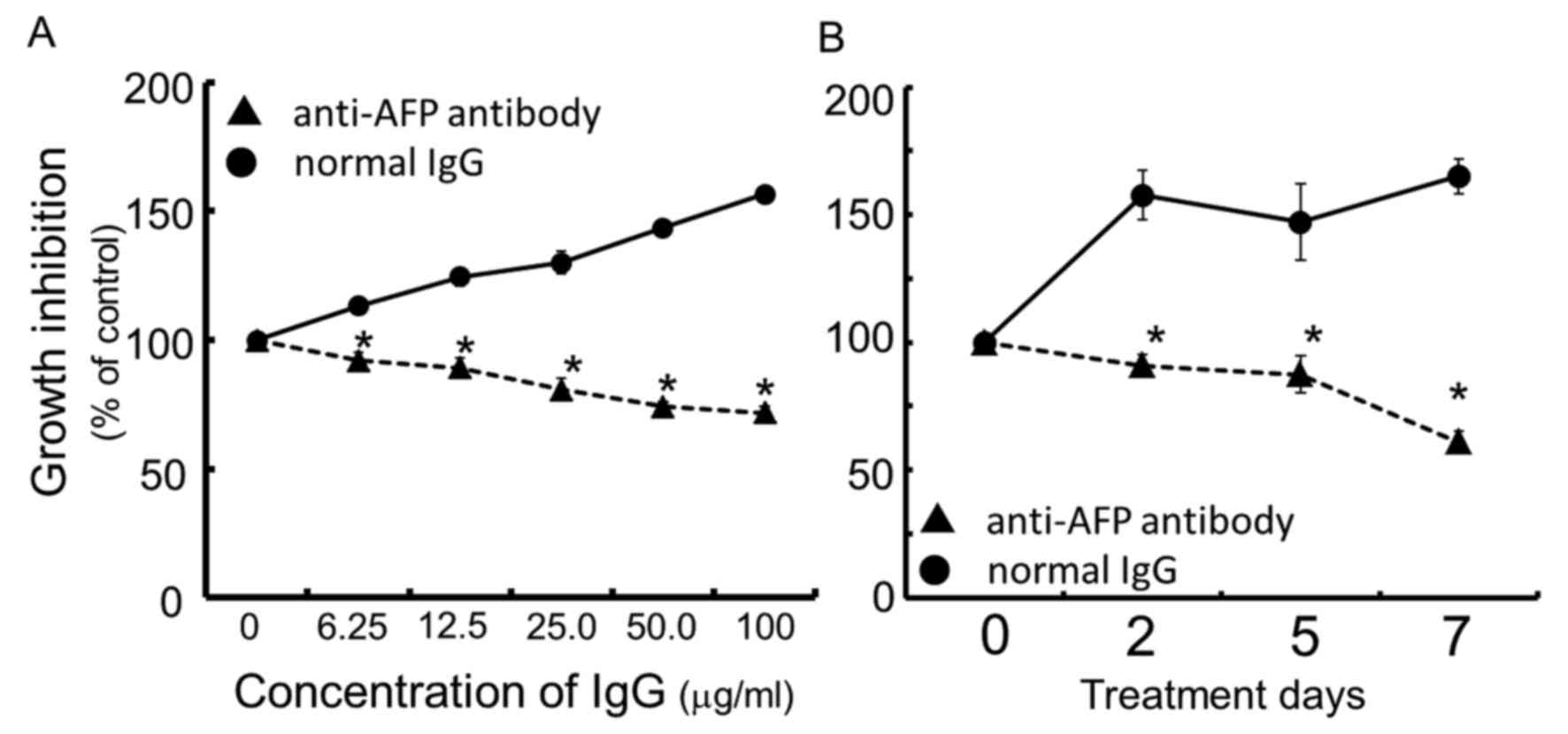
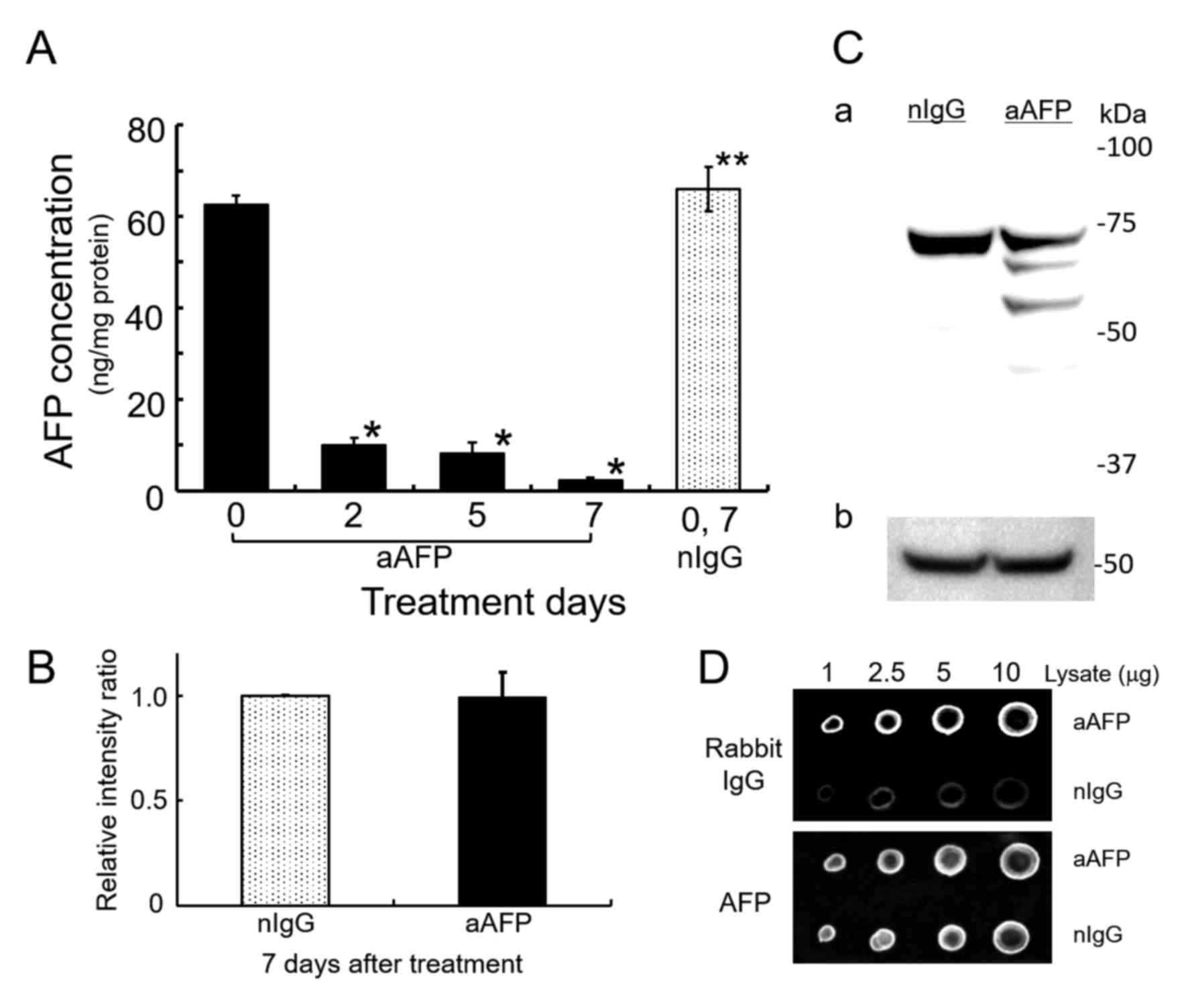
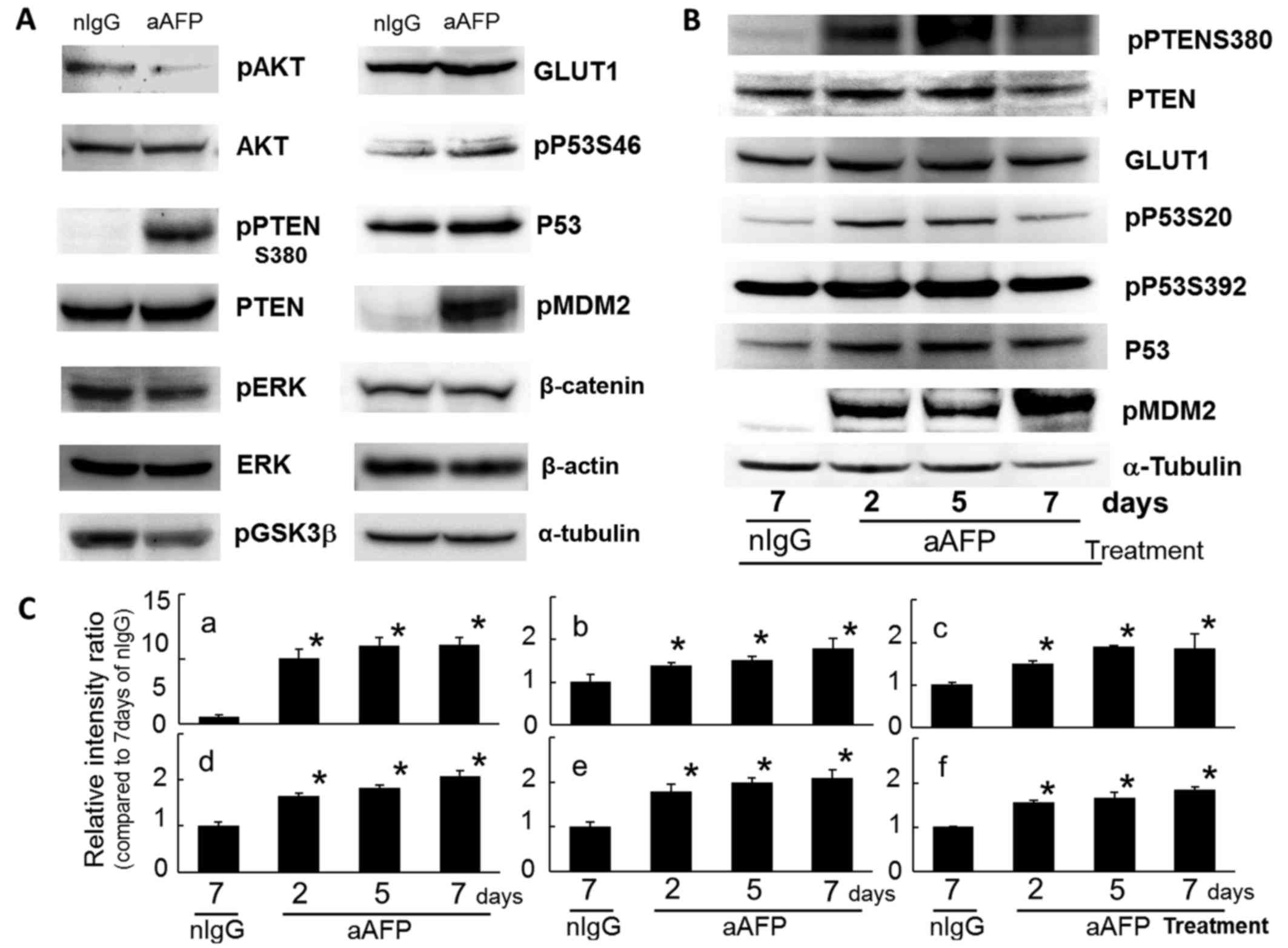
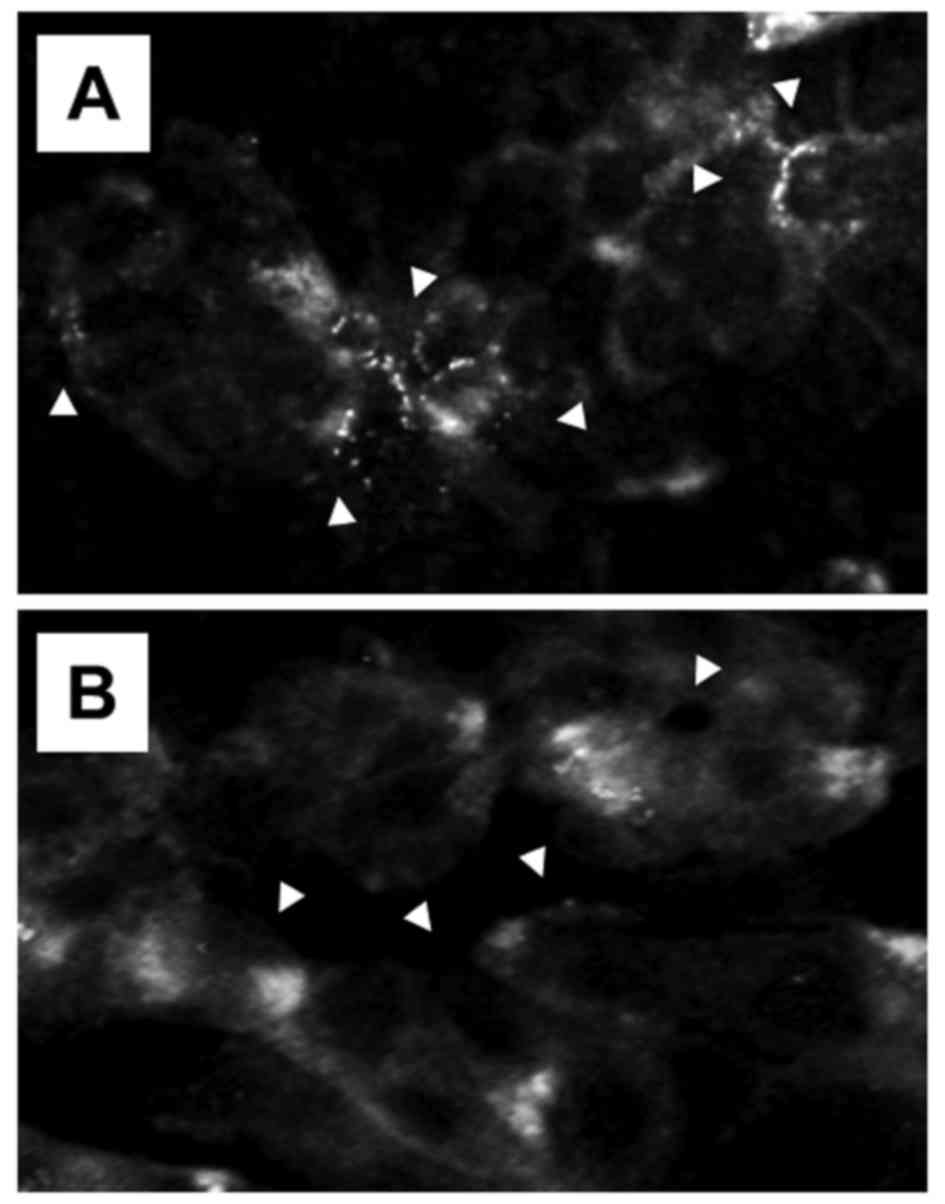
|
1
|
Mizejewski GJ and Allen RP:
Immunotherapeutic suppression in transplantable solid tumours.
Nature. 250:50–52. 1974. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mizejewski GJ, Young SR and Allen RP: α
fetoprotein: Effect of heterologous antiserum on hepatoma cells in
vitro. J Natl Cancer Inst. 54:1361–1367. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mizejewski GJ and Allen RP: α-fetoprotein:
Studies of tumor-associated antigen cytotoxicity in mouse hepatoma
BW7756. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 11:307–317. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mizejewski GJ and Dillon WR:
Immunobiologic studies in hepatoma-bearing mice passively immunized
to α-fetoprotein. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 27:655–662.
1979.
|
|
5
|
Tsukada Y, Mikuni M, Watabe H, Nishi S and
Hirai H: Effect of anti-alpha-fetoprotein serum on some cultured
tumor cells. Int J Cancer. 13:187–195. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wepsic HT, Tsukada Y, Takeichi N, Nishi S
and Hirai H: Effect of horse antibody to rat alpha-fetoprotein upon
the growth of AH-66 in Donryu rats. Int J Cancer. 25:655–661. 1980.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Koji T, Ishii N, Munehisa T, Kusumoto Y,
Nakamura S, Tamenishi A, Hara A, Kobayashi K, Tsukada Y, Nishi S,
et al: Localization of radioiodinated antibody to alpha-fetoprotein
in hepatoma transplanted in rats and a case report of
alpha-fetoprotein antibody treatment of a hepatoma patient. Cancer
Res. 40:3013–3015. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ohkawa K, Tsukada Y, Hibi N and Hirai H:
The inhibitory effects of horse anti-rat AFP antiserum on the
uptake of 2-deoxy-D-glucose by AFP-producing rat hepatoma cells.
Int J Cancer. 33:497–502. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsukada Y, Bischof WK, Hibi N, Hirai H,
Hurwitz E and Sela M: Effect of a conjugate of daunomycin and
antibodies to rat alpha-fetoprotein on the growth of
alpha-fetoprotein-producing tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
79:621–625. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tsukada Y, Kato Y, Umemoto N, Takeda Y,
Hara T and Hirai H: An anti-alpha-fetoprotein antibody-daunorubicin
conjugate with a novel poly-L-glutamic acid derivative as
intermediate drug carrier. J Natl Cancer Inst. 73:721–729.
1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tsukada Y, Hurwitz E, Kashi R, Sela M,
Hibi N, Hara A and Hirai H: Chemotherapy by intravenous
administration of conjugates of daunomycin with monoclonal and
conventional anti-rat alpha-fetoprotein antibodies. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 79:7896–7899. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tsukada Y, Hurwitz E, Kashi R, Sela M,
Hibi N, Hara A and Hirai H: Effect of a conjugate of daunomycin and
purified polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies to rat
alpha-fetoprotein on the growth of alpha-fetoprotein-producing
tumor cells. Ann NY Acad Sci. 417:262–269. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kato Y, Tsukada Y, Hara T and Hirai H:
Enhanced antitumor activity of mitomycin C conjugated with
anti-alpha-fetoprotein antibody by a novel method of conjugation. J
Appl Biochem. 5:313–319. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tsukada Y, Ohkawa K and Hibi N:
Suppression of human alpha-foetoprotein-producing hepatocellular
carcinoma growth in nude mice by an anti alpha-foetoprotein
antibody-daunorubicin conjugate with a poly-L-glutamic acid
derivative as intermediate drug carrier. Br J Cancer. 52:111–116.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ohkawa K, Hibi N and Tsukada Y: Evaluation
of a conjugate of purified antibodies against human
AFP-dextran-daunorubicin to human AFP-producing yolk sac tumor cell
lines. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 22:81–86. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tsukada Y, Ohkawa K and Hibi N:
Therapeutic effect of treatment with polyclonal or monoclonal
antibodies to alpha-fetoprotein that have been conjugated to
daunomycin via a dextran bridge: Studies with an
alpha-fetoprotein-producing rat hepatoma tumor model. Cancer Res.
47:4293–4295. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ohkawa K, Tsukada Y, Hibi N, Umemoto N and
Hara T: Selective in vitro and in vivo growth inhibition against
human yolk sac tumor cell lines by purified antibody against human
alpha-fetoprotein conjugated with mitomycin C via human serum
albumin. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 23:81–86. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim EE, DeLand FH, Nelson MO, Bennett S,
Simmons G, Alpert E and Goldenberg DM: Radioimmunodetection of
cancer with radiolabeled antibodies to alpha-fetoprotein. Cancer
Res. 40:3008–3012. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim EE, Deland FH, Casper S, Corgan RL,
Primus FJ and Goldenberg DM: Radioimmunodetection of colorectal
cancer. Cancer. 45(Suppl): 1243–1247. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Uriel J, Villacampa MJ, Moro R, Naval J
and Failly-Crépin C: Uptake of radiolabeled a-fetoprotein by mouse
mammary carcinomas and its usefulness in tumor scintigraphy. Cancer
Res. 44:5314–5319. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Goldenberg DM: Cancer imaging with CEA
antibodies: Historical and current perspectives. Int J Biol
Markers. 7:183–188. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Behr TM, Liersch T, Greiner-Bechert L,
Griesinger F, Béhé M, Markus PM, Gratz S, Angerstein C, Brittinger
G, Becker H, et al: Radioimmunotherapy of small-volume disease of
metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer. 94(Suppl): 1373–1381. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Aarts F, Boerman OC, Sharkey RM, Hendriks
T, Chang CH, McBride WJ, Bleichrodt RP, Oyen WJ and Goldenberg DM:
Pretargeted radioimmunoscintigraphy in patients with primary
colorectal cancer using a bispecific anticarcinoembryonic antigen
CEA X anti-di-diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid F(ab′)2 antibody.
Cancer. 116(Suppl): 1111–1117. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mizejewski GJ: Biological role of
alpha-fetoprotein in cancer: Prospects for anticancer therapy.
Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2:709–735. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li MS, Li PF, Yang FY, He SP, Du GG and Li
G: The intracellular mechanism of alpha-fetoprotein promoting the
proliferation of NIH 3T3 cells. Cell Res. 12:151–156. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li MS, Li PF, He SP, Du GG and Li G: The
promoting molecular mechanism of alpha-fetoprotein on the growth of
human hepatoma Bel7402 cell line. World J Gastroenterol. 8:469–475.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li P, Wang SS, Liu H, Li N, McNutt MA, Li
G and Ding HG: Elevated serum alpha fetoprotein levels promote
pathological progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 17:4563–4571. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Moro R, Gulyaeva-Tcherkassova J and
Stieber P: Increased alpha-fetoprotein receptor in the serum of
patients with early-stage breast cancer. Curr Oncol. 19:e1–e8.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang S, Jiang W, Chen X, Zhang C, Li H,
Hou W, Liu Z, McNutt MA, Lu F and Li G: Alpha-fetoprotein acts as a
novel signal molecule and mediates transcription of Fn14 in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 57:322–329. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhu M, Lin B, Zhou P and Li M: Molecular
analysis of AFP and HSA interactions with PTEN potein. BioMed Res
Int. 2015:2569162015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Mizejewski GJ: Nonsecreted cytoplasmic
alpha-fetoprotein: A newly discovered role in intracellular
signaling and regulation. An update and commentary. Tumour Biol.
36:9857–9864. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li M, Li H, Li C, Wang S, Jiang W, Liu Z,
Zhou S, Liu X, McNutt MA and Li G: Alpha-fetoprotein: A new member
of intracellular signal molecules in regulation of the PI3K/AKT
signaling in human hepatoma cell lines. Int J Cancer. 128:524–532.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Gao R, Cai C, Gan J, Yang X, Shuang Z, Liu
M, Li S and Tang H: miR-1236 down-regulates alpha-fetoprotein, thus
causing PTEN accumulation, which inhibits the PI3K/Akt pathway and
malignant phenotype in hepatoma cells. Oncotarget. 6:6014–6028.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu M, Guo J, Li W, Lu Y, Fu S, Xie X, Xia
H, Dong X, Chen Y, Quan M, et al: Hepatitis B virus X protein
induces expression of alpha-fetoprotein and activates PI3K/mTOR
signaling pathway in liver cells. Oncotarget. 6:12196–12208. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Su R, Nan H, Guo H, Ruan Z, Jiang L, Song
Y and Nan K: Associations of components of PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway
with cancer stem cell markers and prognostic value of these
biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 46:1380–1391.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhu M, Guo J, Xia H, Li W, Lu Y, Dong X,
Chen Y, Xie X, Fu S and Li M: Alpha-fetoprotein activates AKT/mTOR
signaling to promote CXCR4 expression and migration of hepatoma
cells. Oncoscience. 2:59–70. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ji X, Shen Y, Sun H and Gao X: A novel
anti-alpha-fetoprotein single-chain variable fragment displays
anti-tumor effects in HepG2 cells as a single agent or in
combination with paclitaxel. Tumour Biol. 37:10085–10096. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Matsumoto M, Matsuura T, Aoki K, Maehashi
H, Iwamoto T, Ohkawa K, Yoshida K, Yanaga K and Takada K: An
efficient system for secretory production of fibrinogen using a
hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. Hepatol Res. 45:315–325. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Nakabayashi H, Taketa K, Miyano K, Yamane
T and Sato J: Growth of human hepatoma cells lines with
differentiated functions in chemically defined medium. Cancer Res.
42:3858–3863. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ohkawa K, Tsukada Y, Murae M, Kimura E,
Takada K, Abe T, Terashima Y and Mitani K: Serum levels and
biochemical characteristics of human ovarian carcinoma-associated
antigen defined by murine monoclonal antibody, CF511. Br J Cancer.
60:953–960. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Baumann H and Doyle D: Metabolic fate of
cell surface glycoproteins during immunoglobulin-induced
internalization. Cell. 21:897–907. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Press OW, Hansen JA, Farr A and Martin PJ:
Endocytosis and degradation of murine anti-human CD3 monoclonal
antibodies by normal and malignant T-lymphocytes. Cancer Res.
48:2249–2257. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kyriakos RJ, Shih LB, Ong GL, Patel K,
Goldenberg DM and Mattes MJ: The fate of antibodies bound to the
surface of tumor cells in vitro. Cancer Res. 52:835–842.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
McEwan WA, Tam JC, Watkinson RE, Bidgood
SR, Mallery DL and James LC: Intracellular antibody-bound pathogens
stimulate immune signaling via the Fc receptor TRIM21. Nat Immunol.
14:327–336. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Watkinson RE, McEwan WA and James LC:
Intracellular antibody immunity. J Clin Immunol. 34(Suppl 1):
S30–S34. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yoshikawa M, Mukai Y, Okada Y, Tsumori Y,
Tsunoda S, Tsutsumi Y, Aird WC, Yoshioka Y, Okada N, Doi T, et al:
Robo4 is an effective tumor endothelial marker for antibody-drug
conjugates based on the rapid isolation of the anti-Robo4
cell-internalizing antibody. Blood. 121:2804–2813. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ha KD, Bidlingmaier SM, Su Y, Lee NK and
Liu B: Identification of novel macropinocytosing human antibodies
by phage display and high-content analysis. Methods Enzymol.
585:91–110. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Miura K, Law SW, Nishi S and Tamaoki T:
Isolation of alphafetoprotein messenger RNA from mouse yolk sac. J
Biol Chem. 254:5515–5521. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhou BP, Liao Y, Xia W, Spohn B, Lee MH
and Hung MC: Cytoplasmic localization of p21Cip1/WAF1 by
Akt-induced phosphorylation in HER-2/neu-overexpressing cells. Nat
Cell Biol. 3:245–252. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chung JH and Eng C: Nuclear-cytoplasmic
partitioning of phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on
chromosome 10 (PTEN) differentially regulates the cell cycle and
apoptosis. Cancer Res. 65:8096–8100. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chung JH, Ginn-Pease ME and Eng C:
Phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN)
has nuclear localization signal-like sequences for nuclear import
mediated by major vault protein. Cancer Res. 65:4108–4116. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chung JH, Ostrowski MC, Romigh T,
Minaguchi T, Waite KA and Eng C: The ERK1/2 pathway modulates
nuclear PTEN-mediated cell cycle arrest by cyclin D1
transcriptional regulation. Hum Mol Genet. 15:2553–2559. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gil A, Andrés-Pons A, Fernández E,
Valiente M, Torres J, Cervera J and Pulido R: Nuclear localization
of PTEN by a Ran-dependent mechanism enhances apoptosis:
Involvement of an N-terminal nuclear localization domain and
multiple nuclear exclusion motifs. Mol Biol Cell. 17:4002–4013.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Al-Khouri AM, Ma Y, Togo SH, Williams S
and Mustelin T: Cooperative phosphorylation of the tumor suppressor
phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) by casein kinases and
glycogen synthase kinase 3beta. J Biol Chem. 280:35195–35202. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tamguney T and Stokoe D: New insights into
PTEN. J Cell Sci. 120:4071–4079. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Georgescu MM, Kirsch KH, Akagi T, Shishido
T and Hanafusa H: The tumor-suppressor activity of PTEN is
regulated by its carboxyl-terminal region. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
96:10182–10187. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Tolkacheva T and Chan AM: Inhibition of
H-Ras transformation by the PTEN/MMAC1/TEP1 tumor suppressor gene.
Oncogene. 19:680–689. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Maccario H, Perera NM, Davidson L, Downes
CP and Leslie NR: PTEN is destabilized by phosphorylation on
Thr366. Biochem J. 405:439–444. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Torres J and Pulido R: The tumor
suppressor PTEN is phosphorylated by the protein kinase CK2 at its
C terminus. Implications for PTEN stability to proteasome-mediated
degradation. J Biol Chem. 276:993–998. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Milella M, Falcone I, Conciatori F, Cesta
Incani U, Del Curatolo A, Inzerilli N, Nuzzo CM, Vaccaro V, Vari S,
Cognetti F, et al: PTEN: Multiple functions in human malignant
tumors. Front Oncol. 5:242015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Vazquez F, Ramaswamy S, Nakamura N and
Sellers WR: Phosphorylation of the PTEN tail regulates protein
stability and function. Mol Cell Biol. 20:5010–5018. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Birle D, Bottini N, Williams S, Huynh H,
deBelle I, Adamson E and Mustelin T: Negative feedback regulation
of the tumor suppressor PTEN by phosphoinositide-induced serine
phosphorylation. J Immunol. 169:286–291. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Okahara F, Ikawa H, Kanaho Y and Maehama
T: Regulation of PTEN phosphorylation and stability by a tumor
suppressor candidate protein. J Biol Chem. 279:45300–45303. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Okahara F, Itoh K, Nakagawara A, Murakami
M, Kanaho Y and Maehama T: Critical role of PICT-1, a tumor
suppressor candidate, in phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate
signals and tumorigenic transformation. Mol Biol Cell.
17:4888–4895. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Doble BW and Woodgett JR: GSK-3: Tricks of
the trade for a multi-tasking kinase. J Cell Sci. 116:1175–1186.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Saini MK and Sanyal SN: PTEN regulates
apoptotic cell death through PI3-K/Akt/GSK3p signaling pathway in
DMH induced early colon carcinogenesis in rat. Exp Mol Pathol.
93:135–146. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Tibarewal P, Zilidis G, Spinelli L,
Schurch N, Maccario H, Gray A, Perera NM, Davidson L, Barton GJ and
Leslie NR: PTEN protein phosphatase activity correlates with
control of gene expression and invasion, a tumor-suppressing
phenotype, but not with AKT activity. Sci Signal. 5:ra182012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Freeman DJ, Li AG, Wei G, Li HH, Kertesz
N, Lesche R, Whale AD, Martinez-Diaz H, Rozengurt N, Cardiff RD, et
al: PTEN tumor suppressor regulates p53 protein levels and activity
through phosphatase-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Cancer
Cell. 3:117–130. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Li AG, Piluso LG, Cai X, Wei G, Sellers WR
and Liu X: Mechanistic insights into maintenance of high p53
acetylation by PTEN. Mol Cell. 23:575–587. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Hupp TR, Meek DW, Midgley CA and Lane DP:
Regulation of the specific DNA binding function of p53. Cell.
71:875–886. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Sakaguchi K, Sakamoto H, Lewis MS,
Anderson CW, Erickson JW, Appella E and Xie D: Phosphorylation of
serine 392 stabilizes the tetramer formation of tumor suppressor
protein p53. Biochemistry. 36:10117–10124. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Shieh SY, Taya Y and Prives C: DNA
damage-inducible phosphorylation of p53 at N-terminal sites
including a novel site, Ser20, requires tetramerization. EMBO J.
18:1815–1823. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Oda K, Arakawa H, Tanaka T, Matsuda K,
Tanikawa C, Mori T, Nishimori H, Tamai K, Tokino T, Nakamura Y, et
al: p53AIP1, a potential mediator of p53-dependent apoptosis, and
its regulation by Ser-46-phosphorylated p53. Cell. 102:849–862.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Hirao A, Kong YY, Matsuoka S, Wakeham A,
Ruland J, Yoshida H, Liu D, Elledge SJ and Mak TW: DNA
damage-induced activation of p53 by the checkpoint kinase Chk2.
Science. 287:1824–1827. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A and Oren M: Mdm2
promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature. 387:296–299. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Mayo LD and Donner DB: A
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway promotes translocation of
Mdm2 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:11598–11603. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Zhou BP, Liao Y, Xia W, Zou Y, Spohn B and
Hung MC: HER-2/neu induces p53 ubiquitination via Akt-mediated MDM2
phosphorylation. Nat Cell Biol. 3:973–982. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Morani F, Phadngam S, Follo C, Titone R,
Aimaretti G, Galetto A, Alabiso O and Isidoro C: PTEN regulates
plasma membrane expression of glucose transporter 1 and glucose
uptake in thyroid cancer cells. J Mol Endocrinol. 53:247–258. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Samih N, Hovsepian S, Aouani A, Lombardo D
and Fayet G: Glut-1 translocation in FRTL-5 thyroid cells: Role of
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and N-glycosylation. Endocrinology.
141:4146–4155. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Hajduch E, Litherland GJ and Hundal HS:
Protein kinase B (PKB/Akt) - a key regulator of glucose transport?
FEBS Lett. 492:199–203. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Ciampi R, Vivaldi A, Romei C, Del Guerra
A, Salvadori P, Cosci B, Pinchera A and Elisei R: Expression
analysis of facilitative glucose transporters (GLUTs) in human
thyroid carcinoma cell lines and primary tumors. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 291:57–62. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Wang CH, Wey KC, Mo LR, Chang KK, Lin RC
and Kuo JJ: Current trends and recent advances in diagnosis,
therapy, and prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 16:3595–3604. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Taketomi A: Clinical trials of
antiangiogenic therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin
Oncol. 21:213–218. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Dhir M, Melin AA, Douaiher J, Lin C, Zhen
WK, Hussain SM, Geschwind JF, Doyle MB, Abou-Alfa GK and Are C: A
review and update of treatment options and controversies in the
management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 263:1112–1125.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Lin J, Wu L, Bai X, Xie Y, Wang A, Zhang
H, Yang X, Wan X, Lu X, Sang X, et al: Combination treatment
including targeted therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 7:71036–71051. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Nakata K, Muro T, Furukawa R, Kono K,
Kusumoto Y, Ishii N, Munehisa T, Koji T and Nagataki S: Presence of
immunoglobulin G in human sera binding to alphafetoprotein. Oncodev
Biol Med. 4:C101–C104. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Asano T, Yamada N, Ochiai T, Sato H and
Fukao T: Presence of anti-AFP-antibody producing B cells in
peripheral blood lymphocyte of hepatocellular carcinoma patient.
Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 81:2781984.In Japanese.
|
|
88
|
Sassi F, Ayed K, el Gaied A and Dellagi K:
Presence of antialphafetoprotein immunoglobulin G in serum of a
patient with hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterol Clin Biol.
15:661–662. 1991.in French.
|
|
89
|
Liu H, Zhang J, Wang S, Pang Z, Wang Z,
Zhou W and Wu M: Screening of autoantibodies as potential
biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma by using T7 phase display
system. Cancer Epidemiol. 36:82–88. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Negm OH, Hamed MR, Schoen RE, Whelan RL,
Steele RJ, Scholefield J, Dilnot EM, Shantha Kumara HM, Robertson
JF and Sewell HF: Human blood autoantibodies in the detection of
colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 11:e01569712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Ura Y, Ochi Y, Hamazu M, Ishida M,
Nakajima K and Watanabe T: Studies on circulating antibody against
carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and CEA-like antigen in cancer
patients. Cancer Lett. 25:283–295. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Konstadoulakis MM, Syrigos KN,
Albanopoulos C, Mayers G and Golematis B: The presence of
anti-carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) antibodies in the sera of
patients with gastrointestinal malignancies. J Clin Immunol.
14:310–313. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Haidopoulos D, Konstadoulakis MM,
Antonakis PT, Alexiou DG, Manouras AM, Katsaragakis SM and
Androulakis GF: Circulating anti-CEA antibodies in the sera of
patients with breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 26:742–746. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Ladd J, Lu H, Taylor AD, Goodell V, Disis
ML and Jiang S: Direct detection of carcinoembryonic antigen
autoantibodies in clinical human serum samples using a surface
plasmon resonance sensor. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 70:1–6.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Zhu M, Li W, Lu Y, Dong X, Lin B, Chen Y,
Zhang X, Guo J and Li M: HBx drives alpha fetoprotein expression to
promote initiation of liver cancer stem cells through activating
PI3K/AKT signal pathway. Int J Cancer. 140:1346–1355. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|