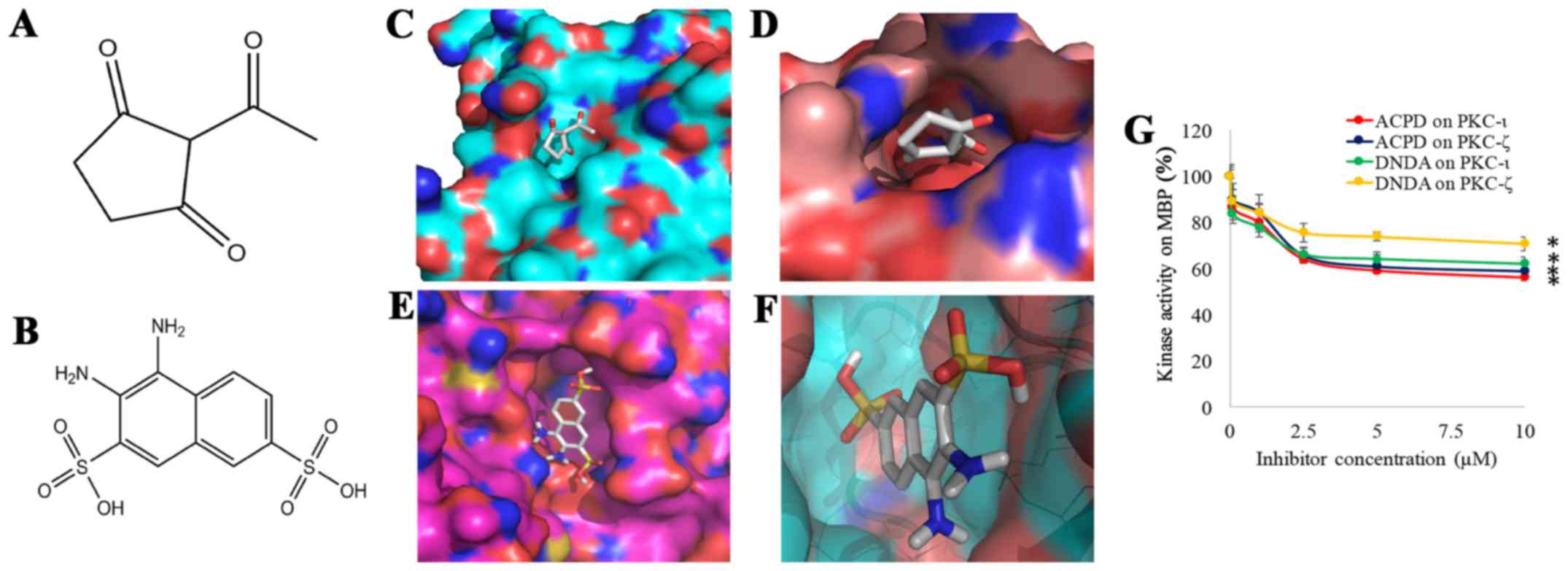
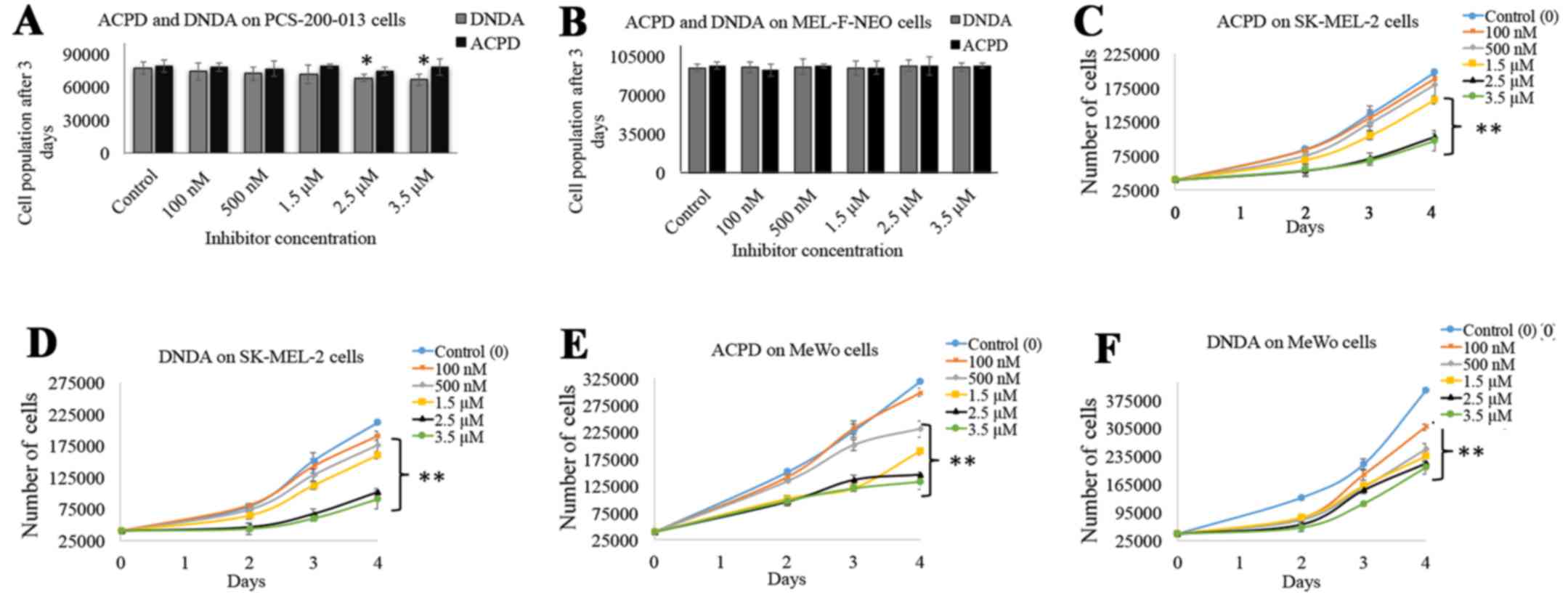
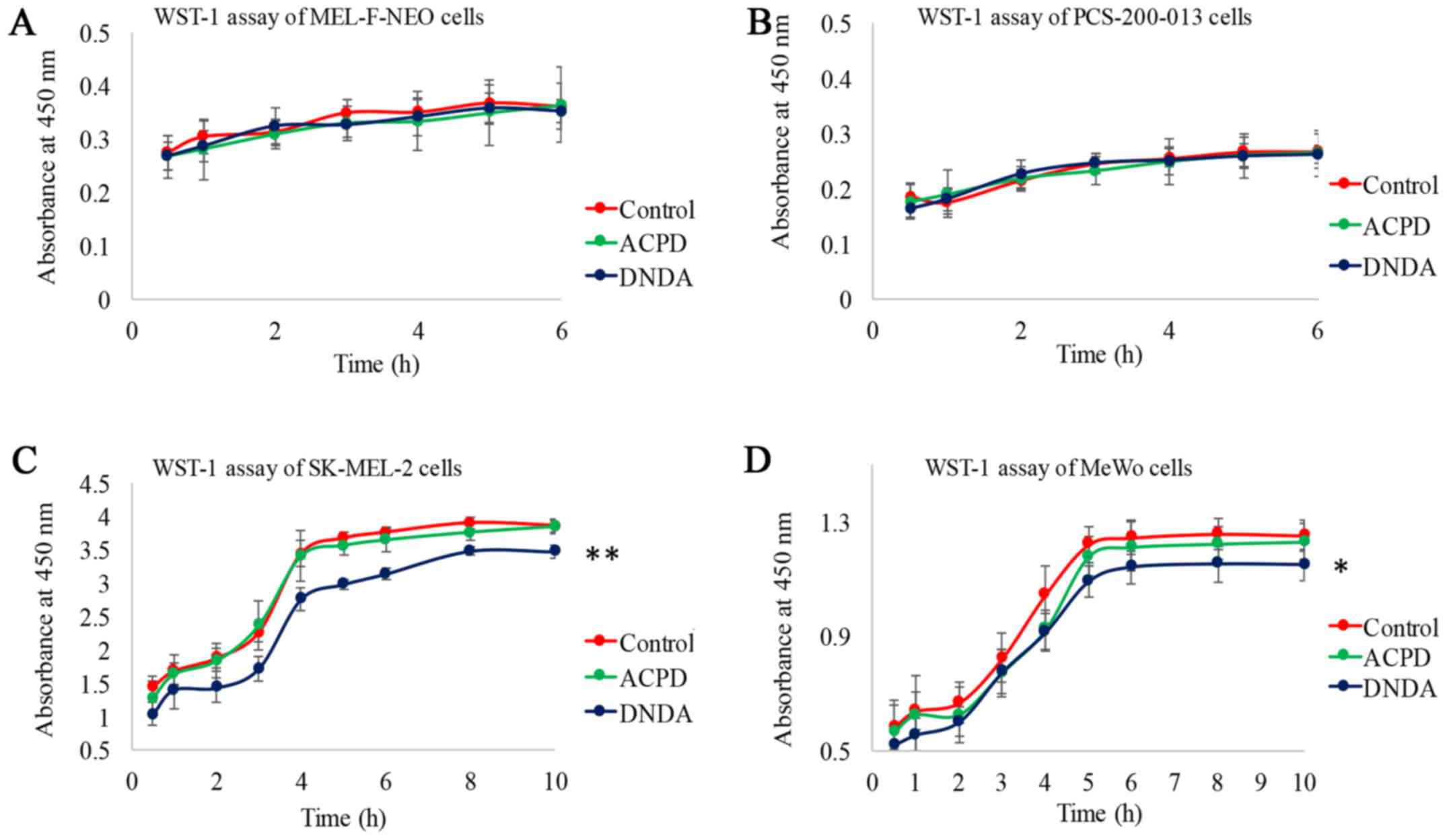
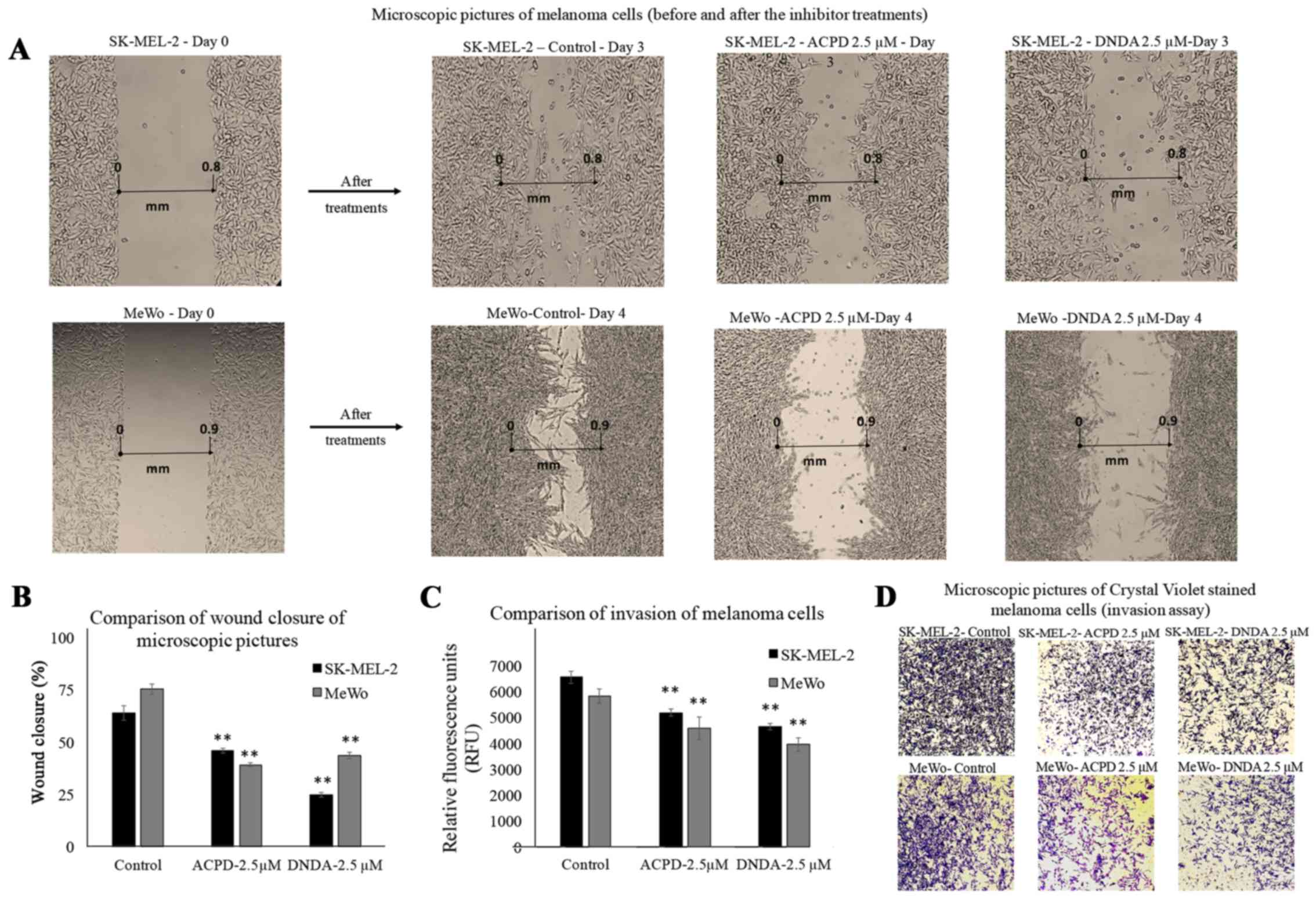
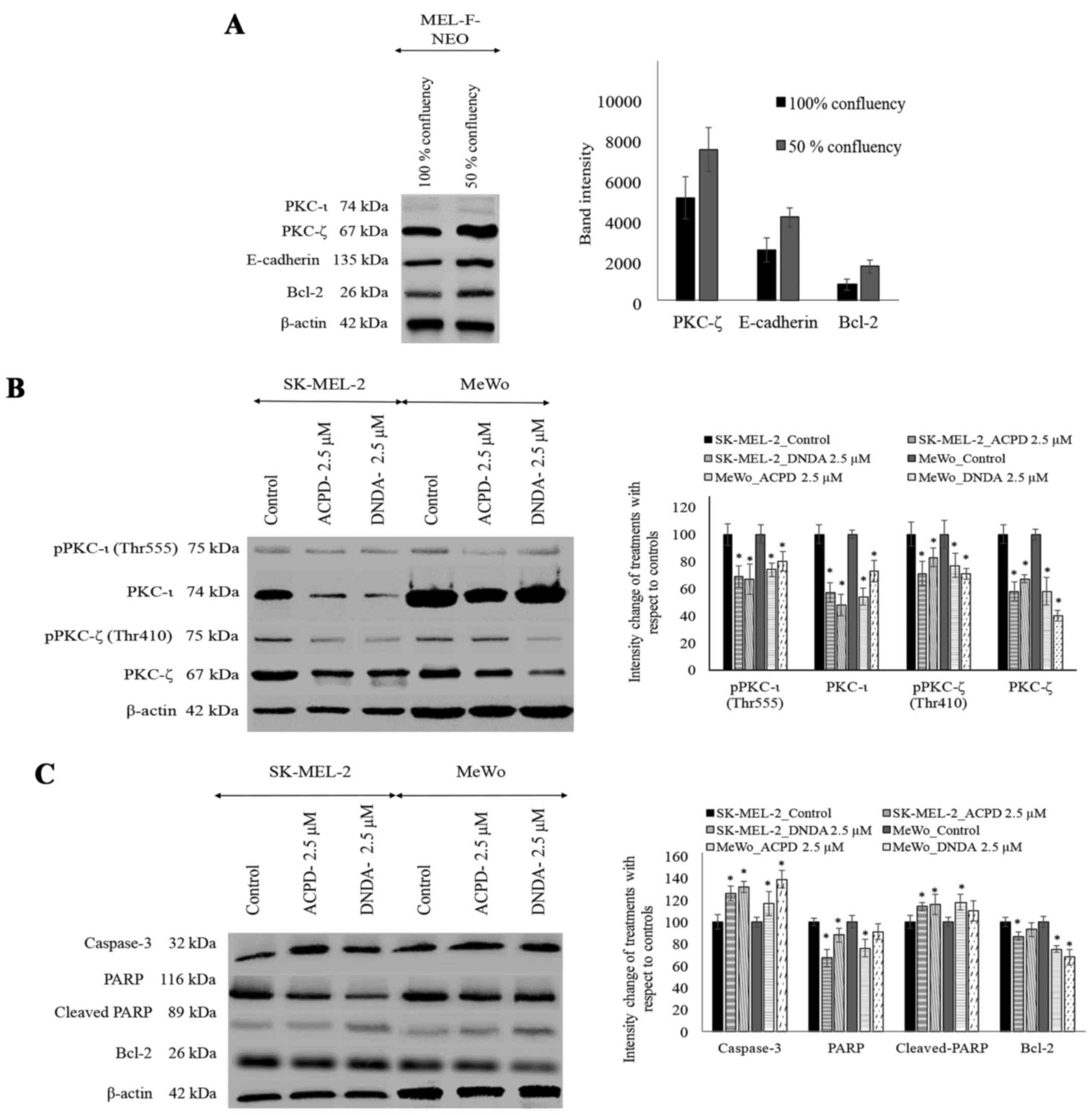
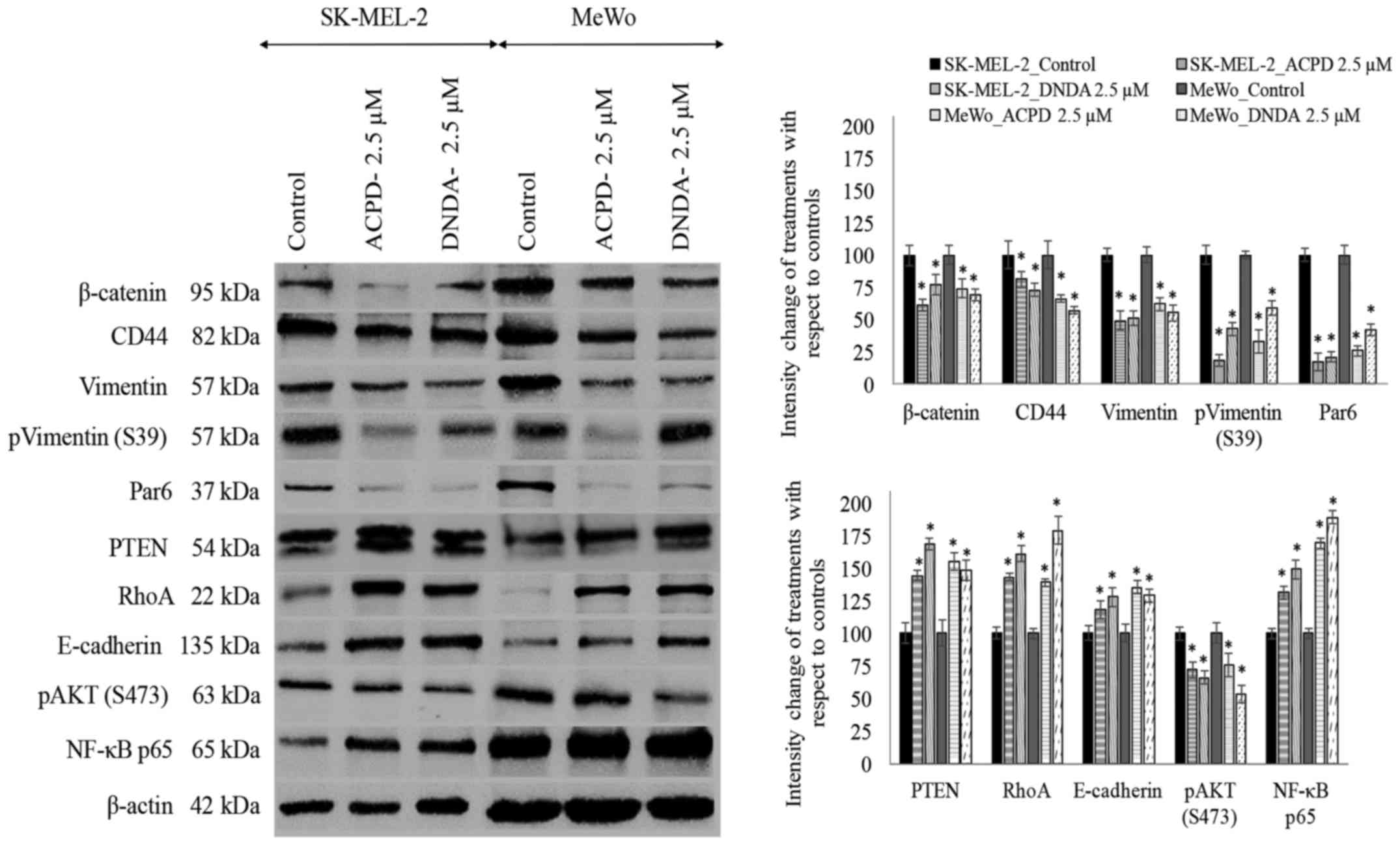
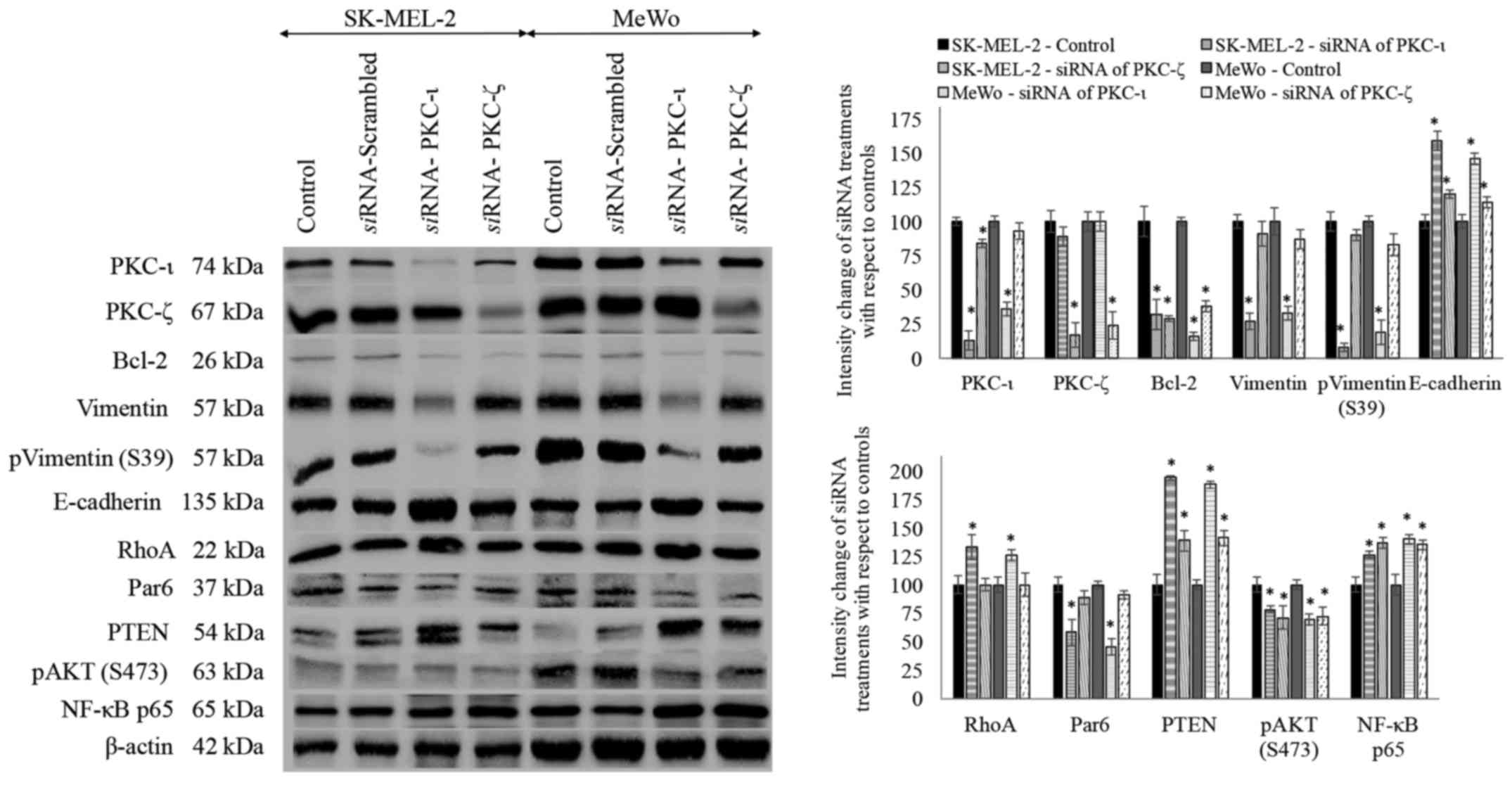
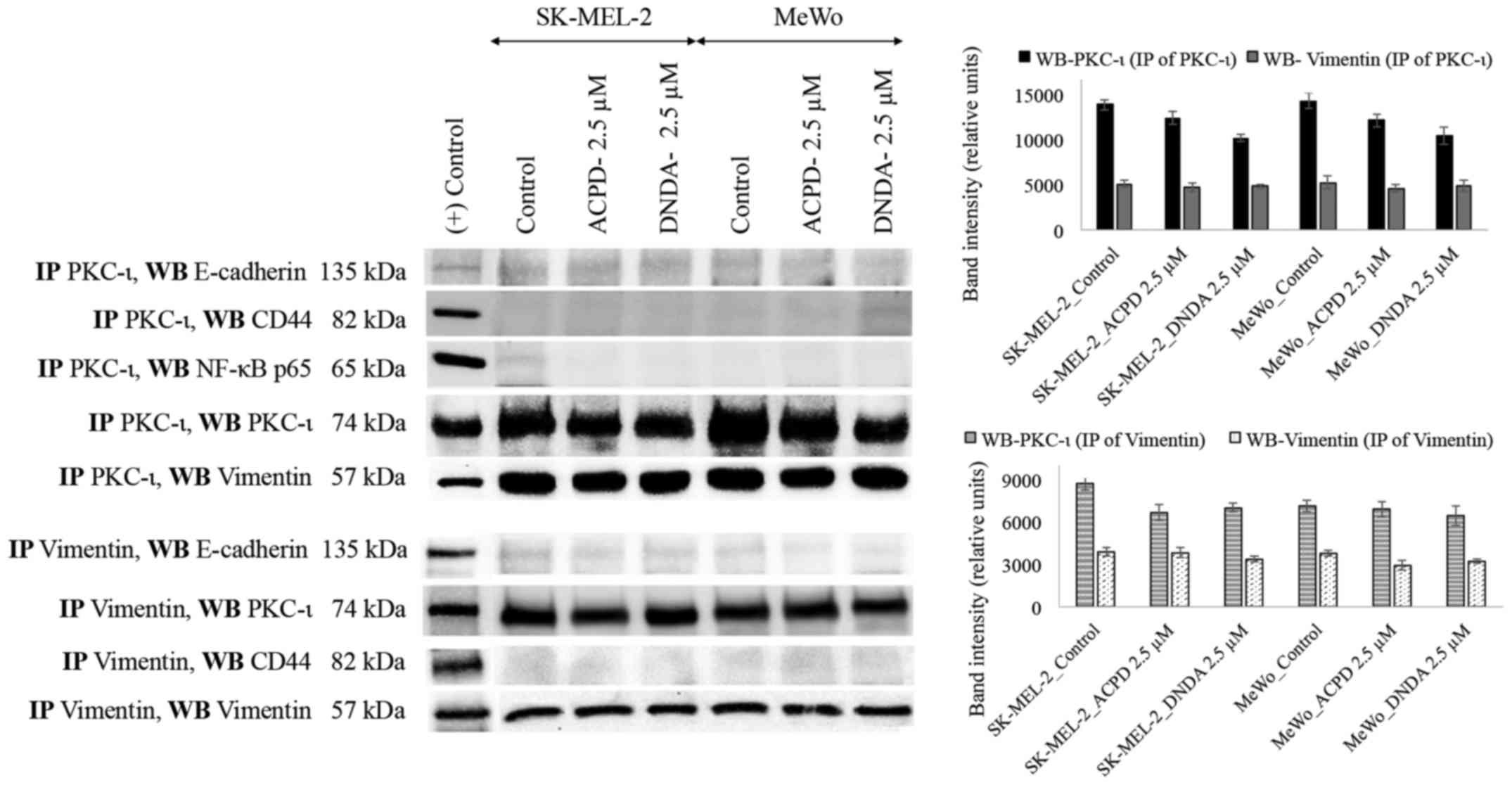
|
1
|
Eggermont AM: Adjuvant ipilimumab in stage
III melanoma: New landscape, new questions. Eur J Cancer. 69:39–42.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hao M, Song F, Du X, Wang G, Yang Y, Chen
K and Yang J: Advances in targeted therapy for unresectable
melanoma: New drugs and combinations. Cancer Lett. 359:1–8. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Melanoma of the Skin - Cancer Stat Facts.
<http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/melan.html>,
03/30/2017.
|
|
4
|
Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, Hunter T
and Sudarsanam S: The protein kinase complement of the human
genome. Science. 298:1912–1934. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Koivunen J, Aaltonen V and Peltonen J:
Protein kinase C (PKC) family in cancer progression. Cancer Lett.
235:1–10. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Regala RP, Weems C, Jamieson L, Khoor A,
Edell ES, Lohse CM and Fields AP: Atypical protein kinase C iota is
an oncogene in human non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res.
65:8905–8911. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Murray NR and Fields AP: Atypical protein
kinase C ι protects human leukemia cells against drug-induced
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 272:27521–27524. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Acevedo-Duncan M, Patel R, Whelan S and
Bicaku E: Human glioma PKC-iota and PKC-betaII phosphorylate
cyclin-dependent kinase activating kinase during the cell cycle.
Cell Prolif. 35:23–36. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Patel R, Win H, Desai S, Patel K, Matthews
JA and Acevedo-Duncan M: Involvement of PKC-iota in glioma
proliferation. Cell Prolif. 41:122–135. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Regala RP, Thompson EA and Fields AP:
Atypical protein kinase C iota expression and aurothiomalate
sensitivity in human lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 68:5888–5895.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gunaratne A, Thai BL and Di Guglielmo GM:
Atypical protein kinase C phosphorylates Par6 and facilitates
transforming growth factor β-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Mol Cell Biol. 33:874–886. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Kim KK, Kugler MC, Wolters PJ, Robillard
L, Galvez MG, Brumwell AN, Sheppard D and Chapman HA: Alveolar
epithelial cell mesenchymal transition develops in vivo during
pulmonary fibrosis and is regulated by the extracellular matrix.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:13180–13185. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wei J, Xu G, Wu M, Zhang Y, Li Q, Liu P,
Zhu T, Song A, Zhao L, Han Z, et al: Overexpression of vimentin
contributes to prostate cancer invasion and metastasis via src
regulation. Anticancer Res. 28(1A): 327–334. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Selzer E, Okamoto I, Lucas T, Kodym R,
Pehamberger H and Jansen B: Protein kinase C isoforms in normal and
transformed cells of the melanocytic lineage. Melanoma Res.
12:201–209. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ratnayake WS and Acevedo-Duncan M: Use of
ACPD and ICA-1 as inhibitors of atypical protein kinase C-zeta (ζ)
and iota (ι) in metastasized melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 76(14
suppl): Abs 4569. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Dissanayake SK, Wade M, Johnson CE,
O'Connell MP, Leotlela PD, French AD, Shah KV, Hewitt KJ, Rosenthal
DT, Indig FE, et al: The Wnt5A/protein kinase C pathway mediates
motility in melanoma cells via the inhibition of metastasis
suppressors and initiation of an epithelial to mesenchymal
transition. J Biol Chem. 282:17259–17271. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Weeraratna AT, Jiang Y, Hostetter G,
Rosenblatt K, Duray P, Bittner M and Trent JM: Wnt5a signaling
directly affects cell motility and invasion of metastatic melanoma.
Cancer Cell. 1:279–288. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qureshi R, Arora H and Rizvi MA: EMT in
cervical cancer: Its role in tumour progression and response to
therapy. Cancer Lett. 356:321–331. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Pillai P, Desai S, Patel R, Sajan M,
Farese R, Ostrov D and Acevedo-Duncan M: A novel PKC-ι inhibitor
abrogates cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in
neuroblastoma. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 43:784–794. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Win HY and Acevedo-Duncan M: Role of
protein kinase C-iota in transformed non-malignant RWPE-1 cells and
androgen-independent prostate carcinoma DU-145 cells. Cell Prolif.
42:182–194. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
O'Connell MP, French AD, Leotlela PD and
Weeraratna AT: Assaying Wnt5A-mediated invasion in melanoma cells.
Methods Mol Biol. 468:243–253. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Win HY and Acevedo-Duncan M: Atypical
protein kinase C phosphorylates IKKalphabeta in transformed
non-malignant and malignant prostate cell survival. Cancer Lett.
270:302–311. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Selbie LA, Schmitz-Peiffer C, Sheng Y and
Biden TJ: Molecular cloning and characterization of PKC iota, an
atypical isoform of protein kinase C derived from insulin-secreting
cells. J Biol Chem. 268:24296–24302. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xiao H and Liu M: Atypical protein kinase
C in cell motility. Cell Mol Life Sci. 70:3057–3066. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Sajan MP, Acevedo-Duncan ME, Standaert ML,
Ivey RA, Lee M and Farese RV: Akt-dependent phosphorylation of
hepatic FoxO1 is compartmentalized on a WD40/ProF scaffold and is
selectively inhibited by aPKC in early phases of diet-induced
obesity. Diabetes. 63:2690–2701. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sajan MP, Ivey RA III and Farese RV:
Metformin action in human hepatocytes: Coactivation of atypical
protein kinase C alters 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase effects on
lipogenic and gluconeogenic enzyme expression. Diabetologia.
56:2507–2516. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sajan MP, Ivey RA, Lee MC and Farese RV:
Hepatic insulin resistance in ob/ob mice involves increases in
ceramide, aPKC activity, and selective impairment of Akt-dependent
FoxO1 phosphorylation. J Lipid Res. 56:70–80. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Wooten MW, Seibenhener ML, Zhou G,
Vandenplas ML and Tan TH: Overexpression of atypical PKC in PC12
cells enhances NGF-responsiveness and survival through an NF-kappaB
dependent pathway. Cell Death Differ. 6:753–764. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ukeda H, Maeda S, Ishii T and Sawamura M:
Spectro-photometric assay for superoxide dismutase based on
tetrazolium salt
3′-{1-[phenylamino)-carbonyl]3,4-tetrazolium]-bis(4-methoxy-6-nitro)benzenesulfonic
acid hydrate reduction by xanthine-xanthine oxidase. Anal Biochem.
251:206–209. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xu S, Wang H, Pan H, Shi Y, Li T, Ge S,
Jia R, Zhang H and Fan X: ANRIL lncRNA triggers efficient
therapeutic efficacy by reprogramming the aberrant INK4-hub in
melanoma. Cancer Lett. 381:41–48. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Farese RV: Function and dysfunction of
aPKC isoforms for glucose transport in insulin-sensitive and
insulin-resistant states. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
283:E1–E11. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Suzuki A, Yamanaka T, Hirose T, Manabe N,
Mizuno K, Shimizu M, Akimoto K, Izumi Y, Ohnishi T and Ohno S:
Atypical protein kinase C is involved in the evolutionarily
conserved par protein complex and plays a critical role in
establishing epithelia-specific junctional structures. J Cell Biol.
152:1183–1196. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Du R, Lu KV, Petritsch C, Liu P, Ganss R,
Passegué E, Song H, Vandenberg S, Johnson RS, Werb Z, et al: HIF1α
induces the recruitment of bone marrow-derived vascular modulatory
cells to regulate tumor angiogenesis and invasion. Cancer Cell.
13:206–220. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Suzuki A, Akimoto K and Ohno S: Protein
kinase C lambda/iota (PKClambda/iota): A PKC isotype essential for
the development of multicellular organisms. J Biochem. 133:9–16.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mamidipudi V, Lin C, Seibenhener ML and
Wooten MW: Regulation of interleukin receptor-associated kinase
(IRAK) phosphorylation and signaling by iota protein kinase C. J
Biol Chem. 279:4161–4165. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Mah IK, Soloff R, Hedrick SM and Mariani
FV: Atypical PKC-iota controls Stem cell expansion via regulation
of the Notch pathway. Stem Cell Rep. 5:866–880. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Brady SC, Allan LA and Clarke PR:
Regulation of caspase 9 through phosphorylation by protein kinase C
zeta in response to hyperosmotic stress. Mol Cell Biol.
25:10543–10555. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shultz JC, Vu N, Shultz MD, Mba M-UU,
Shapiro BA and Chalfant CE: The Proto-oncogene PKCι regulates the
alternative splicing of Bcl-x pre-mRNA. Mol Cancer Res. 10:660–669.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
do Carmo A, Balça-Silva J, Matias D and
Lopes MC: PKC signaling in glioblastoma. Cancer Biol Ther.
14:287–294. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jänicke RU, Sprengart ML, Wati MR and
Porter AG: Caspase-3 is required for DNA fragmentation and
morphological changes associated with apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
273:9357–9360. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kroemer G: The proto-oncogene Bcl-2 and
its role in regulating apoptosis. Nat Med. 3:614–620. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Watson AJ, Askew JN and Benson RS:
Poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose) polymerase inhibition prevents
necrosis induced by H2O2 but not apoptosis. Gastroenterology.
109:472–482. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Soldani C and Scovassi AI:
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 cleavage during apoptosis: An update.
Apoptosis. 7:321–328. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
van Raam BJ, Drewniak A, Groenewold V, van
den Berg TK and and Kuijpers TW: Granulocyte colony-stimulating
factor delays neutrophil apoptosis by inhibition of calpains
upstream of caspase-3. Blood. 112:2046–2054. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cohen GM: Caspases: The executioners of
apoptosis. Biochem J. 326:1–16. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kasof GM, Lu JJ, Liu D, Speer B, Mongan
KN, Gomes BC and Lorenzi MV: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces
the expression of DR6, a member of the TNF receptor family, through
activation of NF-kappaB. Oncogene. 20:7965–7975. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mendez MG, Kojima S and Goldman RD:
Vimentin induces changes in cell shape, motility, and adhesion
during the epithelial to mesenchymal transition. FASEB J.
24:1838–1851. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chaw SY, Majeed AA, Dalley AJ, Chan A,
Stein S and Farah CS: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT)
biomarkers -E-cadherin, beta-catenin, APC and Vimentin - in oral
squamous cell carcinogenesis and transformation. Oral Oncol.
48:997–1006. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Gunaratne A and Di Guglielmo GM: Par6 is
phosphorylated by aPKC to facilitate EMT. Cell Adhes Migr.
7:357–361. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Xi G, Shen X, Rosen CJ and Clemmons DR:
IRS-1 functions as a molecular scaffold to coordinate IGF-I/IGFBP-2
signaling during osteoblast differentiation. J Bone Miner Res.
31:1300–1314. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Brumatti G, Salmanidis M and Ekert PG:
Crossing paths: Interactions between the cell death machinery and
growth factor survival signals. Cell Mol Life Sci. 67:1619–1630.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Scott ML, Fujita T, Liou HC, Nolan GP and
Baltimore D: The p65 subunit of NF-kappa B regulates I kappa B by
two distinct mechanisms. Genes Dev. 7(7A): 1266–1276. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|