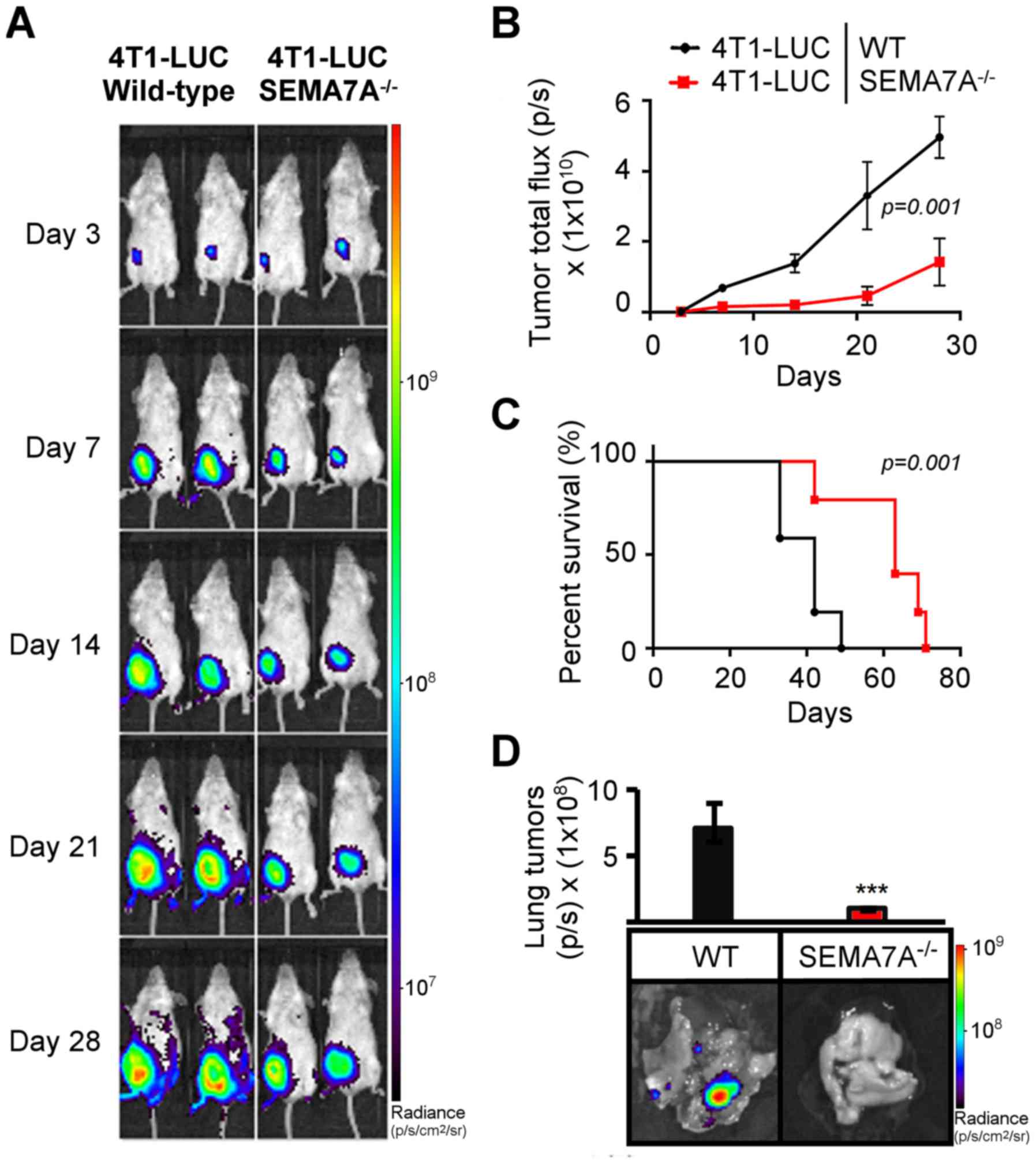
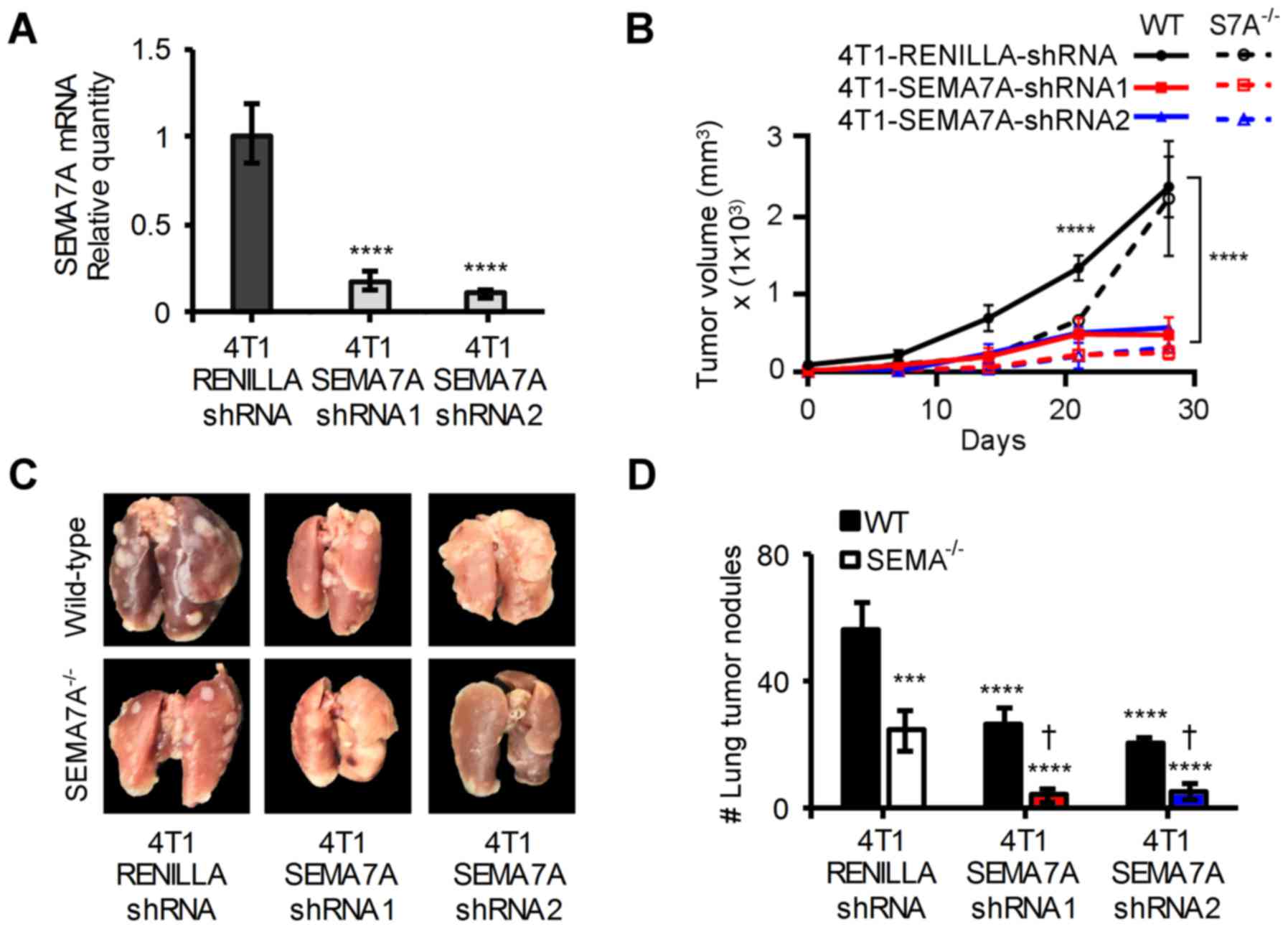
|
1
|
Pasterkamp RJ and Kolodkin AL: Semaphorin
junction: Making tracks toward neural connectivity. Curr Opin
Neurobiol. 13:79–89. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhou Y, Gunput RA and Pasterkamp RJ:
Semaphorin signaling: Progress made and promises ahead. Trends
Biochem Sci. 33:161–170. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Műzes G and Sipos F: Relation of immune
semaphorin/plexin signaling to carcinogenesis. Eur J Cancer Prev.
23:469–476. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Epstein JA, Aghajanian H and Singh MK:
Semaphorin signaling in cardiovascular development. Cell Metab.
21:163–173. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Garcia-Areas R, Libreros S and
Iragavarapu-Charyulu V: Semaphorin7A: Branching beyond axonal
guidance and into immunity. Immunol Res. 57:81–85. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ito D, Nojima S and Kumanogoh A: The role
of Semaphorin family in immune systems. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai
Kaishi. 37:1–10. 2014.In Japanese. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Morihana T and Kumanogoh A: Immune
semaphorins and allergic diseases. Arerugi. 62:155–162. 2013.In
Japanese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ma B, Herzog EL, Lee CG, Peng X, Lee CM,
Chen X, Rockwell S, Koo JS, Kluger H, Herbst RS, et al: Role of
chitinase 3-like-1 and Semaphorin 7a in pulmonary melanoma
metastasis. Cancer Res. 75:487–496. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Allegra M, Zaragkoulias A, Vorgia E,
Ioannou M, Litos G, Beug H and Mavrothalassitis G: Semaphorin-7a
reverses the ERF-induced inhibition of EMT in Ras-dependent mouse
mammary epithelial cells. Mol Biol Cell. 23:3873–3881. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Black SA, Nelson AC, Gurule NJ, Futscher
BW and Lyons TR: Semaphorin 7a exerts pleiotropic effects to
promote breast tumor progression. Oncogene. 35:5170–5178. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Formolo CA, Williams R, Gordish-Dressman
H, MacDonald TJ, Lee NH and Hathout Y: Secretome signature of
invasive glioblastoma multiforme. J Proteome Res. 10:3149–3159.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jongbloets BC, Ramakers GM and Pasterkamp
RJ: Semaphorin7A and its receptors: Pleiotropic regulators of
immune cell function, bone homeostasis, and neural development.
Semin Cell Dev Biol. 24:129–138. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fong KP, Barry C, Tran AN, Traxler EA,
Wannemacher KM, Tang HY, Speicher KD, Blair IA, Speicher DW,
Grosser T, et al: Deciphering the human platelet sheddome. Blood.
117:e15–e26. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Holmes S, Downs AM, Fosberry A, Hayes PD,
Michalovich D, Murdoch P, Moores K, Fox J, Deen K, Pettman G, et
al: Sema7A is a potent monocyte stimulator. Scand J Immunol.
56:270–275. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Garcia-Areas R, Libreros S, Amat S,
Keating P, Carrio R, Robinson P, Blieden C and Iragavarapu-Charyulu
V: Semaphorin7A promotes tumor growth and exerts a pro-angiogenic
effect in macrophages of mammary tumor-bearing mice. Front Physiol.
5:172014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu H, Juo ZS, Shim AH, Focia PJ, Chen X,
Garcia KC and He X: Structural basis of semaphorin-plexin
recognition and viral mimicry from Sema7A and A39R complexes with
PlexinC1. Cell. 142:749–761. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kang HR, Lee CG, Homer RJ and Elias JA:
Semaphorin 7A plays a critical role in TGF-beta1-induced pulmonary
fibrosis. J Exp Med. 204:1083–1093. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Suzuki K, Okuno T, Yamamoto M, Pasterkamp
RJ, Takegahara N, Takamatsu H, Kitao T, Takagi J, Rennert PD,
Kolodkin AL, et al: Semaphorin 7A initiates T-cell-mediated
inflammatory responses through alpha1beta1 integrin. Nature.
446:680–684. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Markel P, Shu P, Ebeling C, Carlson GA,
Nagle DL, Smutko JS and Moore KJ: Theoretical and empirical issues
for marker-assisted breeding of congenic mouse strains. Nat Genet.
17:280–284. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wakeland E, Morel L, Achey K, Yui M and
Longmate J: Speed congenics: A classic technique in the fast lane
(relatively speaking). Immunol Today. 18:472–477. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fellmann C, Hoffmann T, Sridhar V,
Hopfgartner B, Muhar M, Roth M, Lai DY, Barbosa IA, Kwon JS, Guan
Y, et al: An optimized microRNA backbone for effective single-copy
RNAi. Cell Rep. 5:1704–1713. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wojcikiewicz EP, Zhang X, Chen A and Moy
VT: Contributions of molecular binding events and cellular
compliance to the modulation of leukocyte adhesion. J Cell Sci.
116:2531–2539. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hoh JH and Schoenenberger CA: Surface
morphology and mechanical properties of MDCK monolayers by atomic
force microscopy. J Cell Sci. 107:1105–1114. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Aslakson CJ and Miller FR: Selective
events in the metastatic process defined by analysis of the
sequential dissemination of subpopulations of a mouse mammary
tumor. Cancer Res. 52:1399–1405. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tao K, Fang M, Alroy J and Sahagian GG:
Imagable 4T1 model for the study of late stage breast cancer. BMC
Cancer. 8:2282008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ridley AJ: RhoA, RhoB and RhoC have
different roles in cancer cell migration. J Microsc. 251:242–249.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Brown GT and Murray GI: Current
mechanistic insights into the roles of matrix metalloproteinases in
tumour invasion and metastasis. J Pathol. 237:273–281. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xiang X, Zhuang X, Ju S, Zhang S, Jiang H,
Mu J, Zhang L, Miller D, Grizzle W and Zhang HG: miR-155 promotes
macroscopic tumor formation yet inhibits tumor dissemination from
mammary fat pads to the lung by preventing EMT. Oncogene.
30:3440–3453. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pickup M, Novitskiy S and Moses HL: The
roles of TGFβ in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Cancer.
13:788–799. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Padua D and Massagué J: Roles of TGFbeta
in metastasis. Cell Res. 19:89–102. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sánchez-Tilló E, Siles L, de Barrios O,
Cuatrecasas M, Vaquero EC, Castells A and Postigo A: Expanding
roles of ZEB factors in tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Am J
Cancer Res. 1:897–912. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Serrano-Gomez SJ, Maziveyi M and Alahari
SK: Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through
epigenetic and post-translational modifications. Mol Cancer.
15:182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lekka M: Discrimination between normal and
cancerous cells using AFM. Bionanoscience. 6:65–80. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lekka M, Laidler P, Gil D, Lekki J,
Stachura Z and Hrynkiewicz AZ: Elasticity of normal and cancerous
human bladder cells studied by scanning force microscopy. Eur
Biophys J. 28:312–316. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cross SE, Jin YS, Rao J and Gimzewski JK:
Nanomechanical analysis of cells from cancer patients. Nat
Nanotechnol. 2:780–783. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
De Minicis S, Rychlicki C, Agostinelli L,
Saccomanno S, Trozzi L, Candelaresi C, Bataller R, Millán C,
Brenner DA, Vivarelli M, et al: Semaphorin 7A contributes to
TGF-β-mediated liver fibrogenesis. Am J Pathol. 183:820–830. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Saito T, Kasamatsu A, Ogawara K, Miyamoto
I, Saito K, Iyoda M, Suzuki T, Endo-Sakamoto Y, Shiiba M, Tanzawa
H, et al: Semaphorin7A promotion of tumoral growth and metastasis
in human oral cancer by regulation of G1 cell cycle and matrix
metalloproteases: Possible contribution to tumoral angiogenesis.
PLoS One. 10:e01379232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wetzig A, Alaiya A, Al-Alwan M, Pradez CB,
Pulicat MS, Al-Mazrou A, Shinwari Z, Sleiman GM, Ghebeh H,
Al-Humaidan H, et al: Differential marker expression by cultures
rich in mesenchymal stem cells. BMC Cell Biol. 14:542013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bongiorno T, Kazlow J, Mezencev R,
Griffiths S, Olivares-Navarrete R, McDonald JF, Schwartz Z, Boyan
BD, McDevitt TC and Sulchek T: Mechanical stiffness as an improved
single-cell indicator of osteoblastic human mesenchymal stem cell
differentiation. J Biomech. 47:2197–2204. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Guck J, Schinkinger S, Lincoln B, Wottawah
F, Ebert S, Romeyke M, Lenz D, Erickson HM, Ananthakrishnan R,
Mitchell D, et al: Optical deformability as an inherent cell marker
for testing malignant transformation and metastatic competence.
Biophys J. 88:3689–3698. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
van Rijn A, Paulis L, te Riet J, Vasaturo
A, Reinieren-Beeren I, van der Schaaf A, Kuipers AJ, Schulte LP,
Jongbloets BC, Pasterkamp RJ, et al: Semaphorin 7A promotes
chemokine-driven dendritic cell migration. J Immunol. 196:459–468.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|