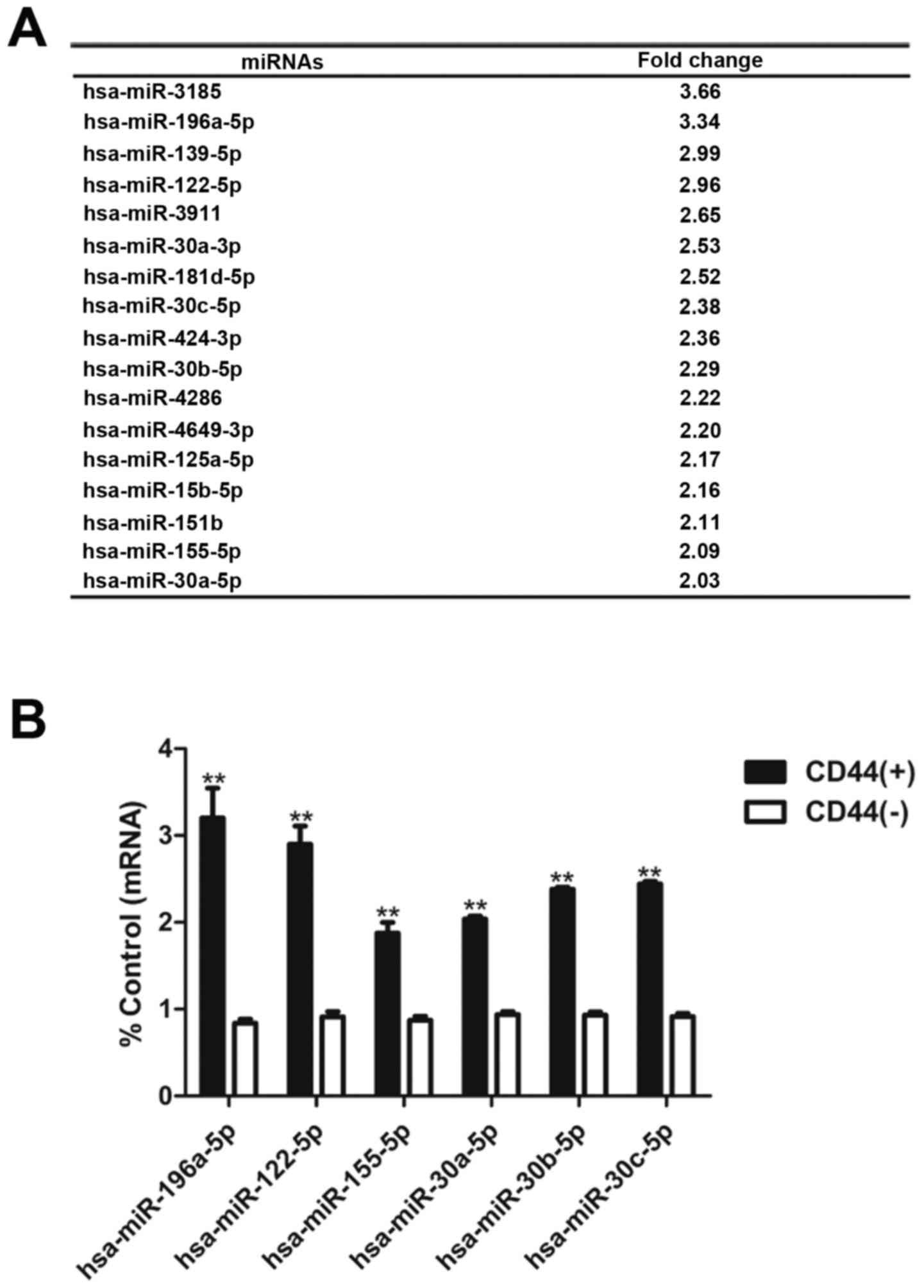
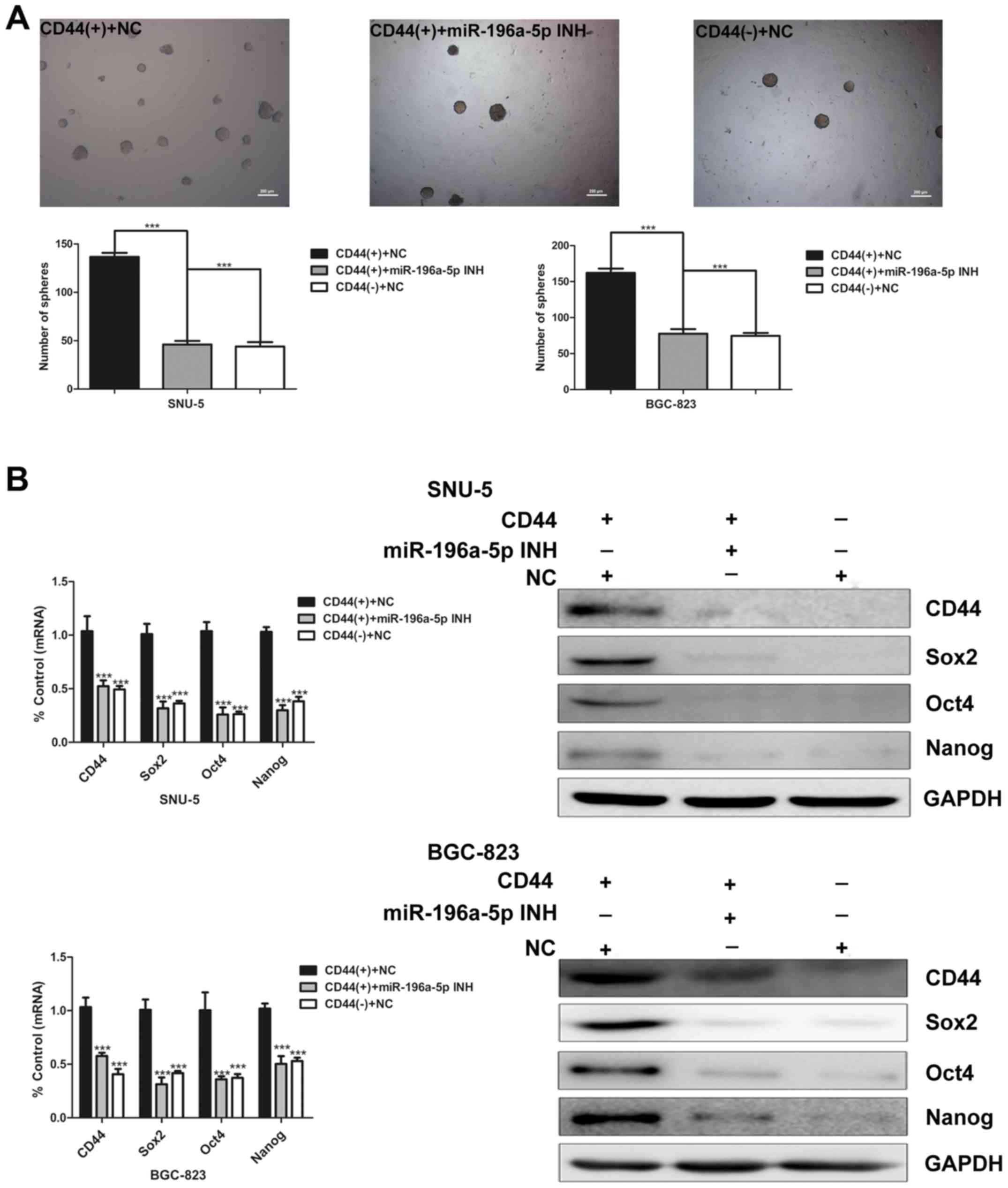
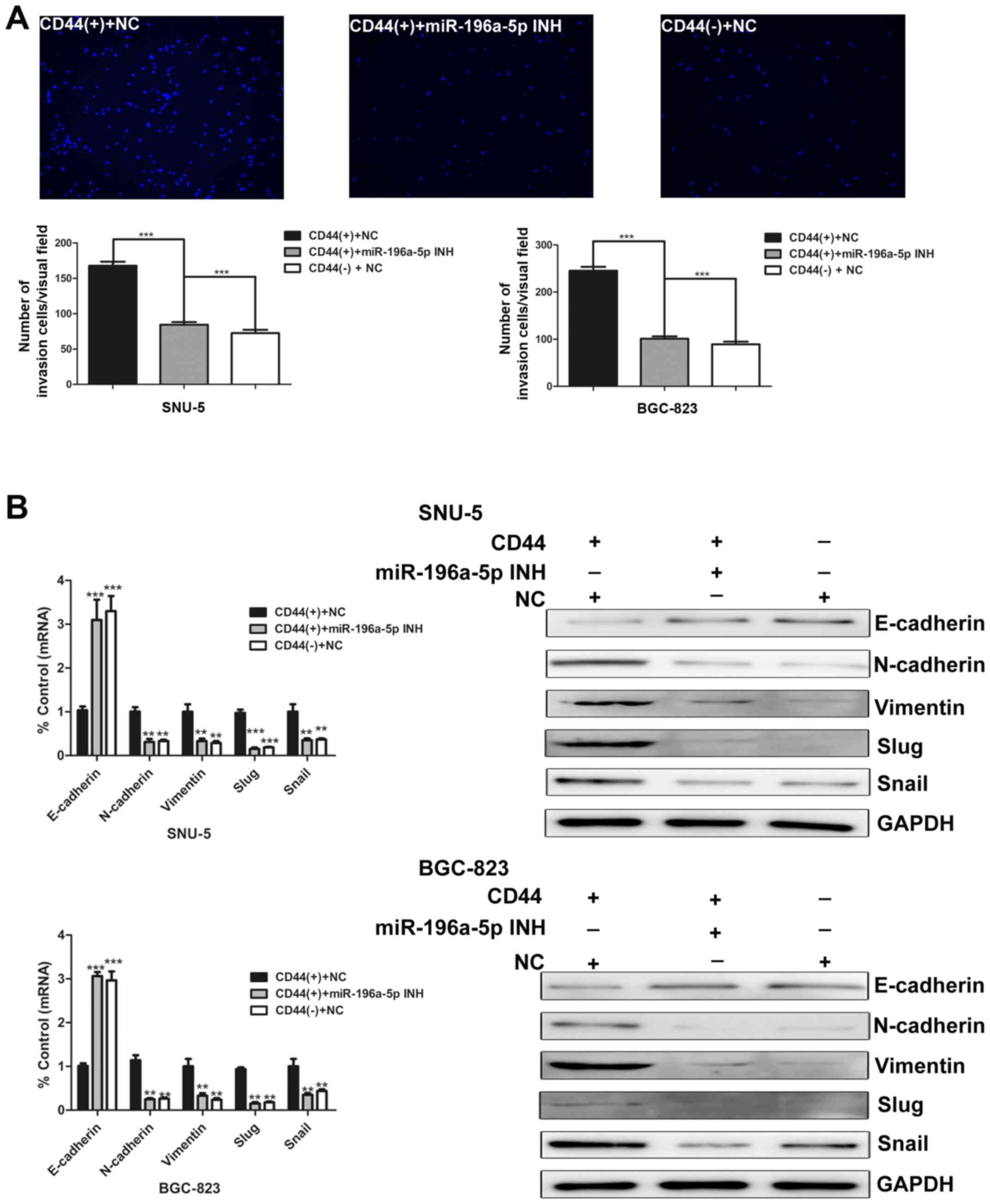
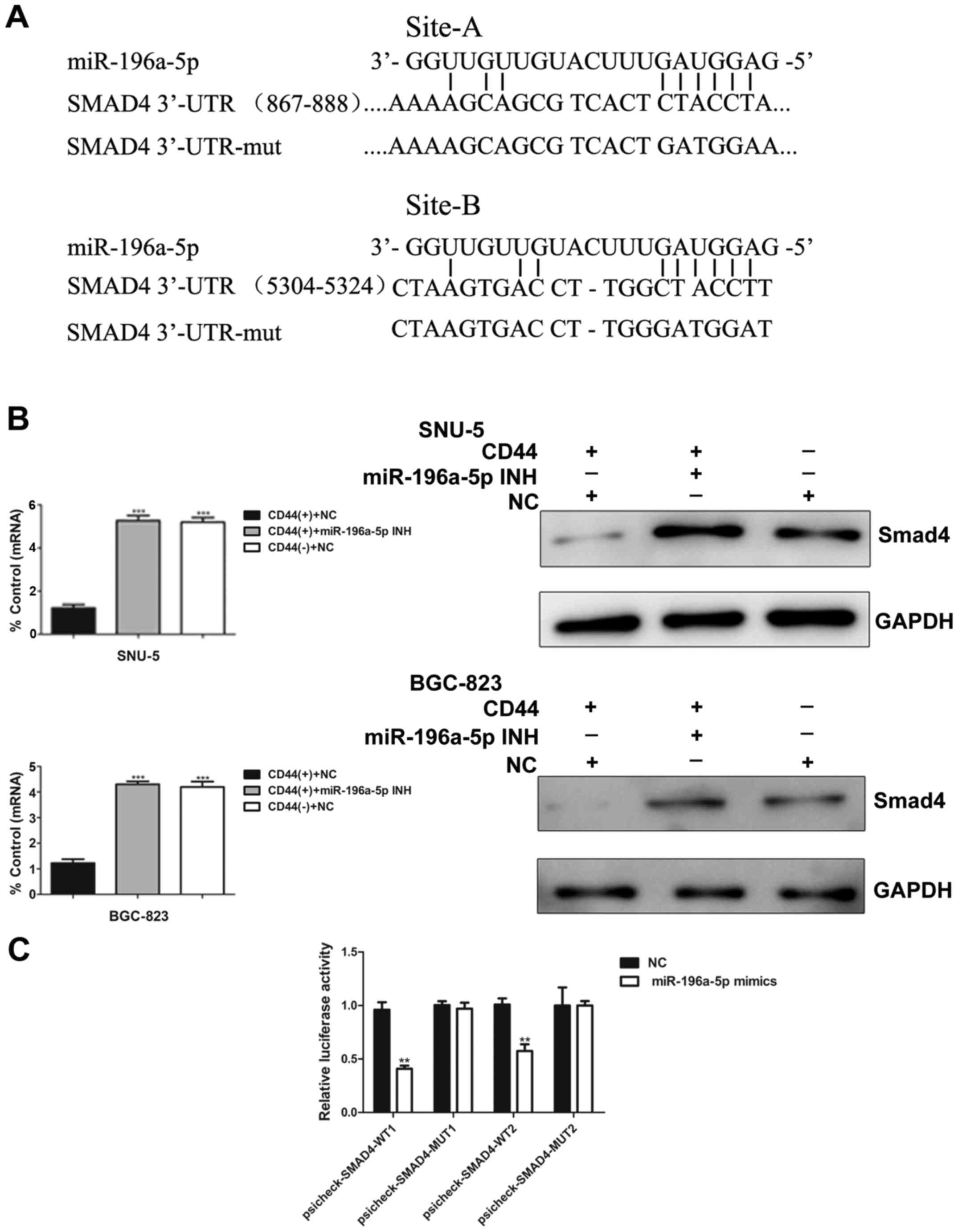
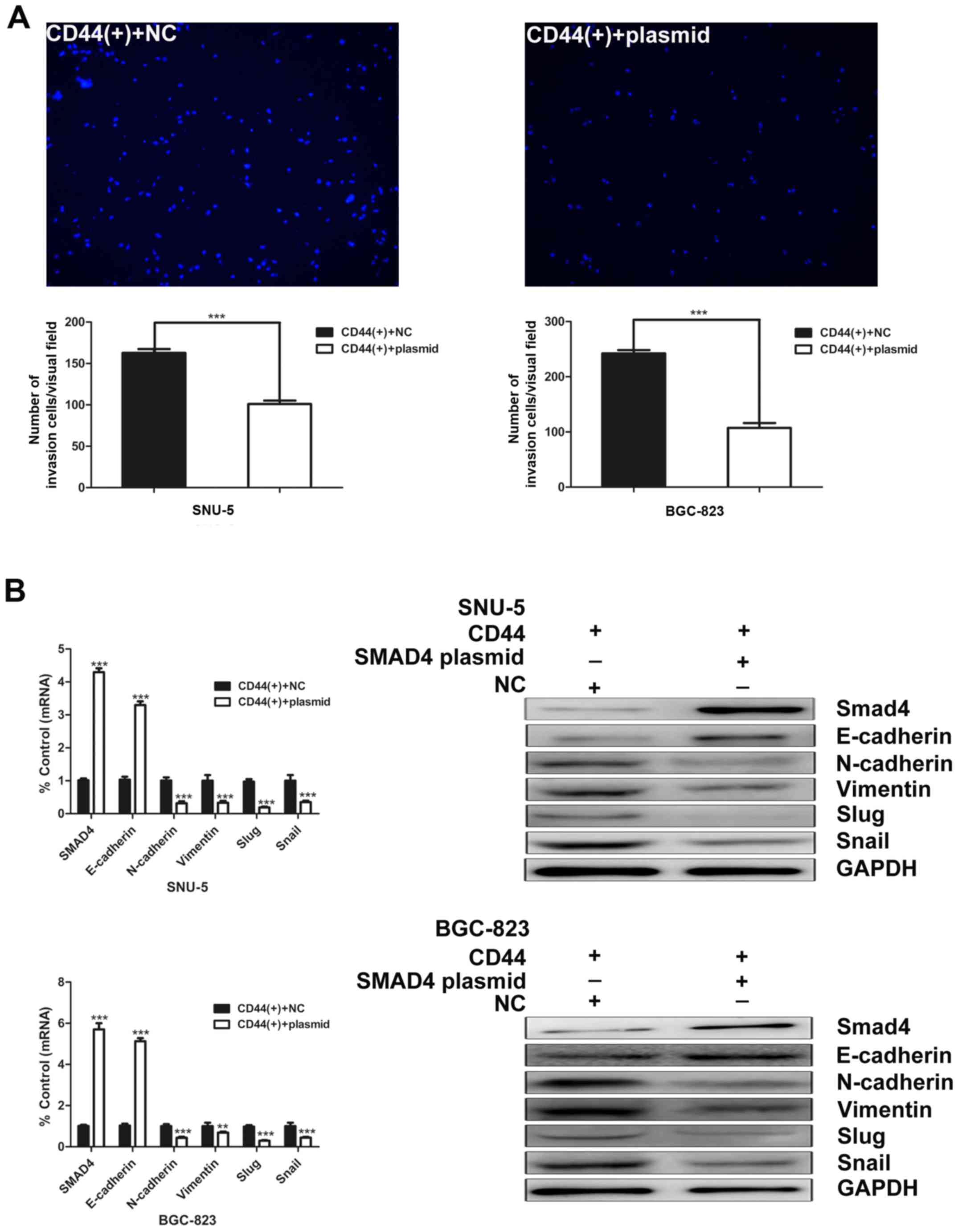
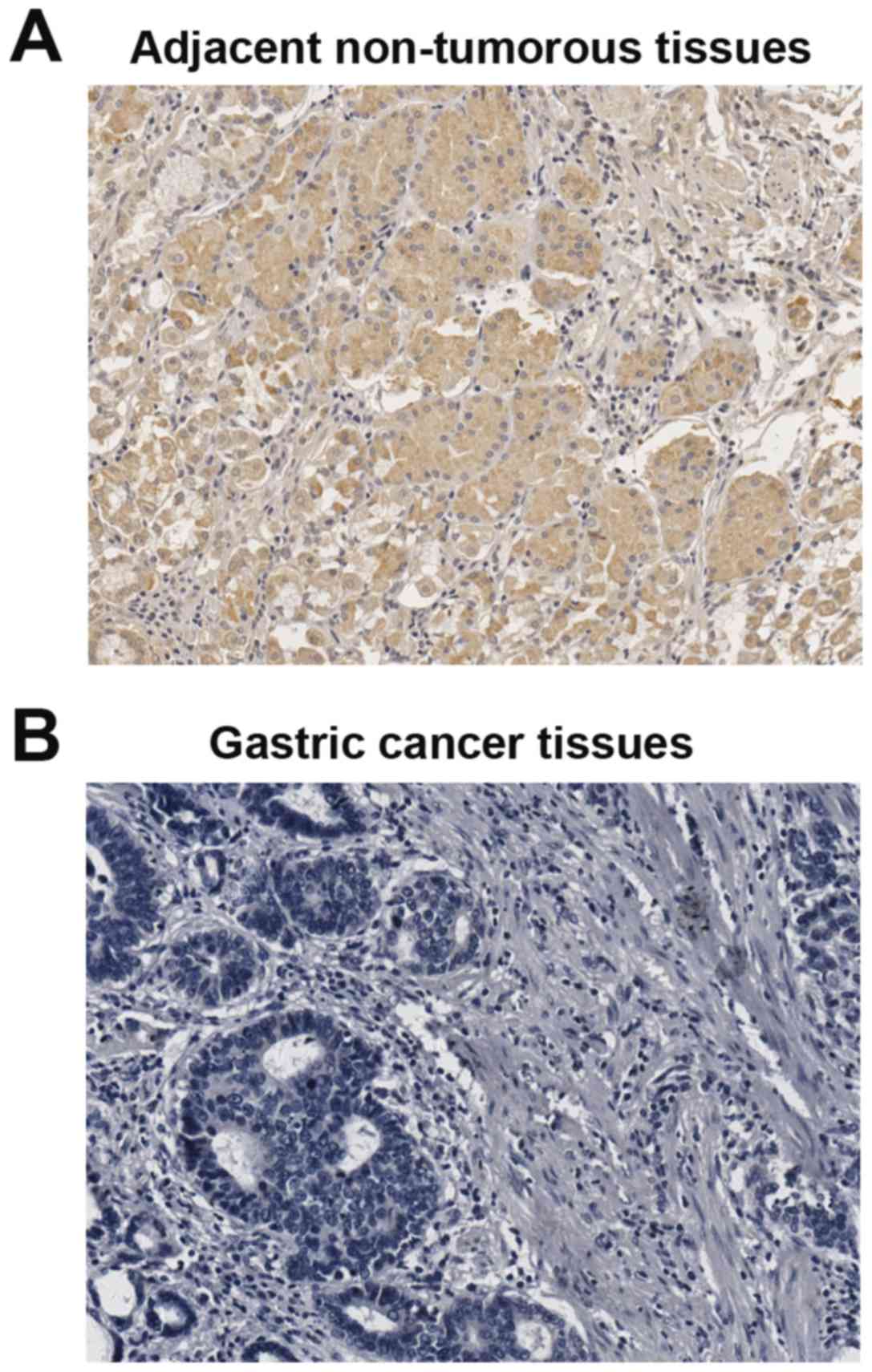
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zhang S, Zhao P,
Li G, Wu L and He J: Report of incidence and mortality in China
cancer registries, 2009. Chin J Cancer Res. 25:10–21.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim TH and Shivdasani RA: Stomach
development, stem cells and disease. Development. 143:554–565.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jordan CT, Guzman ML and Noble M: Cancer
stem cells. N Engl J Med. 355:1253–1261. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang X, Hua R, Wang X, Huang M, Gan L, Wu
Z, Zhang J, Wang H, Cheng Y and Li J: Identification of stem-like
cells and clinical significance of candidate stem cell markers in
gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 7:9815–9831. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Alison MR, Lin WR, Lim SM and Nicholson
LJ: Cancer stem cells: In the line of fire. Cancer Treat Rev.
38:589–598. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu TJ, Sun BC, Zhao XL, Zhao XM, Sun T,
Gu Q, Yao Z, Dong XY, Zhao N and Liu N: CD133+ cells
with cancer stem cell characteristics associates with vasculogenic
mimicry in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogene. 32:544–553.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sakakini N, Turchi L, Bergon A, Holota H,
Rekima S, Lopez F, Paquis P, Almairac F, Fontaine D, Baeza-Kallee
N, et al: A positive feed-forward loop associating EGR1 and PDGFA
promotes proliferation and self-renewal in glioblastoma stem cells.
J Biol Chem. 291:10684–10699. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nataraj SM, Prema CL, Vimalambike MG,
Shivalingaiah SC, Sundaram S, Kumar AP, Math AK and Prashant A:
Major protein of carcinoembryonic antigen gene family - CD66c, a
novel marker in colon carcinoma. J Clin Diagn Res. 10:XC01–XC04.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu J, Ma L, Xu J, Liu C, Zhang J, Liu J,
Chen R and Zhou Y: Spheroid body-forming cells in the human gastric
cancer cell line MKN-45 possess cancer stem cell properties. Int J
Oncol. 42:453–459. 2013.
|
|
11
|
Takebe N, Harris PJ, Warren RQ and Ivy SP:
Targeting cancer stem cells by inhibiting Wnt, Notch, and Hedgehog
pathways. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 8:97–106. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sounni NE and Noel A: Targeting the tumor
microenvironment for cancer therapy. Clin Chem. 59:85–93. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lim YC, Kang HJ, Kim YS and Choi EC:
All-trans-retinoic acid inhibits growth of head and neck cancer
stem cells by suppression of Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Eur J Cancer.
48:3310–3318. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li Y, Zhang T, Korkaya H, Liu S, Lee HF,
Newman B, Yu Y, Clouthier SG, Schwartz SJ, Wicha MS and Sun D:
Sulforaphane, a dietary component of broccoli/broccoli sprouts,
inhibits breast cancer stem cells. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2580–2590.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang T and Rycaj K: Targeted therapy
against cancer stem cells. Oncol Lett. 10:27–33. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Leon G, MacDonagh L, Finn SP, Cuffe S and
Barr MP: Cancer stem cells in drug resistant lung cancer: Targeting
cell surface markers and signaling pathways. Pharmacol Ther.
158:71–90. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lau WM, Teng E, Chong HS, Lopez KA, Tay
AY, Salto-Tellez M, Shabbir A, So JB and Chan SL: CD44v8-10 is a
cancer-specific marker for gastric cancer stem cells. Cancer Res.
74:2630–2641. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mansour SF and Atwa MM:
Clinicopathological significance of CD133 and ALDH1 cancer stem
cell marker expression in invasive ductal breast carcinoma. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:7491–7496. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nishikawa S, Konno M, Hamabe A, Hasegawa
S, Kano Y, Fukusumi T, Satoh T, Takiguchi S, Mori M, Doki Y, et al:
Surgically resected human tumors reveal the biological significance
of the gastric cancer stem cell markers CD44 and CD26. Oncol Lett.
9:2361–2367. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tseng JY, Yang CY, Yang SH, Lin JK, Lin CH
and Jiang JK: Circulating CD133(+)/ESA(+) cells in colorectal
cancer patients. J Surg Res. 199:362–370. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shitara K, Doi T, Nagano O, Imamura CK,
Ozeki T, Ishii Y, Tsuchihashi K, Takahashi S, Nakajima TE, Hironaka
S, et al: Dose-escalation study for the targeting of CD44v cancer
stem cells by sulfasalazine in patients with advanced gastric
cancer (EPOC1205). Gastric Cancer. 20:341–349. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang W, Dong LP, Zhang N and Zhao CH: Role
of cancer stem cell marker CD44 in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis.
Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:5059–5066. 2014.
|
|
23
|
Takahashi RU, Miyazaki H and Ochiya T: The
role of microRNAs in the regulation of cancer stem cells. Front
Genet. 4:2952014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu C and Tang DG: MicroRNA regulation of
cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 71:5950–5954. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma C, Huang T, Ding YC, Yu W, Wang Q, Meng
B and Luo SX: MicroRNA-200c overexpression inhibits
chemoresistance, invasion and colony formation of human pancreatic
cancer stem cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:6533–6539.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu D, Shin HS, Lee YS and Lee YC: miR-106b
modulates cancer stem cell characteristics through TGF-β/Smad
signaling in CD44-positive gastric cancer cells. Lab Invest.
94:1370–1381. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu Q, Yang Z, Wang F, Hu S, Yang L, Shi Y
and Fan D: MiR-19b/20a/92a regulates the self-renewal and
proliferation of gastric cancer stem cells. J Cell Sci.
126:4220–4229. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Takaishi S, Okumura T, Tu S, Wang SS,
Shibata W, Vigneshwaran R, Gordon SA, Shimada Y and Wang TC:
Identification of gastric cancer stem cells using the cell surface
marker CD44. Stem Cells. 27:1006–1020. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu H, Tian Y, Yuan X, Wu H, Liu Q, Pestell
RG and Wu K: The role of CD44 in epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and cancer development. Onco Targets Ther. 8:3783–3792. 2015.
|
|
30
|
Li LC, Wang DL, Wu YZ, Nian WQ, Wu ZJ, Li
Y, Ma HW and Shao JH: Gastric tumor-initiating CD44 (+) cells and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition are inhibited by γ-secretase
inhibitor DAPT. Oncol Lett. 10:3293–3299. 2015.
|
|
31
|
Zhang W and Li Y: miR-148a downregulates
the expression of transforming growth factor-β2 and SMAD2 in
gastric cancer. Int J Oncol. 48:1877–1885. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang XH, Liu MN, Sun X, Xu CH, Liu J, Chen
J, Xu RL and Li BX: TGF-beta 1 pathway affects the protein
expression of many signaling pathways, markers of liver cancer stem
cells, cytokeratins, and TERT in liver cancer HepG2 cells. Tumour
Biol. 37:3675–3681. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Hoshino Y, Nishida J, Katsuno Y, Koinuma
D, Aoki T, Kokudo N, Miyazono K and Ehata S: Smad4 decreases the
population of pancreatic cancer-initiating cells through
transcriptional repression of ALDH1A1. Am J Pathol. 185:1457–1470.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhao S, Ammanamanchi S, Brattain M, Cao L,
Thangasamy A, Wang J and Freeman JW: Smad4-dependent TGF-beta
signaling suppresses RON receptor tyrosine kinase-dependent
motility and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. J Biol Chem.
283:11293–11301. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|