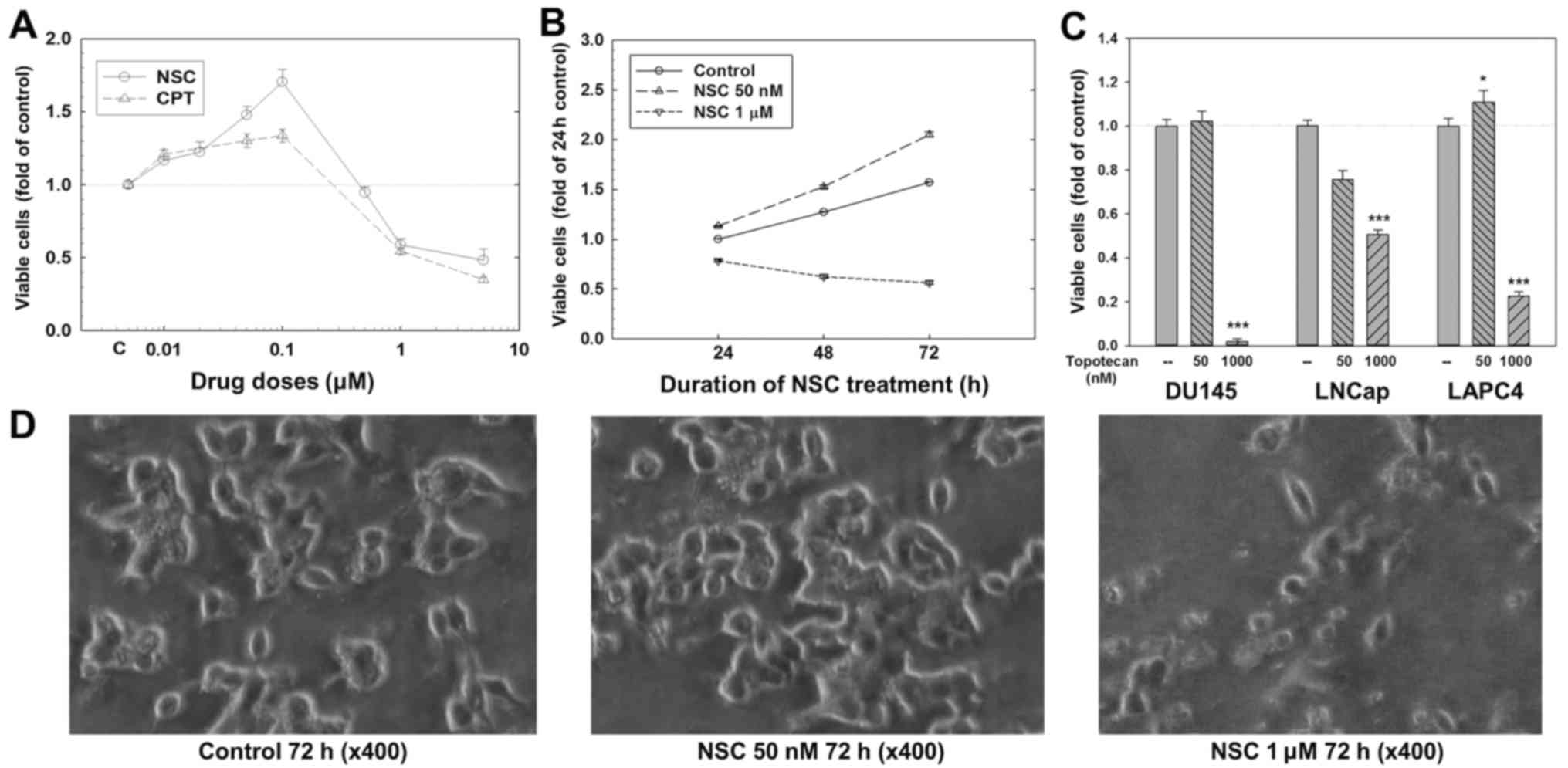
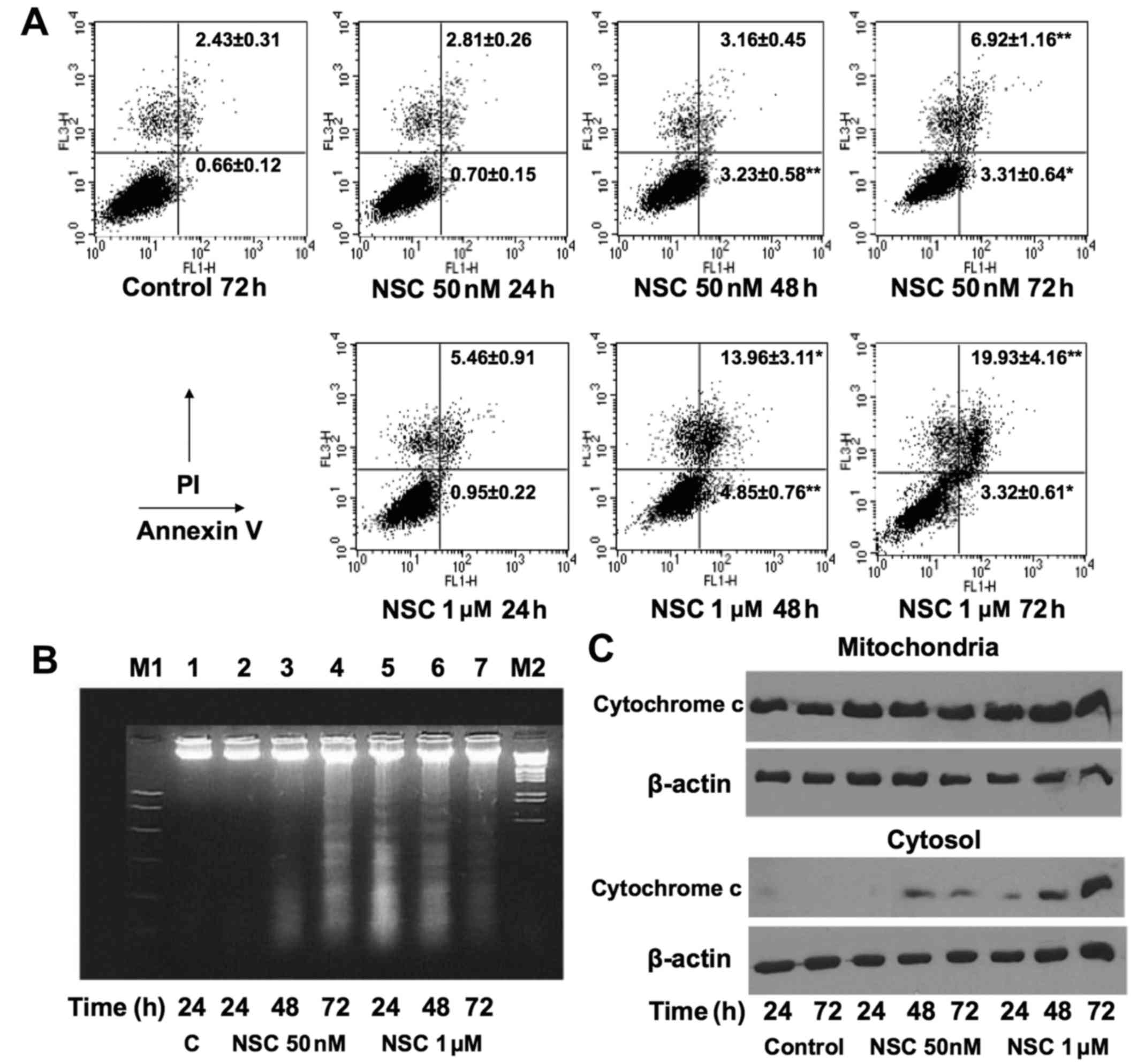
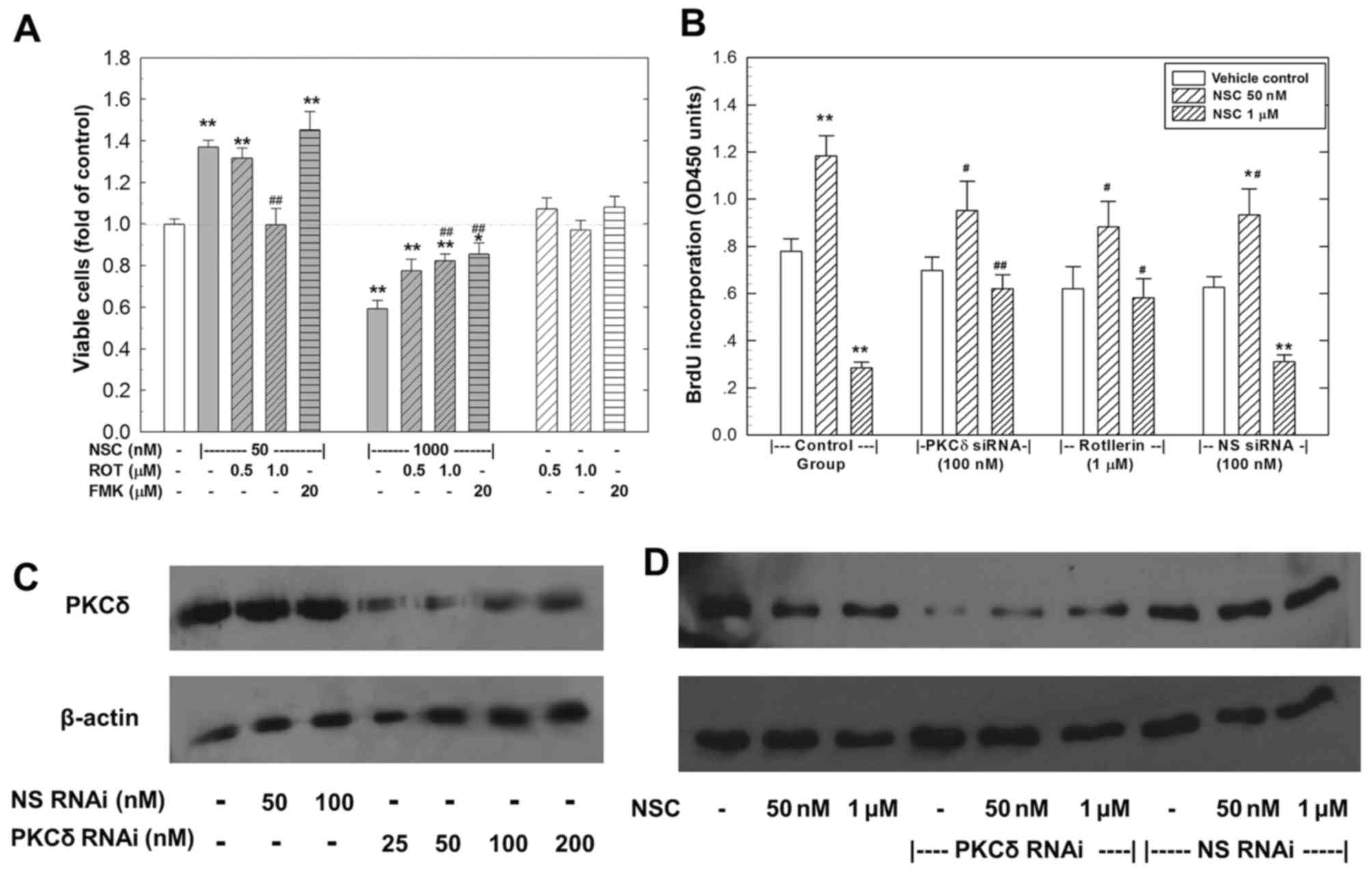
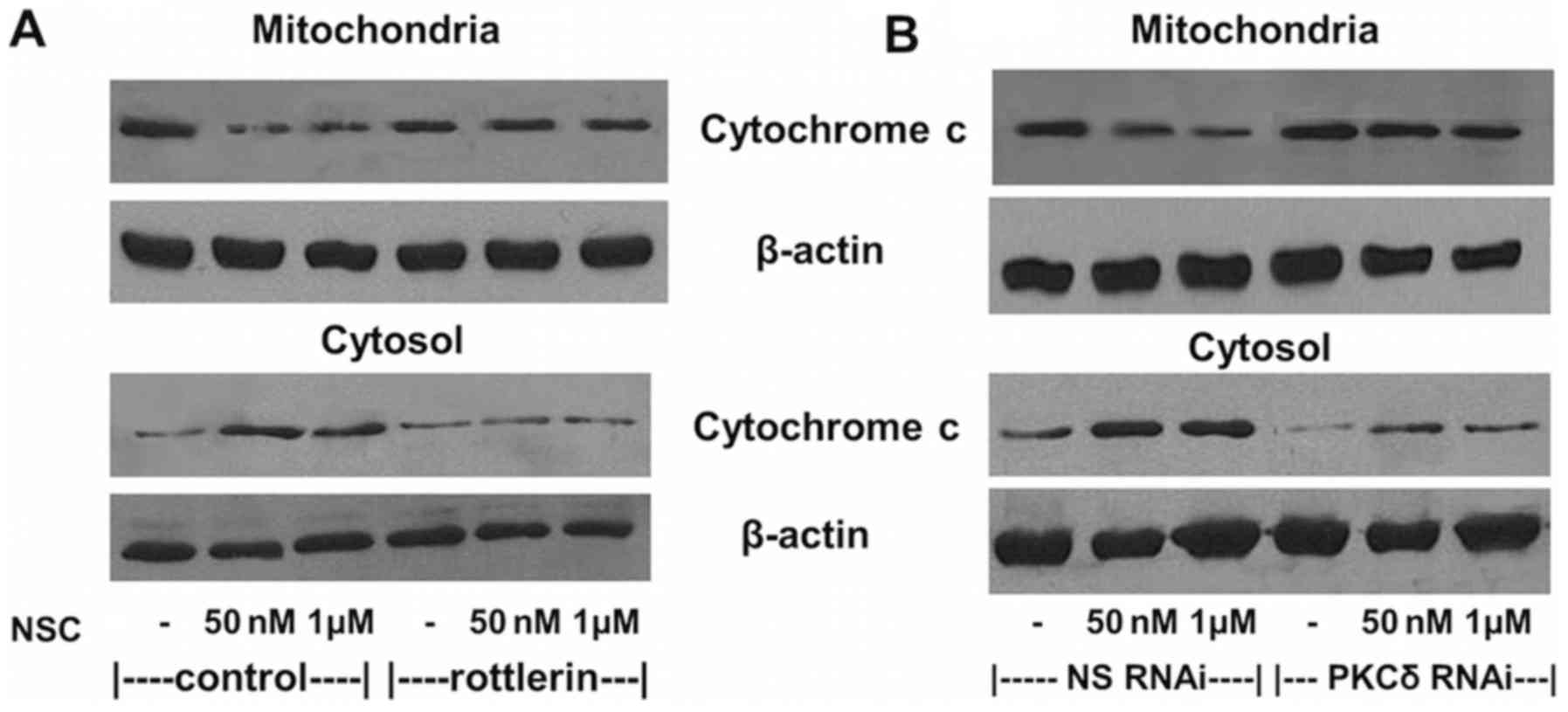
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Petrylak DP: The treatment of
hormone-refractory prostate cancer: Docetaxel and beyond. Rev Urol.
8(Suppl 2): S48–S55. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Silvestris N, Leone B, Numico G, Lorusso V
and De Lena M: Present status and perspectives in the treatment of
hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Oncology. 69:273–282. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Aziz MH, Dreckschmidt NE and Verma AK:
Plumbagin, a medicinal plant-derived naphthoquinone, is a novel
inhibitor of the growth and invasion of hormone-refractory prostate
cancer. Cancer Res. 68:9024–9032. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Frese S, Schüller A, Frese-Schaper M,
Gugger M and Schmid RA: Cytotoxic effects of camptothecin and
cisplatin combined with tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand (Apo2L/TRAIL) in a model of primary
culture of non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res.
29:2905–2911. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Legarza K and Yang LX: Novel camptothecin
derivatives. In Vivo. 19:283–292. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Srivastava V, Negi AS, Kumar JK, Gupta MM
and Khanuja SP: Plant-based anticancer molecules: A chemical and
biological profile of some important leads. Bioorg Med Chem.
13:5892–5908. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
National Cancer (NC) Institute: NCI Drug
Dictionary. https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-drug.
|
|
9
|
Hörmann V, Kumi-Diaka J, Durity M and
Rathinavelu A: Anticancer activities of genistein-topotecan
combination in prostate cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med. 16:2631–2636.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Minelli R, Cavalli R, Ellis L, Pettazzoni
P, Trotta F, Ciamporcero E, Barrera G, Fantozzi R, Dianzani C and
Pili R: Nanosponge-encapsulated camptothecin exerts anti-tumor
activity in human prostate cancer cells. Eur J Pharm Sci.
47:686–694. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Klein CE, Tangen CM, Braun TJ, Hussain MH,
Peereboom DM, Nichols CR, Rivkin SE, Dakhil SR and Crawford ED:
SWOG-9510: evaluation of topotecan in hormone refractory prostate
cancer: a Southwest Oncology Group study. Prostate. 52:264–268.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Reese DM, Tchekmedyian S, Chapman Y,
Prager D and Rosen PJ: A phase II trial of irinotecan in
hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Invest New Drugs. 16:353–359.
1998–1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hudes GR, Kosierowski R, Greenberg R,
Ramsey HE, Fox SC, Ozols RF, McAleer CA and Giantonio BJ: Phase II
study of topotecan in metastatic hormone-refractory prostate
cancer. Invest New Drugs. 13:235–240. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tan C, Cai LQ, Wu W, Qiao Y,
Imperato-McGinley J, Chen GQ and Zhu YS: NSC606985, a novel
camptothecin analog, induces apoptosis and growth arrest in
prostate tumor cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 63:303–312. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Albihn A, Mo H, Yang Y and Henriksson M:
Camptothecin- induced apoptosis is enhanced by Myc and involves
PKCdelta signaling. Int J Cancer. 121:1821–1829. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Song MG, Gao SM, Du KM, Xu M, Yu Y, Zhou
YH, Wang Q, Chen Z, Zhu YS and Chen GQ: Nanomolar concentration of
NSC606985, a camptothecin analog, induces leukemic-cell apoptosis
through protein kinase Cdelta-dependent mechanisms. Blood.
105:3714–3721. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Parker PJ and Murray-Rust J: PKC at a
glance. J Cell Sci. 117:131–132. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gonzalez-Guerrico AM and Kazanietz MG:
Phorbol ester-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells via
autocrine activation of the extrinsic apoptotic cascade: A key role
for protein kinase C delta. J Biol Chem. 280:38982–38991. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yin L, Bennani-Baiti N and Powell CT:
Phorbol ester-induced apoptosis of C4-2 cells requires both a
unique and a redundant protein kinase C signaling pathway. J Biol
Chem. 280:5533–5541. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jackson DN and Foster DA: The enigmatic
protein kinase Cdelta: Complex roles in cell proliferation and
survival. FASEB J. 18:627–636. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Basu A and Pal D: Two faces of protein
kinase Cδ: The contrasting roles of PKCδ in cell survival and cell
death. Sci World J. 10:2272–2284. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Steinberg SF: Distinctive activation
mechanisms and functions for protein kinase Cdelta. Biochem J.
384:449–459. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Curtis MJ, Bond RA, Spina D, Ahluwalia A,
Alexander SP, Giembycz MA, Gilchrist A, Hoyer D, Insel PA, Izzo AA,
et al: Experimental design and analysis and their reporting: New
guidance for publication in BJP. Br J Pharmacol. 172:3461–3471.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Afzal O, Kumar S, Haider MR, Ali MR, Kumar
R, Jaggi M and Bawa S: A review on anticancer potential of
bioactive heterocycle quinoline. Eur J Med Chem. 97:871–910. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang N, Zhang H, Xia L, Zheng Y, Yu Y,
Zhu Y, Chen G and Di W: NSC606985 induces apoptosis, exerts
synergistic effects with cisplatin, and inhibits hypoxia-stabilized
HIF-1alpha protein in human ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
278:139–144. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gavrielides MV, Gonzalez-Guerrico AM,
Riobo NA and Kazanietz MG: Androgens regulate protein kinase Cdelta
transcription and modulate its apoptotic function in prostate
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 66:11792–11801. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao M, Xia L and Chen GQ: Protein kinase
cδ in apoptosis: A brief overview. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz).
60:361–372. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Majumder PK, Pandey P, Sun X, Cheng K,
Datta R, Saxena S, Kharbanda S and Kufe D: Mitochondrial
translocation of protein kinase C delta in phorbol ester-induced
cytochrome c release and apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 275:21793–21796.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li L, Lorenzo PS, Bogi K, Blumberg PM and
Yuspa SH: Protein kinase Cdelta targets mitochondria, alters
mitochondrial membrane potential, and induces apoptosis in normal
and neoplastic keratinocytes when overexpressed by an adenoviral
vector. Mol Cell Biol. 19:8547–8558. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sumitomo M, Ohba M, Asakuma J, Asano T,
Kuroki T, Asano T and Hayakawa M: Protein kinase Cdelta amplifies
ceramide formation via mitochondrial signaling in prostate cancer
cells. J Clin Invest. 109:827–836. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Toyoda M, Gotoh N, Handa H and Shibuya M:
Involvement of MAP kinase-independent protein kinase C signaling
pathway in the EGF-induced p21(WAF1/Cip1) expression and growth
inhibition of A431 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 250:430–435.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mauro LV, Grossoni VC, Urtreger AJ, Yang
C, Colombo LL, Morandi A, Pallotta MG, Kazanietz MG, Bal de Kier
Joffé ED and Puricelli LL: PKC Delta (PKCdelta) promotes tumoral
progression of human ductal pancreatic cancer. Pancreas.
39:e31–e41. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Clark AS, West KA, Blumberg PM and Dennis
PA: Altered protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms in non-small cell lung
cancer cells: PKCdelta promotes cellular survival and
chemotherapeutic resistance. Cancer Res. 63:780–786.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Datta K, Nambudripad R, Pal S, Zhou M,
Cohen HT and Mukhopadhyay D: Inhibition of insulin-like growth
factor-I-mediated cell signaling by the von Hippel-Lindau gene
product in renal cancer. J Biol Chem. 275:20700–20706. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kiley SC, Clark KJ, Duddy SK, Welch DR and
Jaken S: Increased protein kinase C delta in mammary tumor cells:
Relationship to transformtion and metastatic progression. Oncogene.
18:6748–6757. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
McKiernan E, O'Brien K, Grebenchtchikov N,
Geurts-Moespot A, Sieuwerts AM, Martens JW, Magdolen V, Evoy D,
McDermott E, Crown J, et al: Protein kinase Cdelta expression in
breast cancer as measured by real-time PCR, western blotting and
ELISA. Br J Cancer. 99:1644–1650. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
McCracken MA, Miraglia LJ, McKay RA and
Strobl JS: Protein kinase C delta is a prosurvival factor in human
breast tumor cell lines. Mol Cancer Ther. 2:273–281.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kumar V, Pandey P, Sabatini D, Kumar M,
Majumder PK, Bharti A, Carmichael G, Kufe D and Kharbanda S:
Functional interaction between RAFT1/FRAP/mTOR and protein kinase
cdelta in the regulation of cap-dependent initiation of
translation. EMBO J. 19:1087–1097. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
De Boer L, Oakes V, Beamish H, Giles N,
Stevens F, Somodevilla-Torres M, Desouza C and Gabrielli B: Cyclin
A/cdk2 coordinates centrosomal and nuclear mitotic events.
Oncogene. 27:4261–4268. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ariens EJ, Simonis AM and Van Rossum JM:
Theory and experiments concerning the effects of drugs. Pharm
Weekbl. 91:617–635. 1956.In Dutch. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Szeto HH, Zhu YS, Umans JG, Dwyer G, Clare
S and Amione J: Dual action of morphine on fetal breathing
movements. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 245:537–542. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhu YS and Szeto HH: Morphine-induced
tachycardia in fetal lambs: A bell-shaped dose-response curve. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 249:78–82. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Czifra G, Tóth IB, Marincsák R, Juhász I,
Kovács I, Acs P, Kovács L, Blumberg PM and Bíró T: Insulin-like
growth factor-I-coupled mitogenic signaling in primary cultured
human skeletal muscle cells and in C2C12 myoblasts. A central role
of protein kinase Cdelta. Cell Signal. 18:1461–1472. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang H, Okamoto M, Panzhinskiy E, Zawada
WM and Das M: PKCδ/midkine pathway drives hypoxia-induced
proliferation and differentiation of human lung epithelial cells.
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 306:C648–C658. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|