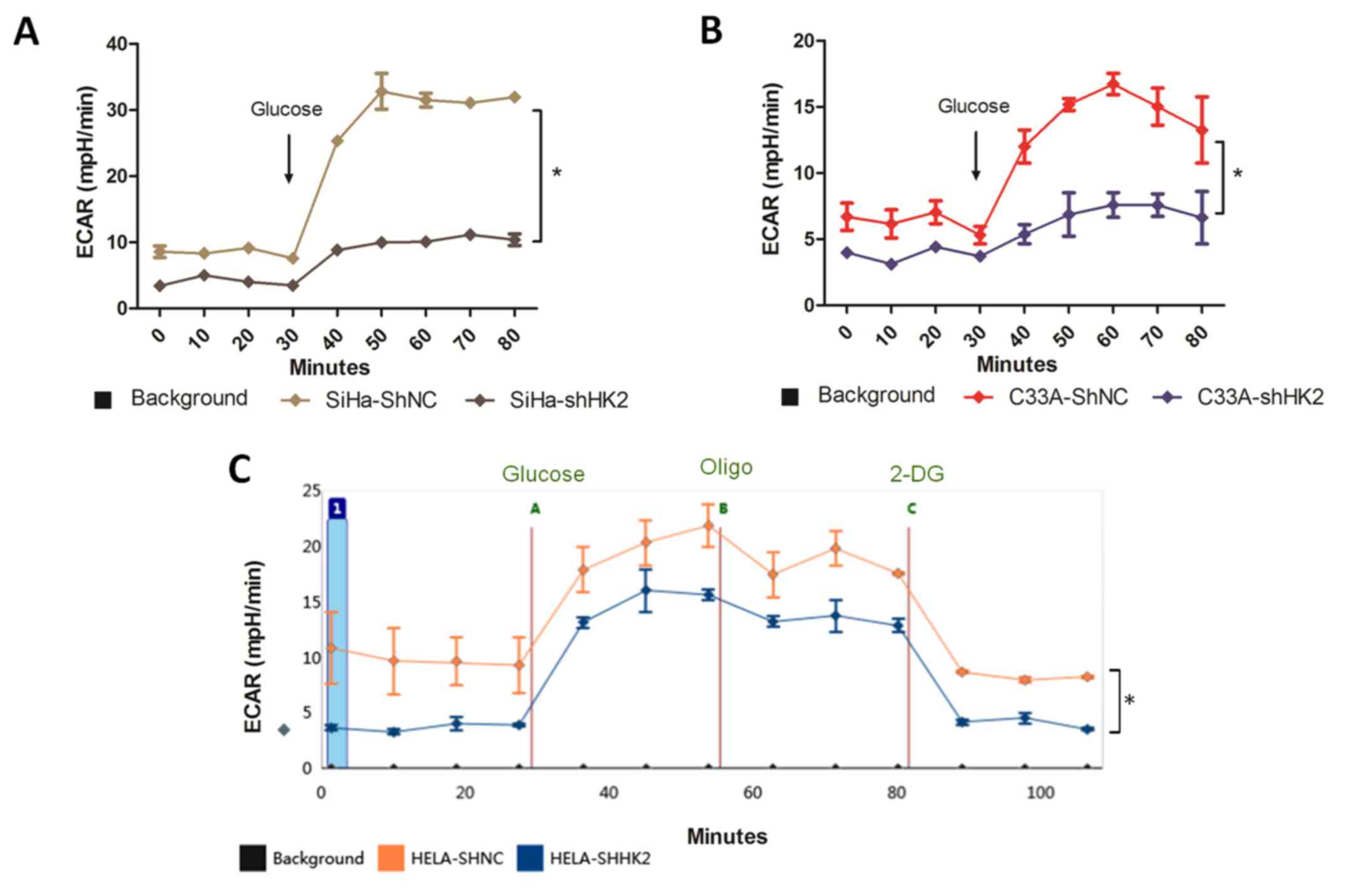
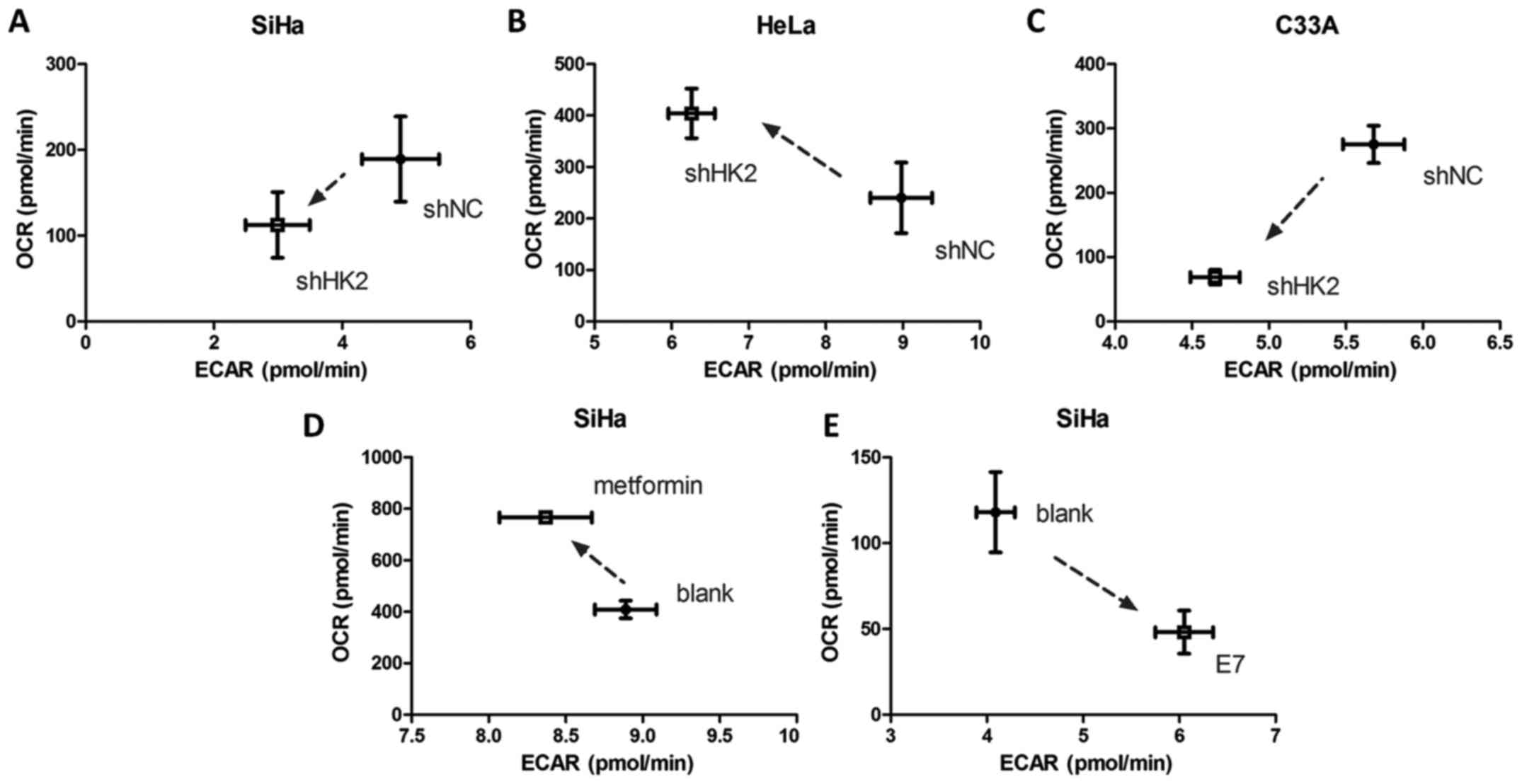
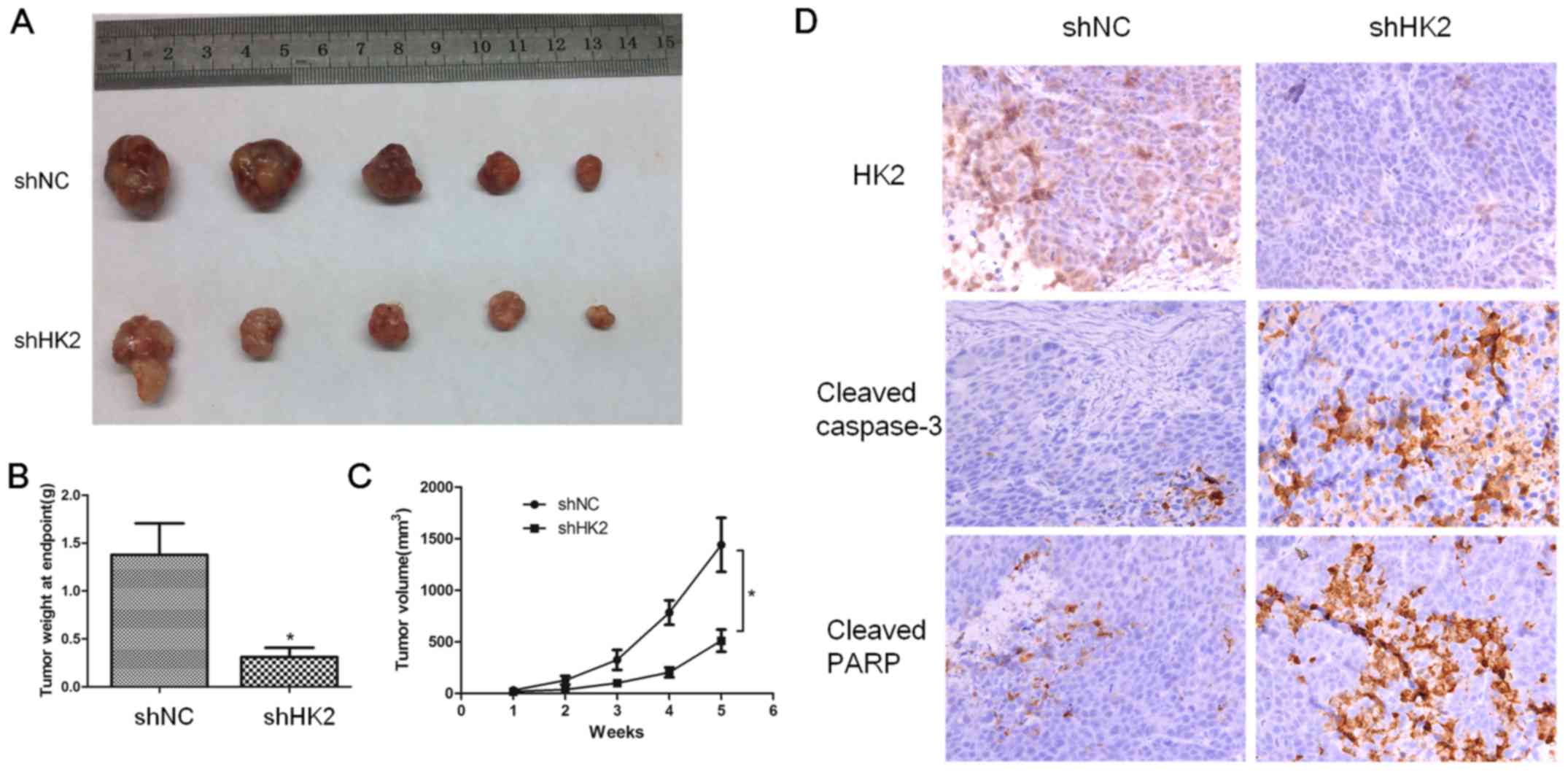
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kroemer G and Pouyssegur J: Tumor cell
metabolism: Cancer's Achilles' heel. Cancer Cell. 13:472–482. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hsu PP and Sabatini DM: Cancer cell
metabolism: Warburg and beyond. Cell. 134:703–707. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mathupala SP, Ko YH and Pedersen PL:
Hexokinase II: Cancer's double-edged sword acting as both
facilitator and gatekeeper of malignancy when bound to
mitochondria. Oncogene. 25:4777–4786. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mathupala SP, Rempel A and Pedersen PL:
Glucose catabolism in cancer cells: Identification and
characterization of a marked activation response of the type II
hexokinase gene to hypoxic conditions. J Biol Chem.
276:43407–43412. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang W, Liu Z, Zhao L, Sun J, He Q, Yan W,
Lu Z and Wang A: Hexokinase 2 enhances the metastatic potential of
tongue squamous cell carcinoma via the
SOD2–H2O2 pathway. Oncotarget. 8:3344–3354.
2017.
|
|
7
|
Patra KC, Wang Q, Bhaskar PT, Miller L,
Wang Z, Wheaton W, Chandel N, Laakso M, Muller WJ, Allen EL, et al:
Hexokinase 2 is required for tumor initiation and maintenance and
its systemic deletion is therapeutic in mouse models of cancer.
Cancer Cell. 24:213–228. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wolf A, Agnihotri S, Micallef J, Mukherjee
J, Sabha N, Cairns R, Hawkins C and Guha A: Hexokinase 2 is a key
mediator of aerobic glycolysis and promotes tumor growth in human
glioblastoma multiforme. J Exp Med. 208:313–326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bustamante E and Pedersen PL: High aerobic
glycolysis of rat hepatoma cells in culture: Role of mitochondrial
hexokinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 74:3735–3739. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim JW and Dang CV: Multifaceted roles of
glycolytic enzymes. Trends Biochem Sci. 30:142–150. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mathupala SP, Ko YH and Pedersen PL:
Hexokinase-2 bound to mitochondria: Cancer's stygian link to the
'Warburg Effect' and a pivotal target for effective therapy. Semin
Cancer Biol. 19:17–24. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Pastorino JG, Shulga N and Hoek JB:
Mitochondrial binding of hexokinase II inhibits Bax-induced
cytochrome c release and apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 277:7610–7618.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Majewski N, Nogueira V, Bhaskar P, Coy PE,
Skeen JE, Gottlob K, Chandel NS, Thompson CB, Robey RB and Hay N:
Hexokinase-mitochondria interaction mediated by Akt is required to
inhibit apoptosis in the presence or absence of Bax and Bak. Mol
Cell. 16:819–830. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gottlob K, Majewski N, Kennedy S, Kandel
E, Robey RB and Hay N: Inhibition of early apoptotic events by
Akt/PKB is dependent on the first committed step of glycolysis and
mitochondrial hexokinase. Genes Dev. 15:1406–1418. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rockwell S, Dobrucki IT, Kim EY, Marrison
ST and Vu VT: Hypoxia and radiation therapy: Past history, ongoing
research, and future promise. Curr Mol Med. 9:442–458. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shimura T, Kakuda S, Ochiai Y, Nakagawa H,
Kuwahara Y, Takai Y, Kobayashi J, Komatsu K and Fukumoto M:
Acquired radioresistance of human tumor cells by
DNA-PK/AKT/GSK3beta-mediated cyclin D1 overexpression. Oncogene.
29:4826–4837. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bolderson E, Richard DJ, Zhou BB and
Khanna KK: Recent advances in cancer therapy targeting proteins
involved in DNA double-strand break repair. Clin Cancer Res.
15:6314–6320. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lehmann BD, McCubrey JA, Jefferson HS,
Paine MS, Chappell WH and Terrian DM: A dominant role for
p53-dependent cellular senescence in radiosensitization of human
prostate cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 6:595–605. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bergkvist GT, Argyle DJ, Pang LY, Muirhead
R and Yool DA: Studies on the inhibition of feline EGFR in squamous
cell carcinoma: Enhancement of radiosensitivity and rescue of
resistance to small molecule inhibitors. Cancer Biol Ther.
11:927–937. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Baumann M, Krause M and Hill R: Exploring
the role of cancer stem cells in radioresistance. Nat Rev Cancer.
8:545–554. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Brown JM and Giaccia AJ: The unique
physiology of solid tumors: Opportunities (and problems) for cancer
therapy. Cancer Res. 58:1408–1416. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Milosevic M, Warde P, Menard C, Chung P,
Toi A, Ishkanian A, McLean M, Pintilie M, Sykes J, Gospodarowicz M,
et al: Tumor hypoxia predicts biochemical failure following
radiotherapy for clinically localized prostate cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:2108–2114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Harada H: Hypoxia-inducible factor
1-mediated characteristic features of cancer cells for tumor
radioresistance. J Radiat Res (Tokyo). 57(Suppl 1): i99–i105. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sattler UG and Mueller-Klieser W: The
anti-oxidant capacity of tumour glycolysis. Int J Radiat Biol.
85:963–971. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Trachootham D, Alexandre J and Huang P:
Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: A radical
therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 8:579–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bui T and Thompson CB: Cancer's sweet
tooth. Cancer Cell. 9:419–420. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nakashima RA, Paggi MG and Pedersen PL:
Contributions of glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation to
adenosine 5′-triphosphate production in AS-30D hepatoma cells.
Cancer Res. 44:5702–5706. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Meng MB, Wang HH, Guo WH, Wu ZQ, Zeng XL,
Zaorsky NG, Shi HS, Qian D, Niu ZM, Jiang B, et al: Targeting
pyruvate kinase M2 contributes to radiosensitivity of non-small
cell lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett.
356B:985–993. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Bol V, Bol A, Bouzin C, Labar D, Lee JA,
Janssens G, Porporato PE, Sonveaux P, Feron O and Grégoire V:
Reprogramming of tumor metabolism by targeting mitochondria
improves tumor response to irradiation. Acta Oncol. 54:266–274.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Pena-Rico MA, Calvo-Vidal MN,
Villalonga-Planells R, Martínez-Soler F, Giménez-Bonafé P,
Navarro-Sabaté À, Tortosa A, Bartrons R and Manzano A: TP53 induced
glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR) knockdown results in
radio-sensitization of glioma cells. Radiother Oncol. 101:132–139.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
BelAiba RS, Djordjevic T, Bonello S,
Flügel D, Hess J, Kietzmann T and Görlach A: Redox-sensitive
regulation of the HIF pathway under non-hypoxic conditions in
pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Biol Chem. 385:249–257. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chandel NS, McClintock DS, Feliciano CE,
Wood TM, Melendez JA, Rodriguez AM and Schumacker PT: Reactive
oxygen species generated at mitochondrial complex III stabilize
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha during hypoxia: A mechanism of
O2 sensing. J Biol Chem. 275:25130–25138. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cheng Y, Chen G, Hong L, Zhou L, Hu M, Li
B, Huang J, Xia L and Li C: How does hypoxia inducible factor-1α
participate in enhancing the glycolysis activity in cervical
cancer? Ann Diagn Pathol. 17:305–311. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang Z, Zhou D, Lai Y, Liu Y, Tao X, Wang
Q, Zhao G, Gu H, Liao H, Zhu Y, et al: Estrogen induces endometrial
cancer cell proliferation and invasion by regulating the fat mass
and obesity-associated gene via PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling
pathways. Cancer Lett. 319:89–97. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Salani B, Del Rio A, Marini C, Sambuceti
G, Cordera R and Maggi D: Metformin, cancer and glucose metabolism.
Endocr Relat Cancer. 21:R461–R471. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Salani B, Marini C, Rio AD, Ravera S,
Massollo M, Orengo AM, Amaro A, Passalacqua M, Maffioli S, Pfeffer
U, et al: Metformin impairs glucose consumption and survival in
Calu-1 cells by direct inhibition of hexokinase-II. Sci Rep.
3:20702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1
(HIF-1) pathway. Sci STKE. 2007:cm82007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Roberts DJ, Tan-Sah VP, Smith JM and
Miyamoto S: Akt phosphorylates HK-II at Thr-473 and increases
mitochondrial HK-II association to protect cardiomyocytes. J Biol
Chem. 288:23798–23806. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Marini C, Salani B, Massollo M, Amaro A,
Esposito AI, Orengo AM, Capitanio S, Emionite L, Riondato M,
Bottoni G, et al: Direct inhibition of hexokinase activity by
metformin at least partially impairs glucose metabolism and tumor
growth in experimental breast cancer. Cell Cycle. 12:3490–3499.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Peng G-Q, Yang Y, Zhong C-G, Yin H, Hu G
and Tian Y: A study of association between expression of hOGG1,
VDAC1, HK-2 and cervical carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
29:1292010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Jin Z, Gu J, Xin X, Li Y and Wang H:
Expression of hexokinase 2 in epithelial ovarian tumors and its
clinical significance in serous ovarian cancer. Eur J Gynaecol
Oncol. 35:519–524. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Huang X, Liu M, Sun H, Wang F, Xie X, Chen
X, Su J, He Y, Dai Y, Wu H, et al: HK2 is a radiation resistant and
independent negative prognostic factor for patients with locally
advanced cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:4054–4063. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Husseinzadeh N and Husseinzadeh HD: mTOR
inhibitors and their clinical application in cervical, endometrial
and ovarian cancers: A critical review. Gynecol Oncol. 133:375–381.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li Y, Padmanabha D, Gentile LB, Dumur CI,
Beckstead RB and Baker KD: HIF- and non-HIF-regulated hypoxic
responses require the estrogen-related receptor in Drosophila
melanogaster. PLoS Genet. 9:e10032302013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fraga A, Ribeiro R and Medeiros R: Tumor
hypoxia: The role of HIF. Actas Urol Esp. 33:941–951. 2009.In
Spanish. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pitroda SP, Wakim BT, Sood RF, Beveridge
MG, Beckett MA, MacDermed DM, Weichselbaum RR and Khodarev NN:
STAT1-dependent expression of energy metabolic pathways links
tumour growth and radioresistance to the Warburg effect. BMC Med.
7:682009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hirschhaeuser F, Sattler UG and
Mueller-Klieser W: Lactate: A metabolic key player in cancer.
Cancer Res. 71:6921–6925. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shimura T, Noma N, Sano Y, Ochiai Y,
Oikawa T, Fukumoto M and Kunugita N: AKT-mediated enhanced aerobic
glycolysis causes acquired radioresistance by human tumor cells.
Radiother Oncol. 112:302–307. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Moeller BJ, Richardson RA and Dewhirst MW:
Hypoxia and radiotherapy: Opportunities for improved outcomes in
cancer treatment. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 26:241–248. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Cullis PM, Jones GD, Symons MC and Lea JS:
Electron transfer from protein to DNA in irradiated chromatin.
Nature. 330:773–774. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bhatt AN, Chauhan A, Khanna S, Rai Y,
Singh S, Soni R, Kalra N and Dwarakanath BS: Transient elevation of
glycolysis confers radio-resistance by facilitating DNA repair in
cells. BMC Cancer. 15:3352015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Pathania D, Millard M and Neamati N:
Opportunities in discovery and delivery of anticancer drugs
targeting mitochondria and cancer cell metabolism. Adv Drug Deliv
Rev. 61:1250–1275. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Deng Q, Yu X, Xiao L, Hu Z, Luo X, Tao Y,
Yang L, Liu X, Chen H, Ding Z, et al: Neoalbaconol induces energy
depletion and multiple cell death in cancer cells by targeting
PDK1-PI3-K/Akt signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 4:e8042013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Roden R and Wu TC: How will HPV vaccines
affect cervical cancer? Nat Rev Cancer. 6:753–763. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Doorbar J: Molecular biology of human
papillomavirus infection and cervical cancer. Clin Sci (Lond).
110:525–541. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Münger K, Basile JR, Duensing S, Eichten
A, Gonzalez SL, Grace M and Zacny VL: Biological activities and
molecular targets of the human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein.
Oncogene. 20:7888–7898. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Rodolico V, Arancio W, Amato MC, Aragona
F, Cappello F, Di Fede O, Pannone G and Campisi G: Hypoxia
inducible factor-1 alpha expression is increased in infected
positive HPV16 DNA oral squamous cell carcinoma and positively
associated with HPV16 E7 oncoprotein. Infect Agent Cancer.
6:182011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Bodily JM, Mehta KP and Laimins LA: Human
papillomavirus E7 enhances hypoxia-inducible factor 1-mediated
transcription by inhibiting binding of histone deacetylases. Cancer
Res. 71:1187–1195. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Nakamura M, Bodily JM, Beglin M, Kyo S,
Inoue M and Laimins LA: Hypoxia-specific stabilization of
HIF-1alpha by human papillomaviruses. Virology. 387:442–448. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Li G, He L, Zhang E, Shi J, Zhang Q, Le
AD, Zhou K and Tang X: Overexpression of human papillomavirus (HPV)
type 16 oncoproteins promotes angiogenesis via enhancing HIF-1α and
VEGF expression in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
311:160–170. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Gao JL and Chen YG: Natural compounds
regulate glycolysis in hypoxic tumor microenvironment. BioMed Res
Int. 2015:3541432015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Marín-Hernández A, Gallardo-Pérez JC,
Ralph SJ, Rodríguez-Enríquez S and Moreno-Sánchez R: HIF-1alpha
modulates energy metabolism in cancer cells by inducing
overexpression of specific glycolytic isoforms. Mini Rev Med Chem.
9:1084–1101. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Wang L, Xiong H, Wu F, Zhang Y, Wang J,
Zhao L, Guo X, Chang LJ, Zhang Y, You MJ, et al: Hexokinase
2-mediated Warburg effect is required for PTEN- and
p53-deficiency-driven prostate cancer growth. Cell Rep.
8:1461–1474. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhuo B, Li Y, Li Z, Qin H, Sun Q, Zhang F,
Shen Y, Shi Y and Wang R: PI3K/Akt signaling mediated Hexokinase-2
expression inhibits cell apoptosis and promotes tumor growth in
pediatric osteosarcoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 464:401–406.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|