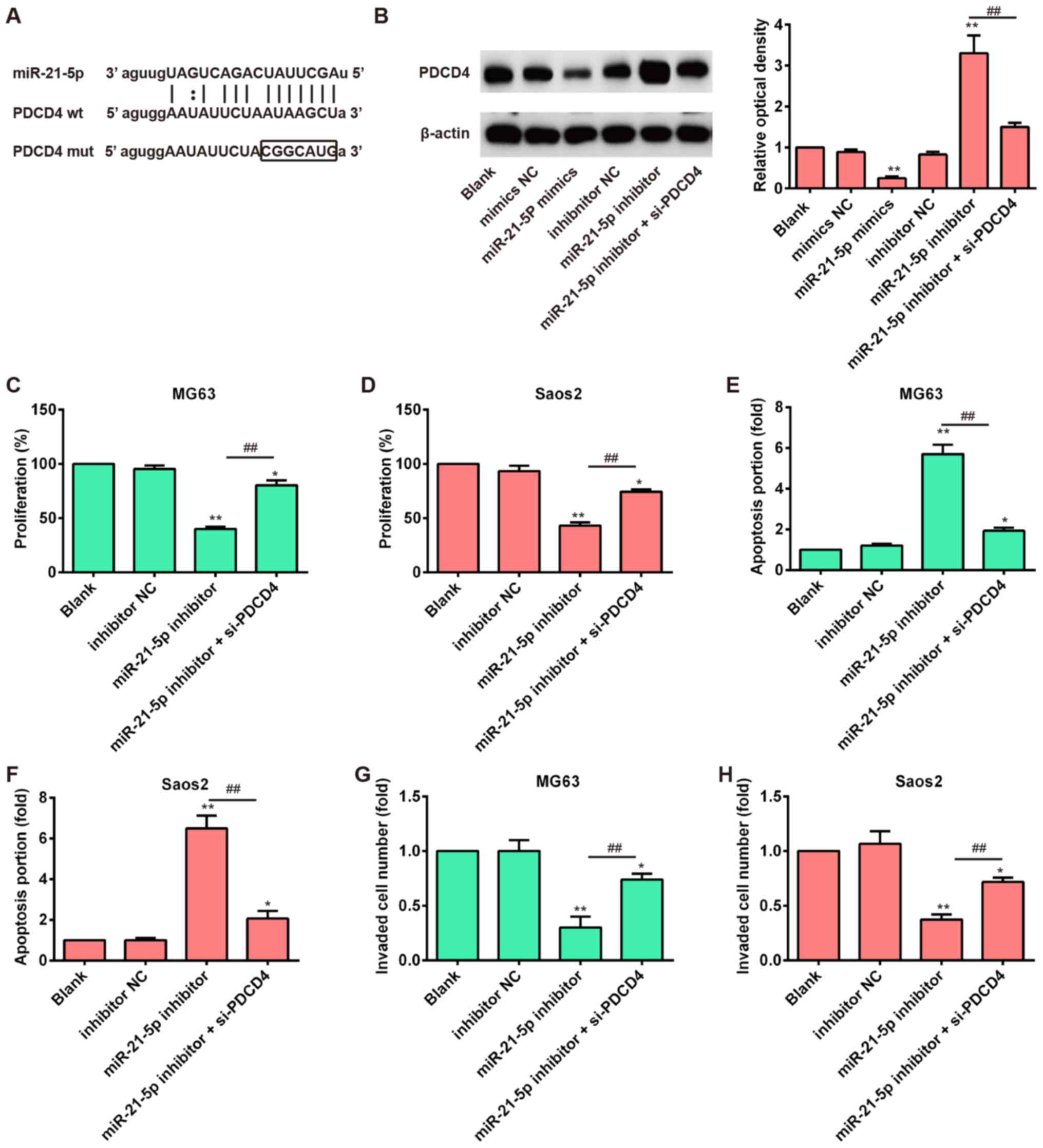
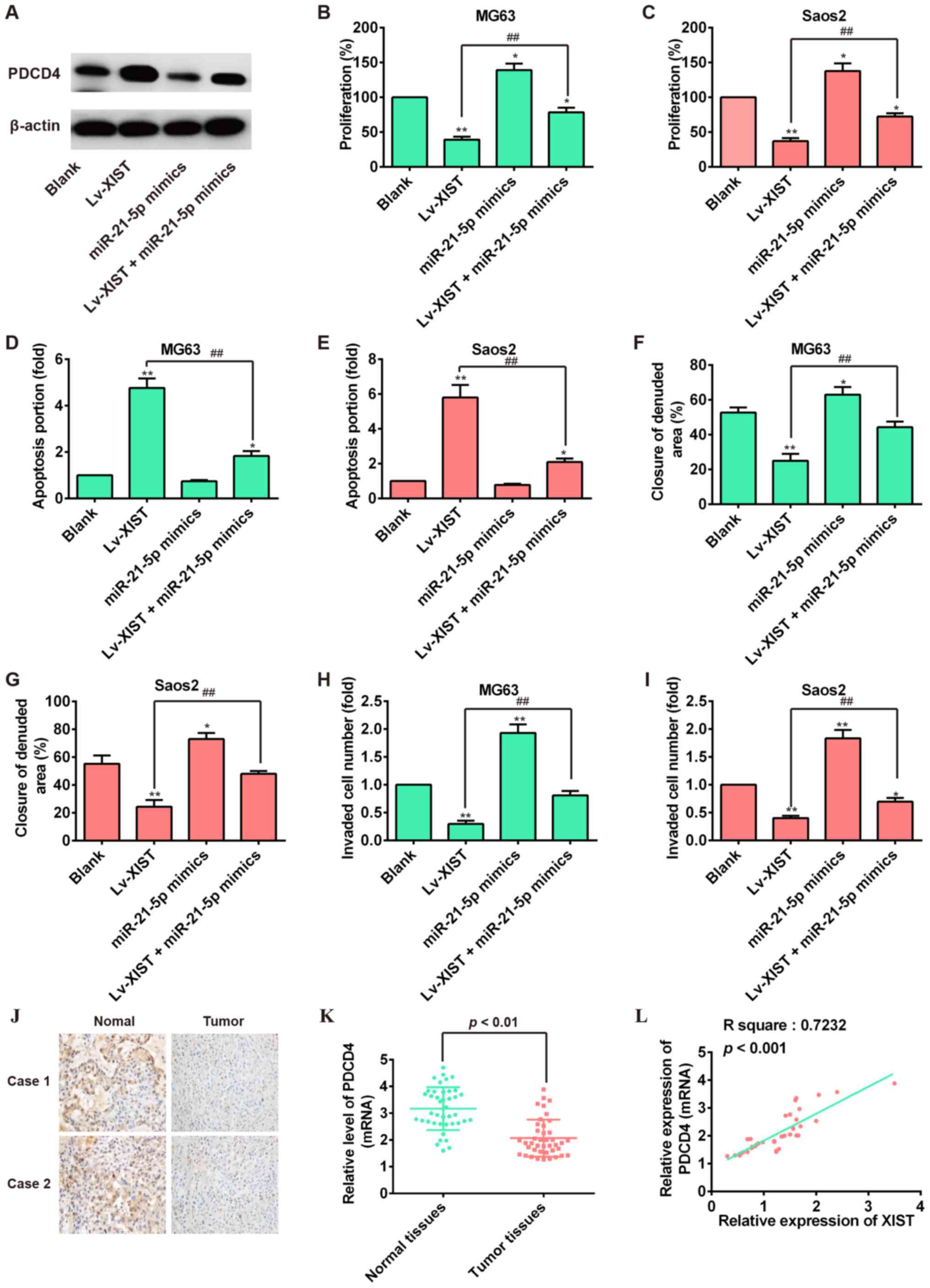
|
1
|
Ottaviani G and Jaffe N: The epidemiology
of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 152:3–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Meazza C, Luksch R, Daolio P, Podda M,
Luzzati A, Gronchi A, Parafioriti A, Gandola L, Collini P, Ferrari
A, et al: Axial skeletal osteosarcoma: A 25-year monoinstitutional
experience in children and adolescents. Med Oncol. 31:8752014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ando K, Heymann MF, Stresing V, Mori K,
Rédini F and Heymann D: Current therapeutic strategies and novel
approaches in osteosarcoma. Cancers (Basel). 5:591–616. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wittig JC, Bickels J, Priebat D, Jelinek
J, Kellar-Graney K, Shmookler B and Malawer MM: Osteosarcoma: A
multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam
Physician. 65:1123–1132. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shi X, Sun M, Liu H, Yao Y and Song Y:
Long non-coding RNAs: A new frontier in the study of human
diseases. Cancer Lett. 339:159–166. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wapinski O and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs and human disease. Trends Cell Biol. 21:354–361. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tian ZZ, Guo XJ, Zhao YM and Fang Y:
Decreased expression of long non-coding RNA MEG3 acts as a
potential predictor biomarker in progression and poor prognosis of
osteosarcoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:15138–15142. 2015.
|
|
8
|
Zhang Q, Geng PL, Yin P, Wang XL, Jia JP
and Yao J: Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA TUG1 inhibits
osteosarcoma cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 14:2311–2315. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mo Y, Lu Y, Wang P, Huang S, He L, Li D,
Li F, Huang J, Lin X, Li X, et al: Long non-coding RNA XIST
promotes cell growth by regulating miR-139-5p/PDK1/AKT axis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283176909992017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma L, Zhou Y, Luo X, Gao H, Deng X and
Jiang Y: Long non-coding RNA XIST promotes cell growth and invasion
through regulating miR-497/mACC1 axis in gastric cancer.
Oncotarget. 8:4125–4135. 2017.
|
|
11
|
Song P, Ye LF, Zhang C, Peng T and Zhou
XH: Long non-coding RNA XIST exerts oncogenic functions in human
nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting miR-34a-5p. Gene. 592:8–14.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yildirim E, Kirby JE, Brown DE, Mercier
FE, Sadreyev RI, Scadden DT and Lee JT: Xist RNA is a potent
suppressor of hematologic cancer in mice. Cell. 152:727–742. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang YS, Chang CC, Lee SS, Jou YS and
Shih HM: Xist reduction in breast cancer upregulates AKT
phosphorylation via HDAC3-mediated repression of PHLPP1 expression.
Oncotarget. 7:43256–43266. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chang S, Chen B, Wang X, Wu K and Sun Y:
Long non-coding RNA XIST regulates PTEN expression by sponging
miR-181a and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression. BMC
Cancer. 17:2482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yao Y, Ma J, Xue Y, Wang P, Li Z, Liu J,
Chen L, Xi Z, Teng H, Wang Z, et al: Knockdown of long non-coding
RNA XIST exerts tumor-suppressive functions in human glioblastoma
stem cells by up-regulating miR-152. Cancer Lett. 359:75–86. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
John-Aryankalayil M, Palayoor ST, Makinde
AY, Cerna D, Simone CB II, Falduto MT, Magnuson SR and Coleman CN:
Fractionated radiation alters oncomir and tumor suppressor miRNAs
in human prostate cancer cells. Radiat Res. 178:105–117. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cesana M, Cacchiarelli D, Legnini I,
Santini T, Sthandier O, Chinappi M, Tramontano A and Bozzoni I: A
long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning
as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell. 147:358–369. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu XH, Sun M, Nie FQ, Ge YB, Zhang EB,
Yin DD, Kong R, Xia R, Lu KH, Li JH, et al: Lnc RNA HOTAIR
functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate HER2 expression
by sponging miR-331-3p in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 13:922014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liang WC, Fu WM, Wong CW, Wang Y, Wang WM,
Hu GX, Zhang L, Xiao LJ, Wan DC, Zhang JF, et al: The lncRNA H19
promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition by functioning as
miRNA sponges in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 6:22513–22525.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen DL, Ju HQ, Lu YX, Chen LZ, Zeng ZL,
Zhang DS, Luo HY, Wang F, Qiu MZ, Wang DS, et al: Long non-coding
RNA XIST regulates gastric cancer progression by acting as a
molecular sponge of miR-101 to modulate EZH2 expression. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 35:1422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bonnomet A, Brysse A, Tachsidis A, Waltham
M, Thompson EW, Polette M and Gilles C: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transitions and circulating tumor cells. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 15:261–273. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA
language? Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lv C, Hao Y and Tu G: MicroRNA-21 promotes
proliferation, invasion and suppresses apoptosis in human
osteosarcoma line mG63 through PTeN/Akt pathway. Tumour Biol.
37:9333–9342. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu B, Xia H, Cao J, Wang Z, Yang Y and Lin
Y: MicroRNA-21 inhibits the apoptosis of osteosarcoma cell line
SAOS-2 via targeting caspase 8. Oncol Res. 25:1161–1168. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Selcuklu SD, Donoghue MT and Spillane C:
miR-21 as a key regulator of oncogenic processes. Biochem Soc
Trans. 37:918–925. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dillhoff M, Liu J, Frankel W, Croce C and
Bloomston M: MicroRNA-21 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and
a potential predictor of survival. J Gastrointest Surg.
12:2171–2176. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun Z, Li S, Kaufmann AM and Albers AE:
miR-21 increases the programmed cell death 4 gene-regulated cell
proliferation in head and neck squamous carcinoma cell lines. Oncol
Rep. 32:2283–2289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lin Z, Song D, Wei H, Yang X, Liu T, Yan W
and Xiao J: TGF-β1-induced miR-202 mediates drug resistance by
inhibiting apoptosis in human osteosarcoma. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 142:239–246. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA,
Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S and Allgayer H: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21)
post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and
stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal
cancer. Oncogene. 27:2128–2136. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Dong Y, Liang G, Yuan B, Yang C, Gao R and
Zhou X: MALAT1 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of
osteosarcoma cells by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Tumour Biol.
36:1477–1486. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wang B, Su Y, Yang Q, Lv D, Zhang W, Tang
K, Wang H, Zhang R and Liu Y: Overexpression of long non-coding RNA
HOTAIR promotes tumor growth and metastasis in human osteosarcoma.
Mol Cells. 38:432–440. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Escamilla-Del-Arenal M, da Rocha ST and
Heard E: Evolutionary diversity and developmental regulation of
X-chromosome inactivation. Hum Genet. 130:307–327. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Benoît MH, Hudson TJ, Maire G, Squire JA,
Arcand SL, Provencher D, Mes-Masson AM and Tonin PN: Global
analysis of chromosome X gene expression in primary cultures of
normal ovarian surface epithelial cells and epithelial ovarian
cancer cell lines. Int J Oncol. 30:5–17. 2007.
|
|
34
|
Kawakami T, Zhang C, Taniguchi T, Kim CJ,
Okada Y, Sugihara H, Hattori T, Reeve AE, Ogawa O and Okamoto K:
Characterization of loss-of-inactive X in Klinefelter syndrome and
female-derived cancer cells. Oncogene. 23:6163–6169. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xiao C, Sharp JA, Kawahara M, Davalos AR,
Difilippantonio MJ, Hu Y, Li W, Cao L, Buetow K, Ried T, et al: The
XIST noncoding RNA functions independently of BRCA1 in X
inactivation. Cell. 128:977–989. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Marahrens Y, Panning B, Dausman J, Strauss
W and Jaenisch R: Xist-deficient mice are defective in dosage
compensation but not spermatogenesis. Genes Dev. 11:156–166. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Penny GD, Kay GF, Sheardown SA, Rastan S
and Brockdorff N: Requirement for Xist in X chromosome
inactivation. Nature. 379:131–137. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhuang LK, Yang YT, Ma X, Han B, Wang ZS,
Zhao QY, Wu LQ and Qu ZQ: MicroRNA-92b promotes hepatocellular
carcinoma progression by targeting Smad7 and is mediated by long
non-coding RNA XIST. Cell Death Dis. 7:e22032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Soudyab M, Iranpour M and Ghafouri-Fard S:
The role of long non-coding RNAs in breast cancer. Arch Iran Med.
19:508–517. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Salvador MA, Wicinski J, Cabaud O, Toiron
Y, Finetti P, Josselin E, Lelièvre H, Kraus-Berthier L, Depil S,
Bertucci F, et al: The histone deacetylase inhibitor abexinostat
induces cancer stem cells differentiation in breast cancer with low
Xist expression. Clin Cancer Res. 19:6520–6531. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Vincent-Salomon A, Ganem-Elbaz C, Manié E,
Raynal V, Sastre-Garau X, Stoppa-Lyonnet D, Stern MH and Heard E: X
inactive-specific transcript RNA coating and genetic instability of
the X chromosome in BRCA1 breast tumors. Cancer Res. 67:5134–5140.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Schouten PC, Vollebergh MA, Opdam M,
Jonkers M, Loden M, Wesseling J, Hauptmann M and Linn SC: High XIST
and low 53BP1 expression predict poor outcome after high-dose
alkylating chemotherapy in patients with a BRCA1-like breast
cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 15:190–198. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Sirchia SM, Tabano S, Monti L, Recalcati
MP, Gariboldi M, Grati FR, Porta G, Finelli P, Radice P and Miozzo
M: Misbehaviour of XIST RNA in breast cancer cells. PLoS One.
4:e55592009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lv GY, Miao J and Zhang XL: Long
non-coding RNA: Long non-coding RNA XIST promotes osteosarcoma
progression by targeting Ras-related protein RAP2B via miR-320b.
Oncol Res. Apr 12–2017.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lindsey BA, Markel JE and Kleinerman ES:
Osteosarcoma overview. Rheumatol Ther. 4:25–43. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
46
|
Smeland S, Müller C, Alvegard TA, Wiklund
T, Wiebe T, Björk O, Stenwig AE, Willén H, Holmström T, Follerås G,
et al: Scandinavian Sarcoma Group Osteosarcoma Study SSG VIII:
Prognostic factors for outcome and the role of replacement salvage
chemotherapy for poor histological responders. Eur J Cancer.
39:488–494. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yang J, Mani SA, Donaher JL, Ramaswamy S,
Itzykson RA, Come C, Savagner P, Gitelman I, Richardson A and
Weinberg RA: Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an
essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell. 117:927–939. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ma CC, Xiong Z, Zhu GN, Wang C, Zong G,
Wang HL, Bian EB and Zhao B: Long non-coding RNA ATB promotes
glioma malignancy by negatively regulating miR-200a. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 35:902016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yang HS, Jansen AP, Nair R, Shibahara K,
Verma AK, Cmarik JL and Colburn NH: A novel transformation
suppressor, Pdcd4, inhibits AP-1 transactivation but not NF-kappaB
or ODC transactivation. Oncogene. 20:669–676. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mudduluru G, Medved F, Grobholz R, Jost C,
Gruber A, Leupold JH, Post S, Jansen A, Colburn NH and Allgayer H:
Loss of programmed cell death 4 expression marks adenoma-carcinoma
transition, correlates inversely with phosphorylated protein kinase
B, and is an independent prognostic factor in resected colorectal
cancer. Cancer. 110:1697–1707. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yang HS, Knies JL, Stark C and Colburn NH:
Pdcd4 suppresses tumor phenotype in JB6 cells by inhibiting AP-1
transactivation. Oncogene. 22:3712–3720. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Feng G, Li P, You H, Liu W, Zhang X, Xu X,
Sun G and Li F: The expression and clinical pathological
significance of PDCD in laryngocarcinoma. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou
Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 25:16–19. 2011.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhen Y, Liu Z, Yang H, Yu X, Wu Q, Hua S,
Long X, Jiang Q, Song Y, Cheng C, et al: Tumor suppressor PDCD4
modulates miR-184-mediated direct suppression of C-MYC and BCL2
blocking cell growth and survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell
Death Dis. 4:e8722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Li X, Xin S, Yang D, Li X, He Z, Che X,
Wang J, Chen F, Wang X and Song X: Down-regulation of PDCD4
expression is an independent predictor of poor prognosis in human
renal cell carcinoma patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
138:529–535. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Leupold JH, Asangani IA, Mudduluru G and
Allgayer H: Promoter cloning and characterization of the human
programmed cell death protein 4 (pdcd4) gene: Evidence for ZBP-89
and Sp-binding motifs as essential Pdcd4 regulators. Biosci Rep.
32:281–297. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Li JZ, Gao W, Lei WB, Zhao J, Chan JY, Wei
WI, Ho WK and Wong TS: MicroRNA 744-3p promotes MMP-9-mediated
metastasis by simultaneously suppressing PDCD4 and PTEN in
laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:58218–58233. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Li C, Deng L, Zhi Q, Meng Q, Qian A, Sang
H, Li X and Xia J: MicroRNA-183 functions as an oncogene by
regulating PDCD4 in gastric cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
16:447–455. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ma QQ, Huang JT, Xiong YG, Yang XY, Han R
and Zhu WW: MicroRNA-96 regulates apoptosis by targeting PDCD4 in
human glioma cells. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 16:92–98. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|