|
1
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer
Brain Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups; National Cancer Institute of
Canada Clinical Trials Group: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and
adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Arvold ND and Reardon DA: Treatment
options and outcomes for glioblastoma in the elderly patient. Clin
Interv Aging. 9:357–367. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bonnet D and Dick JE: Human acute myeloid
leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a
primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med. 3:730–737. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE,
Hawkins C, Squire J and Dirks PB: Identification of a cancer stem
cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 63:5821–5828.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, Squire JA,
Bayani J, Hide T, Henkelman RM, Cusimano MD and Dirks PB:
Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature.
432:396–401. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Galli R, Binda E, Orfanelli U, Cipelletti
B, Gritti A, De Vitis S, Fiocco R, Foroni C, Dimeco F and Vescovi
A: Isolation and characterization of tumorigenic, stem-like neural
precursors from human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 64:7011–7021. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q,
Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD and Rich JN: Glioma stem
cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA
damage response. Nature. 444:756–760. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim Y, Joo KM, Jin J and Nam DH: Cancer
stem cells and their mechanism of chemo-radiation resistance. Int J
Stem Cells. 2:109–114. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Beier D, Röhrl S, Pillai DR, Schwarz S,
Kunz-Schughart LA, Leukel P, Proescholdt M, Brawanski A, Bogdahn U,
Trampe-Kieslich A, et al: Temozolomide preferentially depletes
cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 68:5706–5715. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mihaliak AM, Gilbert CA, Li L, Daou MC,
Moser RP, Reeves A, Cochran BH and Ross AH: Clinically relevant
doses of chemotherapy agents reversibly block formation of
glioblastoma neurospheres. Cancer Lett. 296:168–177. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ghods AJ, Irvin D, Liu G, Yuan X,
Abdulkadir IR, Tunici P, Konda B, Wachsmann-Hogiu S, Black KL and
Yu JS: Spheres isolated from 9L gliosarcoma rat cell line possess
chemoresistant and aggressive cancer stem-like cells. Stem Cells.
25:1645–1653. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Eramo A, Ricci-Vitiani L, Zeuner A,
Pallini R, Lotti F, Sette G, Pilozzi E, Larocca LM, Peschle C and
De Maria R: Chemotherapy resistance of glioblastoma stem cells.
Cell Death Differ. 13:1238–1241. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Beier D, Schulz JB and Beier CP:
Chemoresistance of glioblastoma cancer stem cells - much more
complex than expected. Mol Cancer. 10:1282011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Mitani M, Yamanishi T and Miyazaki Y:
Salinomycin: A new monovalent cation ionophore. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 66:1231–1236. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Danforth HD, Ruff MD, Reid WM and Johnson
J: Anticoccidial activity of salinomycin in floor-pen experiments
with broilers. Poult Sci. 56:933–938. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou S, Wang F, Wong ET, Fonkem E, Hsieh
TC, Wu JM and Wu E: Salinomycin: A novel anti-cancer agent with
known anti-coccidial activities. Curr Med Chem. 20:4095–4101. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Callaway TR, Edrington TS, Rychlik JL,
Genovese KJ, Poole TL, Jung YS, Bischoff KM, Anderson RC and Nisbet
DJ: Ionophores: Their use as ruminant growth promotants and impact
on food safety. Curr Issues Intest Microbiol. 4:43–51.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lindemann MD, Kornegay ET, Stahly TS,
Cromwell GL, Easter RA, Kerr BJ and Lucas DM: The efficacy of
salinomycin as a growth promotant for swine from 9 to 97 kg. J Anim
Sci. 61:782–788. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, Tao K,
Kuperwasser C, Weinberg RA and Lander ES: Identification of
selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput
screening. Cell. 138:645–659. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lu D, Choi MY, Yu J, Castro JE, Kipps TJ
and Carson DA: Salinomycin inhibits Wnt signaling and selectively
induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 108:13253–13257. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim KY, Yu SN, Lee SY, Chun SS, Choi YL,
Park YM, Song CS, Chatterjee B and Ahn SC: Salinomycin-induced
apoptosis of human prostate cancer cells due to accumulated
reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial membrane depolarization.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 413:80–86. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dong TT, Zhou HM, Wang LL, Feng B, Lv B
and Zheng MH: Salinomycin selectively targets 'CD133+'
cell subpopulations and decreases malignant traits in colorectal
cancer lines. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:1797–1804. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Y: Effects of salinomycin on cancer
stem cell in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Med Chem.
7:106–111. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim YJ, Liu Y, Li S, Rohrs J, Zhang R,
Zhang X and Wang P: Co-eradication of breast cancer cells and
cancer stem cells by cross-linked multilamellar liposomes enhances
tumor treatment. Mol Pharm. 12:2811–2822. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fuchs D, Daniel V, Sadeghi M, Opelz G and
Naujokat C: Salinomycin overcomes ABC transporter-mediated
multidrug and apoptosis resistance in human leukemia stem cell-like
KG-1a cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 394:1098–1104. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fuchs D, Heinold A, Opelz G, Daniel V and
Naujokat C: Salinomycin induces apoptosis and overcomes apoptosis
resistance in human cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
390:743–749. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
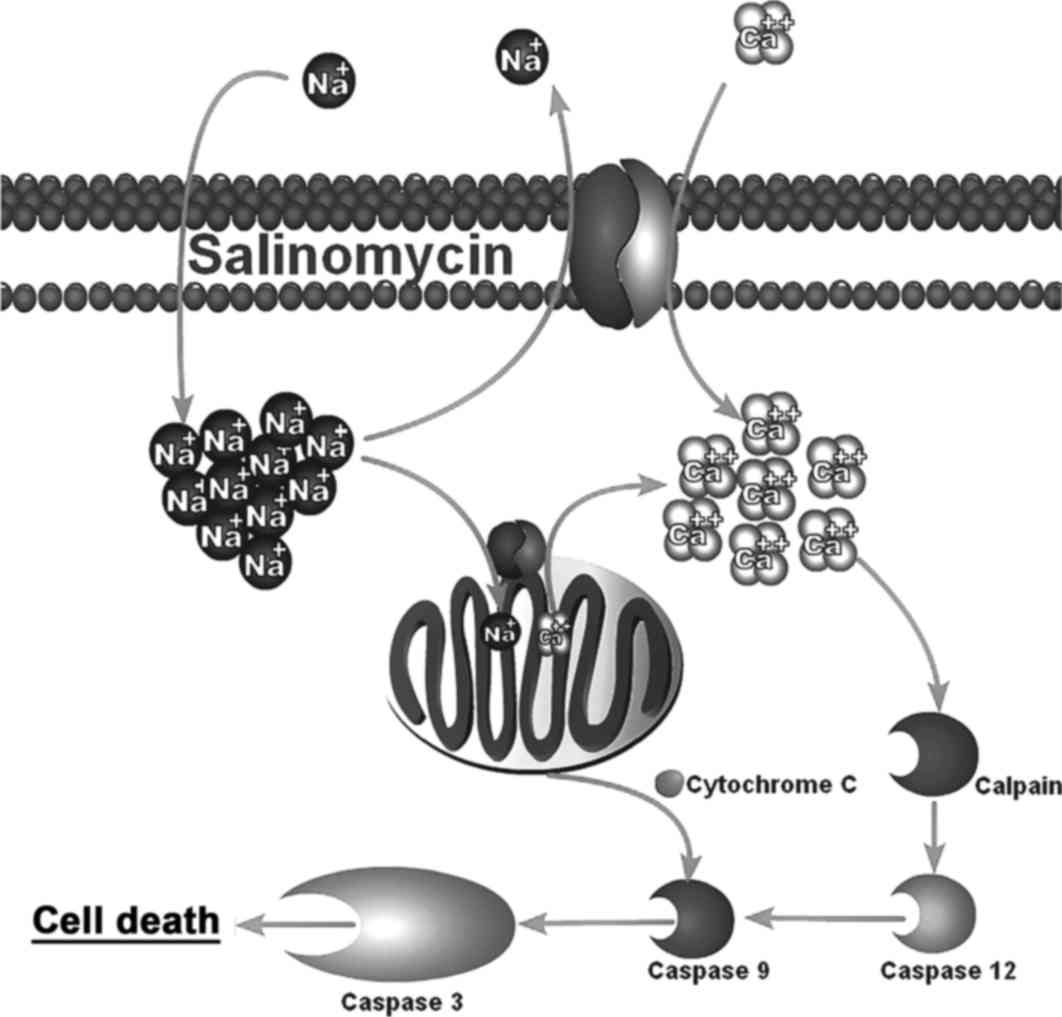
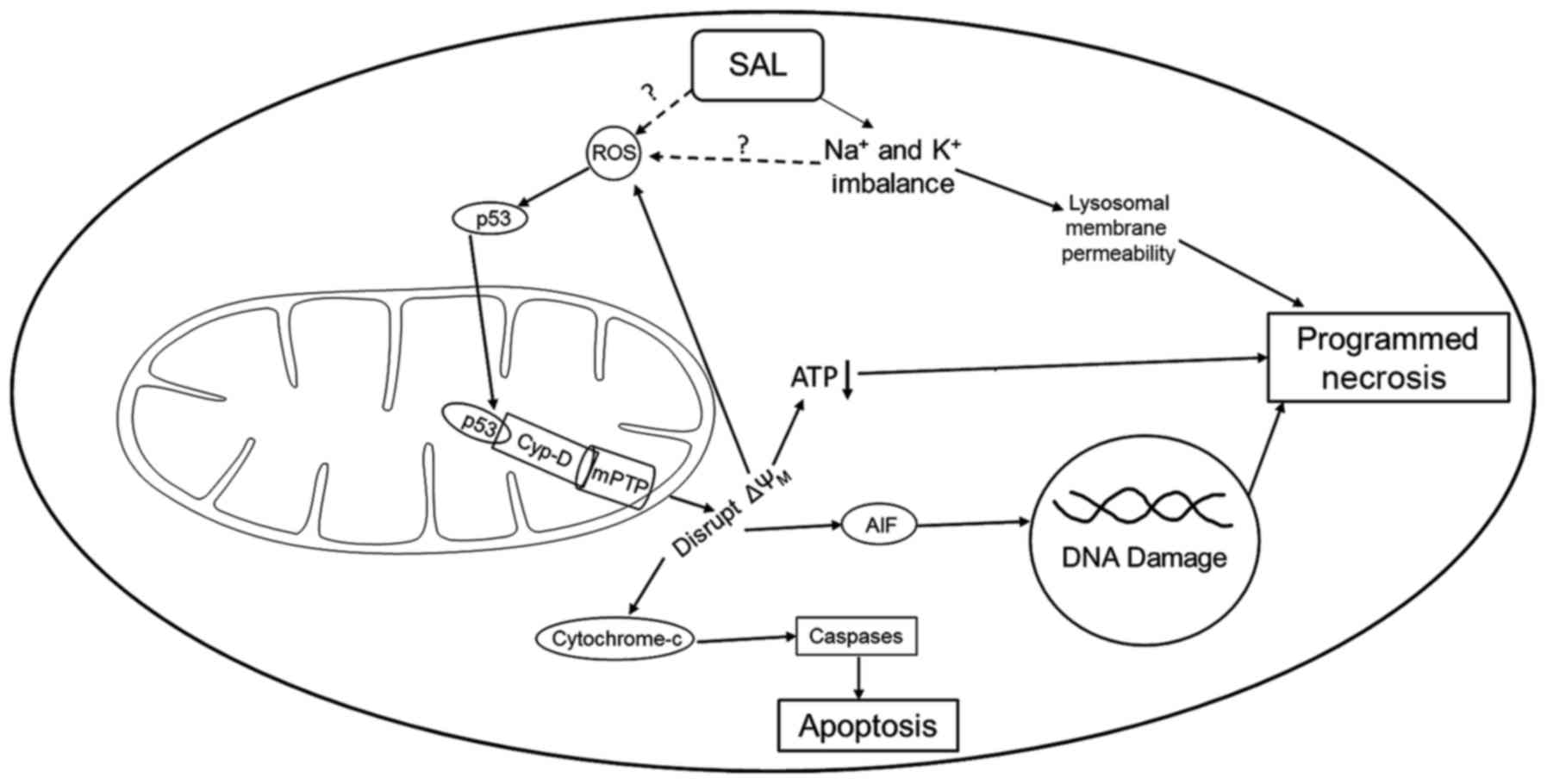
Qin LS, Jia PF, Zhang ZQ and Zhang SM:
ROS-p53-cyclophilin-D signaling mediates salinomycin-induced glioma
cell necrosis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:572015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jangamreddy JR, Ghavami S, Grabarek J,
Kratz G, Wiechec E, Fredriksson BA, Rao Pariti RK, Cieślar-Pobuda
A, Panigrahi S and Łos MJ: Salinomycin induces activation of
autophagy, mitophagy and affects mitochondrial polarity:
Differences between primary and cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1833:2057–2069. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen T, Yi L, Li F, Hu R, Hu S, Yin Y, Lan
C, Li Z, Fu C, Cao L, et al: Salinomycin inhibits the tumor growth
of glioma stem cells by selectively suppressing glioma-initiating
cells. Mol Med Rep. 11:2407–2412. 2015.
|
|
30
|
Xipell E, Gonzalez-Huarriz M, Martinez de
Irujo JJ, García-Garzón A, Lang FF, Jiang H, Fueyo J, Gomez-Manzano
C and Alonso MM: Salinomycin induced ROS results in abortive
autophagy and leads to regulated necrosis in glioblastoma.
Oncotarget. 7:30626–30641. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Neradil J and Veselska R: Nestin as a
marker of cancer stem cells. Cancer Sci. 106:803–811. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Song WS, Yang YP, Huang CS, Lu KH, Liu WH,
Wu WW, Lee YY, Lo WL, Lee SD, Chen YW, et al: Sox2, a stemness
gene, regulates tumor-initiating and drug-resistant properties in
CD133-positive glioblastoma stem cells. J Chin Med Assoc.
79:538–545. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lagadec C, Vlashi E, Frohnen P, Alhiyari
Y, Chan M and Pajonk F: The RNA-binding protein Musashi-1 regulates
proteasome subunit expression in breast cancer- and
glioma-initiating cells. Stem Cells. 32:135–144. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
van der Linde-Sipman JS, van den Ingh TS,
van nes JJ, Verhagen H, Kersten JG, Beynen AC and Plekkringa R:
Salinomycin-induced polyneuropathy in cats: Morphologic and
epidemiologic data. Vet Pathol. 36:152–156. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rollinson J, Taylor FG and Chesney J:
Salinomycin poisoning in horses. Vet Rec. 121:126–128. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Novilla MN, Owen NV and Todd GC: The
comparative toxicology of narasin in laboratory animals. Vet Hum
Toxicol. 36:318–323. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Story P and Doube A: A case of human
poisoning by salinomycin, an agricultural antibiotic. N Z Med J.
117:U7992004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Boehmerle W and Endres M: Salinomycin
induces calpain and cytochrome c-mediated neuronal cell death. Cell
Death Dis. 2:e1682011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lattanzio FA Jr and Pressman BC:
Alterations in intracellular calcium activity and contractility of
isolated perfused rabbit hearts by ionophores and adrenergic
agents. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 139:816–821. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yu JM, Jun ES and Jung JS, Suh SY, Han JY,
Kim JY, Kim KW and Jung JS: Role of Wnt5a in the proliferation of
human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Lett. 257:172–181. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
De A: Wnt/Ca2+ signaling
pathway: A brief overview. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
43:745–756. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
An Y and Ongkeko WM: ABCG2: The key to
chemoresistance in cancer stem cells? Expert Opin Drug Metab
Toxicol. 5:1529–1542. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Dean M: ABC transporters, drug resistance,
and cancer stem cells. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 14:3–9.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sun J, Luo Q, Liu L, Yang X, Zhu S and
Song G: Salinomycin attenuates liver cancer stem cell motility by
enhancing cell stiffness and increasing F-actin formation via the
FAK-ERK1/2 signalling pathway. Toxicology. 384:1–10. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chung SS, Adekoya D, Enenmoh I, Clarke O,
Wang P, Sarkyssian M, Wu Y and Vadgama JV: Salinomycin abolished
STAT3 and STAT1 interactions and reduced telomerase activity in
colorectal cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 37:445–453. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kuo SZ, Blair KJ, Rahimy E, Kiang A,
Abhold E, Fan JB, Wang-Rodriguez J, Altuna X and Ongkeko WM:
Salinomycin induces cell death and differentiation in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma stem cells despite activation of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and Akt. BMC Cancer. 12:5562012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Qu H, Ma B, Yuan HF, Wang ZY, Guo SJ and
Zhang J: Effect of salinomycin on metastasis and invasion of
bladder cancer cell line T24. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 8:578–582.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Beug H: Breast cancer stem cells:
Eradication by differentiation therapy? Cell. 138:623–625. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Klose J, Eissele J, Volz C, Schmitt S,
Ritter A, Ying S, Schmidt T, Heger U, Schneider M and Ulrich A:
Salinomycin inhibits metastatic colorectal cancer growth and
interferes with Wnt/β-catenin signaling in CD133(+) human
colorectal cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 16:8962016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Lu Y, Ma W, Mao J, Yu X, Hou Z, Fan S,
Song B, Wang H, Li J, Kang L, et al: Salinomycin exerts anticancer
effects on human breast carcinoma MCF-7 cancer stem cells via
modulation of Hedgehog signaling. Chem Biol Interact. 228:100–107.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
He M, Fu Y, Yan Y, Xiao Q, Wu H, Yao W,
Zhao H, Zhao L, Jiang Q, Yu Z, et al: The Hedgehog signalling
pathway mediates drug response of MCF-7 mammosphere cells in breast
cancer patients. Clin Sci (Lond). 129:809–822. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Takebe N, Harris PJ, Warren RQ and Ivy SP:
Targeting cancer stem cells by inhibiting Wnt, Notch, and Hedgehog
pathways. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 8:97–106. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Galluzzi L, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Vitale I,
Aaronson SA, Abrams JM, Adam D, Alnemri ES, Altucci L, Andrews D,
Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M, et al: Essential versus accessory
aspects of cell death: Recommendations of the NCCD 2015. Cell Death
Differ. 22:58–73. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Ouyang L, Shi Z, Zhao S, Wang FT, Zhou TT,
Liu B and Bao JK: Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A
review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell
Prolif. 45:487–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH and Currie AR:
Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging
implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 26:239–257. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ghobrial IM, Witzig TE and Adjei AA:
Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer therapy. CA Cancer J Clin.
55:178–194. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kundu M and Thompson CB: Autophagy: Basic
principles and relevance to disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 3:427–455.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
White E: Deconvoluting the
context-dependent role for autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
12:401–410. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Galluzzi L and Kroemer G: Necroptosis: A
specialized pathway of programmed necrosis. Cell. 135:1161–1163.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Al Dhaheri Y, Attoub S, Arafat K, Abuqamar
S, Eid A, Al Faresi N and Iratni R: Salinomycin induces apoptosis
and senescence in breast cancer: Upregulation of p21,
downregulation of survivin and histone H3 and H4 hyperacetylation.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1830:3121–3135. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kaplan F and Teksen F: Apoptotic effects
of salinomycin on human ovarian cancer cell line (OVCAR-3). Tumour
Biol. 37:3897–3903. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Calzolari A, Saulle E, De Angelis ML,
Pasquini L, Boe A, Pelacchi F, Ricci-Vitiani L, Baiocchi M and
Testa U: Salinomycin potentiates the cytotoxic effects of TRAIL on
glioblastoma cell lines. PLoS One. 9:e944382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Booth L, Roberts JL, Conley A,
Cruickshanks N, Ridder T, Grant S, Poklepovic A and Dent P: HDAC
inhibitors enhance the lethality of low dose salinomycin in
parental and stem-like GBM cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 15:305–316.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
64
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdelmohsen K, Abe A, Abedin
MJ, Abeliovich H, Acevedo Arozena A, Adachi H, Adams CM, Adams PD,
Adeli K, et al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays
for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy. 12:1–222. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Vaseva AV, Marchenko ND, Ji K, Tsirka SE,
Holzmann S and Moll UM: p53 opens the mitochondrial permeability
transition pore to trigger necrosis. Cell. 149:1536–1548. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Bernardi P: The mitochondrial permeability
transition pore: A mystery solved? Front Physiol. 4:952013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Szalai G, Krishnamurthy R and Hajnóczky G:
Apoptosis driven by IP(3)-linked mitochondrial calcium signals.
EMBO J. 18:6349–6361. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Delwar ZM, Avramidis D, Siden Å, Cruz M,
Paulsson K and Sebastian Yakisich J: Low concentration of
salinomycin prevents regrowth and partially depletes human glioma
cells surviving high concentrations of alkylating agents. Clin
Cancer Drugs. 1:72–77. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS,
Huang CP, Nicholl JK, Sutherland GR, Smith TD, Rauch C, Smith CA,
et al: Identification and characterization of a new member of the
TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 3:673–682. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Ruppert S, Donahue
CJ, Moore A and Ashkenazi A: Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2
ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family.
J Biol Chem. 271:12687–12690. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Michaelis M, Doerr HW and Cinatl J Jr:
Valproic acid as anti-cancer drug. Curr Pharm Des. 13:3378–3393.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Tığlı Aydın RS, Kaynak G and
Gümüşderelioğlu M: Salinomycin encapsulated nanoparticles as a
targeting vehicle for glioblastoma cells. J Biomed Mater Res A.
104:455–464. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|